Molecular Cloning, In Silico Analysis, and Characterization of a Novel Cellulose Microfibril Swelling Gene Isolated from Bacillus sp. Strain AY8
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. List of Primers Used in PCR and DNA Sequencing
2.3. Strains and Culture Conditions
2.4. Cms Gene Cloning
2.5. Expression of Cms Gene in E. coli
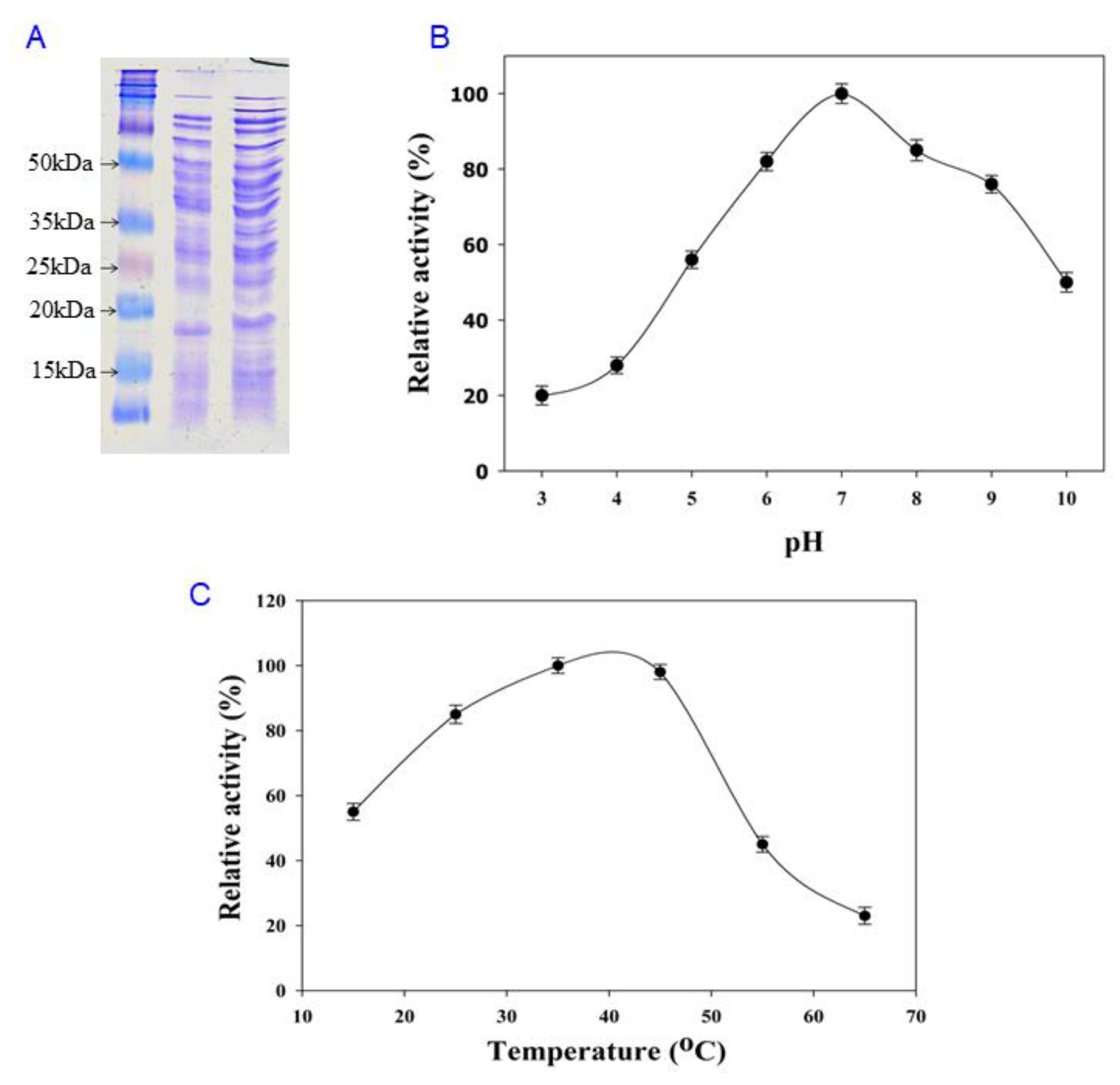
2.6. pH and Temperature Effects
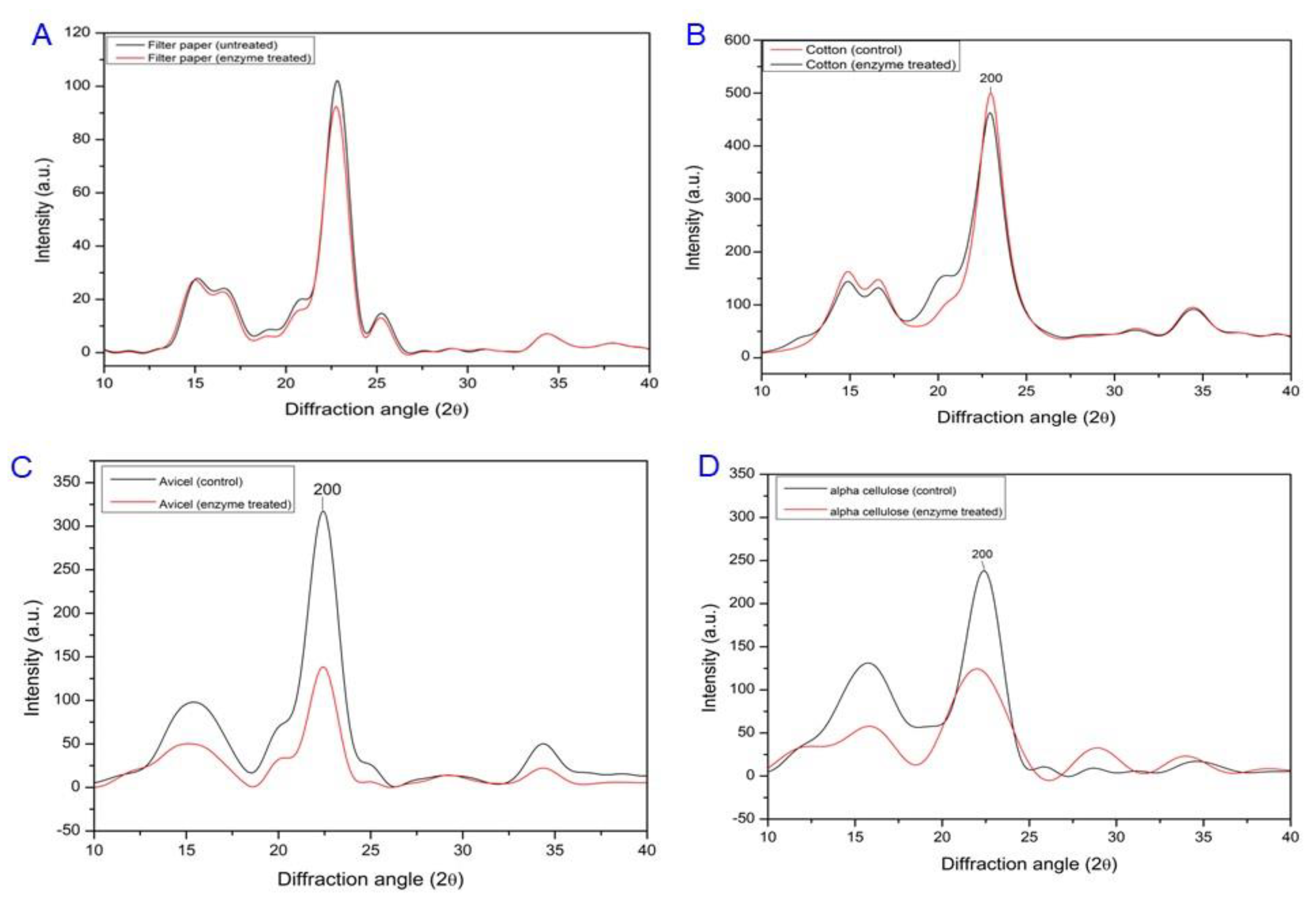
2.7. FT-IR and XRD Analyses of Cms-Treated Filter Paper
2.8. Molecular Docking and Visualization
2.9. Molecular Dynamic Simulations
3. Results
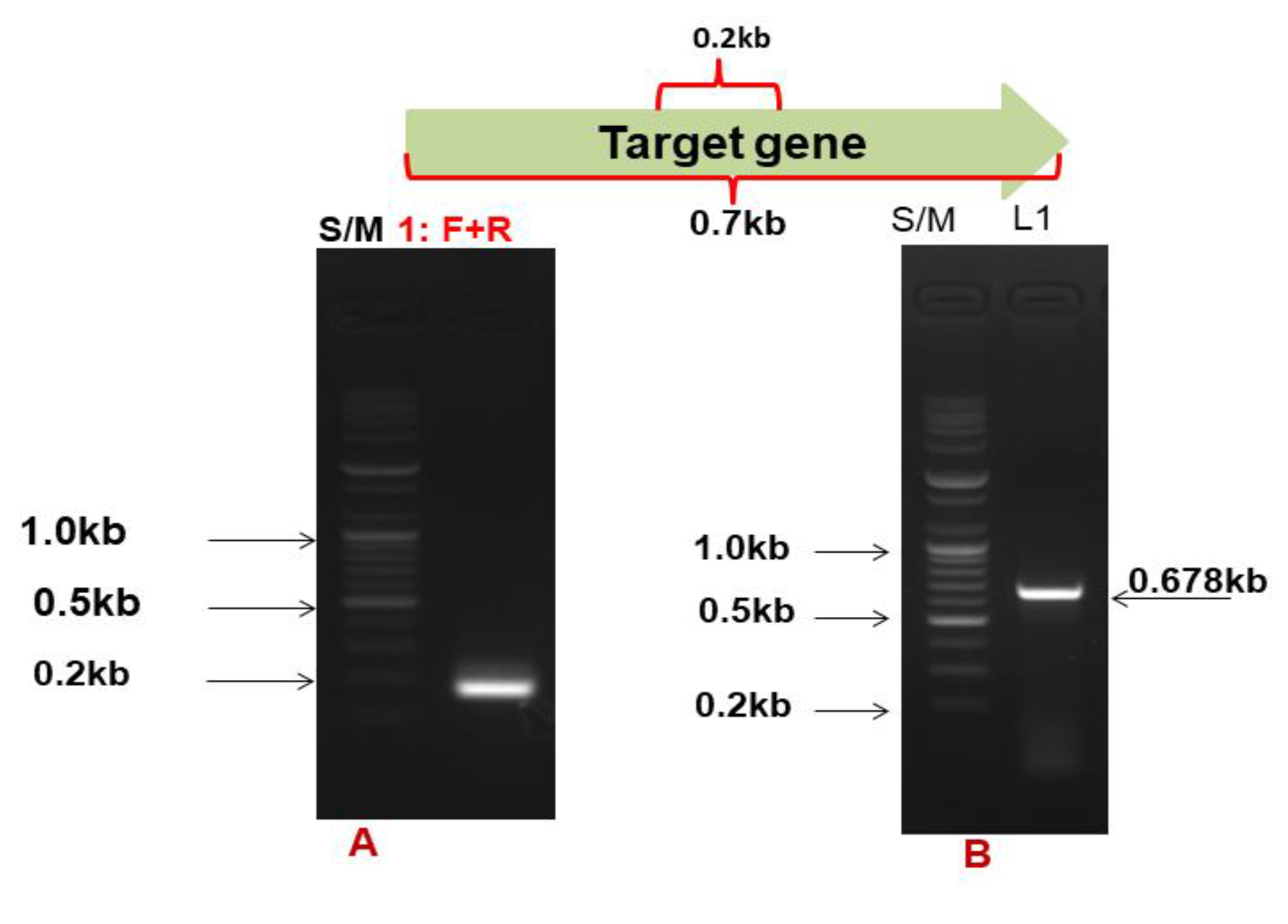
3.1. Gene Target and Cloning of the Cms Gene
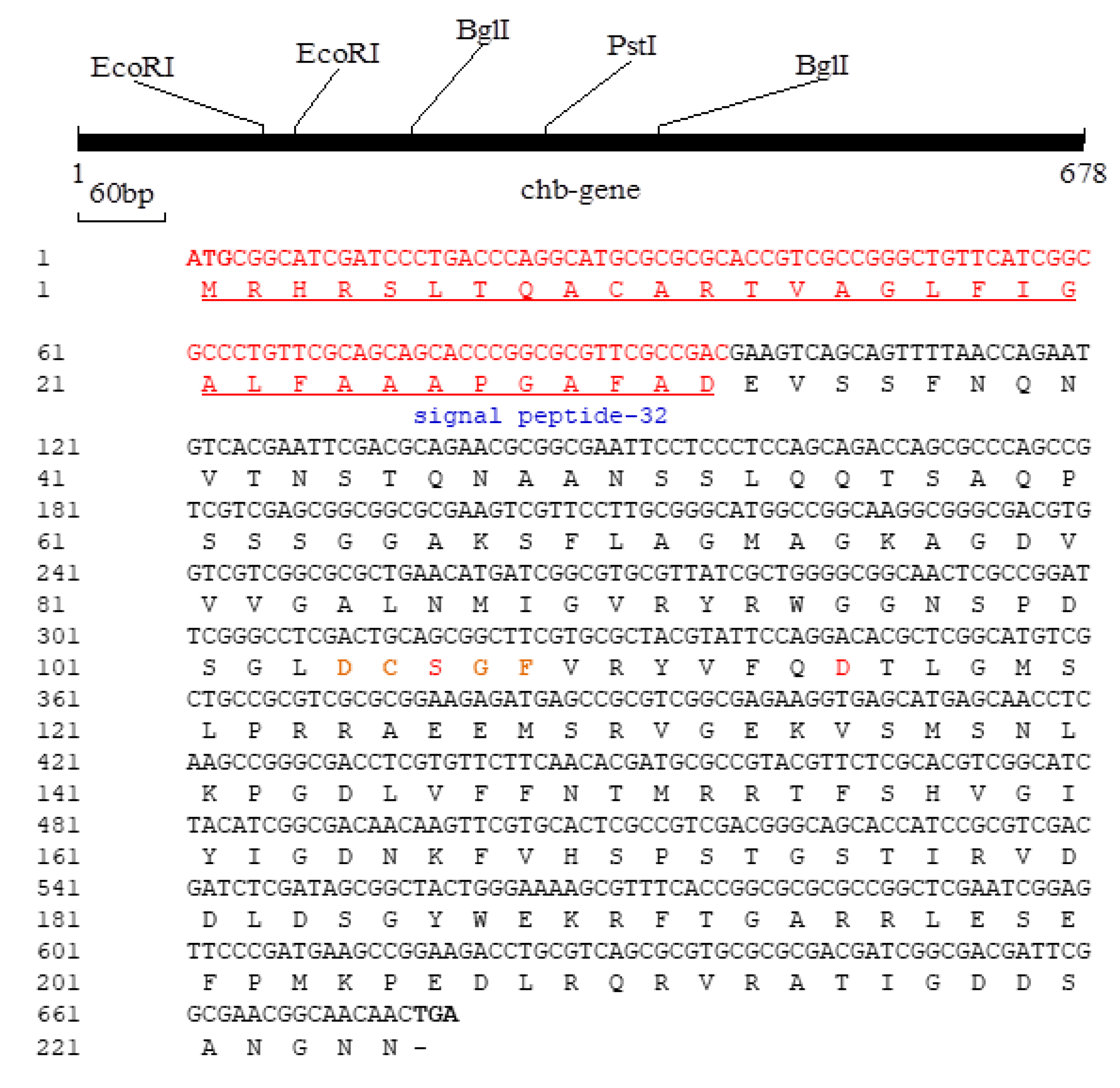
3.2. Structure Analysis and Expression of the Cms Gene
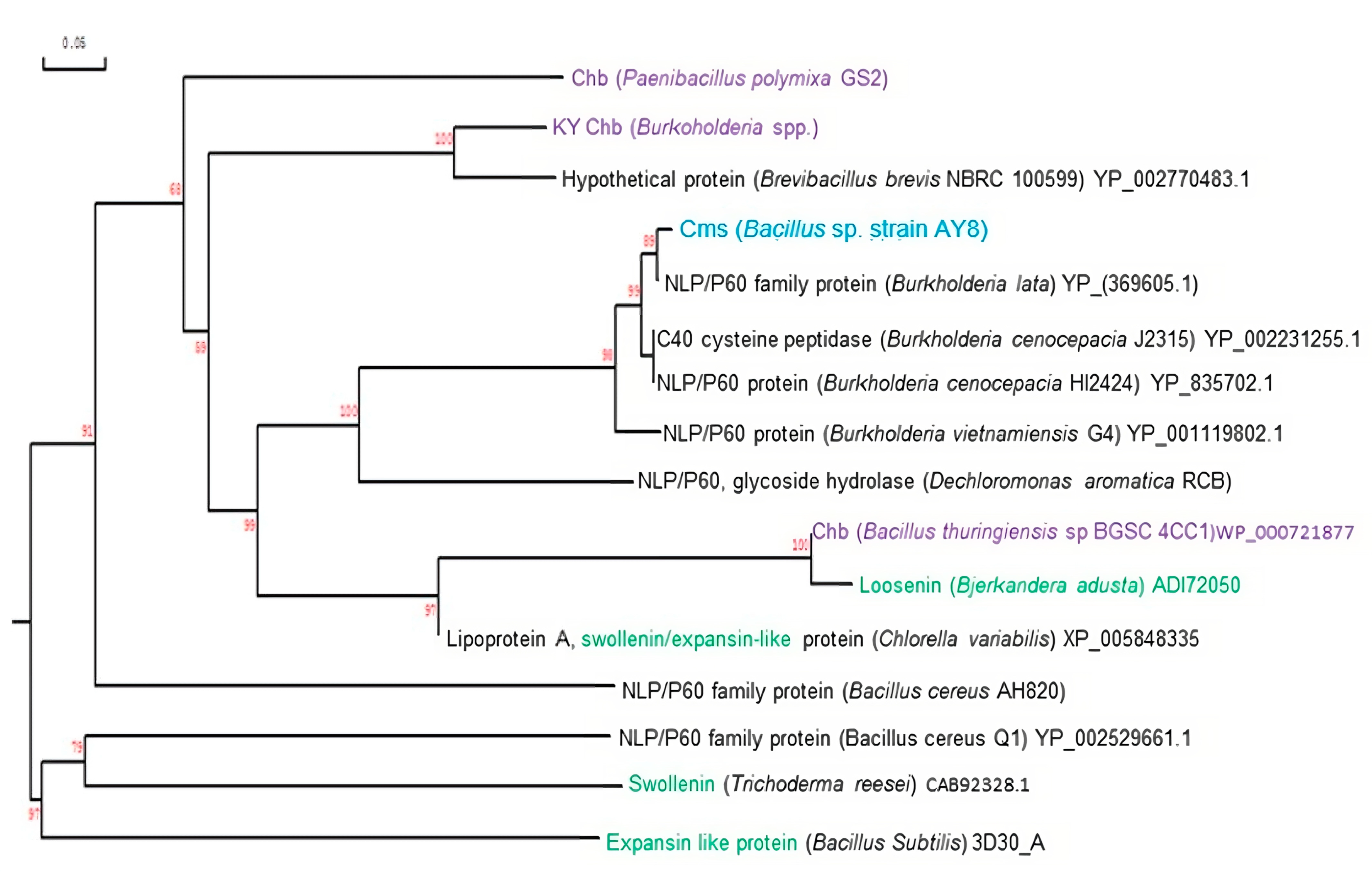
3.3. Comparision of Amino Acids of Cms Enzyme of Bacillus sp. AY8 with Those of Other NlpC/P60 Family Proteins
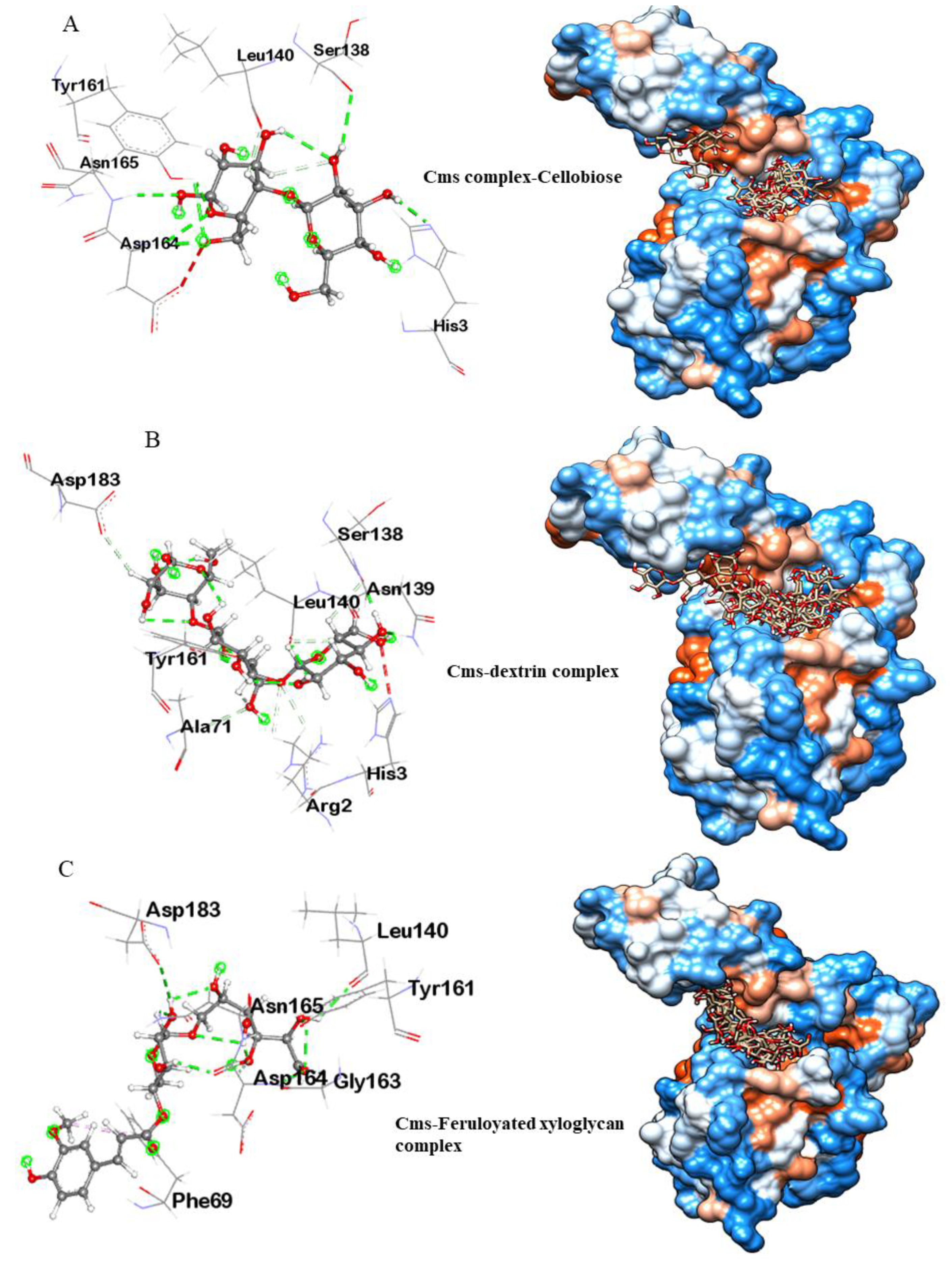
3.3.1. Molecular Docking Analysis of Cms Enzyme
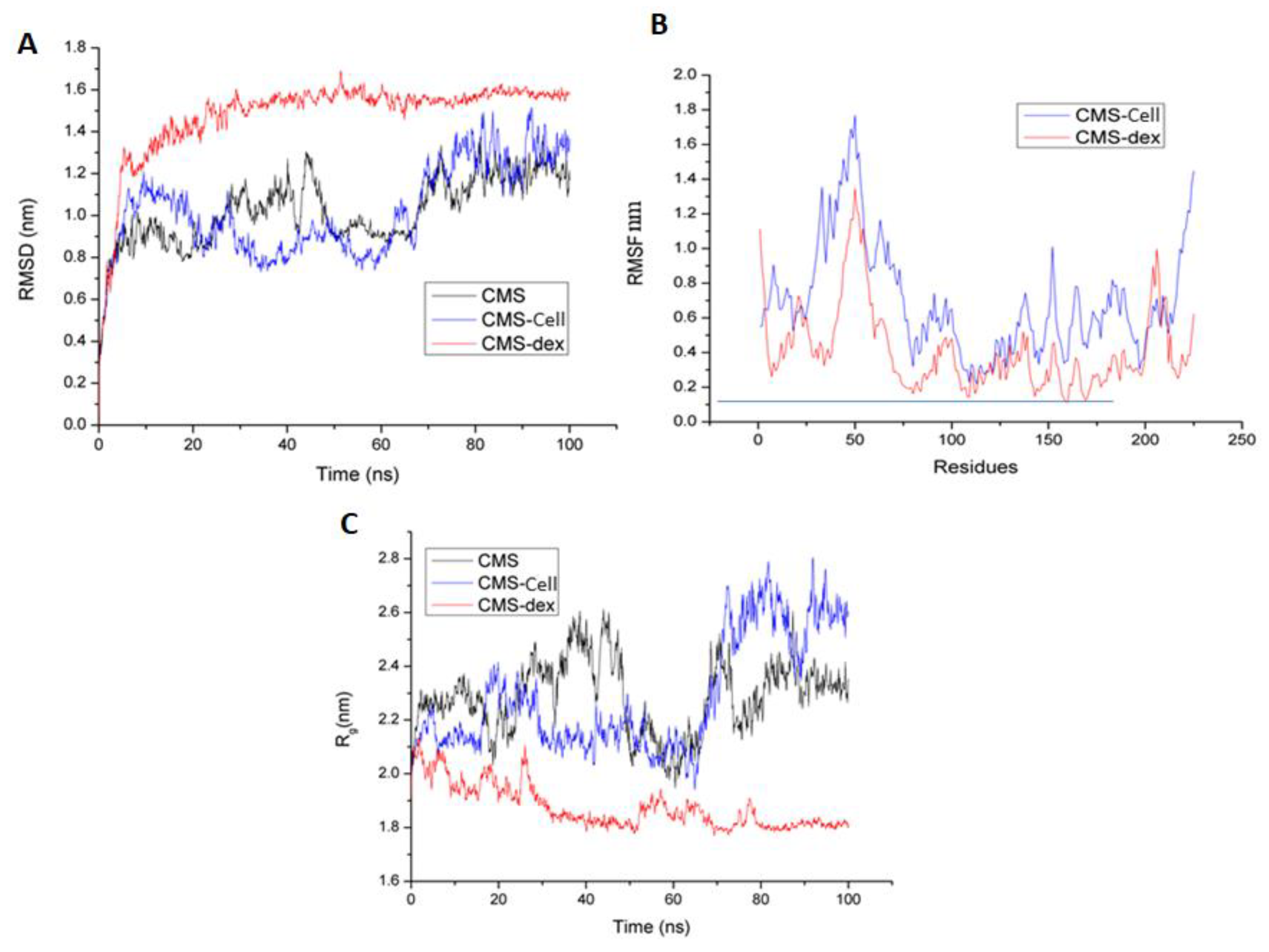
3.3.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
3.4. Cellulose Swelling Evidence of Recombinant Cms Enzyme on Cellulose Substrates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saloheimo, M.; Paloheimo, M.; Hakola, S.; Pere, J.; Swanson, B.; Nyyssönen, E.; Bhatia, A.; Ward, M.; Penttilä, M. Swollenin, a Trichoderma reesei protein with sequence similarity to the plant expansins, exhibits disruption activity on cellulosic materials. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 4202–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäger, G.; Girfoglio, M.; Dollo, F.; Rinaldi, R.; Bongard, H.; Commandeur, U.; Fischer, R.; Spiess, A.C.; Büchs, J. How recombinant swollenin from Kluyveromyces lactis affects cellulosic substrates and accelerates their hydrolysis. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2011, 23, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Brunecky, R.; Yao, B.; Xie, X.; Zheng, F.; Luo, H. A swollenin from Talaromyces leycettanus JCM12802 enhances cellulase hydrolysis toward various substrates. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 658096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; He, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L. Swelling Behaviors of pH- and Salt-Responsive Cellulose-Based Hydrogels. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Ma, B.; Shen, J.; Zhao, S.; Ma, X.; Wang, Z.; Fan, Y.; Tang, Q.; Wei, D. The Evolution of the Expansin Gene Family in Brassica Species. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 167, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitney, S.E.C.; Gidley, M.J.; McQueen-Mason, S.J. Probing expansin action using cellulose/hemicellulose composites. Plant J. 2000, 22, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourlay, K.; Hu, J.; Arantes, V.; Andberg, M.; Saloheimo, M.; Penttilä, M.; Saddler, J. Swollenin aids in the amorphogenesis step during the enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eibinger, M.; Sigl, K.; Sattelkow, J.; Ganner, T.; Ramoni, J.; Seiboth, B.; Plank, H.; Nidetzky, B. Functional characterization of the native swollenin from Trichoderma reesei: Study of its possible role as C1 factor of enzymatic lignocellulose conversion. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzarelou, D.; Billini, M.; Roumelioti, K.; Sophianopoulou, V. EglD, a putative endoglucanase, with an expansin like domain is localized in the conidial cell wall of Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2008, 45, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz-Castañeda, R.E.; Martínez-Anaya, C.; Cuervo-Soto, L.I.; Segovia, L.; Folch-Mallol, J.L. Loosenin, a novel protein with cellulose-disrupting activity from Bjerkandera adusta. Microb. Cell Factories 2011, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotman, Y.; Briff, E.; Viterbo, A.; Chet, I. Role of Swollenin, an Expansin-Like Protein from Trichoderma, in Plant Root Colonization. Plant. Physiol. 2008, 147, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.A.; Ishida, N.; Todaka, N.; Nakamura, R.; Maruyama, J.; Takahashi, H.; Kitamoto, K. Promotion of efficient saccharification of crystalline cellulose by Aspergillus fumigatus Swo1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2556–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.