Lessons from a Multilaboratorial Task Force for Diagnosis of a Fatal Toxoplasmosis Outbreak in Captive Primates in Brazil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement and Official Notification
2.2. Animals
2.3. Sample Collection for Molecular Testing and Genetic Material Extraction
2.4. Necropsy and Histopathology
2.5. Detection of Viral Agents
2.5.1. SARS-CoV-2
2.5.2. Arenavirus and Hantavirus
2.5.3. Arboviruses
2.6. Metagenomic Sequencing
2.7. Bacterial Agents
2.7.1. Yersinia pestis
2.7.2. Escherichia coli
2.8. Protozoan Agents
Toxoplasma gondii
3. Results
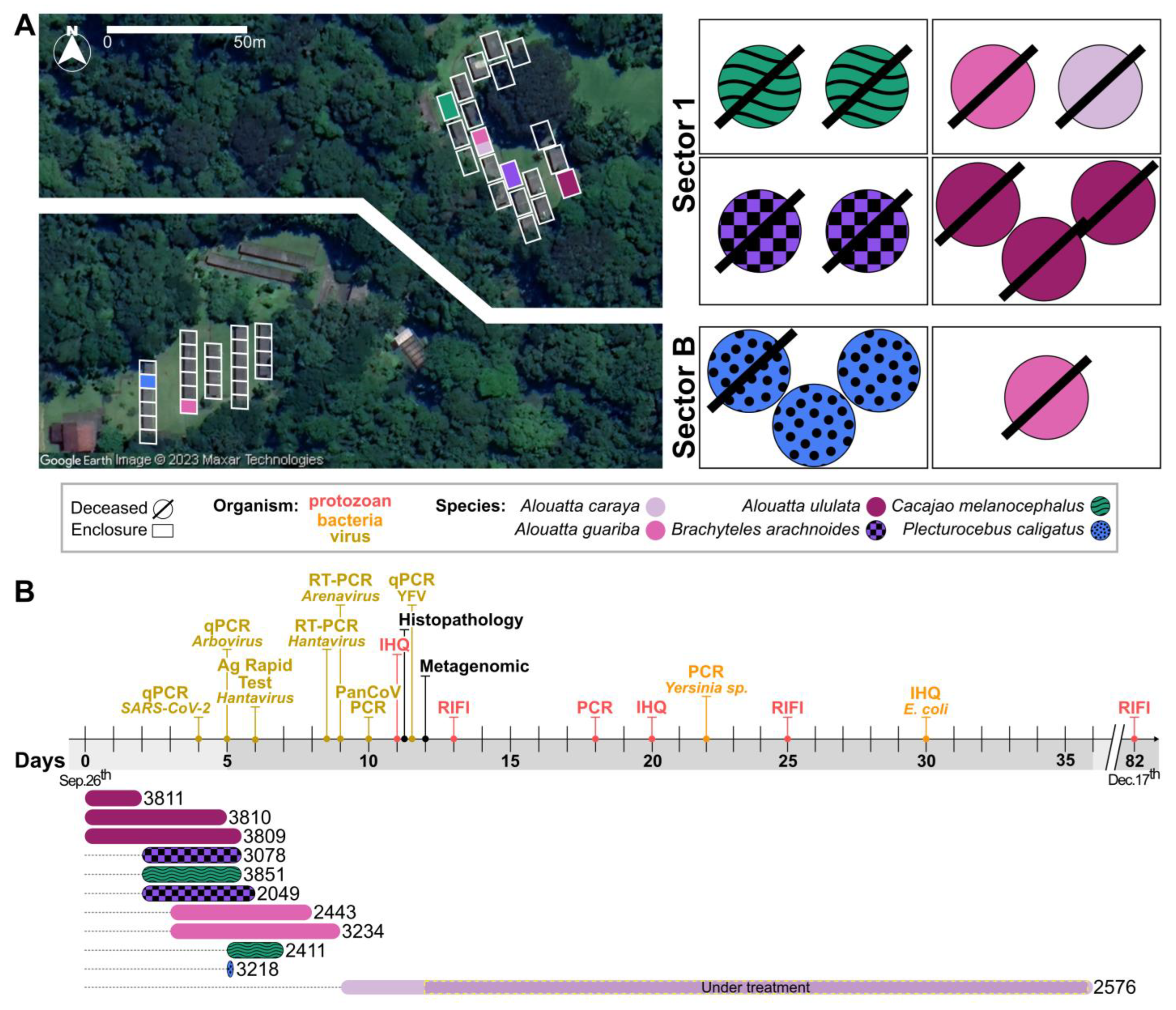
3.1. Clinical Description of the CPRJ Outbreak in Neotropical Primates
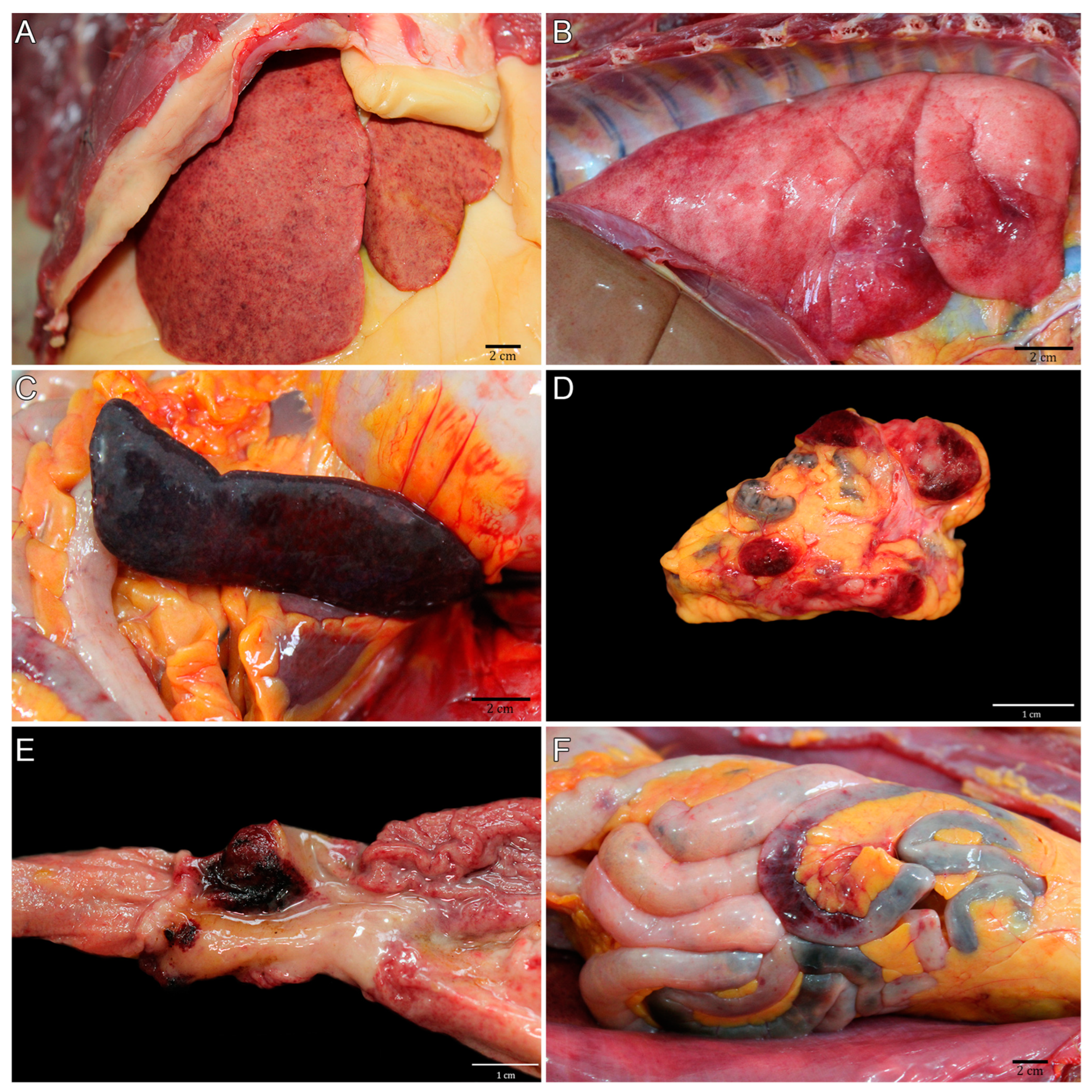
3.2. Pathological Description of the CPRJ Outbreak in Neotropical Primates
3.3. Negative SARS-CoV-2 and Arboviral Diagnoses
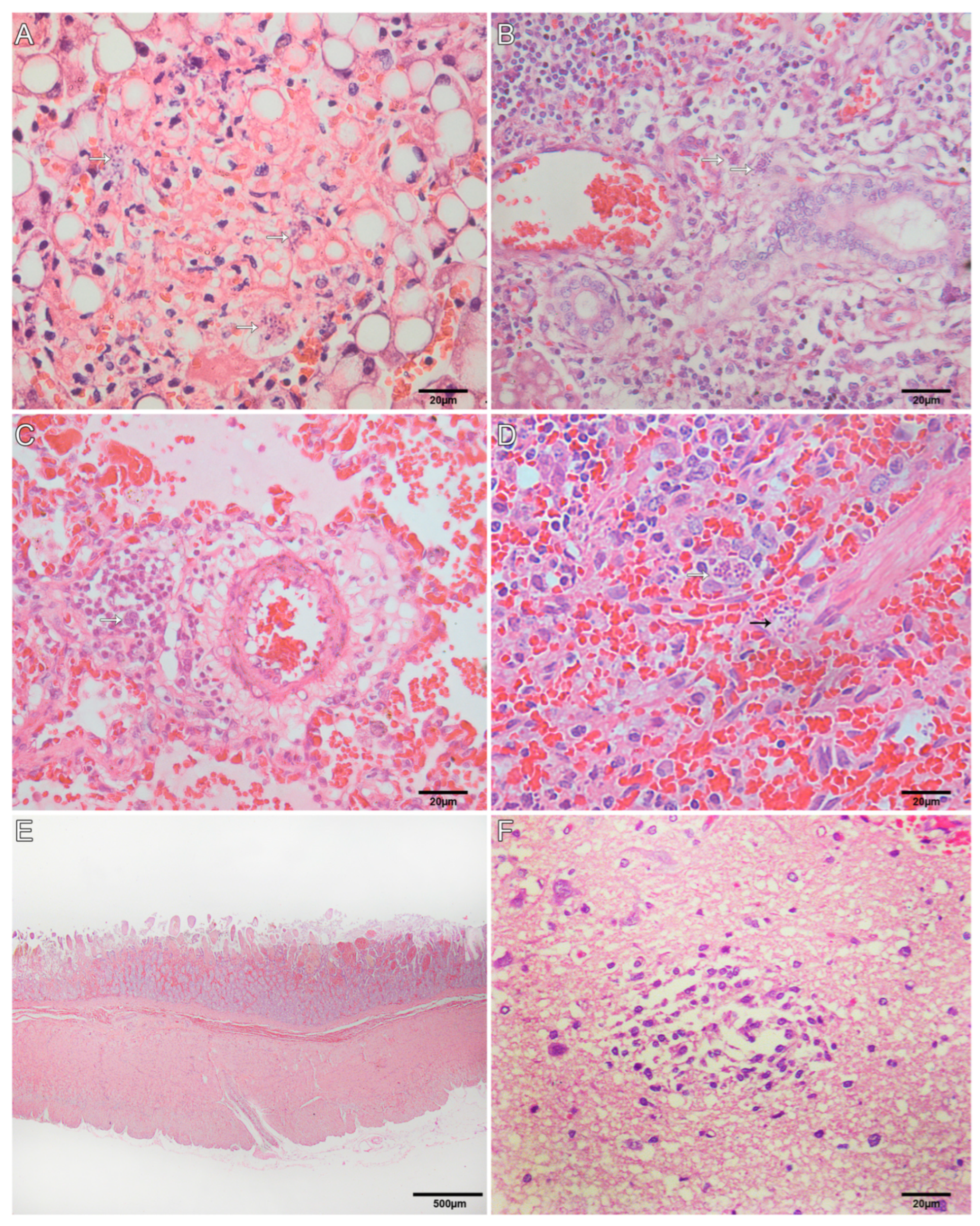
3.4. Histological Findings for Neotropical Primates
3.5. Pathogen Metagenomics Reveals Sepsis Causing Bacterial Infection
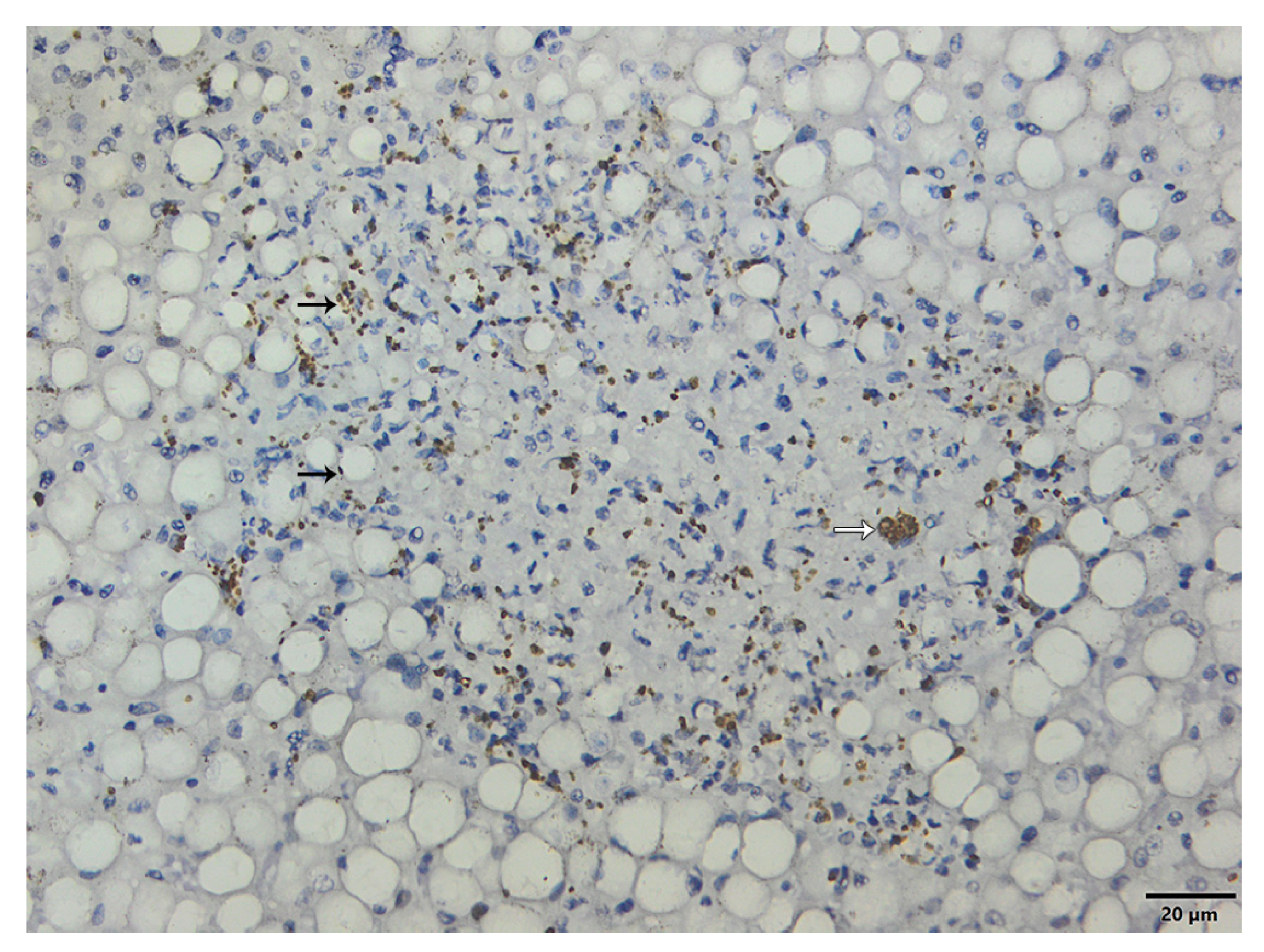
3.6. Immunohistochemistry
3.7. Molecular and Serological Diagnosis of Toxoplasmosis
3.8. Negative Yersinia Bacteriological, Molecular, and Serological Diagnosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Voloch, C.M.; da Silva Francisco, R., Jr.; de Almeida, L.G.P.; Cardoso, C.C.; Brustolini, O.J.; Gerber, A.L.; de Guimarães, A.P.C.; Mariani, D.; da Costa, R.M.; Ferreira, O.C., Jr.; et al. Genomic Characterization of a Novel SARS-CoV-2 Lineage from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. J. Virol. 2021, 95, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministério da Saúde Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde. PORTARIA N.o 5, DE 21 DE FEVEREIRO DE 2006. Available online: https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/saudelegis/svs/2006/prt0005_21_02_2006_comp.html (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- da Saúde, M. PORTARIA No 782, DE 15 DE MARÇO DE 2017. Available online: https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/saudelegis/gm/2017/prt0782_16_03_2017.html (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- Núcleo de Comunicação/GAB/SVS. Guia de Vigilância de Epizootias Em Primatas Não Humanos E Entomologia Aplicada à Vigilância Da Febre Amarela; Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde do Ministério da Saúde. 2014. Available online: https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/publicacoes/guia_vigilancia_epizootias_primatas_entomologia.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- Frenkel, J.K.; Dubey, J.P.; Beattie, C.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Man. J. Parasitol. 1989, 75, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; ISBN 9780429092954. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, J.P.; Murata, F.H.A.