Identification, Genome Sequencing, and Characterizations of Helicobacter pylori Sourced from Pakistan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of H. pylori
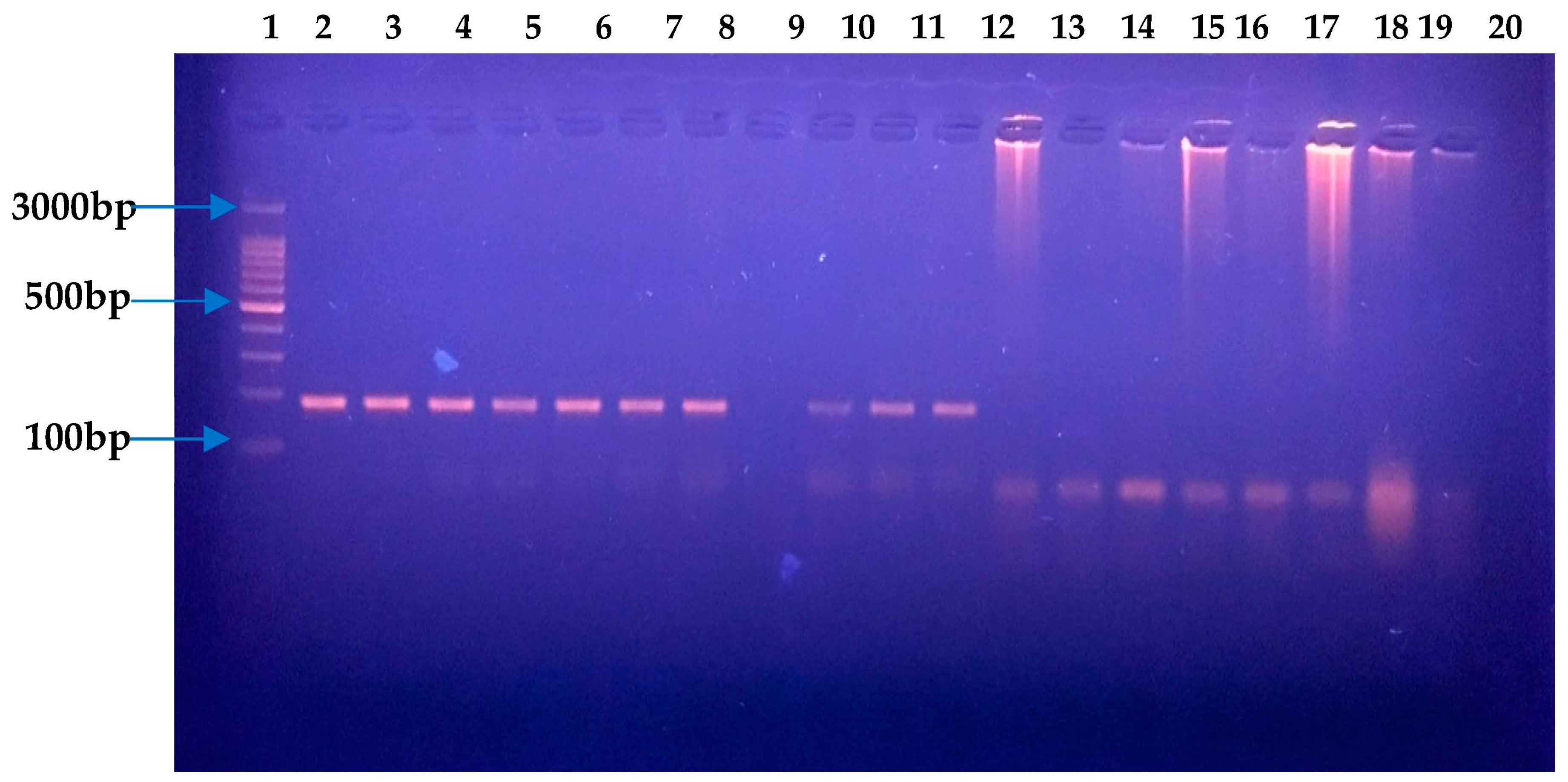
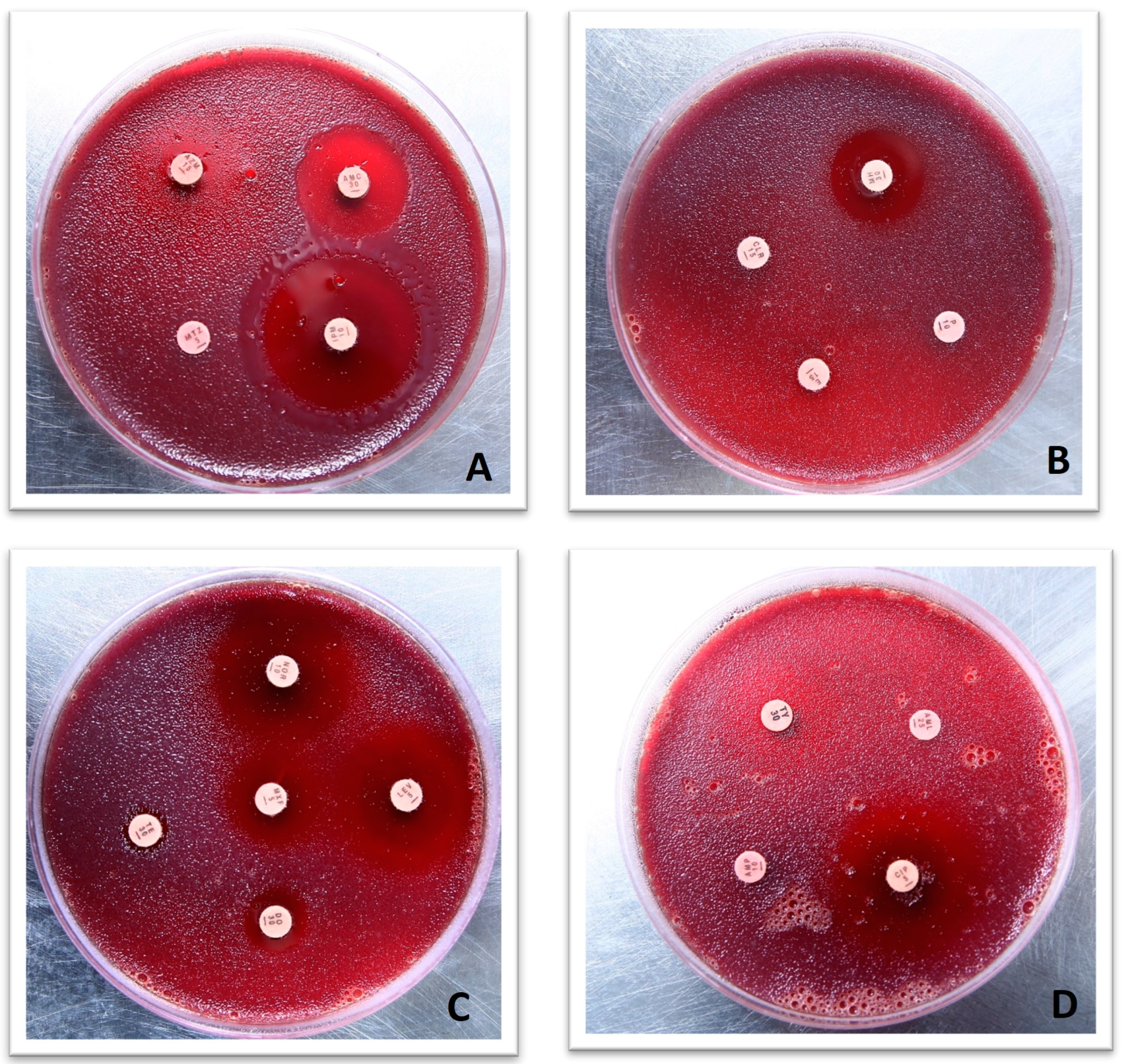
2.2. Molecular Confirmation of H. pylori via 16S RNA and Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
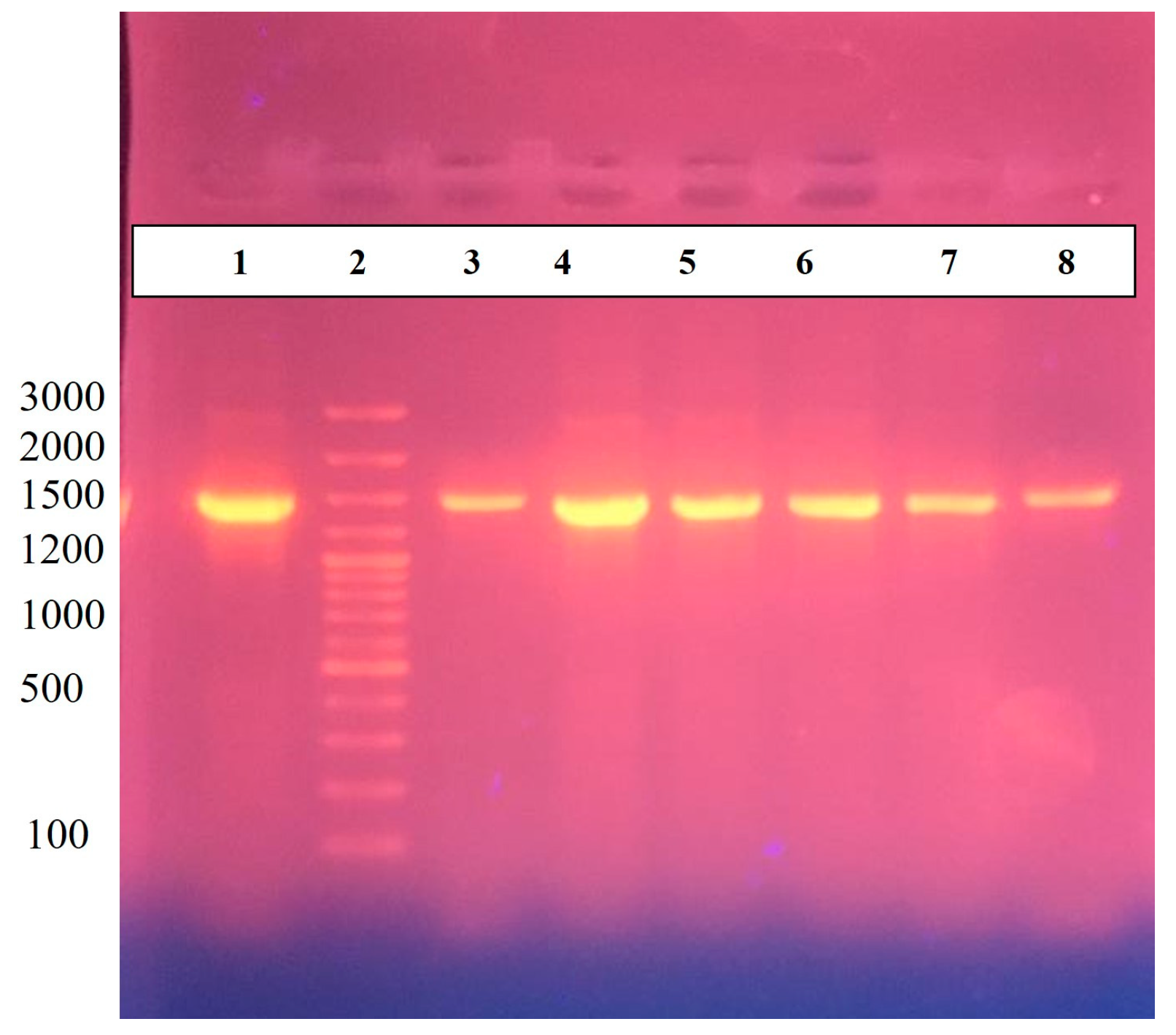
2.3. Library Preparation, Genome Sequencing, and Assembly
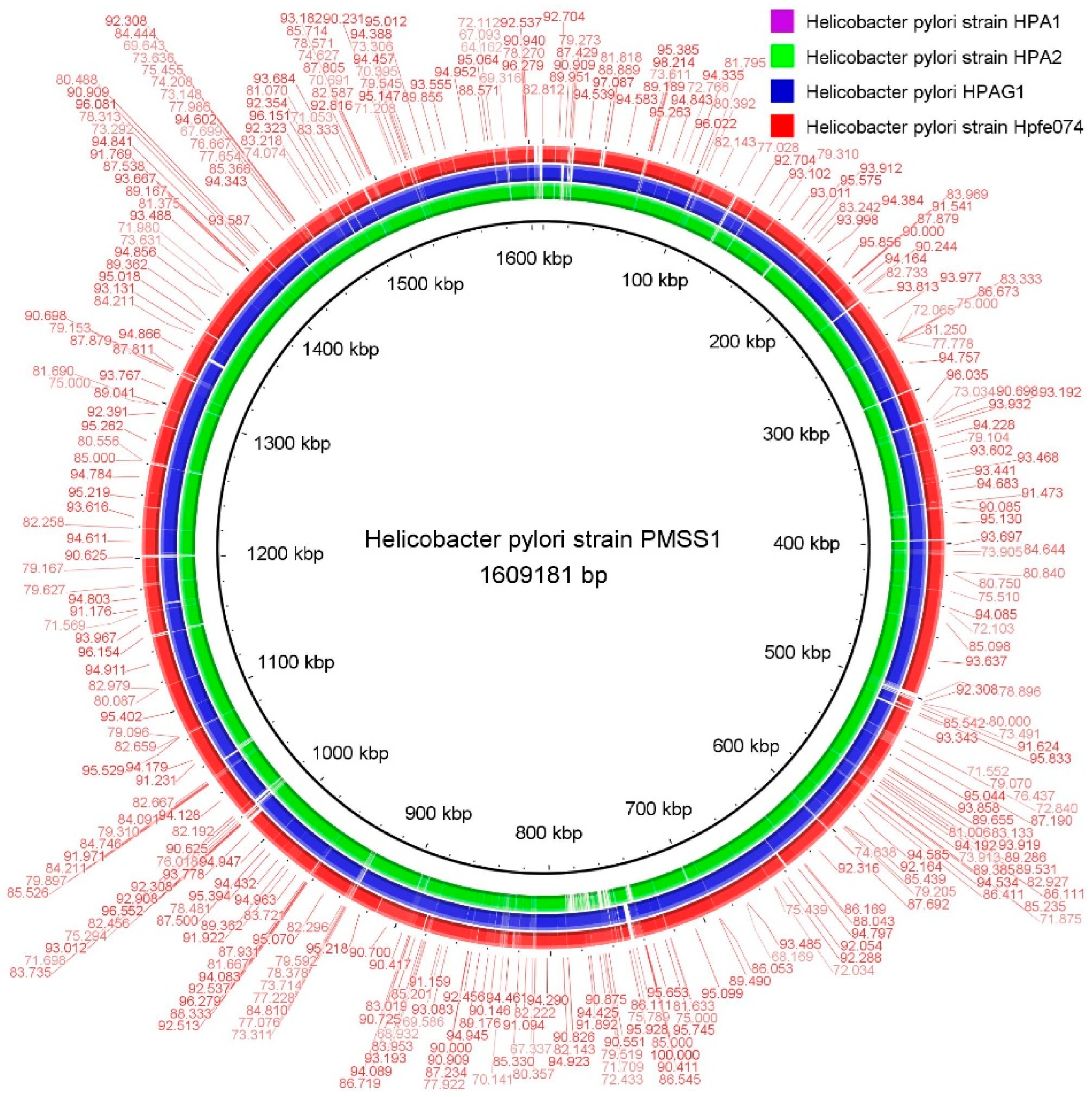
2.4. Comparative Genomes Analysis
2.5. Genome-Wide Drug-Resistant and Virulent Gene Analysis
3. Results
3.1. H. pylori Culture and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
3.2. Identification of H. pylori and Evolutionary Analysis
3.3. Genomic Features of H. pylori Strains
3.4. Comparative Genome Analysis
3.5. Identification and Characterizations of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
3.6. Detection of Virulence Genes and Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khoder, G.; Muhammad, J.S.; Mahmaud, I.; Soliman, S.S.M.; Burucoa, C. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori and Its Associated Factors among Healthy Asymptomatic Residents in the United Arab Emirates. Pathogens 2019, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, B.; Cogdill, A.G. Helicobacter pylori: A Review of Current Diagnostic and Management Strategies. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 1917–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Schistosomes, Liver Flukes and Helicobacter pylori; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 1994; Volume 61. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CAA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, A.; Liou, J.; Gisbert, J.P.; O’Morain, C. Review: Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.K.; Ahn, J.Y.; Won, S.H.; Jung, K.; Na, H.K.; Jung, K.W.