Clostridium butyricum Reduces Obesity in a Butyrate-Independent Way
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of C. butyricum Strains
2.2. Animal Experiments
2.3. Liver and Adipose Tissue Histology
2.4. Detection of Biochemical Indicators
2.5. Determination of Tissue Cytokines
2.6. Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Detection of SCFAs
2.8. Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis
2.9. Fecal Bacterial DNA Extraction and 16S rDNA Sequencing
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. C. butyricum Administration Reduces Diet-Induced Weight Gain and Hyperlipoidemia
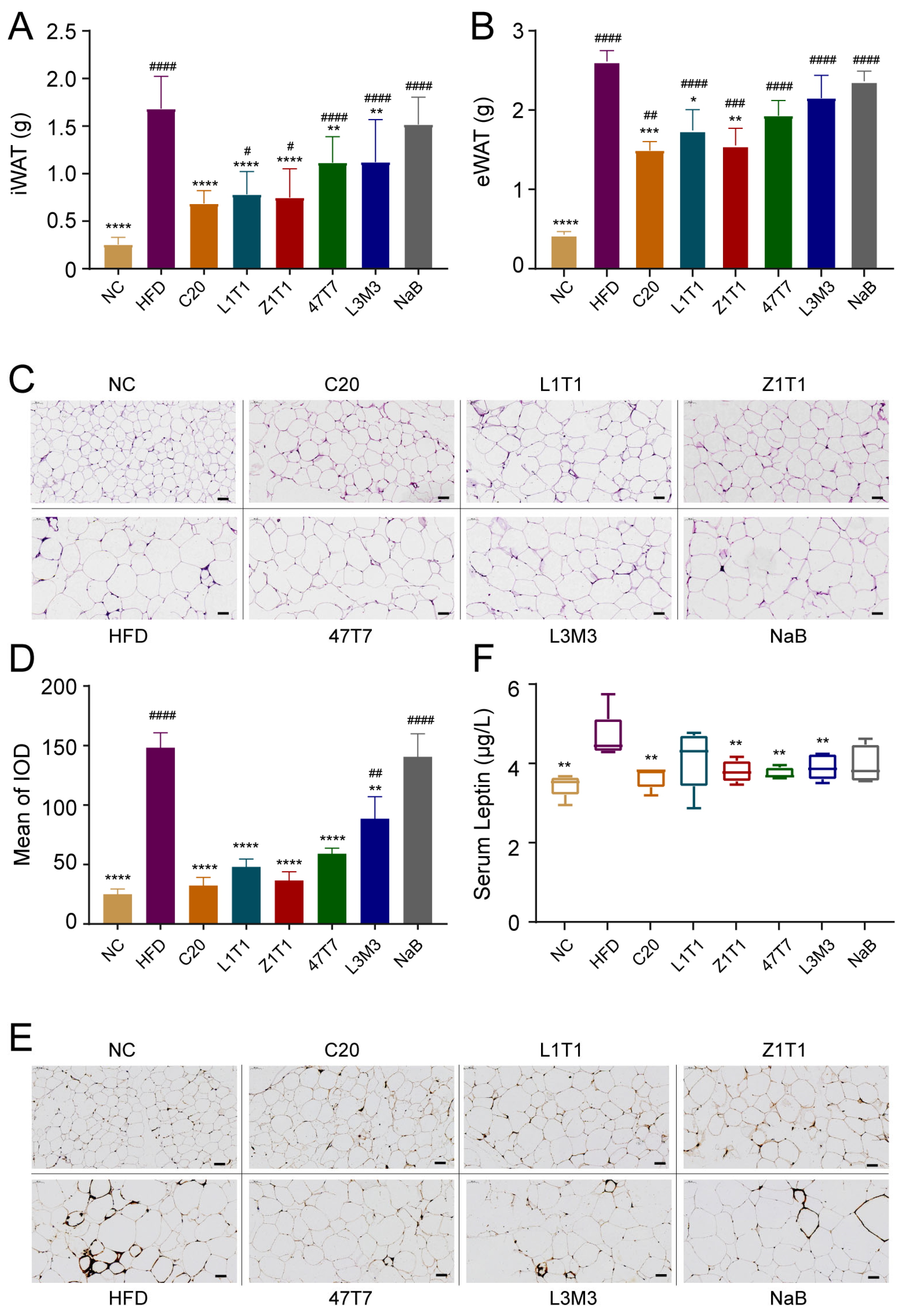
3.2. C. butyricum Administration Decreases Fat Mass and Alleviates the Adipose Inflammation
3.3. C. butyricum Administration Attenuates Fat Deposition and Inflammation in the Liver
3.4. Administration of C. butyricum C20and Z1T1 Alters Purine and Tryptophan Metabolism in Stool
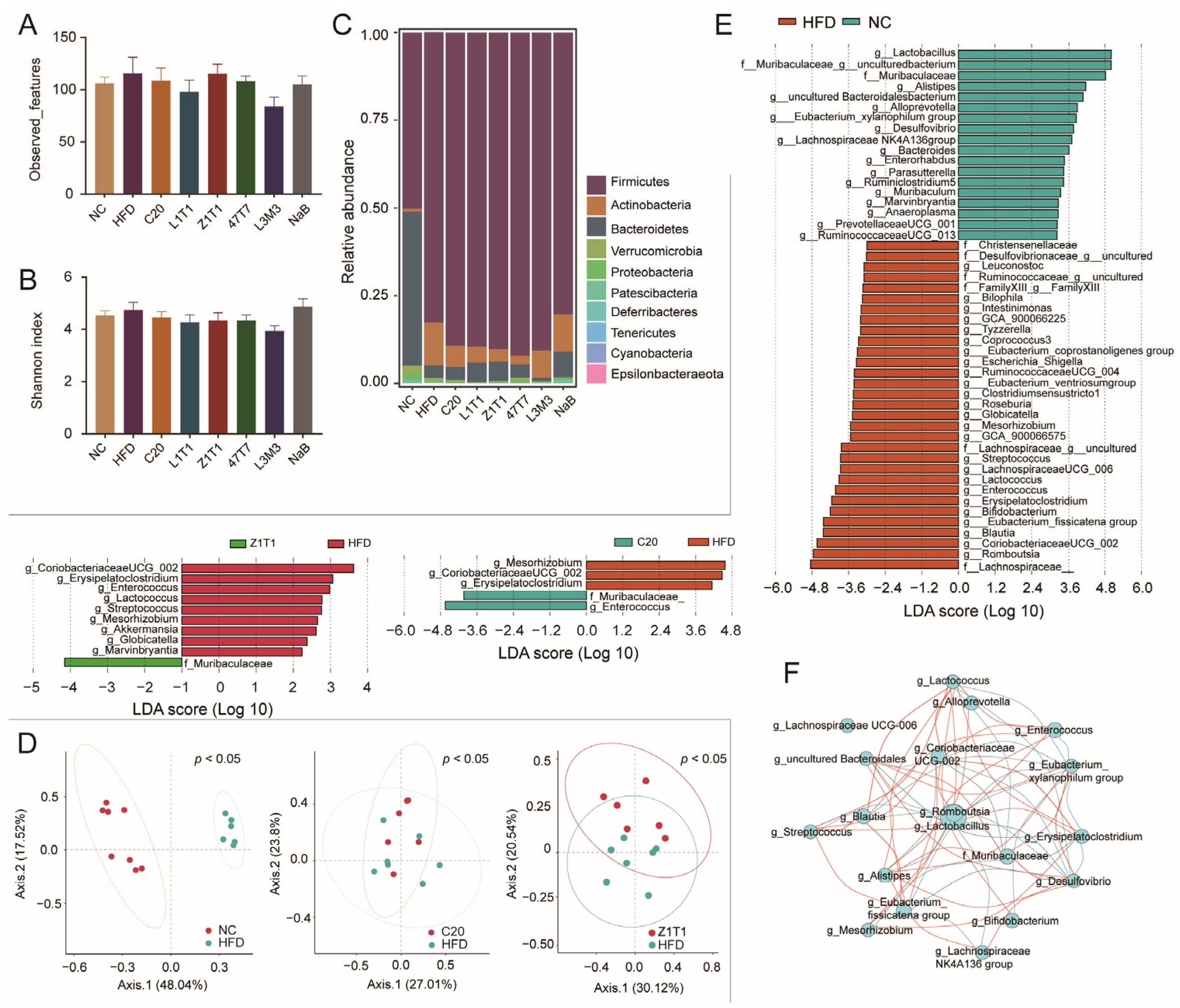
3.5. Effects of C. butyricum on the Gut Microbial Composition of HFD-Treated Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: A pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19·2 million participants. Lancet 2016, 387, 1377–1396. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivimäki, M.; Strandberg, T.; Pentti, J.; Nyberg, S.T.; Frank, P.; Jokela, M.; Ervasti, J.; Suominen, S.B.; Vahtera, J.; Sipilä, P.N.; et al. Body-mass index and risk of obesity-related complex multimorbidity: An observational multicohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, S.M.; Saltiel, A.R. Adapting to obesity with adipose tissue inflammation. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomiyama, A.J. Stress and obesity. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2019, 70, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komaroff, A.L. The Microbiome and Risk for Obesity and Diabetes. JAMA 2017, 317, 355–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deweerdt, S. Microbiome: A complicated relationship status. Nature 2014, 508, S61–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natividad, J.M.; Agus, A.; Planchais, J.; Lamas, B.; Jarry, A.C.; Martin, R.; Michel, M.-L.; Chong-Nguyen, C.; Roussel, R.; Straube, M.; et al. Impaired Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Ligand Production by the Gut Microbiota Is a Key Factor in Metabolic Syndrome. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 737–749.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothhammer, V.; Mascanfroni, I.D.; Bunse, L.; Takenaka, M.C.; Kenison, J.E.; Mayo, L.; Chao, C.-C.; Patel, B.; Yan, R.; Blain, M.; et al. Type I interferons and microbial metabolites of tryptophan modulate astrocyte activity and central nervous system inflammation via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Zhang, M.; Qi, H.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yun, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; et al. Gut microbiota–derived metabolite 3-idoleacetic acid together with LPS induces IL-35+ B cell generation. Microbiome 2022, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canfora, E.E.; Jocken, J.W.; Blaak, E.E. Short-chain fatty acids in control of body weight and insulin sensitivity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitt, J.; Woo, V.; Lee, P.; Moncivaiz, J.; Haberman, Y.; Denson, L.; Tso, P.; Alenghat, T. Disruption of Epithelial HDAC3 in Intestine Prevents Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yi, C.