Characterization of a Lytic Bacteriophage and Demonstration of Its Combined Lytic Effect with a K2 Depolymerase on the Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Strain 52145
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
2.2. Phage Isolation, Propagation, and Titer Determination
2.3. Determination of Host Range and Efficiency of Plating
2.4. One-Step Phage Growth Curve and Adsorption Assay
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.6. Phage DNA Extraction, Genome Sequence and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis of Phage 731
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Features of Phage 731
3.2. Growth Characteristics of Phage 731
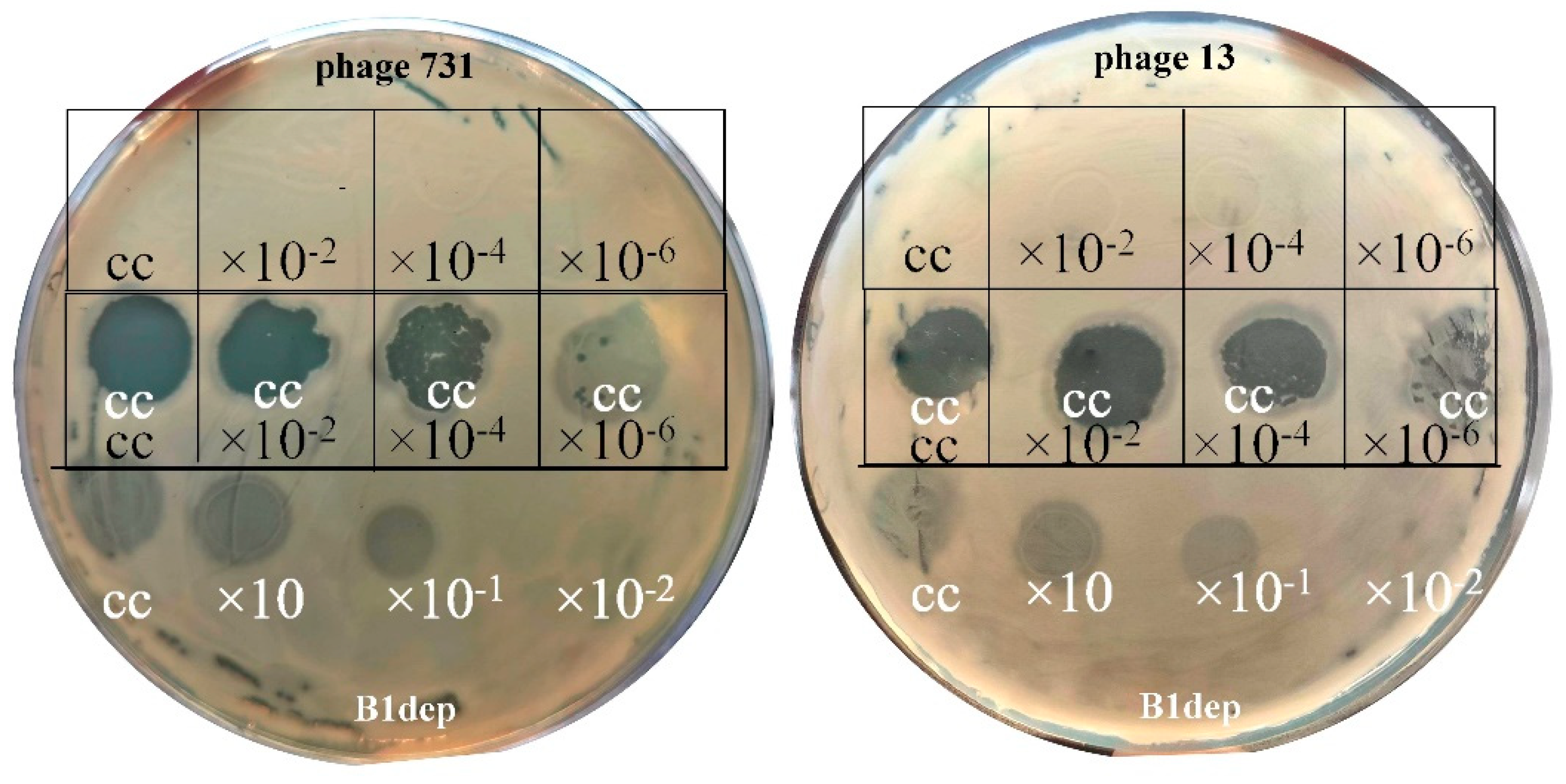
3.3. Host Range and Efficiency of Plating
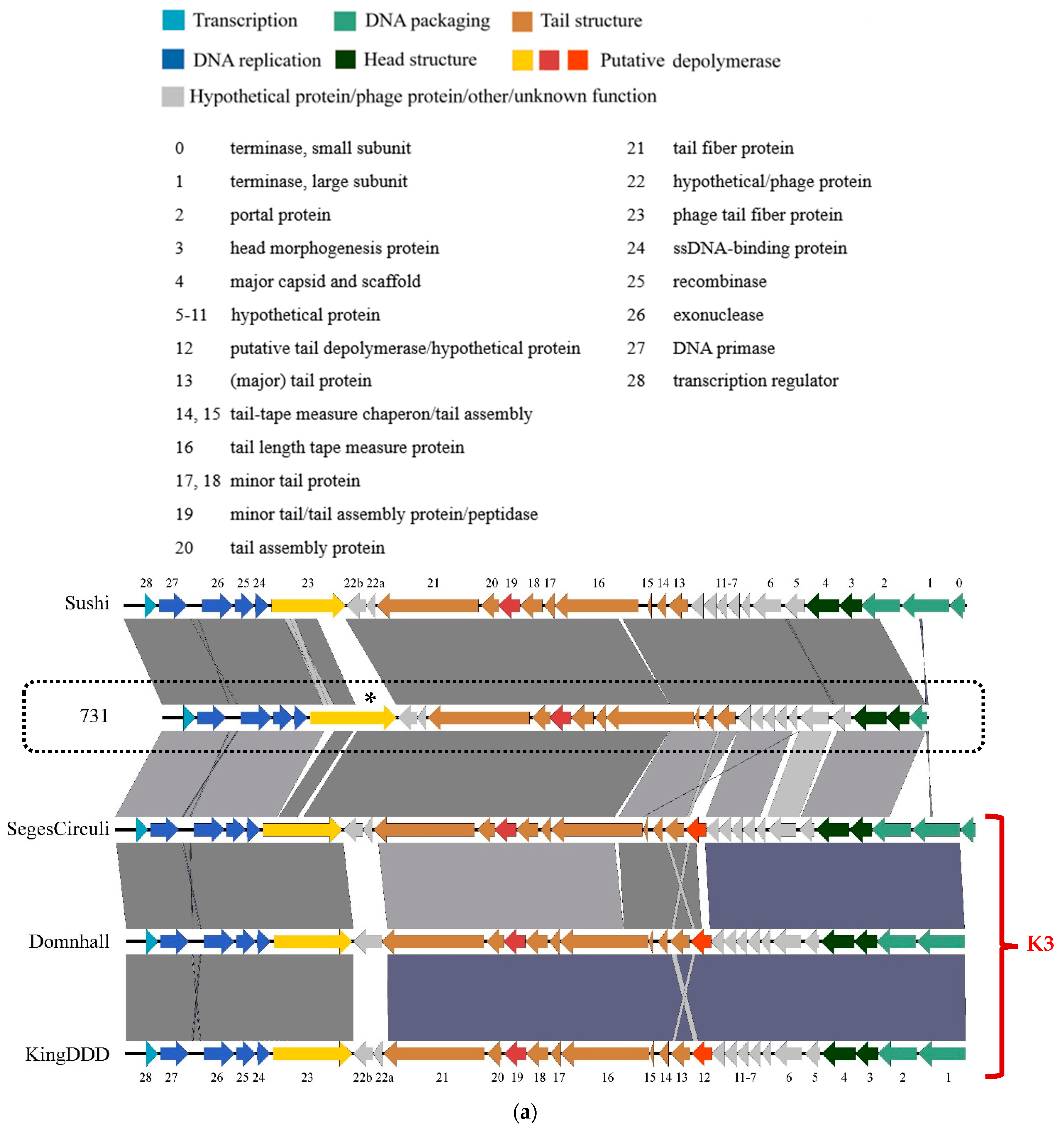
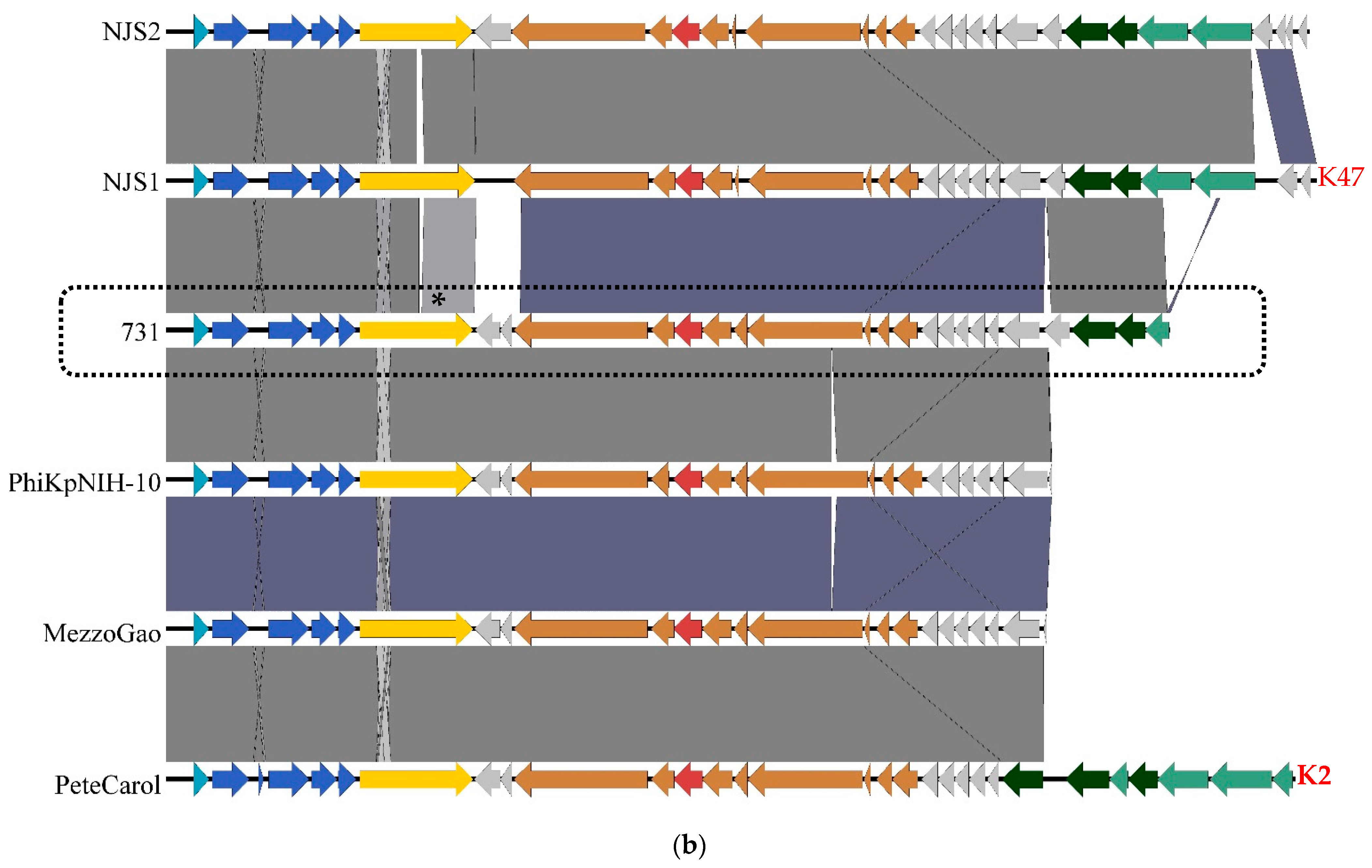
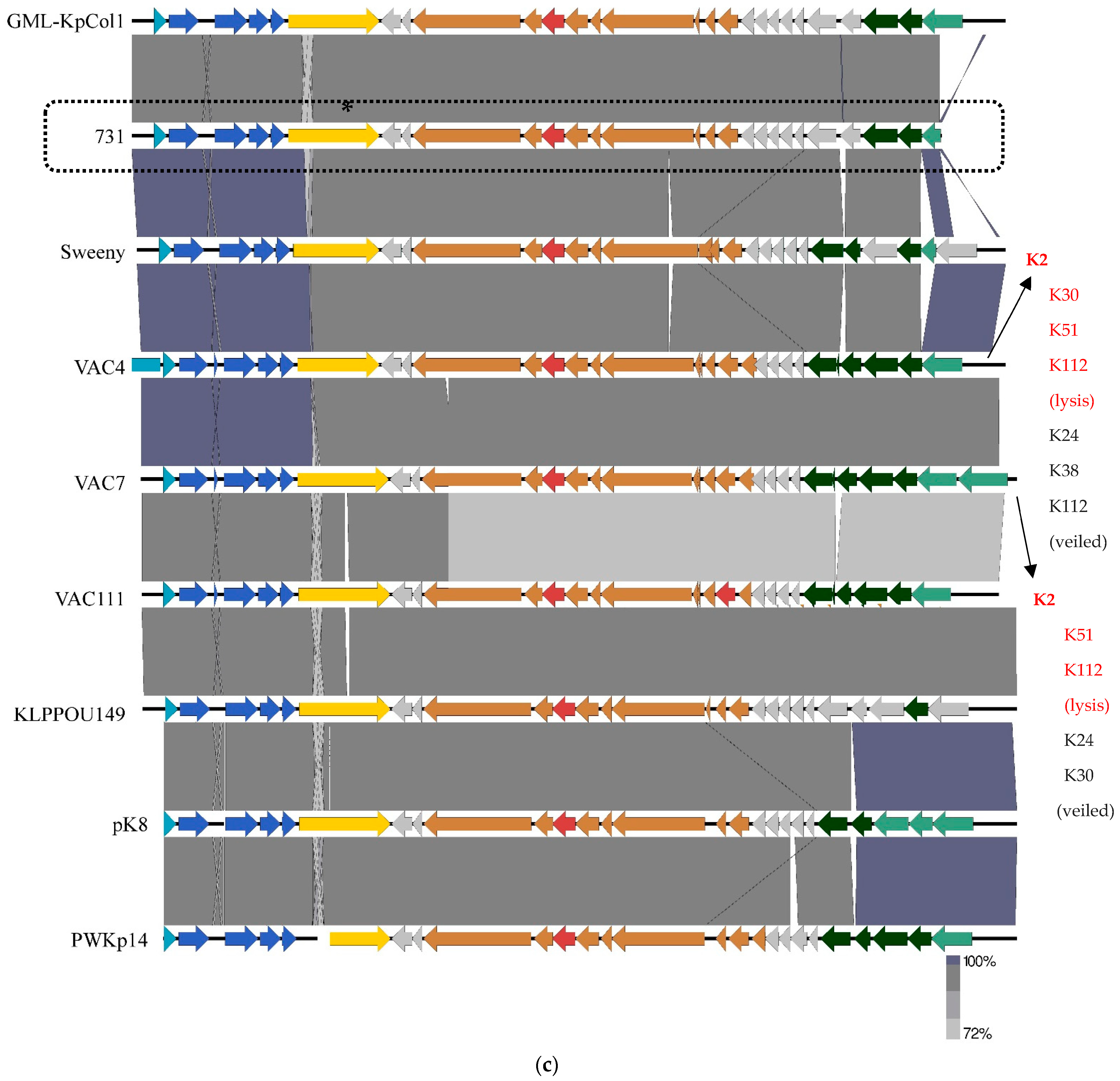
3.4. Genomic and Phylogenetic Properties of Phage 731
3.5. Molecular Properties of the Putative Phage Depolymerase
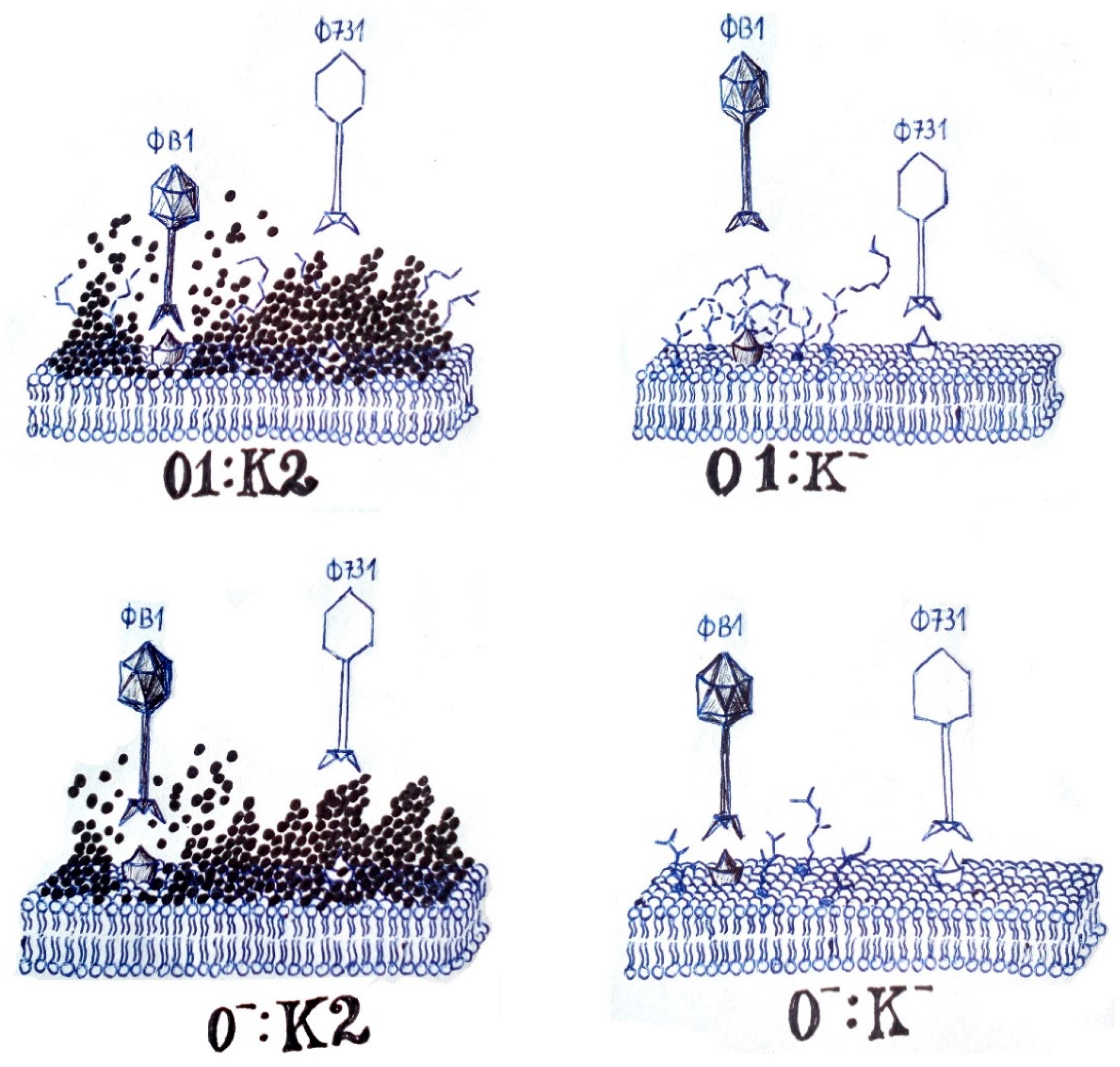
4. Discussion
| Klebsiella Phage | DepolymeraseGene/Protein | Capsule Type | Author, Year of Publication | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0507-KN2-1 | ORF96 | KN2 | Hsu et al., 2013 | [67] |
| NTUH-K2044-K1-1 | K1-ORF34 | K1 | Lin et al., 2014 | [68] |
| KLPN1 | ORF43? ORF34 and/or ORF35 | K2 | Hoyles et al., 2015 | [108] |
| P13 | gene 49, gene 50 | K13 | Shang et al., 2015 | [109] |
| K5 | ORF40, ORF41 | (K. pneumoniae KSM 5-1) | Shneider et al., 2016 | unpub-lished |
| KP36 | gp50 depoKP36 | K63 | Majkowska-Skrobek et al., 2016 | [69] |
| KpV289 | kpv289_orf45 | Volozhantsev et al., 2016 | [110] | |
| K5-2 K5-4 | ORF37 K30/K69dep ORF37 K8dep ORF38 K5dep | K30, K69 K8 K5 | Hsieh et al., 2017 | [74] |
| ΦK64-1 | S1-1 S1-2 S1-3 S2-1 S2-2 S2-3 S2-4 S2-5 S2-6 S2-7 S2-8 | K11 KN4 K21 KN5 K25 K35 K1 K64 K30, K69 / / | Pan et al., 2017 | [38] |
| KP32 | KP32gp37 KP32gp38 | K3 K21 | Majkowska-Skrobek et al., 2018 | [69] |
| KpV41 KpV475 KpV71 KpV74 KpV763 KpV767 KpV766 KpV48 | kpv41_55, kpv41_46 kpv475_51 kpv71_52 Dep_kpv71 kpv74_56 Dep_kpv74 ** kpv763_43 kpv_767_46* kpv766_44 kpv48_57 | K1 K1 K1 K2 K2 K57 ND ND | Solovieva et al., 2018 | [111] |
| SH-KP152226 | ORF42 Dep42 | K47 | Wu et al., 2019 | [112] |
| vB_KpnP_IME321 | ORF42 Dp42 | KN1 | Wang et al., 2019 | [113] |
| vB_KpnS_GH-K3 | gp32 | K2 | Cai et al., 2019 | [114] |
| KN1-1 KN3-1 KN4-1 | KN1dep KN3dep, K56dep KN4dep | KN1 KN3, K56 KN4 | Pan et al., 2019 | [75] |
| 13 | ORF2 | K24 | Horváth et al., 2020 | [29] |
| KpV79 KpV767 | kpv79_42 Dep_kpv79 kpv_767_46 Dep_kpv767 * | K57 K57 | Volozhantsev et al., 2020 | [115] |
| πVLC5 πVLC6 | ORF49, ORF58 ORF51, ORF58 | K22, K37 K22, K37, K13 (halo: K2, K3) | Domingo-Calap et al., 2020 | [28] |
| IME205 | ORF42 Dpo42 ORF43 Dpo43 | K47 K47 (different bac. strains) | Liu et al., 2020 | [95] |
| SH-KP152410 | ORF41 K64-ORF41 | K64 | Li et al., 2021 | [116] |
| B1 | orf61 B1dep | K2 | Pertics et al., 2021 | [42] |
| GBH001 GBH014 GBH038 GBH019 | GBH001_048 GBH001_056 GBH014_001 GBH014_051 GBH038_054 GBH019_279 | K1 (not active) K1 K2 (not active) K2 (not active) K2 K51 | Blundell-Hunter et al., 2021 | [117] |
| KpS8 vB_KpnP_Dlv622 vB_KpnM_Seu621 | kps8_053 DepS8 dlv622_00059 Dep622 Seu621_orf00052 | K23 K23 K23 | Gorodnichev et al., 2021 | [118] |
| SRD2021 | ORF58 | K47 | Hao et al., 2021 | [119] |
| RAD2 | gp02DpK2 | K2 | Dunstan et al., 2021 | [70] |
| KpnM6E1 | gp86 | Nogueira et al., 2021 | [120] | |
| P24 P39 | gene 11 gene 81 | K64 K64 | Fang et al., 2022. jan. | [121] |
| P13 | gene 22, gene 23 | K47 | Fang et al., 2022. febr. | [122] |
| P560 | ORF43 P560dep | K47 | Li et al., 2022 | [123] |
| 1611E-K2-1 | ORF16 K2-ORF16 | K2 | Lin et al., 2022 | [124] |
| vB_KpnM-VAC13 vB_KpnM-VAC66 | ORF104 ORF79 | K13, K15, K24, K36, K52, K64, K102, K107 | Pacios et al., 2021, 2022 | [37] |
| P929 | ORF56 | K19 | Chen et al., 2022 | [125] |
| KPR2 | CDS 48 CDS29 | (K. pn. 033) | Reales-González et al., 2022 | unpublished |
| SH-KP156570 | ORF41 K19-Dpo41 | K19 | Hua et al., 2022 | [126] |
| vB_kpnM_17-11 | orf022 Dep022 | K19 | Bai et al., 2022 | [127] |
| KpV74 | kpv74_56 Dep_kpv74 ** | K2 | Volozhantsev et al., 2022 | [128] |
| 731 | orf22 | K33, K24, K21 (?) | this study |
