Attenuated Replication-Competent Herpes Simplex Virus Expressing an ECM-Modifying Transgene Hyaluronan Synthase 2 of Naked Mole Rat in Oncolytic Gene Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Oncolytic HSV
1.2. Cancer and the ECM
1.3. Hyaluronan
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Viruses
2.3. Virus Infections
2.4. Viral Release Assay
2.5. Gene Expression Assay
2.6. Oncolytic Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roizman, B. The Function of Herpes Simplex Virus Genes: A Primer for Genetic Engineering of Novel Vectors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 11307–11312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.; Rabkin, S.D. Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Vectors for Cancer Virotherapy. Cancer Gene Ther. 2002, 9, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morissette, G.; Flamand, L. Herpesviruses and Chromosomal Integration. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 12100–12109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacein-Bey-Abina, S.; Garrigue, A.; Wang, G.P.; Soulier, J.; Lim, A.; Morillon, E.; Clappier, E.; Caccavelli, L.; Delabesse, E.; Beldjord, K.; et al. Insertional Oncogenesis in 4 Patients after Retrovirus-Mediated Gene Therapy of SCID-X1. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3132–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Watkins, S.C.; Schaffer, P.A.; DeLuca, N.A. Prolonged Gene Expression and Cell Survival after Infection by a Herpes Simplex Virus Mutant Defective in the Immediate-Early Genes Encoding ICP4, ICP27, and ICP22. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 6358–6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Du, M.; Jin, H.; Ma, Y.; He, B.; et al. ICP34.5 Protein of Herpes Simplex Virus Facilitates the Initiation of Protein Translation by Bridging Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2α (EIF2α) and Protein Phosphatase 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 24785–24792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKie, E.A.; MacLean, A.R.; Lewis, A.D.; Cruickshank, G.; Rampling, R.; Barnett, S.C.; Kennedy, P.G.E.; Brown, S.M. Selective in Vitvo Replication of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1) ICP34.5 Null Mutants in Primary Human CNS Tumours- Evaluation of a Potentially Effective Clinical Therapy. Br. J. Cancer 1996, 74, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, J.; Wakimoto, H. Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus-Based Strategies: Toward a Breakthrough in Glioblastoma Therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.; Roizman, B. The Gamma 1(34.5) Gene of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Precludes Neuroblastoma Cells from Triggering Total Shutoff of Protein Synthesis Characteristic of Programed Cell Death in Neuronal Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 3266–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Gross, M.; Roizman, B. The Γ134.5 Protein of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Has the Structural and Functional Attributes of a Protein Phosphatase 1 Regulatory Subunit and Is Present in a High Molecular Weight Complex with the Enzyme in Infected Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 20737–20743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalke, K.; Orpana, J.; Lasanen, T.; Esparta, O.; Lund, L.M.; Frejborg, F.; Vuorinen, T.; Paavilainen, H.; Hukkanen, V. The In Vitro Replication, Spread, and Oncolytic Potential of Finnish Circulating Strains of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1. Viruses 2022, 14, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuhara, H.; Ino, Y.; Todo, T. Oncolytic Virus Therapy: A New Era of Cancer Treatment at Dawn. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.B.; Puzanov, I.; Kelley, M.C. Talimogene Laherparepvec (T-VEC) for the Treatment of Advanced Melanoma. Immunotherapy 2015, 7, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, H.; Silk, A.W.; Kane, M.P.; Kaufman, H.L. Into the Clinic: Talimogene Laherparepvec (T-VEC), a First-in-Class Intratumoral Oncolytic Viral Therapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2016, 4, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andtbacka, R.H.I.; Kaufman, H.L.; Collichio, F.; Amatruda, T.; Senzer, N.; Chesney, J.; Delman, K.A.; Spitler, L.E.; Puzanov, I.; Agarwala, S.S.; et al. Talimogene Laherparepvec Improves Durable Response Rate in Patients with Advanced Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2780–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Jou, T.H.T.; Hsin, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, K.; Ye, J.; Yin, H.; Xing, Y. Talimogene Laherparepvec (T-VEC): A Review of the Recent Advances in Cancer Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, I.R.; Naoe, Y.; Bustos-Villalobos, I.; Ichinose, T.; Tanaka, M.; Zhiwen, W.; Mukoyama, N.; Morimoto, T.; Miyajima, N.; Hitoki, H.; et al. Genomic Signature of the Natural Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus HF10 and Its Therapeutic Role in Preclinical and Clinical Trials. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirooka, Y.; Kasuya, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Kawashima, H.; Ohno, E.; Villalobos, I.B.; Naoe, Y.; Ichinose, T.; Koyama, N.; Tanaka, M.; et al. A Phase I Clinical Trial of EUS-Guided Intratumoral Injection of the Oncolytic Virus, HF10 for Unresectable Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guide, S.V.; Gonzalez, M.E.; Bağcı, I.S.; Agostini, B.; Chen, H.; Feeney, G.; Steimer, M.; Kapadia, B.; Sridhar, K.; Quesada Sanchez, L.; et al. Trial of Beremagene Geperpavec (B-VEC) for Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. New Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krystal Biotech, Inc. Krystal Biotech Receives FDA Approval for the First-Ever Redosable Gene Therapy, VYJUVEK TM (Beremagene Geperpavec-Svdt) for the Treatment of Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. Available online: https://ir.krystalbio.com/news-releases/news-release-details/krystal-biotech-receives-fda-approval-first-ever-redosable-gene (accessed on 26 May 2023).