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Yang, Y.; Su, C. Recent Epidemiologic, Clinical, and Genetic Diversity of Toxoplasma Gondii Infections in Non-Human Primates. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 136, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagrande, R.A.; da Silva, T.C.E.; Pescador, C.A.; Borelli, V.; Souza, J.C., Jr.; Souza, E.R.; Traverso, S.D. Toxoplasmose em primatas neotropicais: Estudo retrospectivo de sete casos. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2013, 33, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, J.S.; Ribeiro, C.T.; de Carvalho Filho, P.R.; Pissinatti, A.; Flausino, W.; Lopes, C.W.G. Infection by Toxoplasma Gondii in Neotropical Non-Human Primates. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2012, 32, 1041–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues Oliveira, A.; Ritter, J.M.; Oliveira Dos Santos, D.; Pizzolato de Lucena, F.; Aquino de Mattos, S.; Parente de Carvalho, T.; Bullock, H.; Giannini Alves Moreira, L.; Magalhães Arthuso Vasconcelos, I.; Barroso Costa, F.; et al. Pathology and Epidemiology of Fatal Toxoplasmosis in Free-Ranging Marmosets (Callithrix spp.) from the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, R.C.; Machado, G.P.; de Cruvinel, T.M.A.; Cruvinel, C.A.; Langoni, H. Frequency of Toxoplasma Gondii Antibodies in Tufted Capuchin Monkeys (Cebus apella nigritus) from an Ecological Station in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2013, 33, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, C.H.; de Oliveira, A.R.; Dos Santos, D.O.; Pimentel, S.P.; de Souza, L.D.R.; Moreira, L.G.A.; Braz, H.M.B.; de Carvalho, T.P.; Lopes, C.E.B.; Oliveira, J.B.S.; et al. Genotyping of Toxoplasma Gondii in a Lethal Toxoplasmosis Outbreak Affecting Captive Howler Monkeys (Alouatta sp.). J. Med. Primatol. 2021, 50, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrik Dietz, H.; Henriksen, P.; Bille-Hansen, V.; Aage Henriksen, S. Toxoplasmosis in a Colony of New World Monkeys. Vet. Parasitol. 1997, 68, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouer, A.; Werther, K.; Catão-Dias, J.L.; Nunes, A.L.V. Outbreak of Toxoplasmosis in Lagothrix Lagotricha. Folia Primatol. 1999, 70, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epiphanio, S.; Guimarães, M.A.B.; Fedullo, D.L.; Correa, S.H.R.; Catão-Dias, J.L. Toxoplasmosis in Golden-Headed Lion Tamarins (Leontopithecus chrysomelas) and Emperor Marmosets (Saguinus imperator) in Captivity. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2000, 31, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epiphanio, S.; Sá, L.R.; Teixeira, R.H.; Catão-Dias, J.L. Toxoplasmosis in a Wild-Caught Black Lion Tamarin (Leontopithecus chrysopygus). Vet. Rec. 2001, 149, 627–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epiphanio, S.; Sinhorini, I.L.; Catão-Dias, J.L. Pathology of Toxoplasmosis in Captive New World Primates. J. Comp. Pathol. 