High Levels of Antibiotic Resistance in MDR-Strong Biofilm-Forming Salmonella Typhimurium ST34 in Southern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Collection and Isolate Identification
2.2. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification and Multi-Locus Sequence Typing (MLST)
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Detection of Biofilm Formation Ability
2.5. Detection of Resistance Genes and Mutations
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. S. typhimurium Isolation and Identification
3.2. MLST Analysis
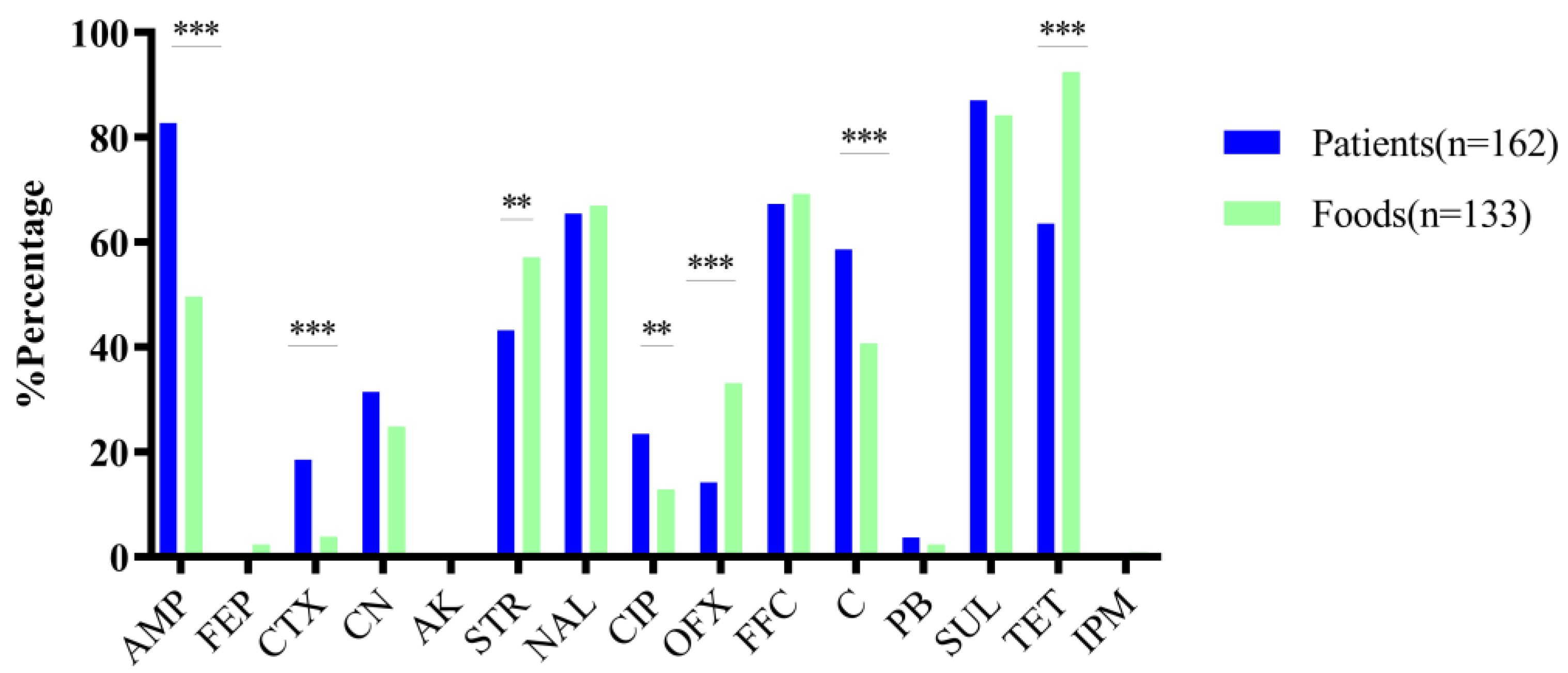
3.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing and Distribution of MDR
3.4. Biofilm Formation Ability
3.5. Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Mutations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirk, M.D.; Pires, S.M.; Black, R.E.; Caipo, M.; Crump, J.A.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Dopfer, D.; Fazil, A.; Fischer-Walker, C.L.; Hald, T.; et al. World Health Organization Estimates of the Global and Regional Disease Burden of 22 Foodborne Bacterial, Protozoal, and Viral Diseases, 2010: A Data Synthesis. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Aydin, M.; Khatiwara, A.; Dolan, M.C.; Gilmore, D.F.; Bouldin, J.L.; Ahn, S.; Ricke, S.C. Current and emerging technologies for rapid detection and characterization of Salmonella in poultry and poultry products. Food Microbiol. 2014, 38, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X.; Jiang, M.; Lin, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Qian, Z.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, L. Clonal Expansion of Biofilm-Forming Salmonella Typhimurium ST34 with Multidrug-Resistance Phenotype in the Southern Coastal Region of China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genotyping using whole-genome sequencing is a realistic alternative to surveillance based on phenotypic antimicrobial susceptibility testing. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 771–777. [CrossRef]
- Hendriksen, R.S.; Vieira, A.R.; Karlsmose, S.; Lo Fo Wong, D.M.; Jensen, A.B.; Wegener, H.C.; Aarestrup, F.M. Global monitoring of Salmonella serovar distribution from the World Health Organization Global Foodborne Infections Network Country Data Bank: Results of quality assured laboratories from 2001 to 2007. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Li, Y.; Elbediwi, M.; Yue, M. Emergence and Dissemination of mcr-Carrying Clinically Relevant Salmonella Typhimurium Monophasic Clone ST34. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Bai, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, K.; Lin, Q.; Xu, C.; Qu, X.; Zhang, H.; Liao, M.; et al. Highly prevalent multidrug resistance and QRDR mutations in Salmonella isolated from chicken, pork and duck meat in Southern China, 2018–2019. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 340, 109055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoke-Kqueen, C.; Learn-Han, L.; Noorzaleha, A.S.; Son, R.; Sabrina, S.; Jiun-Horng, S.; Chai-Hoon, K. Characterization of multiple-antimicrobial-resistant Salmonella enterica Subsp. enterica isolated from indigenous vegetables and poultry in Malaysia. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, R.; Qi, C.; Gao, H.; Sun, F. Mechanisms of polymyxin resistance induced by Salmonella Typhimurium in vitro. Veterinary Microbiol. 2021, 257, 109063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wei, Z.; Shen, P.; Ji, J.; Sun, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhang, T.; Ji, P.; Ni, Y.; Hu, Z.; et al. Bacterial-resistance among outpatients of county hospitals in China: Significant geographic distinctions and minor differences between central cities. Microbes Infect. 2015, 17, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Liang, B.; Wu, F.; Yang, X.; Ma, Q.; Yang, C.; Hu, X.; Liu, H.