Regulation of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin-Induced Inflammation in Spleen Cells from Diabetic Mice by Polyphenols
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
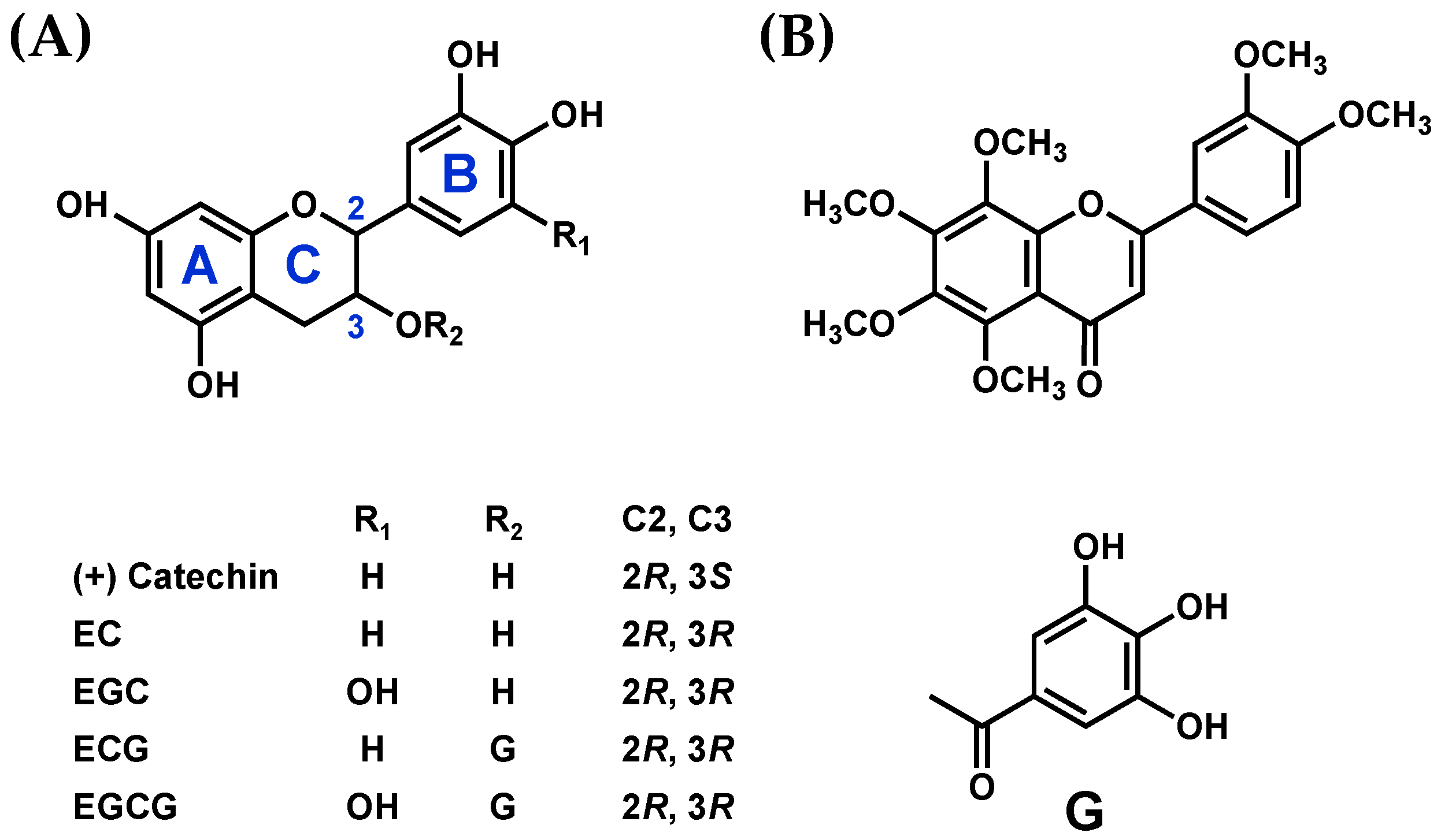
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Assessment of the Interactions between SEA and Polyphenols Using the Thermal Shift Assay
2.3. Effect of pH on the Interactions between SEA and Polyphenols
2.4. Analysis of SEA-Induced Inflammation-Related Genes in Spleen Cells from Diabetic Mice
2.4.1. Animals
2.4.2. Preparation of the Diabetic Mouse Model
2.4.3. Preparation of Mouse Spleen Cells
2.4.4. SEA Exposure in Mouse Spleen Cells
2.4.5. Inhibitory Effects of Polyphenols on SEA-Induced Inflammation-Related Genes
2.4.6. Total RNA Extraction and Real-Time RT-PCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Interaction Analysis of SEA and Polyphenols
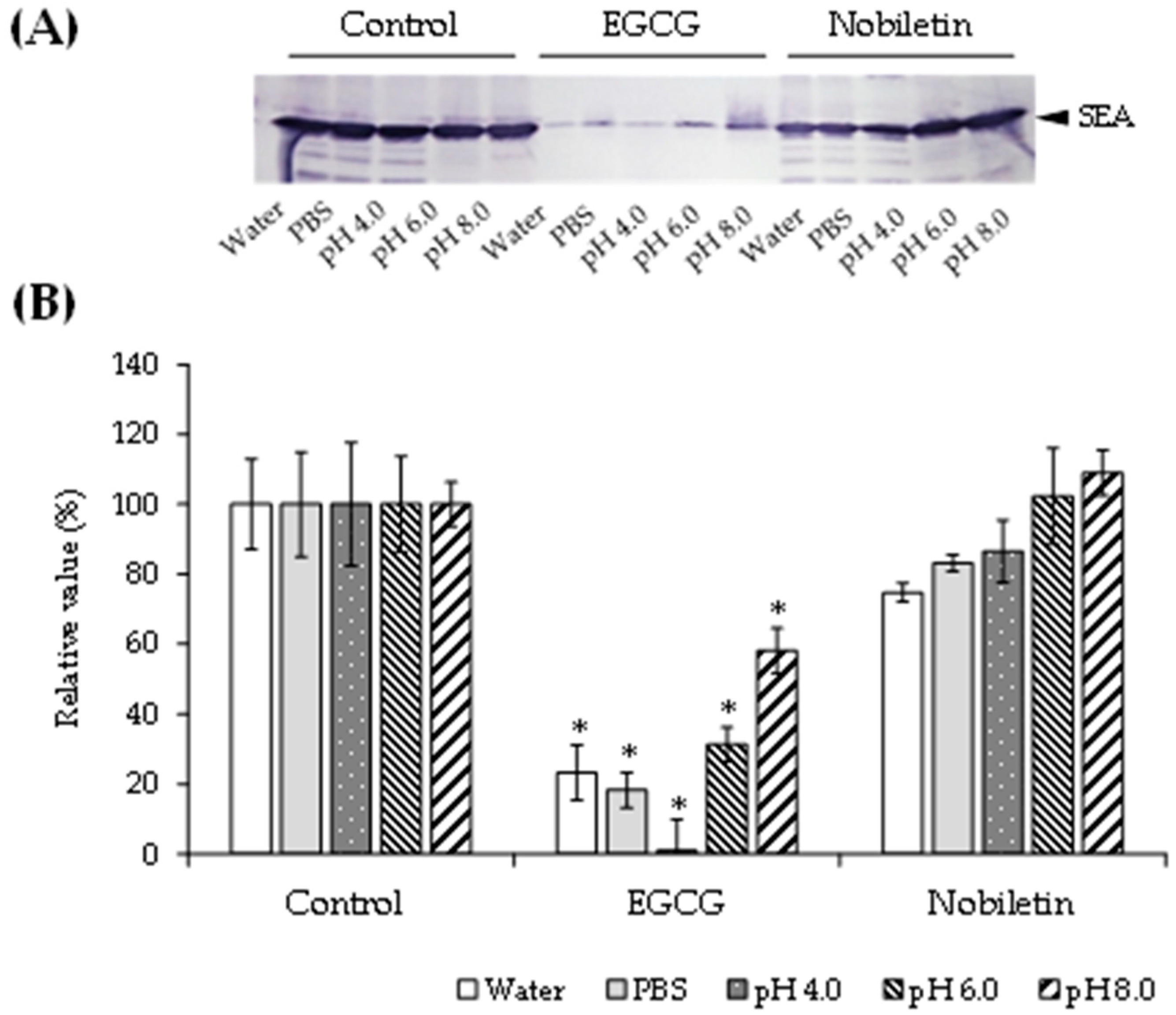
3.2. Effect of pH on the Interaction between SEA and Polyphenols
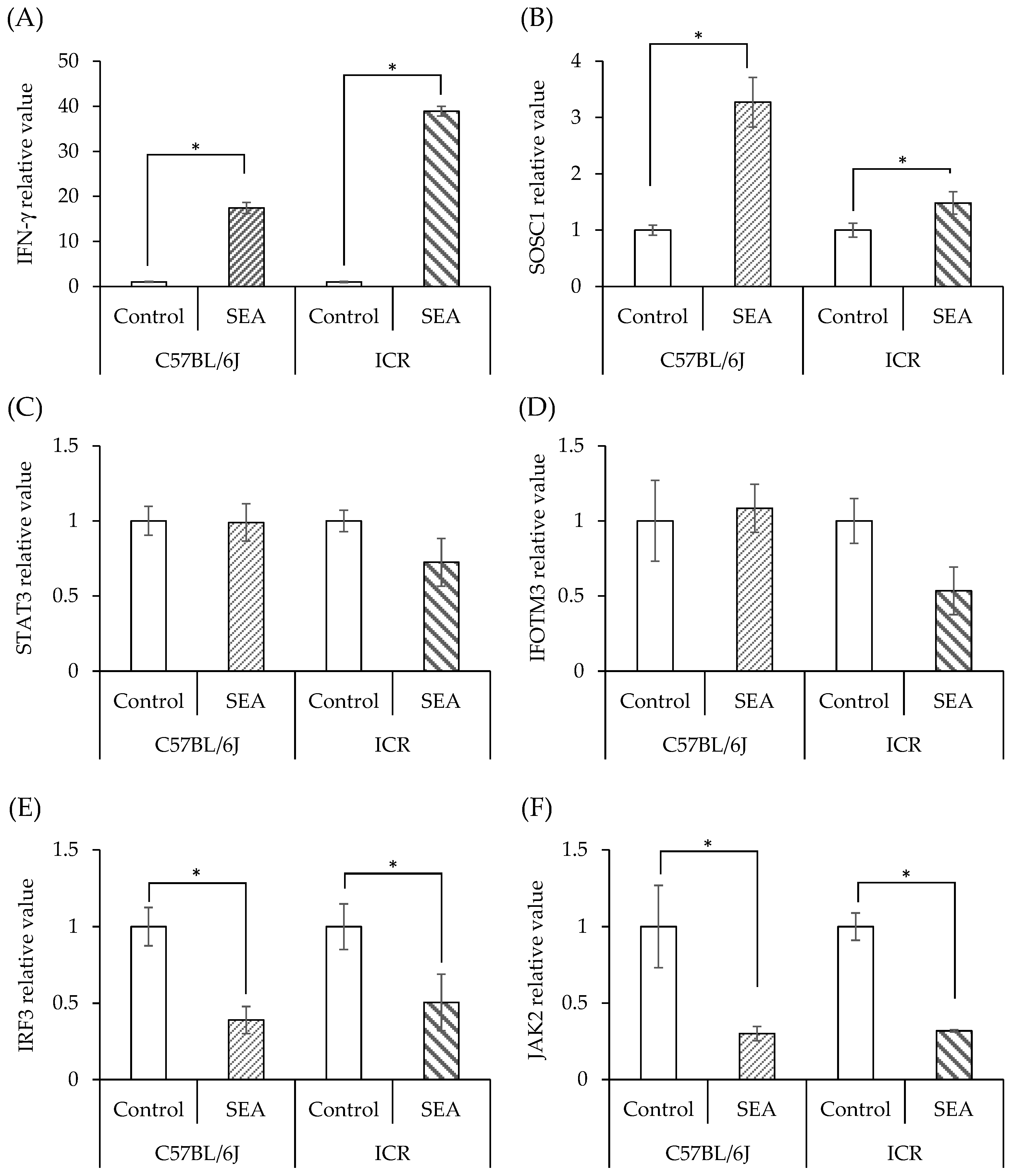
3.3. SEA-Induced Inflammation in Normal Mouse Spleen Cells
3.4. SEA-Induced Inflammation in Spleen Cells from Mice with Diabetes
3.5. Inhibitory Effects of Polyphenols on SEA-Induced Inflammation-Related Genes in the Spleen Cells of Diabetic Mice
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Omoe, K.; Hu, D.L.; Takahashi-Omoe, H.; Nakane, A.; Shinagawa, K. Identification and characterization of a new staphylococcal enterotoxin-related putative toxin encoded by two kinds of plasmids. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 6088–6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, H.K.; Hirose, S.; Narita, K.; Sugiyama, M.; Asano, K.; Hu, D.L.; Nakane, A. Histamine release from intestinal mast cells induced by staphylococcal enterotoxin a (SEA) evokes vomiting reflex in common marmoset. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Jeffry, J.; Zeng, L.; Zou, Z.; Chen, H.; Tao, A. Synergistic activation of Src, ERK and STAT pathways in PBMCs for Staphylococcal enterotoxin A induced production of cytokines and chemokines. Asian Pacific J. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 38, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Haan, S.; Hermanns, H.M.; Müller-Newen, G.; Schaper, F. Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem. J. 2003, 374, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagathu, C.; Bastard, J.P.; Auclair, M.; Maachi, M.; Capeau, J.; Caron, M. Chronic interleukin-6 (IL-6) treatment increased IL-6 secretion and induced insulin resistance in adipocyte: Prevention by rosiglitazone. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 311, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banke, E.; Rödström, K.; Ekelund, M.; Dalla-Riva, J.; Lagerstedt, J.O.; Nilsson, S.; Degerman, E.; Lindkvist-Petersson, K.; Nilson, B. Superantigen activates the gp130 receptor on adipocytes resulting in altered adipocyte metabolism. Metabolism 2014, 63, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, B.G.; Stach, C.S.; Kulhankova, K.; Salgado-Pabón, W.; Klingelhutz, A.J.; Schlievert, P.M. Chronic superantigen exposure induces systemic inflammation, elevated bloodstream endotoxin, and abnormal glucose tolerance in rabbits: Possible role in diabetes. MBio 2015, 6, e02554-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, J.; Søgaard, M.; Schønheyder, H.C.; Nielsen, H.; Frøslev, T.; Thomsen, R.W. Diabetes and risk of community-acquired Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: A population-based case-control study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 174, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Caputo, G.M.; Weitekamp, M.R.; Karchmer, A.W. Infections in patients with diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1906–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunyach-Remy, C.; Ngba Essebe, C.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.P. Staphylococcus aureus toxins and diabetic foot ulcers: Role in pathogenesis and interest in diagnosis. Toxins 2016, 8, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Sekimizu, K.; Kaito, C. Evaluation of Staphylococcus aureus virulence factors using a silkworm model. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 326, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liau, N.P.D.; Laktyushin, A.; Lucet, I.S.; Murphy, J.M.; Yao, S.; Whitlock, E.; Callaghan, K.; Nicola, N.A.; Kershaw, N.J.; Babon, J.J. The molecular basis of JAK/STAT inhibition by SOCS1. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, S.; Mantovani, A. Inflammatory bowel disease and intestinal cancer: A paradigm of the Yin-Yang interplay between inflammation and cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 3313–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atreya, R.; Neurath, M.F. Signaling molecules: The pathogenic role of the IL-6/STAT-3 trans signaling pathway in intestinal inflammation and in colonic cancer. Curr. Drug Targets 2008, 9, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotto, S.; Esposito, E.; di Paola, R.; Ciampa, A.; Mazzon, E.; de Prati, A.C.; Darra, E.; Vincenzi, S.; Cucinotta, G.; Caminiti, R.; et al. Protective effect of Arbutus unedo aqueous extract in carrageenan-induced lung inflammation in mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2008, 57, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimamura, Y.; Utsumi, M.; Hirai, C.; Kurokawa, A.; Kan, T.; Ohashi, N.; Masuda, S. Effect of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate to staphylococcal enterotoxin A on toxin activity. Molecules 2020, 25, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Q.; Xia, T.; Hu, Y.H.; Sun, M.S.; Yan, S.; Lei, C.Q.; Shu, H.B.; Guo, J.H.; Liu, Y. IFITM3 inhibits virus-triggered induction of type I interferon by mediating autophagosome-dependent degradation of IRF3. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, Y.; Utsumi, M.; Hirai, C.; Nakano, S.; Ito, S.; Tsuji, A.; Ishii, T.; Hosoya, T.; Kan, T.; Ohashi, N.; et al. Binding of catechins to staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Molecules 2018, 23, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, Y.; Noaki, R.; Kurokawa, A.; Utsumi, M.; Hirai, C.; Kan, T.; Masuda, S. Effect of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate on activation of JAK/STAT signaling pathway by staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Toxins 2021, 13, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshigai, E.; Machida, T.; Okuyama, T.; Mori, M.; Murase, H.; Yamanishi, R.; Okumura, T.; Ikeya, Y.; Nishino, H.; Nishizawa, M. Citrus nobiletin suppresses inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression in interleukin-1β-treated hepatocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 439, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Cha, B.Y.; Saito, K.; Yamakawa, H.; Choi, S.S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yonezawa, T.; Teruya, T.; Nagai, K.; Woo, J.T. Nobiletin improves hyperglycemia and insulin resistance in obese diabetic ob/ob mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 