- Frantz, C.; Stewart, K.M.; Weaver, V.M. The Extracellular Matrix at a Glance. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 4195–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Kosaric, N.; Bonham, C.A.; Gurtner, G.C. Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 665–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankov, R.; Yamada, K.M. Fibronectin at a Glance. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 3861–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinke, J.M.; Sorg, H. Wound Repair and Regeneration. Eur. Surg. Res. 2012, 49, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lullo, G.A.; Sweeney, S.M.; Körkkö, J.; Ala-Kokko, L.; San Antonio, J.D. Mapping the Ligand-Binding Sites and Disease-Associated Mutations on the Most Abundant Protein in the Human, Type I Collagen. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 4223–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubow, K.E.; Vukmirovic, R.; Zhe, L.; Klotzsch, E.; Smith, M.L.; Gourdon, D.; Luna, S.; Vogel, V. Mechanical Forces Regulate the Interactions of Fibronectin and Collagen I in Extracellular Matrix. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, J.R.E.; Laurent, T.C.; Laurent, U.B.G. Hyaluronan: Its Nature, Distribution, Functions and Turnover. J. Intern. Med. 1997, 242, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, N.; Paus, R.; Bayat, A. Functional Histopathology of Keloid Disease. Histol. Histopathol. 2015, 30, 1033–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybinski, B.; Franco-Barraza, J.; Cukierman, E. The Wound Healing, Chronic Fibrosis, and Cancer Progression Triad. Physiol. Genom. 2014, 46, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodison, S.; Urquidi, V.; Tarin, D. CD44 Cell Adhesion Molecules. J. Clin. Pathol. Mol. Pathol. 1999, 52, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tolg, C.; Turley, E. Dissecting the Dual Nature of Hyaluronan in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, R.A.; Tian, Y.a.C.; Steadman, R.; Phillips, A.O. TGF-Β1-Mediated Fibroblast–Myofibroblast Terminal Differentiation—The Role of Smad Proteins. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 282, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashida, T.; Wu, M.-H.; Pierce, A.; Poncelet, A.