Description of Aequorivita aurantiaca sp. nov. Isolated from Coastal Sediment, and Comparative Genomic Analysis and Biogeographic Distribution of the Genus Aequorivita
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolation and Cultivation
2.2. The 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Whole-Genome Sequencing, Genomic and Phylogenomic Analyses
2.4. Comparative Genomic Analysis and Biogeographic Distribution of the Genus Aequorivita
2.5. Morphology, Physiology, and Biochemistry
2.6. Chemotaxonomy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phenotypic Properties
3.2. Chemotaxonomic Characteristics
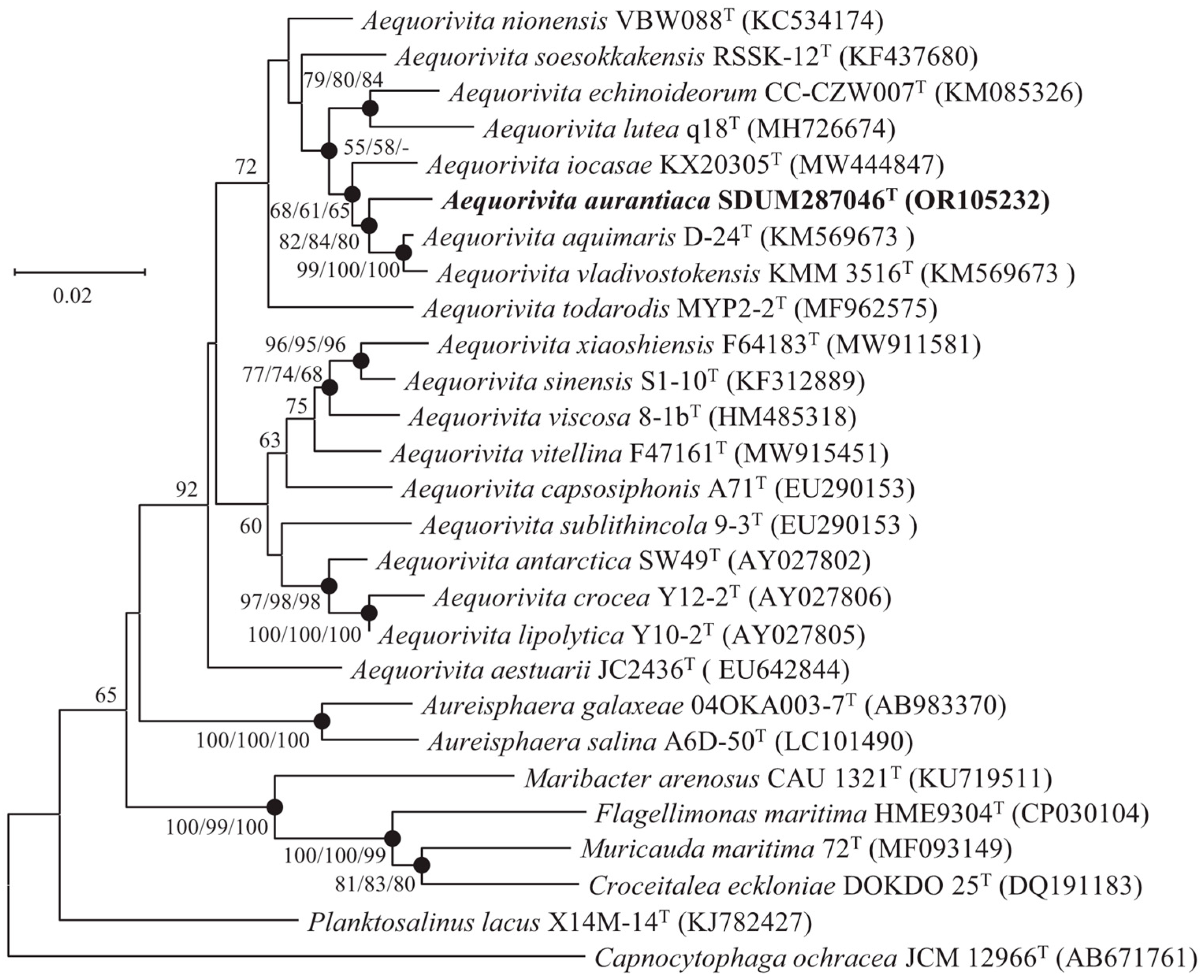
3.3. The 16S rRNA Gene Sequence and Phylogenetics
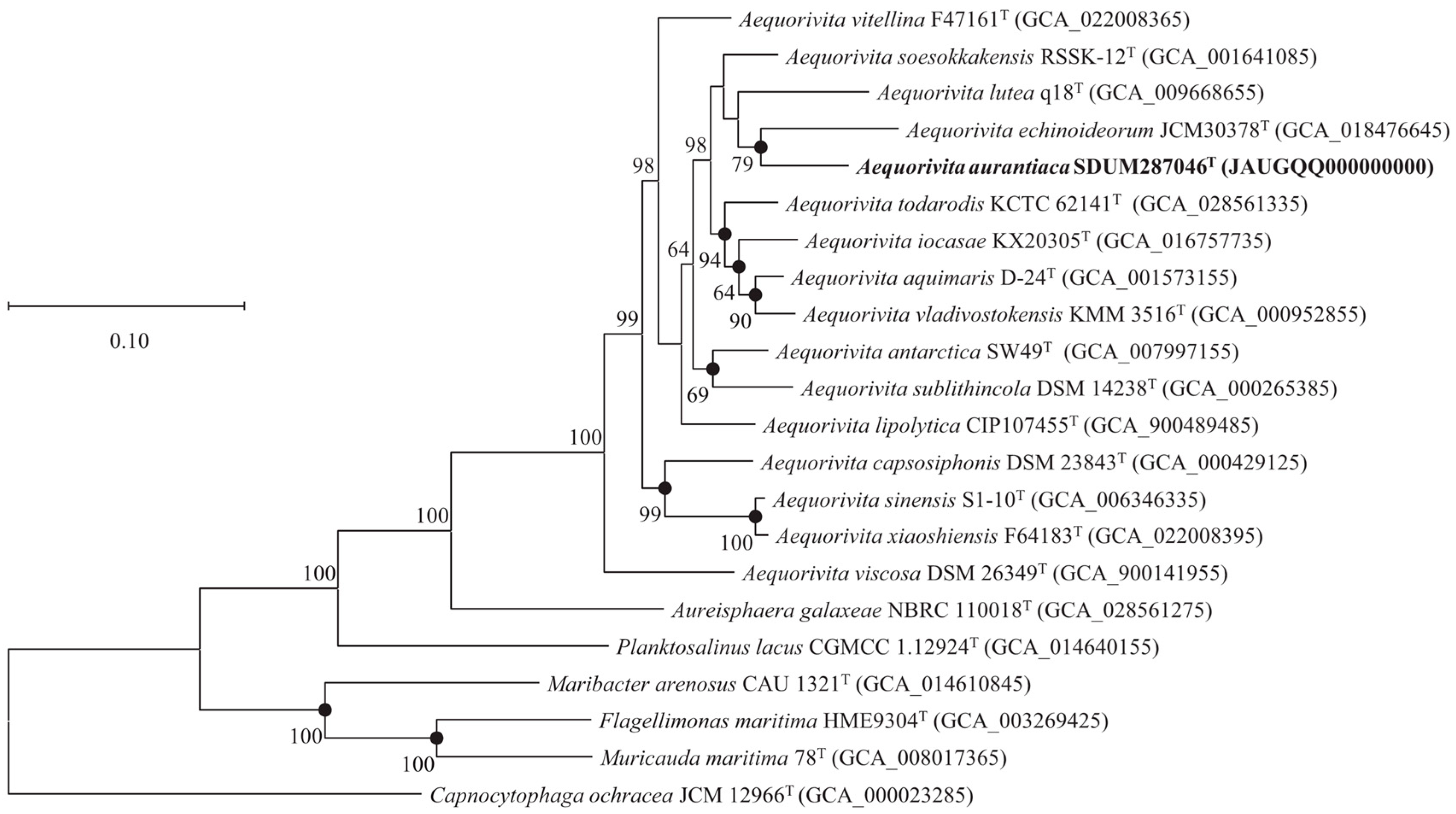
3.4. Genomic Features and Phylogenomics
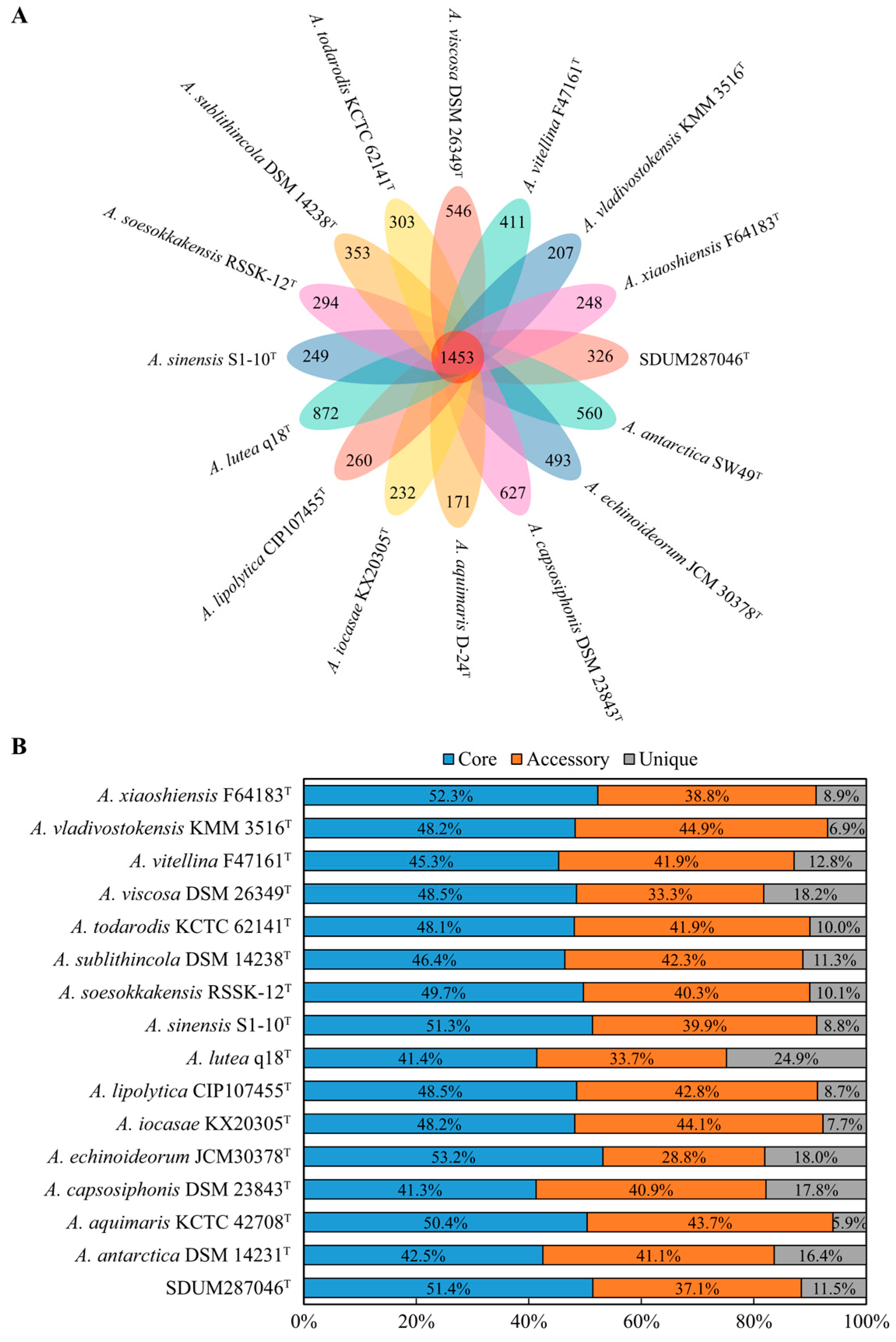
3.5. Comparative Genomic Analysis of the Genus Aequorivita
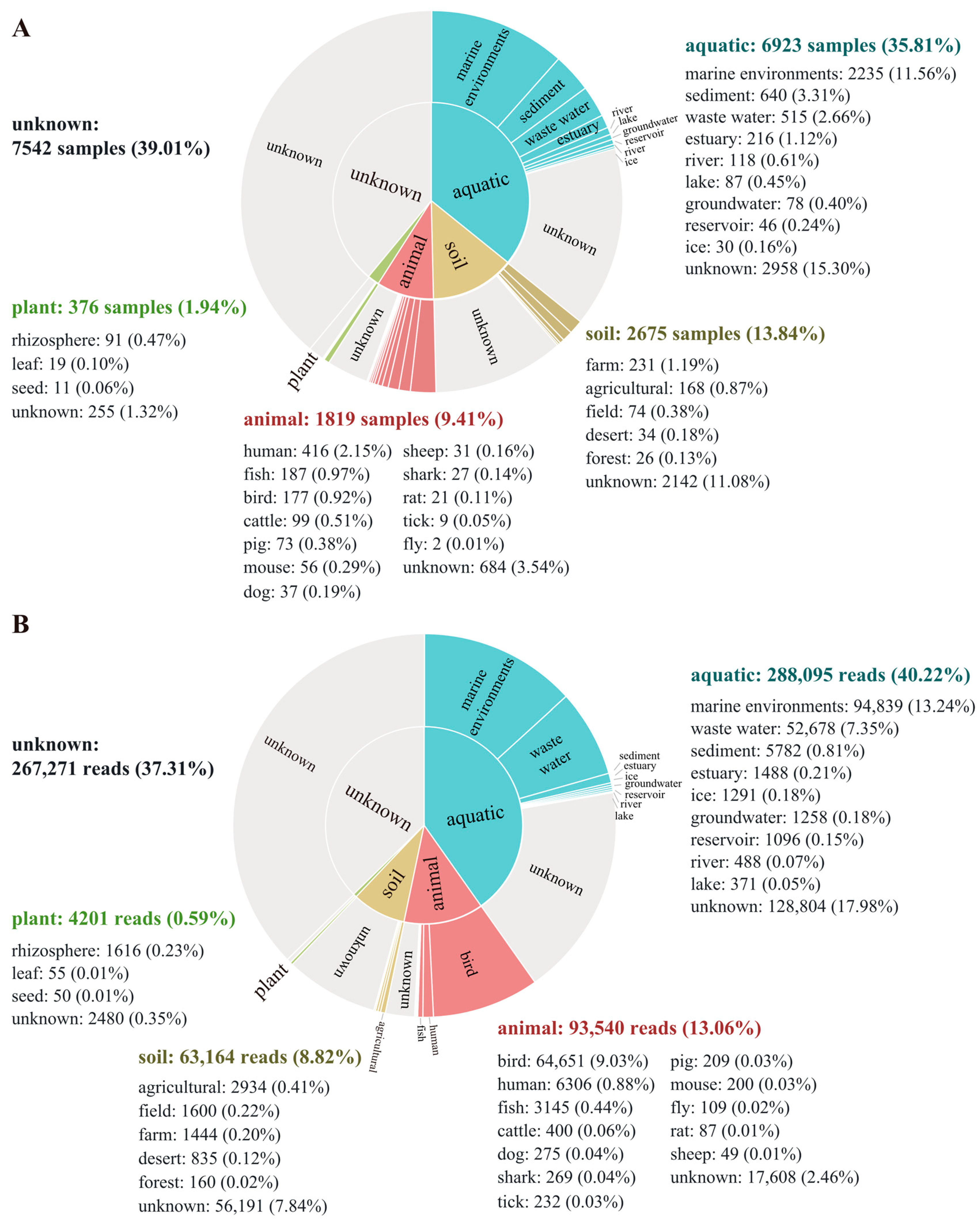
3.6. Biogeographic Distribution of the Genus Aequorivita
3.7. Description of Aequorivita aurantiaca sp. nov.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bowman, J.P.; Nichols, D.S. Aequorivita gen. nov., a member of the family Flavobacteriaceae isolated from terrestrial and marine Antarctic habitats. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.C.; Baik, K.S.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, S.R.; Oh, M.-J.; Kim, D.; Bang, B.-H.; Seong, C.N. Aequorivita capsosiphonis sp. nov., isolated from the green alga Capsosiphon fulvescens, and emended description of the genus Aequorivita. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hahnke, R.L.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; García-López, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Huntemann, M.; Ivanova, N.N.; Woyke, T.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Klenk, H.-P.; Göker, M. Genome-Based Taxonomic Classification of Bacteroidetes. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-López, M.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Tindall, B.J.; Gronow, S.; Woyke, T.