Clonal Flux and Spread of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Meat and Its Genetic Relatedness to Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Patients in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Ethical Approval
2.3. Identification and Confirmation of S. aureus and MRSA Isolates
2.4. Culture-Based Method
2.5. Molecular-Based Methods
2.6. Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
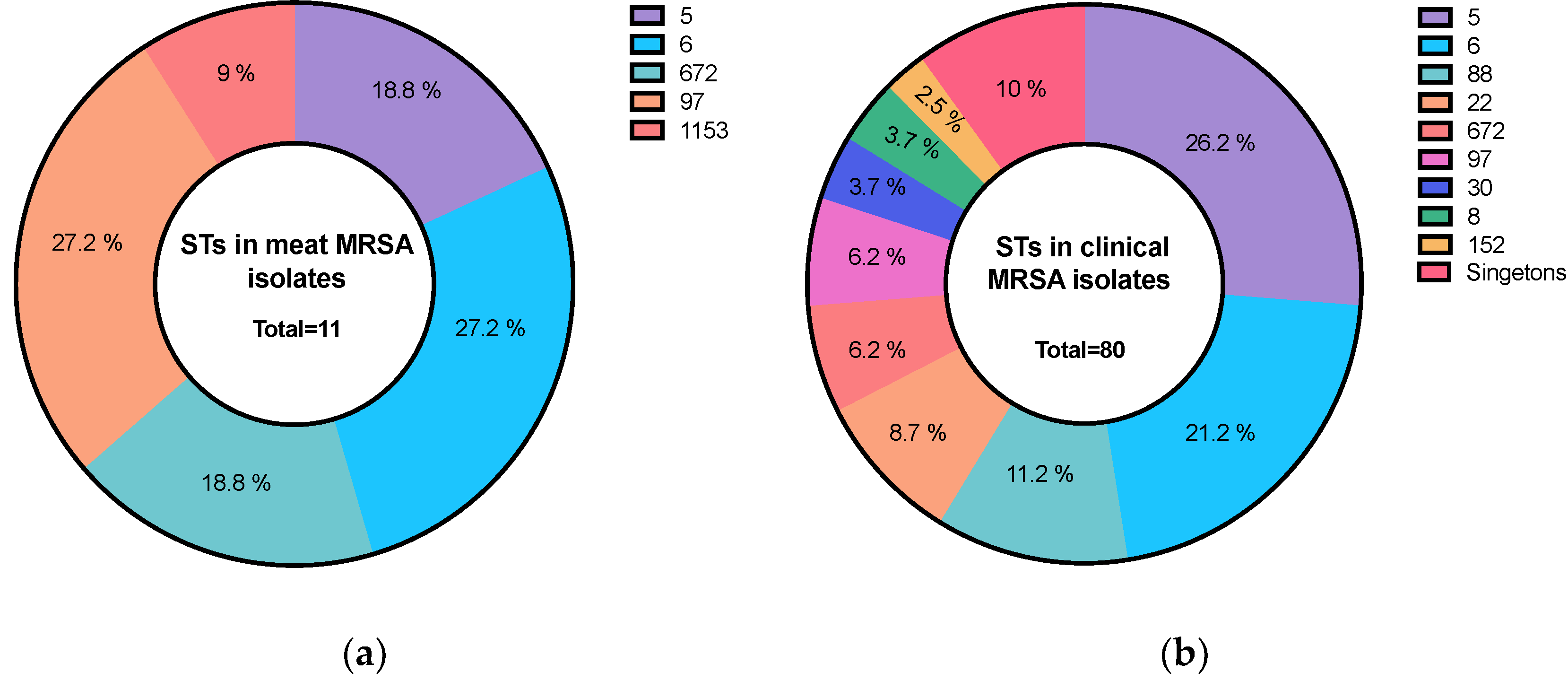
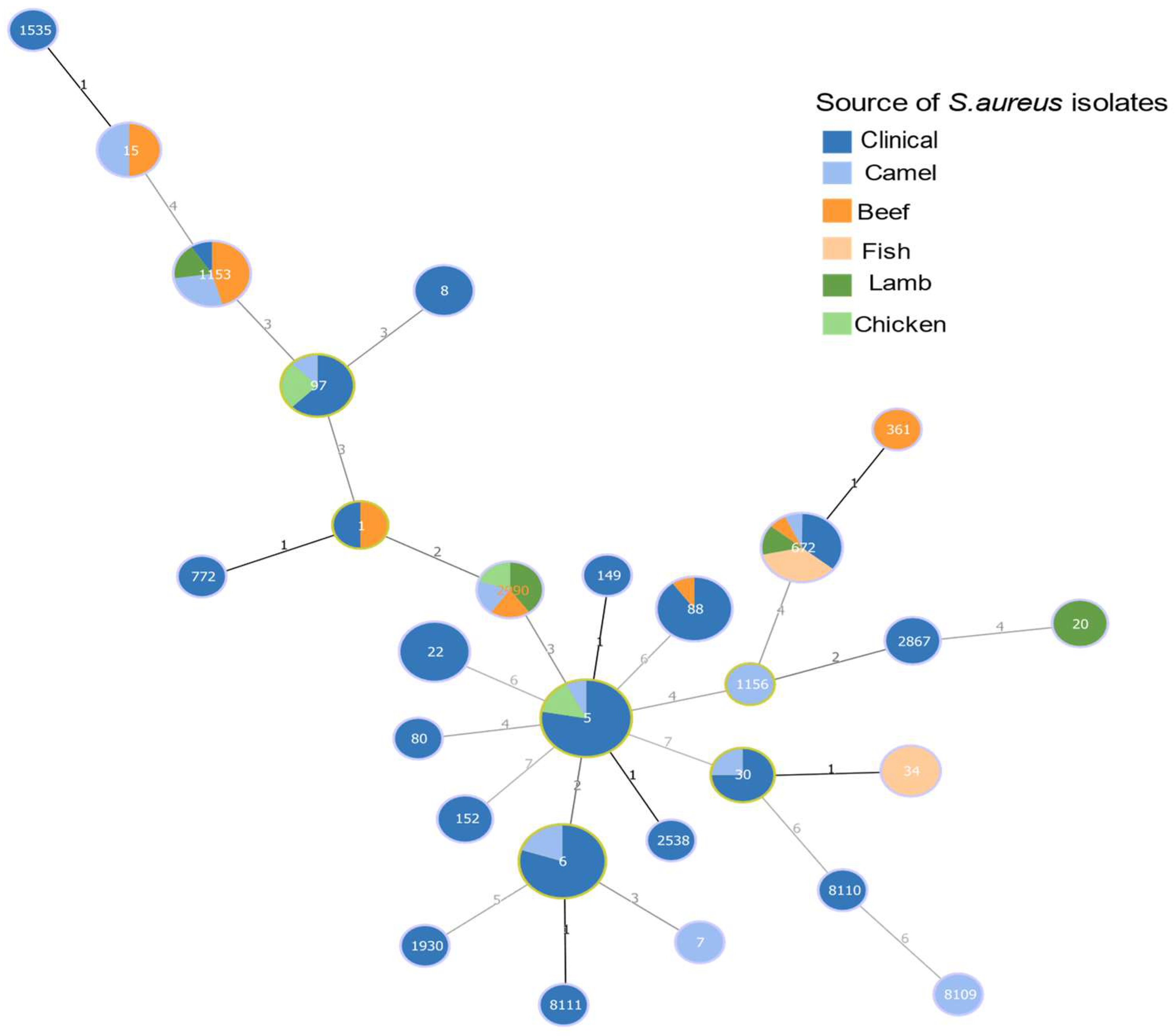
3.1. Molecular Types of Staphylococci Isolates from Meat
3.2. SCCmec Types and Spa Types of S. aureus from Meat
3.3. Molecular Types of Staphylococci Isolate from Patients
3.4. SCCmec Types and Spa Types of S. aureus from Patients
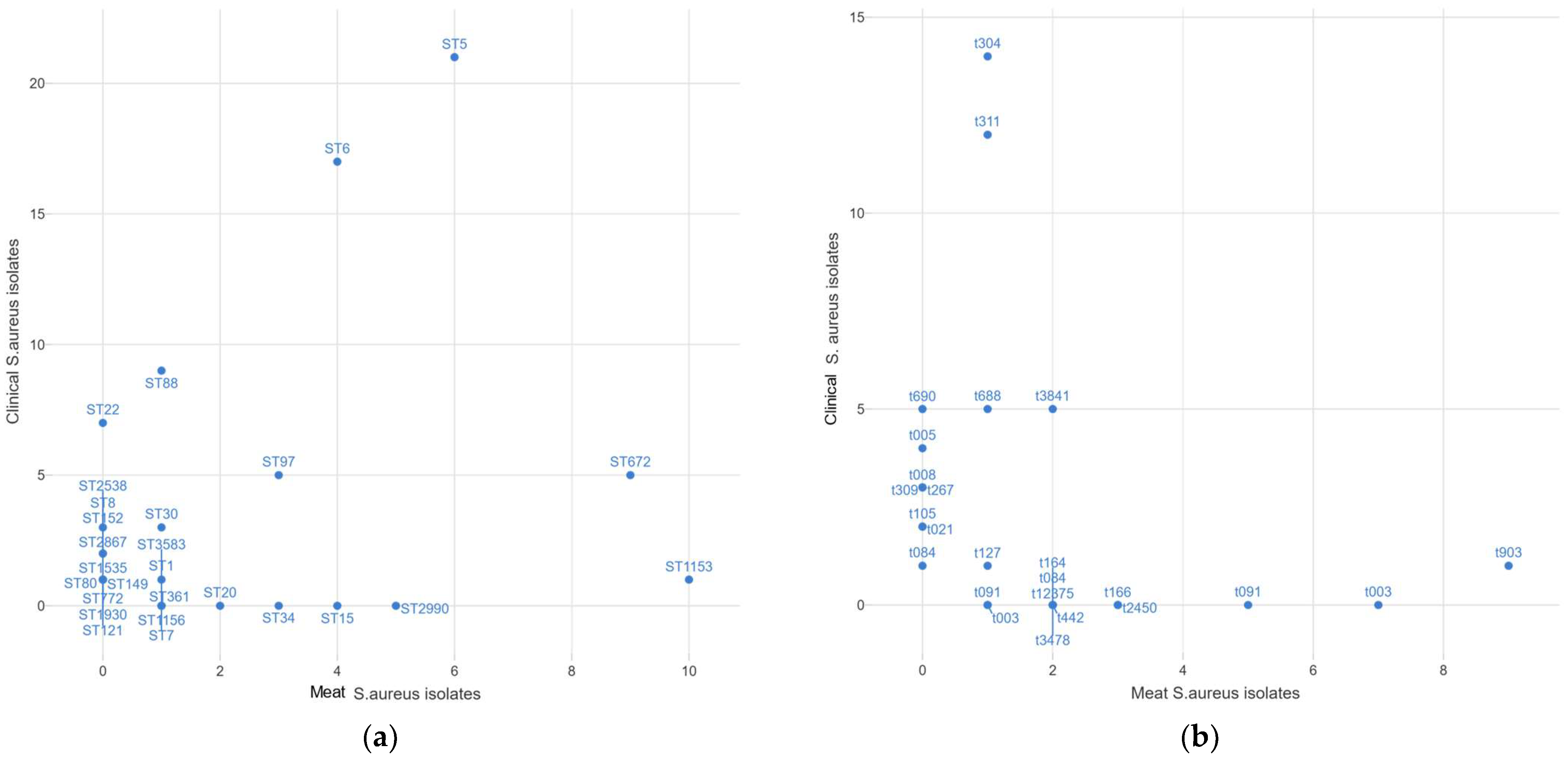
3.5. Shared Sequence Types and Spa Types among Meat and Clinical S. aureus Isolates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kwiecinski, J.M.; Horswill, A.R. Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections: Pathogenesis and regulatory mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2020, 53, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevons, M.P. “Celbenin”-resistant staphylococci. Br. Med. J. 1961, 1, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.R.; Davis, J.A.; Barrett, J.B. Prevalence and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from retail meat and humans in Georgia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibl, A.M.; Memish, Z.A.; Kambal, A.M.; Ohaly, Y.A.; Ishaq, A.; Senok, A.C.; Livermore, D.M. National surveillance of antimicrobial resistance among Gram-positive bacteria in Saudi Arabia. J. Chemother. 2014, 26, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljeldah, M.M. Prevalence of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Saudi Arabia: A systematic review. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 14, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landers, T.F.; Cohen, B.; Wittum, T.E.; Larson, E.L. A Review of Antibiotic Use in Food Animals: Perspective, Policy, and Potential. Public Health Rep. 2012, 127, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, A.; Loeffen, F.; Bakker, J.; Klaassen, C.; Wulf, M. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Pig Farming. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1965–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizerwetter-Świda, M.; Chrobak-Chmiel, D.; Rzewuska, M.; Pławińska-Czarnak, J.; Binek, M. Characterisation of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from meat processing plants—A preliminary study. J. Vet. Res. 2016, 60, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccarthy, A.J.; Lindsay, J.A.; Loeffler, A. Are all meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) equal in all hosts? Epidemiological and genetic comparison between animal and human MRSA. Vet. Dermatol. 