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, K.D.; Song, H.J.; et al. Eradication Rate of Helicobacter pylori Reinfection in Korea: A Retrospective Study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 1696–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savoldi, A.; Carrara, E.; Graham, D.Y.; Conti, M.; Tacconelli, E. Prevalence of Antibiotic Resistance in Helicobacter pylori: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis in World Health Organization Regions. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Publishes List of Bacteria for Which New Antibiotics are Urgently Needed. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/27-02-2017-who-publishes-list-of-bacteria-for-which-new-antibiotics-are-urgently-needed (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Theuretzbacher, U.; Outterson, K.; Engel, A.; Karlen, A. The Global Preclinical Antibacterial Pipeline. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 18, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miró-Canturri, A.; Ayerbe-Algaba, R.; Smani, Y. Drug Repurposing for the Treatment of Bacterial and Fungal Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Yang, H.; Su, D.; Song, X.; Deng, X.; Yu, C.; Sun, C.; He, L.; You, Y.; Gong, Y.; et al. Geographic distribution of the cagA, vacA, iceA, oipA and dupA genes of Helicobacter pylori strains isolated in China. Gut Pathog. 2021, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baj, J.; Forma, A.; Sitarz, M.; Portincasa, P.; Garruti, G.; Krasowska, D.; Maciejewski, R. Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factors-Mechanisms of Bacterial Pathogenicity in the Gastric Microenvironment. Cells 2020, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rout, S.; Patra, N.P.; Mahapatra, R.K. An In-Silico Strategy for Identification of Novel Drug Targets against Plasmodium falciparum. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 2539–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Han, C.; Hu, T.; Zhang, J.; Wu, D.