Extracts from Wallis Sponges Inhibit Vibrio harveyi Biofilm Formation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Antibiofilm Activity of Sponge Extracts
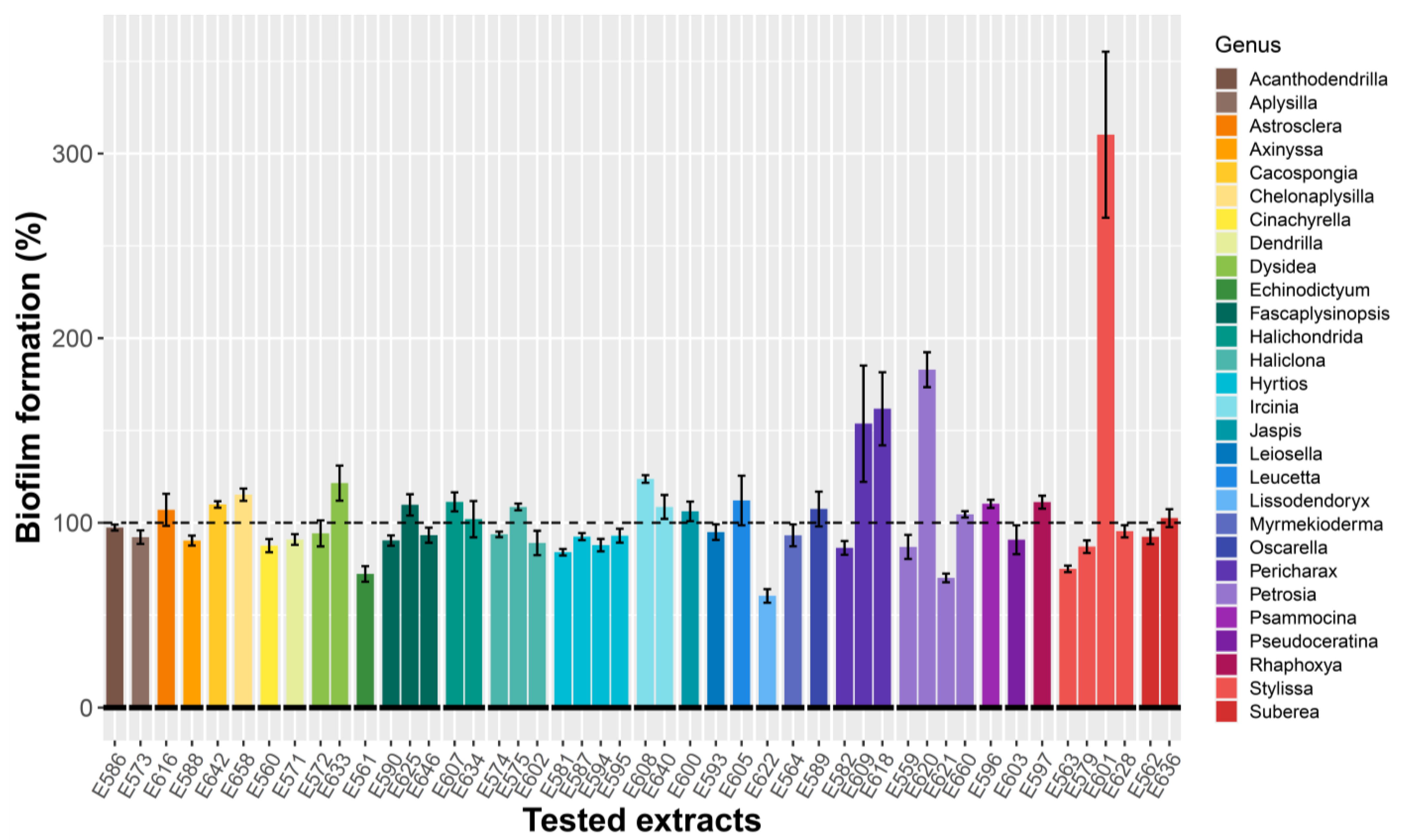
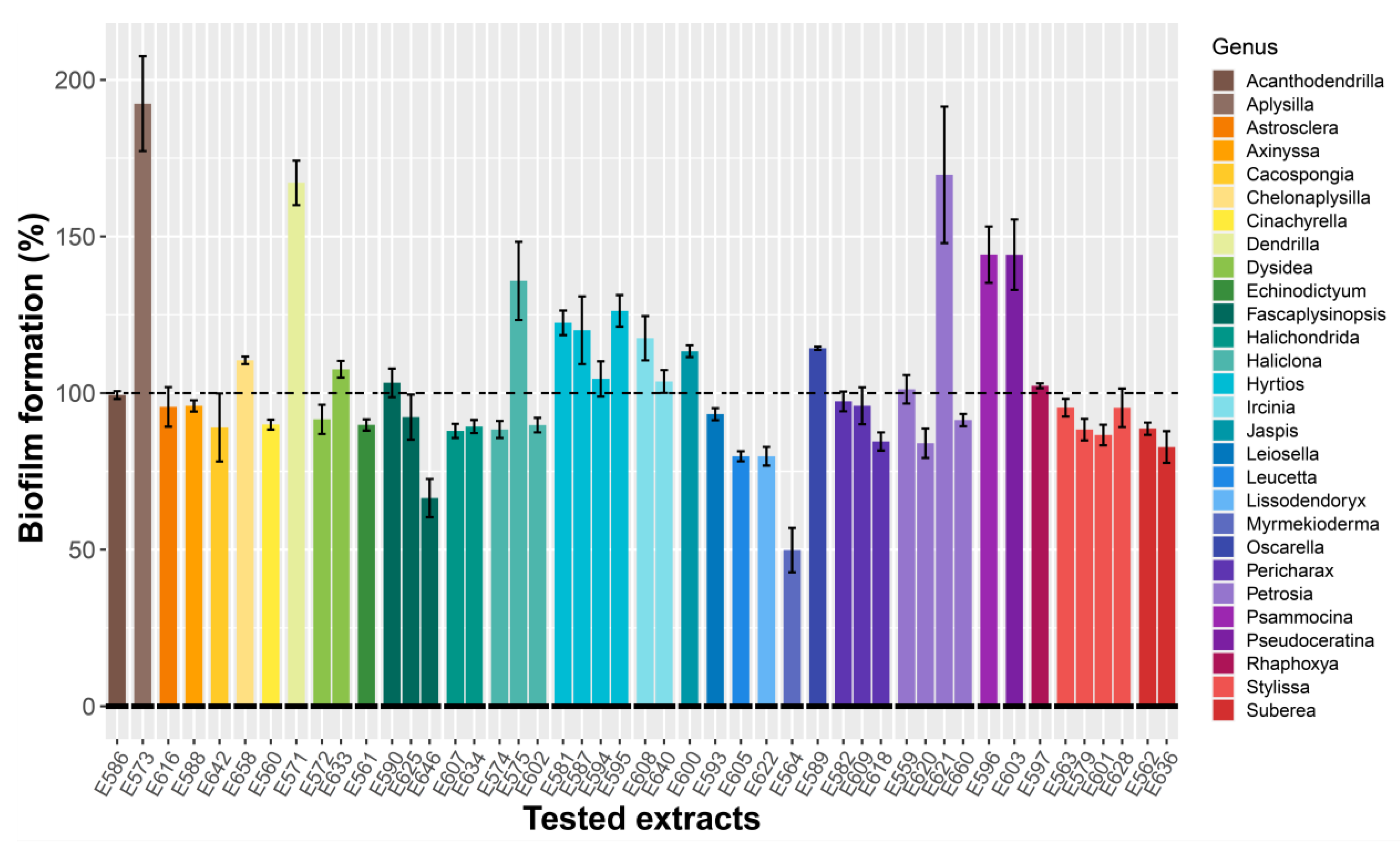
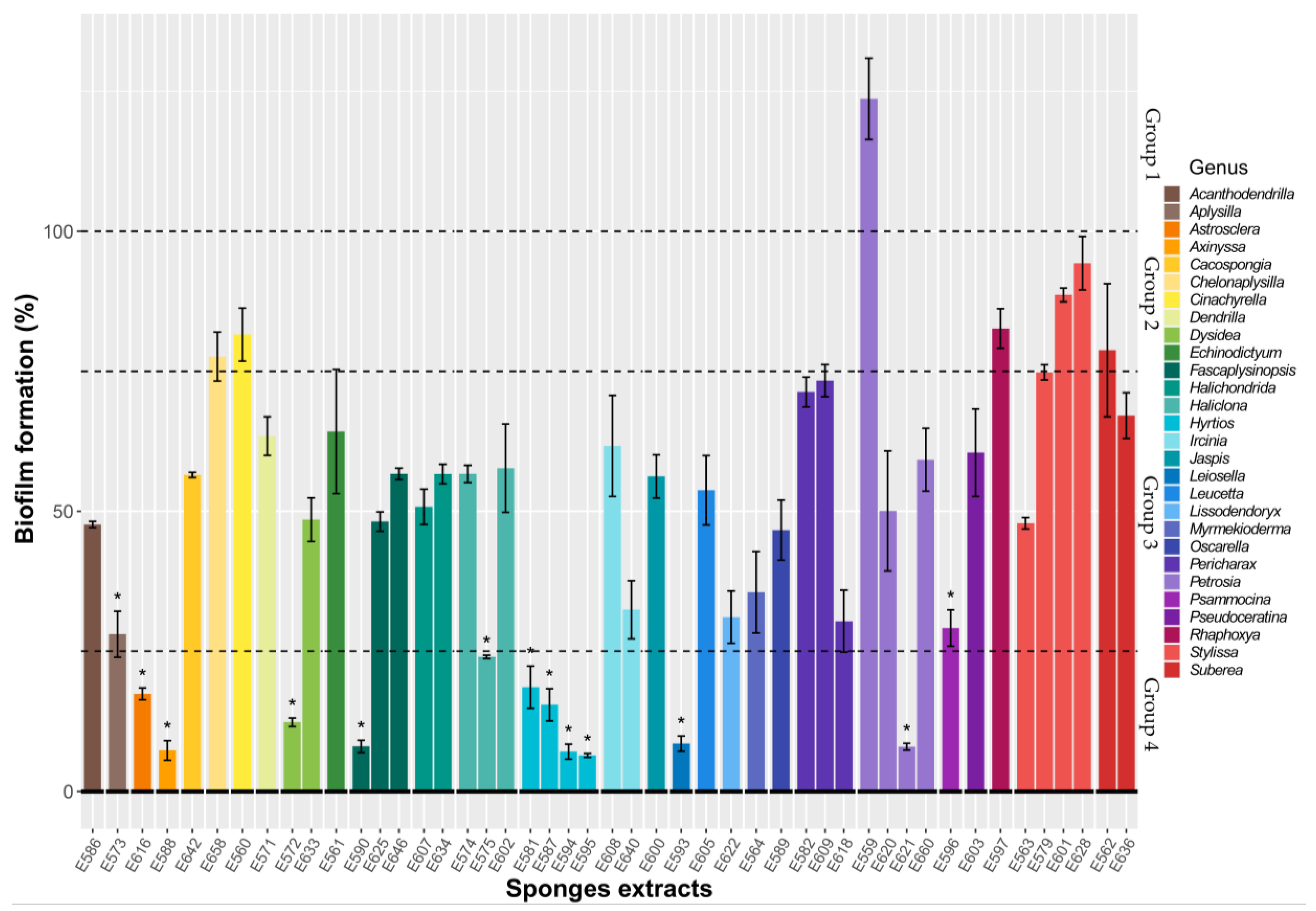
2.1.1. Antibiofilm Activity Screening on Microtiter Plate
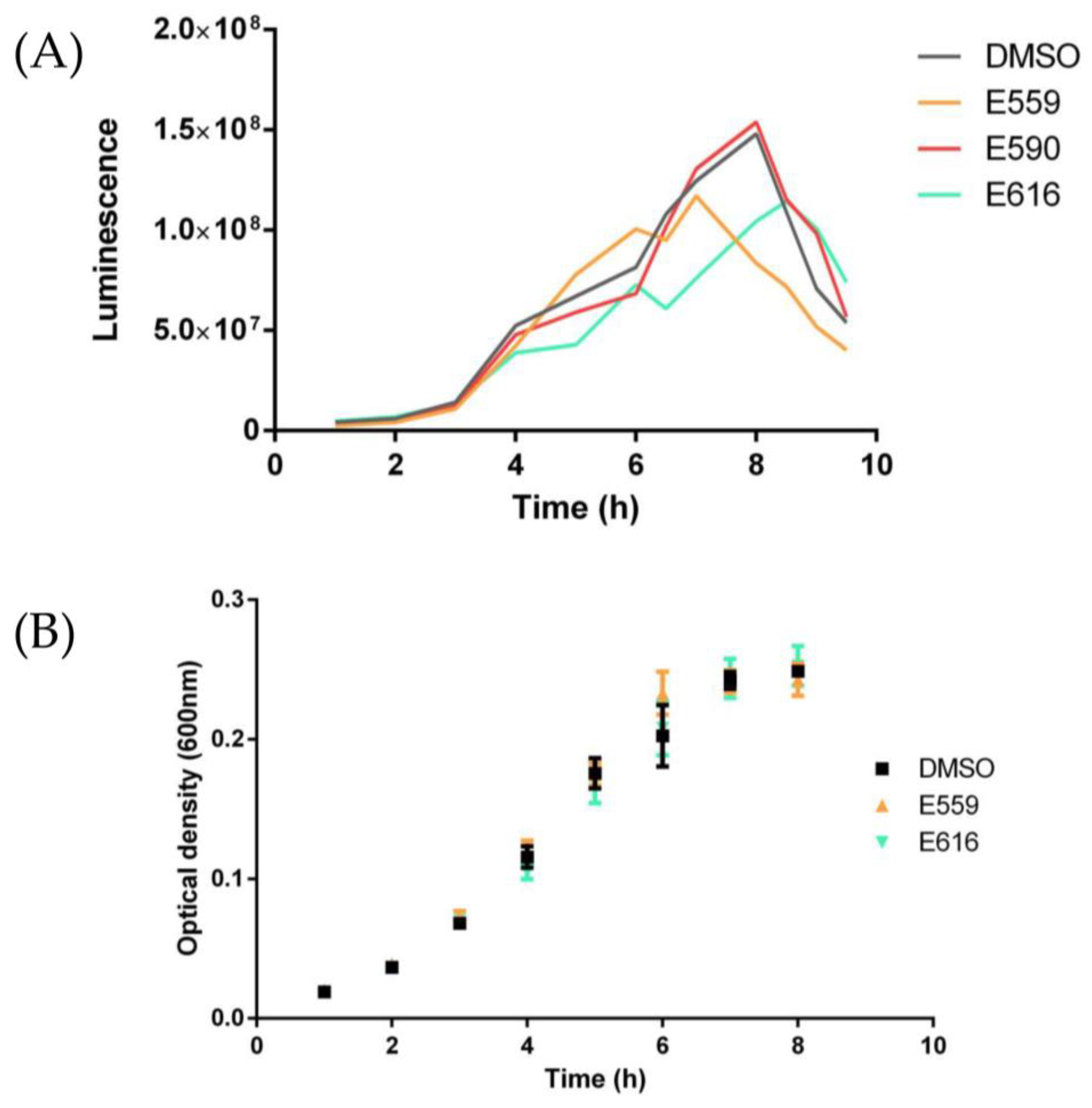
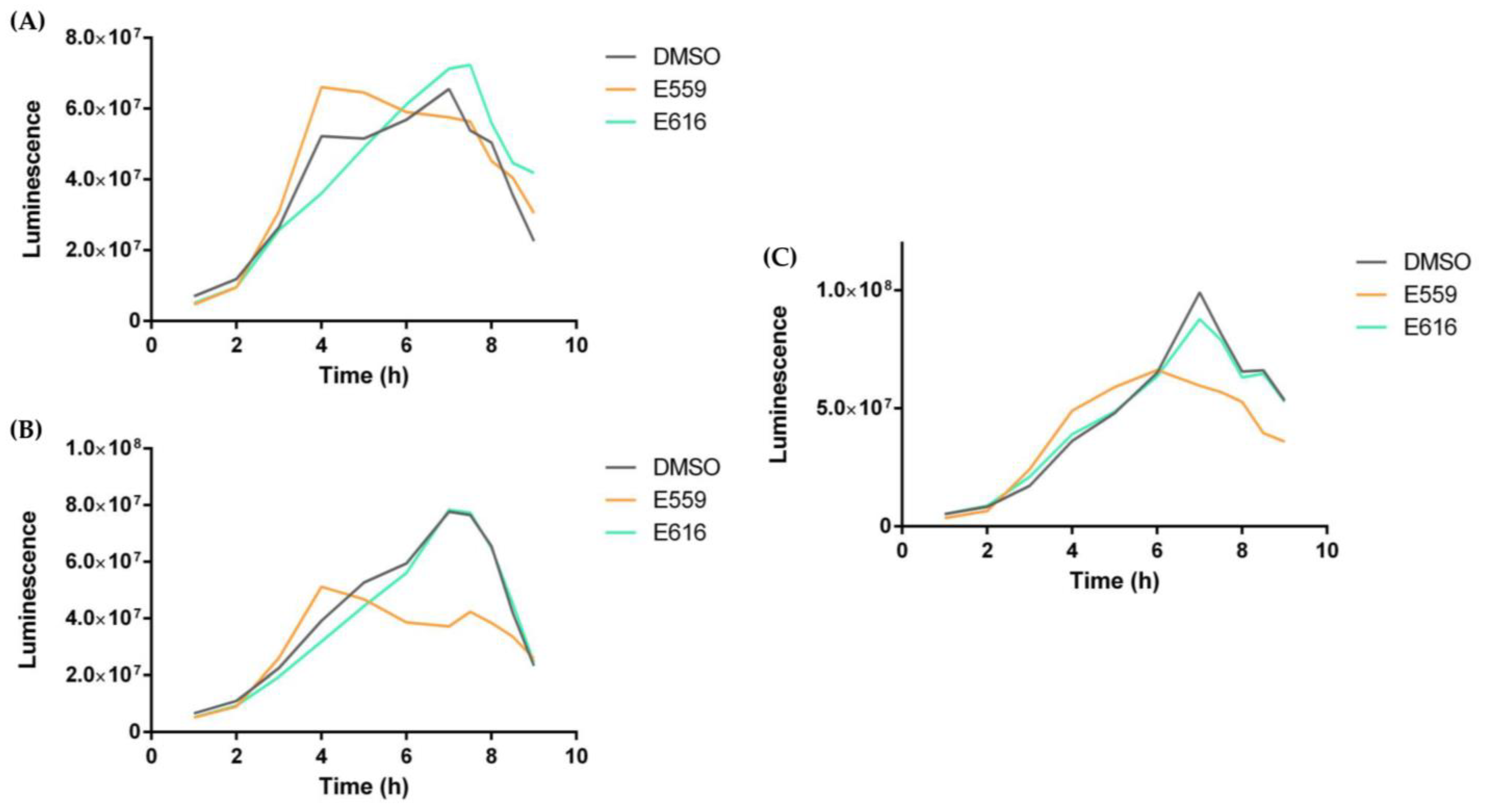
2.1.2. Antibiofilm Activity of Selected SEs against V. harveyi ORM4 in a Dynamic Condition of Growth
2.2. Extracts and Quorum Sensing
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Biological Material
3.2. Sponge Extraction
3.3. Antibiofilm Assays
3.3.1. Microtiter Plate Assay (Static Conditions/Polystyrene Surface)
3.3.2. Anti-Adhesion Assay (Static Conditions/Glass Surface)
3.3.3. Impact on Biofilm Formation in Flow Cell Chamber Assay (Dynamic Conditions/Glass Surface)
3.3.4. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
3.4. Antibacterial Assays
3.5. Anti-Quorum Sensing Assays
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; He, J. Biofilms: The Microbial “Protective Clothing” in Extreme Environments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, P.S. Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance in Bacterial Biofilms. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. IJMM 2002, 292, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funari, R.; Shen, A.Q. Detection and Characterization of Bacterial Biofilms and Biofilm-Based Sensors. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderl, J.N.; Franklin, M.J.; Stewart, P.S. Role of Antibiotic Penetration Limitation in Klebsiella Pneumoniae Biofilm Resistance to Ampicillin and Ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 1818–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, L.R.; D’Argenio, D.A.; MacCoss, M.J.; Zhang, Z.; Jones, R.A.; Miller, S.I. Aminoglycoside Antibiotics Induce Bacterial Biofilm Formation. Nature 2005, 436, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salcedo, D.E.; Lee, J.H.; Ha, U.H.; Kim, S.P. The Effects of Antibiotics on the Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance Gene Transfer. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 54, 3582–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquero, F.; Martínez, J.-L.; Cantón, R. Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance in Water Environments. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2008, 19, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Nomura, N.; Suzuki, S. Biofilms: Hot Spots of Horizontal Gene Transfer (HGT) in Aquatic Environments, with a Focus on a New HGT Mechanism. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, Y.; Parsek, M.R. Quorum Sensing and Microbial Biofilms. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 322, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluch, E.; Rewak-Soroczyńska, J.; Jędrusik, I.; Mazurkiewicz, E.; Jermakow, K. Prevention of Biofilm Formation by Quorum Quenching. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.K.; Yeung, A.T.Y.; Hancock, R.E.W. Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms: Towards the Development of Novel Anti-Biofilm Therapies. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 191, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pletzer, D.; Hancock, R.E.W. Antibiofilm Peptides: Potential as Broad-Spectrum Agents. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 2572–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheilly, A.; Soum-Soutéra, E.; Klein, G.L.; Bazire, A.; Compère, C.; Haras, D.; Dufour, A. Antibiofilm Activity of the Marine Bacterium Pseudoalteromonas Sp. Strain 3J6. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3452–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayem, S.A.; Manzo, E.; Ciavatta, L.; Tramice, A.; Cordone, A.; Zanfardino, A.; Felice, M.D.; Varcamonti, M. Anti-Biofilm Activity of an Exopolysaccharide from a Sponge-Associated Strain of Bacillus Licheniformis. Microb. Cell Factories 2011, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slaby, B.M.; Hackl, T.; Horn, H.; Bayer, K.; Hentschel, U. Metagenomic Binning of a Marine Sponge Microbiome Reveals Unity in Defense but Metabolic Specialization. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2465–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentschel, U.; Usher, K.M.; Taylor, M.W. Marine Sponges as Microbial Fermenters. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 55, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakus, G.J.; Targett, N.M.; Schulte, B. Chemical Ecology of Marine Organisms: An Overview. J. Chem. Ecol. 1986, 12, 951–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proksch, P. Defensive Roles for Secondary Metabolites from Marine Sponges and Sponge-Feeding Nudibranchs. Toxicon 1994, 32, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwabusola, E.T.; Katermeran, N.P.; Poh, W.H.; Goh, T.M.B.; Tan, L.T.; Diyaolu, O.; Tabudravu, J.; Ebel, R.; Rice, S.A.; Jaspars, M. Inhibition of the Quorum Sensing System, Elastase Production and Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa by Psammaplin A and Bisaprasin. Molecules 2022, 27, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moitinho-Silva, L.; Bayer, K.; Cannistraci, C.V.; Giles, E.C.; Ryu, T.; Seridi, L.; Ravasi, T.; Hentschel, U. Specificity and Transcriptional Activity of Microbiota Associated with Low and High Microbial Abundance Sponges from the Red Sea. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 1348–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.W.; Radax, R.; Steger, D.; Wagner, M. Sponge-Associated Microorganisms: Evolution, Ecology, and Biotechnological Potential. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 295–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, J.; Basuyaux, O.; Mazurié, J.; Thébault, A. Vibrio Carchariae, a Pathogen of the Abalone Haliotis Tuberculata. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2002, 50, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morot, A.; El Fekih, S.; Bidault, A.; Le Ferrand, A.; Jouault, A.; Kavousi, J.; Bazire, A.; Pichereau, V.; Dufour, A.; Paillard, C.; et al. Virulence of Vibrio Harveyi ORM4 towards the European Abalone Haliotis Tuberculata Involves Both Quorum Sensing and a Type III Secretion System. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 5273–5288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shady, N.H.; El-Hossary, E.M.; Fouad, M.A.; Gulder, T.A.M.; Kamel, M.S.