Hydrogel-Containing Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: Antibacterial Action, Evaluation of Wound Healing, and Bioaccumulation in Wistar Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles
2.2. Preparation of Hydrogels
2.3. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of Formulations
2.3.1. Bacterial Samples
2.3.2. Time–kill Assay
2.4. In Vivo Study of Formulations
2.4.1. General Design of In Vivo Experiment
2.4.2. Surgical Excision of Skin
2.4.3. Treatment of Animals with Hydrogel Formulations
2.4.4. Wound Colonization
2.4.5. Wound Healing Analysis
2.4.6. Animal Euthanasia
2.4.7. Histopathological Analysis
2.4.8. Silver Bioaccumulation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
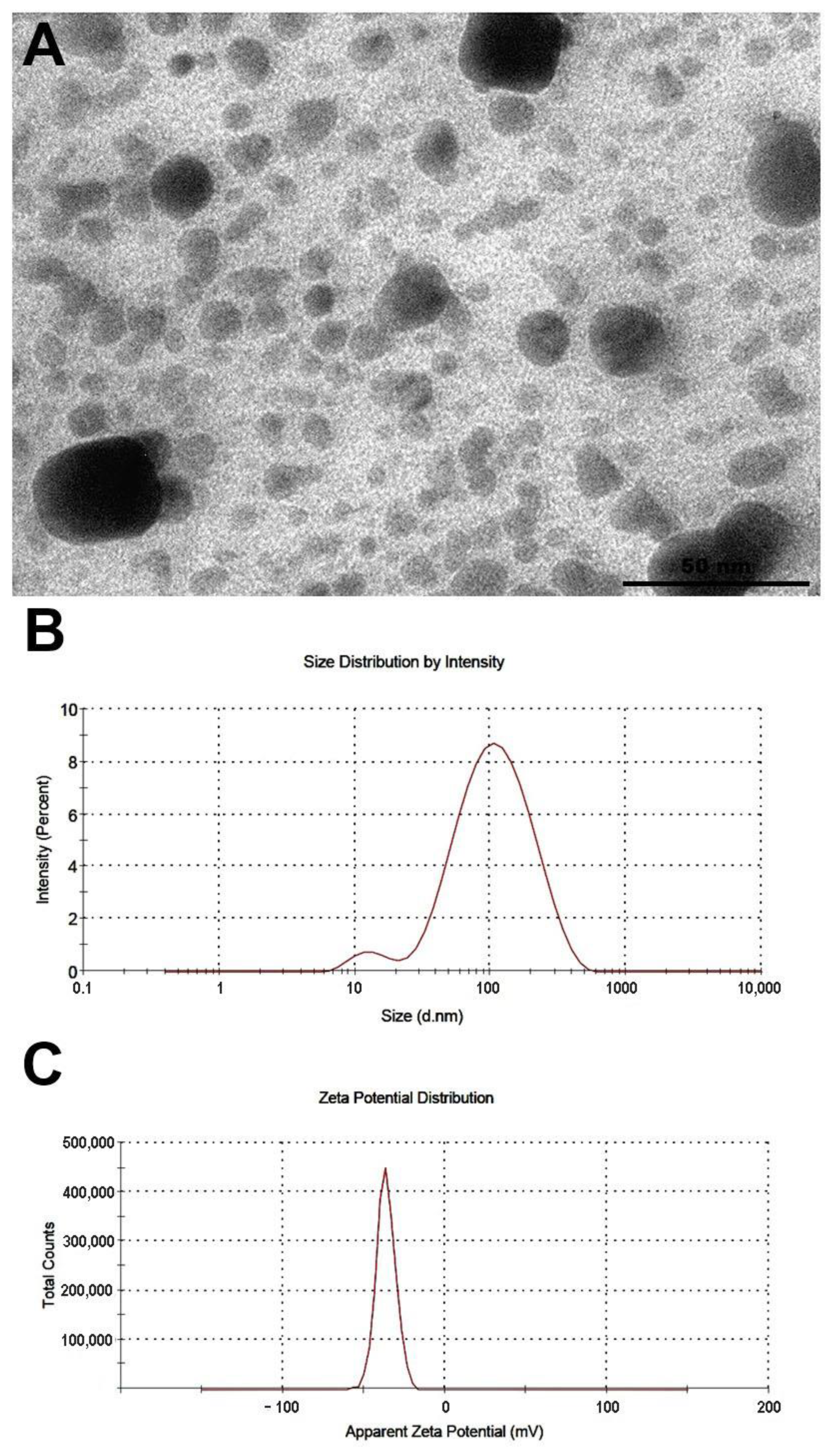
3.1. Characteristics of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles (bioAgNPs)
3.2. Time–kill Assay (In Vitro Antibacterial Test)
3.3. Results of In Vivo Study
3.3.1. Wound healing
3.3.2. Quantification of Bacterial Cells in Wounds
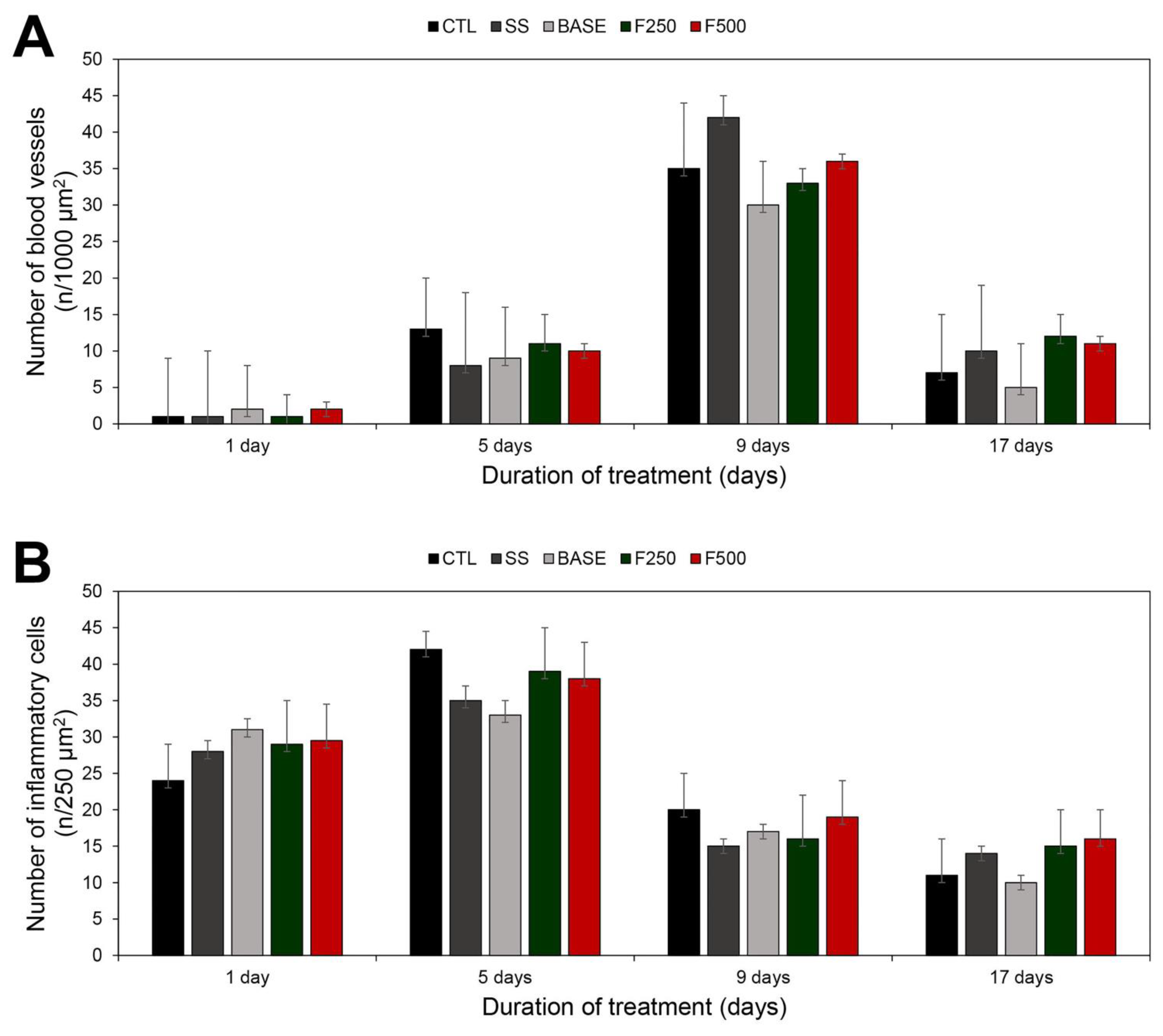
3.3.3. Histopathological Analysis
3.3.4. Silver Quantification of Tissues
4. Discussion
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Gel Color Analysis

References
- Lefèvre-Utile, A.; Braun, C.; Haftek, M.; Aubin, F. Five Functional Aspects of the Epidermal Barrier. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaney, M.H.; Kalan, L.R. Living in Your Skin: Microbes, Molecules, and Mechanisms. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e00695-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris-Tryon, T.A.; Grice, E.A. Microbiota and Maintenance of Skin Barrier Function. Science 2022, 376, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, T.F.; Bordoni, B. Wound Classification; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kindred Hospitals Types of Wounds. Available online: https://www.kindredhospitals.com/our-services/ltac/conditions/wound-care (accessed on 17 June 2023).
- Zabaglo, M.; Sharman, T. Postoperative Wound Infection; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Warriner, R.; Burrell, R. Infection and the Chronic Wound. Adv. Skin. Wound Care 2005, 18, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, C.V.; Amin, A.; Ford, W.T.; Finley, R.; Kaye, K.S.; Nguyen, H.H.; Rybak, M.J.; Talan, D. Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infections (ABSSSI): Practice Guidelines for Management and Care Transitions in the Emergency Department and Hospital. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 48, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punjataewakupt, A.; Napavichayanun, S.; Aramwit, P. The Downside of Antimicrobial Agents for Wound Healing. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/pdf/threats-report/2019-ar-threats-report-508.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2023).
- Japoni, A.; Hayati, M.; Alborzi, A.; Farshad, S.; Abbasian, S.A. In Vitro Susceptibility of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Isolated from a Burn Center to Silver Sulfadiazine and Silver Nitrate in Shiraz, South of Iran. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2005, 30, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Modak, S.M. Sulfadiazine Silver-Resistant Pseudomonas in Burns. Arch. Surg. 1981, 116, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heggers, J.P.; Robson, M.C. The Emergence of Silver Sulphadiazine-Resistant Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Burns 1978, 5, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://amr-review.org/sites/default/files/160525_Final%20paper_with%20cover.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2023).
- Feldman, C.; Anderson, R. The Role of Co-Infections and Secondary Infections in Patients with COVID-19. Pneumonia 2021, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, R.; Goodarzi, P.; Asadi, M.; Soltani, A.; Aljanabi, H.A.A.; Jeda, A.S.; Dashtbin, S.; Jalalifar, S.; Mohammadzadeh, R.; Teimoori, A.; et al. Bacterial Co-infections with SARS-CoV-2. IUBMB Life 2020, 72, 2097–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization Prioritization of Pathogens to Guide Discovery, Research and Development of New Antibiotics for Drug-Resistant Bacterial Infections, Including Tuberculosis. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-EMP-IAU-2017.12 (accessed on 28 May 2023).