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Ding, J.; Chen, K.; Yue, J.; et al. Peptide Deformylase is a Potential Target for Anti-Helicobacter pylori drugs: Reverse Docking, Enzymatic Assay, and X-ray Crystallography Validation. Protein Sci. 2006, 15, 2071–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, K.A.; Helmy, O.M.; Kashef, M.T.; Elkhamissy, T.R.; Ramadan, M.A. Identification of Potential Drug Targets in Helicobacter pylori Using in Silico Subtractive Proteomics Approaches and their Possible Inhibition through Drug Repurposing. Pathogens 2020, 9, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, A.M.; Urrea, D.A.; Prada, C.F. Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factors: Relationship between Genetic Variability and Phylogeographic Origin. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthenet, E.; Yahara, K.; Thorell, K.; Pascoe, B.; Meric, G.; Mikhail, J.M.; Engstrand, L.; Enroth, H.; Burette, A.; Megraud, F.; et al. A GWAS on Helicobacter pylori strains points to genetic variants associated with gastric cancer risk. BMC Biol. 2018, 16, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauener, F.N.; Frank Imkamp, F.; Lehours, P.; Buissonnière, A.; Benejat, L.; Zbinden, R.; Keller, P.K.; Wagner, K. Genetic Determinants and Prediction of Antibiotic Resistance Phenotypes in Helicobacter pylori. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Yeh, C.Y.; Sheu, B.S. The impacts of H. pylori virulence factors on the development of gastroduodenal diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharel, S.; Bist, A.; Shrestha, S.; Homagain, S. Helicobacter pylori healthy South Asians. JGH Open 2020, 4, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qumar, S.; Nguyen, T.H.; Nahar, S.; Sarker, N.; Baker, S.; Bulach, D.; Ahmed, N.; Rahman, M. A comparative whole genome analysis of Helicobacter pylori from a human dense South Asian setting. Helicobacter 2021, 1, e12766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzia, K.A.; Aftab, H.; Tshibangu-Kabamba, E.; Alfaray, R.I.; Saruuljavkhlan, B.; Cimuanga-Mukanya, A.; Matsumoto, T.; Subsomwong, P.; Akada, J.; Miftahussurur, M.; et al. Mutations Related to Antibiotics Resistance in Helicobacter pylori Clinical Isolates from Bangladesh. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Patra, R.; De, R.; Baddam, R.; Shaik, S.; Alam, J.; Tiruvayipati, S.; Ahmed, N. Next-generation sequencing and de novo assembly, genome organization, and comparative genomic analyses of the genomes of two Helicobacter pylori isolates from duodenal ulcer patients in India. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 4, 5963–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, V.; Lamichhane, B.; Tay, C.Y.; Pai, G.C.; Lingadakai, R.; Balaraju, G.; Shetty, S.; Ballal, M.; Chua, E.G. High primary resistance to metronidazole and levofloxacin, and a moderate resistance to clarithromycin in Helicobacter pylori isolated from Karnataka patients. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enroth, H.; Nyrén, O.; Engstrand, L. One Stomach-One Strain: Does Helicobacter pylori Strain Variation Influence Disease Outcome? Dig. Dis. Sci. 1999, 44, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramley, W.A.; Asghar, A.; Frierson, H.F., Jr.; Powell, S.M. Detection of Helicobacter pylori DNA in Fecal Samples from Infected Individuals. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 2236–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpellini, M.; Mora, D.; Colombo, S.; Franzetti, L. Development of Genus/Species-Specific PCR Analysis for Identification of Carnobacterium strains. Curr. Microbiol. 2002, 45, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhan, N.F.; Petty, N.K.; Zakour, N.L.B.; Beatson, S.A.A. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): Simple Prokaryote Genome Comparisons. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, J.R.; Stothard, P. The CGView Server: A Comparative Genomics Tool for Circular Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua-Contreras, G.L.; Monroy-Pérez, E.; Díaz-Velásquez, C.E.; Uribe-García, A.; Labastida, A.; Peñaloza-Figueroa, F.; Domínguez-Trejo, P.; García, L.R.; Vaca-Paniagua, F. Whole-Genome Sequence Analysis of Multidrug-Resistant Uropathogenic Strains of Escherichia coli from Mexico. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2363–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsan, N.; Ahmad, S.; Navid, A.; Azam, S.S. Identification of Potential Antibiotic Targets in The Proteome of Multi-Drug Resistant Proteus mirabilis. Meta Gene 2018, 18, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.Y.; Wagner, J.R.; Laird, M.R.; Melli, G.; Rey, S.; Lo, R.; Dao, P.; Sahinalp, C.S.; Ester, M.; Foster, L.J.; et al. PSORTb 3.0: Improved Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction with Refined Localization Subcategories and Predictive Capabilities for All Prokaryotes. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 160815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, Y.; Itoh, M.; Okuda, M.; Yoshizawa, A.C.; Kanehisa, M. KAAS: An Automatic Genome Annotation and Pathway Reconstruction Server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, M.; Ranucci, E.; Romagnoli, P.; Giaccone, V. Antimicrobial resistance: A global emerging threat to public health systems. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2857–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zeng, J.; Li, L.; Yang, J.; Tang, Z.; Xiong, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Zeng, Z. Coexistence of Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Virulence Factors Deciphered by Large-Scale Complete Genome Analysis. mSystems 2020, 5, e00821-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mehrotra, T.; Talukdar, D.; Verma, J.; Karmakar, B.C.; Paul, S.; Chaudhuri, S.; Pragasam, A.K.; Bakshi, S.; Kumari, S.; et al. Region-specific genomic signatures of multidrug-resistant Helicobacter pylori isolated from East and South India. Gene 2022, 847, 146857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Shin, H.R.; Bray, F.; Forman, D.