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Bioactive Natural Products of Marine Sponges from the Genus Hyrtios. Molecules 2017, 22, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Småge, S.B.; Frisch, K.; Brevik, Ø.J.; Watanabe, K.; Nylund, A. First Isolation, Identification and Characterisation of Tenacibaculum Maritimum in Norway, Isolated from Diseased Farmed Sea Lice Cleaner Fish Cyclopterus Lumpus L. Aquaculture 2016, 464, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICES. Tenacibaculum Maritimum, Causal Agent of Tenacibaculosis in Marine Fish. 2019. Available online: https://doi.org/10.17895/ICES.PUB.4681 (accessed on 16 May 2021).
- Jouault, A.; Gobet, A.; Simon, M.; Portier, E.; Perennou, M.; Corre, E.; Gaillard, F.; Vallenet, D.; Michel, G.; Fleury, Y.; et al. Alterocin, an Antibiofilm Protein Secreted by Pseudoalteromonas Sp. Strain 3J6. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00893-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, C.M.; Bassler, B.L. The Vibrio Harveyi Quorum-Sensing System Uses Shared Regulatory Components to Discriminate between Multiple Autoinducers. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 2754–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, B.K.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum Sensing Controls Biofilm Formation in Vibrio Cholerae. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassler, B.L.; Greenberg, E.P.; Stevens, A.M. Cross-Species Induction of Luminescence in the Quorum-Sensing Bacterium Vibrio Harveyi. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 4043–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, J.M.; Bassler, B.L. Three Parallel Quorum-Sensing Systems Regulate Gene Expression in Vibrio Harveyi. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 6902–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, K.C.; Waters, C.M.; Svenningsen, S.L.; Bassler, B.L. A Small-RNA-Mediated Negative Feedback Loop Controls Quorum-Sensing Dynamics in Vibrio Harveyi. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 70, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petek, S. WALLIS 2018 Cruise, Alis R/V. 2018. Available online: https://doi.org/10.17600/18000524 (accessed on 7 June 2022).
- Freeman, J.A.; Bassler, B.L. A Genetic Analysis of the Function of LuxO, a Two-Component Response Regulator Involved in Quorum Sensing in Vibrio Harveyi. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 31, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, E.P.; Hastings, J.W.; Ulitzur, S. Induction of Luciferase Synthesis in Beneckea Harveyi by Other Marine Bacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 1979, 120, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukerb, A.M.; Simon, M.; Pernet, E.; Jouault, A.; Portier, E.; Persyn, E.; Bouffartigues, E.; Bazire, A.; Chevalier, S.; Feuilloley, M.G.J.; et al. Draft Genome Sequences of Four Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Clinical Strains with Various Biofilm Phenotypes. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, e01286-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures GmbH: Details. Available online: https://www.dsmz.de/collection/catalogue/details/culture/DSM-17995 (accessed on 7 June 2023).