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium in Shanghai, China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molbak, K. Human health consequences of antimicrobial drug-resistant Salmonella and other foodborne pathogens. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Gao, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.; He, H.; Chen, Z.; Liao, M.; Zhang, J. Increased Drug Resistance and Biofilm Formation Ability in ST34-Type Salmonella Typhimurium Exhibiting Multicellular Behavior in China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 876500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, A.; Azim, S.; Ali, A.; Andleeb, S.; Ahsan, A.; Imran, M.; Rahman, A. Antimicrobial Resistance Profiling of Biofilm Forming Non Typhoidal Salmonella enterica Isolates from Poultry and Its Associated Food Products from Pakistan. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algammal, A.M.; Abo Hashem, M.E.; Alfifi, K.J.; Al-Otaibi, A.S.; Alatawy, M.; ElTarabili, R.M.; Abd El-Ghany, W.A.; Hetta, H.F.; Hamouda, A.M.; Elewa, A.A.; et al. Sequence Analysis, Antibiogram Profile, Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance Genes of XDR and MDR Gallibacterium anatis Isolated from Layer Chickens in Egypt. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 4321–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algammal, A.M.; Ibrahim, R.A.; Alfifi, K.J.; Ghabban, H.; Alghamdi, S.; Kabrah, A.; Khafagy, A.R.; Abou-Elela, G.M.; Abu-Elala, N.M.; Donadu, M.G.; et al. A First Report of Molecular Typing, Virulence Traits, and Phenotypic and Genotypic Resistance Patterns of Newly Emerging XDR and MDR Aeromonas veronii in Mugil seheli. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Ke, B.; Huang, Y.; He, D.; Li, X.; Liang, Z.; Ke, C. The molecular epidemiological characteristics and genetic diversity of Salmonella Typhimurium in Guangdong, China, 2007–2011. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Cui, Y.; Shi, C.; Shi, X. Prevalence and Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance in Salmonella enterica Isolates from Retail Foods in Shanghai, China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2020, 17, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, W.; Jacobson, A.; Hammack, T. Bacteriological Analytical Manual: Salmonella; US Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Popoff, M.Y.; Bockemühl, J.; Gheesling, L.L. Supplement 2002 (no. 46) to the Kauffmann–White scheme. Res. Microbiol. 2004, 155, 568–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI, C. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Clin. Lab Stand. Inst. 2016, 35, 16–38. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, X.; Fu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, L.; Qu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhan, Z. High-levels of resistance to quinolone and cephalosporin antibiotics in MDR-ACSSuT Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis mainly isolated from patients and foods in Shanghai, China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 286, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, T.-X.; Wang, X.-N.; Wu, H.-Y.; Bi, J.-R.; Hao, H.-S.; Hou, H.-M.; Zhang, G.-L. Transcriptomic Analysis, Motility and Biofilm Formation Characteristic s of Salmonella Typhimurium Exposed to Benzyl Isothiocyanate Tr eatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 21, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, L.; You, L.; Wang, D.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Bai, G.; Li, J.; Wei, X.; Li, S. Highly prevalent MDR, frequently carrying virulence genes and antimicrobial resistance genes in Salmonella enterica serovar 4,[5],12:i:- isolates from Guizhou Province, China. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. NARMS: 2019 Intergrated Report Summary; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2022.