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M. Estimates of Worldwide Burden of Cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2893–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessi, G.; Williams, F.; Hindle, Z.; Heurlier, K.; Holden, M.T.; Cámara, M.; Haas, D.; Williams, P. The Global Posttranscriptional Regulator RsmA Modulates Production of Virulence Determinants and N-acylhomoserine Lactones in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 184, 6676–6683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, J.; Chizimu, J.Y.; Kitamura, S.; Akapelwa, M.L.; Suwanthada, P.; Miura, N.; Toyting, J.; Nishimura, T.; Hasegawa, N.; Nishiuchi, Y.; et al. Characterization of DNA Gyrase Activity and Elucidation of the Impact of Amino Acid Substitution in GyrA on Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Mycobacterium avium. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0508822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dighe, S.N.; Collet, T.A. Recent Advances in DNA Gyrase-Targeted Antimicrobial Agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 199, 112326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caza, M.; Kronstad, J.W. Shared and Distinct Mechanisms of Iron Acquisition by Bacterial and Fungal Pathogens of Humans. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nairz, M.; Weiss, G. Iron in Infection and Immunity. Mol. Aspects Med. 2020, 75, 100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imkamp, F.; Lauener, F.N.; Pohl, D.; Lehours, P.; Vale, F.F.; Jehanne, Q.; Zbinden, R.; Keller, P.M.; Wagner, K. Rapid Characterization of Virulence Determinants in Helicobacter pylori Isolated from Non-Atrophic Gastritis Patients by Next-Generation Sequencing. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Antibiotic | Resistance | Sensitive | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Strains | Percentage | No. of Strains | Percentage | |
| Metronidazole | 82 | 98 | 2 | 2 |
| Ampicillin | 0 | 0 | 84 | 100 |
| Clarithromycin | 62 | 74 | 22 | 26 |
