New Lactones Produced by Streptomyces sp. SN5431 and Their Antifungal Activity against Bipolaris maydis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Experimental Procedures
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Isolation of Actinomycetes
2.4. Screening and Identification of Antagonistic Actinobacteria Strains
2.5. Extraction and Isolation
2.6. Microdilution Broth Assay
2.7. Mycelial Growth Inhibition Assay
3. Results
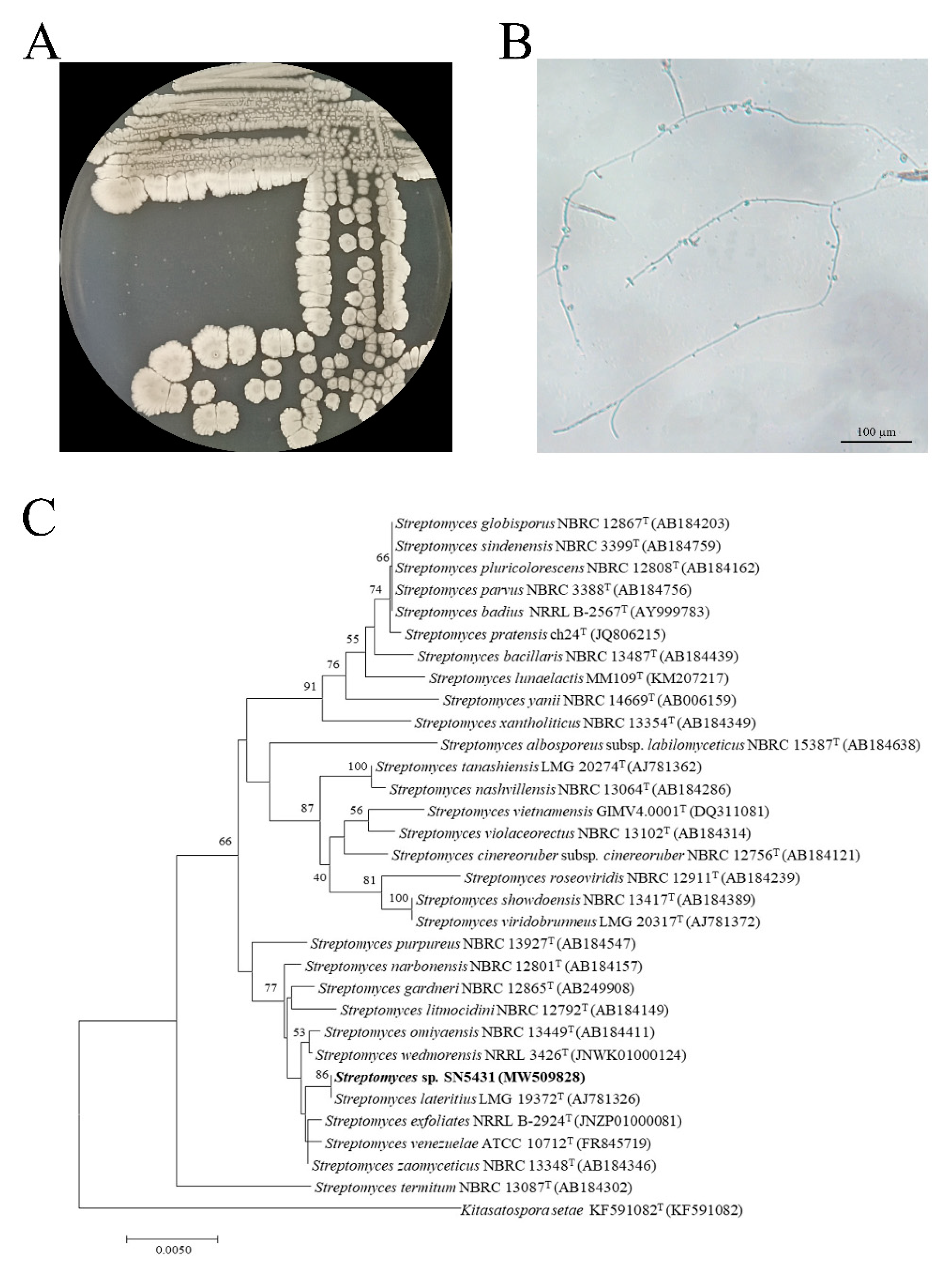
3.1. Isolation and Screening of Strain SN5431
3.2. Identification of Strain SN5431
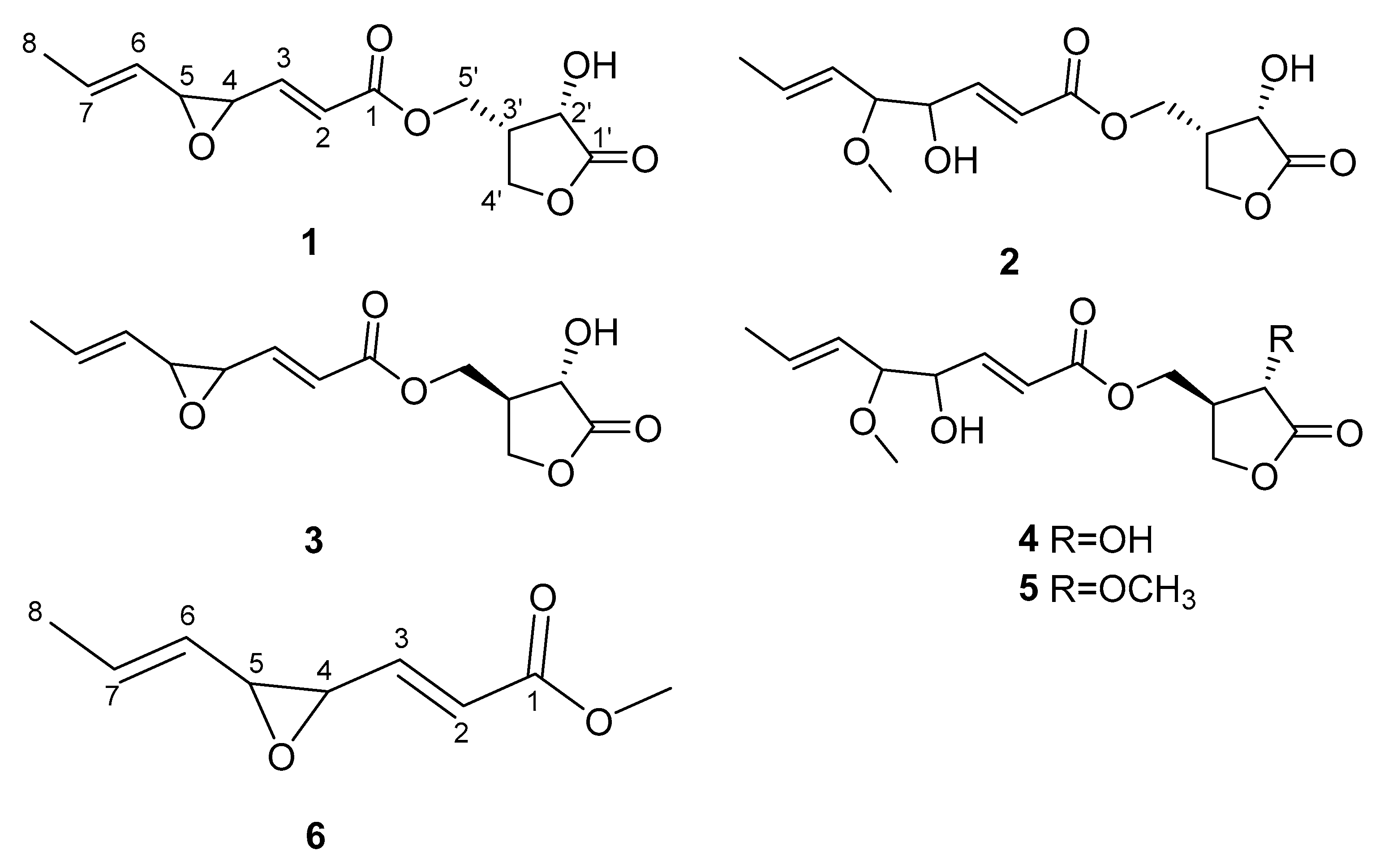
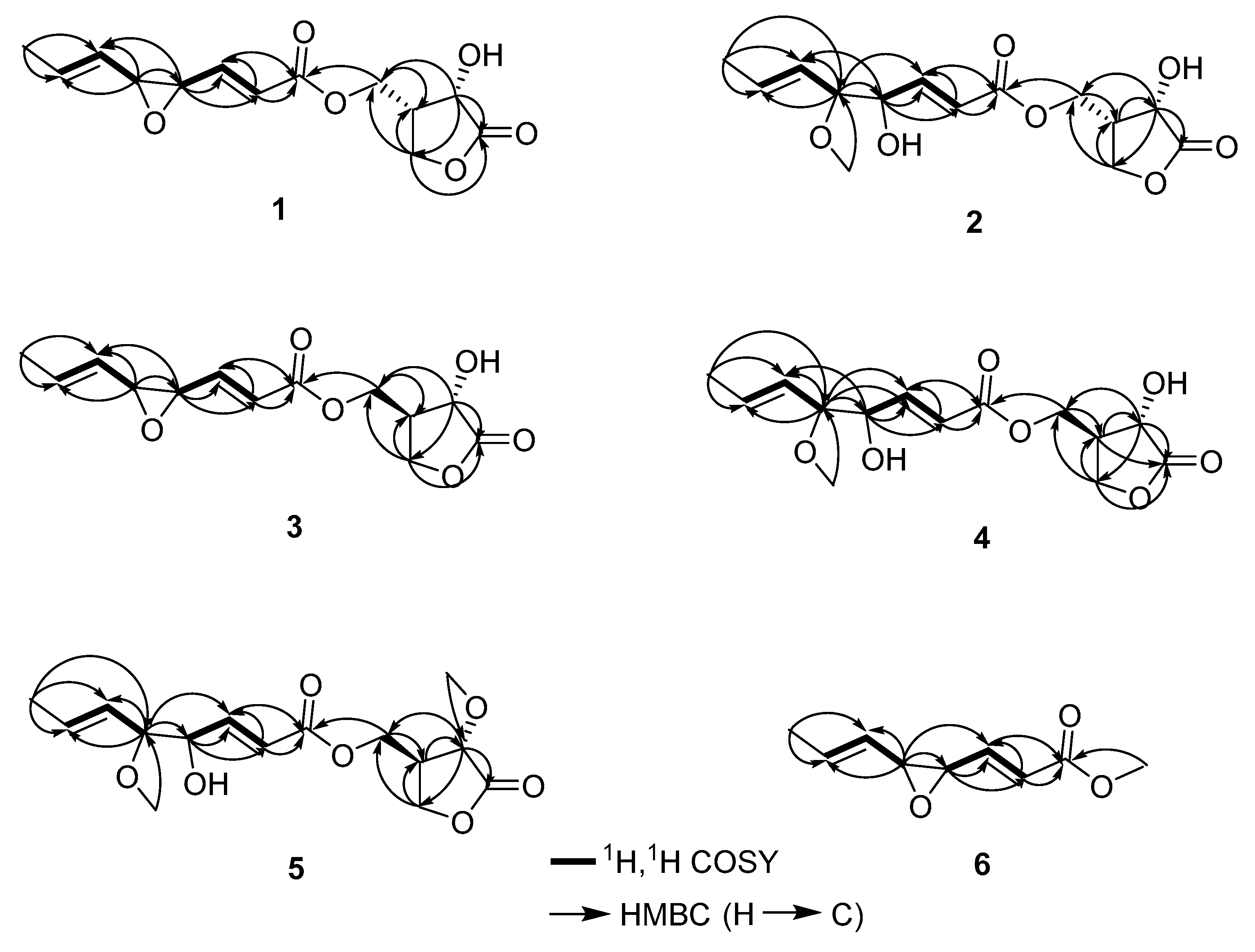
3.3. Structure Elucidation of Compounds
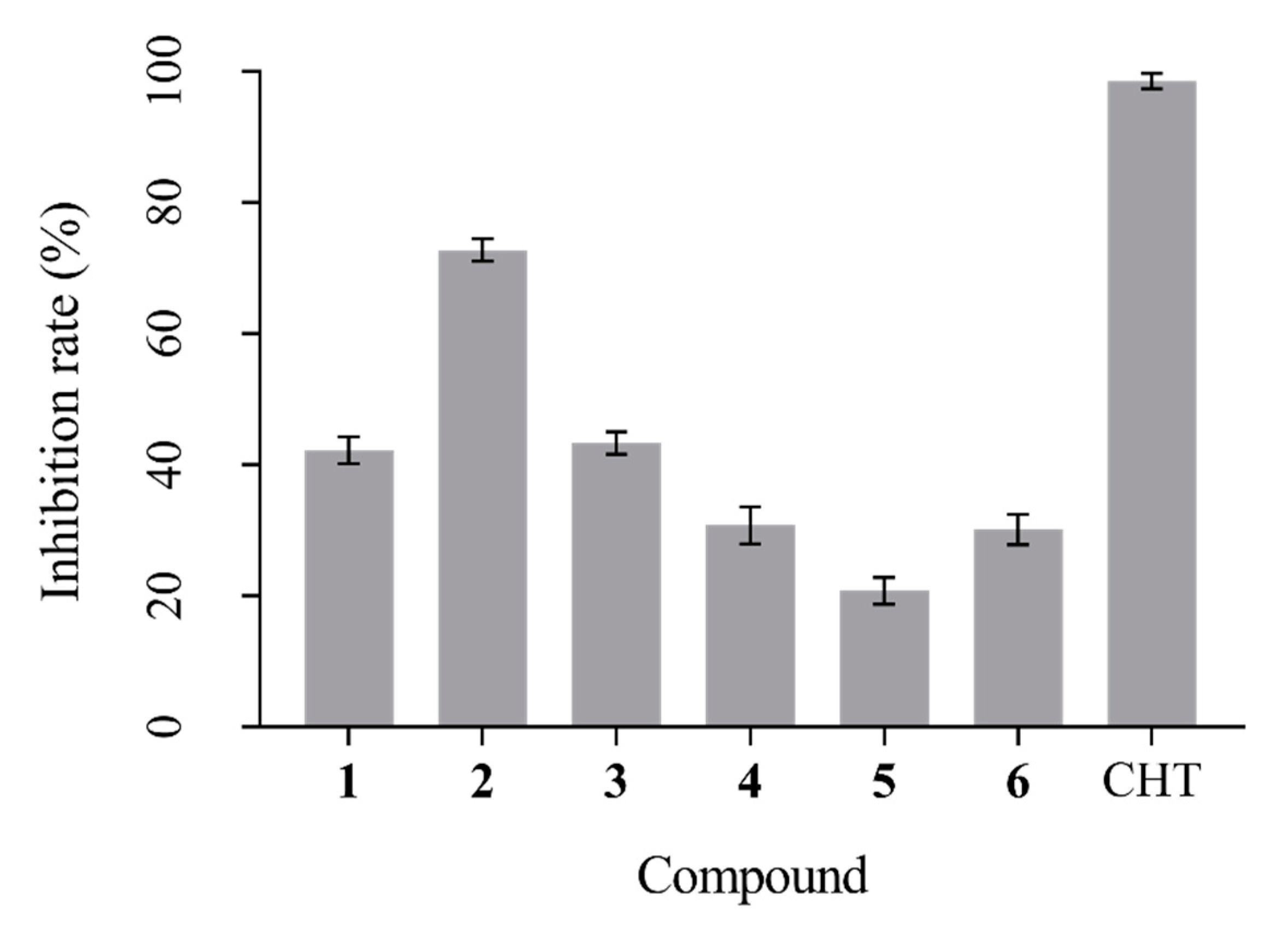
3.4. Antifungal Activity Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ullstrup, A.J. The impacts of the southern corn leaf blight epidemics of 1970–1971. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1972, 10, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Mao, X.W.; Wang, J.X.; Wu, L.Y.; Zhou, M.G.; Hou, Y.P. Activity of the dinitroaniline fungicide fluazinam against Bipolaris maydis. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 148, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzar, N.; Kashyap, A.S.; Maurya, A.; Rajawat, M.V.S.; Sharma, P.K.; Srivastava, A.K.; Roy, M.; Saxena, A.K.; Singh, H.V. Multi-Gene Phylogenetic Approach for Identification and Diversity Analysis of Bipolaris maydis and Curvularia lunata Isolates Causing Foliar Blight of Zea mays. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranum, P.; Peña-Rosas, J.P.; Garcia-Casal, M.N. Global maize production, utilization, and consumption. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1312, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.V.; Subbaiah, G.; Veeraraghavaiah, R. Agronomic responses of maize to plant population and nitrogen availability-a review. Int. J. Plant Anim. Environ. Sci. 2014, 4, 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Kong, L.X.; Qiu, D.W.; Francis, F.; Wang, S.C. Biocontrol potential and mode of action of entomopathogenic bacteria Xenorhabdus budapestensis C72 against Bipolaris maydis. Biol. Control 2021, 158, 104605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.X.; Li, X.; Li, B.; Xu, M.Q.; Qiu, L.Y. Disease and treatment of maize leaf spot. Sci. Technol. China Rural Prosper. 2010, 12, 54–55. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.L.; Gan, L.; Ruan, H.C.; Shi, N.N.; Du, Y.X.; Liao, L.; Wei, Z.X.; Teng, Z.Y.; Chen, F.R.; Yang, X.J. Sensitivity of Cochliobolus heterostrophus to three demethylation inhibitor fungicides, propiconazole, diniconazole and prochloraz, and their efficacy against southern corn leaf blight in Fujian Province, China. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 152, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhao, H.; Ren, W.C.; Lv, C.Y.; Chen, C.J. Resistance risk assessment for fludioxonil in Bipolaris maydis. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 139, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrázek, J.; Strosová, L.; Fliegerová, K.; Kott, T.; Kopecný, J. Diversity of insect intestinal microflora. Folia Microbiol. 2008, 53, 229–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, Y.L.; Callen, W.N.; Christoffersen, L.; Dupree, P.; Goubet, F.; Healey, S.; Hernández, M.; Keller, M.; Li, K.; Palackal, N.; et al. Unusual microbial xylanases from insect guts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 3609–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Y.H.; Yu, Z.G. Diterpenoids from Streptomyces sp. SN194 and their antifungal activity against Botrytis cinerea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8525–8529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.M.; Yang, J.S.; Peng, C.Z.; Caer, V.; Cong, P.Z.; Zou, Z.M.; Lu, Y.; Yang, S.Y.; Gu, Y.C. Lactones from Angiopteris caudatiformis. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, X.F.; Yang, C.J.; Morris-Natschke, S.L.; Li, J.C.; Yin, X.D.; Liu, Y.Q.; Guo, X.; Peng, J.W.; Goto, M.; Zhang, J.Y.; et al. Biologically active isoquinoline alkaloids covering 2014–2018. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 2212–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Y.H.; Gao, C.Z.; Yu, Z.G. Rhabdopeptides from Xenorhabdus budapestensis SN84 and their nematicidal activities against Meloidogyne incognita. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3833–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, T.; Welzel, K.; Pelzer, S.; Vente, A.; Wohlleben, W. Exploiting the genetic potential of polyketide producing streptomycetes. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 106, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Wang, M.; Tian, J.; Liu, J.; Guo, Z.Y.; Tang, W.; Chen, Y.H. Activation of paulomycin production by exogenous γ-butyrolactone signaling molecules in Streptomyces albidoflavus J1074. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, E. Gamma-butyrolactones: Streptomyces signalling molecules regulating antibiotic production and differentiation. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, E.; Nihira, T.; Hara, Y.; Jones, J.J.; Gershater, C.J.; Yamada, Y.; Bibb, M. Purification and structural determination of SCB1, a γ-butyrolactone that elicits antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 11010–11016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremenkova, O.V. A-factor-like autoregulators. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2016, 42, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, N.H.; Gottelt, M.; Takano, E. Chapter 6. Regulation of antibiotic production by bacterial hormones. Methods Enzymol. 2009, 458, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, N.H.; Nakayama, S.; Merlo, M.E.; Vries, M.; Bunet, R.; Kitani, S.; Nihira, T.; Takano, E. Analysis of two additional signaling molecules in Streptomyces coelicolor and the development of a butyrolactone-specific reporter system. Chem. Biol. 2009, 16, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, M.; Reiser, O. Synthetic approaches towards structurally diverse γ-butyrolactone natural-product-like compounds. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2005, 9, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.N.; Huang, X.Y.; Feng, Z.M.; Jiang, J.S.; Zhang, P.C. New butyrolactone type lignans from Arctii Fructus and their anti-inflammatory activities. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2015, 63, 7958–7966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, R.M. Handbook of microbiological media. Q. Rev. Biol. 2006, 2, 364–365. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.P.; Chen, Y.L.; Qu, X.P.; Wang, J.X.; Zhou, M.G. Effects of a novel SDHI fungicide pyraziflumid on the biology of the plant pathogenic fungi Bipolaris maydis. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 149, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.N.; Yang, D.; Bi, Y.H.; Yu, Z.G. Macrolides from Streptomyces sp. SN5452 and Their Antifungal Activity against Pyricularia oryzae. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.S.; An, R.; Zhang, W.B.; Zhang, G.L.; Yu, Z.G. Stilbene Derivatives from Photorhabdus temperata SN259 and Their Antifungal Activities against Phytopathogenic Fungi. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiewe, H.J.; Zeeck, A. Cineromycins, γ-butyrolactones and ansamycins by analysis of the secondary metabolite pattern created by a single strain of Streptomyces. J. Antibiot. 1999, 52, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, T.; Kinoshita, T. Stereoselective synthesis and structure of butalactin and lactone II isolated from Streptomyces species. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 2777–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueki, T.; Morimoto, Y.; Kinoshita, T. Synthesis and absolute configuration of lactone II isolated from Streptomyces sp. Go 40/10. Chem. Commun. 2001, 18, 1820–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzhingi, T.; Yeum, K.J.; Russell, R.M.; Johnson, E.J.; Qin, J.; Tang, G. Determination of carotenoids in yellow maize, the effects of saponification and food preparations. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2008, 78, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Gan, L.; Ruan, H.; Shi, N.; Du, Y.; Chen, F.; Yang, X. Characterization of Natural Isolates of Bipolaris maydis Associated with Mating Types, Genetic Diversity, and Pathogenicity in Fujian Province, China. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.P.; Chen, Y.L.; Wu, L.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Chen, C.J.; Zhou, M.G. Baseline sensitivity of Bipolaris maydis to the novel succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor benzovindiflupyr and its efficacy. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 149, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.N.; Yao, Z.L.; Yang, D.; Ke, J.; Wu, Q.L.; Li, J.K.; Zhou, X.D. Chemical Constituents from Fraxinus hupehensis and Their Antifungal and Herbicidal Activities. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, G.; Daisy, B.; Castillo, U.; Harper, J. Natural products from endophytic microorganisms. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Position | δH, Mult (J in Hz) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 1-OCH3 | 3.75 s (1.3) | |||||