- Campioni, F.; Moratto Bergamini, A.M.; Falcão, J.P. Genetic diversity, virulence genes and antimicrobial resistance of Sal monella Enteritidis isolated from food and humans over a 24-year perio d in Brazil. Food Microbiol. 2012, 32, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Moreno, M.O.; Picó-Plana, E.; de Toro, M.; Grande-Armas, J.; Quiles-Fortuny, V.; Pons, M.J.; Gomes, C.; Sáenz, Y.; Torres, C.; Ruiz, J. β-Lactamases, transferable quinolone resistance determinants, and clas s 1 integron-mediated antimicrobial resistance in human clinical Salmo nella enterica isolates of non-Typhimurium serotypes. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 303, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wen, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, X.; Zhan, Z.; Chen, Z.; Bai, J.; Qu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. Plasmid-Encoded blaNDM-5 Gene That Confers High-Leve l Carbapenem Resistance in Salmonella Typhimurium of Pork Origin. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 1485–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridier, A.; Sanchez-Vizuete, P.; Guilbaud, M.; Piard, J.C.; Naïtali, M.; Briandet, R. Biofilm-associated persistence of food-borne pathogens. Food Microbiol. 2015, 45, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressaire, C.; Moreira, R.N.; Barahona, S.; Alves de Matos, A.P.; Arraiano, C.M. BolA is a transcriptional switch that turns off motility and turns on biofilm development. mBio 2015, 6, e02352-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, B.; Sun, J.; He, D.; Li, X.; Liang, Z.; Ke, C.-W. Serovar distribution, antimicrobial resistance profiles, and PFGE typing of Salmonella enterica strains isolated from 2007–2012 in Guangdong, China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Xi, M.; Cui, S.; Zhang, X.; Shen, J.; Sheng, M.; Qu, D.; Wang, X.; Meng, J. Mutations in gyrase and topoisomerase genes associated with fluoroquinolone resistance in Salmonella serovars from retail meats. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ma, H.; Wang, J.; Liang, B.; Du, X.; Wu, F.; Xia, S.; Yang, X.; et al. The phenotypic and molecular characteristics of antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium in Henan Province, China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Xu, C.; Qu, X.; Chen, Z.; Bai, J.; Liao, M.; Zhang, J. Antimicrobial resistance and molecular characterization of Salmonella enterica serovar Corvallis isolated from human patients and animal source foods in China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 335, 108859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robicsek, A.; Strahilevitz, J.; Jacoby, G.A.; Macielag, M.; Abbanat, D.; Park, C.H.; Bush, K.; Hooper, D.C. Fluoroquinolone-modifying enzyme: A new adaptation of a common aminogl ycoside acetyltransferase. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiratisin, P.; Apisarnthanarak, A.; Saifon, P.; Laesripa, C.; Kitphati, R.; Mundy, L.M. The emergence of a novel ceftazidime-resistant CTX-M extended-spectrum beta-lactamase, CTX-M-55, in both community-onset and hospital-acquir ed infections in Thailand. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 58, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevan, E.R.; Jones, A.M.; Hawkey, P.M. Global epidemiology of CTX-M β-lactamases: Temporal and geographical s hifts in genotype. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2145–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Z.; Bai, J.; Liao, M.; Zhang, J. Fourth Generation Cephalosporin Resistance Among Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Isolates in Shanghai, China Conferred by blaCTX-M-55 Harboring Plasmids. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.-X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in a nimals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biol ogical study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zeng, M.; Xu, J.; Zhou, H.; Gu, B.; Li, Z.; Jin, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; et al. Epidemiologic and genomic insights on mcr-1-harbouring Salmonella from diarrhoeal outpatients in Shanghai, China, 2006–2016. EBioMedicine 2019, 42, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| STs | eBG | Sources | Isolates Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST34 | 1 | Human (132), food (111) | 243 | 82.4% |