2003, 129, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvim, R.G.F.; Lima, T.M.; Rodrigues, D.A.S.; Marsili, F.F.; Bozza, V.B.T.; Higa, L.M.; Monteiro, F.L.; Abreu, D.P.B.; Leitão, I.C.; Carvalho, R.S.; et al. From a Recombinant Key Antigen to an Accurate, Affordable Serological Test: Lessons Learnt from COVID-19 for Future Pandemics. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 186, 108537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Jung, K.; Wang, Q.; Saif, L.J.; Vlasova, A.N. Development of a One-Step RT-PCR Assay for Detection of Pancoronaviruses (α-, β-, γ-, and δ-Coronaviruses) Using Newly Designed Degenerate Primers for Porcine and Avianfecal Samples. J. Virol. Methods 2018, 256, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.H.; Vasconcelos, A.L.; Silva, V.L.; Nogueira, B.S.; Silva, A.C.; Pacheco, R.C.; Souza, M.A.; Colodel, E.M.; Ubiali, D.G.; Biondo, A.W.; et al. Natural SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Free-Ranging Black-Tailed Marmoset (Mico melanurus) from an Urban Area in Mid-West Brazil. J. Comp. Pathol. 2022, 194, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera, L.M.; Feuillade, M.R.; Saavedra, M.C.; Ambrosio, A.M. Evaluation of an Enzyme Immunosorbent Assay for the Diagnosis of Argentine Haemorrhagic Fever. Acta Virol. 1997, 41, 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Padula, P.J.; Rossi, C.M.; Valle, M.O.D.; Martínez, P.V.; Colavecchia, S.B.; Edelstein, A.; Miguel, S.D.L.; Rabinovich, R.D.; Segura, E.L. Development and Evaluation of a Solid-Phase Enzyme Immunoassay Based on Andes Hantavirus Recombinant Nucleoprotein. J. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 49, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klempa, B.; Fichet-Calvet, E.; Lecompte, E.; Auste, B.; Aniskin, V.; Meisel, H.; Denys, C.; Koivogui, L.; Ter Meulen, J.; Krüger, D.H. Hantavirus in African Wood Mouse, Guinea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 838–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guterres, A.; de Oliveira, R.C.; Fernandes, J.; Schrago, C.G.; de Lemos, E.R.S. Detection of Different South American Hantaviruses. Virus Res. 2015, 210, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.B.; Morzunov, S.P.; Levis, S.; Rowe, J.; Calderón, G.; Enría, D.; Sabattini, M.; Buchmeier, M.J.; Bowen, M.D.; St Jeor, S.C. Genetic Diversity of the Junin Virus in Argentina: Geographic and Temporal Patterns. Virology 2000, 272, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emonet, S.; Retornaz, K.; Gonzalez, J.-P.; de Lamballerie, X.; Charrel, R.N. Mouse-to-Human Transmission of Variant Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, C.; Patel, P.; Yillah, J.; Weidmann, M.; Méndez, J.A.; Nakouné, E.R.; Niedrig, M. Advanced Yellow Fever Virus Genome Detection in Point-of-Care Facilities and Reference Laboratories. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 4054–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanciotti, R.S.; Kosoy, O.L.; Laven, J.J.; Velez, J.O.; Lambert, A.J.; Johnson, A.J.; Stanfield, S.M.; Duffy, M.R. Genetic and Serologic Properties of Zika Virus Associated with an Epidemic, Yap State, Micronesia, 2007. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.O.; Godoy, D.T.; Fontana-Maurell, M.; Costa, E.M.; Andrade, E.F.; Rocha, D.R.; Ferreira, A.G.P.; Brindeiro, R.; Tanuri, A.; Alvarez, P. Analytical and Clinical Performance of Molecular Assay Used by the Brazilian Public Laboratory Network to Detect and Discriminate Zika, Dengue and Chikungunya Viruses in Blood. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 25, 101542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanciotti, R.S.; Kosoy, O.L.; Laven, J.J.; Panella, A.J.; Velez, J.O.; Lambert, A.J.; Campbell, G.L. Chikungunya Virus in US Travelers Returning from India, 2006. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 764–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula Silveira-Lacerda, E.; Laschuk Herlinger, A.; Tanuri, A.; Rezza, G.; Anunciação, C.E.; Ribeiro, J.P.; Tannous, I.P.; Abrantes, G.R.; da Silva, E.G.; Arruda, K.F.; et al. Molecular Epidemiological Investigation of Mayaro Virus in Febrile Patients from Goiania City, 2017–2018. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 95, 104981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanciotti, R.S.; Kerst, A.J.; Nasci, R.S.; Godsey, M.S.; Mitchell, C.J.; Savage, H.M.; Komar, N.; Panella, N.A.; Allen, B.C.; Volpe, K.E.; et al. Rapid Detection of West Nile Virus from Human Clinical Specimens, Field-Collected Mosquitoes, and Avian Samples by a TaqMan Reverse Transcriptase-PCR Assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 4066–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveca, F.G.; do Nascimento, V.A.; de Souza, V.C.; Nunes, B.T.D.; Rodrigues, D.S.G.; da Vasconcelos, P.F.C. Multiplexed Reverse Transcription Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction for Simultaneous Detection of Mayaro, Oropouche, and Oropouche-like Viruses. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2017, 112, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claro, I.M.; Ramundo, M.S.; Coletti, T.M.; da Silva, C.A.M.; Valenca, I.N.; Candido, D.S.; Sales, F.C.S.; Manuli, E.R.; de Jesus, J.G.; de Paula, A.; et al. Rapid Viral Metagenomics Using SMART-9N Amplification and Nanopore Sequencing. Wellcome Open Res. 2021, 6, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.E.; Lu, J.; Langmead, B. Improved Metagenomic Analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondov, B.D.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Interactive Metagenomic Visualization in a Web Browser. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Minimap2: Pairwise Alignment for Nucleotide Sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, I.; Bayer, M.; Stephen, G.; Cardle, L.; Marshall, D. Tablet: Visualizing Next-Generation Sequence Assemblies and Mappings. In Plant Bioinformatics: Methods and Protocols; Edwards, D., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 253–268. ISBN 9781493931675. [Google Scholar]