2012, 23, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghizzi, M.; Shami, A. The prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in milk and dairy products in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 7098–7104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senok, A.; Somily, A.M.; Nassar, R.; Garaween, G.; Kim Sing, G.; Müller, E.; Reissig, A.; Gawlik, D.; Ehricht, R.; Monecke, S. Emergence of novel methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains in a tertiary care facility in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2739–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Peng, H.; Zhang, N.; Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Shang, W.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; et al. Genomic Epidemiology and Phenotypic Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus from a Tertiary Hospital in Tianjin Municipality, Northern China. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e04209-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Huang, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Yang, X.; Wu, H.; Zeng, H.; Chen, M.; Ding, Y.; et al. Staphylococcus aureusisolated from retail meat and meat products in China: Incidence, antibiotic resistance and genetic diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senok, A.; Ehricht, R.; Monecke, S.; Al-Saedan, R.; Somily, A. Molecular characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in nosocomial infections in a tertiary-care facility: Emergence of new clonal complexes in Saudi Arabia. New Microbes New Infect. 2016, 14, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senok, A.; Somily, A.; Raji, A.; Gawlik, D.; Al-Shahrani, F.; Baqi, S.; Boswihi, S.; Skakni, L.; Udo, E.E.; Weber, S.; et al. Diversity of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus CC22-MRSA-IV from Saudi Arabia and the Gulf region. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 51, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eed, E.M.; Ghonaim, M.M.; Hussein, Y.M.; Saber, T.M.; Khalifa, A.S. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of HA-MRSA in Taif hospitals, Saudi Arabia. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2015, 9, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkharsah, K.R.; Rehman, S.; Alkhamis, F.; Alnimr, A.; Diab, A.; Al-Ali, A.K. Comparative and molecular analysis of MRSA isolates from infection sites and carrier colonization sites. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2018, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, D.; Speck, M.; Daschner, F.D.; Grundmann, H. Rapid PCR-Based Identification of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Screening Swabs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1821–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, R.A.; Read, T.D. Bactopia: A Flexible Pipeline for Complete Analysis of Bacterial Genomes. mSystems 2020, 5, 1110–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, A.P.; Vaz, C.; Monteiro, P.T.; Melo-Cristino, J.; Ramirez, M.; Carriço, J.A. PHYLOViZ: Phylogenetic inference and data visualization for sequence based typing methods. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, A.J.; Chipeta, M.G.; Haines-Woodhouse, G.; Kumaran, E.P.; Hamadani, B.H.K.; Zaraa, S.; Henry, N.J.; Deshpande, A.; Reiner, R.C.; Day, N.P.; et al. Global antibiotic consumption and usage in humans, 2000–2018: A spatial modelling study. Lancet Planet Health 2021, 5, e893–e904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, B.M.; Levy, S.B. Food animals and antimicrobials: Impacts on human health. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Mukherjee, S.; Hsu, C.H.; Davis, J.A.; Tran, T.T.T.; Yang, Q.; Abbott, J.W.; Ayers, S.L.; Young, S.R.; Crarey, E.T.; et al. MRSA and multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in U.S. retail meats, 2010–2011. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadiq, A.; Samad, M.; Saddam; Basharat, N.; Ali, S.; Roohullah; Saad, Z.; Khan, A.N.; Ahmad, Y.; Khan, A.; et al. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Slaughter Houses and Meat Shops in Capital Territory of Pakistan During 2018–2019. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raji, M.A.; Garaween, G.; Ehricht, R.; Monecke, S.; Shibl, A.M.; Senok, A. Genetic characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from retail meat in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, G.; Gamaleldin, M.S.; Ahmed, S.; Abdullah, A.; Mohammad, K. Frequency of antibiotic resistant Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Enterococcus, and Staphylococcus aureus in meat in Saudi Arabia. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 7, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghizzi, M.J.; Alansari, M.; Shami, A. The prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in processed food samples in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 15, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhout, C.; Elgroud, R.; Butaye, P. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Other Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococci and Mammaliicoccus (MRNaS) Associated with Animals and Food Products in Arab Countries: A Review. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Yousef, S.; Taha, E. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Saudi Arabia: Genotypes distribution review. Saudi J. Med. Med. Sci. 2016, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mahdy, T.S.; Al-Agamy, M.H.; Emara, M.; Barakat, A.; Goering, R.V. Complex Clonal Diversity of Staphylococcus aureus Nasal Colonization among Community Personnel, Healthcare Workers, and Clinical Students in the Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zahrani, I.A.; Azhar, E.I.; Jiman-Fatani, A.A.; Siddig, L.A.; Yasir, M.; Al-Ghamdi, A.K.; Harwood, C.R. Impact of mass migrations on the clonal variation of clinical Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from the Western region of Saudi Arabia. J. Infect. Public Health 2019, 12, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.S.; De Lencastre, H.; Garau, J.; Kluytmans, J.; Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Peschel, A.; Harbarth, S. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monecke, S.; Skakni, L.; Hasan, R.; Ruppelt, A.; Ghazal, S.S.; Hakawi, A.; Slickers, P.; Ehricht, R. Characterisation of MRSA strains isolated from patients in a hospital in Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boswihi, S.S.; Udo, E.E.; Monecke, S.; Mathew, B.; Noronha, B.; Verghese, T.; Tappa, S.B. Emerging variants of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus genotypes in Kuwait hospitals. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monecke, S.; Müller, E.; Braun, S.D.; Armengol-Porta, M.; Bes, M.; Boswihi, S.; El-Ashker, M.; Engelmann, I.; Gawlik, D.; Gwida, M.; et al. Characterisation of S. aureus/MRSA CC1153 and review of mobile genetic elements carrying the fusidic acid resistance gene fusc. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shady, H.M.A.; Bakr, A.E.A.; Hashad, M.E.; Alzohairy, M.A. Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage among outpatients attending primary health care centers: A comparative study of two cities in Saudi Arabia and Egypt. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 19, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Deeb, W.; Cave, R.; Fayez, M.; Alhumam, N.; Quadri, S.; Mkrtchyan, H.V. Methicillin Resistant Staphylococci Isolated from Goats and Their Farm Environments in Saudi Arabia Genotypically Linked to Known Human Clinical Isolates: A Pilot Study of Saudi Arabia. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e00387-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaipadungpanit, J.; Amornchai, P.; Nickerson, E.K.; Wongsuvan, G.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; Peacock, S.J. Clinical and Molecular Epidemiology of Staphylococcus argenteus Infections in Thailand. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1005–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantratita, N.; Wikraiphat, C.; Tandhavanant, S.; Wongsuvan, G.; Ariyaprasert, P.; Suntornsut, P.; Thaipadungpanit, J.; Teerawattanasook, N.; Jutrakul, Y.; Srisurat, N.; et al. Comparison of community-onset Staphylococcus argenteus and Staphylococcus aureus sepsis in Thailand: A prospective multicentre observational study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 458.e11–458.