-X.; Katiraei, S.; Kooijman, S.; Zhou, E.; Chung, C.K.; Gao, Y.; van den Heuvel, J.K.; Meijer, O.C.; Berbée, J.F.P.; et al. Butyrate reduces appetite and activates brown adipose tissue via the gut-brain neural circuit. Gut 2018, 67, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Zhu, C.; Li, H.; Yin, M.; Pan, C.; Huang, L.; Kong, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, S.; et al. Dysbiosis Signatures of Gut Microbiota Along the Sequence from Healthy, Young Patients to Those with Overweight and Obesity. Obesity 2018, 26, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, J.; Xie, F.; He, H.; Lee, J.J.; Dai, X.; Wu, C.; Ma, X. Dietary fiber-derived short-chain fatty acids: A potential therapeutic target to alleviate obesity-related non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hing, N.Y.L.; Woon, Y.L.; Lee, Y.K.; Kim, H.J.; Lothfi, N.M.; Wong, E.; Perialathan, K.; Sanusi, N.H.A.; Isa, A.; Leong, C.T.; et al. When do persuasive messages on vaccine safety steer COVID-19 vaccine acceptance and recommendations? Behavioural insights from a randomised controlled experiment in Malaysia. BMJ Glob. Health 2022, 7, e009250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obanda, D.N.; Husseneder, C.; Raggio, A.M.; Page, R.; Marx, B.; Stout, R.W.; Guice, J.; Coulon, D.; Keenan, M.J. Abundance of the species Clostridium butyricum in the gut microbiota contributes to differences in obesity phenotype in outbred Sprague-Dawley CD rats. Nutrition 2020, 78, 110893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; An, J.; Kim, J.; Choi, D.; Song, Y.; Lee, C.-K.; Kong, H.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, K. A Novel Bacterium, Butyricimonas virosa, Preventing HFD-Induced Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders in Mice via GLP-1 Receptor. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 8192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.; Montez, K.; Orr, C.; Konrath, J.; Oddiri, U.; Russell, C.J.; Gambill, L.; Nesiama, J.-A.; Chung, P.J.; McNeal-Trice, K. Changing Who Has a Seat and Voice at the Table: How the Academic Pediatric Association is Responding to Systemic Racism. Acad. Pediatr. 2022, 22, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Kang, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, Q.; Tian, H.; Xue, Y.; Ren, P.; Kuang, X.; et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus ameliorates obesity in mice through modulation of gut microbiota dysbiosis and intestinal permeability. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 175, 106020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, B.; Li, D.; Ai, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Lactulose Differently Modulates the Composition of Luminal and Mucosal Microbiota in C57BL/6J Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6240–6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Qian, L.; Fang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Lee, Y.-K.