Abstract
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is the most common autosomal recessive disease among Caucasians. Over the last 20 years, culture-independent analysis, including next-generation sequencing, has paired with culture-based microbiology, offering deeper insight into CF lung and gut microbiota. The aim of this review is to analyse the features of gut microbiota in patients with CF and its possible role in the progression of the disease, establishing the basis for a potential role in microbe-based therapies. The literature analysis showed that the gut environment in CF patients has unique features due to the characteristics of the disease, such as decreased bicarbonate secretion, increased luminal viscosity, and an acidic small intestinal environment, which, due to the treatment, includes regular antibiotic use or a high-energy and fat-dense diet. As a result, the gut microbial composition appears altered, with reduced richness and diversity. Moreover, the population of pro-inflammatory bacteria is higher, while immunomodulatory genera, such as Bacteroides and Bifidobacterium, are scarcer. The imbalanced gut microbial population has a potential role in the development of systemic inflammation and may influence clinical outcomes, such as respiratory exacerbations, spirometry results, and overall growth. Although a better understanding of the pathophysiology behind the gut–lung axis is needed, these findings support the rationale for considering gut microbiota manipulation as a possible intervention to regulate the severity and progression of the disease.
1. Introduction
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is the most common autosomal recessive disease among Caucasians, affecting nearly 50,000 individuals in Europe and more than 85,000 individuals worldwide [1,2]. CF is associated with mutations in the gene coding for the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein [3]. The CFTR protein functions on the apical surface of epithelial cells in the airways, pancreas, intestines, and hepatobiliary tree as an anion-selective ion channel (mainly chloride and bicarbonate) and thus contributes to epithelial fluid secretion and intra-luminal mucus hydration [4].
The lungs are the most seriously affected organ in CF, and respiratory diseases are the main cause of reduced life expectancy. As a result, the respiratory tract has received the greatest research attention. However, the CFTR protein is located throughout the body on the apical layer of the epithelial cells, resulting in multiple morbidities, including altered gastrointestinal functioning [4]. Patients with CF have reduced bicarbonate secretion from the pancreas, intestine, and biliary tree as part of the primary CFTR defect. A lack of bicarbonate results in increased luminal viscosity due to the formation of inspissated mucus in the intestinal tract as well as in a more acidic small intestinal environment. These features, along with the regular use of antibiotics due to recurrent pulmonary infections, the increased load of malabsorbed luminal contents, a high-energy and fat-dense diet, the use of a pancreatic enzyme, and impaired innate immunity may contribute to the development of microbial gut dysbiosis that has been observed in patients suffering from CF [5].
Over the last 20 years, culture-independent analysis, including next-generation sequencing, has paired with culture-based microbiology, offering deeper insight into CF lung and gut microbiota. In particular, 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequencing has allowed for the identification and relative enumeration of the bacterial taxa within a clinical sample in a way that would have been unachievable using culture-based approaches [6]. The role of gut microbiota in driving a healthy immune response is generally acknowledged, and several studies have addressed its role in various chronic respiratory conditions, such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and CF [7,8]. The aim of this review is to analyse the features of gut microbiota in patients with CF and its possible role in the progression of the disease, establishing the basis for a potential role in microbe-based therapies.
2. Gut Microbiome in CF: Development and Influences
Microbiota acquisition begins in the uterus and progresses during childhood. Its composition is influenced by many factors, including delivery method, maternal physical contact, feeding, and exposure to antibiotics [9,10,11]. Those factors, which are well-known influences on gut microbiota composition in the general population, also play a role in the CF population along with CFTR dysfunction (Table 1).

Table 1.
Evidence on factors influencing microbial acquisition and development.
Age is a further key point in gut microbiome development. In the general population, the greatest inter-individual variability in gut microbiota occurs within the first 3 years of life [23,24]. After that, it resembles that of the adult, remaining relatively stable with few further perturbations. Loman et al. noted that age is the strongest predictive factor of overall faecal microbial composition in CF children as well [12]. Dietary factors, the introduction of solid food, and the subsequent different substrate availability are the main drivers for such changes.
2.1. CFTR Dysfunction
CFTR dysfunction actively modulates and selects the gut microbiome, as demonstrated in a study performed on mice in the absence of confounding factors, such as diet or antibiotic treatment [13].