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; De Lencastre, H.; Tomasz, A. Genetic organization of the mecA region in methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus sciuri. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, A. Prevalence and genetic diversity of coagulase negative Staphylococcus in food products collected from Riyadh region. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 15, 1987–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegegne, H.A.; Koláčková, I.; Florianová, M.; Gelbíčová, T.; Madec, J.Y.; Haenni, M.; Karpíšková, R. Detection and molecular characterisation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from raw meat in the retail market. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 26, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boer, E.; Zwartkruis-Nahuis, J.T.M.; Wit, B.; Huijsdens, X.W.; De Neeling, A.J.; Bosch, T.; Van Oosterom, R.A.A.; Vila, A.; Heuvelink, A.E. Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in meat. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 134, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, B.M.; Dressler, A.E.; Harper, A.L.; Scheibel, R.P.; Wardyn, S.E.; Roberts, L.K.; Kroeger, J.S.; Smith, T.C. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) on retail meat in Iowa. J. Infect. Public Health 2011, 4, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Clonal Complex | ST | No. (%) of Meat MRSA Isolates (n = 11) | No. (%) of Clinical MRSA Isolates (n = 80) | No. (%) of Meat MSSA Isolates (n = 42) | No. (%) of Clinical MSSA Isolates (n = 3) | No. (%) of Meat MRS Isolates (n= 6) | No. (%) of Meat MSS Isolates (n = 17) | No. (%) of Clinical MSS Isolates (n = 1) | No. (%) of Total Staphylococci Isolates (n = 160) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | CC5 | 5 | 2 (2) | 21 (23) | 4 (9) | – | – | – | – | 27 (17) |
| 6 | 3 (3) | 16 (20) | 1 (2) | – | – | – | – | 20 (13) | ||
| 149 | – | 1 (1) | – | – | – | – | – | 1 (0.6) | ||
| 2538 | – | 1 (1) | – | – | – | – | – | 1 (0.6) | ||
| * 8111 | – | 1 (1) | – | – | – | – | – | 1 (0.6) | ||
| CC1 | 1 | – | 1 (1) | 1 (2) | – | – | – | – | 2 (1.2) | |
| 2990 | – | – | 5 (11) | – | – | – | – | 5 (3) | ||
| 772 | – | 1 (1) | – | – | – | – | – | 1 (0.6) | ||
| CC97 | 97 | 3 (3) | 5 (5) | – | – | – | – | – | 8 (5) | |
| 1153 | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 9 (20) | – | – | – | – | 11 (7) | ||
| CC361 | 361 | – | – | 1 (2) | – | – | – | – | 1(0.6) | |
| 672 | 2 (2) | 5 (5) | 7 (14) | – | – | – | – | 14 (9) | ||
| CC30 | 30 | – | 3 (3) | 1 (2) | – | – | – | – | 4 (2.5) | |
| 34 | – | – | 3 (7) | – | – | – | – | 3 (1.8) | ||
| CC15 | 15 | – | – | 4 (9) | – | – | – | – | 4 (2.5) | |
| 1535 | – | 1 (1) | – | – | – | – | – | 1 (0.6) | ||
| CC88 | 88 | – | 9 (10) | 1 (2) | – | – | – | – | 10 (6) | |
| CC22 | 22 | – | 7 (8) | – | – | – | – | – | 7 (4) | |
| CC8 | 8 | – | 3 (3) | – | – | – | – | – | 3 (1.8) | |
