Whole-Genome Sequencing Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Factors, and Genetic Diversity of Salmonella from Wenzhou, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Salmonella Isolation and DNA Extraction
2.2. WGS, Assembly and Genome Annotation
2.3. Bioinformatics Analyses
2.4. Data Availability
3. Results
3.1. Genomic Features of the Salmonella Strains
3.2. The Serotyping of Salmonella Isolates Using MLST Typing
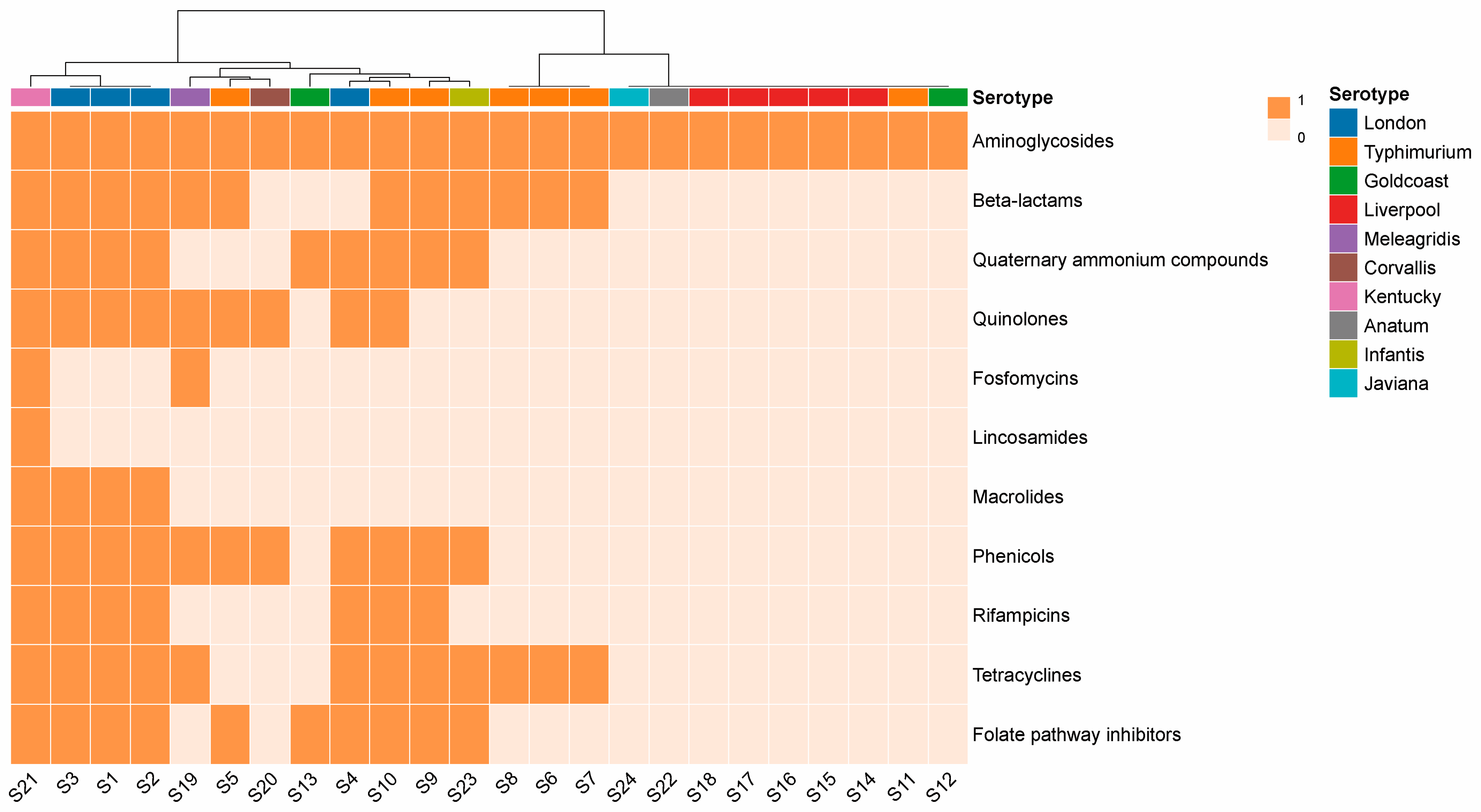
3.3. Identification of ARGs
3.4. Plasmid and I Integron
3.5. Virulence Genes
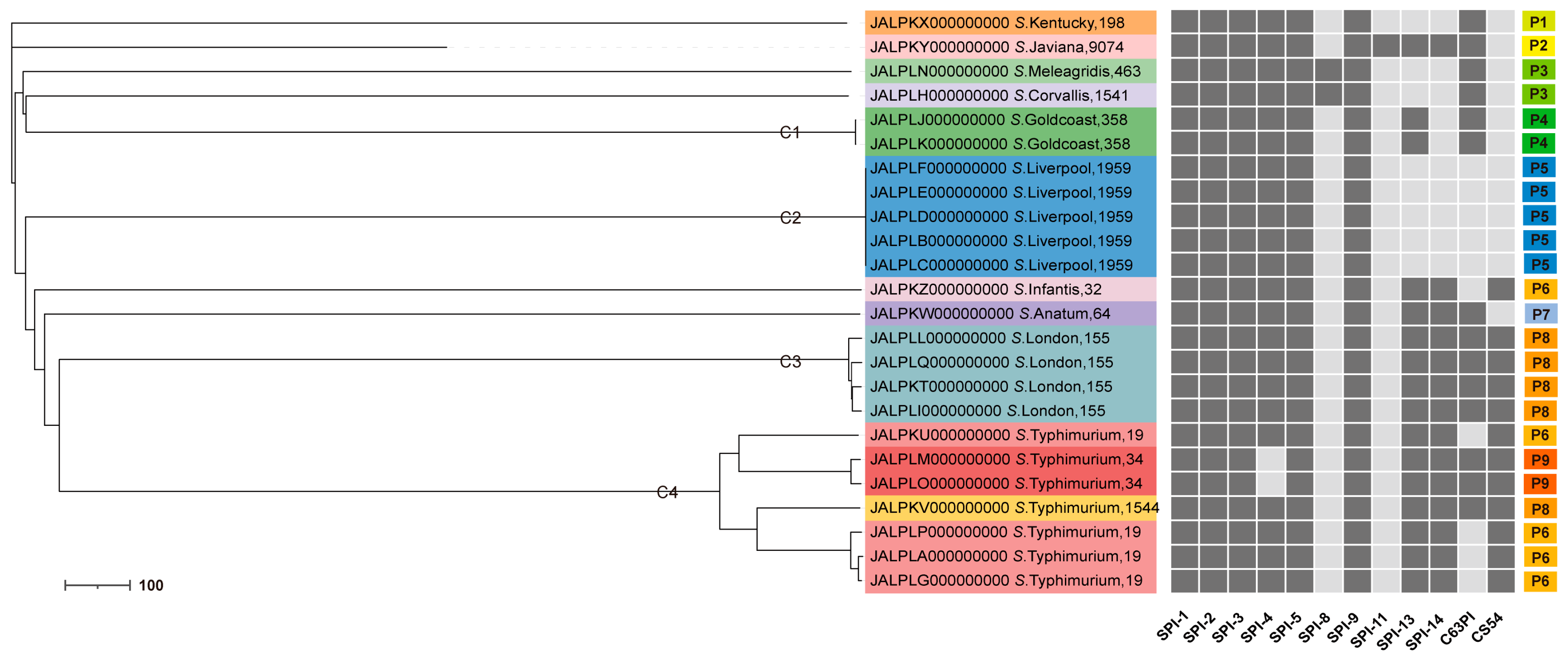
3.6. The SPI Profiles
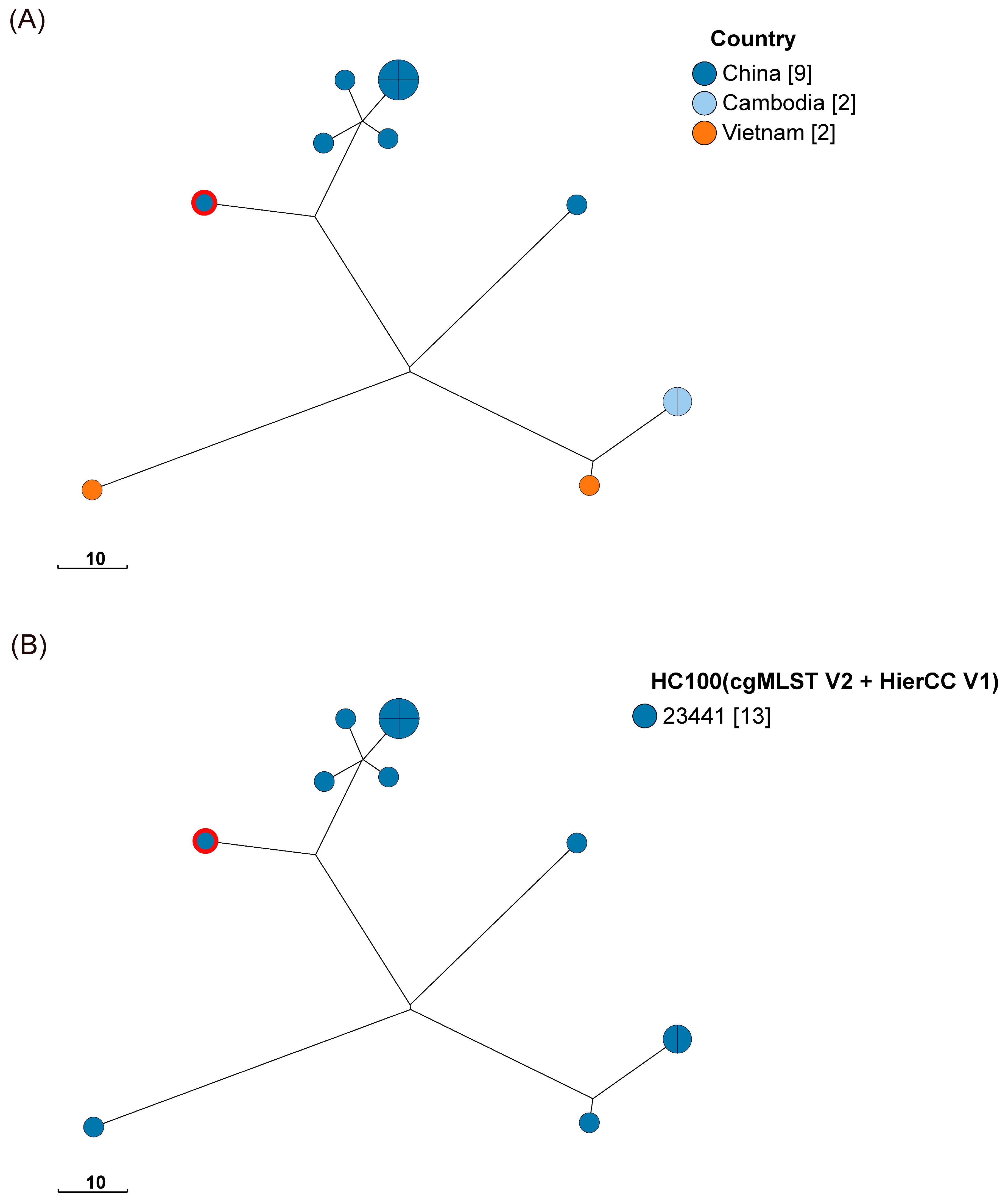
3.7. Phylogenetic Relationship of Salmonella Strains by cgMLST Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Serotyping and MLST
4.2. Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants
4.3. Virulence Determinants
4.4. Genetic Diversity of the Salmonella Isolates
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aduah, M.; Adzitey, F.; Amoako, D.G.; Teye, G.A.; Shariff, A.H.M.; Huda, N. Low Prevalence of Antibiotic-Resistant Salmonella enterica in Ready-to-Eat (RTE) Meats in Ghana Is Associated with Good Vendors’ Knowledge of Meat Safety. Foods 2021, 10, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavijo, V.; Baquero, D.; Hernandez, S.; Farfan, J.; Arias, J.; Arévalo, A.; Donado-Godoy, P.; Vives-Flores, M. Phage cocktail SalmoFREE® reduces Salmonella on a commercial broiler farm. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5054–5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majowicz, S.E.; Musto, J.; Scallan, E.; Angulo, F.J.; Kirk, M.; OBrien, S.J.; Jones, T.F.; Fazil, A.; Hoekstra, R.M. The global burden of nontyphoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Estimates of the Global Burden of Foodborne Diseases: Foodborne Disease Burden Epidemiology Reference Group 2007–2015. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/199350/9789241565165_eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Grimont, P.A.D.; Weill, F.X. Antigenic formulae of the Salmonella serovars. WHO Collab. Cent. Ref. Res. Salmonella 2007, 9, 1–166. [Google Scholar]
- Issenhuth-Jeanjean, S.; Roggentin, P.; Mikoleit, M.; Guibourdenche, M.; De Pinna, E.; Nair, S.; Fields, P.I.; Weill, F.-X. Supplement 2008–2010 (no. 48) to the white–Kauffmann–Le minor scheme. Res. Microbiol. 2014, 165, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibourdenche, M.; Roggentin, P.; Mikoleit, M.; Fields, P.I.; Bockemühl, J.; Grimont, P.A.D.; Weill, F.-X. Supplement 2003–2007 (No. 47) to the White-Kauffmann-Le Minor scheme. Res. Microbiol. 2010, 161, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, J.; Guiney, D.G. Diverse virulence traits underlying different clinical outcomes of Salmonella infection. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jajere, S.M. A review of Salmonella enterica with particular focus on the pathogenicity and virulence factors, host specificity and antimicrobial resistance including multidrug resistance. Vet. World 2019, 12, 504–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngoi, S.T.; Teh, C.S.J.; Chai, L.C.; Thong, K.L. Overview of Molecular Typing Tools for The Characterization of Salmonella enterica in Malaysia. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, L. Genes that are involved in high hydrostatic pressure treatments in a Listeria monocytogenes Scott A ctsR deletion mutant. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2012, 4, 050–056. [Google Scholar]
- Ceruso, M.; Liu, Y.; Gunther, N.; Pepe, T.; Anastasio, A.; Qi, P. Anti-listerial activity of thermophilin 110 and pediocin in fermented milk and whey. Food Control 2021, 125, 107941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godínez-Oviedo, A.; Arvizu-Medrano, S.M.; Bowman, J.P.; Tamplin, M.L.; Garcés-Vega, F.J.; Cabrera-Diaz, E.; Gómez-Baltazar, A.; Hernández-Iturriaga, M. Linking intraspecies variability of Salmonella enterica isolates under acidic conditions to genotype. J. Food Sci. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manikandan, R.; Rajagunalan, S.; Malmarugan, S.; Gupta, C. First report on whole genome sequencing and comparative genomics of Salmonella enterica serovar Abortusequi isolated from Donkey in India. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, R.A.; Eade, C.R.; Wiedmann, M. Embracing Diversity: Differences in Virulence Mechanisms, Disease Severity, and Host Adaptations Contribute to the Success of Nontyphoidal Salmonella as a Foodborne Pathogen. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kombade, S.; Kaur, N. Pathogenicity Island in Salmonella. In Salmonella spp.—A Global Challenge; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriken, B. Salmonella pathogenicity islands. Mikrobiyoloji Bul. 2013, 47, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Asten, A.J.; van Dijk, J.E. Distribution of “classic” virulence factors among Salmonella spp. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 44, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Xiang, Y.; Qiu, S. Resistance in Enteric Shigella and nontyphoidal Salmonella: Emerging concepts. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 36, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miriagou, V.; Carattoli, A.; Fanning, S. Antimicrobial resistance islands: Resistance gene clusters in Salmonella chromosome and plasmids. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, X.; Tan, H.; Ke, B.; He, D.; Wang, H.; Chen, Q.; Ke, C.; Zhang, Y. Whole genome sequencing analysis of Salmonella enterica serovar Weltevreden isolated from human stool and contaminated food samples collected from the Southern coastal area of China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 266, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassena, A.B.; Haendiges, J.; Zormati, S.; Guermazi, S.; Gdoura, R.; Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Siala, M. Virulence and resistance genes profiles and clonal relationships of non-typhoidal food-borne Salmonella strains isolated in Tunisia by whole genome sequencing. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 337, 108941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punina, N.V.; Makridakis, N.M.; Remnev, M.A.; Topunov, A.F. Whole-genome sequencing targets drug-resistant bacterial infections. Hum. Genom. 2015, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, G.M.; Morin, P.M. Salmonella Serotyping Using Whole Genome Sequencing. Front Microbiol 2018, 9, 2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.-F.; Mohamed, K.; Fan, Y.; Achtman, M.; Brown, D.; Chattaway, M.; Dallman, T.; Delahay, R.; Kornschober, C. The EnteroBase user’s guide, with case studies on Salmonella transmissions, Yersinia pestis phylogeny, and Escherichia core genomic diversity. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yin, Y.; Jones, M.B.; Zhang, Z.; Kaiser, B.L.D.; Dinsmore, B.A.; Fitzgerald, C.; Fields, P.I.; Deng, X. Salmonella Serotype Determination Utilizing High-Throughput Genome Sequencing Data. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernández, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Møller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob Agents Chemothererapy 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cury, J.; Jove, T.; Touchon, M.; Neron, B.; Rocha, E.P. Identification and analysis of integrons and cassette arrays in bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 4539–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, D.; Jin, Q.; Chen, L.; Yang, J. VFDB 2019: A comparative pathogenomic platform with an interactive web interface. Nucleic Acids Res 2019, 47, D687–D692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roer, L.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Lukjancenko, O.; Kaas, R.S.; Hasman, H.; Aarestrup, F.M. Is the Evolution of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica Linked to Restriction-Modification Systems? mSystems 2016, 1, e00009-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Cui, M.; Li, T.; Cheng, M. Predictive analysis of whole genome sequencing for Salmonella serotype and antimicrobial resistance phenotypes. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2021, 61, 4038–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, C.; Flint, J.; Lilly, K.; Hope, K.; Wang, Q.; Howard, P.; Sintchenko, V.; Durrheim, D.N. Retrospective use of whole genome sequencing to better understand an outbreak of Salmonella enterica serovar Mbandaka in New South Wales, Australia. West. Pac. Surveill. Response J. 2017, 9, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouws, S.; Bogaerts, B.; Verhaegen, B.; Denayer, S.; Crombé, F.; Rauw, K.D.; Piérard, D.; Marchal, K.; Vanneste, K.; Roosens, N.H.C.; et al. The Benefits of Whole Genome Sequencing for Foodborne Outbreak Investigation from the Perspective of a National Reference Laboratory in a Smaller Country. Foods 2020, 9, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, S.J.; Neale, B.M.; Huang, H.; Werling, D.M.; Dong, S.; Abecasis, G.; Arguello, P.A.; Blangero, J.; Boehnke, M.; Daly, M.J.; et al. Whole genome sequencing in psychiatric disorders: The WGSPD consortium. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, A.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wu, Y. Contamination and characteristics of foodborne Salmonella in Wenzhou. Chin. J. Food Hyg. 2019, 31, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Wang, L.; Shan, R.; Cai, Y.; Gao, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, B.; Shang, G.; Wu, K. Epidemiological analysis of 317 cases with foodborne diseases in Wenzhou in 2014. Chin. Prev. Med. 2017, 18, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Lin, D.; Wang, L.L.; Hu, H. Monitoring the Results of Foodborne Diseases in Sentinel Hospitals in Wenzhou City, China from 2014 to 2015. Iran. J. Public Health 2018, 47, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, C.J.; Mohan, C.V.; Peeler, E.J. The spread of pathogens through trade in aquatic animals and their products. Rev Sci Tech 2011, 30, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ke, B.; Huang, Y.; He, D.; Li, X.; Liang, Z.; Ke, C. The molecular epidemiological characteristics and genetic diversity of Salmonella typhimurium in Guangdong, China, 2007-2011. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, N.; Sekizuka, T.; Tamamura-Andoh, Y.; Barco, L.; Hinenoya, A.; Yamasaki, S.; Iwata, T.; Watanabe-Yanai, A.; Kuroda, M.; Akiba, M.; et al. Identification of a Recently Dominant Sublineage in Salmonella 4,[5],12:i:-Sequence Type 34 Isolated from Food Animals in Japan. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 690947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, L.M.; Pierneef, R.; Mathole, M.; Matle, I. Genomic Characterization of Endemic and Ecdemic Non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica Lineages Circulating Among Animals and Animal Products in South Africa. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 4, 748611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Shen, L. Distribution of serotypes and drug resistance of ESBLs-producing Salmonella in Wenzhou. Dis. Surveill. 2019, 34, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrag, H.A.; Abdallah, N.; Shehata, M.M.K.; Awad, E.M. Natural outer membrane permeabilizers boost antibiotic action against irradiated resistant bacteria. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassuna, N.A.; Khairalla, A.S.; Farahat, E.M.; Hammad, A.M.; Abdel-Fattah, M. Molecular characterization of Extended-spectrum β lactamase-producing E. coli recovered from community-acquired urinary tract infections in Upper Egypt. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Sirous, M.; Javaherizadeh, H.; Motamedifar, M.; Saki, M.; Veisi, H.; Ebrahimi, S.; SeyedMohammadi, S.; Hashemzadeh, M. Antibiotic resistance pattern and molecular characterization of extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing enteroaggregative Escherichia coli isolates in children from southwest Iran. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 8, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Gou, J.; Guo, X.; Cao, Z.; Li, Y.; Jiao, H.; He, X.; Ren, Y.; Tian, F. Genetic contexts related to the diffusion of plasmid-mediated CTX-M-55 extended-spectrum beta-lactamase isolated from Enterobacteriaceae in China. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2018, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, L.B. Mechanisms of resistance and clinical relevance of resistance to β-lactams, glycopeptides, and fluoroquinolones. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2012, 87, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Cattoir, V.; Nordmann, P. Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance; Interactions between Human, Animal, and Environmental Ecologies. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 21386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Mitra, U.; Dutta, S.; De, A.; Chatterjee, M.K.; Bhattacharya, S.K. Ceftriaxone therapy in ciprofloxacin treatment failure typhoid fever in children. Indian J. Med. Res. 2001, 113, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Magnet, S.; Courvalin, P.; Lambert, T. Activation of the Cryptic aac(6′)-Iy Aminoglycoside Resistance Gene of Salmonella by a Chromosomal Deletion Generating a Transcriptional Fusion. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 6650–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Baert, L.; Jagadeesan, B.; Ngom-Bru, C.; Griswold, T.; Katz, L.S.; Carleton, H.A.; Deng, X. Implications of mobile genetic elements for Salmonella enterica single-nucleotide polymorphism subtyping and source tracking investigations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01985-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Thorsness, J.L.; Anderson, C.P.; Lynne, A.M.; Foley, S.L.; Han, J.; Fricke, W.F.; McDermott, P.F.; White, D.G.; Khatri, M. Horizontal gene transfer of a ColV plasmid has resulted in a dominant avian clonal type of Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayward, M.R.; Jansen, V.A.; Woodward, M.J. Comparative genomics of Salmonella enterica serovars Derby and Mbandaka, two prevalent serovars associated with different livestock species in the UK. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solnick, J.V.; Young, G.M. Chapter 10—Bacterial Pathogenicity Islands and Infectious Diseases. In Horizontal Gene Transfer; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensel, M. Evolution of pathogenicity islands of Salmonella enterica. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 294, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velásquez, J.C.; Hidalgo, A.A.; Villagra, N.; Santiviago, C.A.; Mora, G.C.; Fuentes, J.A. SPI-9 of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi is constituted by an operon positively regulated by RpoS and contributes to adherence to epithelial cells in culture. Microbiology 2016, 162, 1367–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, R.A.; Silva-Valenzuela, C.A.; Amaya, F.A.; Urrutia, T.M.; Contreras, I.; Santiviago, C.A. Differential roles for pathogenicity islands SPI-13 and SPI-8 in the interaction of Salmonella Enteritidis and Salmonella Typhi with murine and human macrophages. Biol. Res. 2017, 50, 2465–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Ojima, S.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, X.; Sugiyama, M.; Haneda, T.; Okamura, M.; Ono, H.K.; Hu, D.L. Salmonella pathogenicity island-14 is a critical virulence factor responsible for systemic infection in chickens caused by Salmonella gallinarum. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1401392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwan, C.L.; Lomonaco, S.; Bastos, L.M.; Cook, P.W.; Maher, J.; Trinetta, V.; Bhullar, M.; Phebus, R.K.; Gragg, S.; Kastner, J.; et al. Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles in Non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica Strains Isolated From Cambodian Informal Markets. Front Microbiol 2021, 12, 711472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufresne, K.; Saulnier-Bellemare, J.; Daigle, F. Functional analysis of the chaperone-usher fimbrial gene clusters of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulig, P.A.; Danbara, H.; Guiney, D.G.; Lax, A.J.; Norel, F.; Rhen, M. Molecular analysis of spv virulence genes of the Salmonella virulence plasmids. Mol. Microbiol. 1993, 7, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Genome Accession | Source | Serotype | ST | ARGs | QRDR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GyrA | ParC | ||||||
| S1 | JALPKT000000000 | raw poultry | London | 155 | aac(3)-Iid, aac(6’)-Iaa, aac(6’)-Ib-cr, aadA16, aph(3’’)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, blaTEM-1B, qnrB6, tet(A), sul1, sul2, catA2, floR, ARR-3, dfrA27, qacE, mph(A) | - | T57S |
| S2 | JALPLI000000000 | raw poultry | London | 155 | aac(3)-Iid, aac(6’)-Iaa, aac(6’)-Ib-cr, aadA16, aph(3’’)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, blaTEM-1B, qnrB6, tet(A), sul1, sul2, floR, ARR-3, dfrA27, qacE, mph(A) | - | T57S |
| S3 | JALPLL000000000 | raw poultry | London | 155 | aac(3)-Iid, aac(6’)-Iaa, aac(6’)-Ib-cr, aadA16, aph(3’’)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, blaTEM-1B, qnrB6, tet(A), sul1, sul2, floR, ARR-3, dfrA27, qacE, mph(A) | - | T57S |
