Microbial Communities Affected by Hydraulic Fracturing and Environmental Factors within an In Situ Coal Reservoir
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
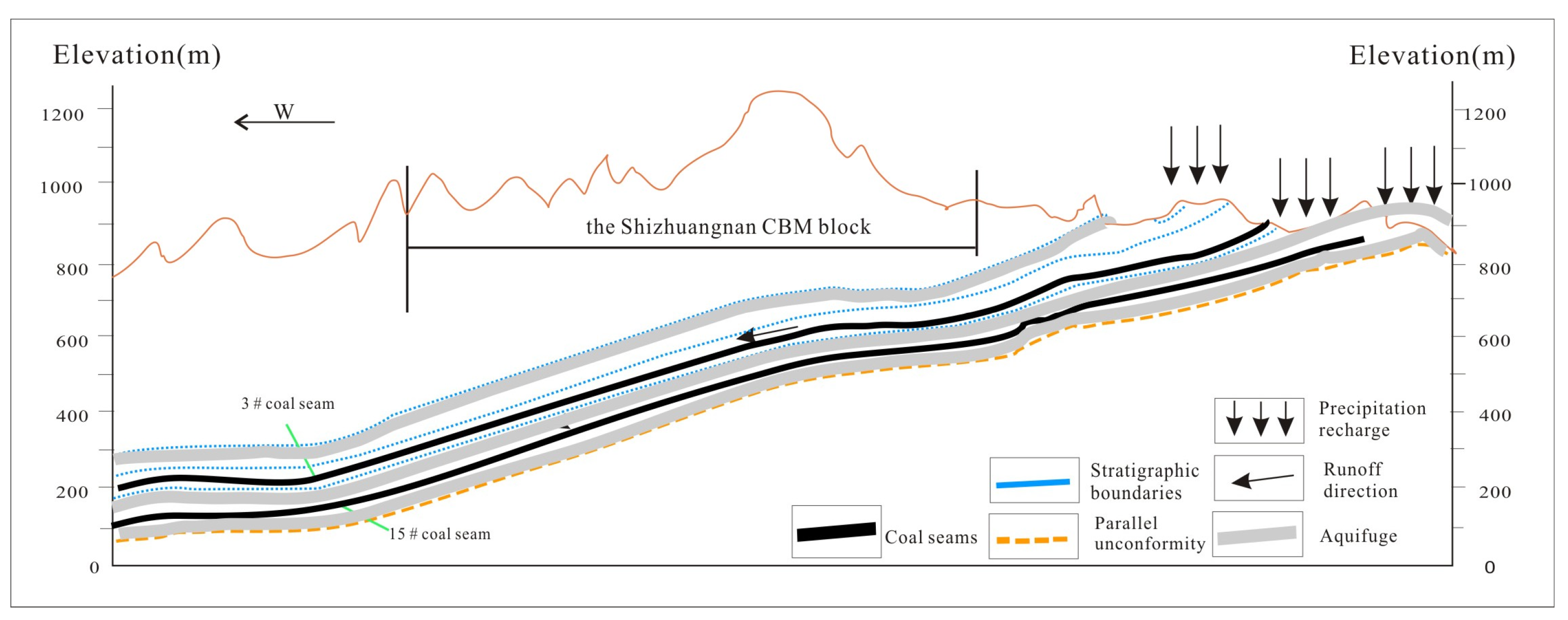
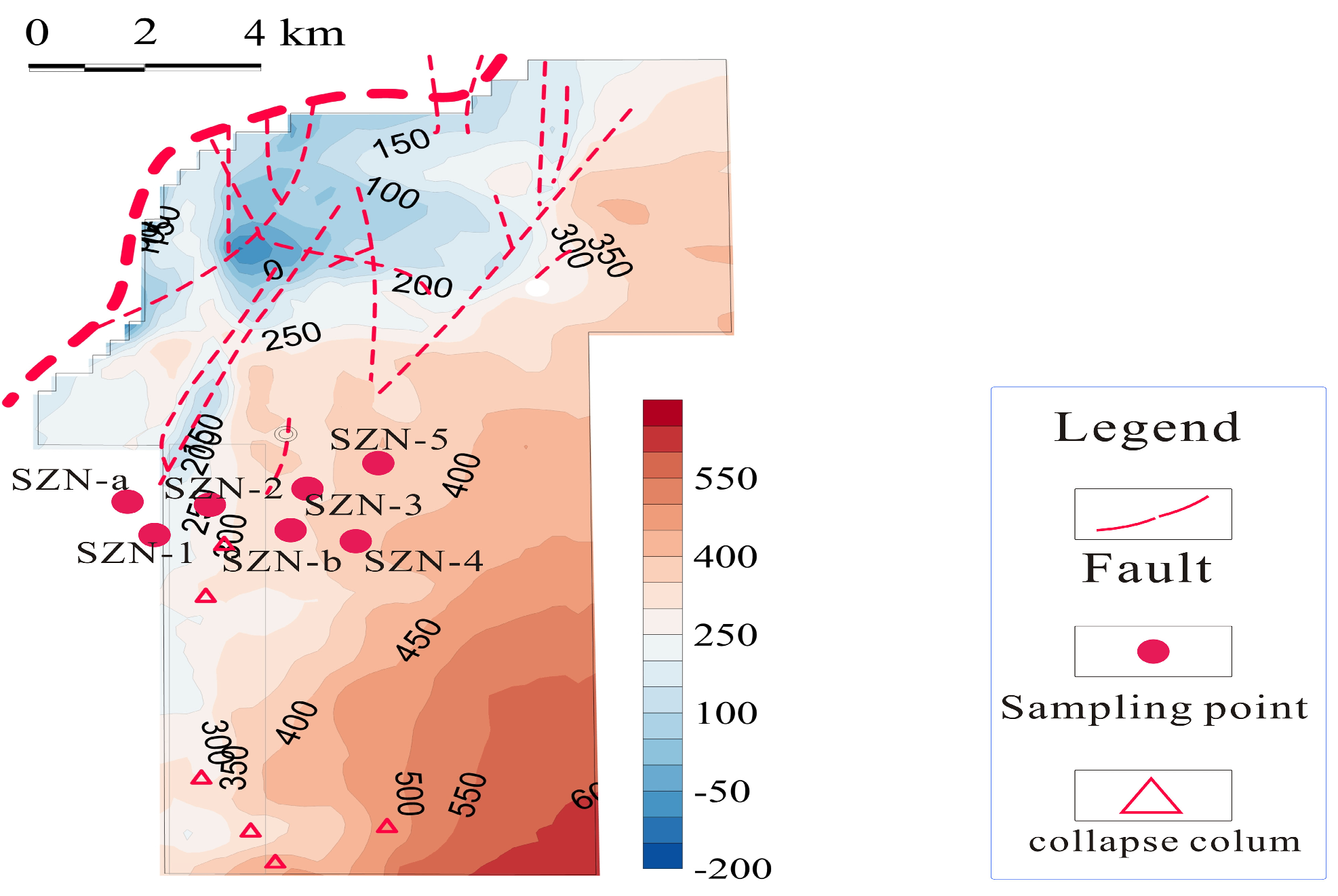
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Collection of Samples and Geochemical Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction and Sequencing Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
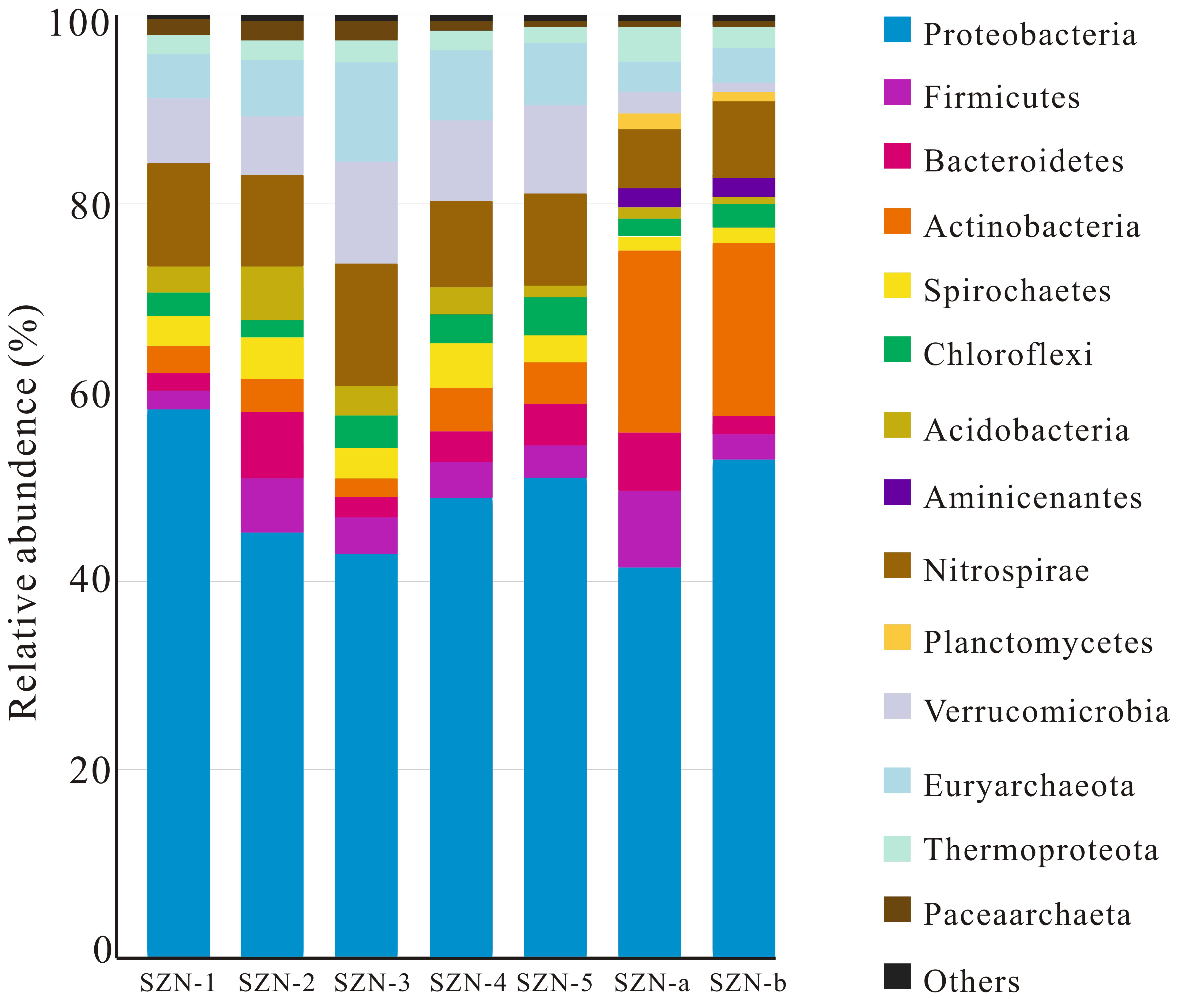
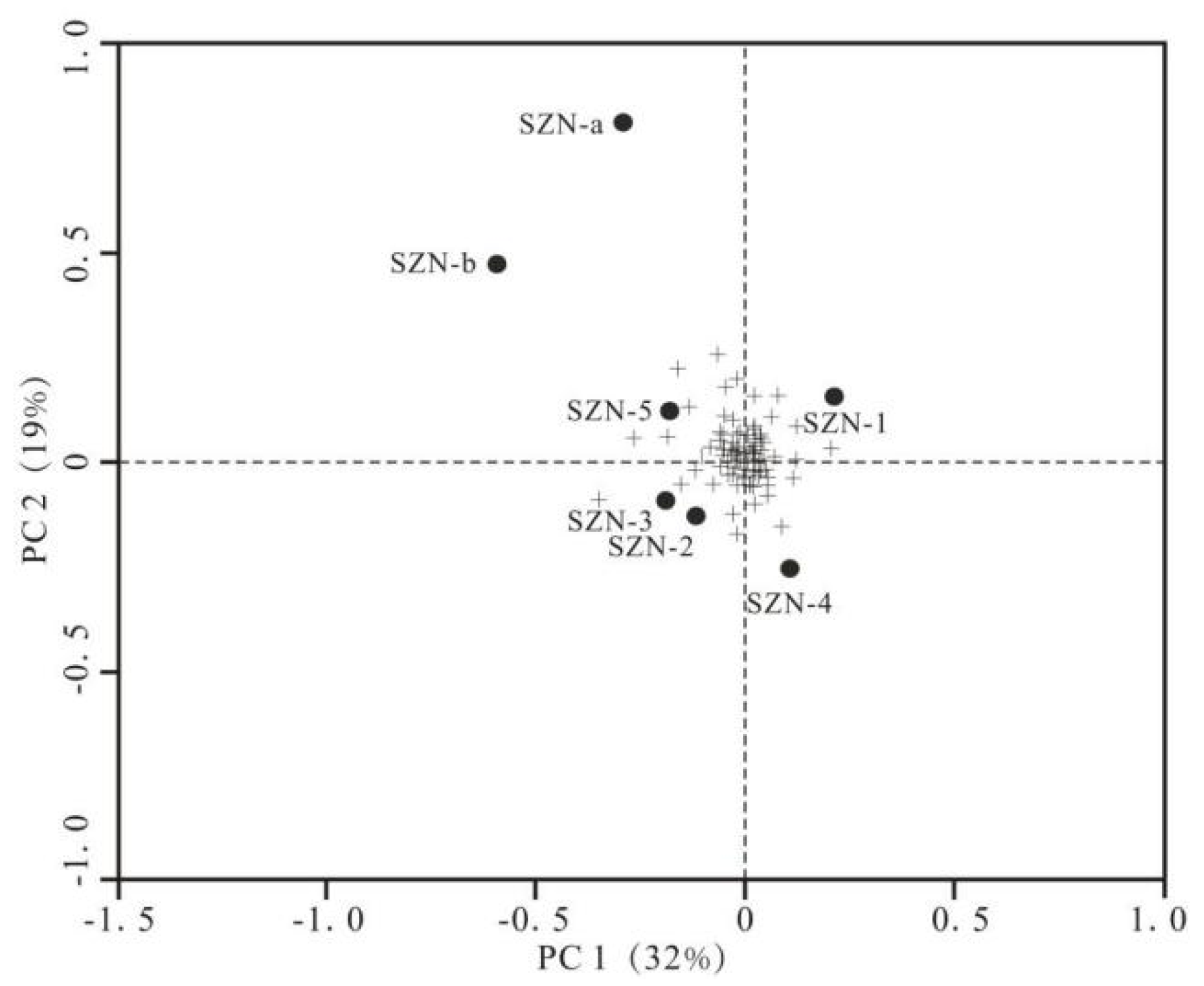
3.1. Geochemistry and Microbial Structure
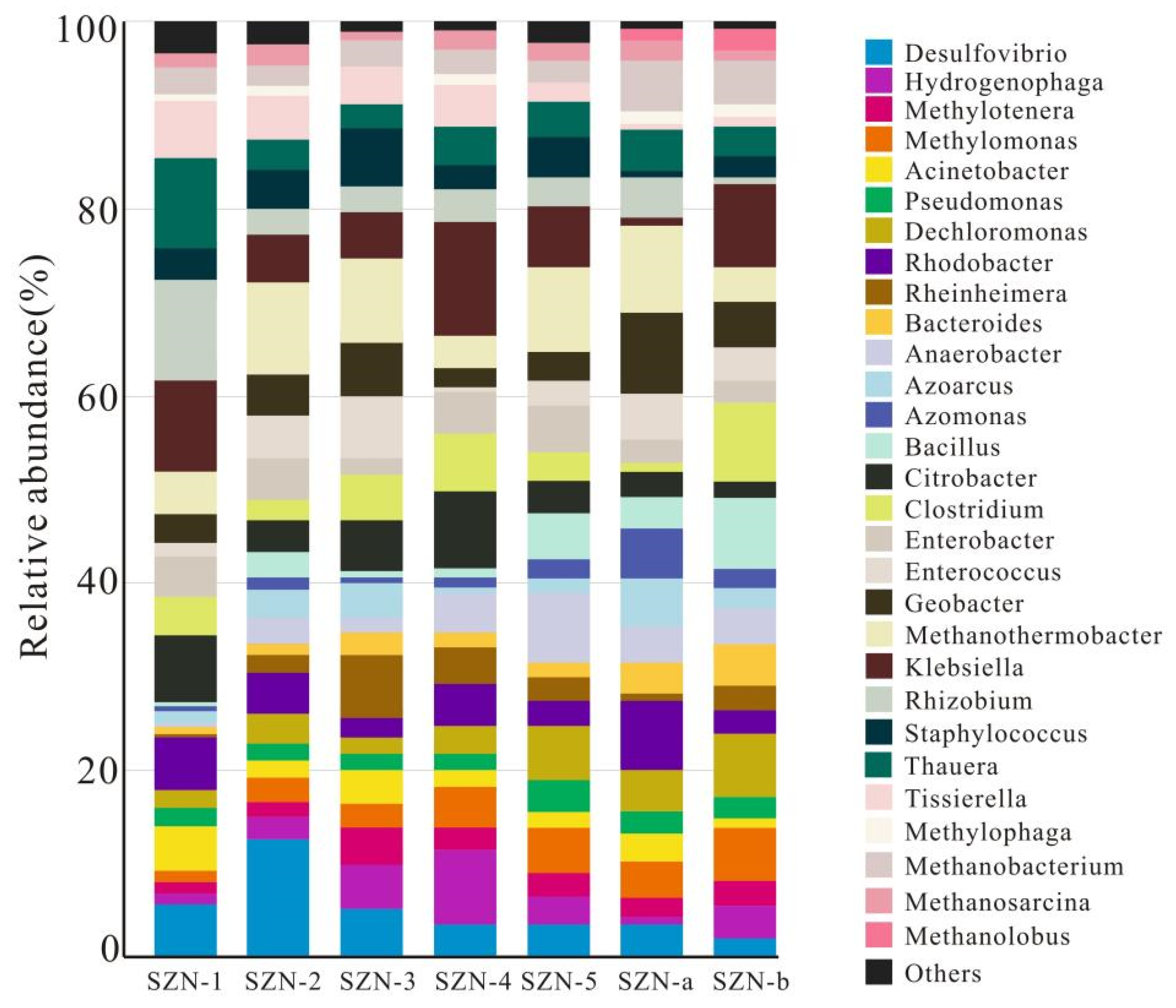
3.2. Microbial Evidence for Coal Biosolubilization and Methanogenesis
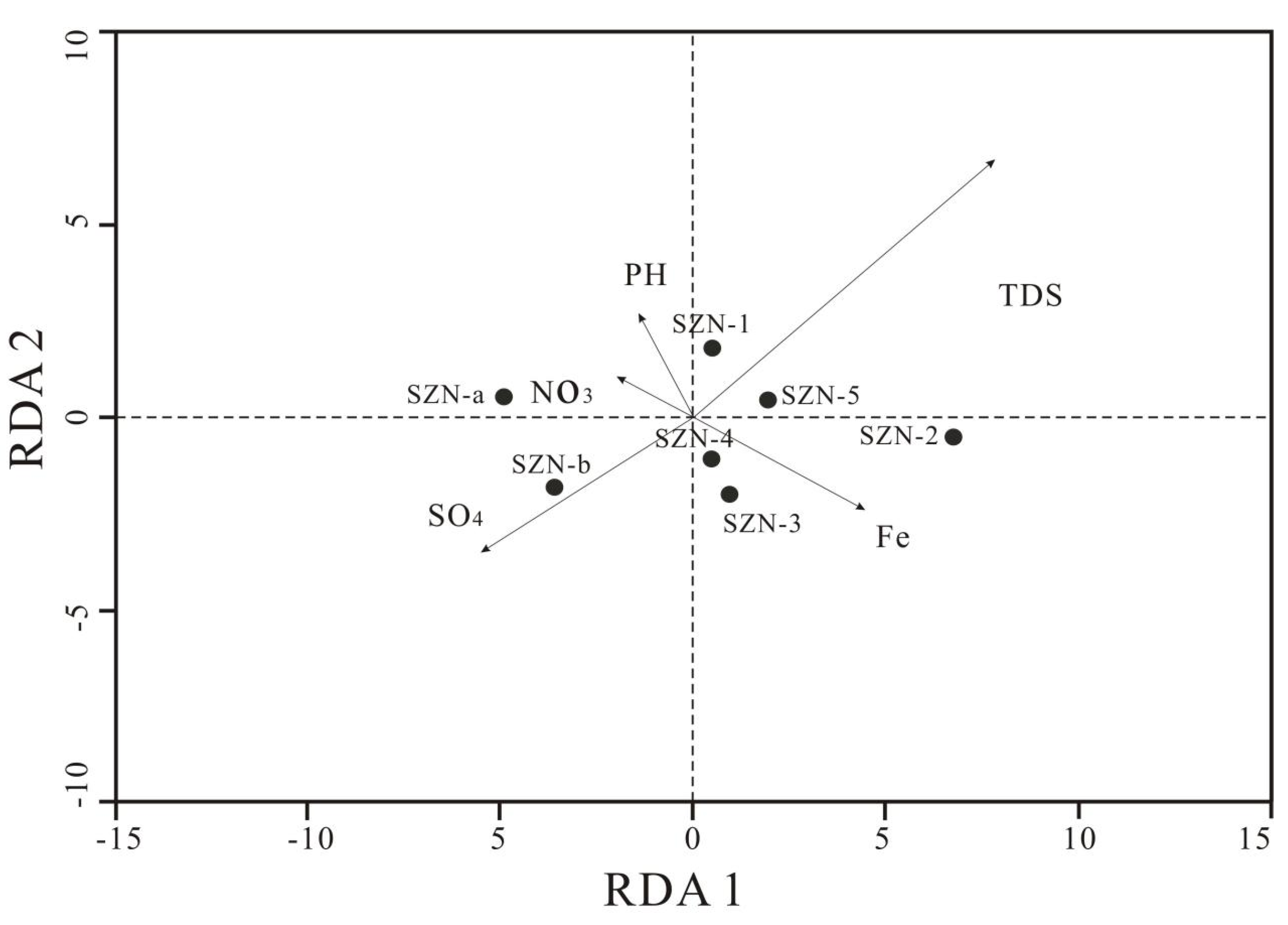
3.3. Environmental Factors Affecting Microbial Composition
3.4. Microbial Communities and Metabolism Shift for Methanogenesis after Hydraulic Fracturing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, H.J.; Tang, D.Z.; Pan, Z.J.; Yan, D.T.; Yang, S.G.; Zhuang, X.G.; Li, G.Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, G. A study of hydrogeology and its effect on coalbed methane enrichment in the southern Junggar Basin, China. AAPG Bull. 2019, 103, 189–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Pan, Z. Variation in permeability during CO2–CH4 displacement in coal seams: Part 1—Experimental insights. Fuel 2020, 263, 116666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Pan, Z.; Tong, W. Nanoscale pore structure and mechanical property analysis of coal: An insight combining AFM and SEM images. Fuel 2020, 