| Levofloxacin | 2 | 2 | 82 | 98 |
| Amoxicillin | 4 | 5 | 80 | 95 |
| Tetracycline | 3 | 4 | 81 | 96 |
| H. pylori Strain | HPA1 | HPA2 | HPGA1 | hpfe074 | ATCC 43504 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Origin | Human | Human | Human | Human | Human |
| Accession No. | JAUDRP000000000 | JAUDRQ000000000 | GCA022923055.1 | CP000241.1 | AP017632.1 |
| Contigs No. | 24 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| Genome Size (Mb) | 1.66 | 1.67 | 1.59 | 1.67 | 1.60 |
| Coding Genes. | 1650 | 1625 | 1596 | 1629 | 2522 |
| G+C Content (%) | 38.8 | 38.7 | 39.1 | 38.71 | 39.02 |
| tRNA No. | 33 | 35 | 36 | 35 | 35 |
| rRNA No. | 10 | 9 | 4 | 4 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fatima, A.; Ibrahim, M.; Naseer, A.; Pervez, A.; Asad, M.; Shah, A.A.; Hasan, F.; Alonazi, W.B.; Ferheen, I.; Khan, S. Identification, Genome Sequencing, and Characterizations of Helicobacter pylori Sourced from Pakistan. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112658
Fatima A, Ibrahim M, Naseer A, Pervez A, Asad M, Shah AA, Hasan F, Alonazi WB, Ferheen I, Khan S. Identification, Genome Sequencing, and Characterizations of Helicobacter pylori Sourced from Pakistan. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(11):2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112658
Chicago/Turabian StyleFatima, Anees, Muhammad Ibrahim, Adil Naseer, Arshid Pervez, Muhammad Asad, Aamer Ali Shah, Fariha Hasan, Wadi B. Alonazi, Ifra Ferheen, and Samiullah Khan. 2023. "Identification, Genome Sequencing, and Characterizations of Helicobacter pylori Sourced from Pakistan" Microorganisms 11, no. 11: 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112658
APA StyleFatima, A., Ibrahim, M., Naseer, A., Pervez, A., Asad, M., Shah, A. A., Hasan, F., Alonazi, W. B., Ferheen, I., & Khan, S. (2023). Identification, Genome Sequencing, and Characterizations of Helicobacter pylori Sourced from Pakistan. Microorganisms, 11(11), 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112658