- Coffey, B.M.; Anderson, G.G. Biofilm Formation in the 96-Well Microtiter Plate. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1149, 631–641. [Google Scholar]
- Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Sternberg, C. Methods for Studying Biofilm Formation: Flow Cells and Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. In Pseudomonas Methods and Protocols; Filloux, A., Ramos, J.-L., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 1149, pp. 615–629. ISBN 978-1-4939-0472-3. [Google Scholar]
- Pamp, S.J.; Sternberg, C.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. Insight into the Microbial Multicellular Lifestyle via Flow-Cell Technology and Confocal Microscopy. Cytometry A 2009, 75A, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydorn, A.; Nielsen, A.T.; Hentzer, M.; Sternberg, C.; Givskov, M.; Ersbøll, B.K.; Molin, S. Quantification of Biofilm Structures by the Novel Computer Program Comstat. Microbiology 2000, 146, 2395–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in Vitro Evaluating Antimicrobial Activity: A Review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
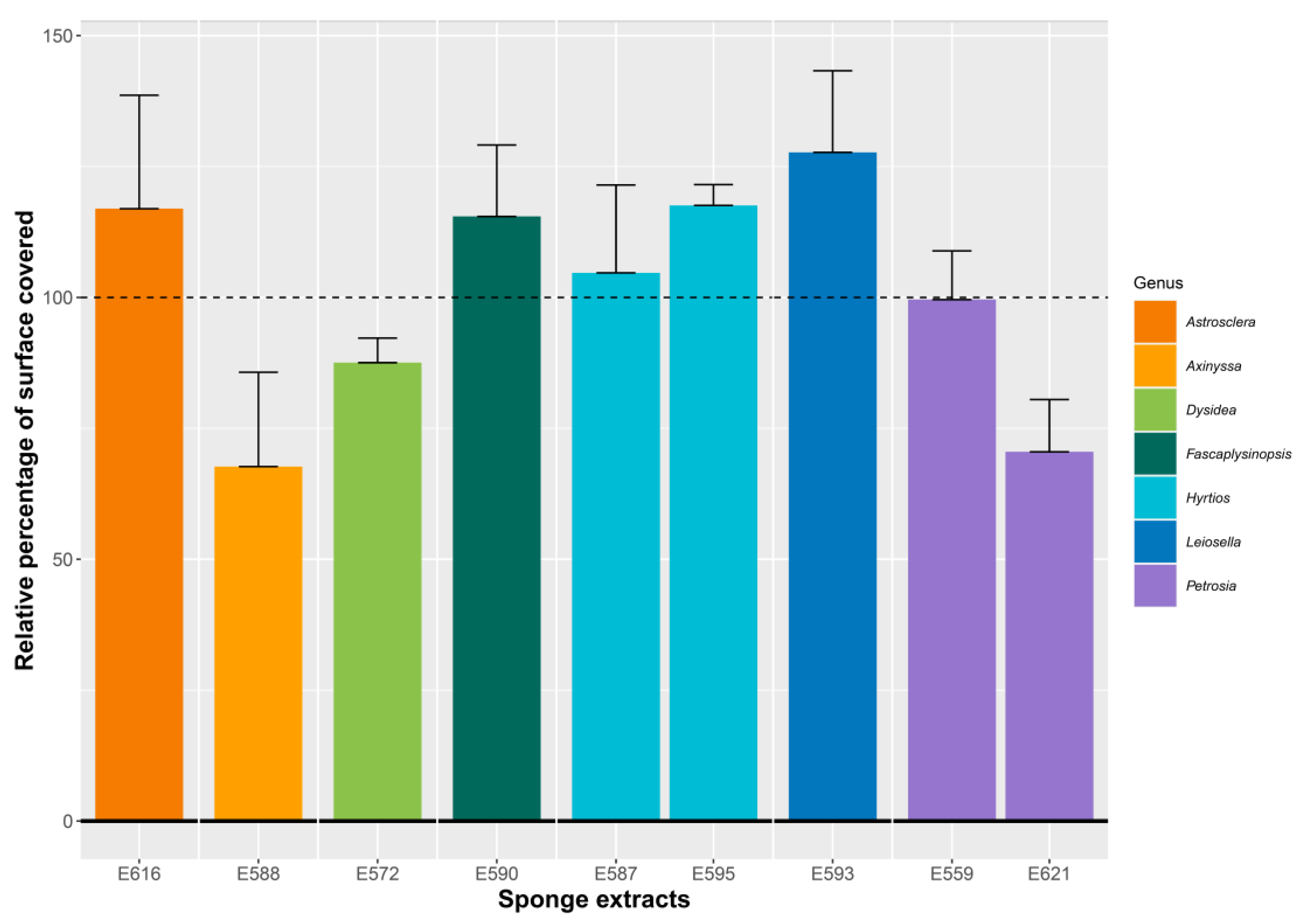
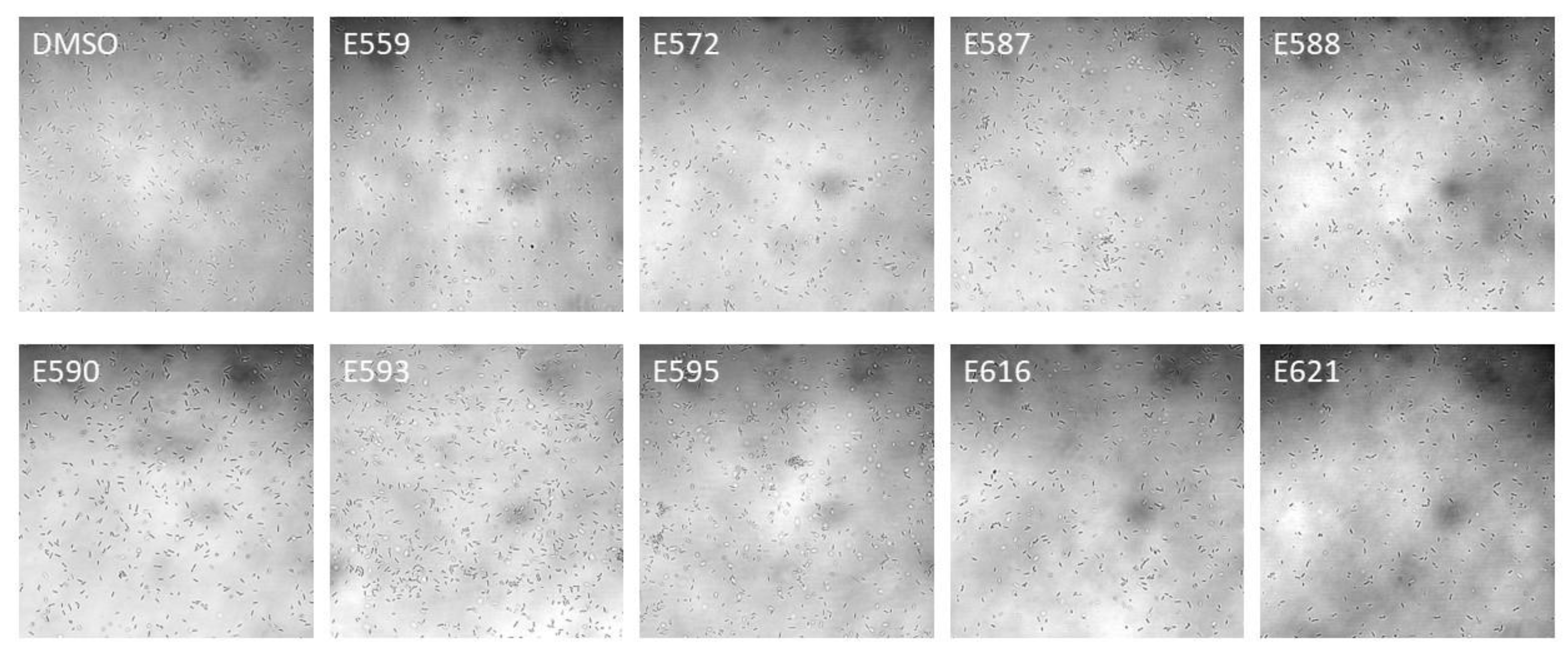

| E559 | E590 | E616 | E621 | E572 | E587 | E593 | E595 | E588 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % Inhibition in biovolume | 41.76 ± 10.01 | 33.20 ± 6.61 | 37.91 ± 3.87 | 34.65 ± 6.32 | 26.41 ± 16.01 | 30.35 ± 12.90 | 28.21 ± 14.39 | 26.86 ± 7.75 | 0.72 ± 17.41 |