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shon, A.S.; Bajwa, R.P.S.; Russo, T.A. Hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae: A new and dangerous breed. Virulence 2013, 4, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, C.; Cano, V.; Moranta, D.; Llobet, E.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, C.; Tomás, J.M.; Suárez, T.; Garmendia, J.; Bengoechea, J.A. Role of Bacterial Surface Structures on the Interaction of Klebsiella pneumoniae with Phagocytes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsaro, M.M.; De Castro, C.; Naldi, T.; Parrilli, M.; Tomás, J.M.; Regué, M. 1H and 13C NMR characterization and secondary structure of the K2 polysaccharide of Klebsiella pneumoniae strain 52145. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 2212–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podschun, R.; Ullmann, U. Klebsiella spp. as Nosocomial Pathogens: Epidemiology, Taxonomy, Typing Methods, and Pathogenicity Factors. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paczosa, M.K.; Mecsas, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the Offense with a Strong Defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edwards, J.E.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J. Bad bugs, no drugs: No ESKAPE! An update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2009, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, G.; Borrell, N.; De Astorza, B.; Gómez, C.; Sauleda, J.; Albertí, S. Molecular analysis of the contribution of the capsular polysaccharide and the lipopolysaccharide O side chain to the virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae in a murine model of pneumonia. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 2583–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.J.; Lin, T.L.; Lin, Y.T.; Su, P.A.; Chen, C.T.; Hsieh, P.F.; Hsu, C.R.; Chen, C.C.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Wang, J.T. Identification of capsular types in carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strains by wzc sequencing and implications for capsule depolymerase treatment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, V.; Moranta, D.; Llobet-Brossa, E.; Bengoechea, J.A.; Garmendia, J.; Llobet, E.; Bengoechea, J.A.; Garmendia, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae triggers a cytotoxic effect on airway epithelial cells. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassif, X.; Fournier, J.M.; Arondel, J.; Sansonetti, P.J. Mucoid phenotype of Klebsiella pneumoniae is a plasmid-encoded virulence factor. Infect. Immun. 1989, 57, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, J.; Sakanashi, D.; Kinjo, T.; Haranaga, S.; Fujita, J. The First Case of Community-Acquired Pneumonia Due to Capsular Genotype K2-ST86 Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in Okinawa, Japan: A Case Report and Literature Review. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 2237–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoda, T.; Harada, S.; Okamoto, K.; Ishino, S.; Kaneko, M.; Suzuki, M.; Ito, R.; Mizoguchi, M. COVID-19 and Fatal Sepsis Caused by Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae, Japan, 2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 556–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.T.; Chen, C.S.; Chen, H.A.; Hsu, H.S.; Liang, M.H.; Chang, M.H.; Liao, C.H. Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia revisited: Comparison between 2007 and 2017 prospective cohorts at a medical center in Taiwan. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piednoir, P.; Clarac, U.; Rolle, A.; Bastian, S.; Gruel, G.; Martino, F.; Mehdaoui, H.; Valette, M.; Breurec, S.; Carles, M. Spontaneous community-acquired bacterial meningitis in adults admitted to the intensive care units in the Caribbean French West Indies: Unusual prevalence of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 100, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solgi, H.; Shahcheraghi, F.; Bolourchi, N.; Ahmadi, A. Molecular characterization of carbapenem-resistant serotype K1 hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 harbouring blaNDM-1 and blaOXA-48 carbapenemases in Iran. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaper, K.; Wendt, S.; Lübbert, C.; Lippmann, N.; Pfeifer, Y.; Werner, G. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae of Lineage ST66-K2 Caused Tonsillopharyngitis in a German Patient. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.C.; Chang, F.Y.; Fung, C.P.; Xu, J.Z.; Cheng, H.P.; Wang, J.J.; Huang, L.Y.; Siu, L.K. High prevalence of phagocytic-resistant capsular serotypes of Klebsiella pneumoniae in liver abscess. Microbes Infect. 2004, 6, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedon, S.T.; Kuhl, S.J.; Blasdel, B.G.; Kutter, E.M. Phage treatment of human infections. Bacteriophage 2011, 1, 66–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.T.; Chang, S.Y.; Yen, M.R.; Yang, T.C.; Tseng, Y.H. Characterization of extended-host-range pseudo-T-even bacteriophage Kpp95 isolated on Klebsiella pneumoniae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 2532–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.H.; Kuo, C.F.; Wang, C.H.; Wu, C.M.; Tsao, N. Experimental phage therapy in treating Klebsiella pneumoniae-mediated liver abscesses and bacteremia in mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karumidze, N.; Kusradze, I.; Rigvava, S.; Goderdzishvili, M.; Rajakumar, K.; Alavidze, Z. Isolation and characterisation of lytic bacteriophages of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Klebsiella oxytoca. Curr. Microbiol. 2013, 66, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kęsik-Szeloch, A.; Drulis-Kawa, Z.; Weber-Dąbrowska, B.; Kassner, J.; Majkowska-Skrobek, G.; Augustyniak, D.; Lusiak-Szelachowska, M.; Zaczek, M.; Górski, A.; Kropinski, A.M. Characterising the biology of novel lytic bacteriophages infecting multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Che, J.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jin, L.; et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of a bacteriophage in the treatment of pneumonia induced by multidrug resistance Klebsiella pneumoniae in mice. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 752930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.; Hussain, T.; Das, C.R.; Andleeb, S. Characterization of Siphoviridae phage Z and studying its efficacy against multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae planktonic cells and biofilm. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, B.; Roszniowski, B.; Espaillat, A.; Kęsik-Szeloch, A.; Majkowska-Skrobek, G.; Kropinski, A.M.; Briers, Y.; Cava, F.; Lavigne, R.; Drulis-Kawa, Z. Klebsiella phages representing a novel clade of viruses with an unknown DNA modification and biotechnologically interesting enzymes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.A.; Kim, Y.T.; Cho, J.H.; Ryu, S.; Lee, J.H. Characterization and genome analysis of novel bacteriophages infecting the opportunistic human pathogens Klebsiella oxytoca and K. pneumoniae. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, M.M.; Marmo, P.; Henrici De Angelis, L.; Palmieri, M.; Ciacci, N.; Di Lallo, G.; Demattè, E.; Vannuccini, E.; Lupetti, P.; Rossolini, G.M.; et al. φBO1E, a newly discovered lytic bacteriophage targeting carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae of the pandemic Clonal Group 258 clade II lineage. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo-Calap, P.; Beamud, B.; Vienne, J.; González-Candelas, F.; Sanjuán, R. Isolation of Four Lytic Phages Infecting Klebsiella pneumoniae K22 Clinical Isolates from Spain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, M.; Kovács, T.; Koderivalappil, S.; Ábrahám, H.; Rákhely, G.; Schneider, G. Identification of a newly isolated lytic bacteriophage against K24 capsular type, carbapenem resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; You, B.; Liu, X.; Chen, P.; Liu, M.; Zhang, C.; Luo, X.; et al. Characterization and genome sequencing of a novel T7-like lytic phage, kpssk3, infecting carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.H. An enzyme produced by a phage-host cell system. I. The properties of a Klebsiella phage. Virology 1956, 2, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, C.; Wyss, O. Enzyme Associated with Bacteriophage Infection. J. Bacteriol. 1962, 84, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drulis-Kawa, Z.; Majkowska-Skrobek, G.; Maciejewska, B.; Delattre, A.; Lavigne, R. Learning from bacteriophages-advantages and limitations of phage and phage-encoded protein applications. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2012, 13, 699–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Mao, J.; Xie, J. Bacteriophage polysaccharide depolymerases and biomedical applications. BioDrugs 2014, 28, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squeglia, F.; Maciejewska, B.; Łątka, A.; Ruggiero, A.; Briers, Y.; Drulis-Kawa, Z.; Berisio, R. Structural and Functional Studies of a Klebsiella Phage Capsule Depolymerase Tailspike: Mechanistic Insights into Capsular Degradation. Structure 2020, 28, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleriot, I.; Blasco, L.; Pacios, O.; Fernández-García, L.; Ambroa, A.; López, M.; Ortiz-Cartagena, C.; Cuenca, F.F.; Oteo-Iglesias, J.; Pascual, Á.; et al. The role of PemIK (PemK/PemI) type II TA system from Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical strains in lytic phage infection. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacios, O.; Fernández-García, L.; Bleriot, I.; Blasco, L.; Ambroa, A.; López, M.; Ortiz-Cartagena, C.; Cuenca, F.F.; Oteo-Iglesias, J.; Pascual, Á.; et al. Phenotypic and Genomic Comparison of Klebsiella pneumoniae Lytic Phages: vB_KpnM-VAC66 and vB_KpnM-VAC13. Viruses 2022, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.J.; Lin, T.L.; Chen, C.C.; Tsai, Y.T.; Cheng, Y.H.; Chen, Y.Y.; Hsieh, P.F.; Lin, Y.T.; Wang, J.T. Klebsiella Phage ΦK64-1 Encodes Multiple Depolymerases for Multiple Host Capsular Types. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02457-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riottot, M.M.; Fournier, J.M.; Jouin, H. Direct Evidence for the Involvement of Capsular Polysaccharide in the Immunoprotective Activity of Klebsiella pneumoniae Ribosomal Preparations. Infect. Immun. 1981, 31, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassif, X.; Sansonetti, P.J. Correlation of the virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae K1 and K2 with the presence of a plasmid encoding aerobactin. Infect. Immun. 1986, 54, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regué, M.; Hita, B.; Piqué, N.; Izquierdo, L.; Merino, S.; Fresno, S.; Benedí, V.J.; Tomás, J.M. A Gene, uge, Is Essential for Klebsiella pneumoniae Virulence. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertics, B.Z.; Cox, A.; Nyúl, A.; Szamek, N.; Kovács, T.; Schneider, G. Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Lytic Bacteriophage against the K2 Capsule-Expressing Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Strain 52145, and Identification of Its Functional Depolymerase. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.M.; Li, L.H.; Yan, J.J.; Tsao, N.; Liao, T.L.; Tsai, H.C.; Tsai, S.F. Genome sequencing and comparative analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae NTUH-K2044, a strain causing liver abscess and meningitis. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 4492–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cranston, A.; Danielson, P.; Arens, D.K.; Barker, A.; Birch, E.K.; Brown, H.; Carr, E.; Cero, P.; Chow, J.; Correa, E.; et al. Genome Sequences of 22 T1-like Bacteriophages That Infect Enterobacteriales. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2022, 11, e0122121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llobet, E.; Tomás, J.M.; Bengoechea, J.A. Capsule polysaccharide is a bacterial decoy for antimicrobial peptides. Microbiology 2008, 154, 3877–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, L.; Coderch, N.; Piqué, N.; Bedini, E.; Corsaro, M.M.; Merino, S.; Fresno, S.; Tomás, J.M.; Regué, M. The Klebsiella pneumoniae wabG gene: Role in biosynthesis of the core lipopolysaccharide and virulence. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 7213–7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A.G.; Ganesamoorthy, D.; Coin, L.; Cooper, M.A.; Cao, M.D. Complete Genome Sequence of Klebsiella quasipneumoniae subsp. similipneumoniae Strain ATCC 700603. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00438-16. [Google Scholar]
- Twest, R.; Kropinski, A.M. Bacteriophage Enrichment from Water and Soil. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 501, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Mullan, W.M.A. Plaque Formation. Available online: https://www.dairyscience.info/index.php/enumeration-of-lactococcal-bacteriophages/plaque-formation.html (accessed on 27 February 2021).
