Ecological Responses of Soil Microbial Communities to Heavy Metal Stress in a Coal-Based Industrial Region in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Soil Physicochemical Determination
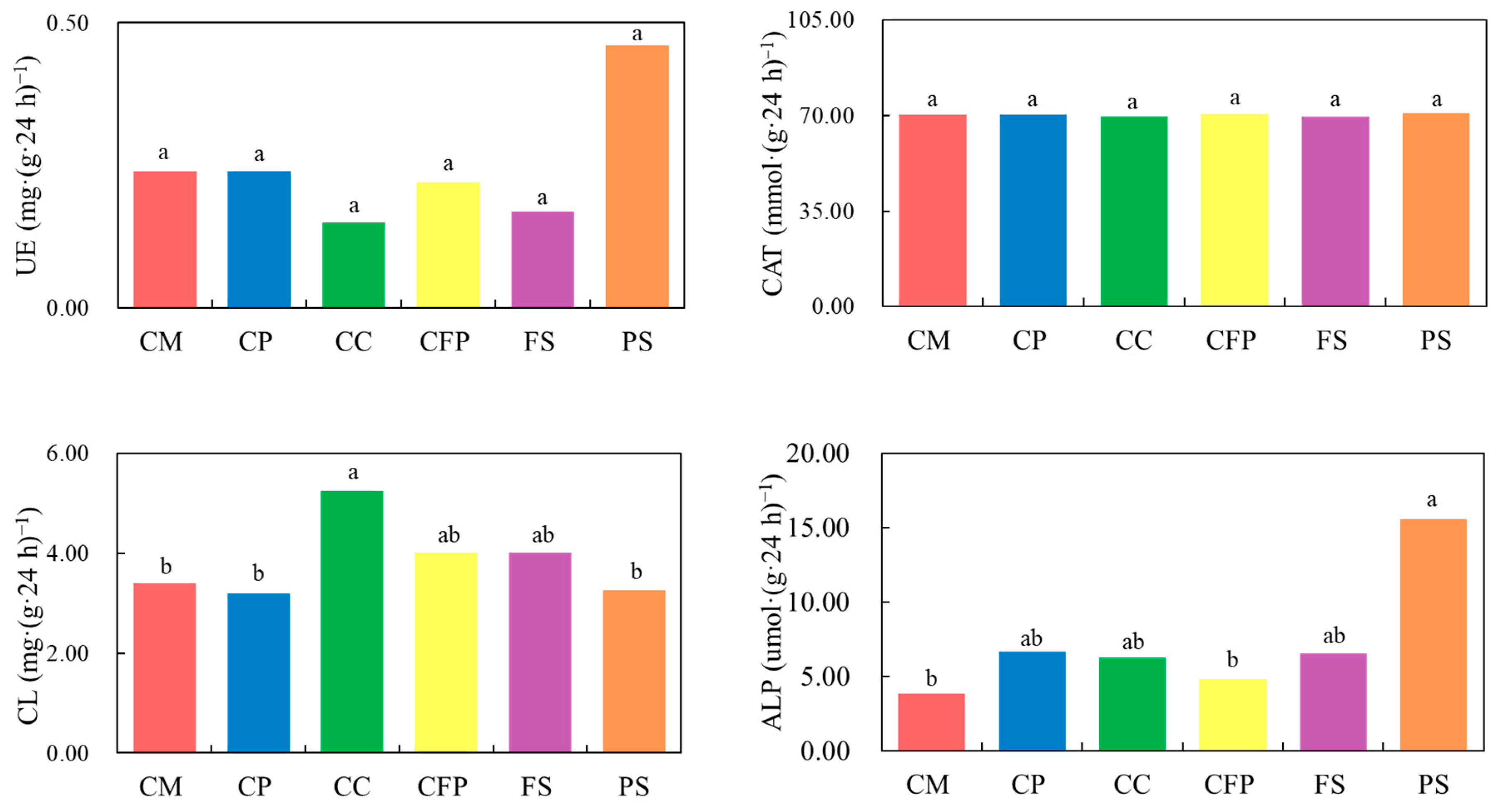
2.3. Soil Enzyme Activities Assays
2.4. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and Illumina Miseq Sequencing
2.5. Analyses of Microbial Community Composition and Divresity
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Soil Physicochemical Properties and Heavy Metal Contamination
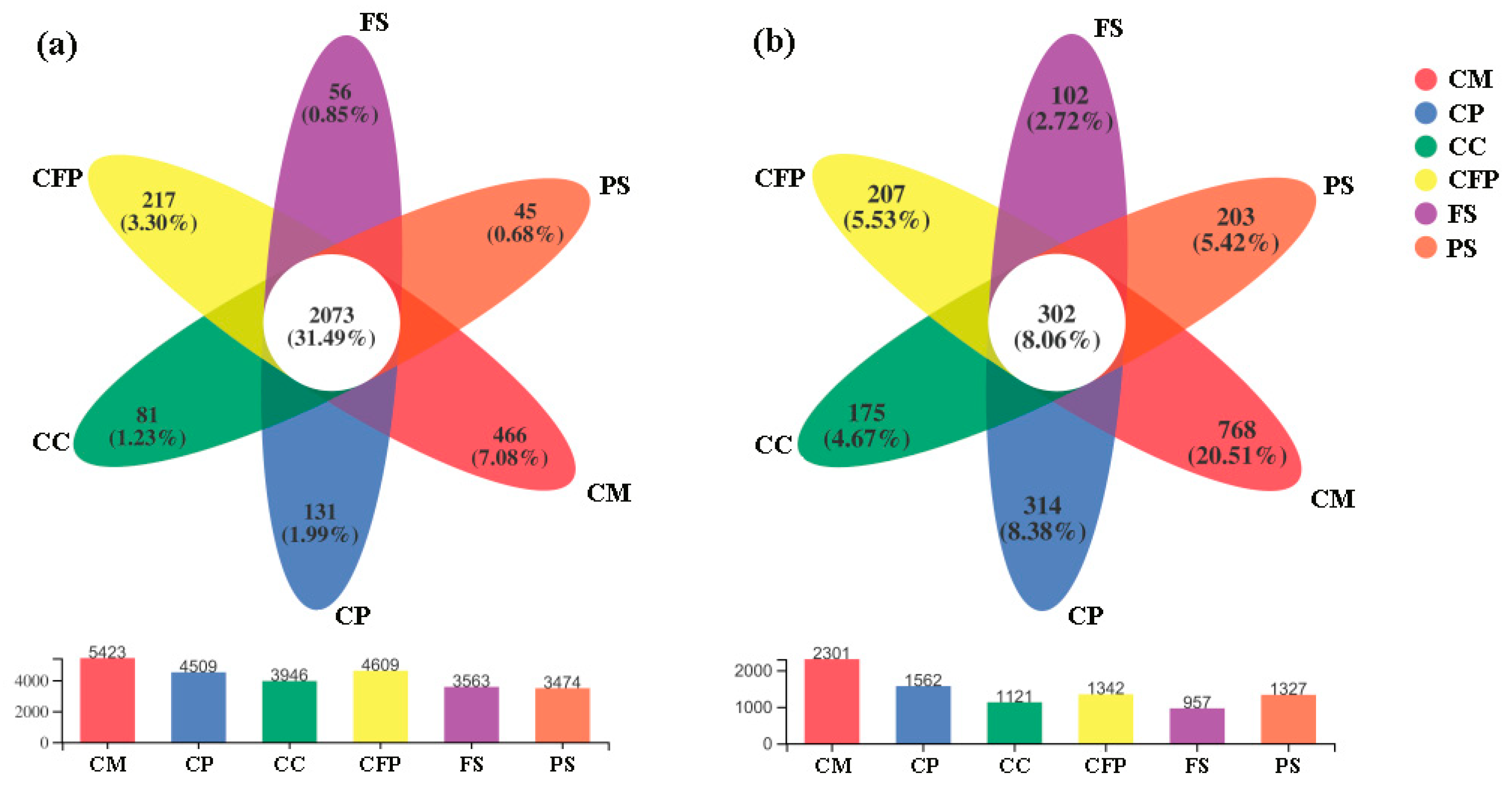
3.2. Composition, Abundance and Diversity of Microbial Communities
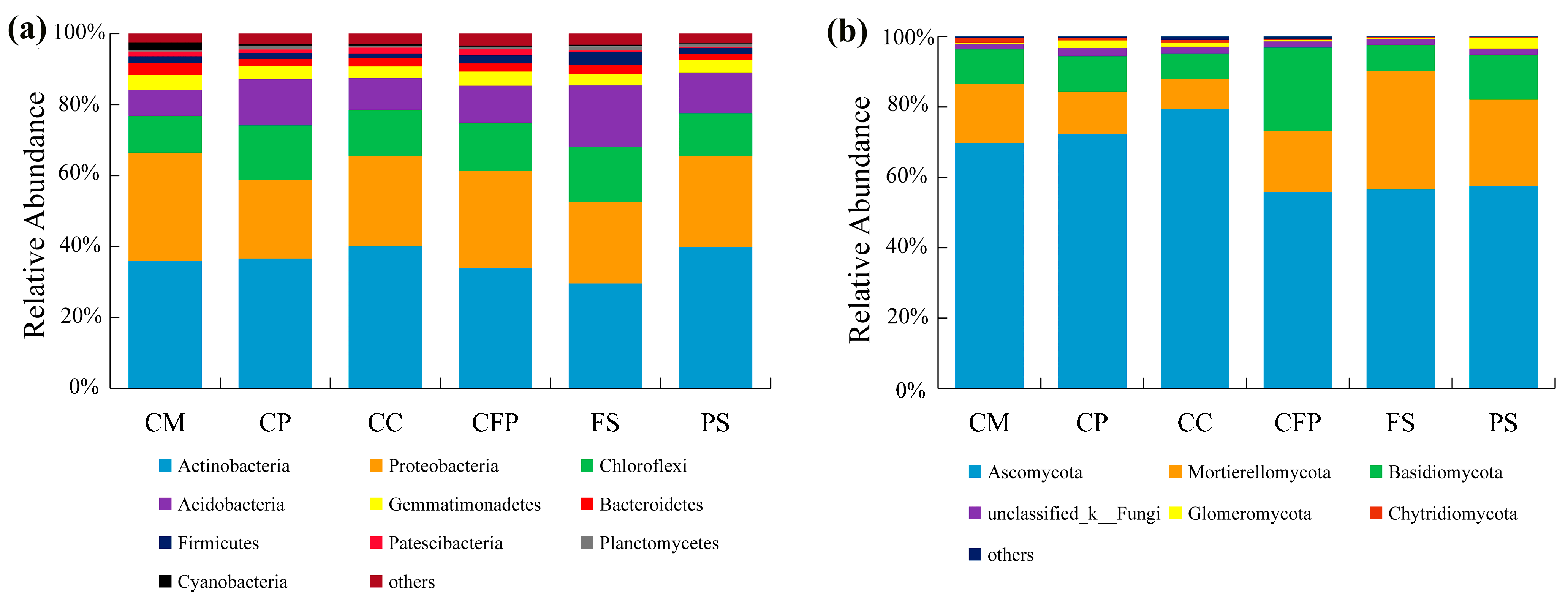
3.2.1. Bacterial Community Composition and Diversity
3.2.2. Fungal Community Composition and Diversity
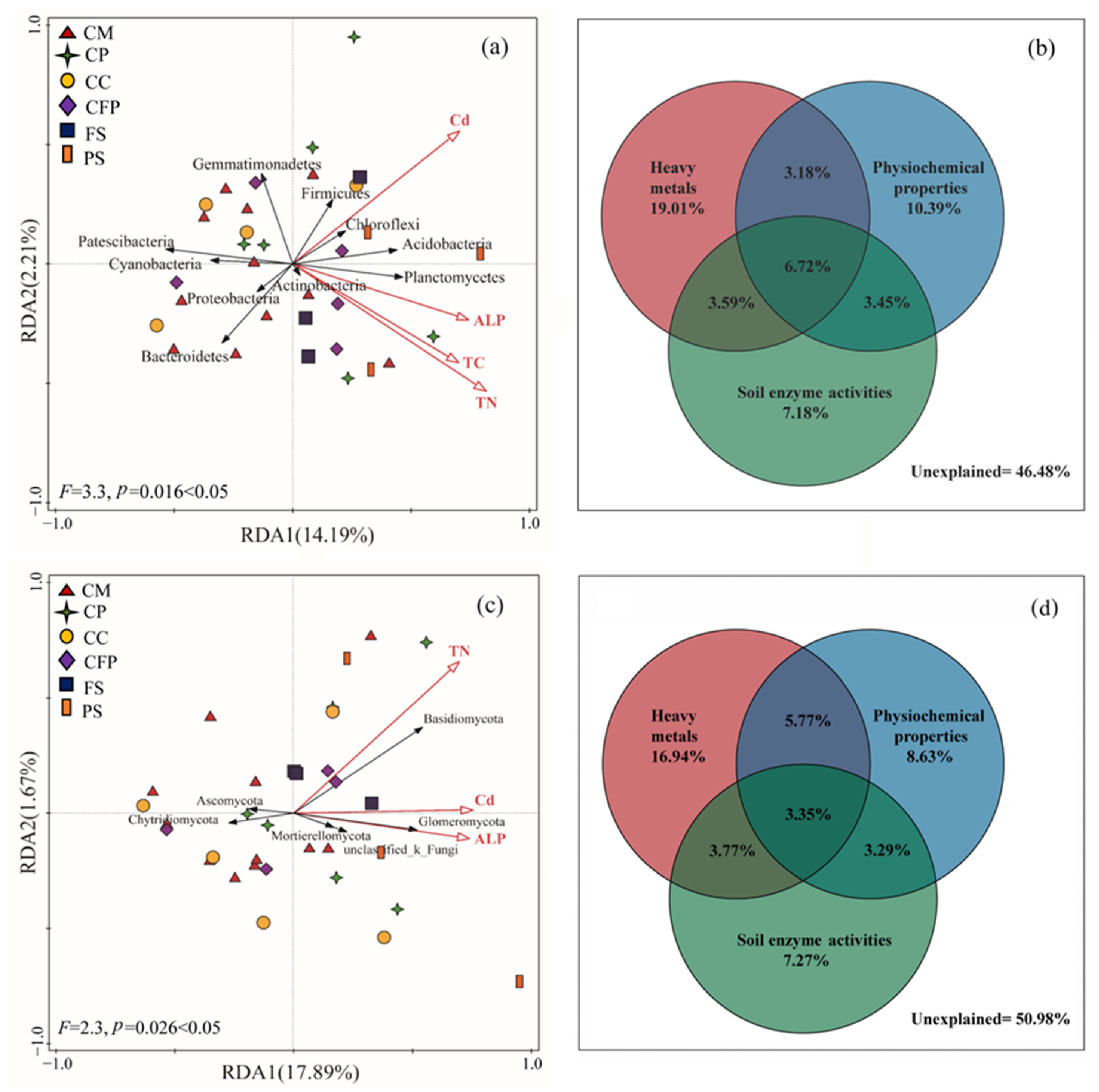
3.3. Relationships between Soil Microbial Communities and Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Heavy Metal Contamination on Soil Enzyme Activities
4.2. Influences of Environmental Factors on Soil Microbial Communities
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gan, Y.; El-Houjeiri, H.M.; Badahdah, A.; Lu, Z.; Cai, H.; Przesmitzki, S.; Wang, M. Carbon footprint of global natural gas supplies to China. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Liu, C. Radiation characteristics of natural gamma-ray from coal and gangue for recognition in top coal caving. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Quadros, P.D.; Zhalnina, K.; Davis-Richardson, A.G.; Drew, J.C.; Menezes, F.B.; Camargo, F.A.d.O.; Triplett, E.W. Coal mining practices reduce the microbial biomass, richness and diversity of soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 98, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, J.; Huo, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xue, L. Profiling multiple heavy metal contamination and bacterial communities surrounding an iron tailing pond in Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Quan, Z.; Sun, Y.; Du, J.; Liu, B. Excess sulfur and Fe elements drive changes in soil and vegetation at abandoned coal gangues, Guizhou China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Su, C. Arsenic and Heavy Metal Accumulation and Risk Assessment in Soils around Mining Areas: The Urad Houqi Area in Arid Northwest China as an Example. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.Y.; Li, Z.G.; Wang, S.X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, R.; Liu, J.L.; Yang, H.M.; Guo, M.Z. Lead isotopic compositions of selected coals, Pb/Zn ores and fuels in China and the application for source tracing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13502–13508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; van der Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, X. Efficacy and microbial responses of biochar-nanoscale zero-valent during in-situ remediation of Cd-contaminated sediment. J. Cleaner Prod. 2021, 287, 125076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Deng, M.; Japenga, J.; Li, T.; Yang, X.; He, Z. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of agricultural soils in a typical peri-urban area in southeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Xie, Y.; Luo, Y.; Sheng, M.; Xu, F.; Xu, H. Ecological responses of soil microbial abundance and diversity to cadmium and soil properties in farmland around an enterprise-intensive region. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierer, N. Embracing the unknown: Disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Gong, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Song, L.; Zhang, S.; Dong, J.; Baoyin, T. Plant–microbial linkages regulate soil organic carbon dynamics under phosphorus application in a typical temperate grassland in northern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 335, 108006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, Y.; Groenigen, K.J.; Hungate, B.A.; Cao, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, R. A keystone microbial enzyme for nitrogen control of soil carbon storage. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaaq1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, A.A.; Mellis, E.V.; Escalas, A.; Lemos, L.N.; Junior, J.L.; Quaggio, J.A.; Zhou, J.; Tsai, S. Zinc concentration affects the functional groups of microbial communities in sugarcane-cultivated soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 236, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Li, G.; Tang, W.; Zhu, Q.; Li, X.; Du, C.; Li, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, L. Role of Sedum alfredii and soil microbes in the remediation of ultra-high content heavy metals contaminated soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 339, 108090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Huang, J.; Lu, J.; Sun, Y. Study on the influence of soil microbial community on the long-term heavy metal pollution of different land use types and depth layers in mine. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golebiewski, M.; Deja-Sikora, E.; Cichosz, M.; Tretyn, A.; Wrobel, B. 16S rDNA Pyrosequencing Analysis of Bacterial Community in Heavy Metals Polluted Soils. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 67, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yu, C. Distribution of the microbial community and antibiotic resistance genes in farmland surrounding gold tailings: A metagenomics approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Moorhead, D.L.; Ochoa-Hueso, R.; Mueller, C.W.; Ying, S.C.; Chen, J. Nitrogen loading enhances phosphorus limitation in terrestrial ecosystems with implications for soil carbon cycling. Funct. Ecol. 2022, 36, 2845–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Seshadri, B.; Sarkar, B.; Wang, H.; Rumpel, C.; Sparks, D.; Farrell, M.; Hall, T.; Yang, X.; Bolan, N. Biochar modulates heavy metal toxicity and improves microbial carbon use efficiency in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorodnikov, M.