CFTR gene variants have been investigated as a possible influencer of gut microbiota in CF patients who are not on antibiotics: Escherichia coli and Eubacterium biforme species were found to be prevalent in patients with F508del mutations, especially in the homozygous state and in more severe CF patients, while beneficial species, such as Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Bifidobacterium spp., and Eubacterium limosum, were reduced [15]. Burke et al. found no significant differences in species richness or microbial diversity between the CF cohort with class 1–3 mutations, which are considered the most severe, and CF individuals with mutations from other classes [14]. However, differences were noted at a genus level and at a family level, with Enterococcaceae being significantly higher and Ruminococcaceae significantly lower than those with less severe mutations [14].
More recently, new studies have been investigating the effect of the initiation of CF modulators on CF microbiota. Ooi et al. noted no significant difference in alpha and beta diversities in 16 CF patients (eight children and eight adults; two are pancreatic sufficient) 6 months after starting ivacaftor [16]. However, they noted a significant reduction in faecal calprotectin and an increase in the relative abundance of the bacterial genus Akkermansia, which resides in the intestinal mucus layer, stimulates host mucosal anti-inflammatory pathways and improves epithelial barrier integrity. An additional study of 14 adults suffering from CF and pancreatic insufficiency confirmed no significant change in gut microbiota diversity and richness after a year of treatment with ivacaftor but did not confirm a reduction in faecal calprotectin [17].
Overall, CFTR dysfunction and CF disease severity contribute to shaping the composition of gut microbiota in CF patients. Very limited data are available on the potential influence of CFTR modulators investigating, in particular, the possible impact of a potentiator. According to the evidence available, there is a possible impact of the ivacaftor on mucus layer commensals and on gut inflammation.
2.2. Delivery Method
Delivery method is a factor known to influence gut microbiota composition in the general population. Few studies investigating its role in CF patients are available, and there is no unified evidence to date.
Birth has been analysed as a possible influencing factor in CF patients by Loman et al. [12]. Using 16S RNA gene sequencing, they analysed faecal samples from a group of children between 3 months and 5 years of age, all suffering from CF, who have at least one copy of the Phe508del mutation and are pancreatic insufficient. Their study noted that birth via Caesarean section was associated with higher alpha diversity than vaginal birth. Additionally, a single genus, Turicibacter, was higher in children born via Caesarean section and undetected in all vaginally born children [25]. This taxon was reported as putatively pro-inflammatory in animal models [26]. These results have not been confirmed by a more recent study performed in 2019 by Antosca et al. [18] that compared stool samples collected from 21 infants with CF during their first year of life with samples collected from 409 infants without CF from the New Hampshire Birth Cohort Study. The delivery mode had been previously shown to significantly affect the gut microbiota of infants in the New Hampshire Birth Cohort Study, yet this effect was not observed in the CF cohort, even after an adjustment for antibiotic use at delivery [18].
2.3. Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding and its influence on the gut microbiome is another factor that has been investigated. Loman et al. compared children affected by CF who were exclusively formula-fed, breastfed, and mixed formula- and breastfed; faecal samples from the three subgroups were found to have similar alpha and beta diversities [12]. However, they noted a higher relative abundance of the genus Lactococcus in children who were exclusively formula-fed. Although the analysed studies involved a small number of patients, it is interesting to note that factors such as the delivery method or feeding (breastfeeding or formula), which are well-known influences on the gut microbiota composition in the general population, seem not to affect it significantly in children with CF. Madan et al. followed up with seven CF patients from birth to 9–21 months of age and noted non-significant overall diversities in the gut microbial populations between breastfed and formula-fed infants; however, they did note the significant effects of breast milk exposure on respiratory tract diversity [19]. A possible explanation for the lack of influence of breastfeeding on gut composition in CF children was proposed by Vernocchi et al.: gut microbiota composition in children with CF may be intrinsically linked to CFTR impairment and minimally influenced by other external or internal factors that are usually involved [20].
A limited number of studies have investigated the impact of breastfeeding on gut microbiota composition in children suffering from CF. However, considering what has been described above, there are no significant effects of breastfeeding on microbiota diversity, probably due to the major influence of CFTR impairment.
2.4. Antibiotic Treatment
The use of antibiotics and their role in driving the gut microbiome in CF patients is a major area for research considering the high frequency of their use as prophylaxis or treatment for respiratory tract infections as well as their effects on gut microbiota. Antibiotic therapies are known to reduce the diversity of intestinal microbiota and to alter the relative abundances of susceptible bacterial species in non-CF individuals [27]. Intestinal microbiota tends to return to normal in a few weeks after the treatment, yet some taxonomic changes may persist for a longer period of time [14]. Moreover, the human gut microbiota acts as a reservoir of resistance, and it is probable that the greater the exposure to antibiotics, the greater the pressure to select resistant microorganisms [28].