| S4 | JALPLQ000000000 | food | London | 155 | aac(6’)-Iaa, aac(6’)-Ib-cr, aadA16, aph(3’’)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, qnrB6, tet(A), sul1, sul2, floR, ARR-3, dfrA27, qacE | - | T57S |
| S5 | JALPKU000000000 | raw poultry | Typhimurium | 19 | aac(6’)-Iaa, blaCTX-M-65, OqxA, OqxB, qnrS2, sul1, floR | - | - |
| S6 | JALPLA000000000 | raw poultry | Typhimurium | 19 | aac(6’)-Iaa, aph(3’’)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, blaTEM-1B, tet(A) | S83Y | - |
| S7 | JALPLG000000000 | raw poultry | Typhimurium | 19 | aac(6’)-Iaa, aph(3’’)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, blaTEM-1B, tet(A) | S83Y | - |
| S8 | JALPLP000000000 | raw poultry | Typhimurium | 19 | aac(6’)-Iaa, aph(3’’)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, blaTEM-1B, tet(A) | S83Y | - |
| S9 | JALPLM000000000 | raw poultry | Typhimurium | 34 | aac(3)-Iid, aac(6’)-Iaa, aph(3’’)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, blaTEM-1B, tet(B), sul1, sul2, floR, ARR-3, dfrA27, qacE | - | - |
| S10 | JALPLO000000000 | raw poultry | Typhimurium | 34 | aac(3)-IV, aac(6’)-Iaa, aac(6’)-Ib-cr, aph(3’’)-Ib, aph(4)-Ia, aph(6)-Id, blaOXA-1, blaTEM-1B, tet(B), sul1, sul2, catB3, ARR-3, qacE | - | - |
| S11 | JALPKV000000000 | raw poultry | Typhimurium | 1544 | aac(6’)-Iaa | - | - |
| S12 | JALPLJ000000000 | raw poultry | Goldcoast | 358 | aac(6’)-Iaa | - | T57S |
| S13 | JALPLK000000000 | raw poultry | Goldcoast | 358 | aac(6’)-Iaa, aac(3)-Iid, sul1, qacE, fosA7 | - | T57S |
| S14 | JALPLB000000000 | human stool | Liverpool | 1959 | aac(6’)-Iaa | - | T57S |
| S15 | JALPLC000000000 | human stool | Liverpool | 1959 | aac(6’)-Iaa | - | T57S |
| S16 | JALPLD000000000 | human stool | Liverpool | 1959 | aac(6’)-Iaa | - | T57S |
| S17 | JALPLE000000000 | human stool | Liverpool | 1959 | aac(6’)-Iaa | - | T57S |
| S18 | JALPLF000000000 | human stool | Liverpool | 1959 | aac(6’)-Iaa | - | T57S |
| S19 | JALPLN000000000 | raw poultry | Meleagridis | 463 | aac(6’)-Iaa, aph(3’)-Ia, blaTEM-1A, OqxA, OqxB, qnrS1, tet(A), floR | - | T57S |
| S20 | JALPLH000000000 | raw poultry | Corvallis | 1541 | aac(6’)-Iaa, qnrS1, floR | - | T57S |
| S21 | JALPKX000000000 | raw poultry | Kentucky | 198 | aac(3)-Id, aac(3)-Iid, aac(6’)-Iaa, aadA17, aadA7, aph(3’)-Ia, rmtB, blaCTX-M-55, blaTEM, qnrS1, tet(A), sul1, floR, ARR-2, dfrA14, qacE, mph(A), fosA3, lnu(F) | S83F, D87N | T57S, S80I |
| S22 | JALPKW000000000 | raw poultry | Anatum | 64 | aac(6’)-Iaa | - | T57S |
| S23 | JALPKZ000000000 | raw poultry | Infantis | 32 | aac(3)-IV, aac(6’)-Iaa, aadA1, aph(4)-Ia, blaCTX-M-65, tet(A), sul1, floR, dfrA14, qacE | D87Y | T57S |
| S24 | JALPKY000000000 | raw poultry | Javiana | 9074 | aac(6’)-Iaa | - | T57S |
