Assessing the Effects of Rotifer Feed Enrichments on Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Larvae and Post-Larvae Gut-Associated Bacterial Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Larviculture
2.2. Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
2.3. High-Throughput Sequencing Data Acquisition
2.4. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manickam, N.; Bhavan, P.S.; Santhanam, P.; Muralisankar, T. Influence of Wild Mixed Zooplankton on Growth and Muscle Biochemical Composition of the Freshwater Prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii Post Larvae. Aquaculture 2020, 522, 735110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadstein, O.; Bergh, Ø.; Gatesoupe, F.; Galindo-Villegas, J.; Mulero, V.; Picchietti, S.; Scapigliati, G.; Makridis, P.; Olsen, Y.; Dierckens, K. Microbiology and Immunology of Fish Larvae. Rev. Aquac. 2013, 5, S1–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-S.; O’Bryen, P.J.; Marcus, N.H. Copepods in Aquaculture; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; ISBN 0470276304. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, C.; Shao, L.; Ricketts, A.; Moorhead, J. The Importance of Copepods as Live Feed for Larval Rearing of the Green Mandarin Fish Synchiropus splendidus. Aquaculture 2018, 491, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haché, R.; Plante, S. The Relationship between Enrichment, Fatty Acid Profiles and Bacterial Load in Cultured Rotifers (Brachionus plicatilis L-Strain) and Artemia (Artemia salina strain Franciscana). Aquaculture 2011, 311, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koven, W.M.; Tandler, A.; Kissil, G.W.; Sklan, D.; Friezlander, O.; Harel, M. The Effect of Dietary (N− 3) Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Growth, Survival and Swim Bladder Development in Sparus aurata Larvae. Aquaculture 1990, 91, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.G.; Castell, J.D.; Tocher, D.R.; MacDonald, F.M.; Sargent, J.R. Effects of Different Dietary Arachidonic Acid: Docosahexaenoic Acid Ratios on Phospholipid Fatty Acid Compositions and Prostaglandin Production in Juvenile Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 1995, 14, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent, J.; Bell, G.; McEvoy, L.; Tocher, D.; Estevez, A. Recent Developments in the Essential Fatty Acid Nutrition of Fish. Aquaculture 1999, 177, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, W.-L.; Turchini, G.M.; Teoh, C.-Y.; Ng, W.-K. Dietary Arachidonic Acid and the Impact on Growth Performance, Health and Tissues Fatty Acids in Malabar Red Snapper (Lutjanus malabaricus) Fingerlings. Aquaculture 2020, 519, 734757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, P.M.; van Someren Gréve, H.; Jørgensen, K.N.; Kjær, K.G.W.; Hansen, B.W. Evaluation of High-Density Tank Cultivation of the Live-Feed Cyclopoid Copepod Apocyclops royi (Lindberg 1940). Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drillet, G.; Frouël, S.; Sichlau, M.H.; Jepsen, P.M.; Højgaard, J.K.; Joarder, A.K.; Hansen, B.W. Status and Recommendations on Marine Copepod Cultivation for Use as Live Feed. Aquaculture 2011, 315, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, A.; McEvoy, L.A.; Bell, J.G.; Sargent, J.R. Growth, Survival, Lipid Composition and Pigmentation of Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Larvae Fed Live-Prey Enriched in Arachidonic and Eicosapentaenoic Acids. Aquaculture 1999, 180, 321–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, L.E.C.; Yúfera, M.; Makridis, P.; Morais, S.; Dinis, M.T. Live Feeds for Early Stages of Fish Rearing. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 613–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, J.H. Use of Borage Oil in Rotifer Production and Artemia Enrichment: Effect on Growth and Survival of Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Larvae. Aquaculture 1998, 161, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches-Fernandes, G.M.M.; Califano, G.; Castanho, S.; Soares, F.; Ribeiro, L.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Mata, L.; Costa, R. Effects of Live Feed Manipulation with Algal-Derived Antimicrobial Metabolites on Fish Larvae Microbiome Assembly: A Molecular-Based Assessment. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 1062–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alvise, P.W.; Lillebø, S.; Prol-Garcia, M.J.; Wergeland, H.I.; Nielsen, K.F.; Bergh, Ø.; Gram, L. Phaeobacter gallaeciensis Reduces Vibrio anguillarum in Cultures of Microalgae and Rotifers, and Prevents Vibriosis in Cod Larvae. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; Shields, R.J.; Birkbeck, T.H. Bacterial Influences on Atlantic Halibut Hippoglossus hippoglossus Yolk Sac Larval Survival and Start Feed Response. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2003, 56, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagadec, E.; Småge, S.B.; Trösse, C.; Nylund, A. Phylogenetic Analyses of Norwegian Tenacibaculum Strains Confirm High Bacterial Diversity and Suggest Circulation of Ubiquitous Virulent Strains. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, R.J. Larviculture of Marine Finfish in Europe. Aquaculture 2001, 200, 55–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.K.; Falk-Petersen, I.B. Effects of Egg Disinfection and Incubation Temperature on Early Life Stages of Spotted Wolffish. Aquac. Int. 2001, 9, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, A.C.; Belmonte, G. Disinfection Efficacy on Cyst Viability of Artemia franciscana (Crustacea), Hexarthra fennica (Rotifera) and Fabrea salina (Ciliophora). Mar. Biol. 2003, 142, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attramadal, K.J.K.; Salvesen, I.; Xue, R.; Øie, G.; Størseth, T.R.; Vadstein, O.; Olsen, Y. Recirculation as a Possible Microbial Control Strategy in the Production of Marine Larvae. Aquac. Eng. 2012, 46, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakke, I.; Coward, E.; Andersen, T.; Vadstein, O. Selection in the Host Structures the Microbiota Associated with Developing Cod Larvae (Gadus morhua). Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3914–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minich, J.J.; Nowak, B.; Elizur, A.; Knight, R.; Fielder, S.; Allen, E.E. Impacts of the Marine Hatchery Built Environment, Water and Feed on Mucosal Microbiome Colonization across Ontogeny in Yellowtail Kingfish, Seriola lalandi. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 676731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkes Walburn, J.; Wemheuer, B.; Thomas, T.; Copeland, E.; O’Connor, W.; Booth, M.; Fielder, S.; Egan, S. Diet and Diet-Associated Bacteria Shape Early Microbiome Development in Yellowtail Kingfish (Seriola lalandi). Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawls, J.F.; Mahowald, M.A.; Ley, R.E.; Gordon, J.I. Reciprocal Gut Microbiota Transplants from Zebrafish and Mice to Germ-Free Recipients Reveal Host Habitat Selection. Cell 2006, 127, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullam, K.E.; Essinger, S.D.; Lozupone, C.A.; O’CONNOR, M.P.; Rosen, G.L.; Knight, R.O.B.; Kilham, S.S.; Russell, J.A. Environmental and Ecological Factors That Shape the Gut Bacterial Communities of Fish: A Meta-analysis. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 3363–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Bäckhed, F.; Fulton, L.; Gordon, J.I. Diet-Induced Obesity Is Linked to Marked but Reversible Alterations in the Mouse Distal Gut Microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakke, I.; Skjermo, J.; Vo, T.A.; Vadstein, O. Live Feed Is Not a Major Determinant of the Microbiota Associated with Cod Larvae (Gadus morhua). Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.K. Role of Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Fish. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1553–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olafsen, J.A. Interactions between Fish Larvae and Bacteria in Marine Aquaculture. Aquaculture 2001, 200, 223–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of General 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene PCR Primers for Classical and Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Diversity Studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornung, B.V.H.; Zwittink, R.D.; Kuijper, E.J. Issues and Current Standards of Controls in Microbiome Research. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5-6 ed. 2019. R package. 2020.