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Probiotic strains alleviated OVA-induced food allergy in mice by regulating the gut microbiota and improving the level of indoleacrylic acid in fecal samples. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 3704–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Fang, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, P.; Lee, Y.-K.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Lu, W.; et al. Lactobacillus mucosae exerted different antiviral effects on respiratory syncytial virus infection in mice. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.E.; Kim, M.S.; Shim, K.W.; Kim, Y.I.; Chu, J.; Kim, B.K.; Choi, I.S.; Kim, J.Y. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum Q180 on postprandial lipid levels and intestinal environment: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-M.; Sun, Y.-S.; Zhao, L.-Q.; Chen, T.-T.; Fan, M.-N.; Jiao, H.-C.; Zhao, J.-P.; Wang, X.-J.; Li, F.-C.; Li, H.-F.; et al. SCFAs-Induced GLP-1 Secretion Links the Regulation of Gut Microbiome on Hepatic Lipogenesis in Chickens. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Pan, Q.; Liu, X.; Yang, R.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Fan, J. Clostridium butyricum B1 alleviates high-fat diet-induced steatohepatitis in mice via enterohepatic immuno-regulation. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, K.R.; Cottam, M.A.; Kennedy, A.J.; Hasty, A.H. Macrophage-Targeted Therapeutics for Metabolic Disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Wu, D.; Zhang, C.; Yan, T.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, H.; Xue, K.; Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, Y. Macrophage IRX3 promotes diet-induced obesity and metabolic inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 1268–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roden, M.; Shulman, G.I. The integrative biology of type 2 diabetes. Nature 2019, 576, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E.A. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolism 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakino, S.; Ohki, T.; Nakayama, H.; Yuan, X.; Otabe, S.; Hashinaga, T.; Wada, N.; Kurita, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Hara, K.; et al. Pivotal Role of TNF-α in the Development and Progression of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Murine Model. Horm. Metab. Res. 2017, 50, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Yan, M.; Cao, H.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Z. Effects of Clostridium butyricum Capsules Combined with Rosuvastatin on Intestinal Flora, Lipid Metabolism, Liver Function and Inflammation in NAFLD Patients. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2022, 68, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Liu, C.-D.; Li, H.-F.; Tian, M.-L.; Pan, J.-Q.; Shu, G.; Jiang, Q.-Y.; Yin, Y.