- Krausz, A.E.; Adler, B.L.; Cabral, V.; Navati, M.; Doerner, J.; Charafeddine, R.A.; Chandra, D.; Liang, H.; Gunther, L.; Clendaniel, A.; et al. Curcumin-Encapsulated Nanoparticles as Innovative Antimicrobial and Wound Healing Agent. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wong, K.K.Y.; Ho, C.-M.; Lok, C.-N.; Yu, W.-Y.; Che, C.-M.; Chiu, J.-F.; Tam, P.K.H. Topical Delivery of Silver Nanoparticles Promotes Wound Healing. ChemMedChem 2007, 2, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scandorieiro, S.; Rodrigues, B.C.D.; Nishio, E.K.; Panagio, L.A.; de Oliveira, A.G.; Durán, N.; Nakazato, G.; Kobayashi, R.K.T. Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles Strategically Combined With Origanum Vulgare Derivatives: Antibacterial Mechanism of Action and Effect on Multidrug-Resistant Strains. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 842600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scandorieiro, S.; de Camargo, L.C.; Lancheros, C.A.C.; Yamada-Ogatta, S.F.; Nakamura, C.V.; de Oliveira, A.G.; Andrade, C.G.T.J.; Duran, N.; Nakazato, G.; Kobayashi, R.K.T. Synergistic and Additive Effect of Oregano Essential Oil and Biological Silver Nanoparticles against Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Strains. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scandorieiro, S.; Teixeira, F.M.M.B.; Nogueira, M.C.L.; Panagio, L.A.; de Oliveira, A.G.; Durán, N.; Nakazato, G.; Kobayashi, R.K.T. Antibiofilm Effect of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles Combined with Oregano Derivatives against Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, F.; Siddiqui, S.; Khan, W.A. Nanoparticles as Novel Emerging Therapeutic Antibacterial Agents in the Antibiotics Resistant Era. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 2552–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-López, E.; Gomes, D.; Esteruelas, G.; Bonilla, L.; Lopez-Machado, A.L.; Galindo, R.; Cano, A.; Espina, M.; Ettcheto, M.; Camins, A.; et al. Metal-Based Nanoparticles as Antimicrobial Agents: An Overview. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Market Research Community Silver Nanoparticles Market Insights. Available online: https://marketresearchcommunity.com/silver-nanoparticles-market/?gad=1&gclid=Cj0KCQjw7aqkBhDPARIsAKGa0oLjd9uUUh6zwvRT4syH_Z9M3m5efjQtevC-wVNJVs9Y2CqsVwlegsYaAiyJEALw_wcB (accessed on 17 June 2023).
- Philips, J.; Verbeeck, K.; Rabaey, K.; Arends, J.B.A.; Scott, K.; Yu, E.H. Microbial Electrochemical and Fuel Cells; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 9781782423751. [Google Scholar]
- Lemire, J.A.; Harrison, J.J.; Turner, R.J. Antimicrobial Activity of Metals: Mechanisms, Molecular Targets and Applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán, N.; Nakazato, G.; Seabra, A.B. Antimicrobial Activity of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles, and Silver Chloride Nanoparticles: An Overview and Comments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6555–6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, N.; Marcato, P.D.; Alves, O.L.; De Souza, G.I.; Esposito, E. Mechanistic Aspects of Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles by Several Fusarium Oxysporum Strains. J. Nanobiotechnology 2005, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambers, H.; Piessens, S.; Bloem, A.; Pronk, H.; Finkel, P. Natural Skin Surface PH Is on Average below 5, Which Is Beneficial for Its Resident Flora. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2006, 28, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, E.; Matias, J.E.F.; Coelho, J.C.U.; Campos, A.C.L.; Stahlke, H.J., Jr.; Timi, J.R.R.; Rocha, L.C.d.A.; Moreira, A.T.R.; Rispoli, D.Z.; Ferreira, L.M. Efeito Do Uso Tópico Do Extrato Aquoso de Orbignya Phalerata (Babaçu) Na Cicatrização de Feridas Cutâneas: Estudo Controlado Em Ratos. Acta Cir. Bras. 2006, 21, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garros, I.D.C.; Campos, A.C.L.; Tâmbara, E.M.; Tenório, S.B.; Torres, O.J.M.; Agulham, M.Â.; Araújo, A.C.F.; Santis-Isolan, P.M.B.; Oliveira, R.M.D.; Arruda, E.C.; et al. Extrato de Passiflora Edulis Na Cicatrização de Feridas Cutâneas Abertas Em Ratos: Estudo Morfológico e Histológico. Acta Cir. Bras. 2006, 21, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, C.P.M.; De Lima, C.S.; Lopes, T.V.; Félix, S.R.; Schons, S.; Fernandes, C.G.; Nobre, M.D.O. The Use of the Andiroba Oil Carapa Guianensis on Cutaneous Wounds in Wistar Rats. Rev. Bras. Hig. E Sanid. Anim. 2014, 8, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirato, G.V.; Monteiro, F.M.F.; Silva, F.d.O.; Filho, J.L.d.L.; Leão, A.M.d.A.C.; Porto, A.L.F. O Polissacarídeo Do Anacardium Occidentale L. Na Fase Inflamatória Do Processo Cicatricial de Lesões Cutâneas. Ciência Rural. 2006, 36, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labno, C. Two Ways to Count Cells with ImageJ. Available online: https://www.unige.ch/medecine/bioimaging/files/3714/1208/5964/CellCounting.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2023).
- Nascimento, C.R.B.; Risso, W.E.; dos Reis Martinez, C.B. Lead Accumulation and Metallothionein Content in Female Rats of Different Ages and Generations after Daily Intake of Pb-Contaminated Food. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 48, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borase, H.P.; Salunke, B.K.; Salunkhe, R.B.; Patil, C.D.; Hallsworth, J.E.; Kim, B.S.; Patil, S.V. Plant Extract: A Promising Biomatrix for Ecofriendly, Controlled Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 173, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iravani, S.; Korbekandi, H.; Mirmohammadi, S.V.; Zolfaghari, B. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles: Chemical, Physical and Biological Methods. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 385–406. [Google Scholar]
- Lansdown, A.B.G. Silver I: Its Antibacterial Properties and Mechanism of Action. J. Wound Care 2002, 11, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, F.W. The Side Effects of Silver Sulfadiazine. J. Burn. Care Res. 2009, 30, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, M.d.S.d.; Scandorieiro, S.; Pereira, G.N.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Seabra, A.B.; Dias, A.P.; Yamashita, F.; Martinez, C.B.D.R.; Kobayashi, R.K.T.; Nakazato, G. Antibacterial Activity of Biodegradable Films Incorporated with Biologically-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles and the Evaluation of Their Migration to Chicken Meat. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocate, K.P.; Reis, G.F.; de Souza, P.C.; Oliveira Junior, A.G.; Durán, N.; Nakazato, G.; Furlaneto, M.C.; de Almeida, R.S.; Panagio, L.A. Antifungal Activity of Silver Nanoparticles and Simvastatin against Toxigenic Species of Aspergillus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 291, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcato, P.D.; Parizotto, N.V.; Martinez, D.S.T.; Paula, A.J.; Ferreira, I.R.; Melo, P.S.; Durán, N.; Alves, O.L. New Hybrid Material Based on Layered Double Hydroxides and Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: Antimicrobial Activity and Cytotoxic Effect. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2013, 24, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puca, V.; Marulli, R.Z.; Grande, R.; Vitale, I.; Niro, A.; Molinaro, G.; Prezioso, S.; Muraro, R.; Di Giovanni, P. Microbial Species Isolated from Infected Wounds and Antimicrobial Resistance Analysis: Data Emerging from a Three-Years Retrospective Study. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ousey, K.; Cutting, K.F.; Rogers, A.A.; Rippon, M.G. The Importance of Hydration in Wound Healing: Reinvigorating the Clinical Perspective. J. Wound Care 2016, 25, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Lee, S.H.; Ryu, D.S.; Choi, S.J.; Lee, D.S. Antibacterial Activity of Silver-Nanoparticles Against Staphylococcus Aureus and Escherichia Coli. Korean J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 39, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.-R.; Xie, X.-B.; Shi, Q.-S.; Zeng, H.-Y.; OU-Yang, Y.-S.; Chen, Y.-B. Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles on Escherichia Coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, C.-N.; Ho, C.-M.; Chen, R.; He, Q.-Y.; Yu, W.-Y.; Sun, H.; Tam, P.K.-H.; Chiu, J.-F.; Che, C.-M. Proteomic Analysis of the Mode of Antibacterial Action of Silver Nanoparticles. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibrov, P.; Dzioba, J.; Gosink, K.K.; Hase, C.C. Chemiosmotic Mechanism of Antimicrobial Activity of Ag+ in Vibrio Cholerae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2668–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachiewicz, A.M.; Hauck, C.G.; Weber, D.J.; Cairns, B.A.; van Duin, D. Bacterial Infections After Burn Injuries: Impact of Multidrug Resistance. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 2130–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robben, P.M.; Ayalew, M.D.; Chung, K.K.; Ressner, R.A. Multi-Drug–Resistant Organisms in Burn Infections. Surg. Infect. 2021, 22, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, J.J.; Branski, L.K.; Williams-Bouyer, N.; Villarreal, C.; Herndon, D.N. Treatment of Infection in Burns. In Total Burn Care; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 137–156.e2. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.L.; Wu, J.; Chen, G.Q.; Cui, F.Z.; Kim, T.N.; Kim, J.O. A Mechanistic Study of the Antibacterial Effect of Silver Ions on Escherichia Coli and Staphylococcus Aureus. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 662–668. [Google Scholar]