- Adriaenssens, E.; Brister, J.R. How to Name and Classify Your Phage: An Informal Guide. Viruses 2017, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besemer, J.; Lomsadze, A.; Borodovsky, M. GeneMarkS: A self-training method for prediction of gene starts in microbial genomes. Implications for finding sequence motifs in regulatory regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 2607–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Göker, M. VICTOR: Genome-based phylogeny and classification of prokaryotic viruses. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3396–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Auchm, A.F.; Klenk, H.P.; Göker, M. Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefort, V.; Desper, R.; Gascuel, O. FastME 2.0: A comprehensive, accurate, and fast distance-based phylogeny inference program. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 2798–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farris, J.S. Estimating phylogenetic trees from distance matrices. Am. Nat. 1972, 106, 645–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G. Using ggtree to visualize data on tree-like structures. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 69, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göker, M.; García-Blázquez, G.; Voglmayr, H.; Tellería, M.T.; Martín, M.P. Molecular taxonomy of phytopathogenic fungi: A case study in Peronospora. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Hahnke, R.L.; Petersen, J.; Scheuner, C.; Michael, V.; Fiebig, A.; Rohde, C.; Rohde, M.; Fartmann, B.; Goodwin, L.A.; et al. Complete genome sequence of DSM 30083(T), the type strain (U5/41(T)) of Escherichia coli, and a proposal for delineating subspecies in microbial taxonomy. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2014, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.L.; Nang, S.C.; Lin, Y.W.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, H.H.; Wickremasinghe, H.; Barlow, C.K.; Creek, D.J.; Crawford, S.; Rao, G.; et al. Comparative metabolomics revealed key pathways associated with the synergistic killing of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae by a bacteriophage-polymyxin combination. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 20, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Linden, S.B.; Nelson, D.C. Complete Genome Sequence of Klebsiella pneumoniae Phages SopranoGao, MezzoGao, and AltoGao. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e01009-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, S.; Rajaure, M.; Wall, E.; Johnson, J.; Bliskovsky, V.; Gottesman, S.; Adhya, S. Phage Resistance in Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST258 Evolves via Diverse Mutations That Culminate in Impaired Adsorption. mBio 2020, 11, e02530-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, G.; Yuan, C.; Shu, R.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, S.; Xie, S.; Liu, M.; Zhou, H.; Sun, S.; Wang, H. O-antigen serves as a two-faced host factor for bacteriophage NJS1 infecting nonmucoid Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 155, 104897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, N.; Williams, E.; Newkirk, H.; Liu, M.; Gill, J.J.; Ramsey, J. Complete Genome Sequence of Klebsiella pneumoniae Phage Sweeny. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e01047-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurgood, T.L.; Sharmam, R.; Call, J.J.; Chronis, J.D.; Dawson, D.D.; Finnegan, Z.K.; Foster, K.W.; Meek, T.; Potts, E.; Sirrine, M.R.; et al. Genome Sequences of 12 Phages That Infect Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, e00024-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, W.M.B.S.; Li, M.; Sands, K.; Lenzi, M.H.; Portal, E.; Mathias, J.; Dantas, P.P.; Migliavacca, R.; Hunter, J.R.; Medeiros, E.A.; et al. Effective phage cocktail to combat the rising incidence of extensively drug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 16. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Lessor, L.E.; Cahill, J.L.; Rasche, E.S.; Kuty Everett, G.F. Complete Genome Sequence of Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase-Producing K. pneumoniae Siphophage Sushi. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e00994-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.R.; Lin, T.L.; Pan, Y.J.; Hsieh, P.F.; Wang, J.T. Isolation of a Bacteriophage Specific for a New Capsular Type of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Characterization of Its Polysaccharide Depolymerase. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.L.; Hsieh, P.F.; Huang, Y.T.; Lee, W.C.; Tsai, Y.T.; Su, P.A.; Pan, Y.J.; Hsu, C.R.; Wu, M.C.; Wang, J.T. Isolation of a bacteriophage and its depolymerase specific for K1 capsule of Klebsiella pneumoniae: Implication in typing and treatment. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1734–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majkowska-Skrobek, G.; Łątka, A.; Berisio, R.; Maciejewska, B.; Squeglia, F.; Romano, M.; Lavigne, R.; Struve, C.; Drulis-Kawa, Z. Capsule-Targeting Depolymerase, Derived from Klebsiella KP36 Phage, as a Tool for the Development of Anti-Virulent Strategy. Viruses 2016, 8, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunstan, R.A.; Bamert, R.S.; Belousoff, M.J.; Short, F.L.; Barlow, C.K.; Pickard, D.J.; Wilksch, J.J.; Schittenhelm, R.B.; Strugnell, R.A.; Dougan, G.; et al. Mechanistic Insights into the Capsule-Targeting Depolymerase from a Klebsiella pneumoniae Bacteriophage. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0102321-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhuba, D.V.; Kolomiets, E.I.; Dey, E.S.; Novik, G.I. Bacteriophage receptors, mechanisms of phage adsorption and penetration into host cell. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, K.A.; Sutherland, I.W.; Jones, M.V.; Rutherford, D. Biofilm susceptibility to bacteriophage attack: The role of phage-borne polysaccharide depolymerase. Microbiology 1998, 144, 3039–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.; Wu, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, M.; Guo, Z.; Ji, Y.; Xi, H.; Wang, X.; Xue, Y.; et al. A Smooth-Type, Phage-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Mutant Strain Reveals that OmpC Is Indispensable for Infection by Phage GH-K3. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01585-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.F.; Lin, H.H.; Lin, T.L.; Chen, Y.Y.; Wang, J.T. Two T7-like Bacteriophages, K5-2 and K5-4, Each Encodes Two Capsule Depolymerases: Isolation and Functional Characterization. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.J.; Lin, T.L.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lai, P.H.; Tsai, Y.T.; Hsu, C.R.; Hsieh, P.F.; Lin, Y.T.; Wang, J.T. Identification of three podoviruses infecting Klebsiella encoding capsule depolymerases that digest specific capsular types. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fresno, S.; Jimenez, N.; Izquierdo, L.; Merino, S.; Corsaro, M.M.; De Castro, C.; Parrilli, M.; Naldi, T.; Regue, M.; Tomas, J.M. The ionic interaction of Klebsiella pneumoniae K2 capsule and core lipopolysaccharide. Microbiology 2006, 152, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fresno, S.; Jimenez, N.; Canals, R.; Merino, S.; Corsaro, M.M.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Pieretti, G.; Regue, M.; Tomas, J.M. A second galacturonic acid transferase is required for core lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis and complete capsule association with the cell surface in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, A.; Lery, L.; Regueiro, V.