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Hahnke, R.L.; Göker, M. Analysis of 1000 Type-Strain Genomes Improves Taxonomic Classification of Bacteroidetes. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, H.; Sun, C.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H. Aequorivita lutea sp. nov., a novel bacterium isolated from the estuarine sediment of the Pearl River in China, and transfer of Vitellibacter todarodis and Vitellibacter aquimaris to the genus Aequorivita as Aequorivita todarodis comb. nov. and Aequorivita aquimaris comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 3117–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevarajoo, S.; Selvaratnam, C.; Goh, K.M.; Hong, K.W.; Chan, X.Y.; Chan, K.G.; Chong, C.S. Vitellibacter aquimaris sp. nov., a marine bacterium isolated from seawater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 3662–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cai, S.D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D.C. Aequorivita sinensis sp. nov., isolated from sediment of the East China Sea, and reclassification of Vitellibacter todarodis as Aequorivita todarodis comb. nov. and Vitellibacter aquimaris as Aequorivita aquimaris comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 3323–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.X.; Du, Z.J.; Mu, D.S. Aequorivita vitellina sp. nov. and Aequorivita xiaoshiensis sp. nov., isolated from marine sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2023, 73, 005801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Cao, L.; Chen, H.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, C. Aequorivita iocasae sp. nov., a halophilic bacterium isolated from sediment collected at a cold seep field in the South China Sea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 005199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasabapathy, R.; Mohandass, C.; Yoon, J.H.; Dastager, S.G.; Liu, Q.; Khieu, T.N.; Son, C.K.; Li, W.J.; Colaço, A. Vitellibacter nionensis sp. nov., isolated from a shallow water hydrothermal vent. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Zhang, X.Q.; Pan, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.Q.; Zhu, X.F.; Wu, M. Aequorivita viscosa sp. nov., isolated from an intertidal zone, and emended descriptions of Aequorivita antarctica and Aequorivita capsosiphonis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 3192–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedashkovskaya, O.I.; Suzuki, M.; Vysotskii, M.V.; Mikhailov, V.V. Vitellibacter vladivostokensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the phylum Cytophaga-Flavobacterium-Bacteroides. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Kim, Y.O.; Park, S.; Nam, B.H.; Kim, D.G.; Park, J.M.; Yoon, J.H. Vitellibacter todarodis sp. nov., isolated from intestinal tract of a squid (Todarodes pacificus). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 1233–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianese, G.; Esposito, F.P.; Parrot, D.; Ingham, C.; De Pascale, D.; Tasdemir, D. Linear Aminolipids with Moderate Antimicrobial Activity from the Antarctic Gram-Negative Bacterium Aequorivita sp. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma Esposito, F.; Ingham, C.J.; Hurtado-Ortiz, R. Isolation by Miniaturized Culture Chip of an Antarctic bacterium Aequorivita sp. with antimicrobial and anthelmintic activity. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 20, e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Perez-Garcia, P.; Dierkes, R.F.; Applegate, V.; Schumacher, J.; Chibani, C.M.; Sternagel, S.; Preuss, L.; Weigert, S.; Schmeisser, C.; et al. The Bacteroidetes Aequorivita sp. and Kaistella jeonii Produce Promiscuous Esterases with PET-Hydrolyzing Activity. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 803896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, F.B.; Jiang, S.; Zhu, K.L.; Shang, D.D.; Zhang, J.; Du, Z.J. Salegentibacter maritimus sp. nov., isolated from marine coastal sediment. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 44, 126209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.J. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics; Stackebrandt, E., Goodfellow, M., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 115–175. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.Q.; Hao, Z.P.; Yue, Y.Y.; Ma, L.; Ye, M.Q.; Du, Z.J. Characterization of Kordiimonas marina sp. nov. and Kordiimonas laminariae sp. nov. and comparative genomic analysis of the genus Kordiimonas, a marine-adapted taxon. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 919253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: A maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 1981, 17, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. A stepwise algorithm for finding minimum evolution trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1996, 13, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Chalita, M.; Ha, S.M.; Na, S.I.; Yoon, S.H.; Chun, J. ContEst16S: An algorithm that identifies contaminated prokaryotic genomes using 16S RNA gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 2053–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medema, M.H.; Blin, K.; Cimermancic, P.; De Jager, V.; Zakrzewski, P.; Fischbach, M.A.; Weber, T.; Takano, E.; Breitling, R. antiSMASH: Rapid identification, annotation and analysis of secondary metabolite biosynthesis gene clusters in bacterial and fungal genome sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W339–W346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.; Rosselló-Móra, R.; Oliver Glöckner, F.; Peplies, J. JSpeciesWS: A web server for prokaryotic species circumscription based on pairwise genome comparison. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Carbasse, J.S.; Peinado-Olarte, R.L.; Göker, M. TYGS and LPSN: A database tandem for fast and reliable genome-based classification and nomenclature of prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaumeil, P.A.; Mussig, A.J.; Hugenholtz, P.; Parks, D.H. GTDB-Tk: A toolkit to classify genomes with the Genome Taxonomy Database. Bioinformatics 2019, 36, 1925–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree: Computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.L.; LoCascio, P.F.; Land, M.L.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L.J. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, N.M.; Gupta, V.K.; Dutta, C. BPGA—An ultra-fast pan-genome analysis pipeline. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias Rodrigues, J.F.; Schmidt, T.S.; Tackmann, J.; von Mering, C. MAPseq: Highly efficient k-mer search with confidence estimates, for rRNA sequence analysis. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3808–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smibert, R.M.; Krieg, N.R. Phenotypic characterization. In Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology; Gerhardt, P., Murray, R., Wood, W., Krieg, N.R., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; pp. 607–654. [Google Scholar]
- Fautz, E.; Reichenbach, H. A simple test for flexirubin-type pigments. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1980, 8, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardet, J.; Bowman, J. The genus Flavobacterium. In The Prokaryotes, a Handbook on the Biology of Bacteria, 3rd ed.; Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Schleifer, K.-H., Stackebrandt, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 7, pp. 481–531. [Google Scholar]
- Bowman, J.P. Description of Cellulophaga algicola sp. nov., isolated from the surfaces of Antarctic algae, and reclassification of Cytophaga uliginosa (ZoBell and Upham 1944) Reichenbach 1989 as Cellulophaga uliginosa comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 1861–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, J.H.; Turnidge, J.D. Susceptibility test methods. In Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 11th ed.; Jorgensen, J.H., Carroll, K.C., Funke, G., Pfaller, M.A., Landry, M.L., Richter, S.S., Warnock, D.W., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1253–1273. ISBN 9781683672807. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.Z.; Cai, M.Y. Determination of biochemical characteristics. In Manual for the Systematic Identification of General Bacteria, 14th ed.; Dong, X.Z., Cai, M.Y., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 370–398. [Google Scholar]