260, 116352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, S.; Luk, A.W.S.; Gutierrez-Zamora, M.L.; Chong, N.H.H.; Thomas, T.; Lee, M.; Manefield, M. Long-term succession in a coal seam microbiome during in situ biostimulation of coalbed methane generation. ISME J. 2019, 13, 632–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Tang, S.H.; Zhang, S.H.; Xi, Z.D. Biogeochemical assessment of the coalbed methane source, migration, and fate: A case study of the Shizhuangnan Block, Southern Qinshui Basin. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 7715–7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Tang, S.H.; Huang, W.H.; Zhang, S.H.; Li, Z.C. Distribution characteristics of C–N–S microorganism genes in different hydraulic zones of high-rank coal reservoirs in Southern Qinshui Basin. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 21395–21409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Ju, Y.W.; Huang, H.P.; Yun, J.L.; Guo, C. Potential and constraints of biogenic methane generation from coals and mudstones from Huaibei coalfield, eastern China. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.B.; Zhao, W.Z.; Xia, D.P. The diversity of hydrogen-producing bacteria and methanogens within an in situ coal seam. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.Z.; Su, X.B.; Xia, D.P.; Hou, S.H.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y.X. Enhanced coalbed methane recovery by the modification of coal reservoir under the supercritical CO2 extraction and anaerobic digestion. Energy 2022, 259, 124914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, S.; Akiyama, M.; Naganuma, T.; Fujioka, M.; Nako, M.; Ishijima, Y. Molecular characterization of microbial communities in deep coal seam groundwater of northern Japan. Geobiology 2007, 5, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.X.; Su, X.B.; Zhao, W.Z.; Xia, D.P.; Fu, H.J.; Wang, G. Culture medium optimization for producing biomethane by coal anaerobic digestion. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 348, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tang, S.H.; Zhang, S.H.; Xi, Z.D. In situ analysis of methanogenic pathways and biogeochemical features of CBM co-produced water from the Shizhuangnan block in the southern Qinshui Basin, China. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 5466–5475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandt, M.H.I.; Beckmann, S.; Rijkers, R.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Manefield, M.; Welte, C.U. Nutrient and acetate amendment leads to acetoclastic methane production and microbial community change in a non-producing Australian coal well. Microb. Biotechnol. 2018, 11, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, S.J.; Evans, P.N.; Parks, D.H.; Golding, S.D.; Tyson, G.W. Genome-centric analysis of microbial populations enriched by hydraulic fracture fluid additives in a coal bed methane production well. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudsepp, M.J.; Gagen, E.J.; Evans, P.; Tyson, G.W.; Golding, S.D.; Southam, G. The influence of hydrogeological disturbance and mining on coal seam microbial communities. Geobiology 2016, 14, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.G.; Fu, H.J.; Yan, D.T.; Su, X.B.; Wang, X.M.; Zhao, W.Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, G. Effects of simulated surface freshwater environment on in situ microorganisms and their methanogenesis after tectonic uplift of a deep coal seam. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2022, 257, 104014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, W.; Tang, S.H. Microbial geochemical characteristics of the coalbed methane in the Shizhuangnan block of Qinshui Basin, north China and their geological implications. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. 2019, 93, 660–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tang, S.; Elsworth, D. Re-evaluating adsorbed and free methane content in coal and its ad- and desorption processes analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Bao, Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; An, C.; Chang, J.N. Multiple-experimental investigation on the physicochemical structures alternation during coal biogasification. Fuel 2023, 339, 127433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.G.; Zhang, Y.W.; Zhang, J.L.; Huang, Z.X.; Urynowicz, M.A.; Liang, W.G.; Han, Z.Y.; Liu, J. Characterization of anthracite-degrading methanogenic microflora enriched from Qinshui Basin in China. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 6380–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawale, J.T.; Edeki, O.G.; Cowan, A.K. Bacterial degradation of coal discard and geologically weathered coal. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2020, 7, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.B.; Yu, Z.S.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, H.X. Microbial communities from the Huaibei Coalfield alter the physicochemical properties of coal in methanogenic bioconversion. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2019, 202, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liang, Y.N.; Pandey, R.; Harpalani, S. Characterizing microbial communities dedicated for conversion of coal to methane in situ and ex situ. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 146, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.B.; Zhao, W.Z.; Xia, D.P.; Hou, S.H.; Fu, H.J.; Zhou, Y.X. Experimental study of advantages of coalbed gas bioengineering. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2022, 102, 104585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Li, H.; Ding, L.; Zhou, J.; Song, W.; Li, Y.; Lin, R. Improving hydrogen and methane co-generation in cascading dark fermentation and anaerobic digestion: The effect of magnetite nanoparticles on microbial electron transfer and syntrophism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397, 125394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, L. Facet-engineered hematite boosts microbial electrogenesis by synergy of promoting electroactive biofilm formation and extracellular electron transfer. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 153154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.J.; Yan, D.T.; Su, X.B.; Wang, J.W.; Li, Q.