-C.; Varga, J.; Schnaper, H.W. MAP-Kinase Activity Necessary for TGFβ1-Stimulated Mesangial Cell Type I Collagen Expression Requires Adhesion-Dependent Phosphorylation of FAK Tyrosine 397. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 4230–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Ma, Y.; Cao, G.; Ma, Z.; Chen, R.; Cvijic, M.E.; Cheng, D. Integrin AVβ1 Regulates Procollagen I Production through a Non-Canonical Transforming Growth Factor β Signaling Pathway in Human Hepatic Stellate Cells. Biochem. J. 2021, 478, 1689–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.-W.; Yevsa, T.; Woller, N.; Hoenicke, L.; Wuestefeld, T.; Dauch, D.; Hohmeyer, A.; Gereke, M.; Rudalska, R.; Potapova, A.; et al. Senescence Surveillance of Pre-Malignant Hepatocytes Limits Liver Cancer Development. Nature 2011, 479, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, N. The Roles and Mechanisms of Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP): Can It Be Controlled by Senolysis? Inflamm. Regen. 2022, 42, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.R.; Trowbridge, J.M.; Rudisill, J.A.; Termeer, C.C.; Simon, J.C.; Gallo, R.L. Hyaluronan Fragments Stimulate Endothelial Recognition of Injury through TLR4. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 17079–17084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Liang, J.; Noble, P.W. Hyaluronan as an Immune Regulator in Human Diseases. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 221–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghose, S.; Biswas, S.; Datta, K.; Tyagi, R.K. Dynamic Hyaluronan Drives Liver Endothelial Cells towards Angiogenesis. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Takahashi, N.; Hirabara, S.; Ishiguro, N.; Kojima, T. Hyaluronan Inhibits Tlr-4-Dependent RANKL Expression in Human Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothapalli, D.; Zhao, L.; Hawthorne, E.A.; Cheng, Y.; Lee, E.; Puré, E.; Assoian, R.K. Hyaluronan and CD44 Antagonize Mitogen-Dependent Cyclin D1 Expression in Mesenchymal Cells. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 176, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.S.; Dejesus, J.; Short, A.R.; Otero, J.J.; Sarkar, A.; Winter, J.O. Glioblastoma Behaviors in Three-Dimensional Collagen-Hyaluronan Composite Hydrogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 9276–9284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pibuel, M.A.; Poodts, D.; Díaz, M.; Hajos, S.E.; Lompardía, S.L. The Scrambled Story between Hyaluronan and Glioblastoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enegd, B.; King, J.A.J.; Stylli, S.; Paradiso, L.; Kaye, A.H.; Novak, U. Overexpression of Hyaluronan Synthase-2 Reduces the Tumorigenic Potential of Glioma Cells Lacking Hyaluronidase Activity. Neurosurgery 2002, 50, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, Y.; Sato, N.; Adachi, Y.; Amaike, T.; Koga, A.; Kohi, S.; Noguchi, H.; Nakayama, T.; Hirata, K. Overexpression of Transmembrane Protein 2 (TMEM2), a Novel Hyaluronidase, Predicts Poor Prognosis in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 1479–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Azpurua, J.; Hine, C.; Vaidya, A.; Myakishev-Rempel, M.; Ablaeva, J.; Mao, Z.; Nevo, E.; Gorbunova, V.; Seluanov, A. High-Molecular-Mass Hyaluronan Mediates the Cancer Resistance of the Naked Mole Rat. Nature 2013, 499, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Qiao, S.; Hou, X.; Tian, H.; Deng, S.; Ye, K.; Nie, Y.; Chen, X.; Yan, H.; Tian, W. Bioengineered Tumor Microenvironments with Naked Mole Rats High-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronan Induces Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cells. Oncogene 2019, 38, 4297–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Tian, X.; Lu, J.Y.; Boit, K.; Ablaeva, J.; Zakusilo, F.T.; Emmrich, S.; Firsanov, D.; Rydkina, E.; Biashad, S.A.; et al. Increased Hyaluronan by Naked Mole-Rat Has2 Improves Healthspan in Mice. Nature 2023, 621, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygårdas, M.; Paavilainen, H.; Müther, N.; Nagel, C.H.; Röyttä, M.; Sodeik, B.; Hukkanen, V. A Herpes Simplex Virus-Derived Replicative Vector Expressing LIF Limits Experimental Demyelinating Disease and Modulates Autoimmunity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, R.K.; Harila, K.; Kangas, S.M.; Paavilainen, H.; Heape, A.M.; Mohr, I.J.; Hukkanen, V. An Investigation of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Latency in a Novel Mouse Dorsal Root Ganglion Model Suggests a Role for ICP34.5 in Reactivation. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 2304–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paavilainen, H.; Romanovskaya, A.; Nygårdas, M.; Bamford, D.H.; Poranen, M.M.; Hukkanen, V. Innate Responses to Small Interfering RNA Pools Inhibiting Herpes Simplex Virus Infection in Astrocytoid and Epithelial Cells. Innate Immun. 2015, 21, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanovskaya, A.; Paavilainen, H.; Nygårdas, M.; Bamford, D.H.; Hukkanen, V.; Poranen, M.M. Enzymatically Produced Pools of Canonical and Dicer-Substrate SiRNA Molecules Display Comparable Gene Silencing and Antiviral Activities against Herpes Simplex Virus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broberg, E.K.; Nygårdas, M.; Salmi, A.A.; Hukkanen, V. Low Copy Number Detection of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 MRNA and Mouse Th1 Type Cytokine MRNAs by Light Cycler Quantitative Real-Time PCR. J. Virol. Methods 2003, 112, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennisi, R.; Sciortino, M.T.; Lo Gullo, M.A. Study of Intracellular Signaling Network Triggered by HSV- 1 and Graphene Based Nanomaterials: Their Use as Potential Tools in Gene Therapy. Ph.D. Thesis, Università degli Studi di Messina, Messina, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Peri, P.; Mattila, R.K.; Kantola, H.; Broberg, E.; Karttunen, H.S.; Waris, M.; Vuorinen, T.; Hukkanen, V. Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Us3 Gene Deletion Influences Toll-like Receptor Responses in Cultured Monocytic Cells. Virol. J. 2008, 5, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygårdas, M.; Vuorinen, T.; Aalto, A.P.; Bamford, D.H.; Hukkanen, V. Inhibition of Coxsackievirus B3 and Related Enteroviruses by Antiviral Short Interfering RNA Pools Produced Using Φ6 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2468–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xafis, V.; Schaefer, G.O.; Labude, M.K.; Zhu, Y.; Holm, S.; Foo, R.S.Y.; Lai, P.S.; Chadwick, R. Germline Genome Modification through Novel Political, Ethical, and Social Lenses. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
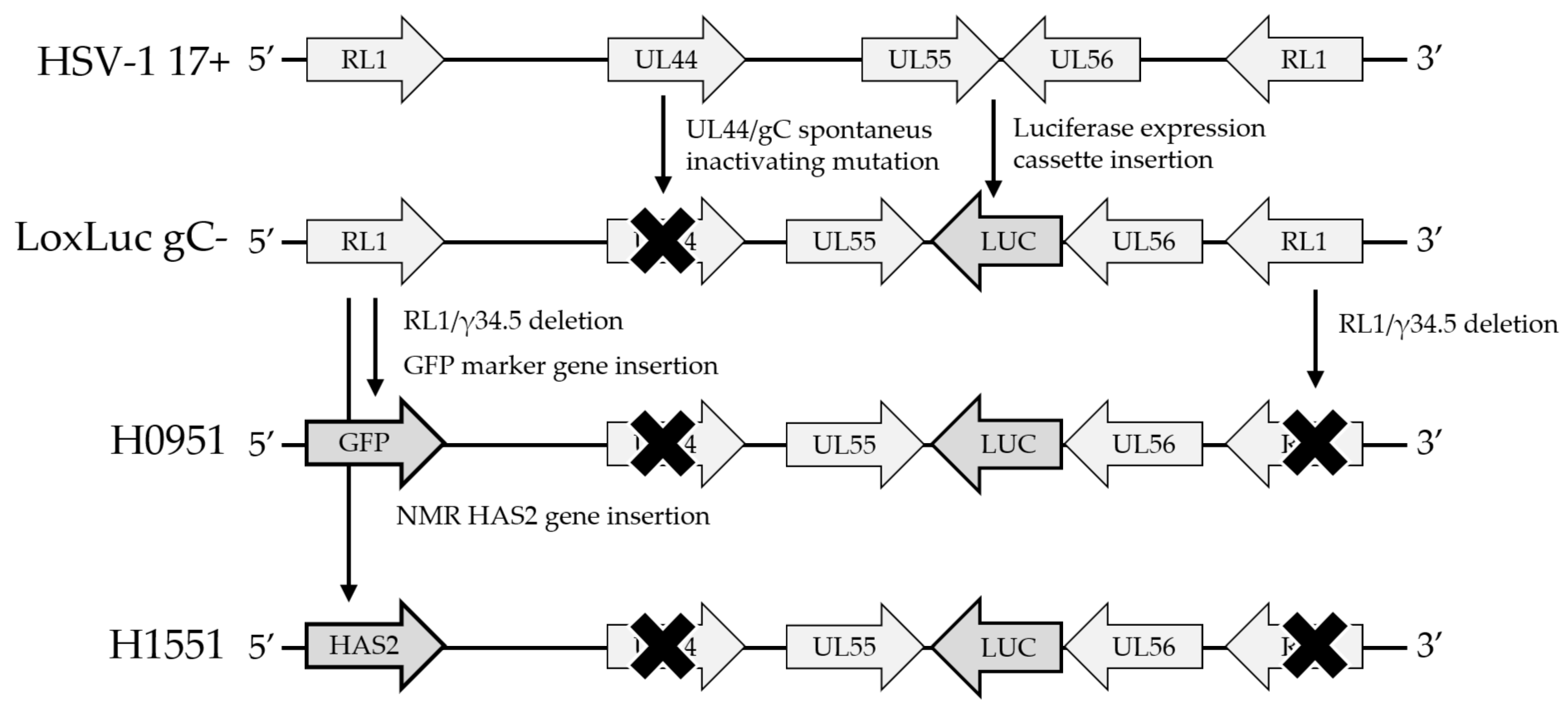




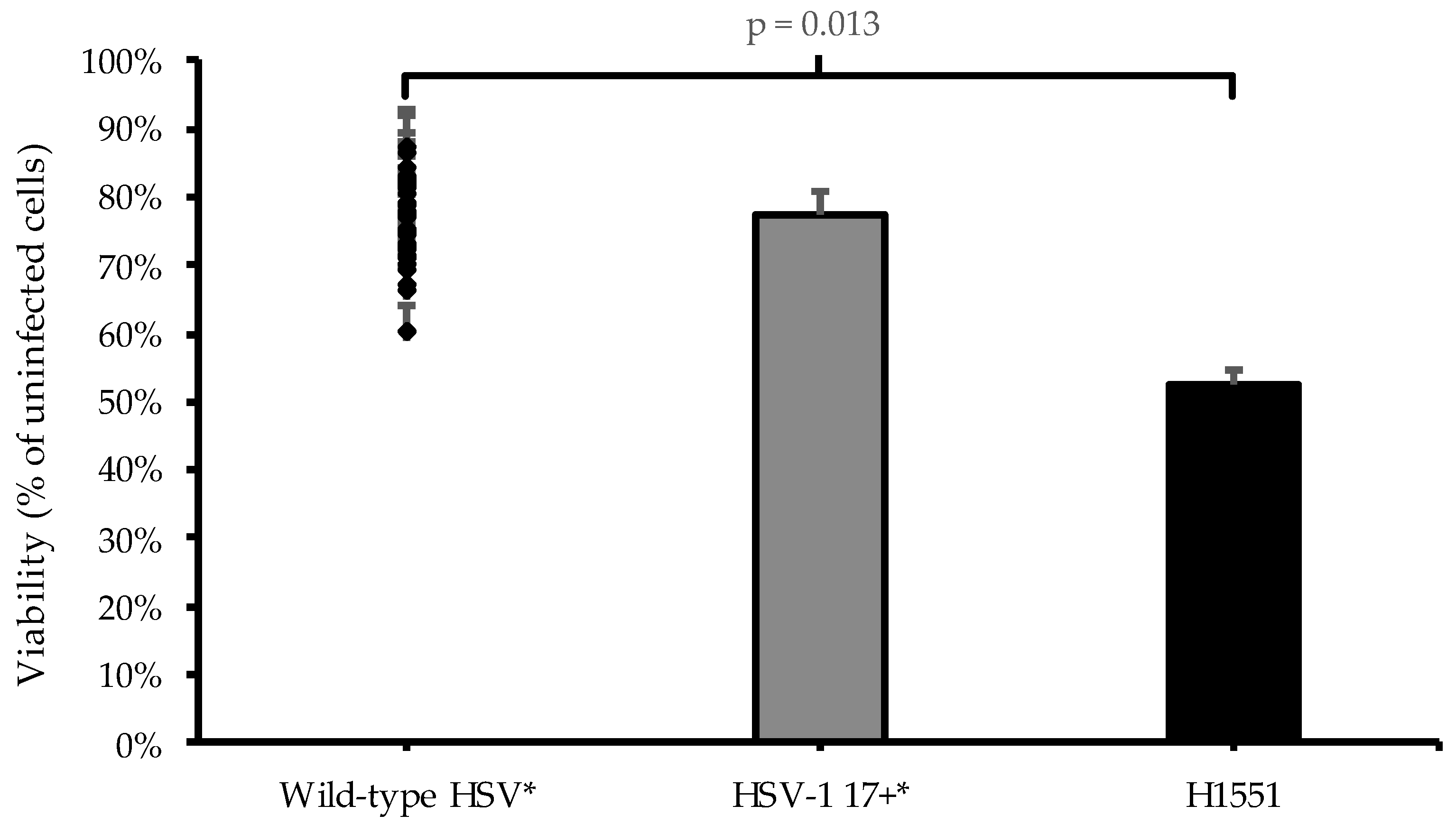
| HSV Strain | RL1/γ134.5 | UL55/UL56 Insertion | UL44 | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17+ | + | - | + | Parental strain |
| LoxLuc | + | Luc | + | [49] |
| H1052 | GFP | Luc | + | [50] |
| LoxLuc gC- | + | Luc | - | This study |