-M.; Tao, H.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.-D.; Zhang, J.-R.; Tang, A.-X. A novel non-hydrolytic protein from Pseudomonas oryzihabitans enhances the enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 168, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Cho, K.M.; Barman, D.N.; Kim, M.K.; Yun, H.D. A potential cellulose microfibril swelling enzyme isolated from Bacillus sp. AY8 enhances cellulose hydrolysis. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Hossain, M.S.; Debnath, G.C.; Sultana, S.; Rahman, A.; Hasan, Z.; Das, S.R.; Ashik, M.A.; Prodhan, M.Y.; Aktar, S.; et al. Unveiling Lignocellulolytic Trait of a Goat Omasum Inhabitant Klebsiella Variicola Strain HSTU-AAM51 in Light of Biochemical and Genome Analyses; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Sharker, B.; Islam, M.A.; Hossain, M.A.; Ahmad, I.; Mamun, A.A.; Ghosh, S.; Rahman, A.; Hossain, M.S.; Ashik, M.A.; Hoque, M.R.; et al. Characterization of lignin and hemicellulos e degradin g bacteria isolated from cow rumen and forest soil: Unveiling a novel enzymatic model for rice straw deconstruction. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, M.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Ahmad, I.; Akbor, M.A.; Rahman, A.; Manir, M.S.; Patel, H.M.; Cho, K.M. Unveiling chlorpyrifos mineralizing and tomato plant-growth activities of Enterobacter sp. strain HSTU-ASh6 using biochemical tests, field experiments, genomics, and in silico analyses. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1060554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.R.; Haque, M.A.; Akbor, M.A.; Abdullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Debnath, G.C.; Hossain, M.S.; Hasan, Z.; Rahman, A.; Islam, M.A.; Hossain, M.A.; et al. Organophosphorus insecticides mineralizing endophytic and rhizospheric soil bacterial consortium influence eggplant growth promotion. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Hwang, C.E.; Kim, S.C.; Cho, D.Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Cho, K.M.; Lee, J.H. Biodegradation of organophosphorus insecticides by two organophosphorus hydrolase genes (opdA and opdE) from isolated Leuconostoc mesenteroides WCP307 of kimchi origin. Process Biochem. 2020, 94, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.J.; Hong, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, S.R.; Kim, M.K.; Lim, W.J.; Shin, E.C.; Kim, E.J.; Cho, Y.U.; Yun, H.D. Endophytic Bacillus sp. CY22 from a balloon flower (Platycodon grandiflorum) produces surfactin isoforms. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 13, 859–865. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Cho, D.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Jung, J.G.; Jeong, E.H.; Haque, M.A.; Cho, K.M. Biodegradable properties of organophosphorus insecticides by the potential probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum WCP931 with a degrading gene (opdC). Appl. Biol. Chem. 2021, 64, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. Rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.; Akhtar, M.; Halilu, A.; Yun, H. Validation and extended application of cellulose microfibril swelling enzyme assay method to alkali induced swelling of cellulose. J. Chem. Eng. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 2, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- French, A.D. Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 2014, 21, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, A.D. Increment in evolution of cellulose crystallinity analysis. Cellulose 2020, 27, 5445–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Cho, D.Y.; Ahmad, I.; Patel, H.M.; Kim, M.J.; Jung, J.G.; Jeong, E.H.; Haque, M.A.; Cho, K.M. Mining of a novel esterase (est3S) gene from a cow rumen metagenomic library with organosphosphorus insecticides degrading capability: Catalytic insights by site directed mutations, docking, and molecular dynamic simulations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 190, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.M.; Shaikh, M.; Ahmad, I.; Lokwani, D.; Surana, S.J. BREED