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Found. Stat. Comput. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madden, T. The BLAST Sequence Analysis Tool; NCBI Handbook Bethesda (MD); National Center for Biotechnology Information (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Schwartz, S.; Wagner, L.; Miller, W. A Greedy Algorithm for Aligning DNA Sequences. J. Comput. Biol. 2000, 7, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quero, G.M.; Piredda, R.; Basili, M.; Maricchiolo, G.; Mirto, S.; Manini, E.; Seyfarth, A.M.; Candela, M.; Luna, G.M. Host-Associated and Environmental Microbiomes in an Open-Sea Mediterranean Gilthead Sea Bream Fish Farm. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, D.F.R.; Swierts, T.; Coelho, F.J.R.C.; Polónia, A.R.M.; Huang, Y.M.; Ferreira, M.R.S.; Putchakarn, S.; Carvalheiro, L.; van der Ent, E.; Ueng, J.-P. The Sponge Microbiome within the Greater Coral Reef Microbial Metacommunity. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schryver, P.; Vadstein, O. Ecological Theory as a Foundation to Control Pathogenic Invasion in Aquaculture. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2360–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, M.; Li, B.; Rong, X.; Chen, G. Responses of Microbial Community Structure in Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Larval Intestine to the Regulation of Probiotic Introduced through Live Feed. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmann, K.K.; Rasmussen, B.B.; Melchiorsen, J.; Sonnenschein, E.C.; Gram, L.; Bentzon-Tilia, M. Changes in the Microbiome of Mariculture Feed Organisms after Treatment with a Potentially Probiotic Strain of Phaeobacter inhibens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00499-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Ge, M.; Zheng, X.; Tao, Z.; Zhou, S.; Wang, G. Investigation of Vibrio alginolyticus, V. Harveyi, and V. Parahaemolyticus in Large Yellow Croaker, Pseudosciaena crocea (Richardson) Reared in Xiangshan Bay, China. Aquac. Rep. 2016, 3, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Al-saari, N.; Mohamad, A.; Mursidi, F.-A.; Mohd-Aris, A.; Amal, M.N.A.; Kasai, H.; Mino, S.; Sawabe, T.; Zamri-Saad, M. Vibriosis in Fish: A Review on Disease Development and Prevention. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2019, 31, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, H.I.; Treasurer, J.W.; Adam, B.; Birkbeck, T.H. Analysis of Bacterial Populations in the Gut of Developing Cod Larvae and Identification of Vibrio logei, Vibrio anguillarum and Vibrio splendidus as Pathogens of Cod Larvae. Aquaculture 2009, 288, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, O.; Gutiérrez, M.S.; Caruffo, M.; Valderrama, B.; Medina, D.A.; García, K.; Reyes-Jara, A.; Toro, M.; Feijóo, C.G.; Navarrete, P. Probiotic Yeasts and Vibrio anguillarum Infection Modify the Microbiome of Zebrafish Larvae. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanho, S.; Califano, G.; Soares, F.; Costa, R.; Mata, L.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Ribeiro, L. The Effect of Live Feeds Bathed with the Red Seaweed Asparagopsis armata on the Survival, Growth and Physiology Status of Sparus aurata Larvae. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Song, T.; Lu, J.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. Shrimp AHPND Causing Vibrio anguillarum Infection: Quantitative Diagnosis and Identifying Antagonistic Bacteria. Mar. Biotechnol. 2021, 23, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porsby, C.H.; Nielsen, K.F.; Gram, L. Phaeobacter and Ruegeria Species of the Roseobacter Clade Colonize Separate Niches in a Danish Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus)-Rearing Farm and Antagonize Vibrio anguillarum under Different Growth Conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 7356–7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, F.; Yasir, M.; Al-Sofyani, A.; Naseer, M.I.; Azhar, E.I. Antimicrobial Activity of Bacteria from Marine Sponge Suberea mollis and Bioactive Metabolites of Vibrio sp. EA348. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.; Coelho, F.J.R.C.; Cleary, D.F.R.; Pires, A.C.C.; Marques, B.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Quintino, V.; Gomes, N.C.M. Seasonal Patterns of Bacterioplankton Composition in a Semi-Intensive European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Aquaculture System. Aquaculture 2018, 490, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, D.; Perez-Losada, M.; Severino, R.; Cable, J.; Xavier, R. Characterization of the Skin and Gill Microbiomes of the Farmed Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and Seabream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture 2019, 500, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedashkovskaya, O.I.; Vancanneyt, M.; Kim, S.B.; Zhukova, N. V Winogradskyella