- Sasser, M. Identification of Bacteria by Gas Chromatography of Cellular Fatty Acids; MIDI Inc.: Newark, DE, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Minnikin, D.E.; O’donnell, A.G.; Goodfellow, M.; Alderson, G.; Athalye, M.; Schaal, A.; Parlett, J.H. An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J. Microbiol. Meth. 1984, 2, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraishi, A.; Ueda, Y.; Ishihara, J.; Mori, T. Comparative lipoquinone analysis of influent sewage and activated sludge by high-performance liquid chromatography and photodiode array detection. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 1996, 42, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komagata, K.; Suzuki, K. Lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Method Microbiol. 1987, 19, 161–207. [Google Scholar]
- Goris, J.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Klappenbach, J.A.; Coenye, T.; Vandamme, P.; Tiedje, J.M. DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Auch, A.F.; Klenk, H.P.; Göker, M. Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, T.; Von Blohn, C.; Stanek, A.; Moses, S.; Barzantny, H.; Bremer, E. Synthesis, release, and recapture of compatible solute proline by osmotically stressed Bacillus subtilis cells. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2012, 78, 5753–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, L.; Williams, T.J.; Cowley, M.J.; Lauro, F.M.; Guilhaus, M.; Raftery, M.J.; Cavicchioli, R. Cold adaptation in the marine bacterium, Sphingopyxis alaskensis, assessed using quantitative proteomics. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 2658–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, S.; Sharma, S.S.; Mehta, I.K. Free radical scavenging potential of L-proline: Evidence from in vitro assays. Amino Acids 2008, 34, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, M.; Takagi, H. Role of the yeast acetyltransferase Mpr1 in oxidative stress: Regulation of oxygen reactive species caused by a toxic proline catabolism intermediate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12616–12621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isolation | Coastal sediments | Seawater | Under-ice sea water |