- Giles, J.; Peterson, A.T.; Almeida, A. Ecology and Geography of Plague Transmission Areas in Northeastern Brazil. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.F.; Xavier, C.C.; de Almeida, A.M.P.; de Reis, C.R.S. Evaluation of a Multi-Species Protein A-ELISA Assay for Plague Serologic Diagnosis in Humans and Other Mammal Hosts. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0009805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.C. Laboratory Manual of Plague Diagnostic Tests; Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Atlanta, GA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Leal, N.C.; Almeida, A.M. Diagnosis of Plague and Identification of Virulence Markers in Yersinia Pestis by Multiplex-PCR. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 1999, 41, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konradt, G.; Bassuino, D.M.; Prates, K.S.; Bianchi, M.V.; Snel, G.G.M.; Sonne, L.; Driemeier, D.; Pavarini, S.P. Suppurative Infectious Diseases of the Central Nervous System in Domestic Ruminants. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2017, 37, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.O.; Pereira, A.H.B.; de Brito, M.F.; Pescador, C.A.; Ubiali, D.G. Toxoplasma Gondii Induced Abortions in a Goat Herd in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Cienc. Rural 2021, 51, e20200568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Echarte, G.; Arruda, I.F.; da Barbosa, A.S.; Guzmán, R.G.; Augusto, A.M.; Troccoli, F.; Segón, A.M.R.; Santos, A.L.C.; de Zanotto, P.F.C.; Gava, M.Z.E.; et al. Toxoplasma Gondii among Captive Wild Mammals in Zoos in Brazil and Cuba: Seroprevalence and Associated Risk Factors. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2021, 30, e001921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, W.L.; Vercammen, M.; De Braekeleer, J.; Verschueren, H. Identification of a 200- to 300-Fold Repetitive 529 Bp DNA Fragment in Toxoplasma Gondii, and Its Use for Diagnostic and Quantitative PCR. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.; Biosciences, I.; Carlsbad, C. Others BioEdit: An Important Software for Molecular Biology. GERF Bull. Biosci. 2011, 2, 60–61. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, S.B.; Pereira, A.H.B.; de Pissinatti, T.A.; Arruda, I.F.; de Azevedo, R.R.M.; Schiffler, F.B.; Outbreak Workgroup; Amendoeira, M.R.R.; Dos Santos, A.F.A.; Pissinatti, A.; et al. Subacute Multisystemic Toxoplasmosis in a Captive Black-and-Gold Howler Monkey (Alouatta caraya) Indicates Therapy Challenging. J. Med. Primatol. 2022, 51, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.V.; Pena, H.F.J.; Talebi, M.G.; Teixeira, R.H.F.; Kanamura, C.T.; Diaz-Delgado, J.; Gennari, S.M.; Catão-Dias, J.L. Fatal Toxoplasmosis in a Southern Muriqui (Brachyteles arachnoides) from São Paulo State, Brazil: Pathological, Immunohistochemical, and Molecular Characterization. J. Med. Primatol. 