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, C.; Martínez, V.; Moranta, D.; Llobet, E.; González-Nicolau, M.; Insua, J.L.; Tomas, J.M.; et al. Functional Genomic Screen Identifies Klebsiella pneumoniae Factors Implicated in Blocking Nuclear Factor κB (NF-κB) Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 16678–16697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Han, W.; Lei, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Gao, Y.; Song, J.; Lu, R.; et al. A Method for Generation Phage Cocktail with Great Therapeutic Potential. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.; Wang, G.; Le, S.; Wu, M.; Cheng, M.; Guo, Z.; Ji, Y.; Xi, H.; Zhao, C.; Wang, X.; et al. Three Capsular Polysaccharide Synthesis-Related Glucosyltransferases, GT-1, GT-2 and WcaJ, Are Associated With Virulence and Phage Sensitivity of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, P.M.; Williams, J.M.; Hart, C.A.; Saunders, J.R. Identification of Two Chemical Types of K21 Capsular Polysaccharide from Klebsiellae. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1987, 133, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casewell, M.; Talsania, H.G. Predominance of certain Klebsiella capsular types in hospitals in the United Kingdom. J. Infect. 1979, 1, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, D.; Allen, P.; Saunders, J.R.; Hart, C.A. Surface Properties of Klebsiella and E. coli: Role of Capsular Polysaccharide in Protection Against Phagocytosis. In Separations Using Aqueous Phase Systems; Fisher, D., Sutherland, I.A., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, L.N.; Novais, Â.; Stegani, L.M.M.; Ferreira, J.C.; Rodrigues, C.; Darini, A.L.C.; Peixe, L.; Novais, Â.; Stegani, L.M.M.; Ferreira, J.C.; et al. Virulence genes, capsular and plasmid types of multidrug-resistant CTX-M (-2, -8, -15) and KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from four major hospitals in Brasil. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 91, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisse, S.; Passet, V.; Haugaard, A.B.; Babosan, A.; Kassis-Chikhani, N.; Struve, C.; Decré, D. wzi gene sequencing, a rapid method for determination of capsular type for Klebsiella strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 4073–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Lokate, M.; Deurenberg, R.H.; Tepper, M.; Arends, J.P.; Raangs, E.G.; Lo-Ten-Foe, J.; Grundmann, H.; Rossen, J.W.; Friedrich, A.W. Use of whole-genome sequencing to trace, control and characterize the regional expansion of extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing ST15 Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcioglu, N.H.; Bilkay, I.S. Antibiotic resistance, multidrug resistance and enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus polymerase chain reaction profiles of clinically important Klebsiella species. Asian Biomed. 2016, 10, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Kiseleva, B.S.; Krasnogolovets, V.N. Rol’ Klebsiella pneumoniae v étiologii bakterial’nogo sepsisa [Role of Klebsiella pneumoniae in the etiology of bacterial sepsis]. Zhurnal Mikrobiol. Epidemiol. I Immunobiol. 1983, 2, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Albassam, W.W. Detection of antibiotics resistance genes in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Iraqi J. Sci. 2015, 56, 407–416. [Google Scholar]
- Hasdemir, U.O.; Chevalier, J.; Nordmann, P.; Pagès, J.M. Detection and prevalence of active drug efflux mechanism in various multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strains from Turkey. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 2701–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, M.; Palmieri, M.; Mirande, C.; El-Mahallawy, H.; Rashed, H.G.; Abd-El-Reheem, F.; El-Manakhly, A.R.; Abdel-Latif, R.A.R.; Aboulela, A.G.; Saeed, L.Y.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing of Egyptian multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates: A multi-center pilot study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 40, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryadevara, N.; Kwan, Y.I.; Shanmugam, G.; Ponmurugan, P.; Ganapathy, B.; Subramonie, S.; Sai, V.; Velaga, A.R. Molecular Docking of Multidrug Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from River Water of Klang Valley, Malaysia. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 13, 2141–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirot, J.; Chanal, C.; Petit, A.; Sirot, D.; Labia, R.; Gerbaud, G. Klebsiella pneumoniae and Other Enterobacteriaceae Producing Novel Plasmid-Mediated β-Lactamases Markedly Active against Third-Generation Cephalosporins: Epidemiologic Studies. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1988, 10, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anğ-Küçüker, M.; Küçükbasmacı, Ö.; Tekin, M.; Akbulut, D.; Büyükbaba-Boral, Ö.; Anğ, Ö. Serotyping, Siderophore Synthesis, Serum Resistance and Extended Spectrum Beta-Lactamase Activity of Uropathogen Klebsiella Strains. Türk. Mikrobiyol. Cem. Derg. 2002, 33, 265–269. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.H.; Song, X.Y.; Ma, X.B.; Zhang, S.Y.; Zhang, J.Q. Molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podschun, R.; Pietsch, S.; Höller, C.; Ullmann, U. Incidence of Klebsiella Species in Surface Waters and Their Expression of Virulence Factors. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3325–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Li, P.; Tian, J.; Zhang, K.; Luo, C. Homology analysis between clinically isolated extraintestinal and enteral Klebsiella pneumoniae among neonates. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Valdez, M.; Ares, M.A.; Rosales-Reyes, R.; Torres, J.; Girón, J.A.; Weimer, B.C.; Mendez-Tenorio, A.; De la Cruz, M.A. Whole Genome Sequencing of Pediatric Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains Reveals Important Insights Into Their Virulence-Associated Traits. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 711577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Banna, T.E.S.; Sonbol, F.I.; El-Aziz, A.A.A.; Al-Fakharany, O.M. Modulation of Antibiotic Efficacy against Klebsiella pneumoniae by Antihistaminic Drugs. J. Med. Microb. Diagn. 2016, 5, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieroni, P. Application of Bacteriophage Typing to Klebsiella pneumoniae. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Miaobiology University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sechter, I.; Mestre, F.; Hansen, D.S. Twenty-three years of Klebsiella phage typing: A review of phage typing of 12 clusters of nosocomial infections, and a comparison of phage typing with K serotyping. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2000, 6, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla Rincón, N. Efecto de Bacteriófagos en el Control de Biopelículas de Klebsiella pneumoniae Productoras de Carbapenemasas (KPC); Universidad de los Andes: Bogotá, Colombia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Majkowska-Skrobek, G.; Latka, A.; Berisio, R.; Squeglia, F.; Maciejewska, B.; Briers, Y.; Drulis-Kawa, Z. Phage-Borne Depolymerases Decrease Klebsiella pneumoniae Resistance to Innate Defense Mechanisms. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Leung, S.S.Y.; Huang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, N.; Li, P.; Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Bai, C.; Mi, Z.; et al. Identification of Two Depolymerases From Phage IME205 and Their Antivirulent Functions on K47 Capsule of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drulis-Kawa, Z.; Majkowska-Skrobek, G.; Maciejewska, B. Bacteriophages and phage-derived proteins—Application approaches. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 1757–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.P.; Oliveira, H.; Melo, L.D.R.; Sillankorva, S.; Azeredo, J. Bacteriophage-encoded depolymerases: Their diversity and biotechnological applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaszowska, M.; Majkowska-Skrobek, G.; Markwitz, P.; Lood, C.; Jachymek, W.; Maciejewska, A.; Lukasiewicz, J.; Drulis-Kawa, Z. The Mutation in wbaP cps Gene Cluster Selected by Phage-Borne Depolymerase Abolishes Capsule Production and Diminishes the Virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyles, L.; Murphy, J.; Neve, H.; Heller, K.J.; Turton, J.F.; Mahony, J.; Sanderson, J.D.; Hudspith, B.; Gibson, G.R.; McCartney, A.L.; et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae subsp. pneumoniae-bacteriophage combination from the caecal effluent of a healthy woman. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, A.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Mo, Z.; Li, G.; Mou, H. Complete nucleotide sequence of Klebsiella phage P13 and prediction of an EPS depolymerase gene. Virus Genes 2015, 50, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volozhantsev, N.V.; Myakinina, V.P.; Popova, A.V.; Kislichkina, A.A.; Komisarova, E.V.; Knyazeva, A.I.; Krasilnikova, V.M.; Fursova, N.K.; Svetoch, E.A. Complete genome sequence of novel T7-like virus vB_KpnP_KpV289 with lytic activity against Klebsiella pneumoniae. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 499–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solovieva, E.V.; Myakinina, V.P.; Kislichkina, A.A.; Krasilnikova, V.M.; Verevkin, V.V.; Mochalov, V.V.; Lev, A.I.; Fursova, N.K.; Volozhantsev, N.V. Comparative genome analysis of novel Podoviruses lytic for hypermucoviscous Klebsiella pneumoniae of K1, K2, and K57 capsular types. Virus Res. 2018, 243, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, R.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Qiu, J.; Liu, Q.; He, P.; Li, Q. A Novel Polysaccharide Depolymerase Encoded by the Phage SH-KP152226 Confers Specific Activity Against Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae via Biofilm Degradation. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, P.; Niu, W.; Yuan, X.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y.; An, X.; Fan, H.; Zhangxiang, L.; Mi, L.; et al. Protective and therapeutic application of the depolymerase derived from a novel KN1 genotype of Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteriophage in mice. Res. Microbiol. 2019, 170, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, M.; Guo, Z.; Ji, Y.; Xi, H.; Wang, X.; Xue, Y.; et al. Biological properties and genomics analysis of vB_KpnS_GH-K3, a Klebsiella phage with a putative depolymerase-like protein. Virus Genes. 2019, 55, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volozhantsev, V.N.; Shpirt, M.A.; Borzilov, I.A.; Komisarova, V.E.; Krasilnikova, M.V.; Shashkov, S.A.; Verevkin, V.V.; Knirel, A.Y. Characterization and Therapeutic Potential of Bacteriophage-Encoded Polysaccharide Depolymerases with β Galactosidase Activity against Klebsiella pneumoniae K57 Capsular Type. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sheng, Y.; Ma, R.; Xu, M.; Liu, F.; Qin, R.; Zhu, M.; Zhu, X.; He, P. Identification of a Depolymerase Specific for K64-Serotype Klebsiella pneumoniae: Potential Applications in Capsular Typing and Treatment. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blundell-Hunter, G.; Enright, M.C.; Negus, D.; Dorman, M.J.; Beecham, G.E.; Pickard, D.J.; Wintachai, P.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P.; Thomson, N.R.; Taylor, P.W. Characterisation of Bacteriophage-Encoded Depolymerases Selective for Key Klebsiella pneumoniae Capsular Exopolysaccharides. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 686090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorodnichev, R.B.; Volozhantsev, N.V.; Krasilnikova, V.M.; Bodoev, I.N.; Kornienko, M.A.; Kuptsov, N.S.; Popova, A.V.; Makarenko, G.I.; Manolov, A.I.; Slukin, P.V.; et al. Novel Klebsiella pneumoniae K23-Specific Bacteriophages From Different Families: Similarity of Depolymerases and Their Therapeutic Potential. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 669618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, G.; Shu, R.; Ding, L.; Chen, X.; Miao, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H. Bacteriophage SRD2021 Recognizing Capsular Polysaccharide Shows Therapeutic Potential in Serotype K47 Klebsiella pneumoniae Infections. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, C.L.; Pires, D.P.; Monteiro, R.; Santos, S.B.; Carvalho, C.M. Exploitation of a Klebsiella Bacteriophage Receptor-Binding Protein as a Superior Biorecognition Molecule. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 3077–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Feng, Y.; McNally, A.; Zong, Z. Characterization of phage resistance and phages capable of intestinal decolonization of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in mice. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Q.; Zong, Z. Lytic Phages against ST11 K47 Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and the Corresponding Phage Resistance Mechanisms. mSphere 2022, 7, e0008022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Guo, G.; Li, P.; Ma, J.; Chen, R.; Du, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W. Identification of a phage-derived depolymerase specific for KL47 capsule of Klebsiella pneumoniae and its therapeutic potential in mice. Virol. Sin. 2022, 37, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.L.; Yang, F.L.; Ren, C.T.; Pan, Y.J.; Liao, K.S.; Tu, I.F.; Chang, Y.P.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Wu, C.Y.; Wu, S.H.; et al. Development of Klebsiella pneumoniae Capsule Polysaccharide-Conjugated Vaccine Candidates Using Phage Depolymerases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 843183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tang, Q.; Li, X.; Zheng, X.; Li, P.; Li, M.; Wu, F.; Xu, Z.; Lu, R.; Zhang, W. Isolation, characterization, and genome analysis of bacteriophage P929 that could specifically lyase the KL19 capsular type of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Virus Res. 2022, 314, 198750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Y.; Wu, Y.; Guo, M.; Ma, R.; Li, Q.; Hu, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; et al. Characterization and Functional Studies of a Novel Depolymerase Against K19-Type Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 878800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Chen, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.J.; Sjöling, Å.; Hu, R.; Zhou, Y. Isolation and Characterization of vB_kpnM_17-11, a Novel Phage Efficient Against Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 897531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volozhantsev, N.V.; Borzilov, A.I.; Shpirt, A.M.; Krasilnikova, V.M.; Verevkin, V.V.; Denisenko, E.A.; Kombarova, T.I.; Shashkov, A.S.; Knirel, Y.A.; Dyatlov, I.A. Comparison of the therapeutic potential of bacteriophage KpV74 and phage-derived depolymerase (β-glucosidase) against Klebsiella pneumoniae capsular type K2. Virus Res. 2022, 322, 198951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
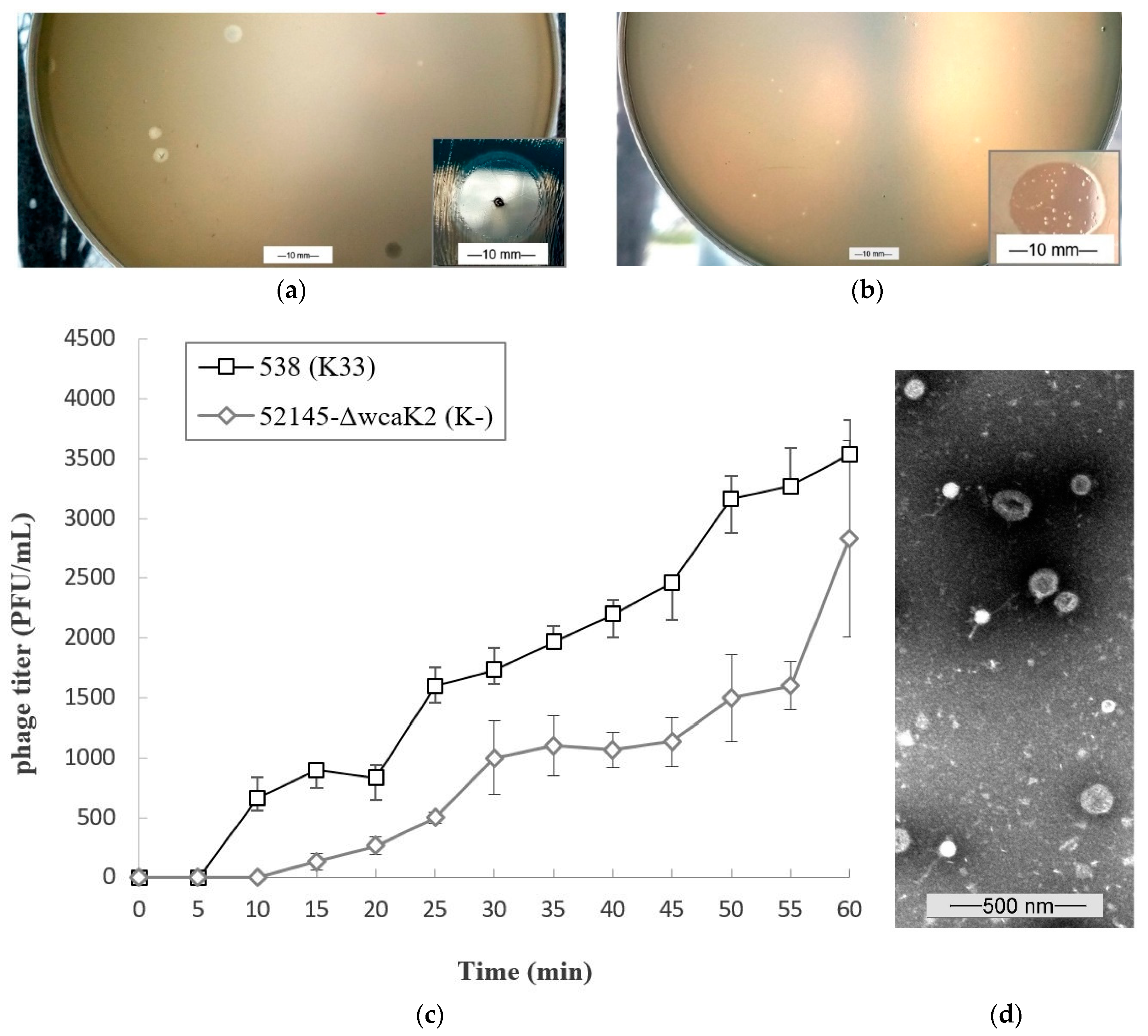
 ).
).
 ).
).