| 2 | 6.08 d (15.6) | 6.09 dd (15.7, 1.9) | 6.13 dd (15.7, 0.7) | 6.12 dd (15.7, 1.9) | 6.10 dd (15.7, 1.8) | 6.13 dd (16.2, 1.8) |
| 3 | 6.71 dd (15.7, 6.7) | 6.96 dd (15.7, 4.3) | 6.78 dd (15.7, 6.6) | 7.00 dd (15.7, 0.7) | 6.97 dd (15.7, 4.4) | 6.96 dd (15.8, 4.6) |
| 4 | 3.35 dd (6.6, 1.4) | 4.29 overlap | 3.37 m | 4.33 overlap | 4.33 overlap | 4.34 dd (4.4, 1.7) |
| 5 | 3.28 m | 3.66 m | 3.28 dd (8.6, 1.8) | 3.65 dd (8.4, 4.6) | 3.65 m | 4.19 m |
| 5-OCH3 | 3.29 s | 3.28 s | 3.29 s | |||
| 6 | 5.22 m | 5.35 m | 5.23 m | 5.33 m | 5.34 m | 5.51 m |
| 7 | 5.98 dq (15.4, 6.6) | 5.80 m | 5.99 dq (15.4, 6.5) | 5.79 m | 5.79 m | 5.82 m |
| 8 | 1.75 dd (6.7, 1.6) | 1.76 dd (6.5, 1.5) | 1.76 dd (6.6, 1.6) | 1.76 dd (6.5, 1.6) | 1.76 dd (6.5, 1.4) | 1.74 m |
| 2′ | 4.58 d (8.0) | 4.57 d (8.0) | 4.34 overlap | 4.33 overlap | 4.33 overlap | |
| 2′-OCH3 | 3.81 s | |||||
| 3′ | 2.98 m | 2.98 d (1.7) | 2.87 m | 2.86 m | 2.45 m | |
| 4′α | 4.35 overlap | 4.29 overlap | 4.44 overlap | 4.05 t (9.8) | 4.33 overlap | |
| 4′β | 4.45 dd (11.6, 3.9) | 4.47 dd (11.6, 4.0) | 4.04 dd (10.1, 9.6) | 4.04 dd (10.1, 9.6) | 3.76 dd (13.2, 6.6) | |
| 5′α | 4.35 overlap | 4.37 m | 4.44 overlap | 4.33 overlap | 4.33 overlap | |
| 5′β | 4.35 overlap | 4.37 m | 4.34 overlap | 4.41 dd (8.6, 1.8) | 4.33 overlap | |
| Position | δC, Type | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 1 | 165.3 qC | 166.0 qC | 165.3 qC | 166.0 qC | 166.4 qC | 166.7 qC |
| 1-OCH3 | 51.7 CH3 | |||||
| 2 | 122.2 CH | 120.8 CH | 122.1 CH | 120.6 CH | 121.3 CH | 122.1 CH |
| 3 | 145.7 CH | 147.5 CH | 145.8 CH | 147.7 CH | 146.9 CH | 145.7 CH |
| 4 | 57.8 CH | 72.8 CH2 | 57.7 CH | 72.8 CH2 | 72.9 CH2 | 73.7 CH |
| 5 | 61.4 CH | 84.6 CH | 61.5 CH | 84.6 CH | 84.6 CH | 75.2 CH |