based de novo hybridization approach: Generating novel T790M/C797S-EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors to overcome the problem of mutation and resistance in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 2838–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squeglia, F.; Moreira, M.; Ruggiero, A.; Berisio, R. The Cell Wall Hydrolytic NlpC/P60 Endopeptidases in Mycobacterial Cytokinesis: A Structural Perspective. Cells 2019, 8, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peek, K.; Veitch, D.P.; Prescott, M.; Daniel, R.M.; MacIver, B.; Bergquist, P.L. Some characteristics of a proteinase from a thermophilic Bacillus sp. expressed in 2020: Comparison with the native enzyme and its processing in E. coli and in vitro. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.; Wu, X.; Wong, S. Cloning and expression of a novel protease gene encoding an extracellular neutral protease from Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 6364–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloma, A.L.A.N.; Rufo Jr, G.A.; Theriault, K.A.; Dwyer, M.; Wilson, S.W.; Pero, J. Cloning and characterization of the gene for an additional extracellular serine protease of Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 6889–6895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Power, S.D.; Adams, R.M.; Wells, J.A. Secretion and autoproteolytic maturation of subtilisin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 3096–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uusi-Tarkka, E.-K.; Skrifvars, M.; Haapala, A. Fabricating Sustainable All-Cellulose Composites. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Hippel, P.H.; Delagoutte, E. A general model for nucleic acid helicases and their “coupling” within macromolecular machines. Cell 2001, 104, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.J.; Lohman, T.M. Helicase-catalyzed DNA unwinding: Energy coupling by DNA motor proteins. Biophys. J. 1995, 68, 180S–185S. [Google Scholar]