-L.; Zhang, L. LSD1 mediates microbial metabolite butyrate-induced thermogenesis in brown and white adipose tissue. Metabolism 2019, 102, 154011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowah, S.A.; Riedl, L.; Damms-Machado, A.; Johnson, T.S.; Schübel, R.; Graf, M.; Kartal, E.; Zeller, G.; Schwingshackl, L.; Stangl, G.; et al. Effects of Weight-Loss Interventions on Short-Chain Fatty Acid Concentrations in Blood and Feces of Adults: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2019, 10, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, R.; Ilha, M.; Vaittinen, M.; Kaminska, D.; Männistö, V.; Kärjä, V.; Tuomainen, M.; Hanhineva, K.; Romeo, S.; Pajukanta, P.; et al. Indole-3-Propionic Acid, a Gut-Derived Tryptophan Metabolite, Associates with Hepatic Fibrosis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.V.; Ashrafian, H.; Sarafian, M.; Homola, D.; Rushton, L.; Barker, G.; Cabrera, P.M.; Lewis, M.R.; Darzi, A.; Lin, E.; et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass-induced bacterial perturbation contributes to altered host-bacterial co-metabolic phenotype. Microbiome 2021, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtue, A.T.; McCright, S.J.; Wright, J.M.; Jimenez, M.T.; Mowel, W.K.; Kotzin, J.J.; Joannas, L.; Basavappa, M.G.; Spencer, S.P.; Clark, M.L.; et al. The gut microbiota regulates white adipose tissue inflammation and obesity via a family of microRNAs. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaav1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, J.; Ison, J.; Voor, M.J.; Tyagi, N. Probiotics Stimulate Bone Formation in Obese Mice via Histone Methylations. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8605–8623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickert, S.; Pierik, A.J.; Buckel, W. Molecular characterization of phenyllactate dehydratase and its initiator from Clostridium sporogenes. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 44, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Costales, M.G.; Cavanaugh, C.; Williams, K. Extracellular adenosine generation in the regulation of pro-inflammatory responses and pathogen colonization. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 775–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemann, B.; Haufs-Brusberg, S.; Puetz, L.; Feickert, M.; Jaeckstein, M.Y.; Hoffmann, A.; Zurkovic, J.; Heine, M.; Trautmann, E.-M.; Müller, C.E.; et al. Apoptotic brown adipocytes enhance energy expenditure via extracellular inosine. Nature 2022, 609, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Xiang, Q.; Mao, B.; Tang, X.; Cui, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Protective Effects of microbiome-derived inosine on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver damage and in-flammation in mice via mediating the TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7619–7628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenaka, M.C.; Gabriely, G.; Rothhammer, V.; Mascanfroni, I.D.; Wheeler, M.A.; Chao, C.-C.; Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Kenison, J.; Tjon, E.C.; Barroso, A.; et al. Control of tumor-associated macrophages and T cells in glioblastoma via AHR and CD39. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Guryn, K.; Hubert, N.; Frazier, K.; Urlass, S.; Musch, M.W.; Ojeda, P.; Pierre, J.F.; Miyoshi, J.; Sontag, T.J.; Cham, C.M.; et al. Small Intestine Microbiota Regulate Host Digestive and Absorptive Adaptive Responses to Dietary Lipids. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 458–469.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridaura, V.K.; Faith, J.J.; Rey, F.E.; Cheng, J.; Duncan, A.E.; Kau, A.L.; Griffin, N.W.