| % Inhibition in average thickness | 30.59 ± 6.37 | 21.38 ± 4.53 | 13.49 ± 5.17 | 28.83 ± 6.86 | 16.85 ± 12.97 | 17.49 ± 16.37 | 15.31 ± 10.42 | 21.71 ± 5.71 | 1.59 ± 8.78 |
| % Inhibition in maximum thickness | 28.75 ± 0.97 | 15.18 ± 3.21 | 8.71 ± 5.56 | 11.81 ± 6.50 | 5.54 ± 6.19 | 6.35 ± 7.87 | 8.68 ± 5.31 | 19.94 ± 5.33 | 0.51 ± 3.45 |
| Strong inhibitor group | Moderate inhibitor group | No effect | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caudal, F.; Rodrigues, S.; Dufour, A.; Artigaud, S.; Le Blay, G.; Petek, S.; Bazire, A. Extracts from Wallis Sponges Inhibit Vibrio harveyi Biofilm Formation. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071762
Caudal F, Rodrigues S, Dufour A, Artigaud S, Le Blay G, Petek S, Bazire A. Extracts from Wallis Sponges Inhibit Vibrio harveyi Biofilm Formation. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(7):1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071762
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaudal, Flore, Sophie Rodrigues, Alain Dufour, Sébastien Artigaud, Gwenaelle Le Blay, Sylvain Petek, and Alexis Bazire. 2023. "Extracts from Wallis Sponges Inhibit Vibrio harveyi Biofilm Formation" Microorganisms 11, no. 7: 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071762
APA StyleCaudal, F., Rodrigues, S., Dufour, A., Artigaud, S., Le Blay, G., Petek, S., & Bazire, A. (2023). Extracts from Wallis Sponges Inhibit Vibrio harveyi Biofilm Formation. Microorganisms, 11(7), 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071762






