Different Responses of Bacteria and Archaea to Environmental Variables in Brines of the Mahai Potash Mine, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sites Descriptions and Sampling
2.2. Physicochemical Characterization
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.4. Sequence Processing and Bioinformatic and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physiochemical Characterization of Brine Samples of Mahai Lake Potash Mine
3.2. Alpha Diversity of the Prokaryotic Communities within the Mahai Potash Mine Area
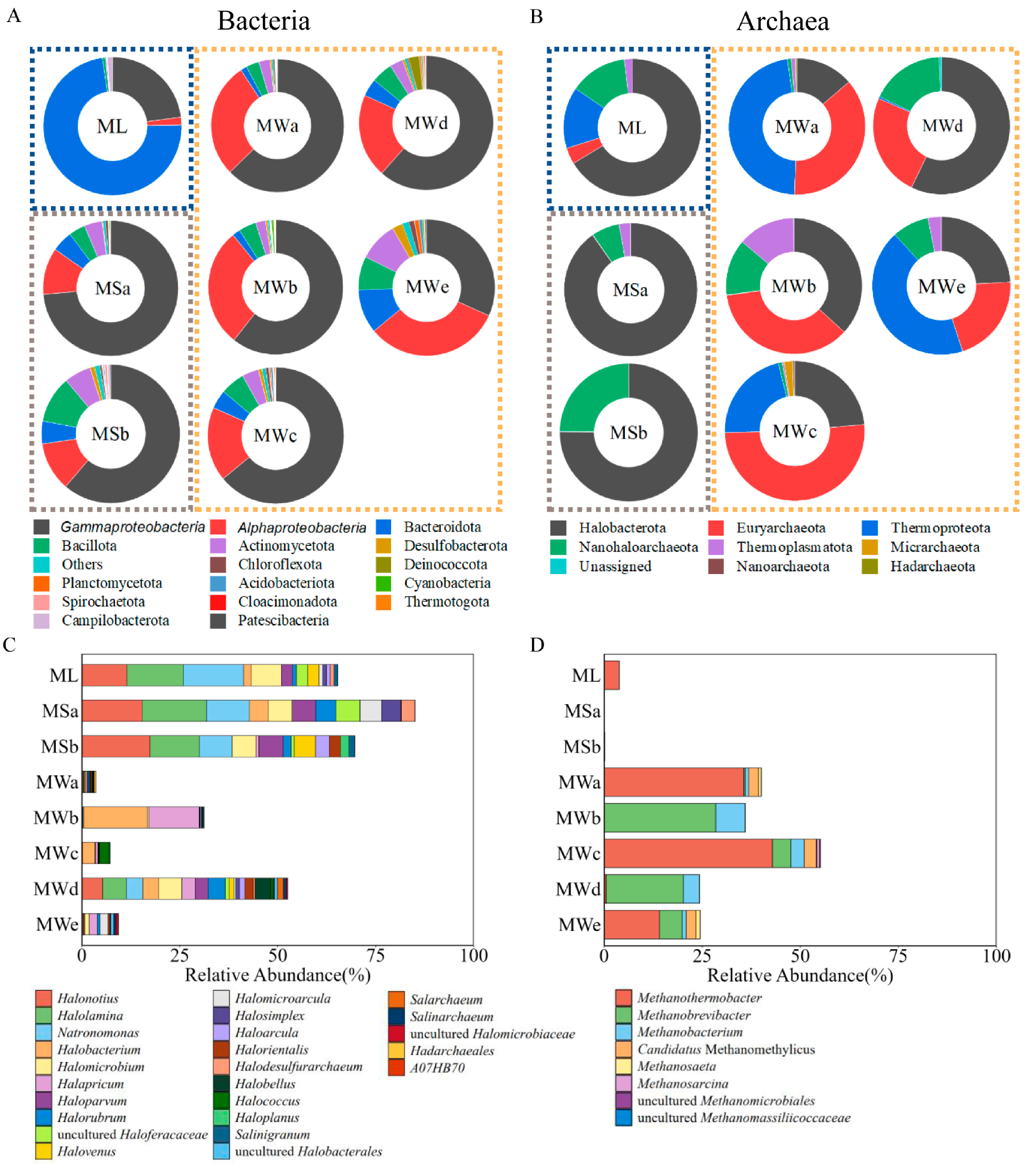
3.3. Characterization of the Prokaryotic Communities
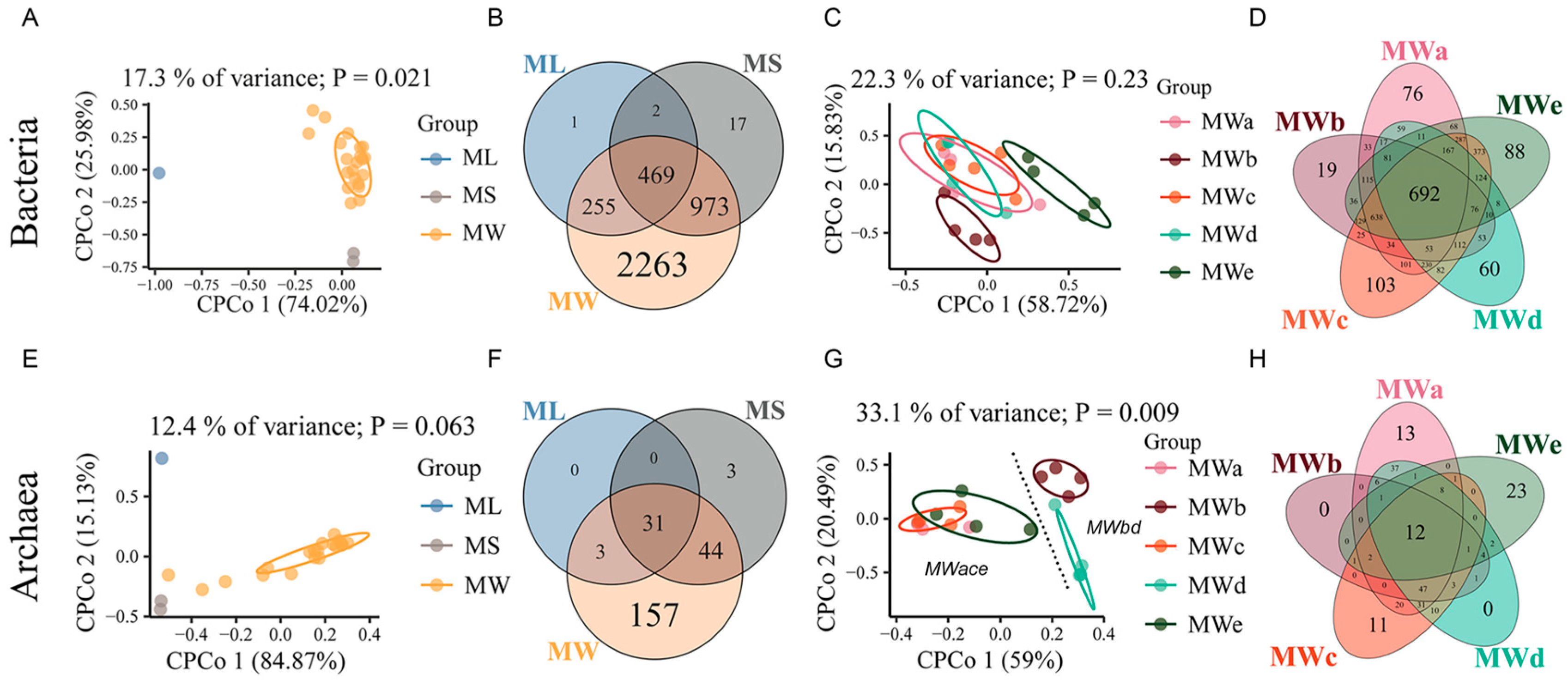
3.4. Microbial Community Comparison among Sample Groups
3.5. Potential Correlations between Microbial Communities and Variables of Brines
4. Discussion
4.1. Prokaryotic Compositions in the Mahai Potash Area
4.2. Bacteria and Archaea Responded Differently to Environmental Factors
4.3. Archea and Brine Chemistry
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oren, A. Thermodynamic limits to microbial life at high salt concentrations. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1908–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DasSarma, S.; DasSarma, P. Halophiles. In enPcyclopedia of Life Sciences (eLS); John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- McGenity, T.; Oren, A. Hypersaline Environments; CABI International: Wallingford, UK, 2012; pp. 402–437. [Google Scholar]
- Oren, A. Taxonomy of the family Halobacteriaceae: A paradigm for changing concepts in prokaryote systematics. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oren, A. Halophilic Archaea. In Encyclopedia of Microbiology, 4th ed.; Schmidt, T.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 495–503. [Google Scholar]
- Narasingarao, P.; Podell, S.; Ugalde, J.A.; Brochier-Armanet, C.; Emerson, J.B.; Brocks, J.J.; Heidelberg, K.B.; Banfield, J.F.; Allen, E.E. De novo metagenomic assembly reveals abundant novel major lineage of Archaea in hypersaline microbial communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, D.Y.; Makarova, K.S.; Abbas, B.; Ferrer, M.; Golyshin, P.N.; Galinski, E.A.; Ciordia, S.; Mena, M.C.; Merkel, A.Y.; Wolf, Y.I.; et al. Discovery of extremely halophilic, methyl-reducing euryarchaea provides insights into the evolutionary origin of methanogenesis. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventosa, A.; de la Haba, R.R.; Sánchez-Porro, C.; Papke, R.T. Microbial diversity of hypersaline environments: A metagenomic approach. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2015, 25, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Prasongsuk, S.; Akbar, A.; Aslam, M.; Lotrakul, P.; Punnapayak, H.; Rakshit, S. Hypersaline habitats and halophilic microorganisms. Maejo. Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 10, 330–345. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Abdallah, M.; Karray, F.; Kallel, N.; Armougom, F.; Mhiri, N.; Quéméneur, M.; Cayol, J.-L.; Erauso, G.; Sayadi, S. Abundance and diversity of prokaryotes in ephemeral hypersaline lake Chott El Jerid using Illumina Miseq sequencing, DGGE and qPCR assays. Extremophiles 2018, 22, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Villegas, P.; Vigara, J.; León, R. Characterization of the microbial population inhabiting a solar saltern pond of the odiel marshlands (SW Spain). Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachran, M.; Kluge, S.; Lopez-Fernandez, M.; Cherkouk, A. Microbial diversity in an arid, naturally saline environment. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 78, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto-Rodríguez, R.L.; Montalvo-Rodríguez, R. Temporal analysis of the microbial community from the crystallizer ponds in Cabo Rojo, Puerto Rico, using metagenomics. Genes 2019, 10, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, L.; Guo, Q.; Cao, S. Archaeal community diversity in different types of saline-alkali soil in arid regions of Northwest China. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2020, 130, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáenz de Miera, L.E.; Gutiérrez-González, J.J.; Arroyo, P.; Falagán, J.; Ansola, G. Prokaryotic community diversity in the sediments of saline lagoons and its resistance to seasonal disturbances by water level cycles. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 3169–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, F.; Sun, S.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S. Species diversity of culturable halophilic microorganisms isolated from Dingyuan salt mine, Anhui. Microbiol. China 2019, 46, 2186–2197. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, G.; Srivastava, S.; Khare, S.; Prakash, V. Extremophiles: An overview of microorganism from extreme environment. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Biotechnol. 2014, 7, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L. A review on the exploration of global potash resources with an emphasis on the past and present status of China with a methodological perspective. J. Salt Lake Res. 2007, 15, 56–72. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Geng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Z.; Li, M. Dynamic potassium flows analysis in China for 2010–2019. Resour. Policy 2022, 78, 102803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, C.; Jiao, P.; Hu, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, S. Simulation study on the mining conditions of dissolution of low grade solid potash ore in Qarhan Salt Lake. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chairawiwut, W.; McMartin, D.W.; Azam, S. Salts Removal from Synthetic Solution-Potash Brine by Non-Planted Constructed Wetlands. Water 2016, 8, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.Y.; Zhao, Q.S.; Ma, J.Y.; Bian, H.L.; Ye, S.Y. Hydrochemical characteristics of pressurized brine in Mahai potash area in Qinghai province. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Water Resources and Environment (WRE), Beijing, China, 25–28 July 2015; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Feng, J. Hydrochemical Dynamic Characteristics and Evolution of Underground Brine in the Mahai Salt Lake of the Qaidam Basin Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. Ed. 2018, 92, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Q.; He, J.; Hu, Y.; Long, P. Influence of sedimentary characteristics on water solution mining of low-grade potassium ore: A case study of Holocene in the northern ore section of Mahai Salt Lake, Qaidam Basin. Acta Petrol. Et Mineral. 2022, 41, 929–940. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.G.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.R.; Wang, X. Mineral Slat of Mahai Salt Lake Dissolution Experiment and Numerical Simulation. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 468, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.Y.; Zhao, Q.S.; Zhang, J.W.; Chen, J.L. Analysis of the Hydrochemical Characteristics and the Evolutionary Stages of Brine in Mahai Salt Lake in the Qaidam Basin. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 98, 07011. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, N. Hypersaline Potash Mine Tailings and Brine: Microbial Communities and Metal Biosorption Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Z.; Han, W.; Yu, G.; Han, E. Short-term exposure of low-alloyed steels in Qinghai Salt Lake atmosphere. