Application of Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus lactis on Lipid Metabolism, Anti-Inflammatory, and Fecal Microbiota in Cats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Lyophilized Lactic Acid Bacteria
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Detection of Blood Lipid-Related Indexes and Inflammation-Related Indicators
2.4. Extraction of Fecal DNA
2.5. PCR Amplification
2.6. Library Construction and Hands-On Sequencing
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
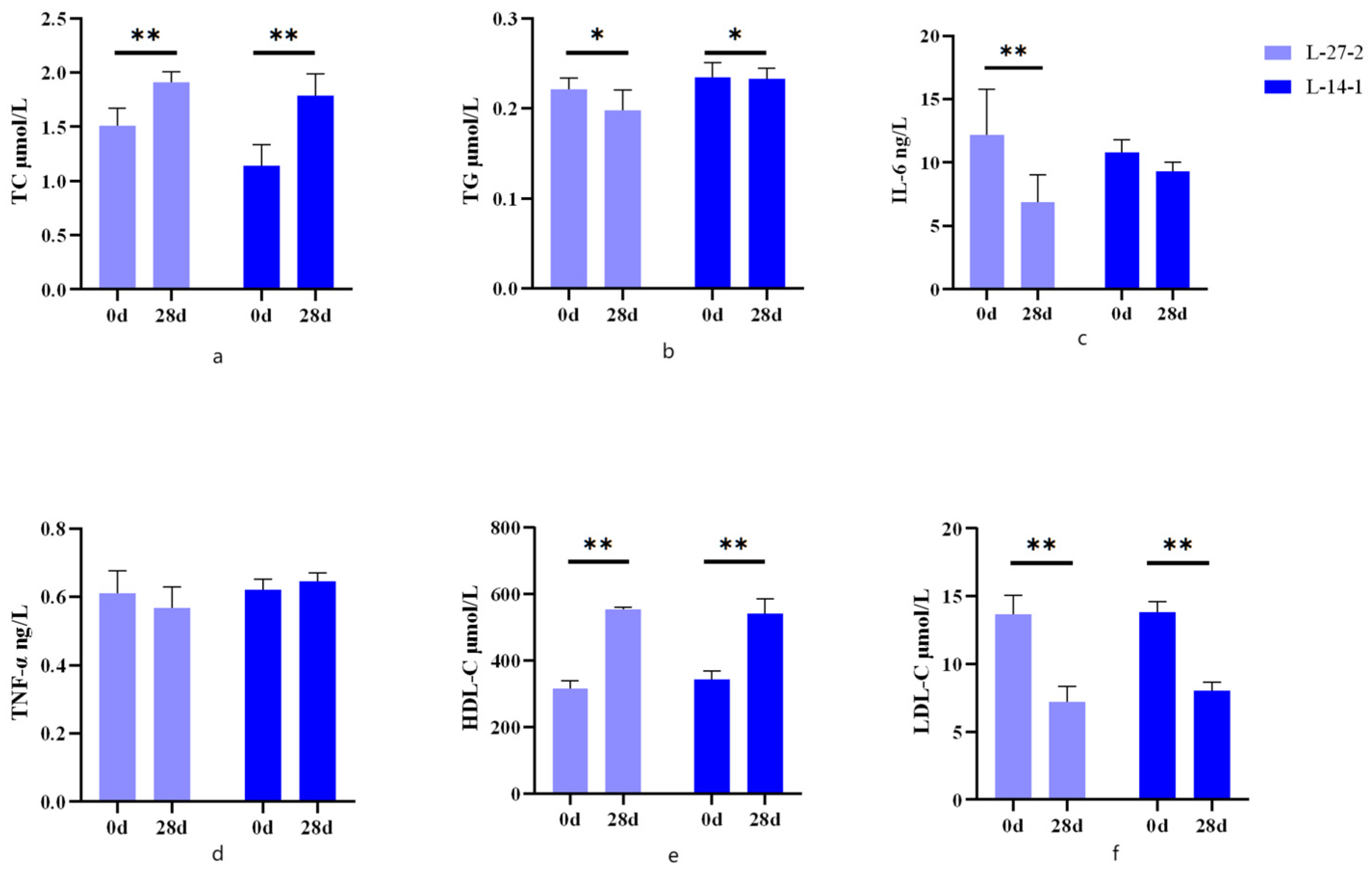
3.1. Blood Biochemistry
3.2. Fecal Microbiota
4. Discussion
4.1. Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus lactis Reduced Blood Lipid Levels
4.2. Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus lactis Reduced the Levels of Blood Inflammatory Factors
4.3. Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus lactis Altered the Microbial Composition of Cat Feces
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khare, A.; Gaur, S. Cholesterol-Lowering Effects of Lactobacillus Species. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, M.; Park, E.; Ko, S.; Choi, E.; Kim, S. Therapeutic effects of kefir grain Lactobacillus-derived extracellular vesicles in mice with 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced inflammatory bowel disease. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8662–8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiennimitr, P.; Yasom, S.; Tunapong, W.; Chunchai, T.; Wanchai, K.; Pongchaidecha, A.; Lungkaphin, A.; Sirilun, S.; Chaiyasut, C.; Chattipakorn, N.; et al. Lactobacillus paracasei HII01, xylooligosaccharides, and synbiotics reduce gut disturbance in obese rats. Nutrition 2018, 54, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Wen, Z.; Hua, J. Effects of dietary inclusion of Lactobacillus and inulin on growth performance, gut microbiota, nutrient utilization, and immune parameters in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 4656–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoukat, S. Potential anti-carcinogenic effect of probiotic and lactic acid bacteria in detoxification of benzo[a]pyrene: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.; Hoenig, M. Metabolic Effects of Obesity and Its Interaction with Endocrine Diseases. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2016, 46, 797–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kershaw, E.E.; Flier, J.S. Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 2548–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcinelli, S.; Rodiles, A.; Hatef, A.; Picchietti, S.; Cossignani, L.; Merrifield, D.L.; Unniappan, S.; Carnevali, O. Influence of Probiotics Administration on Gut Microbiota Core: A Review on the Effects on Appetite Control, Glucose, and Lipid Metabolism. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 52, S50–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beau, A.; Benoit, B.; Le Barz, M.; Meugnier, E.; Penhoat, A.; Calzada, C.; Pinteur, C.; Loizon, E.; Chanon, S.; Vieille-Marchiset, A.; et al. Inhibition of intestinal FXR activity as a possible mechanism for the beneficial effects of a probiotic mix supplementation on lipid metabolism alterations and weight gain in mice fed a high fat diet. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2281015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Zhuang, M.; Guo, T.; Bao, S.; Wu, S.; Ke, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, A.; Zhou, Z. Gut microbiota, host lipid metabolism and regulation mechanism of high-fat diet induced mice following different probiotics-fermented wheat bran intervention. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamper, B. Current Topics in Canine and Feline Obesity. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2016, 46, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, K.T.; McGreevy, P.D.; Toribio, J.-A.L.M.L.; Dhand, N.K. Positive attitudes towards feline obesity are strongly associated with ownership of obese cats. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, M. Canine and Feline Obesity Management. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 51, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeon, K.