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Blagodatsky, S.; Marhan, S.; Fangmeier, A.; Kuzyakov, Y. Stimulation of microbial extracellular enzyme activities by elevated CO2 depends on soil aggregate size. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannelli, R.; Bianchi, V.; Macci, C.; Peruzzi, E.; Chiellini, C.; Petroni, G.; Masciandaro, G. Assessment of pollution impact on biological activity and structure of seabed bacterial communities in the Port of Livorno (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 426, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.M.; Cao, W.Q.; Chen, X.X.; Yu, B.G.; Lang, M.; Chen, X.P.; Zou, C.Q. The responses of soil enzyme activities, microbial biomass and microbial community structure to nine years of varied zinc application rates. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyaeva, O.N.; Haynes, R.J.; Birukova, O.A. Barley yield and soil microbial and enzyme activities as affected by contamination of two soils with lead, zinc or copper. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2005, 41, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelovičová, L.; Lodenius, M.; Tulisalo, E.; Fazekašová, D. Effect of heavy metals on soil enzyme activity at different field conditions in Middle Spis mining area (Slovakia). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 93, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Shen, Q.; Wang, L.; Qiu, G.; Liu, X. Effects of Cd, Cu, Zn and their combined action on microbial biomass and bacterial community structure. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosavljevic, J.S.; Serbula, S.M.; Cokesa, D.M.; Milanovic, D.B.; Radojevic, A.A.; Kalinovic, T.S.; Kalinovic, J.V. Soil enzyme activities under the impact of long-term pollution from mining-metallurgical copper production. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2020, 101, 103232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, H.; Lin, Q.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y. The influence of soil heavy metals pollution on soil microbial biomass, enzyme activity, and community composition near a copper smelter. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2007, 67, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Li, Y.; Shang, W.; Dong, X.; Tang, Q.; Cheng, H. The inhibitory effect of cadmium and/or mercury on soil enzyme activity, basal respiration, and microbial community structure in coal mine-affected agricultural soil. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Cao, J.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Shelton, S.; Jin, Z.; Walker, L.M.; et al. Costimulation of soil glycosidase activity and soil respiration by nitrogen addition. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Shao, H.; Li, W.; Bi, R.; Bai, Z. Improving Soil Enzyme Activities and Related Quality Properties of Reclaimed Soil by Applying Weathered Coal in Opencast-Mining Areas of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Clean Soil Air Water 2012, 40, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liber, K. Influence of different revegetation choices on plant community and soil development nine years after initial planting on a reclaimed coal gob pile in the Shanxi mining area, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, B.; Agrawal, M.; Singh, S. Coal mining activities change plant community structure due to air pollution and soil degradation. Ecotoxicology 2014, 23, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, B.; Mukherjee, A.; Agrawal, M.; Singh, S. Assessment of Seasonal and Site-Specific Variations in Soil Physical, Chemical and Biological Properties around Opencast Coal Mines. Pedosphere 2019, 29, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, X.; Liu, C.; Li, F.; Xu, X.; Lv, Y. Heavy metal contaminations in soil-rice system: Source identification in relation to a sulfur-rich coal burning power plant in Northern Guangdong Province, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Zong, Y.; Lu, S. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 120, 377–385. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, S.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, G.; Mayes, M.A.; Dzantor, K.E.; Hui, D.; Luo, Y. Soil extracellular enzyme activities, soil carbon and nitrogen storage under nitrogen fertilization: A meta-analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 101, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dai, Q.; Jin, X.; Dong, X.; Peng, J.; Wu, M.; Liang, N.; Pan, B.; Xing, B. Negative impacts of biochars on urease activity: High pH, heavy metals, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, or free radicals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12740–12747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.K. Colorimetric assay of catalase. Anal. Biochem. 1972, 47, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Xu, H.; Song, F.; Ge, H.; Yue, S. Effects of heavy metals on microorganisms and enzymes in soils of lead–zinc tailing ponds. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, T.; Guo, T.; Yao, Y.; Wang, R.; Chai, B. Seasonal microbial community characteristic and its driving factors in a copper tailings dam in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Sun, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Cai, Z.; Qin, G.; Song, Y. Response of Soil Microbes to Vegetation Restoration in Coal Mining Subsidence Areas at Huaibei Coal Mine, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, W.J.; Niu, Z.F.; Wang, X.R.; Zhao, H.P. How the Soil Microbial Communities and Activities Respond to Long-Term Heavy Metal Contamination in Electroplating Contaminated Site. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humberto, A.; Wence, H.; Clare, C.; Helaina, B.; Sebastian, M.; Jorge, P.; Yasna, T.; Pablo, C. Alteration of enzyme activities and functional diversity of a soil contaminated with copper and arsenic. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 192, 110264. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Yu, L. Effects of Cd or/and Pb on soil enzyme activities and microbial community structure. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Singh, N.S.; Singh, D.K. Impact of heavy metal contamination and seasonal variations on enzyme’s activity of Yamuna river soil in Delhi and NCR. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.; Pal, D.; Prasad, R. Alkaline phosphatase: An overview. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 29, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, J.; Mehandia, S.; Singh, G.; Raina, A.; Arya, S.K. Catalase enzyme: Application in bioremediation and food industry. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, S.; Lemanowicz, J.; Abd El-Azeim, M. Cellulose decomposition in clay and sandy soils contaminated with heavy metals. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 3275–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Tabatabai, M. Cellulase activity of soils: Effect of trace elements. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1995, 27, 977–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Niu, J.; Ren, Y.; Cong, J.; Zhang, X.; Fan, F.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Deng, J.; Xie, M.; et al. An integrated insight into the response of sedimentary microbial communities to heavy metal contamination. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris-Hellal, J.; Vallaeys, T.; Garnier-Zarli, E.; Bousserrhine, N. Effects of mercury on soil microbial communities in tropical soils of French Guyana. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2009, 41, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, S.R.; Frey, B. Methyl-mercury affects microbial activity and biomass, bacterial community structure but rarely the fungal community structure. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 64, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Dong, C.; Wu, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, S. Ecological effects of soil properties and metal concentrations on the composition and diversity of microbial communities associated with land use patterns in an electronic waste recycling region. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibanda, T.; Selvarajan, R.; Msagati, T.; Venkatachalam, S.; Meddows-Taylor, S. Defunct gold mine tailings are natural reservoir for unique bacterial communities revealed by high-throughput sequencing analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2199–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fashola, M.O.; Ngole-Jeme, V.M.; Babalola, O.O. Heavy Metal Pollution from Gold Mines: Environmental Effects and Bacterial Strategies for Resistance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshri, J.; Mankazana, B.B.J.; Momba, M.N.B. Profile of bacterial communities in South African mine-water samples using Illumina next-generation sequencing platform. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 3233–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, L.; Bond, P.L.; Lu, Y.; Vink, S. Bacterial diversity in response to direct revegetation in the Pb-Zn-Cu tailings under subtropical and semi-arid conditions. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 68, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, A.; Hallsworth, J.E. Water and temperature relations of soil Actinobacteria. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2014, 6, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Wen, H.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, T.; Gao, X. 454 Pyrosequencing Analysis of Bacterial Diversity Revealed by a Comparative Study of Soils from Mining Subsidence and Reclamation Areas. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, X.; Guan, D.; Zhao, B.; Ma, M.; Zhou, B.; Cao, F.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Li, J. Influence of inorganic fertilizer and organic manure application on fungal communities in a long-term field experiment of Chinese Mollisols. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 111, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousk, J.; Bååth, E.; Brookes, P.C.; Lauber, C.L.; Lozupone, C.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikandari, R.; Hasniah, N.; Taherzadeh, M.J. The role of filamentous fungi in advancing the development of a sustainable circular bioeconomy. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 345, 126531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, T.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zuo, M.; He, Y.; Li, H.; Li, G.; Li, C.; Li, X. Characteristics and diversity of microbial communities in lead–zinc tailings under heavy metal stress in north-west China. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 74, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Yao, J.; Chen, Z.; Ma, B.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Li, M.; Cao, Y.; Pang, W. Unraveling ecological risk of As/Sb and other metal (loid) s and fungal community responses in As/Sb smelting-intensive zone: A typical case study of Southwest China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.Y.; Li, S.W.; Leng, Y.; Kang, X.H. Structural and functional responses of bacterial and fungal communities to multiple heavy metal exposure in arid loess. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S.K.; Duan, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, S.; Liu, H.; Varjani, S.; Awasthi, M.K.; Zhang, Z.; Pandey, A. Sequential presence of heavy metal resistant fungal communities influenced by biochar amendment in the poultry manure composting process. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladipo, O.G.; Ezeokoli, O.T.; Maboeta, M.S.; Bezuidenhout, J.J.; Bezuidenhout, C.C. Tolerance and growth kinetics of bacteria isolated from gold and gemstone mining sites in response to heavy metal concentrations. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 212, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Mao, W.H.; Zhang, G.P.; Wu, F.B.; Cai, Y. Root excretion and plant tolerance to cadmiun toxicity-A review. Plant Soil Environ. 2007, 53, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodak, M.; Gołebiewski, M.; Morawska-Płoskonka, J.; Kuduk, K.; Niklińska, M. Diversity of microorganisms from forest soils differently polluted with heavy metals. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2013, 64, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenarova, A.; Radeva, G.; Traykov, I.; Boteva, S. Community level physiological profiles of bacterial communities inhabiting uranium mining impacted sites. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 100, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Deng, Y.; Ding, J.; Hu, H.; Xu, T.; Li, F.; Yang, G.; Yang, Y. Distinct microbial communities in the active and permafrost layers on the Tibetan Plateau. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 26, 6608–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, S.D.; Palmer, A.S.; Winsley, T.; Lamb, E.; Bissett, A.; Brown, M.V.; Dorst, J.; Ji, M.; Ferrari, B.C.; Grogan, P.; et al. Soil fertility is associated with fungal and bacterial richness, whereas pH is associated with community composition in polar soil microbial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Khalid, S.; Niazi, N.K.; Antunes, P.M.C. Cadmium bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and detoxification in soil-plant system. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 241, 73–137. [Google Scholar]
- Millard, P.; Singh, B. Does grassland vegetation drive soil microbial diversity? Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2010, 88, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CM (n = 11) | CP (n = 6) | CC (n = 4) | CFP (n = 5) | FS (n = 3) | PS (n = 3) | Study Area | Background Value of Shanxi Province | Risk Screening Values * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.70 ± 0.14 a | 8.72 ± 0.12 a | 8.74 ± 0.20 a | 8.72 ± 0.08 a | 8.65 ± 0.06 a | 8.57 ± 0.13 a | 8.70 ± 0.13 | - | - |
| NO3––N (mg/kg) | 39.10 ± 7.75 a | 45.42 ± 9.16 a | 38.27 ± 1.18 a | 37.20 ± 3.54 a | 36.42 ± 8.84 a | 39.37 ± 11.25 a | 39.39 ± 7.56 | - | - |
| NH4+–N (mg/kg) | 3.93 ± 1.56 b | 4.86 ± 1.91 b | 3.89 ± 2.04 b | 4.29 ± 1.71 b | 10.10 ± 0.53 a | 4.17 ± 0.70 b | 4.89 ± 2.41 | - | - |
| TC (g/kg) | 19.22 ± 13.46 b | 36.46 ± 7.96 a | 19.66 ± 2.92 b | 23.64 ± 12.32 ab | 24.52 ± 1.39 ab | 31.49 ± 7.87 a | 25.18 ± 13.35 | - | - |
| TN (g/kg) | 0.70 ± 0.44 b | 1.03 ± 0.62 ab | 0.50 ± 0.19 b | 0.88 ± 0.48 ab | 1.05 ± 0.09 ab | 1.36 ± 0.30 a | 0.86 ± 0.47 | - | - |
| Cr (mg/kg) | 59.92 ± 10.29 a | 54.47 ± 6.62 a | 57.48 ± 18.68 a | 61.41 ± 11.94 a | 61.87 ± 3.49 a | 65.03 ± 7.16 a | 59.33 ± 10.22 | 55.30 | 250 |