| Sample | Serotype | Plasmids | Gene Found on Plasmids | Presence of Class I Integron | Gene Cassette Found on Integron |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | London | IncFIB(K) | - | 1 | aadA16, dfrA27, ARR-3,aac(6’)-Ib-cr |
| S2 | London | IncFIB(K) | - | 1 | aadA16, dfrA27, ARR-3,aac(6’)-Ib-cr |
| S3 | London | IncFIB(K), IncI1-I(Alpha) | - | 1 | aadA16, dfrA27, ARR-3,aac(6’)-Ib-cr |
| S4 | London | IncFIB(K) | - | 1 | aadA16, dfrA27, ARR-3,aac(6’)-Ib-cr |
| S5 | Typhimurium | IncHI2A, IncHI2, IncFIB(S), IncFII(S) | - | - | - |
| S6 | Typhimurium | IncFIB(S), IncFII(S) | - | - | - |
| S7 | Typhimurium | IncFIB(S), IncFII(S) | - | - | - |
| S8 | Typhimurium | IncFIB(S), IncFII(S) | - | - | - |
| S9 | Typhimurium | IncQ1 | sul2, aph(6)-Id, aph(3’’)-Ib | - | - |
| S10 | Typhimurium | IncHI2A, IncHI2, IncFIB(S), IncFII(S), IncQ1 | - | CALIN | aac(6’)-Ib-cr |
| S11 | Typhimurium | IncFIB(S), IncFII(S) | - | - | - |
| S12 | Goldcoast | - | - | - | - |
| S13 | Goldcoast | - | - | - | - |
| S14 | Liverpool | - | - | - | - |
| S15 | Liverpool | - | - | - | - |
| S16 | Liverpool | - | - | - | - |
| S17 | Liverpool | - | - | - | - |
| S18 | Liverpool | - | - | - | - |
| S19 | Meleagridis | IncFIA(HI1), IncFIB(K) | - | - | - |
| S20 | Corvallis | - | - | - | - |
| S21 | Kentucky | - | - | - | - |
| S22 | Anatum | IncFII(p96A), Col(pHAD28), Col440II | - | - | - |
| S23 | Infantis | IncFIB(pN55391) | - | 1 | aadA1 |
| S24 | Javiana | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, S.; Hong, C.; Feng, X.; Cai, H.; Xia, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Lou, Y.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Factors, and Genetic Diversity of Salmonella from Wenzhou, China. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2166. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112166
Jin Y, Li Y, Huang S, Hong C, Feng X, Cai H, Xia Y, Li S, Zhang L, Lou Y, et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Factors, and Genetic Diversity of Salmonella from Wenzhou, China. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(11):2166. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112166
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Yafang, Yi Li, Shaojie Huang, Chengji Hong, Xucong Feng, Huidi Cai, Yanmei Xia, Shengkai Li, Leyi Zhang, Yongliang Lou, and et al. 2024. "Whole-Genome Sequencing Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Factors, and Genetic Diversity of Salmonella from Wenzhou, China" Microorganisms 12, no. 11: 2166. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112166
APA StyleJin, Y., Li, Y., Huang, S., Hong, C., Feng, X., Cai, H., Xia, Y., Li, S., Zhang, L., Lou, Y., & Guan, W. (2024). Whole-Genome Sequencing Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Factors, and Genetic Diversity of Salmonella from Wenzhou, China. Microorganisms, 12(11), 2166. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112166