Numerous studies have tried to address the influence of antibiotic use on gut composition in CF patients. Vernocchi et al. analysed faecal samples from 31 children suffering from CF between 1 and 6 years of age and compared them with healthy controls [20]. CF patients were classified based on chronic antibiotic regimen (no antibiotics, aerosol antibiotic therapy, or azithromycin plus aerosol) and on the requirement of a pulmonary exacerbation regimen. In their study, a single antibiotic therapy regimen did not significantly impact the alpha diversity of gut microbiota, while azithromycin plus aerosol antibiotic therapy worsened the alpha diversity as compared to healthy controls [20].
De Freitas et al. compared two subgroups of children/adolescents with CF, one requiring antibiotic therapy (CFAB) and one not (CFnAB). Bifidobacterium was the only microorganism analysed that was significantly lower in the CFAB group than in the CFnAB group. Their study also noted a positive correlation between body mass index (BMI), nutritional status, and Bifidobacterium in the CF group [21]. Many studies have already reported an antibiotic-induced decrease in the Bifidobacterium count in the general population. Duytschaever et al. confirmed this finding by comparing CF children and their siblings [29]. A lower count of Bifidobacterium in CF patients that received macrolides, higher levels of Firmicutes, and lower levels of Bacteroides were also noted in CF patients requiring more courses of intravenous (IV) antibiotics in a study performed on CF adults compared to the healthy population, although patients were investigated during a period of stability [14]. More recently, Kristensen et al. reported an independent association between antibiotic treatment (mainly co-trimoxazole) and lower alpha diversity in CF infants, a reduced abundance of Bifidobacterium and Bacteroides, and a higher abundance of Enterococcus [22]. Bifidobacterium has been related to a healthy gut, as it is involved in immune maturation, the production of vitamin B, antioxidants, and the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs); the low abundance of Bifidobacterium and the higher abundance of Enterococcus may contribute to a pro-inflammatory profile [22].
Human gut microbiota act as a reservoir of antibiotic resistance in the general population [30]. Using shotgun metagenomic sequencing, Fouhy et al. analysed faecal samples from six CF patients during a period of clinical stability who had been exposed to oral, IV, inhaled, and long-term maintenance antibiotics in the 12 months prior to the sample collection and compared it with six non-CF controls [28]. They found a higher abundance of gene families and pathways involved in antibiotic resistance, including porin activity and penicillin-binding, in particular in Lachnospiracheae, E. faecalis, Clostridium, and Bacteroides [28]. A higher prevalence of amoxicillin and amoxicillin-clavulanic acid-resistant Enterobacteriaceae has been found in CF patients compared to their healthy siblings by Duytschaever et al. [31], and, more recently, higher proportions of aminoglycoside-resistant Gram-negative bacteria and extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (EBLS) E. coli were found in CF patients compared to healthy adults from another group [32].
Therefore, it is clear that the use of a combination of multiple antibiotics in CF patients reduces the gut composition diversity, causes a reduced abundance of immunomodulating genera, and increases the prevalence of the gene families and pathways involved in antibiotic resistance.
3. Gut Microbiome in Cystic Fibrosis: Composition and Features
CF patients are known to have imbalanced gut microbial compositions, with a higher degree of gut dysbiosis observed among patients with severe phenotypic expression and homozygous F508del mutations [15]. A microbial imbalance is characterized by a higher amount of pro-inflammatory microbiota, such as Escherichia and Enterococcus, than immunomodulatory genera, such as Bacteroides and Bifidobacterium [33]. The abundance of Enterobacteriaceae, particularly Escherichia coli, has been shown to be 10 times higher in CF compared to healthy controls [34].
Species richness is defined as the number of microbial species identified in an ecosystem. Overall, the gut microbiome in CF patients is characterized by the trend of lower species richness compared to the healthy population [12] and by an altered gut microbial balance known as dysbiosis [34,35] (Figure 1).
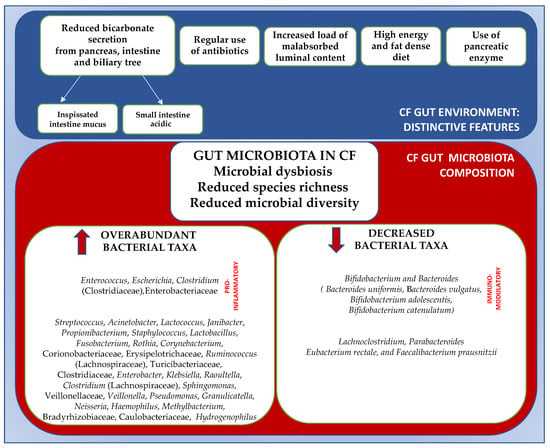
Figure 1.