echinorum sp. nov., a Marine Bacterium of the Family Flavobacteriaceae Isolated from the Sea Urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 1465–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Sun, F.; Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, G.; Lai, Q.; Luo, J.; Shao, Z. Meridianimaribacter flavus gen. nov., sp. nov., a Member of the Family Flavobacteriaceae Isolated from Marine Sediment of the South China Sea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Blain, S.; Crispi, O.; Rembauville, M.; Obernosterer, I. Seasonal Dynamics of Prokaryotes and Their Associations with Diatoms in the Southern Ocean as Revealed by an Autonomous Sampler. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 3968–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhuo, X.; Chen, Y.-L.; He, C.; Zheng, Q.; Lin, T.-H.; Sun, J.; Guo, W.; Shi, Q.; et al. Microbial Transformation of Distinct Exogenous Substrates into Analogous Composition of Recalcitrant Dissolved Organic Matter. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 2389–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.-H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Lee, M.-H.; Oh, T.-K.; Yoon, J.-H. Paraperlucidibaca baekdonensis gen. nov., sp. nov., Isolated from Seawater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levican, A.; Fisher, J.C.; McLellan, S.L.; Avendaño-Herrera, R. Microbial Communities Associated with Farmed Genypterus chilensis: Detection in Water Prior to Bacterial Outbreaks Using Culturing and High-Throughput Sequencing. Animals 2020, 10, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoina, E.; Doulgeraki, A.I.; Miliou, H.; Nychas, G.-J.E. Dynamics of Water and Biofilm Bacterial Community Composition in a Mediterranean Recirculation Aquaculture System. Aquac. J. 2022, 2, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Ji, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, T.; Li, Z.; Li, B.; Shi, X.; Zhang, X.-H. Litoribacillus peritrichatus gen. nov., sp. nov., Isolated from Coastal Sediment of an Amphioxus Breeding Zone in Qingdao, China. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2013, 103, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Jia, Q.; Li, T.; Dai, S.; Wu, H.; He, H.; Fan, J.; Xiang, W.; Li, X. Bacterioplanes sanyensis Gen. Nov., sp. nov., a PHB-Accumulating Bacterium Isolated from a Pool of Spirulina platensis Cultivation. Arch. Microbiol. 