- Oaks, R.J.; Cindass, R. Silver Sulfadiazine. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556054/ (accessed on 27 May 2023).
- Surowiecka, A.; Strużyna, J.; Winiarska, A.; Korzeniowski, T. Hydrogels in Burn Wound Management—A Review. Gels 2022, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, Characterization, and Applications: A Review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konop, M.; Damps, T.; Misicka, A.; Rudnicka, L. Certain Aspects of Silver and Silver Nanoparticles in Wound Care: A Minireview. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbaum, S.H.; Di Santis, É.P.; Sant’Ana Mandelbaum, M.H. Cicatrization: Current Concepts and Auxiliary Resources—Part I. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2003, 78, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbino, C.A.; Pereira, L.M.; Curi, R. Mecanismos Envolvidos Na Cicatrização: Uma Revisão. Rev. Bras. Ciências Farm. 2005, 41, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, A.J.; Clark, R.A.F. Cutaneous Wound Healing. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.; Harding, K.G. Bacteria and Wound Healing. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 17, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorg, H.; Tilkorn, D.J.; Hager, S.; Hauser, J.; Mirastschijski, U. Skin Wound Healing: An Update on the Current Knowledge and Concepts. Eur. Surg. Res. 2017, 58, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefkovits, J.; Plow, E.F.; Topol, E.J. Platelet Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Receptors in Cardiovascular Medicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Thakur, V.; Kumar, V.; Raj, M.; Gupta, S.; Devi, N.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Macho, M.; Banerjee, A.; Ewe, D.; et al. Silver Nanoparticles and Its Mechanistic Insight for Chronic Wound Healing: Review on Recent Progress. Molecules 2022, 27, 5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morguette, A.E.B.; Bigotto, B.G.; Varella, R.D.L.; Andriani, G.M.; Spoladori, L.F.D.A.; Pereira, P.M.L.; De Andrade, F.G.; Lancheros, C.A.C.; Nakamura, C.V.; Arakawa, N.S.; et al. Hydrogel Containing Oleoresin From Copaifera Officinalis Presents Antibacterial Activity Against Streptococcus Agalactiae. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzulukov, Y.P.; Arianova, E.A.; Demin, V.F.; Safenkova, I.V.; Gmoshinski, I.V.; Tutelyan, V.A. Bioaccumulation of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles in Organs and Tissues of Rats Studied by Neutron Activation Analysis. Biol. Bull. 2014, 41, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, R.; Seabra, A.B.; Durán, N. Silver Nanoparticles: A Brief Review of Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Chemically and Biogenically Synthesized Nanoparticles. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2012, 32, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larese Filon, F.; Mauro, M.; Adami, G.; Bovenzi, M.; Crosera, M. Nanoparticles Skin Absorption: New Aspects for a Safety Profile Evaluation. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 72, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larese, F.F.; D’Agostin, F.; Crosera, M.; Adami, G.; Renzi, N.; Bovenzi, M.; Maina, G. Human Skin Penetration of Silver Nanoparticles through Intact and Damaged Skin. Toxicology 2009, 255, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Sato, M.; Sato, Y.; Ando, N.; Takayama, T.; Fujita, M.; Ishihara, M. Synthesis and Application of Silver Nanoparticles (Ag NPs) for the Prevention of Infection in Healthcare Workers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruela, A.L.M.; Perissinato, A.G.P.; Lino, M.E.S.; Mudrik, P.S. Evaluation of skin absorption of drugs from topical and transdermal formulations. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 52, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

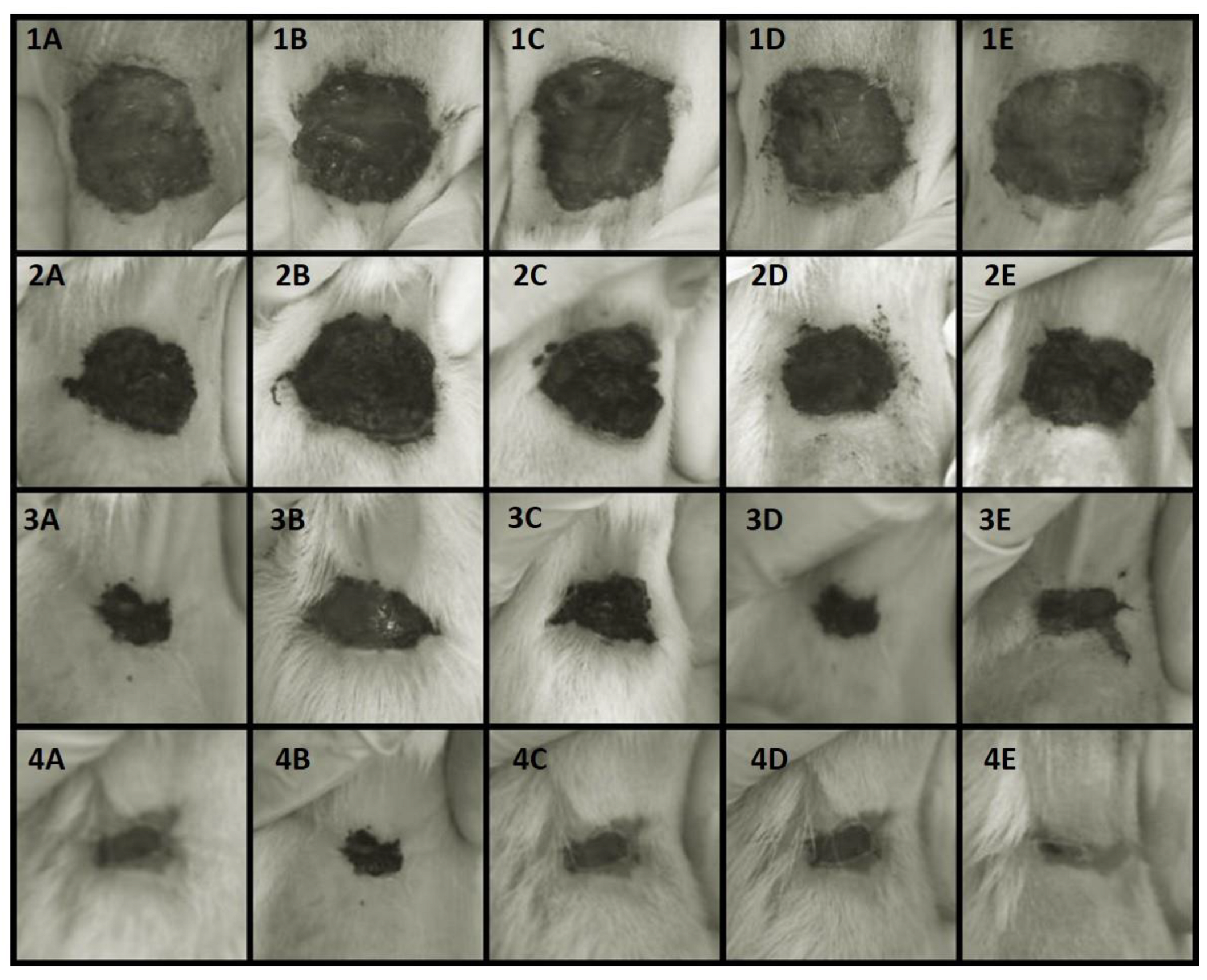




| Groups | Lesion Area (cm2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Day 5 | Day 9 | Day 17 | |
| CTL | 3.69 ± 0.61 | 2.51 ± 0.37 | 1.21 ± 0.38 | 0.20 ± 0.08 |
| SS | 4.32 ± 0.51 | 3.83 ± 0.45 | 1.73 ± 0.21 | 0.21 ± 0.02 |
| BASE | 4.97 ± 0.75 | 2.75 ± 0.25 | 1.23 ± 0.01 | 0.26 ± 0.05 |
| F250 | 3.65 ± 0.14 | 2.19 ± 0.16 | 1.14 ± 0.36 | 0.07 ± 0.03 |
| F500 | 4.94 ± 0.42 | 3.71 ± 0.28 | 1.58 ± 0.19 | 0.20 ± 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scandorieiro, S.; Kimura, A.H.; de Camargo, L.C.; Gonçalves, M.C.; da Silva, J.V.H.; Risso, W.E.; de Andrade, F.G.; Zaia, C.T.B.V.; Lonni, A.A.S.G.; dos Reis Martinez, C.B.; et al. Hydrogel-Containing Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: Antibacterial Action, Evaluation of Wound Healing, and Bioaccumulation in Wistar Rats. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1815. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071815
Scandorieiro S, Kimura AH, de Camargo LC, Gonçalves MC, da Silva JVH, Risso WE, de Andrade FG, Zaia CTBV, Lonni AASG, dos Reis Martinez CB, et al. Hydrogel-Containing Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: Antibacterial Action, Evaluation of Wound Healing, and Bioaccumulation in Wistar Rats. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(7):1815. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071815
Chicago/Turabian StyleScandorieiro, Sara, Angela Hitomi Kimura, Larissa Ciappina de Camargo, Marcelly Chue Gonçalves, João Vinícius Honório da Silva, Wagner Ezequiel Risso, Fábio Goulart de Andrade, Cássia Thaïs Bussamra Vieira Zaia, Audrey Alesandra Stinghen Garcia Lonni, Claudia Bueno dos Reis Martinez, and et al. 2023. "Hydrogel-Containing Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: Antibacterial Action, Evaluation of Wound Healing, and Bioaccumulation in Wistar Rats" Microorganisms 11, no. 7: 1815. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071815
APA StyleScandorieiro, S., Kimura, A. H., de Camargo, L. C., Gonçalves, M. C., da Silva, J. V. H., Risso, W. E., de Andrade, F. G., Zaia, C. T. B. V., Lonni, A. A. S. G., dos Reis Martinez, C. B., Durán, N., Nakazato, G., & Kobayashi, R. K. T. (2023). Hydrogel-Containing Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: Antibacterial Action, Evaluation of Wound Healing, and Bioaccumulation in Wistar Rats. Microorganisms, 11(7), 1815. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071815