2017, 47, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, J.; Bogich, T.; Olival, K.; Epstein, J.; Johnson, C.; Karesh, W.; Daszak, P. Targeting Surveillance for Zoonotic Virus Discovery. Emerg. Infect. Dis. J. 2013, 19, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompalic-Cristo, A.; Britto, C.; Fernandes, O. Diagnóstico molecular da toxoplasmose: Revisão. J. Bras. Patol. Med. Lab. 2005, 41, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula, N.F.; Dutra, K.S.; de Oliveira, A.R.; Santos, D.O.D.; Rocha, C.E.V.; de Vitor, R.W.A.; Tinoco, H.P.; da Costa, M.E.L.T.; da Paixão, T.A.; Santos, R.L. Host Range and Susceptibility to Toxoplasma Gondii Infection in Captive Neotropical and Old-World Primates. J. Med. Primatol. 2020, 49, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis Amendoeira, M.R.; Arruda, I.F.; Moreira, S.B.; Ubiali, D.G.; da Silva Barbosa, A.; Jesus Pena, H.F.; Barbosa Pereira, A.H.; Nascimento da Silveira, C.; Bonifácio, T.F.; Clemes, Y.S.; et al. Isolation and Genetic Characterization of Toxoplasma Gondii from a Captive Black-and-Gold Howler Monkey (Alouatta Caraya Humboldt, 1812) in Brazil. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2022, 19, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, H.F.J.; Vitaliano, S.N.; Beltrame, M.A.V.; Pereira, F.E.L.; Gennari, S.M.; Soares, R.M. PCR-RFLP Genotyping of Toxoplasma Gondii from Chickens from Espírito Santo State, Southeast Region, Brazil: New Genotypes and a New SAG3 Marker Allele. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 192, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.C.R.; Buery, J.C.; Moreira, N.I.B.; Santos, C.B.; Costa, J.G.L.; Pinto, L.V.; de Baraviera, R.C.A.; Vitor, R.W.A.; Fux, B. Toxoplasma Gondii: Isolation, Biological and Molecular Characterisation of Samples from Free-Range Gallus Gallus Domesticus from Countryside Southeast Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2018, 27, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.A.; Andrade, R.O.; Carneiro, A.C.A.V.; Vitor, R.W.A. Overlapping Toxoplasma Gondii Genotypes Circulating in Domestic Animals and Humans in Southeastern Brazil. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, A.C.A.V.; Andrade, G.M.; Costa, J.G.L.; Pinheiro, B.V.; Vasconcelos-Santos, D.V.; Ferreira, A.M.; Su, C.; Januário, J.N.; Vitor, R.W.A. Genetic Characterization of Toxoplasma Gondii Revealed Highly Diverse Genotypes for Isolates from Newborns with Congenital Toxoplasmosis in Southeastern Brazil. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IUCN The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2022-2. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 22 March 2023).