2014, 196, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedlund, B.P.; Staley, J.T. Phylogeny of the Genus Simonsiella and Other Members of the Neisseriaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aujoulat, F.; Mazuet, C.; Criscuolo, A.; Popoff, M.R.; Enault, C.; Diancourt, L.; Jumas-Bilak, E.; Lavigne, J.-P.; Marchandin, H. Peptoniphilus nemausensis sp. Nov. A New Gram-Positive Anaerobic Coccus Isolated from Human Clinical Samples, an Emendated Description of the Genus Peptoniphilus and an Evaluation of the Taxonomic Status of Peptoniphilus Species with Not Validly Published. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 44, 126235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdoch, D.A.; Collins, M.D.; Willems, A.; Hardie, J.M.; Young, K.A.; Magee, J.T. Description of Three New Species of the Genus Peptostreptococcus from Human Clinical Specimens: Peptostreptococcus harei sp. Nov., Peptostreptococcus ivorii sp. nov., and Peptostreptococcus octavius sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1997, 47, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, J.S.; Whitman, W.B. Phylogenomic Analyses of a Clade within the Roseobacter Group Suggest Taxonomic Reassignments of Species of the Genera Aestuariivita, Citreicella, Loktanella, Nautella, Pelagibaca, Ruegeria, Thalassobius, Thiobacimonas and Tropicibacter, and the Proposal. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 2393–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchan, A.; González, J.M.; Moran, M.A. Overview of the Marine Roseobacter Lineage. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5665–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnenschein, E.C.; Jimenez, G.; Castex, M.; Gram, L. The Roseobacter-Group Bacterium Phaeobacter as a Safe Probiotic Solution for Aquaculture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 87, e02581-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curé, K.; Gajardo, G.; Coutteau, P. The Effect of DHA/EPA Ratio in Live Feed on the Fatty Acid Composition, Survival, Growth and Pigmentation of Turbot larvae Scophthalmus maximus L. In Improvement of the Commercial Production of Marine Aquaculture Species: Proceedings of a Workshop on Fish and Mollusc Larviculture; Impresora Creces: Santiago, Chile, 1996; pp. 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Aydın, İ.; Öztürk, R.Ç.; Küçük, E.; Polat, H.; Altınok, İ. Temperature Appeared to Be an Effective Factor on Growth Performance of Diploid and Triploid Turbot, Scophthalmus maximus, during the Early Life Stage. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintz, C.; Mair, W. You Are What You Host: Microbiome Modulation of the Aging Process. Cell 2014, 156, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