1674–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PREDIMED Study Investigators. Intake of total polyphenols and some classes of polyphenols is inversely associated with diabetes in elderly people at high cardiovascular disease risk. J. Nutr. 2015, 146, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakawa, T.; Hiza, A.; Nakayama, M.; Inai, M.; Oyama, D.; Koide, H.; Shimizu, K.; Wakimoto, T.; Harada, N.; Tsukada, H.; et al. PET imaging of nobiletin based on a practical total synthesis. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2868–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babicki, S.; Arndt, D.; Marcu, A.; Liang, Y.; Grant, J.R.; Maciejewski, A.; Wishart, D.S. Heatmapper: Web-enabled heat mapping for all. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W147–W153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canon, F.; Paté, F.; Cheynier, V.; Sarni-Manchado, P.; Giuliani, A.; Pérez, J.; Durand, D.; Li, J.; Cabane, B. Aggregation of the salivary proline-rich protein IB5 in the presence of the tannin EgCG. Langmuir 2013, 29, 1926–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbisa, S.; Biggin, S.; Cavallarin, N.; Sartor, L.; Benelli, R.; Albini, A. Tumor invasion: Molecular shears blunted by green tea. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourassa, P.; Bariyanga, J.; Tajmir-Riahi, H.A. Binding sites of resveratrol, genistein, and curcumin with milk α-and β-caseins. J. Phys. Chem. 2013, 117, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, Y.; Aoki, N.; Sugiyama, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Murata, M.; Masuda, S. Plant-derived polyphenols interact with staphylococcal enterotoxin A and inhibit toxin activity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, Y.; Hirai, C.; Sugiyama, Y.; Utsumi, M.; Yanagida, A.; Murata, M.; Ohashi, N.; Masuda, S. Interaction between various apple procyanidin and staphylococcal enterotoxin A and their inhibitory effects on toxin activity. Toxins 2017, 9, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGillicuddy, F.C.; Chiquoine, E.H.; Hinkle, C.C.; Kim, R.J.; Shah, R.; Roche, H.M.; Smyth, E.M.; Reilly, M.P. Interferon γ attenuates insulin signaling, lipid storage, and differentiation in human adipocytes via activation of the JAK/STAT pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 31936–31944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.; Lee, Y.L.; Hsu, K.Y. Determination of (+)-catechin in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography using fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 1995, 665, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Taylor, L.S.