- Sdrobiş, A.; Cazacu, G.; Totolin, M.; Vasile, C. Alkaline solution swelling of fatty acids modified softwood kraft pulp fibers under cold plasma conditions. Cell. Chem. Technol. 2011, 45, 329–338. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, V.; Huber, G.W.; Conner, W.C., Jr.; Auerbach, S.M. Simulating infrared spectra and hydrogen bonding in cellulose Iβ at elevated temperatures. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 135, 134506–134519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artzi, L.; Morag, E.; Shamshoum, M.; Bayer, E.A. Cellulosomal expansin: Functionality and incorporation into the complex. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevo, B.; Peterman, E.J. Forster resonance energy transfer and kinesin motor proteins. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nada, A.M.A.; Kamel, S.; El-Sakhawy, M. Thermal behaviour and infrared spectroscopy of cellulose carbamates. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2000, 70, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.Y.; Yoo, D.I.; Shin, Y.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, H.Y.; Chung, Y.S.; Park, W.H.; Youk, J.H. Crystalline structure analysis of cellulose treated with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide by means of X-ray diffraction and FTIR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 2376–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, M.; Heux, L.; Nishiyama, Y.; Langan, P. X-ray crystallographic, scanning microprobe X-ray diffraction, and cross-polarized/magic angle spinning 13C NMR studies of the structure of cellulose III. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaidos, G.; Soni, S.; Oswald, D.J.; Toselli, P.A.; Kirsch, K.H. Structure and function analysis of the CMS/CIN85 protein family identifies actin-bundling properties and heterotypic-complex formation. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 2366–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]


| Number | Uses | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| #2672F | Cloning | CCC AAT ACA ATT GCC AGC AG |
| #2673R | Cloning | GCT ATT TCC AAC ATT CCG RAG C |