| NHP | Species | Sex | Age * | Body Condition Score ** | Hepatomegaly | Splenomegaly | Lymphadenomegaly | Hemorrhages | Necrosis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lungs | Liver | Lymph Node | Small Intestine | Large Intestine | Stomach | Intestine | |||||||||
| Atelidae | 1 | B. arachnoides | M | 6 | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + |
| 2 | B. arachnoides | F | 20 | 4 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | |
| 3 | A. ululata | F | Adult | - | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | - | - | |
| 4 | A. ululata | F | Adult | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | |
| 5 | A. ululata | F | Adult | 3 | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | |
| 6 | A. guariba | M | 11 | 3 | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 7 | A. guariba | M | 7 | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 8 | A. caraya | M | 10 | 2 | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | |
| Pitheciidae | 9 | C. melanocephalus | F | 12 | 2 | - | + | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| 10 | C. melanocephalus | M | Adult | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||
| 11 | P. caligatus | F | 4 | 3 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | |
| Atelidae. Affected Monkeys/Severity | Pitheciidae. Affected Monkeys/Severity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. arachnoides (n = 2) | A. ululata (n = 3) | A. guariba (n = 2) | A. caraya (n = 1) | C. melanocephalus (n = 2) | P. caligatus (n = 1) | |
| Liver | ||||||
| Lymphocytic periportal hepatitis | 2/++ | 3/++ | 2/+ | 1/++ | 2/++ | 1/+++ |
| Random necrosis | 2/++ | 3/++ | 2/+ | 1/++ | 2/++ | 1/++ |
| Hemorrhage | 1/+ | 2/+ | 1/+ | 1/+ | ||
| Fibrin deposition | 2/++ | 1/+ | - | |||
| Hemosiderosis | 1/+ | 1/+ | 1/+ | 1/+ | ||
| Steatosis | 2/+++ | 2/+++ | 1/++ | 1/+++ | ||
| Lung | ||||||
| Interstitial pneumonia | 2/++ | 2/++ | 2/+ | 1/++ | 2/++ | |
| Edema | 2/++ | 2/++ | 2/+++ | 1/++ | 2/+++ | 1/+ |
| Hemorrhage | 2/++ | 2/++ | 1/+ | 1/+++ | 1/+++ | |
| Fibrin deposition | 1/+ | 2/++ | 1/+ | 1/++ | 1/+ | |
| Lymphocytic perivascular infiltrate | 1/++ | 1/+++ | 1/+++ | |||
| Lymph Node | ||||||
| Necrotic lymphadenitis | 1/+++ | 2/+++ | 2/++ | 1/+++ | ||
| Hemorrhage | 1/++ | 2/+++ | 1/++ | 1/++ | 1/+++ | |
| Hemosiderosis | 1/+++ | 2/++ | 1/+++ | |||
| Spleen | ||||||
| Necrotic splenitis | 1/++ | 2/++ | 2/++ | |||
| Hemorrhage | 1/+++ | 2/+ | 1/+ | 1/++ | 1/+++ | |
| Fibrin deposition | 1/+++ | 2/+ | 1/++ | 1/+ | 1/+++ | |
| Alimentary system | ||||||
| Necrohemorrhagic gastritis | 1/+++ | |||||
| Necrohemorrhagic duodenitis | 2/+++ | 1/+++ | ||||
| Necrohemorrhagic jejunitis | 1/+++ | |||||
| Necrohemorrhagic typhlitis | 1/+++ | |||||
| Brain | ||||||
| Multifocal malacia | - | 2/++ | 1/+ | |||
| Hemorrhage | - | |||||
| White matter | - | 2/+ | 1/+ | 1/+++ | ||
| Gray matter | - | 2/+ | 1/+ | 1/+++ | ||