| H0951 | GFP | Luc | - | This study |
| H1551 | NMR-HAS2 | Luc | - | This study |
| Name | Sequence | References |
|---|---|---|
| HAS2 sense | 5′-AAGTGGGGTGGAAAACGAG-3′ | This study |
| HAS2 antisense | 5′-GTCCAGCATGGTATCGGAGT-3′ | This study |
| VP16 sense | 5′-TTTGACCCGCGAGATCCTAT-3′ | [50,53] |
| VP16 antisense | 5′-GCTCCGTTGACGAACATGAA-3′ | [50,53] |
| PKR sense | 5′-GGCCGCTAAACTTGCATATC-3′ | [54] |
| PKR antisense | 5′-GCGAGTGTGCTGGTCACTAA-3′ | [54] |
| IFNβ sense | 5′-TCTCCACGACAGCTCTTTCCA-3′ | [51,55] |
| IFNβ antisense | 5′-ACACTGACAATTGCTGCTTCTTTG-3′ | [51,55] |
| IL-29/IFNλ1 sense | 5′-GGAGCTAGCGAGCTTCAAGA-3′ | [51,52] |
| IL-29/IFNλ1 antisense | 5′-GGAAGACAGGAGAGCTGCAA-3′ | [51,52] |
| GAPDH sense | 5′-GAGAAGGCTGGGGCTCAT-3′ | [51,56] |
| GAPDH antisense | 5′-TGCTGATGATCTTGAGGCTG-3′ | [51,56] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palomäki, J.; Kalke, K.; Orpana, J.; Lund, L.; Frejborg, F.; Paavilainen, H.; Järveläinen, H.; Hukkanen, V. Attenuated Replication-Competent Herpes Simplex Virus Expressing an ECM-Modifying Transgene Hyaluronan Synthase 2 of Naked Mole Rat in Oncolytic Gene Therapy. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112657
Palomäki J, Kalke K, Orpana J, Lund L, Frejborg F, Paavilainen H, Järveläinen H, Hukkanen V. Attenuated Replication-Competent Herpes Simplex Virus Expressing an ECM-Modifying Transgene Hyaluronan Synthase 2 of Naked Mole Rat in Oncolytic Gene Therapy. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(11):2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112657
Chicago/Turabian StylePalomäki, Jussi, Kiira Kalke, Julius Orpana, Liisa Lund, Fanny Frejborg, Henrik Paavilainen, Hannu Järveläinen, and Veijo Hukkanen. 2023. "Attenuated Replication-Competent Herpes Simplex Virus Expressing an ECM-Modifying Transgene Hyaluronan Synthase 2 of Naked Mole Rat in Oncolytic Gene Therapy" Microorganisms 11, no. 11: 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112657
APA StylePalomäki, J., Kalke, K., Orpana, J., Lund, L., Frejborg, F., Paavilainen, H., Järveläinen, H., & Hukkanen, V. (2023). Attenuated Replication-Competent Herpes Simplex Virus Expressing an ECM-Modifying Transgene Hyaluronan Synthase 2 of Naked Mole Rat in Oncolytic Gene Therapy. Microorganisms, 11(11), 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112657