| Ni (mg/kg) | 35.67 ± 6.33 a | 34.59 ± 4.32 a | 36.50 ± 11.42 a | 33.88 ± 6.42 a | 33.98 ± 4.27 a | 34.96 ± 1.24 a | 34.85 ± 6.03 | 29.90 | 190 |
| Cu (mg/kg) | 26.70 ± 4.17 a | 27.85 ± 6.10 a | 26.73 ± 7.92 a | 26.19 ± 4.66 a | 27.60 ± 4.47 a | 28.97 ± 2.33 a | 26.97 ± 4.80 | 22.90 | 100 |
| Zn (mg/kg) | 73.93 ± 14.60 a | 79.23 ± 16.69 a | 69.20 ± 21.53 a | 69.52 ± 10.77 a | 70.11 ± 6.20 a | 75.94 ± 2.81 a | 72.91 ± 13.93 | 63.50 | 300 |
| As (mg/kg) | 23.09 ± 13.45 b | 14.14 ± 2.80 b | 20.68 ± 6.89 b | 24.03 ± 12.46 b | 41.08 ± 4.37 a | 13.80 ± 1.64 b | 22.47 ± 11.89 | 9.10 | 25 |
| Pb (mg/kg) | 18.95 ± 4.08 b | 84.70 ± 151.5 a | 19.97 ± 4.80 b | 19.75 ± 6.00 b | 19.47 ± 3.13 b | 24.88 ± 2.58 b | 31.61 ± 65.18 | 14.70 | 170 |
| Cd (mg/kg) | 0.19 ± 0.04 a | 0.24 ± 0.06 a | 0.18 ± 0.05 a | 0.21 ± 0.05 a | 0.23 ± 0.06 a | 0.24 ± 0.02 a | 0.21 ± 0.05 | 0.102 | 0.6 |
| Hg (mg/kg) | 0.03 ± 0.02 b | 0.05 ± 0.02 ab | 0.02 ± 0.01 b | 0.04 ± 0.03 ab | 0.04 ± 0.01 ab | 0.09 ± 0.08 a | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 0.023 | 3.4 |
| Sampling Field | Shannon | Simpson | Ace | Chao1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CM | 5.73 b | 0.0478 a | 2869 b | 2615 b |
| CP | 6.34 a | 0.0077 c | 3038 ab | 3017 a |
| CC | 6.01 ab | 0.0157 b | 3073 ab | 2875 ab |
| CFP | 6.51 a | 0.0048 c | 3224 ab | 3194 a |
| FS | 6.52 a | 0.0045 c | 3190 ab | 3235 a |
| PS | 6.44 a | 0.0045 c | 3418 a | 3261 a |
| Sampling Field | Shannon | Simpson | Ace | Chao1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CM | 3.48 b | 0.1359 ab | 548 b | 549 b |
| CP | 3.45 b | 0.1250 ab | 574 b | 574 b |
| CC | 3.82 ab | 0.0886 b | 511 b | 514 b |
| CFP | 3.19 b | 0.1897 a | 560 b | 568 b |
| FS | 3.58 b | 0.0872 b | 626 b | 631 b |
| PS | 4.10 a | 0.0605 b | 903 a | 900 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, C.; Xie, R.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Liang, R. Ecological Responses of Soil Microbial Communities to Heavy Metal Stress in a Coal-Based Industrial Region in China. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061392
Su C, Xie R, Liu D, Liu Y, Liang R. Ecological Responses of Soil Microbial Communities to Heavy Metal Stress in a Coal-Based Industrial Region in China. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(6):1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061392
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Chao, Rong Xie, Di Liu, Yong Liu, and Ruoyu Liang. 2023. "Ecological Responses of Soil Microbial Communities to Heavy Metal Stress in a Coal-Based Industrial Region in China" Microorganisms 11, no. 6: 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061392
APA StyleSu, C., Xie, R., Liu, D., Liu, Y., & Liang, R. (2023). Ecological Responses of Soil Microbial Communities to Heavy Metal Stress in a Coal-Based Industrial Region in China. Microorganisms, 11(6), 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061392