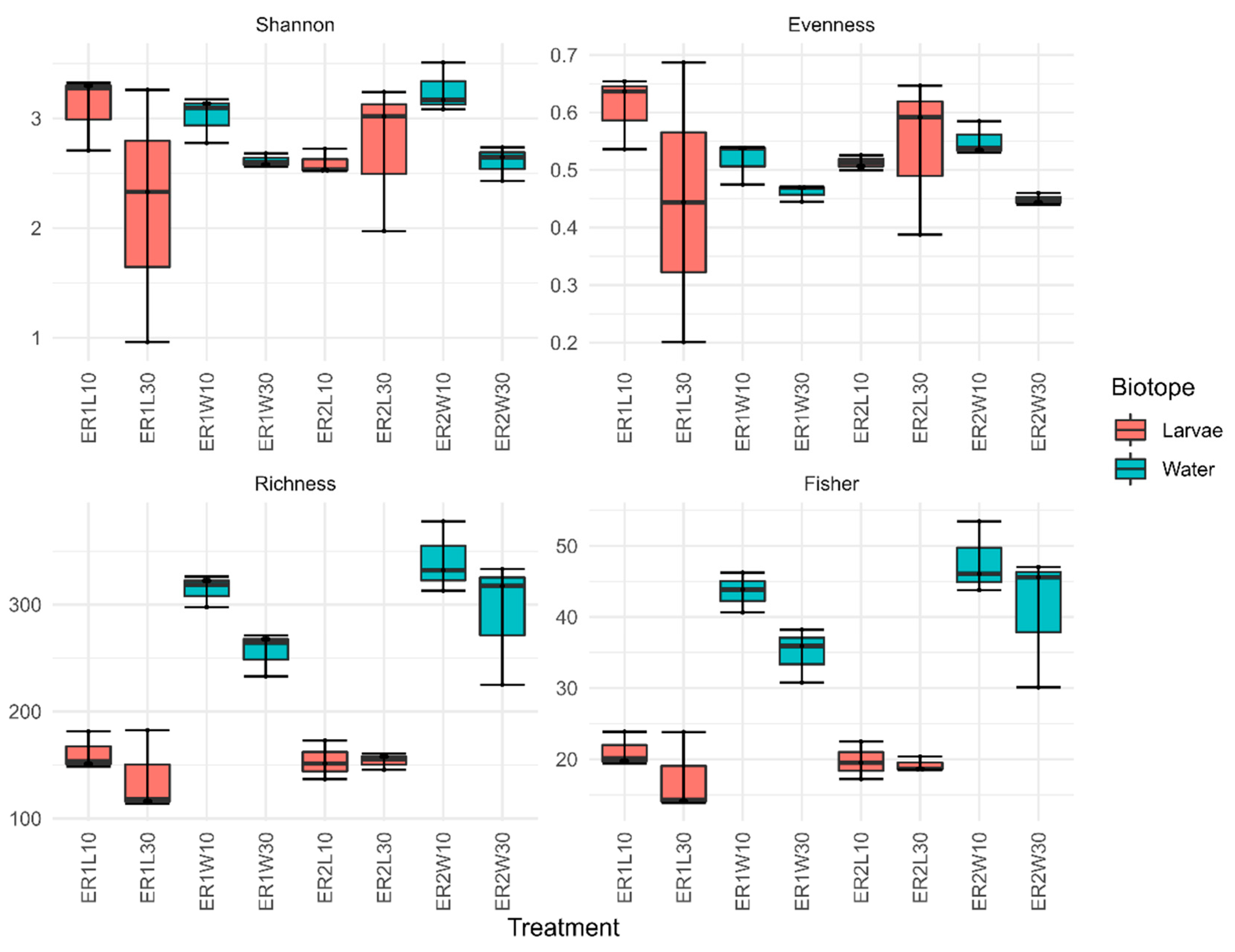


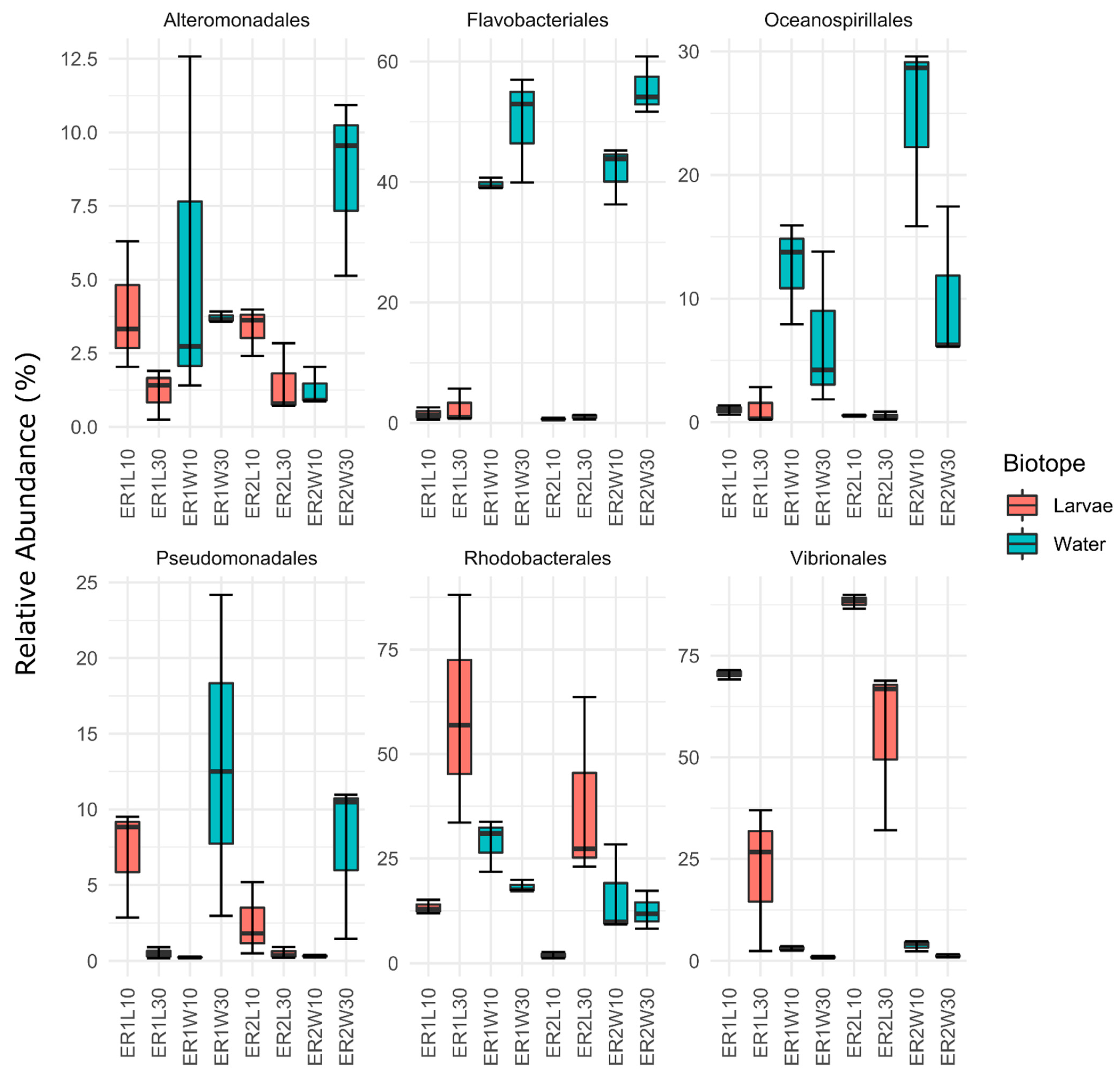
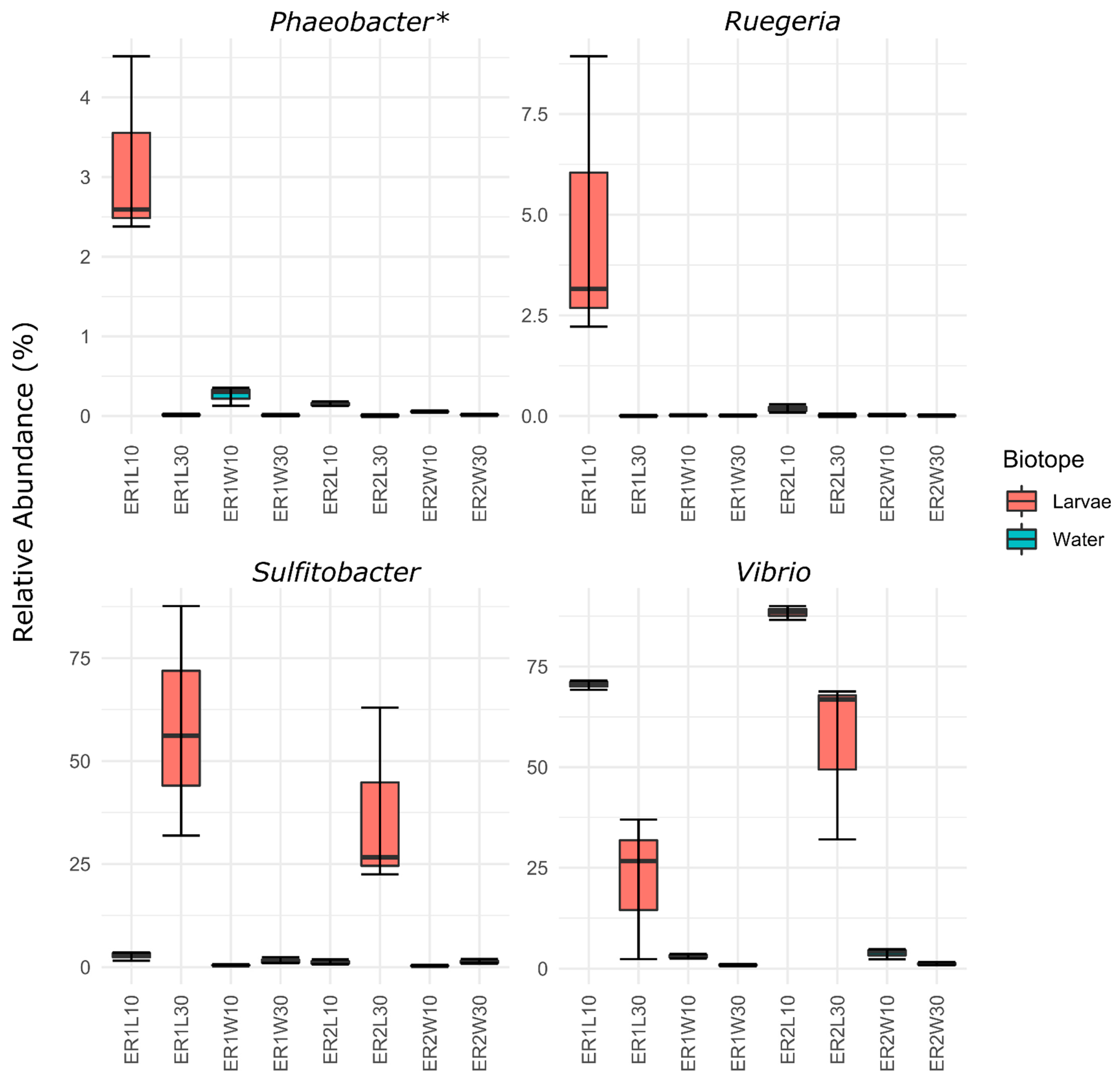
| Factor | F1,23 | R2 | P | FDR-P | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diet | 2.4999 | 0.02844 | 0.037 | 0.432 | * |
| Biotope | 25.7843 | 0.29331 | 0.001 | 0.002 | ** |
| Age | 19.0044 | 0.21619 | 0.001 | 0.002 | ** |
| Diet:Biotope | 2.0005 | 0.02276 | 0.064 | 0.064 | ns |
| Diet:Age | 3.0973 | 0.03523 | 0.010 | 0.015 | * |
| Biotope:age | 16.5838 | 0.18865 | 0.001 | 0.002 | ** |
| Diet:Biotope:Age | 2.9368 | 0.03341 | 0.011 | 0.015 | * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Louvado, A.; Castro, C.; Silva, D.A.M.; Oliveira, V.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Cleary, D.F.R.; Gomes, N.C.M. Assessing the Effects of Rotifer Feed Enrichments on Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Larvae and Post-Larvae Gut-Associated Bacterial Communities. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020520
Louvado A, Castro C, Silva DAM, Oliveira V, Conceição LEC, Cleary DFR, Gomes NCM. Assessing the Effects of Rotifer Feed Enrichments on Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Larvae and Post-Larvae Gut-Associated Bacterial Communities. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(2):520. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020520
Chicago/Turabian StyleLouvado, Antonio, Carolina Castro, Davide A. M. Silva, Vanessa Oliveira, Luís E. C. Conceição, Daniel F. R. Cleary, and Newton C. M. Gomes. 2023. "Assessing the Effects of Rotifer Feed Enrichments on Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Larvae and Post-Larvae Gut-Associated Bacterial Communities" Microorganisms 11, no. 2: 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020520
APA StyleLouvado, A., Castro, C., Silva, D. A. M., Oliveira, V., Conceição, L. E. C., Cleary, D. F. R., & Gomes, N. C. M. (2023). Assessing the Effects of Rotifer Feed Enrichments on Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Larvae and Post-Larvae Gut-Associated Bacterial Communities. Microorganisms, 11(2), 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020520