Gut distinctive features and gut microbial imbalance in CF patients. ↑, increased; ↓, decreased. Adapted from references [12,13,20,36].
Nielsen et al. compared the microbial communities within the gastrointestinal tracts of children with and without CF (either pancreatic sufficient or insufficient) across a range of ages (0.87–17 years) [5]. They noted that gut microbial richness increases with age for both healthy and CF cohorts, but that it remains systemically lower in the CF cohort. Moreover, the microbial richness in the CF cohort during the teenage years does not even reach the same richness found in the CF cohort in infancy [5,36]. Lower gut microbiota richness in CF children, as compared to healthy controls matched by age and gender, has been confirmed by Coffey et al. [37] and by Duytschaever et al. in a comparison between CF children and their healthy siblings [29].
Microbial diversity takes both richness and evenness (relative abundance of each represented species) into consideration [33]. Paediatric CF patients are known to have a significantly lower α-diversity and a distinct beta diversity compared to healthy children [20]. Nielsen et al. noted also that the diversity of gut microbial communities increases with age in healthy children but not in children with CF. As a result, there is a progressive difference in the species diversity between those two populations, increasing with age [5]. Increased gut diversity has been repeatedly associated with health whilst decreased diversity has been associated with several inflammatory, metabolic, immune-mediated, and systemic diseases. These changes are potentially relevant, as the gastrointestinal microbiota of young children have been proposed as a determinant of respiratory and systemic disease progression [37]. Dysbiosis, reduced species richness and microbial diversity, as well as a higher pro-inflammatory than immunomodulating genera are the changes identified in children suffering from CF in multiple studies with potential influence on disease progression.
4. Gut Microbiota in Cystic Fibrosis: The Gut–lung Axis
The “gut–lung axis” is defined as the ability of the gut microbiota to influence the course or outcome of the underlying lung disease, and vice versa. This concept is well-described in other chronic respiratory diseases, such as asthma and COPD, where the gut microbiota has been suggested to influence lung health outcomes [38]. The interaction between the gut and the lungs is mainly based on the direct impact that the gut microbial community has on the immune system, but it also involves the passage of endotoxins, microbial metabolites, cytokines, and hormones into the bloodstream [39]. The gut microbiome can have a modulating effect on immune function. For example, Bacteroides fragilis modulates the Th type 1/2 (Th1/Th2) balance, and segmented filamentous bacteria directly stimulate Th17 cell differentiation, whereas Clostridium spp. induces Treg production [7]. Furthermore, metabolites such as SCFAs are involved in promoting recruitment, as well as in the maturation of the immune cells, which provide protection against an inflammatory response [40].
The crosstalk between the lungs and the gut in CF is particularly interesting: both sites are disrupted by CFTR loss-of-function and characterized by dysbiosis. Furthermore, this crosstalk and its possible immunomodulatory action are relevant in view of the known role of the pro-inflammatory cascade in CF lung disease [41,42]. This interaction and its effects have been noted in several studies (Table 2), although the exact mechanism of how the intestinal microbiome influences the immune response is not always fully understood.

Table 2.
Study evidence on gut–lung axis in CF children.
Evidence of interaction between lung health and the gut microbiome was noted by Madan et al. during a follow-up with a small group of seven CF patients from birth to 9–21 months of age [19]. In this study, they noted a significant effect of breast milk exposure on respiratory tract diversity. Moreover, they noted that changes in diet also resulted in altered respiratory microflora. This finding confirmed the strong interconnection between the two systems and lay the foundations for further studies that propose probiotic administration in order to decrease pulmonary exacerbation. Moreover, they noted clusters of bacteria, including potential pathogens such as Enterococcus, being present early in life in the gut and later in life in the respiratory tract, which highlights the potential interrelatedness of these two organ systems and their microbiota [19].