-D.; Kim, S.-M.; Kim, J.-H. Association between Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Health and Obesity Status in Cats. Animals 2024, 14, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusi, E.; Rizzi, R.; Polli, M.; Cannas, S.; Giardini, A.; Bruni, N.; Marelli, S.P. Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus D2/CSL (CECT 4529) supplementation on healthy cat performance. Vet. Rec. Open 2019, 6, e000368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathrani, A.; Larsen, J.A.; Kass, P.H.; Fascetti, A.J. Effect of short-term probiotic Enterococcus faecium SF68 dietary supplementation in overweight and obese cats without comorbidities. Vet. Rec. Open 2016, 3, e000164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Jergens, A.; Cerquetella, M.; Berardi, S.; Di Cicco, E.; Bassotti, G.; Pengo, G.; Suchodolski, J. Effects of a probiotic (SLAB51™) on clinical and histologic variables and microbiota of cats with chronic constipation/megacolon: A pilot study. Benef. Microbes 2018, 9, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ali, I.; Lei, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, M.; Yang, C.; Li, L. Effect of a Multistrain Probiotic on Feline Gut Health through the Fecal Microbiota and Its Metabolite SCFAs. Metabolites 2023, 13, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Kang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Tao, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhong, Y.; Han, B. Characterization and potential lipid-lowering effects of lactic acid bacteria isolated from cats. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1392864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, B.V.C.; Rocha, P.O.; Brito, C.A.R.S.; Galvão, L.M.V.; Nunes, L.C.C. Scientific and technological prospection on microencapsulation of probiotics by spray drying. Rev. Geintec-Gestao Inovacao E Tecnol. 2019, 9, 4919–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, F.; Girardeau, A.; Passot, S. Freeze-Drying of Lactic Acid Bacteria: A Stepwise Approach for Developing a Freeze-Drying Protocol Based on Physical Properties. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2180, 703–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall-Jones, Z.V.; Baillon, M.-L.A.; Croft, J.M.; Butterwick, R.F. Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus DSM13241 as a probiotic in healthy adult cats. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2006, 67, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagi, G.; Cipollini, I.; Pompei, A.; Zaghini, G.; Matteuzzi, D. Effect of a Lactobacillus animalis strain on composition and metabolism of the intestinal microflora in adult dogs. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 124, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grześkowiak, L.; Endo, A.; Beasley, S.; Salminen, S. Microbiota and probiotics in canine and feline welfare. Anaerobe 2015, 34, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, S.; Werling, D.; Allenspach, K. Effects of Ex-Vivo and In-Vivo Treatment with Probiotics on the Inflammasome in Dogs with Chronic Enteropathy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilla, R.; Suchodolski, J.S. The Gut Microbiome of Dogs and Cats, and the Influence of Diet. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 51, 605–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekh, S.L.; Boricha, A.A.; Chavda, J.G.; Vyas, B.R.M. Probiotic potential of lyophilized Lactobacillus plantarum GP. Ann. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, P.M.; Hegele, R.A. Functional foods and dietary supplements for the management of dyslipidaemia. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.-W.; Kang, S.-S. In Vitro Antibiofilm and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Bacteriocins Produced by Pediococcus acidilactici Against Enterococcus faecalis. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2020, 17, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, S.; Pradhan, S.N.; Jain, D.; Peter, M.P.D.; Antony, U. Probiotic and Functional Characterization of Pediococcus acidilactici Isolated from Bhaati jaanr, Traditional Fermented Rice Porridge. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 5734–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, N.; Li, G. Probiotic characteristics and whole-genome sequence analysis of Pediococcus acidilactici isolated from the feces of adult beagles. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1179953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Bao, K.; Li, G. Impact of Pediococcus acidilactici GLP06 supplementation on gut microbes and metabolites in adult beagles: A comparative analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1369402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Hu, Z.; Jia, C.; Yang, M.; Li, D.; Xu, A.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Deciphering the mechanisms of Yinlan Tiaozhi capsule in treating hyperlipidemia by combining network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental verification. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Yao, X.; Xia, F.; Yang, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, B.; Liu, Q.; Tang, W.; Yao, X.; Xia, F.; et al. Modulation of the Gut Microbiota in Rats by Hugan Qingzhi Tablets during the Treatment of High-Fat-Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 7261619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.-Z.; Ai, C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Gao, X.-X.; Zhong, R.-T.; Liu, B.; Chen, X.-H.; Zhao, C. Physicochemical Characterization of a Polysaccharide from Green Microalga Chlorella pyrenoidosa and Its Hypolipidemic Activity via Gut Microbiota Regulation in Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 68, 1186–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, B.; Fu, R.; Jiang, Z.; Wen, X.; Ni, Y. Bentong ginger oleoresin mitigates liver injury and modulates gut microbiota in mouse with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease induced by high-fat diet. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1268–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, Q.; Yang, Y.; Bindelle, J.; Ran, C.; Zhou, Z. Intestinal Cetobacterium and acetate modify glucose homeostasis via parasympathetic activation in zebrafish. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Fan, Z.; Yi, M.; Liu, Z.; Ke, X.; Gao, F.; Cao, J.; Wang, M.; Chen, G.; Lu, M. Characterization of the core gut microbiota of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): Indication of a putative novel Cetobacterium species and analysis of its potential function on nutrition. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Xie, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Olsen, R.E.; Ringø, E.; Ran, C.; Zhou, Z. Stabilized fermentation product of Cetobacterium somerae improves gut and liver health and antiviral immunity of zebrafish. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2022, 120, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, S.; Gu, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Tao, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, J.; Han, B. Application of Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus lactis on Lipid Metabolism, Anti-Inflammatory, and Fecal Microbiota in Cats. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122446
Liang S, Gu X, Sun J, Wang X, Tao H, Wang Z, Zhong Y, Wang J, Han B. Application of Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus lactis on Lipid Metabolism, Anti-Inflammatory, and Fecal Microbiota in Cats. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122446
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Shukun, Xinshu Gu, Jintao Sun, Xiumin Wang, Hui Tao, Zhenlong Wang, Yougang Zhong, Jinquan Wang, and Bing Han. 2024. "Application of Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus lactis on Lipid Metabolism, Anti-Inflammatory, and Fecal Microbiota in Cats" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122446
APA StyleLiang, S., Gu, X., Sun, J., Wang, X., Tao, H., Wang, Z., Zhong, Y., Wang, J., & Han, B. (2024). Application of Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus lactis on Lipid Metabolism, Anti-Inflammatory, and Fecal Microbiota in Cats. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122446