| CC80 | 80 | – | 1 (1) | – | – | – | – | – | 1 (0.6) | |
| CC121 | * 8110 | – | – | – | 1 (2) | – | – | – | 1 (0.6) | |
| CC152 | 152 | – | 2 (2) | – | – | – | – | – | 2 (1.2) | |
| CC96 | 1930 | – | 1 (1) | – | – | – | – | – | 1 (0.6) | |
| CC7 | 7 | – | – | 1 (2) | – | – | – | – | 1 (0.6) | |
| CC20 | 20 | – | – | 2 (5) | – | – | – | – | 2 (1.2) | |
| ST2867 | 2867 | – | – | – | 2 (5) | – | – | – | 2 (1.2) | |
| ST1156 | 1156 | – | – | 1 (2) | – | – | – | – | 1 (0.6) | |
| ST8109 | * 8109 | – | – | 1 (2) | – | – | – | – | 1 (0.6) | |
| S. pasteuri | ND | – | – | – | – | – | – | 11 (61) | – | 11 (7) |
| M. sciuri | ND | – | – | – | – | – | 6 (100) | – | – | 6 (4) |
| S. saprophyticus | ND | – | – | – | – | – | - | 4 (22) | – | 4 (2.5) |
| S. argenteus | ST2250 | 2250 | – | – | – | – | - | 1(6) | 1(6) | 2 (1.2) |
| S. haemolyticus | ST29 | 29 | – | – | – | – | - | 1 (6) | – | 1 (0.6) |
| Spa type | ST | Frequency | mecA | Isolation Source | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSSA | MRSA | Meat | Patients | |||
| t304 | 6 | 15 (11.4%) | 1 | 14 | 1 | 14 |
| t311 | 5 | 13 (9.9%) | - | 13 | 1 | 12 |
| t903 | 1153 | 10 (7.6%) | 8 | 2 | 9 | 1 |
| t003 | * 672_* 361 | 8 (6.1%) | 8 | - | 8 | - |
| t3841 | 672 | 7 (5.3%) | - | 7 | 2 | 5 |
| t091 | * 2990_* 7 | 6 (4.5%) | 6 | - | 6 | - |
| t688 | 5 | 6 (4.5%) | - | 6 | 1 | 5 |
| t690 | 88 | 5 (3.8%) | - | 5 | - | 5 |
| t005 | 22 | 4 (3.0%) | - | 4 | - | 4 |
| t2450 | 6 | 3 (2.2%) | - | 3 | 3 | - |
| t084 | * 15_* 1535 | 3 (2.2%) | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| t166 | 34 | 3 (2.2%) | 3 | - | 3 | - |
| t309 | 22 | 3 (2.2%) | - | 3 | - | 3 |
| t008 | 8 | 3 (2.2%) | - | 3 | - | 3 |
| t267 | 97 | 3 (2.2%) | - | 3 | - | 3 |
| t12375 | * 97_* 8109 | 2 (1.5%) | 1 | 2 | 3 | - |
| t3478 | 5 | 2 (1.5%) | 2 | - | 2 | - |
| t442 | 5 | 2 (1.5%) | 2 | - | 2 | - |
| t127 | 1 | 2 (1.5%) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| t164 | 20 | 2 (1.5%) | 2 | - | 2 | - |
| t105 | 5 | 2 (1.5%) | - | 2 | - | 2 |
| t021 | 30 | 2 (1.5%) | - | 2 | - | 2 |
| t434 | 97 | 1 (0.7%) | - | 1 | 1 | - |
| t213 | 1156 | 1 (0.7%) | 1 | - | 1 | - |
| t605 | 15 | 1 (0.7%) | 1 | - | 1 | - |
| t3519 | 30 | 1 (0.7%) | 1 | - | 1 | - |
| t6047 | 15 | 1 (0.7%) | 1 | - | 1 | - |
| t1339 | 88 | 1 (0.7%) | 1 | - | 1 | - |
| t355 | 152 | 1 (0.7%) | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| t018 | 30 | 1 (0.7%) | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| t2297 | 97 | 1 (0.7%) | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| t4019 | 152 | 1 (0.7%) | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| t159 | 8110 | 1 (0.7%) | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| t345 | 772 | 1 (0.7%) | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| t521 | 97 | 1 (0.7%) | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| t2177 | 88 | 1 (0.7%) | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| t9736 | 8111 | 1 (0.7%) | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| t045 | 149 | 1 (0.7%) | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| t4570 | 1930 | 1 (0.7%) | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| t2016 | 2867 | 1 (0.7%) | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| t2649 | 88 | 1 (0.7%) | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| t1627 | 6 | 1 (0.7%) | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| t4494 | 88 | 1 (0.7%) | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| t8657 | 6 | 1 (0.7%) | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| t3778 | 2538 | 1 (0.7%) | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| t12438 | 88 | 1 (0.7%) | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| t319 | 5 | 1 (0.7%) | - | 1 | - | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alkuraythi, D.M.; Alkhulaifi, M.M.; Binjomah, A.Z.; Alarwi, M.; Aldakhil, H.M.; Mujallad, M.I.; Alharbi, S.A.; Alshomrani, M.; Alshahrani, S.M.; Gojobori, T.; et al. Clonal Flux and Spread of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Meat and Its Genetic Relatedness to Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Patients in Saudi Arabia. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2926. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122926
Alkuraythi DM, Alkhulaifi MM, Binjomah AZ, Alarwi M, Aldakhil HM, Mujallad MI, Alharbi SA, Alshomrani M, Alshahrani SM, Gojobori T, et al. Clonal Flux and Spread of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Meat and Its Genetic Relatedness to Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Patients in Saudi Arabia. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(12):2926. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122926
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlkuraythi, Dalal M., Manal M. Alkhulaifi, Abdulwahab Z. Binjomah, Mohammed Alarwi, Hind M. Aldakhil, Mohammed I. Mujallad, Saleh Ali Alharbi, Mohammad Alshomrani, Saeed Mastour Alshahrani, Takashi Gojobori, and et al. 2023. "Clonal Flux and Spread of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Meat and Its Genetic Relatedness to Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Patients in Saudi Arabia" Microorganisms 11, no. 12: 2926. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122926
APA StyleAlkuraythi, D. M., Alkhulaifi, M. M., Binjomah, A. Z., Alarwi, M., Aldakhil, H. M., Mujallad, M. I., Alharbi, S. A., Alshomrani, M., Alshahrani, S. M., Gojobori, T., & Alajel, S. M. (2023). Clonal Flux and Spread of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Meat and Its Genetic Relatedness to Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Patients in Saudi Arabia. Microorganisms, 11(12), 2926. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122926