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.Z.; Zhang, L.W.; Wang, X.M.; Li, Y.G. Biodegradation of early thermogenic gas and generation of secondary microbial gas in the Tieliekedong region of the northern Tarim Basin, NW China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2022, 261, 104075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, S.; Kruger, M.; Engelen, B.; Gorbushina, A.A.; Cypionka, H. Role of bacteria, archaea and fungi involved in methane release in abandoned coal mines. Geomicrobiol. J. 2011, 28, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Q.; Chen, Y.M.; Wu, R.W.; Nie, Z.Q.; Han, Z.Y.; Tan, K.L.; Chen, L.Y. Potential of biogenic methane for pilot-scale fermentation ex situ with lump anthracite and the changes of methanogenic consortia. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 45, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; He, H.; Ren, Y.; Haider, R.; Urynowicz, M.; Fallgren, P.H.; Jin, S.; Ali, M.I.; Jamal, A.; Sabar, M.A.; et al. A mini review on biotransformation of coal to methane by enhancement of chemical pretreatment. Fuel 2022, 308, 121961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.J.; Yan, D.T.; Yang, S.G.; Wang, X.M.; Wang, G.; Zhuang, X.G.; Zhang, L.Y.; Li, G.Q.; Chen, X.; Pan, Z.J. A study of the gas-water characteristics and their implications for the CBM accumulation modes in the southern Junggar Basin, China. AAPG Bull. 2021, 105, 189–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Tang, S.H.; Zhang, S.H. Microbiome of high-rank coal reservoirs in the high-production areas of the Southern Qinshui Basin. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinson, D.S.; Blair, N.E.; Ritter, D.J.; Martini, A.M.; McIntosh, J.C. Carbon mass balance, isotopic tracers of biogenic methane, and the role of acetate in coal beds: Powder River Basin (USA). Chem. Geol. 2019, 530, 119329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Horne, R.N.; Hawkins, A.J.; Primo, J.C.; Gorbatenko, O.; Dekas, A.E. Geological activity shapes the microbiome in deep-subsurface aquifers by advection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2113985119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strapoc, D.; Picardal, F.W.; Turich, C.; Schaperdoth, I.; Macalady, J.L.; Lipp, J.S.; Lin, Y.S.; Ertefai, T.F.; Schubotz, F.; Hinrichs, K.U.; et al. Methane-producing microbial community in a coal bed of the Illinois basin. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2008, 74, 3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.G.; Yang, Z.B.; Qin, Z.H.; Qin, Y.; Li, C.L.; Lu, B.J.; Li, Y.C. Characteristics of microbial communities in water from CBM wells and biogas production potential in eastern Yunnan and western Guizhou, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2023; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | pH | Cl− (mg/L) | HCO3− (mg/L) | NO3− (mg/L) | SO42− (mg/L) | Na+ (mg/L) | Ca2+ (mg/L) | Mg2+ (mg/L) | Fe3+ (mg/L) | TDS (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SZN-1 | 6.8 | 219.36 | 537.84 | 11.47 | 3.89 | 491.39 | 3.57 | 3.84 | 4.84 | 1276.2 |