| NHP | Species | Sex | Age * | Anti-T. gondii (Liver and Lung) | Anti-SARS-CoV (Lung) | Anti-E. coli (Lung) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bradyzoite Cists | Tachyzoites | Type I Pneumocyte | Type II Pneumocyte | Alveolar Septum | Endothelium | Vascular Lumen | ||||||
| Atelidae | 1 | B. arachnoides | M | 6 | + | + | − | +++ | − | ++ | +++ | + |
| 2 | B. arachnoides | F | 20 | + | + | − | +++ | − | − | ++ | ++ | |
| 3 | A. ululata | F | Adult | + | + | − | + | − | − | − | − | |
| 4 | A. ululata | F | Adult | + | + | − | +++ | − | − | ++ | ++ | |
| 5 | A. ululata | F | Adult | + | + | − | +++ | − | − | +++ | +++ | |
| 6 | A. guariba | M | 11 | + | + | − | NP | NP | NP | NP | NP | |
| 7 | A. guariba | M | 7 | + | + | − | NP | NP | NP | NP | NP | |
| 8 | A. caraya | M | 10 | − | − | − | NP | NP | NP | NP | NP | |
| Pitheciidae | 9 | C. melanocephalus | F | 12 | + | + | − | +++ | − | − | ++ | − |
| 10 | C. melanocephalus | M | Adult | + | + | − | NP | NP | NP | NP | NP | |
| 11 | P. caligatus | F | 4 | + | + | − | +++ | − | − | ++ | ++ | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schiffler, F.B.; Pereira, A.H.B.; Moreira, S.B.; Arruda, I.F.; Moreira, F.R.R.; D’arc, M.; Claro, I.M.; Pissinatti, T.d.A.; Cavalcante, L.T.d.F.; Miranda, T.d.S.; et al. Lessons from a Multilaboratorial Task Force for Diagnosis of a Fatal Toxoplasmosis Outbreak in Captive Primates in Brazil. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122888
Schiffler FB, Pereira AHB, Moreira SB, Arruda IF, Moreira FRR, D’arc M, Claro IM, Pissinatti TdA, Cavalcante LTdF, Miranda TdS, et al. Lessons from a Multilaboratorial Task Force for Diagnosis of a Fatal Toxoplasmosis Outbreak in Captive Primates in Brazil. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(12):2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122888
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchiffler, Francine Bittencourt, Asheley Henrique Barbosa Pereira, Silvia Bahadian Moreira, Igor Falco Arruda, Filipe Romero Rebello Moreira, Mirela D’arc, Ingra Morales Claro, Thalita de Abreu Pissinatti, Liliane Tavares de Faria Cavalcante, Thamiris dos Santos Miranda, and et al. 2023. "Lessons from a Multilaboratorial Task Force for Diagnosis of a Fatal Toxoplasmosis Outbreak in Captive Primates in Brazil" Microorganisms 11, no. 12: 2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122888
APA StyleSchiffler, F. B., Pereira, A. H. B., Moreira, S. B., Arruda, I. F., Moreira, F. R. R., D’arc, M., Claro, I. M., Pissinatti, T. d. A., Cavalcante, L. T. d. F., Miranda, T. d. S., Cosentino, M. A. C., de Oliveira, R. C., Fernandes, J., Assis, M. R. d. S., de Oliveira, J. G., da Silva, T. A. C., Galliez, R. M., Faffe, D. S., de Jesus, J. G., ... Santos, A. F. A. (2023). Lessons from a Multilaboratorial Task Force for Diagnosis of a Fatal Toxoplasmosis Outbreak in Captive Primates in Brazil. Microorganisms, 11(12), 2888. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122888