Hoen et al. analysed 120 faecal samples from 13 CF children, collected from birth to 34 months of age [43]. They noted a significant association between increased diversity of the gut microbiota and prolonged periods of health, delays in the time to initial P. aeruginosa colonization, and the first CF exacerbation. Moreover, they noted a reduction in two important gut colonizers, Bacteroides and Bifidobacterium, in stool samples prior to the first CF exacerbation and initial P. aeruginosa colonization, although this finding was non-significant [43]. Similarly, Antosca et al. examined the correlation between the composition of the stool microbiota and airway exacerbations in CF subjects, comparing stool samples from 21 CF infants and 409 controls [18]. During this study, they found a significant association between gut microbiome beta diversity and pulmonary exacerbations during the first year of life and confirmed the reduction in Bacteroides in CF infants as early as 6 weeks of life, a reduction persisting over the entire first year of life and confirmed in adulthood [18]. Bacteroides is a genus known for its immunomodulant role, demonstrated in vitro and in vivo. In vitro, the exposure of the apical face of polarized intestinal cell lines to Bacteroides species supernatants significantly reduces the production of Interleukin 8 (IL-8), suggesting a mechanism whereby changes in the intestinal microbiota may impact inflammation in CF [18]. A low proportion of Bacteroides has been associated with the risk of developing atopy and asthma [44,45], and Bacteroides fragilis in particular is known to be involved in modulating the Th type 1/2 (Th1/Th2) balance [46]. Decreased amounts of Bifidobacterium spp. are observed in the CF population, both in general and, most of all, after antimicrobial treatment, probably because of their high antimicrobial susceptibility, as explained above [21]. High bifidobacterial species richness is positively correlated with the maturation of the mucosal immune system. Conversely, an overall reduction in Bifidobacteria in children with CF may influence extra-intestinal disorders, such as respiratory inflammation and infection [47]. The imbalance in the gut microbiota, in particular, the reduction in immunomodulatory genera, may be a potential target in the development of probiotics dedicated to the CF population [48].
In terms of metabolite disruption, SCFAs, such as acetate, butyrate, propionate, and pantetheine, are known to be reduced in stool samples from CF patients as compared to healthy controls [20,37]. SCFAs are known to be involved in the promotion of differentiation of regulatory T cells [37] and in the regulation of inflammatory processes. In particular, SCFAs act to regulate several leukocyte functions, including the production of cytokines (TNF-α, IL-2, IL-6 and IL-10), eicosanoids, and chemokines (e.g., MCP-1 and CINC-2) [40]. Their reduction is likely the result of CF gut dysbioses, such as the decrease in Bifidobacterium, secondary to antibiotic use, or other butyrate-producing bacteria, such as Eggerthella, Anaerostipes, Butyricicoccus, and Ruminococcus [22]. These findings represent further confirmation of the close correlation between the gut and lungs and confirm the gut–lung axis theory, which has been previously acknowledged in the general population, in CF patients [49].
Overall, characteristics of gut composition in CF patients include reductions in immunomodulating genera and their metabolites. Although studies involving larger numbers are needed, evidence of a possible systemic pro-inflammatory effect and of a direct impact on the respiratory tract’s microbial composition exists. Those findings represent the rationale behind the potential use of dedicated probiotics in the CF population.
5. Gut Microbiota in CF: Possible Influence on Growth and Lung Function
Finally, several studies now address the systemic influence of the altered gut microbiota in patients suffering from CF, looking at its correlation with readings such as growth and lung function, which are known to be related to survival in this group [50]. Loman et al. reported a negative correlation between weight-for-length and a relative abundance of the Staphylococcus and Faecalibacterium species, while no correlation has been noted between the alpha diversity and any anthropometric measurement [12]. Hayden et al. identified an early, progressive faecal dysbiosis, distinguishing between infants with CF, a low length from infants with CF, and normal length [51]. This dysbiosis included altered abundances of taxa that perform important functions for gut health, nutrient harvest, and growth hormone signalling, including decreased Bacteroidetes and increased Proteobacteria. Coffey et al. investigated the composition and function of the bacterial communities inhabiting the intestines of children with CF and analysed their correlation with biomarkers of intestinal inflammation, growth, and lung function [37]. They demonstrated positive correlations between intestinal inflammatory markers, intestinal genera, and both growth z-scores and FEV1%. In particular, a relative abundance of Ruminococcaceae UCG 014 was positively correlated with BMI z-scores, and the Ruminococcaceae NK4A214 group was positively correlated with FEV1%. Intestinal inflammation was measured by faecal calprotectin levels and found to be significantly higher in the CF cohort compared to the healthy control, with a strong positive correlation between calprotectin and Acidaminococcus in CF [37]. An increased relative abundance of Acidaminococcus has been associated with lower future height z -cores in twin cohorts of children from Malawi and Bangladesh [52]. Furthermore, faecal calprotectin has a known negative correlation with height and weight z-scores among CF children [53].
Several studies on CF patients thus evidence a correlation between dysbiosis involving different genera and species that have a direct impact on inflammation, growth, and lung function, therefore confirming the hypothesis that the gut microbiota composition has effects that go well beyond the gut.