| SZN-2 | 7.5 | 223.69 | 328.52 | 5.32 | 5.27 | 684.02 | 5.86 | 4.86 | 2.09 | 1259.63 |
| SZN-3 | 7.1 | 129.37 | 631.83 | 6.16 | 6.85 | 563.84 | 2.26 | 2.27 | 1.07 | 1343.65 |
| SZN-4 | 6.9 | 247.69 | 336.09 | 8.56 | 7.09 | 772.06 | 4.72 | 1.98 | 6.75 | 1384.94 |
| SZN-5 | 7.2 | 165.48 | 296.95 | 7.63 | 8.37 | 684.85 | 3.83 | 5.37 | 3.82 | 1176.3 |
| SZN-a | 7.6 | 297.96 | 528.93 | 6.94 | 2.47 | 685.37 | 6.48 | 2.86 | 2.83 | 1533.84 |
| SZN-b | 6.7 | 262.98 | 619.05 | 5.83 | 4.85 | 863.08 | 5.93 | 3.54 | 1.63 | 1766.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Tang, S.; Xi, Z. Microbial Communities Affected by Hydraulic Fracturing and Environmental Factors within an In Situ Coal Reservoir. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071657
Li Y, Chen J, Tang S, Xi Z. Microbial Communities Affected by Hydraulic Fracturing and Environmental Factors within an In Situ Coal Reservoir. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(7):1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071657
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yang, Jian Chen, Shuheng Tang, and Zhaodong Xi. 2023. "Microbial Communities Affected by Hydraulic Fracturing and Environmental Factors within an In Situ Coal Reservoir" Microorganisms 11, no. 7: 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071657
APA StyleLi, Y., Chen, J., Tang, S., & Xi, Z. (2023). Microbial Communities Affected by Hydraulic Fracturing and Environmental Factors within an In Situ Coal Reservoir. Microorganisms, 11(7), 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071657