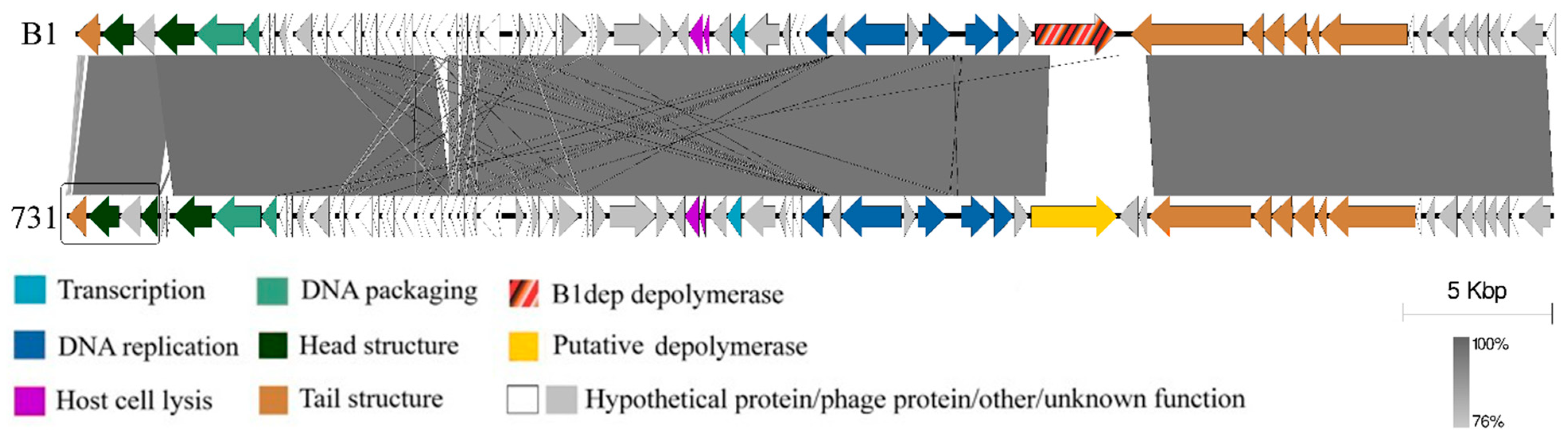

| Strain Code | K Locus | O Locus | 731 | 731 + B1dep | B1dep | B1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NTUH-K2044 [43] | K1 | ND | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | ABC429 | K1 | O1v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 3 | BC-14-31 | K1 | O1v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 4 | BC-15-45 | K1 | O1v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 5 | BC-15-55 | K1 | O1v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 6 | 52145 [44] | K2 | O1 | - | +++ | H | +++ H (high) |
| 7 | 52145-ΔwcaK2 [45] | K– | O1 | +++ (high) | +++ | - | - |
| 8 | 52145-ΔwaaL [46] | K2 | O– | - | +++ | H | +++ H (high) |
| 9 | 52145-ΔwcaK2ΔwaaL [2] | K– | O– | +++ (high) | +++ | - | +++ (low) |
| 10 | CIP 52.145 | K2 | O1 | - | +++ | H | +++ H |
| 11 | ABC83 | K2 | O1v1 | - | H | H * | H |
| 12 | ABC127 | K2 | O1v1 | - | - | - * | - |
| 13 | Kpn-ABC139 | K2 | O1v1 | - | H | H * | H |
| 14 | ABC215 | K2 | O2v1 | - | H | H * | H |
| 15 | ABC220 | K2 | O1v1 | - | H | H * | H |
| 16 | ABC252 | K2 | O1v1 | - | H | H * | H |
| 17 | ABC261 | K2 | O1v1 | - | H | H * | H |
| 18 | ABC270 | K2 | O1v1 | - | - | -/h * | - |
| 19 | BC14-298 | K2 | O1v2 | - | - | -/H * | h |
| 20 | PFZ7 | K2 | O1v1 | - | H | H * | H |
| 21 | PFZ10 | K2 | O1v1 | - | H | H * | H |
| 22 | PFZ336S | K2 | O1v1 | - | H | H * | H |
| 23 | PFZ341 | K2 | O1v1 | - | H | H * | H |
| 24 | PFZ594 | K2 | O1v1 | - | - | - * | h |
| 25 | PFZ761 | K2 | O1v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 26 | CIP 80.51 | K3 | ND | - | - | - | - |
| 27 | PFZ92S | K3 | O1v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 28 | ATCC 700603 [47] | K6 | ND | - | - | - | - |
| 29 | CIP 52.207 | K9 | ND | - | - | - | - |
| 30 | ABC672 | K9 | O2v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 31 | ABC111 | K10 | O3/O3a | - | - | - | - |
| 32 | ABC735 | K10 | O5 | - | - | - | - |
| 33 | CIP 52.215 | K11 | O3 | + | - | - | - |
| 34 | CIP 52.216 | K12 | O1 | - | - | - | - |
| 35 | CIP 52.217 | K13 | ND | - | H | H | H |
| 36 | FD6-1 | K15 | O4 | - | - | - | - |
| 37 | FD6-2 | K15 | O4 | - | - | - | - |
| 38 | CIP 52.221 | K17 | ND | - | - | - | - |
| 39 | ABC621 | K17 | O1v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 40 | ABC785 | K17 | O1v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 41 | CIP 52.223 | K19 | ND | - | - | - | - |
| 42 | ABC39 | K19 | O2v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 43 | ABC213 | K19 | O1v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 44 | PFZ305S | K19 | O102 (?) | - | - | - | - |
| 45 | PFZ401 | K19 | O1v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 46 | PFZ410 | K19 | O1v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 47 | PFZ412 | K19 | O1v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 48 | PFZ604 | K19 | O1v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 49 | CIP 52.224 | K20 | ND | + | - | - | - |
| 50 | ABC147 | K20 | O2v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 51 | ABC484 | K20 | O2v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 52 | KW140 | K20 | O2v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 53 | KW141 | K20 | O2v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 54 | KW144 | K20 | O2v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 55 | CIP 52.225 | K21 | ND | + | + | - | - |
| 56 | ABC355 | K21 | O3b | - | - | - | - |
| 57 | ABC606 | K21 | O3b | +++ (high) | +++ | - | - |
| 58 | 53/3 [29] | K24 | ND | - | - | - | - |
| 59 | CIP 52.229 | K24 | ND | - | - | - | - |
| 60 | ABC60 | K24 | O1v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 61 | ABC360 | K24 | O2v1 | +++ (high) | +++ | - | - |
| 62 | ABC572 | K24 | O2v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 63 | ABC593 | K24 | O2v1 | - | H | H * | H |
| 64 | PFZ517 | K25 | O5 | - | - | - | - |
| 65 | CIP 52.232 | K27 | O2 | + | - | - | - |
| 66 | ABC776 | K27 | O4 | - | - | - | - |
| 67 | PFZ334 | K27 | O4 | + | - | - | - |
| 68 | PFZ560 | K27 | O4 | - | - | - | - |
| 69 | CIP 52.235 | K30 | O1 | - | - | - | - |
| 70 | ABC626 | K30 | O3/O3a (?) | - | - | - | - |
| 71 | KW150 | K30 | O1v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 72 | KW154 | K30 | O1v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 73 | CIP 53.8 | K33 | O3 | +++ (high) | +++ | - | - |
| 74 | KW1 | K43 | O2v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 75 | KW2 | K43 | O2v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 76 | CIP 53.23 | K47 | O1 | - | - | - | - |
| 77 | PFZ679 | K48 | O1v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 78 | PFZ682 | K48 | O1v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 79 | PFZ687 | K48 | O1v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 80 | ABC435 | K51 | O1v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 81 | PFZ151S | K51 | O1v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 82 | PFZ155 | K51 | O1/O2v2 | + | - | - | - |
| 83 | MGH 78578 [47] | K52 | ND | - | - | - | - |
| 84 | ABC92 | K54 | O1v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 85 | ABC196 | K57 | O3b | - | - | - | - |
| 86 | ABC493 | K57 | O2v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 87 | ABC79 | K62 | O1v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 88 | PFZ265 | K62 | O1v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 89 | PFZ758 | K62 | O1v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 90 | CIP 80.47 | K64 | ND | + | + | - | - |
| 91 | ABC217 | K64 | O2v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 92 | ABC375 | K64 | O1v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 93 | ABC669 | K64 | O2v1 | - | - | - | - |
| 94 | ABC105 | K74 | O104 | - | - | - | - |
| 95 | ABC587 | K74 | O104 | - | - | - | - |
| 96 | ABC211 | K106 | O2v2 | - | H | H * | H |
| 97 | ABC646 | K107 | O2v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 98 | PFZ31 | K110 | O3b | - | - | - | - |
| 99 | PFZ673 | K110 | O3b | - | - | - | - |
| 100 | PFZ674 | K110 | O3b | - | - | - | - |
| 101 | PFZ542 | K111 | O3b | - | - | - | - |
| 102 | PFZ281 | K112 | O2v2 (?) | - | - | - | - |
| 103 | ABC135 | K122 | O2v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 104 | ABC91 | K136 | O1v2 | - | - | - | - |
| 105 | ABC718 | K151 | O4 | - | - | - | - |
| Klebsiella Phage | Host Strain | Host Capsule Serotype | Other Susceptible Capsule Serotypes | Depoly-Merases | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 731 | 52145-ΔwcaK2 | no capsule | K21, K24, K33 (clear) K11, K20, K21, K27, K51, K64 (veiled) | orf22 | [42], this study |
| GML-KpCol1 | |||||
| vB_KpnS-VAC4 | ATCC10031 | K2 | K30, K51, K112 (clear) K24, K38, K112 (veiled) | [36] | |
| vB_KpnS-VAC7 | ATCC10031 | K2 | K51, K112 (clear) K24, K30 (veiled) | [36] | |
| vB_Kpn-VAC111 | |||||
| vB_KpnS_15-38_KLPPOU149 | 15-38 | ||||
| pK8 | II-503 | [59] | |||
| MezzoGao | ATCC51503 | [60] | |||
| vB_KpnD_PeteCarol | ATCC10031 | K2 | [44] | ||
| PhiKpNIH-10 | Phage Pharr (P1) and KpNIH-2 (P2) resistant MP103 | no capsule | [61] | ||
| NJS2 | |||||
| NJS1 | no capsule | K47 | [62] | ||
| Sweeny | 1776c | [63] | |||
| vB_KpnS_Domnhall | K3 | [64] | |||
| vB_KpnS_KingDDD | K3 | [64] | |||
| vB_KpnS_SegesCirculi | >K3 | [64] | |||
| PWKp14 | Kpn32 | [65] | |||
| Sushi | A1 | [66] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pertics, B.Z.; Kovács, T.; Schneider, G. Characterization of a Lytic Bacteriophage and Demonstration of Its Combined Lytic Effect with a K2 Depolymerase on the Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Strain 52145. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030669
Pertics BZ, Kovács T, Schneider G. Characterization of a Lytic Bacteriophage and Demonstration of Its Combined Lytic Effect with a K2 Depolymerase on the Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Strain 52145. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(3):669. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030669
Chicago/Turabian StylePertics, Botond Zsombor, Tamás Kovács, and György Schneider. 2023. "Characterization of a Lytic Bacteriophage and Demonstration of Its Combined Lytic Effect with a K2 Depolymerase on the Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Strain 52145" Microorganisms 11, no. 3: 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030669
APA StylePertics, B. Z., Kovács, T., & Schneider, G. (2023). Characterization of a Lytic Bacteriophage and Demonstration of Its Combined Lytic Effect with a K2 Depolymerase on the Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Strain 52145. Microorganisms, 11(3), 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030669