6. Conclusions
The gut environment in CF patients has unique features due to the characteristics of the disease, such as decreased bicarbonate secretion, increased luminal viscosity, and an acidic small intestinal environment, which, due to the treatment, includes regular antibiotic use or a high-energy and fat-dense diet. As a result, the gut microbial composition appears altered, with decreased richness and diversity, both of which are features seen in other inflammatory and systemic diseases. Moreover, the population of pro-inflammatory bacteria is higher, while immunomodulatory genera, such as Bacteroides and Bifidobacterium, are scarcer. The imbalanced gut microbial population has a potential role in the development of systemic inflammation and may influence clinical outcomes, such as respiratory exacerbations, spirometry results, and overall growth. Although a better understanding of the pathophysiology behind the gut–lung axis is needed, these findings support the rationale to consider gut microbiota manipulation as a possible intervention to regulate the severity and progression of the disease.
Author Contributions
I.T. wrote the first draft of the manuscript; O.C. performed the literature review; S.E. gave a scientific contribution and critically revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are included in the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Meoli, A.; Fainardi, V.; Deolmi, M.; Chiopris, G.; Marinelli, F.; Caminiti, C.; Esposito, S.; Pisi, G. State of the Art on Approved Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Modulators and Triple-Combination Therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, A.K.; Loeffler, D.R.; Marshall, B.C.; Goss, C.H.; Morgan, W.J. Data that empower: The success and promise of CF patient registries. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2017, 52, S44–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riordan, J.R. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: Cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science 1989, 245, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riordan, J.R. CFTR function and prospects for therapy. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008, 77, 701–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.; Needham, B.; Leach, S.T.; Day, A.S.; Jaffe, A.; Thomas, T.; Ooi, C.Y. Disrupted progression of the intestinal microbiota with age in children with cystic fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, G.B.; Narkewicz, M.R.; Hoffman, R.H. The CF Gastrointestinal Microbiome: Structure and Clinical Impact. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2016, 51 (Suppl. S44), S35–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frati, F.; Salvatori, C.; Incorvaia, C.; Bellucci, A.; Di Cara, G.; Marcucci, F.; Esposito, S. The Role of the Microbiome in Asthma: The Gut-Lung Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enaud, R.; Prevel, R.; Ciarlo, E.; Beaufils, F.; Wieërs, G.; Guery, B.; Delhaes, L. The Gut-Lung Axis in Health and Respiratory Diseases: A Place for Inter-Organ and Inter-Kingdom Crosstalks. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautava, S.; Luoto, R.; Salnimen, S.; Isolauri, E. Microbial contact during pregnancy, intestinal colonization and human disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrington, J.E.; Stewart, C.J.; Embleton, N.D.; Cummings, S.R. Gut microbiota in preterm infants: Assessment and relevance to health and disease. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2013, 98, F286–F290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballarini, S.; Rossi, G.A.; Principi, N.; Esposito, S. Dysbiosis in Pediatrics Is Associated with Respiratory Infections: Is There a Place for Bacterial-Derived Products? Microorganisms 2021, 9, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loman, B.R.; Shrestha, C.L.; Thompson, R.; Kopp, B.T. Age and Environment Exposure Influence the Fecal Bacteriome of Young Childre with Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeker, S.M.; Mears, K.S.; Sangwan, N.; Brittnacher, M.J.; Weiss, E.J.; Treuting, P.M.; Tolley, N.; Pope, C.E.; Hager, K.R.; Vo, A.T.; et al. 2020 Jan, CFTR dysregulation drives active selection of the gut microbiome. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, D.G.; Fouhy, F.; Harrison, M.J. The altered gut microbiota in adults with cystic fibrosis. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Schippa, S.; Iebba, V.; Santangelo, F.; Gagliardi, A.; De Biase, R.V.; Stamano, A.; Bertasi, S.; Lucarelli, M.; Conte, M.P.; Quattrucci, S. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) allelic viariants relate to shifts in faecal microbiota of cystic fibrosis patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, C.Y.; Syed, S.A.; Rossi, L.; Garg, M.; Needham, B.; Aviolo, J.; Young, K.; Surette, M.G.; Gonska, T. Impact of CFTR modulation with Ivacaftor on Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronan, N.J.; Einarsson, G.G.; Deane, J.; Fouhy, F.; Rea, M.; Hill, C.; Shanahan, F.; Elborn, J.S.; Ross, R.P.; McCarthy, M.; et al. Modulation, microbiota and inflammation in the adult CF gut: A prospective study. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 25, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antosca, K.M.; Chernikova, D.A.; Price, C.E.; Ruoff, K.L.; Li, K.; Guill, M.F.; Sontag, N.R.; Morrison, H.G.; Hao, S.; Drumm, M.L.; et al. Altered Stool Microbiota of Infants with Cystic Fibrosis Shows a Reduction in Genera Associated with Immune Programming from Birth. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, e00274-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, J.C.; Koestler, D.C.; Stanton, B.A.; Davidson, L.; Moulton, L.A.; Housman, M.L.; Moore, J.H.; Guill, M.F.; Morrison, H.G.; Sogin, M.L.; et al. Serial analysys of the gut and respiratory microbiome in CF in infancy: The interaction between intestinal and respiratory tracts and the impact of nutritional exposure. mBio 2012, 3, e00251-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernocchi, P.; Del Chierico, F.; Russo, A.; Majo, F.; Rossitto, M.; Valerio, M.; Casadei, L.; La Storia, A.; De Filippis, F.; Rizzo, C.; et al. Gut microbiota signatures in cystic fibrosis: Loss of host CFTR function drives the microbiota enterophenotype. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, M.B.; Moreira, E.A.M.; Tomio, C.; Moreno, Y.M.F.; Daltoe, F.P.; Barbosa, E.; Neto, N.L.; Buccigrossi, V.; Guarino, A. Altered intestinal microbiota composition, antibiotic therapy and intestinal inflammation in children and adolescents with cystic fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, M.; Prevaes, S.M.P.J.; Kalkman, G.; Tramper-Stranders, G.A.; Hasrat, R.; de Winter-de Groot, K.M.; Janseen, H.M.; Tiddens, H.A.; van Westreenen, M.; Sanders, E.A.M.; et al. Development of the gut microbiota in early life: The impact of cistic fibrosis and antibiotic treatment. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2020, 19, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatsuneko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albenberg, L.; Kelsen, J. Advances in Gut Microbiome Research and Relevance to Pediatric Diseases. J. Pediatr. 2016, 178, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Wang, A.C.; Parikh, I.; Green, S.J.; Hoffman, J.D.; Chlipala, G.; Murphy, M.P.; Sokola, B.S.; Bauer, B.; Hartz, A.M.S.; et al. Ketogenic diet enhances neurovascular function with altered gut microbiome in young healty mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, J.C.; Hoen, A.G.; Lundgren, S.N.; Farzan, S.F.; Cottingham, K.L.; Morrison, H.G.; Sogin, M.L.; Li, H.; Moore, J.H.; Karagas, M.R. Association of Cesarean delivery and formula supplementation with the intestinal microbiome of 6-week-old infants. JAMA Paediatr. 2016, 170, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, S.; Ballarini, S.; Argentiero, A.; Ruggiero, L.; Rossi, G.A.; Principi, N. Microbiota profiles in pre-school children with respiratory infections: Modifications induced by the oral bacterial lysate OM-85. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouhy, F.; Ronan, N.J.; O’Sullivan, O.; McCarthy, Y.; Walsh, A.M.; Murphy, D.M.; Daly, M.; Flanagan, E.T.; Fleming, C.; McCarthy, M.; et al. A pilot study demonstrating the altered gut microbiota functionality in stable adults with Cystic Fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duytschaever, G.; Huys, G.; Bekaert, M.; Boulanger, L.; De Boeck, K.; Vandamme, P. Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Composition of Prenominant Fecal Microbiota Composition of a Group of Pediatric Patients with Cystic Fibrosis and Their Healty Siblings. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 8015–8024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, M.O.; Church, G.M.; Dantas, G. The human microbiome harbors a diverse reservoiur of antibiotic resistance genes. Virulence 2010, 1, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duytschaever, G.; Huys, G.; Boulanger, L.; De Boeck, K.; Vandamme, P. Amoxicillin–clavulanic acid resistance in fecal Enterobacteriaceae from patients with cystic fibrosis and healthy siblings. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2013, 12, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.L.; Leong, L.E.X.; Sims, S.K.; Keating, R.L.; Papanicolas, L.E.; Richard, A.; Mobegi, F.M.; Wesselingh, S.; Burr, L.D.; Rogers, G.B. The cystic fibrosis gut as a potential source of multidrug resistant pathogens. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2021, 20, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thavamani, A.; Salem, I.; Sferra, T.J.; Sankararaman, S. Impact of Altered Gut Microbiota and Its Metabolites in Cystic Fibrosis. Metabolites 2021, 11, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, L.R.; Pope, C.E.; Hayden, H.S.; Heltshe, S.; Levy, R.; McNamara, S.; Jacobs, M.A.; Rohmer, L.; Radey, M.; Ramsey, B.W.; et al. Escherichia coli Dysbiosis Correlates with Gastrointestinal Dysfunction in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlan, P.D.; Buckling, A.; Kong, W.; Wild, Y.; Lynch, S.V.; Harrison, F. Gut dysbiosis in cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2012, 11, 454–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruzzese, E.; Callegari, M.L.; Raia, V.; Viscovo, S.; Scotto, R.; Ferrari, S.; Morelli, L.; Buccigrossi, V.; Lo Vecchio, A.; Ruberto, E.; et al. Disrupted Intestinal Microbiota and Intestinal Inflammation in Children with Cystic Fibrosis and Its Restoration with Lactobacillus GG: A Randomised Clinical Trial. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, M.J.; Nielsen, S.; Wemheuer, B.; Kaakoush, N.O.; Garg, M.; Needham, B.; Pickford, R.; Jaffe, A.; Thomas, T.; Ooi, C.Y. Gut microbiota in children with cystic fibrosis: A taxonomic and functional dysbiosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, C.E.; O’Toole, G.A. The gut-lung axis in cystic fibrosis. J. Bacteriol. 2021, 203, e00311-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, S.; Wang, N.; Tan, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Y. The Cross-Talk Between Gut Microbiota and Lungs in Common Lung Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinolo, M.A.; Rodriguez, H.G.; Nachbar, R.T.; Curi, R. Regulation of inflammation by short chain faffy acids. Nutrients 2011, 3, 858–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Françoise, A.; Héry-Arnaud, G. The Microbiome in Cystic Fibrosis Pulmonary Disease. Genes 2020, 11, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartl, D.; Gaggar, A.; Bruscia, E.; Hector, A.; Marcos, V.; Jung, A.; Greene, C.; McElvaney, G.; Mall, M.; Döring, G. Innate immunity in cystic fibrosis lung disease. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2012, 11, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoen, A.G.; Li, J.; Moulton, L.A.; O’Toole, G.A.; Housman, M.L.; Koestler, D.C.; Guill, M.F.; Moore, J.H.; Hibberd, P.L.; Morrison, H.G.; et al. Association between gut microbial colonization in early life and respiratory outcomes in cystic fibrosis. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 138–147.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björkstén, B.; Naaber, P.; Sepp, E.; Mikelsaar, M. The intestinal microflora in allergic Estonian and Swedish 2-year-old children. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1999, 29, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalliomäki, M.; Kirjavainen, P.; Eerola, E.; Kero, P.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E. Distinct patterns of neonatal gut microflora in infants in whom atopy was and was not developing. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 107, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazmanian, S.K.; Liu, C.H.; Tzianabos, A.O.; Kasper, D.L. An immunomodulatory molecule of symbiotic bacteria directs maturation of the host immune system. Cell 2005, 122, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duytschaever, G.; Huys, G.; Bekaert, M. Dysbiosis of bifidobacteria and Clostridium cluster XIVa in the cystic fibrosis fecal microbiota. J. Cyst. FIbros. 2013, 12, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, S.; Testa, I.; Mariotti Zani, E.; Cunico, D.; Torelli, L.; Grandinetti, R.; Fainardi, V.; Pisi, G.; Principi, N. Probiotics Administration in Cystic Fibrosis: What Is the Evidence? Nutrients 2022, 14, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grier, A.; McDavid, A.; Wang, B.; Qiu, X.; Java, J.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Yang, H.; Holden-Wiltse, J.; Kessler, H.A.; Gill, A.L.; et al. Neonatal gut and respiratory microbiota: Coordinated development through time and space. Microbiome 2018, 6, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulzebos, E.H.; Bomhof-Roordink, H.; van de Weert-van Leeuwen, P.B.; Twisk, J.W.; Arets, H.G.; van der Ent, C.K.; Takken, T. Prediction of mortality in adolescents with cystic fibrosis. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2014, 46, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, H.S.; Eng, A.; Pope, C.E.; Brittnacher, M.J.; Vo, A.T.; Weiss, E.J.; Hager, K.R.; Martin, B.D.; Leung, D.H.; Heltshe, S.L.; et al. Fecal dysbiosis in infants with cystic fibrosis is associated with early linear growth failure. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gough, E.K.; Stephens, D.A.; Moodie, E.E.; Prendergast, A.J.; Stoltzfus, R.J.; Humphrey, J.H.; Manges, A.R. Linear growth faltering in infants is associated with Acidaminococcus sp. and community-level changes in the gut microbiota. Microbiome 2015, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werlin, S.L.; Benuri-Silbiger, I.; Kerem, E.; Adler, S.N.; Goldin, E.; Zimmerman, J.; Malka, N.; Cohen, L.; Armoni, S.; Yatzkan-Israelit, Y.; et al. Evidence of intestinal inflammation in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).