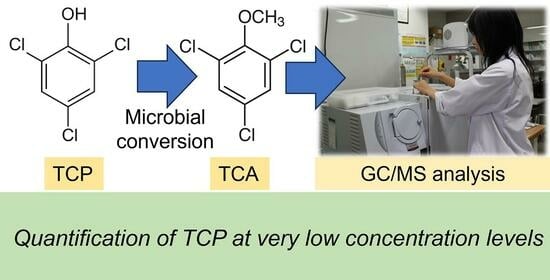
Novel and Simple Method for Quantification of 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol with Microbial Conversion to 2,4,6-Trichloroanisole
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of Microorganisms
2.2. Identification of the Isolates
2.2.1. Fungal Isolates
2.2.2. Bacterial Isolates
2.3. Screening for Producers of TCA from TCP
2.4. Quantitative Analysis of the TCP to TCA Conversion by Mycolicibacterium sp. CB14
3. Results
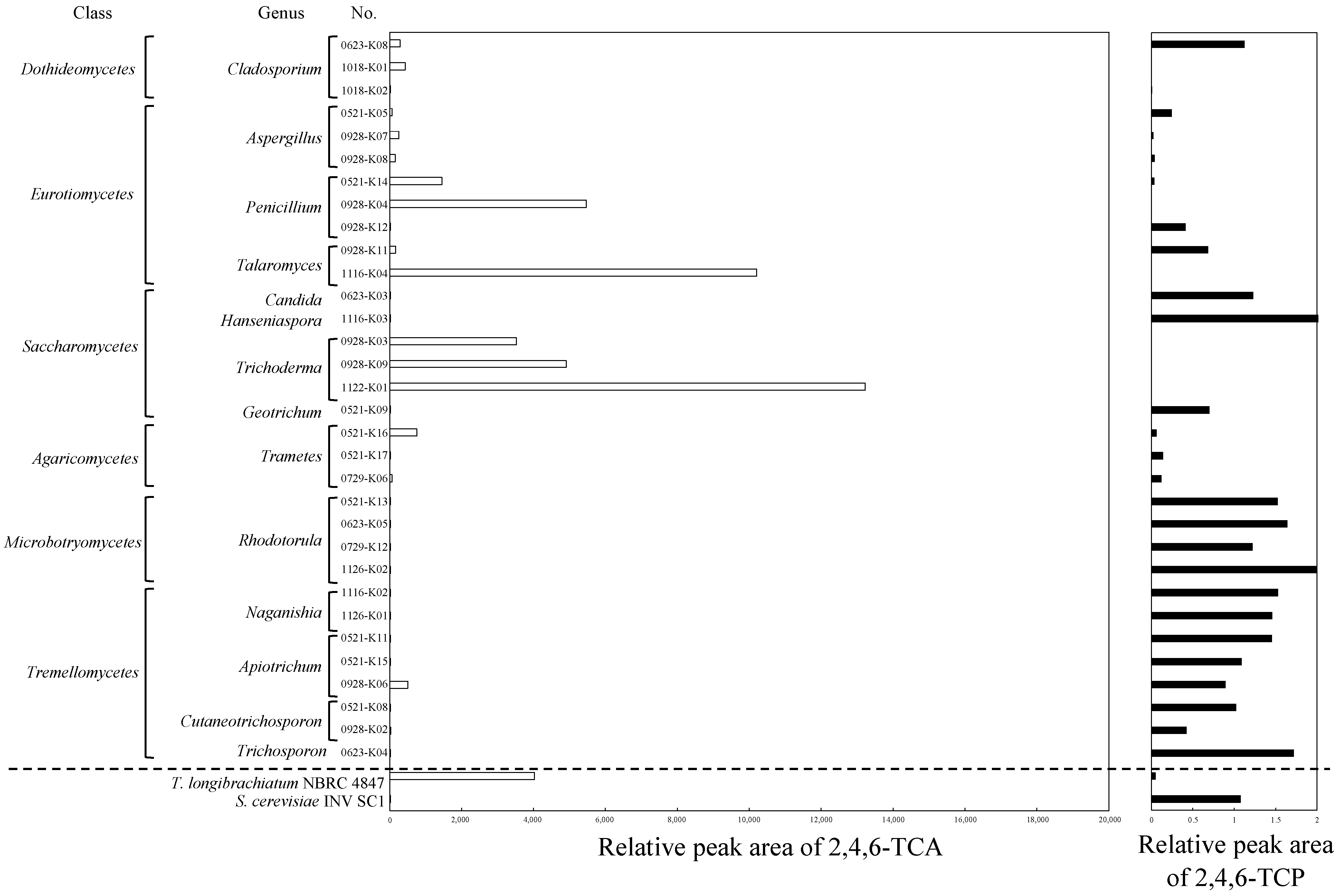
3.1. Isolation of TCA Producer
3.1.1. Fungal Isolates
3.1.2. Bacterial Isolates
3.2. Production of TCA by Mycolicibacterium sp. CB14
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaziur, W.; Salemi, A.; Jochmann, M.A.; Schmidt, T.C. Automated determination of picogram-per-liter level of water taste and odor compounds using solid-phase microextraction arrow coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 2653–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suffet, I.H.; Khiari, D.; Bruchet, A. The drinking water taste and odor wheel for the millennium: Beyond geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.Y.; Lin, Y.L.; Zhang, T.Y.; Hu, C.Y.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, Z.X.; Tang, Y.L.; Xu, B.; Gao, N.Y. The formation, analysis, and control of chlor(am)ination-derived odor problems: A review. Water Res. 2021, 203, 117549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahraei, S.K.; Amir, S.; Torsten, C.S. Sample preparation for determination of water taste and odor compounds: A review. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 32, e00149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, A.; Köster, O.; Schildknecht, A.; Gunten, U. Occurrence of dissolved and particle-bound taste and odor compounds in Swiss lake waters. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2191–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gallagher, D.L.; Dietrich, A.M.; Su, M.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, J.; An, W.; et al. Data analytics determines co-occurrence of odorants in raw water and evaluates drinking water treatment removal strategies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 16770–16782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, D.; Galler, H.; Habib, J.; Melkes, A.; Schlacher, R.; Buzina, W.; Friedl, H.; Marth, E.; Reinthaler, F. Concentrations of viable airborne fungal spores and trichloroanisole in wine cellars. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 144, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piriou, P.; Malleret, L.; Bruchet, A.; Kiene, L. Trichloroanisole kinetics and musty tastes in drinking water distribution systems. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2001, 1, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Xu, B.; Qi, F.; Kumirska, J. The occurrence of haloanisoles as an emerging odorant in municipal tap water of typical cities in China. Water Res. 2016, 98, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Y.; Ye, M.; Pan, R. Formation of odorant haloanisoles and variation of microorganisms during microbial O-methylation in annular reactors equipped with different coupon materials. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 679, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, H.; Reeder, S.; Southard, M. Monitoring programs are an evolving process: Detection of T&O in filter media. J. AWWA 2021, 113, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.X.; Lin, Y.L.; Fang, R.F.; Zhou, X.Y.; Liu, Z.; Dong, Z.Y.; Zhang, T.Y.; Xu, B. Removal of algae and algogenic odor compounds via combined pre-chlorination and powdered activated carbon adsorption for source water pretreatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 304, 122365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, T.; Mao, M.; Fu, J. Study on formation of 2,4,6-trichloroanisole by microbial O-methylation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol in lake water. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, A.; Xu, B.; Xian, Q.; Shuang, C.; Shi, P.; Zhou, Q. Detection, formation and occurrence of 13 new polar phenolic chlorinated and brominated disinfection byproducts in drinking water. Water Res. 2017, 112, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hope, B.; Pillsbury, L.; Boling, B. A state-wide survey in Oregon (USA) of trace metals and organic chemicals in municipal effluent. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 417–418, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urase, T.; Sasaki, Y. Occurrence of earthy and musty odor compounds (geosmin, 2-methylisoborneol and 2,4,6-trichloroanisole) in biologically treated wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 1969–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agus, E.; Zhang, L.; Sedlak, D.L. A framework for identifying characteristic odor compounds in municipal wastewater effluent. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5970–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, N.G.; Cardoso, V.V.; Ferreira, E.; Benoliel, M.J.; Almeida, C.M. Experimental and statistical validation of SPME-GC–MS analysis of phenol and chlorophenols in raw and treated water. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schummer, C.; Delhomme, O.; Appenzeller, B.M.; Wennig, R.; Millet, M. Comparison of MTBSTFA and BSTFA in derivatization reactions of polar compounds prior to GC/MS analysis. Talanta 2009, 77, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsol-Vall, A.; Ainsa, S.; Lopez, R.; Ferreira, V. Development and validation of a method for the analysis of halophenols and haloanisoles in cork bark macerates by stir bar sorptive extraction heart-cutting two-dimensional gas chromatography negative chemical ionization mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1673, 463186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jové, P.; Pareras, A.; De Nadal, R.; Verdum, M. Development and optimization of a quantitative analysis of main odorants causing off flavours in cork stoppers using headspace solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 56, e4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.M.; Han, S.M.; Lee, H.J.; Kang, M.; Jeong, T.Y.; Son, J.; Min, H.; Cha, S.; Oh, H.B.; Oh, W.K.; et al. Influence of mobile phase composition on the analytical sensitivity of LC–ESI–MS/MS for the concurrent analysis of bisphenols, parabens, chlorophenols, benzophenones, and alkylphenols. Environ. Res. 2023, 221, 115305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, S.; Hua, X.; Xia, F.; Tian, D.; Zhou, C. Highly sensitive detection of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol based on HS-β-cyclodextrin/gold nanoparticles composites modified indium tin oxide electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 167, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prak, S.; Gunata, Z.; Guiraud, J.P.; Schorr-Galindo, S. Fungal strains isolated from cork stoppers and the formation of 2,4,6-trichloroanisole involved in the cork taint of wine. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhang, T.; Qu, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, Z. Contribution of filamentous fungi to the musty odorant 2,4,6-trichloroanisole in water supply reservoirs and associated drinking water treatment plants. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Cao, C.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, F.; Sun, Y.; Cai, Z.; Fu, J. Pilot investigation on formation of 2,4,6-trichloroanisole via microbial O-methylation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol in drinking water distribution system: An insight into microbial mechanism. Water Res. 2018, 131, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, T.; Cen, C.; Pan, R. Biotransformation of halophenols into earthy-musty haloanisoles: Investigation of dominant bacterial contributors in drinking water distribution systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-087553-013-0. [Google Scholar]
- Coque, J.R.; Alvarez-Rodríguez, M.L.; Larriba, G. Characterization of an inducible chlorophenol O-methyltransferase from Trichoderma longibrachiatum involved in the formation of chloroanisoles and determination of its role in cork taint of wines. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5089–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltrer, R.; Álvarez-Rodríguez, M.L.; Barreiro, C.; Godio, R.P.; Coque, J.J.R. Characterization of a novel 2,4,6-trichlorophenol-inducible gene encoding chlorophenol O-methyltransferase from Trichoderma longibrachiatum responsible for the formation of chloroanisoles and detoxification of chlorophenols. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2010, 47, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiirola, M.A.; Mannisto, M.K.; Puhakka, J.A.; Kulomaa, M.S. Isolation and characterization of Novosphingobium sp strain MT1, a dominant polychlorophenol-degrading strain in a groundwater bioremediation system. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2002, 68, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, K.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Huang, T.; Guo, H.; Ma, B.; Yang, W.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H. Bacterial community structure and metabolic activity of drinking water pipelines in buildings: A new perspective on dual effects of hydrodynamic stagnation and algal organic matter invasion. Water Res. 2022, 225, 119161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, R.; Luan, T.; Lin, L.; Zou, S.; Yang, Q. Full automatic determination of chlorophenols in water using solid-phase microextraction/on-fiber derivatization and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Rodríguez, M.L.; López-Ocana, L.; López-Coronado, J.M.; Rodríguez, E.; Martínez, M.J.; Larriba, G.; Coque, J.J.R. Cork taint of wines: Role of the filamentous fungi isolated from cork in the formation of 2,4,6-trichloroanisole by O-methylation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5860–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haggblom, M.M.; Nohynek, L.J.; Salkinojasalonen, M.S. Degradation and O-methylation of chlorinated phenolic compounds by Rhodococcus and Mycobacterium strains. Appl. Environ. Microb. 1988, 54, 3043–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campoy, S.; Álvarez-Rodríguez, M.L.; Recio, E.; Rumbero, A.; Coque, J.J.R. Biodegradation of 2,4,6-TCA by the white-rot fungus Phlebia radiata is initiated by a phase I (O-demethylation)–phase II (O-conjugation) reactions system: Implications for the chlorine cycle. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, M.; Recio, E.; Campoy, S.; Martín, J.F.; Coque, J.J.R. Environmental significance of O-demethylation of chloroanisoles by soil bacterial isolates as a mechanism that improves the overall biodegradation of chlorophenols. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2512–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo, G.M.; Kupski, L.; Degang, L.; Marube, L.C.; Caldas, S.S.; Primel, E.G. Determination of fifteen phenols in wastewater from petroleum refinery samples using a dispersive liquid—Liquid microextraction and liquid chromatography with a photodiode array detector. Microchem. J. 2019, 146, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sampling Dates | Sampling Locations | Number of Isolates |
|---|---|---|
| 21 May 2021 | T1 | 9 |
| 20 June 2021 | T2 | 4 |
| 28 July 2021 | T2 | 2 |
| 28 September 2021 | T3 | 9 |
| 18 October 2021 | B1 | 2 |
| 16 November 2021 | R1 | 3 |
| 20 November 2021 | R2 | 1 |
| 26 November 2021 | B2 | 2 |
| Sampling Dates | Sampling Locations | Number of Isolates |
|---|---|---|
| 18 October 2021 | B1 | 5 |
| 16 November 2021 | R1 | 9 |
| 20 November 2021 | R2 | 2 |
| 26 November 2021 | B2 | 6 |
| 16 May 2022 | B3 | 3 |
| 16 May 2022 | B4 | 2 |
| 26 Jun 2022 | B5 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goto, S.; Urase, T.; Nakakura, K. Novel and Simple Method for Quantification of 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol with Microbial Conversion to 2,4,6-Trichloroanisole. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2133. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11092133
Goto S, Urase T, Nakakura K. Novel and Simple Method for Quantification of 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol with Microbial Conversion to 2,4,6-Trichloroanisole. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(9):2133. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11092133
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoto, Saki, Taro Urase, and Kaito Nakakura. 2023. "Novel and Simple Method for Quantification of 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol with Microbial Conversion to 2,4,6-Trichloroanisole" Microorganisms 11, no. 9: 2133. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11092133
APA StyleGoto, S., Urase, T., & Nakakura, K. (2023). Novel and Simple Method for Quantification of 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol with Microbial Conversion to 2,4,6-Trichloroanisole. Microorganisms, 11(9), 2133. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11092133