| #2682F | Cloning | GGR TTT GAT TGT TCG GGR TTA |
| #2683R | Cloning | GCC AAT ATA CAT ACC AAC GTG |
| #2684F | Cloning | GAC TGC AGC GGC TTC GTG CGC TAC |
| #2685R | Cloning | GCC GAT RTA GAT GCC GAC GTG |
| #2709F | Cloning | ATG CRG CAT CGA TCC CTG AC |
| #2708R | Cloning | TCA GTT GTT GCC GTT CGC CG |
| #2710F | Cloning | GGA TCCGAAGTCAGCAGTTTTA |
| #2711R | Cloning | AAG CTT GTTGTTGCCGTTCGC |
| No. | Strains Name | AA | Gene ID | MW (Da) | SP | MW-SP | Conserved | Chr/Plasmid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bacillus cereus Q1 | 174 | 221642232 | 18,540 | 2247.76 | 16,294.24 | NlpC/P60 | plasmid |
| 2 | Bacillus thuringiensis serovar pulsiensis BGSC | 174 | 228918559 | 18,640 | 2419.97 | 16,220.03 | NlpC/P60 | Chr |
| 3 | Ruminococcus obeum ATCC 29174 | 334 | 153810514 | 36,687 | 3464.35 | 33,222.65 | NlpC/P60 | Master WGS * (no chromosome) |
| Clostridium bolteae ATCC BAA-613 | 334 | 160936317 | 36,720 | 3482.38 | 33,237.62 | NlpC/P60 famly; pfam 00877 | Master WGS (no chromosome) | |
| 4 | Clostridium difficile 630 | 334 | 126700956 | 36,623 | 3464.35 | 33,158.65 | NlpC/P60 famly; pfam 00877 | Chr |
| 5 | Mollicutes bacterium D7 | 334 | 237733575 | 36,641 | 3464.35 | 33,176.65 | NlpC/P60 famly; pfam 00877 | Master WGS (no chromosome) |
| 6 | Lacnospiraceae bacterium 3_1_57FAA_CT1 | 334 | 336429196 | 36,642 | 3464.35 | 33,177.65 | NlpC/P60 famly; pfam 00877 | Master WGS (no chromosome) |
| 7 | Lactobacillus vini DSM 20605 | 334 | 406838964 | 35,868 | 2990.79 | 32,877.21 | NlpC/P60 famly; pfam 00877 | No data |
| 8 | Bacillus cereus R309803 | 174 | 229162067 | 18,508 | 2233.74 | 16,284.26 | NlpC/P60 famly; pfam 00877 | chr |
| 9 | Bacillus cereus AH187 | 174 | 190015595 | 18,604 | 2281.78 | 16,322.22 | NlpC/P60 famly; pfam 00877 | plasmid |
| 10 | Bacillus cereus Rock1-15 | 174 | 229113559 | 18,692 | 2497.99 | 16,194.01 | NlpC/P60 famly; pfam 00877 | chr |
| 11 | Bacillus cereus BAG4X12-1 | 174 | 401113141 | 18,881.37 | 2526.04 | 16,355.33 | NlpC/P60 famly; pfam 00877 | Master WGS (no chromosome) |
| 12 | Bacillus cereus VD107 | 174 | 401239705 | 18,639.95 | 2467.96 | 16,171.99 | NlpC/P60 famly; pfam 00877 | Master WGS (no chromosome) |