| 5-OCH3 | 56.4 CH3 | 56.3 CH3 | 56.3 CH3 | |||
| 6 | 127.1 CH | 126.4 CH | 127.0 CH | 126.4 CH | 126.5 CH | 128.3 CH |
| 7 | 133.0 CH | 132.9 CH | 133.2 CH | 133.0 CH | 132.9 CH | 130.7 CH |
| 8 | 17.9 CH3 | 17.9 CH3 | 17.9 CH3 | 17.9 CH3 | 17.9 CH3 | 17.9 CH3 |
| 1′ | 176.5 qC | 176.4 qC | 176.4 qC | 176.5 qC | 174.8 qC | |
| 2′ | 67.5 CH | 67.7 CH | 68.9 CH | 68.8 CH | 69.9 CH | |
| 2′-OCH3 | 52.8 CH3 | |||||
| 3′ | 38.9 CH | 39.0 CH | 43.2 CH | 43.3 CH | 43.5 CH | |
| 4′ | 61.0 CH2 | 60.8 CH2 | 66.8 CH2 | 66.8 CH2 | 60.0 CH2 | |
| 5′ | 67.8 CH2 | 67.8 CH2 | 61.7 CH2 | 61.5 CH2 | 62.2 CH2 | |
| Compound | EC50, µg/mL (±SD) |
|---|---|
| Tiuslactone A, 1 | >150 |
| Tiuslactone B, 2 | 95.31 ± 2.09 |
| Tiuslactone C, 3 | >150 |
| Tiuslactone D, 4 | >150 |
| Tiuslactone E, 5 | >150 |
| Tiusester, 6 | >150 |
| Chlorothalonil a | 3.20 ± 0.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Yu, Z. New Lactones Produced by Streptomyces sp. SN5431 and Their Antifungal Activity against Bipolaris maydis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030616
Wang Y, Yang D, Yu Z. New Lactones Produced by Streptomyces sp. SN5431 and Their Antifungal Activity against Bipolaris maydis. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(3):616. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030616
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yinan, Di Yang, and Zhiguo Yu. 2023. "New Lactones Produced by Streptomyces sp. SN5431 and Their Antifungal Activity against Bipolaris maydis" Microorganisms 11, no. 3: 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030616
APA StyleWang, Y., Yang, D., & Yu, Z. (2023). New Lactones Produced by Streptomyces sp. SN5431 and Their Antifungal Activity against Bipolaris maydis. Microorganisms, 11(3), 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030616