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Mauer, L.J. Kinetic study of catechin stability: Effects of Ph, concentration, and temperature. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 12531–12539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, K.; Kojima, R.; Ito, M. Strain differences in the diabetogenic activity of streptozotocin in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esser, N.; Legrand-Poels, S.; Piette, J.; Scheen, A.J.; Paquot, N. Inflammation as a link between obesity, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 105, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Wang, X.; Lantier, L.; Lyubetskaya, A.; Eguchi, J.; Kang, S.; Tenen, D.; Roh, H.C.; Kong, X.; Kazak, L.; et al. IRF3 promotes adipose inflammation and insulin resistance and represses browning. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2839–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimeri, J.; Tong, C.H. Degradation kinetics of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate as a function of pH and dissolved oxygen in a liquid model system. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.D. The identification of TNFR5 as a therapeutic target in diabetes. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 21, 349–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, A. Signal transduction of inflammatory cytokines and tumor development. Cancer Sci. 2006, 97, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Hirata, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Minamoto, S.; Aono, A.; Nishimoto, N.; Kajita, T.; Taga, T.; Yoshizaki, K.; et al. Structure and function of a new STAT-induced STAT inhibitor. Nature 1997, 387, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Morita, Y.; Fujimoto, M.; Narazaki, M.; Naka, T.; Kishimoto, T. IFN regulatory factor-1-mediated transcriptional activation of mouse STAT-induced STAT inhibitor-1 gene promoter by IFN-gamma. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 5833–5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, M.M.; Chen, Y.; Darwiche, R.; Dudek, N.L.; Irawaty, W.; Santamaria, P.; Allison, J.; Kay, T.W.; Thomas, H.E. Suppressor of cytokine signalling-1 overexpression protects pancreatic beta cells from CD8+ T cell-mediated autoimmune destruction. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 5714–5721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultcrantz, M.; Jacobson, S.; Hill, N.J.; Santamaria, P.; Flodström-Tullberg, M. Target cell expression of suppressor of cytokine signalling-1 prevents diabetes in the NOD mouse. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2696–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Primer | Forward Primer (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Hprt | GTTGGATACAGGCCAGACTTTGTTG | GAGGGTAGGCTGGCCTATAGGCT |
| IFN-γ | CATTGAAAGCCTAGAAAGTCTG | CTCATGAATGCATCCTTTTTCG |
| SOCS1 | GATTCTGCGTGCCGCTCT | TGCGTGCTACCATCCTACTC |
| STAT3 | CTACCTCTACCCCGACATTCC | GATGAACTTGGTCTTCAGGTACG |
| JAK2 | GGAATGGCCTGCCTTACAATG | TGGCTCTATCTGCTTCACAGAAT |
| IFITM3 | GAGTGGCTGTAGCACCAACA | GCGGAGCAAAGGCAGCAC |
| IRF3 | CGGAAAGAAGTGTTGCGGTT | TTTTCCTGGGAGTGAGGCAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shimamura, Y.; Noaki, R.; Oura, Y.; Ichikawa, K.; Kan, T.; Masuda, S. Regulation of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin-Induced Inflammation in Spleen Cells from Diabetic Mice by Polyphenols. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11041039
Shimamura Y, Noaki R, Oura Y, Ichikawa K, Kan T, Masuda S. Regulation of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin-Induced Inflammation in Spleen Cells from Diabetic Mice by Polyphenols. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(4):1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11041039
Chicago/Turabian StyleShimamura, Yuko, Rina Noaki, Yukino Oura, Kenya Ichikawa, Toshiyuki Kan, and Shuichi Masuda. 2023. "Regulation of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin-Induced Inflammation in Spleen Cells from Diabetic Mice by Polyphenols" Microorganisms 11, no. 4: 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11041039
APA StyleShimamura, Y., Noaki, R., Oura, Y., Ichikawa, K., Kan, T., & Masuda, S. (2023). Regulation of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin-Induced Inflammation in Spleen Cells from Diabetic Mice by Polyphenols. Microorganisms, 11(4), 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11041039