| 13 | Bacillus cereus AH603 | 174 | 229065268 | 18,535 | 2437.94 | 16,097.06 | NlpC/P60 famly; pfam 00877 | chr |
| 14 | Bacillus cereus HuA2-1 | 174 | 402445052 | 18,678.13 | 2437.94 | 16,240.16 | NlpC/P60 famly; pfam 00877 | Master WGS (no chromosome) |
| 15 | Bacillus cereus VD142 | 181 | 401073234 | 19,521.11 | 2349.81 | 17,171.3 | NlpC/P60 famly; pfam 00877 | Master WGS (no chromosome) |
| 16 | Bacillus cereus MSX-D12 | 348 | 401201280 | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haque, M.A.; Barman, D.N.; Rahman, A.; Hossain, M.S.; Ghosh, S.; Nahar, M.A.; Nahar, M.N.-E.-N.; Saha, J.K.; Cho, K.M.; Yun, H.D. Molecular Cloning, In Silico Analysis, and Characterization of a Novel Cellulose Microfibril Swelling Gene Isolated from Bacillus sp. Strain AY8. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122857
Haque MA, Barman DN, Rahman A, Hossain MS, Ghosh S, Nahar MA, Nahar MN-E-N, Saha JK, Cho KM, Yun HD. Molecular Cloning, In Silico Analysis, and Characterization of a Novel Cellulose Microfibril Swelling Gene Isolated from Bacillus sp. Strain AY8. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(12):2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122857
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaque, Md. Azizul, Dhirendra Nath Barman, Aminur Rahman, Md. Shohorab Hossain, Sibdas Ghosh, Most. Aynun Nahar, Mst. Nur-E-Nazmun Nahar, Joyanta K. Saha, Kye Man Cho, and Han Dae Yun. 2023. "Molecular Cloning, In Silico Analysis, and Characterization of a Novel Cellulose Microfibril Swelling Gene Isolated from Bacillus sp. Strain AY8" Microorganisms 11, no. 12: 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122857
APA StyleHaque, M. A., Barman, D. N., Rahman, A., Hossain, M. S., Ghosh, S., Nahar, M. A., Nahar, M. N.-E.-N., Saha, J. K., Cho, K. M., & Yun, H. D. (2023). Molecular Cloning, In Silico Analysis, and Characterization of a Novel Cellulose Microfibril Swelling Gene Isolated from Bacillus sp. Strain AY8. Microorganisms, 11(12), 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122857