| ST19 | 1 | Human (25), food (22) | 47 | 15.9% |
| ST36 | 138 | Human (2) | 2 | 0.7% |
| ST99 | 1 | Human (1) | 1 | 0.3% |
| ST1557 | 1 | Human (2) | 2 | 0.7% |
| Number of Antibiotic Classes They Exhibited Resistance to | Sources | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food (%) | Human (%) | |||||||
| ST19 | ST34 | ST19 | ST34 | ST36 | ST99 | ST1557 | ||
| 0 | 3 (13.64%) | 0 (0.00%) | 5 (20.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 9 (3.05%) |
| 1 | 7 (31.82%) | 4 (3.60%) | 3 (12.00%) | 3 (2.27%) | 2 | 0 | 2 | 21 (7.12%) |
| 2 | 3 (13.64%) | 3 (2.70%) | 3 (12.00%) | 7 (5.30%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16 (5.42%) |
| ≥3 | 9 (40.91%) | 105 (94.59%) | 14 (56.00%) | 121 (91.67%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 249 (84.41%) |
| 3 | 5 (22.73%) | 15 (13.51%) | 4 (16.00%) | 22 (16.67%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 46 (15.59%) |
| 4 | 2 (9.09%) | 16 (14.41%) | 6 (24.00%) | 12 (9.09%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 36 (12.20%) |
| 5 | 2 (9.09%) | 19 (17.12%) | 3 (12.00%) | 25 (18.94%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 49 (16.61%) |
| 6 | 0 (0.00%) | 41 (36.94%) | 0 (0.00%) | 44 (33.33%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 85 (28.81%) |
| 7 | 0 (0.00%) | 14 (12.61%) | 1 (4.00%) | 18 (13.64%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33 (11.19%) |
| Total | 22 (100.00%) | 111 (100.00%) | 25 (100.00%) | 132 (100.00%) | 2 | 1 | 2 | 295 (100.00%) |
| STs | ST34 | ST19 | ST36 | ST99 | ST1557 | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sources | Food | Human | Food | Human | Human | ||||
| Biofilm FormationAbility | None | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 6 (27.27%) | 12 (48.00%) | 1 | 1 | 2 | 22 (7.46%) |
| Weak | 19 (17.43%) | 9 (6.72%) | 14 (63.64%) | 10 (40.00%) | 273 (92.54%) | ||||
| Moderate | 8 (7.34%) | 30 (22.39%) | 2 (9.09%) | 2 (8.00%) | 1 | ||||
| Strong | 82 (75.23%) | 95 (70.90%) | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (4.00%) | |||||
| Total | 109 | 134 | 22 | 25 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 295 | |
| Resistance Classification | Genes | Mutation | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PMQR (plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance) | qnrA | 0.0% (0/56) | |
| qnrB | 37.5% (21/56) | ||
| qnrC | 0.0% (0/56) | ||
| qnrD | 0.0% (0/56) | ||
| qnrS | 0.0% (0/56) | ||
| acc6-(lb’)-cr | 80.3% (45/56) | ||
| oqxAB | 87.5% (49/56) | ||
| qepA | 0% (0/56) | ||
| QRDR (quinolone resistance-determining region) | gyrA | D(Asp)87N(Asn) | 82.1% (46/56) |
| D(Asp)87Y(Tyr) | 10.7% (6/56) | ||
| S(Ser)83F(Phe) | 5.4% (3/56) | ||
| No mutation | 0.2% (1/56) | ||
| parC | No mutation | 100.0% (56/56) | |
| β-lactams | blaCTX-M | 27.8% (10/36) | |
| blaTEM | 41.7% (15/36) | ||
| blaOXA | 19.4% (7/36) | ||
| Carbapenem | blaNDM-5 | 100% (1/1) | |
| Colistin | mcr-1 | 100% (9/9) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Chen, K.; Lin, R.; Xu, X.; Xu, F.; Lin, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Liao, M.; et al. High Levels of Antibiotic Resistance in MDR-Strong Biofilm-Forming Salmonella Typhimurium ST34 in Southern China. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082005
Gao Y, Chen K, Lin R, Xu X, Xu F, Lin Q, Hu Y, Zhang H, Zhang J, Liao M, et al. High Levels of Antibiotic Resistance in MDR-Strong Biofilm-Forming Salmonella Typhimurium ST34 in Southern China. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(8):2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082005
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yuan, Kaifeng Chen, Runshan Lin, Xuebin Xu, Fengxiang Xu, Qijie Lin, Yaping Hu, Hongxia Zhang, Jianmin Zhang, Ming Liao, and et al. 2023. "High Levels of Antibiotic Resistance in MDR-Strong Biofilm-Forming Salmonella Typhimurium ST34 in Southern China" Microorganisms 11, no. 8: 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082005
APA StyleGao, Y., Chen, K., Lin, R., Xu, X., Xu, F., Lin, Q., Hu, Y., Zhang, H., Zhang, J., Liao, M., & Qu, X. (2023). High Levels of Antibiotic Resistance in MDR-Strong Biofilm-Forming Salmonella Typhimurium ST34 in Southern China. Microorganisms, 11(8), 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082005