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 3446–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Johns, C.; Shellie, R.A.; Potter, O.G.; O’Reilly, J.W.; Hutchinson, J.P.; Guijt, R.M.; Breadmore, M.C.; Hilder, E.F.; Dicinoski, G.W.; Haddad, P.R. Identification of homemade inorganic explosives by ion chromatographic analysis of post-blast residues. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1182, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christison, T.; Moore, D.; Lopez, L.; Rohrer, J. Configuring the Dionex Integrion HPIC System for Fast Anion Determinations Using Prepared Effluents; TN71954-EN 0716S; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.: Waltham, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Bruns, M.A.; Tiedje, J.M. DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.X.; Qin, Y.; Chen, T.; Lu, M.; Qian, X.; Guo, X.; Bai, Y. A practical guide to amplicon and metagenomic analysis of microbiome data. Protein Cell 2021, 12, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, B.; Simpson, G.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, H.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.2-1. 2015. Available online: http://CRAN.Rproject.org/package=vegan (accessed on 1 January 2015).
- Liu, Y.-X.; Chen, L.; Ma, T.; Li, X.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L.; Qian, X.; Xi, J.; Lu, H.; et al. EasyAmplicon: An easy-to-use, open-source, reproducible, and community-based pipeline for amplicon data analysis in microbiome research. iMeta 2023, 2, e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginestet, C. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. Soc. 2011, 174, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.H.; Yu, G.; Cai, P. ggVennDiagram: An Intuitive, Easy-to-Use, and Highly Customizable R Package to Generate Venn Diagram. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 706907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelle, W. psych: Procedures for Personality and Psychological Research; Northwestern University: Evanston, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kolde, R. pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps, R Package Version 1.0.12. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=pheatmap (accessed on 20 September 2019).
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F. Extract and Visualize the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses [R Package Factoextra Version 1.0.7]. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=factoextra (accessed on 12 April 2020).
- Braak, T.; Smilauer, P. Canoco Reference Manual and User’s Guide: Software for Ordination, Version 5.0; Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vonhof, J. Waste Disposal Problems Near Potash Mines in Saskatchewan, Canada. 1975. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:166219744 (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Perucca, C.F. Potash processing in Saskatchewan-A review of process technologies. CIM Bull. 2003, 96, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Boujelben, I.; Gomariz, M.; Martínez-García, M.; Santos, F.; Peña, A.; López, C.; Antón, J.; Maalej, S. Spatial and seasonal prokaryotic community dynamics in ponds of increasing salinity of Sfax solar saltern in Tunisia. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2012, 101, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalwasińska, A.; Deja-Sikora, E.; Burkowska-But, A.; Szabó, A.; Felföldi, T.; Kosobucki, P.; Krawiec, A.; Walczak, M. Changes in bacterial and archaeal communities during the concentration of brine at the graduation towers in Ciechocinek spa (Poland). Extremophiles 2018, 22, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazière, C.; Agogué, H.; Cravo-Laureau, C.; Cagnon, C.; Lanneluc, I.; Sablé, S.; Fruitier-Arnaudin, I.; Dupuy, C.; Duran, R. New insights in bacterial and eukaryotic diversity of microbial mats inhabiting exploited and abandoned salterns at the Ré Island (France). Microbiol. Res. 2021, 252, 126854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, A.E.; Marshall, D.; Yiannos, L. Increased variability of microbial communities in restored salt marshes nearly 30 years after tidal flow restoration. Estuaries Coasts 2012, 35, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghoni, A.; Emtiazi, G.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Cretoiu, M.S.; Stal, L.J.; Etemadifar, Z.; Shahzadeh Fazeli, S.A.; Bolhuis, H. Microbial diversity in the hypersaline Lake Meyghan, Iran. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinsteuber, S.; Riis, V.; Fetzer, I.; Harms, H.; Müller, S. Population Dynamics within a Microbial Consortium during Growth on Diesel Fuel in Saline Environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3531–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gales, G.; Tsesmetzis, N.; Neria, I.; Alazard, D.; Coulon, S.; Lomans, B.P.; Morin, D.; Ollivier, B.; Borgomano, J.; Joulian, C. Preservation of ancestral Cretaceous microflora recovered from a hypersaline oil reservoir. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, P.N.; Ardley, J.K. Review of the genus Methylobacterium and closely related organisms: A proposal that some Methylobacterium species be reclassified into a new genus, Methylorubrum gen. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 2727–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, J.B.; Delforno, T.P.; do Prado, P.F.; Duarte, I.C. Extremophilic taxa predominate in a microbial community of photovoltaic panels in a tropical region. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2021, 368, fnab105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saralov, A.; Baslerov, R.; Reutskikh, E.; Kuznetsov, B. Halarchaeum solikamskense sp. nov., a thermotolerant neutrophilic haloarchaeon from the foamy products of flotation enrichment of potassium minerals. Microbiology 2012, 81, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saralov, A.; Kuznetsov, B.; Reutskikh, E.; Baslerov, R.; Panteleeva, A.; Suzina, N. Arhodomonas recens sp. nov., a halophilic alkane-utilizing hydrogen-oxidizing bacterium from the brines of flotation enrichment of potassium minerals. Microbiology 2012, 81, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saralov, A.I.; Baslerov, R.V.; Kuznetsov, B.B. Haloferax chudinovii sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon from Permian potassium salt deposits. Extremophiles 2013, 17, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, C.F.; McGenity, T.J.; Grant, W.D. Archaeal halophiles (halobacteria) from two British salt mines. Microbiology 1993, 139, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Helfant, L. Geographical isolation, buried depth, and physicochemical traits drive the variation of species diversity and prokaryotic community in three typical hypersaline environments. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banda, J.F.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, L.; Pei, L.; Du, Z.; Hao, C.; Dong, H. Both pH and salinity shape the microbial communities of the lakes in Badain Jaran Desert, NW China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satari, L.; Guillén, A.; Latorre-Pérez, A.; Porcar, M. Beyond archaea: The table salt bacteriome. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Shen, G.; Wang, Z.; Han, R.; Long, Q.; Gao, X.; Xing, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, R. Distinctive distributions of halophilic Archaea across hypersaline environments within the Qaidam Basin of China. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 2029–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.N.; Sharma, D.; Gulati, S.; Singh, S.; Dey, R.; Pal, K.K.; Kaushik, R.; Saxena, A.K. Haloarchaea endowed with phosphorus solubilization attribute implicated in phosphorus cycle. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán-Viseras, A.; Andrei, A.-S.; Ghai, R.; Sánchez-Porro, C.; Ventosa, A. New Halonotius Species Provide Genomics-Based Insights into Cobalamin Synthesis in Haloarchaea. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmis, K.N.; McGenity, T.; Van Der Meer, J.R.; de Lorenzo, V. Handbook of Hydrocarbon and Lipid Microbiology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Christman, G.D.; León-Zayas, R.I.; Summers, Z.M.; Biddle, J.F. Methanogens Within a High Salinity Oil Reservoir from the Gulf of Mexico. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 570714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oremland, R.; King, G. Methanogenesis in hypersaline environments. In Microbial Materials: Physiological Ecology of Benthic Microbial Communities; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; pp. 180–190. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.M.; Green, S.J.; Kelley, C.A.; Prufert-Bebout, L.; Bebout, B.M. Shifts in methanogen community structure and function associated with long-term manipulation of sulfate and salinity in a hypersaline microbial mat. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, C.S.; Parkes, R.J.; Cragg, B.A.; l’Haridon, S.; Toffin, L. Methanogenic diversity and activity in hypersaline sediments of the centre of the Napoli mud volcano, Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 2078–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Harayama, S. Methanobacterium petrolearium sp. nov. and Methanobacterium ferruginis sp. nov., mesophilic methanogens isolated from salty environments. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Maldonado, J.Q.; Bebout, B.M.; Everroad, R.C.; López-Cortés, A. Evidence of novel phylogenetic lineages of methanogenic archaea from hypersaline microbial mats. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, C.A.; Nicholson, B.E.; Beaudoin, C.S.; Detweiler, A.M.; Bebout, B.M. Trimethylamine and organic matter additions reverse substrate limitation effects on the δ13C values of methane produced in hypersaline microbial mats. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 7316–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadena, S.; García-Maldonado, J.Q.; López-Lozano, N.E.; Cervantes, F.J. Methanogenic and Sulfate-Reducing Activities in a Hypersaline Microbial Mat and Associated Microbial Diversity. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 75, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrós-Alió, C.; Calderón-Paz, J.I.; MacLean, M.H.; Medina, G.; Marrasé, C.; Gasol, J.M.; Guixa-Boixereu, N. The microbial food web along salinity gradients. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2000, 32, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.L.; Zwart, G.; Schauer, M.; Kamst-van Agterveld, M.P.; Hahn, M.W. Bacterioplankton community composition along a salinity gradient of sixteen high-mountain lakes located on the Tibetan Plateau, China. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5478–5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oren, A. Microbial life at high salt concentrations: Phylogenetic and metabolic diversity. Saline Syst. 2008, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Xie, G.; Shao, K.; Bayartu, S.; Chen, Y.; Gao, G. Influence of salinity on the bacterial community composition in Lake Bosten, a large oligosaline lake in arid northwestern China. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 4748–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yao, T.; Jiao, N.; Zhu, L.; Hu, A.; Liu, X.; Gao, J.; Chen, Z.-Q. Salinity impact on bacterial community composition in five high-altitude lakes from the Tibetan Plateau, Western China. Geomicrobiol. J. 2013, 30, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.B.; Ghai, R.; Martin-Cuadrado, A.-B.; Sánchez-Porro, C.; Rodriguez-Valera, F.; Ventosa, A. Prokaryotic taxonomic and metabolic diversity of an intermediate salinity hypersaline habitat assessed by metagenomics. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 88, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ma, L.A.; Jiang, H.; Wu, G.; Dong, H. Salinity shapes microbial diversity and community structure in surface sediments of the Qinghai-Tibetan Lakes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Kong, W.; Yue, L.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; Zhu, L. Salinity reduces bacterial diversity, but increases network complexity in Tibetan Plateau lakes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, S.; Glińska-Lewczuk, K.; Burandt, P.; Kulesza, K.; Kobus, S.; Obolewski, K. Salinity as a Determinant Structuring Microbial Communities in Coastal Lakes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A. The bioenergetic basis for the decrease in metabolic diversity at increasing salt concentrations: Implications for the functioning of salt lake ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 2001, 466, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A. Diversity of halophilic microorganisms: Environments, phylogeny, physiology, and applications. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 28, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchfield, C.D. Survival strategies for microorganisms in hypersaline environments and their relevance to life on early Mars. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 1998, 33, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masmoudi, S.; Tastard, E.; Guermazi, W.; Caruso, A.; Morant-Manceau, A.; Ayadi, H. Salinity gradient and nutrients as major structuring factors of the phytoplankton communities in salt marshes. Aquat. Ecol. 2015, 49, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, K.; Logemann, J.; Heidelberg, K.B.; Emerson, J.B.; Comolli, L.R.; Hug, L.A.; Probst, A.J.; Keillar, A.; Thomas, B.C.; Miller, C.S.; et al. Metagenomic and lipid analyses reveal a diel cycle in a hypersaline microbial ecosystem. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2697–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Ruiz, M.D.R.; Alejandre-Colomo, C.; Ledger, T.; González, B.; Orfila, A.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Non-halophilic endophytes associated with the euhalophyte Arthrocnemum macrostachyum and their plant growth promoting activity potential. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fny208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DC Rubin, S.S.; Marín, I.; Gómez, M.J.; Morales, E.A.; Zekker, I.; San Martín-Uriz, P.; Rodríguez, N.; Amils, R. Prokaryotic diversity and community composition in the Salar de Uyuni, a large scale, chaotropic salt flat. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 3745–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obraztsova, A.Y.; Shipin, O.; Bezrukova, L.; Belyaev, S. Properties of the coccoid methylotrophic methanogen, methanococcoides-euhalobius sp-nov. Microbiology 1987, 56, 523–527. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.R.; Pattnaik, P.; Sethunathan, N.; Adhya, T. Anion-mediated salinity affecting methane production in a flooded alluvial soil. Geomicrobiol. J. 2003, 20, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, D.S.; Rees, G.N.; Mitchell, A.M.; Watson, G.; Williams, J. The short-term effects of salinization on anaerobic nutrient cycling and microbial community structure in sediment from a freshwater wetland. Wetlands 2006, 26, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sampling Sites | Coordinates | Site Groups and Descriptions | Sample ID | Physicochemical Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lat. N | Long. E | Depth (m) | Salinity (%) | Conductivity (us/cm) | pH | |||
| ML | 94°18′4″ | 38°7′59″ | ML site: natural. | ML | 0.2 | 1.50 | 16,928 | 7.95 |
| MSa | 94°06′57” | 38°17′30″ | MS sites: moderate human influence | MSa | 6 | 11.30 | 202,010 | 7.21 |
| MSb | 94°06′17” | 38°18′29″ | MSb | 11 | 9.80 | 205,610 | 7.37 | |
| MWa | 94°14′2″ | 38°19′9″ | MW sites: high human influence. | MWa1 | 2.3 | 10.20 | 215,260 | 7.09 |
| MWa2 | 3.5 | 9.80 | n.a. | 7.13 | ||||
| MWa3 | 4.5 | 10.60 | 215,230 | 7.05 | ||||
| MWa4 | 5.7 | 11.90 | 200,475 | 6.76 | ||||
| MWb | 94°15′10″ | 38°17′51″ | MWb1 | 3 | 10.00 | 240,288 | 7.40 | |
| MWb2 | 5 | 10.30 | 241,540 | 7.38 | ||||
| MWb3 | 7 | 10.20 | 240,660 | 7.35 | ||||
| MWb4 | 10 | 11.60 | 213,816 | 6.91 | ||||
| MWc | 94°12′21″ | 38°20′25″ | MWc1 | 2 | 12.70 | n.a. | 6.54 | |
| MWc2 | 4 | 13.20 | 190,870 | 6.32 | ||||
| MWc3 | 6 | 13.80 | 185,577 | 6.13 | ||||
| MWc4 | 8 | 14.40 | 179,920 | 6.00 | ||||
| MWc5 | 10 | 14.70 | 176,253 | 6.04 | ||||
| MWd | 94°07′15″ | 38°22′10″ | MWd1 | 0.5 | 10.30 | 235,022 | 7.15 | |
| MWd2 | 2 | 10.70 | 235,056 | 7.11 | ||||
| MWd3 | 4 | 10.80 | 232,137 | 7.14 | ||||
| MWd4 | 6 | n.a. | n.a. | n.d. | ||||
| MWe | 94°14′27″ | 38°16′55″ | MWe1 | 3 | 10.60 | n.a. | 7.37 | |
| MWe2 | 6 | 12.10 | 187,704 | 6.89 | ||||
| MWe3 | 9 | 12.20 | 166,525 | 6.54 | ||||
| MWe4 | 12 | 14.10 | 163,480 | 6.32 | ||||
| Brine Groups | Ionic Composition | Bacteria | Archaea | Methanogen | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | |
| ML/MS/MWace/MWbd | 0.718 | ** | 0.298 | * | 0.364 | ** | 0.449 | ** |
| MS/MWa/MWb/MWc/MWd/MWe | 0.658 | ** | 0.275 | 0.19 | 0.454 | ** | 0.425 | ** |
| MS/MWace/MWbd | 0.443 | ** | 0.090 | 0.29 | 0.336 | ** | 0.425 | ** |
| MWace/MWbd | 0.399 | ** | 0.045 | 0.409 | 0.263 | ** | 0.387 | ** |
| MWa/MWb/MWc/MWd/MWe | 0.633 | ** | 0.242 | 0.223 | 0.396 | ** | 0.559 | * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, L.; Yu, S.; Lu, X.; Liu, S.; Tang, Y.; Lu, H. Different Responses of Bacteria and Archaea to Environmental Variables in Brines of the Mahai Potash Mine, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082002
Xie L, Yu S, Lu X, Liu S, Tang Y, Lu H. Different Responses of Bacteria and Archaea to Environmental Variables in Brines of the Mahai Potash Mine, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(8):2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082002
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Linglu, Shan Yu, Xindi Lu, Siwei Liu, Yukai Tang, and Hailong Lu. 2023. "Different Responses of Bacteria and Archaea to Environmental Variables in Brines of the Mahai Potash Mine, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau" Microorganisms 11, no. 8: 2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082002
APA StyleXie, L., Yu, S., Lu, X., Liu, S., Tang, Y., & Lu, H. (2023). Different Responses of Bacteria and Archaea to Environmental Variables in Brines of the Mahai Potash Mine, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Microorganisms, 11(8), 2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082002