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B.; Bain, J.R.; et al. Gut Microbiota from Twins Discordant for Obesity Modulate Metabolism in Mice. Science 2013, 341, 1241214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, S.; Ulloa-Martínez, M.; Martínez-Rojano, H.; Galván-Rodríguez, F.M.; Miranda-Brito, C.; Romano, M.C.; Piña-Escobedo, A.; Pizano-Zárate, M.L.; Hoyo-Vadillo, C.; García-Mena, J. Study of the diversity and short-chain fatty acids production by the bacterial community in overweight and obese Mexican children. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Prifti, E.; Belda, E.; Ichou, F.; Kayser, B.D.; Dao, M.C.; Verger, E.O.; Hedjazi, L.; Bouillot, J.-L.; Chevallier, J.-M.; et al. Major microbiota dysbiosis in severe obesity: Fate after bariatric surgery. Gut 2018, 68, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottosson, F.; Brunkwall, L.; Ericson, U.; Nilsson, P.M.; Almgren, P.; Fernandez, C.; Melander, O.; Orho-Melander, M. Connection Between BMI-Related Plasma Metabolite Profile and Gut Microbiota. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosomi, K.; Saito, M.; Park, J.; Murakami, H.; Shibata, N.; Ando, M.; Nagatake, T.; Konishi, K.; Ohno, H.; Tanisawa, K.; et al. Oral administration of Blautia wexlerae ameliorates obesity and type 2 diabetes via metabolic remodeling of the gut microbiota. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozato, N.; Saito, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Katashima, M.; Tokuda, I.; Sawada, K.; Katsuragi, Y.; Kakuta, M.; Imoto, S.; Ihara, K.; et al. Blautia genus associated with visceral fat accumulation in adults 20–76 years of age. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2019, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Tan, M.; Chen, X. Punicic acid ameliorates obesity and liver steatosis by regulating gut microbiota composition in mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 7897–7908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Lui, E.M.; Xiao, M. Pu-erh tea ameliorates obesity and modulates gut microbiota in high fat diet fed mice. Food Res. Int. 2021, 144, 110360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, J.; Liu, Y.; Pei, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, J.; Lu, W.; Chen, W. Clostridium butyricum Reduces Obesity in a Butyrate-Independent Way. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11051292
Liao J, Liu Y, Pei Z, Wang H, Zhu J, Zhao J, Lu W, Chen W. Clostridium butyricum Reduces Obesity in a Butyrate-Independent Way. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(5):1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11051292
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Jingyi, Yaoliang Liu, Zhangming Pei, Hongchao Wang, Jinlin Zhu, Jianxin Zhao, Wenwei Lu, and Wei Chen. 2023. "Clostridium butyricum Reduces Obesity in a Butyrate-Independent Way" Microorganisms 11, no. 5: 1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11051292
APA StyleLiao, J., Liu, Y., Pei, Z., Wang, H., Zhu, J., Zhao, J., Lu, W., & Chen, W. (2023). Clostridium butyricum Reduces Obesity in a Butyrate-Independent Way. Microorganisms, 11(5), 1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11051292