| Growth at 4 °C | − | + | + |
| NaCl range (%, w/v) | 1–5 | 0–9 * | 0.5–10 † |
| Facultatively anaerobic | + | − | − |
| Enzyme activity: | |||
| Oxidase | − | + | − |
| Trypsin | + | w | + |
| ɑ-chymotrypsin | + | + | − |
| Gelatinase | + | + | w |
| Hydrolysis of: | |||
| Tween 80 | + | − | + |
| Starch | − | − | + |
| Casein | − | + | − |
| Acid production from: | |||
| d-mannose | − | + | − |
| Potassium 2-ketogluconate | − | + | + |
| Oxidation of: | |||
| d-maltose/d-trehalose | − | + | + |
| Gentiobiose | + | − | − |
| β-methyl-d-glucoside | + | − | − |
| N-acetyl-d-galactosamine | + | − | + |
| Inosine/Myo-inositol | − | − | + |
| l-alanine/l-serine | + | − | + |
| l-galactonic acid lacton | + | − | − |
| DNA G + C content (mol %) | 39.3 | 40.6 * | 38.5 † |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.-C.; Ye, Y.-Q.; Tan, X.-Y.; Du, Z.-J.; Ye, M.-Q. Description of Aequorivita aurantiaca sp. nov. Isolated from Coastal Sediment, and Comparative Genomic Analysis and Biogeographic Distribution of the Genus Aequorivita. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102518
Liu J-C, Ye Y-Q, Tan X-Y, Du Z-J, Ye M-Q. Description of Aequorivita aurantiaca sp. nov. Isolated from Coastal Sediment, and Comparative Genomic Analysis and Biogeographic Distribution of the Genus Aequorivita. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(10):2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102518
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jun-Cheng, Yu-Qi Ye, Xin-Yun Tan, Zong-Jun Du, and Meng-Qi Ye. 2023. "Description of Aequorivita aurantiaca sp. nov. Isolated from Coastal Sediment, and Comparative Genomic Analysis and Biogeographic Distribution of the Genus Aequorivita" Microorganisms 11, no. 10: 2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102518
APA StyleLiu, J.-C., Ye, Y.-Q., Tan, X.-Y., Du, Z.-J., & Ye, M.-Q. (2023). Description of Aequorivita aurantiaca sp. nov. Isolated from Coastal Sediment, and Comparative Genomic Analysis and Biogeographic Distribution of the Genus Aequorivita. Microorganisms, 11(10), 2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102518





