Biogeographical Patterns and Assembly of Bacterial Communities in Saline Soils of Northeast China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Field Sampling
2.2. Soil Physicochemical Properties Analysis
2.3. Soil DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.4. Bacterial Community Composition Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Physiochemical Properties
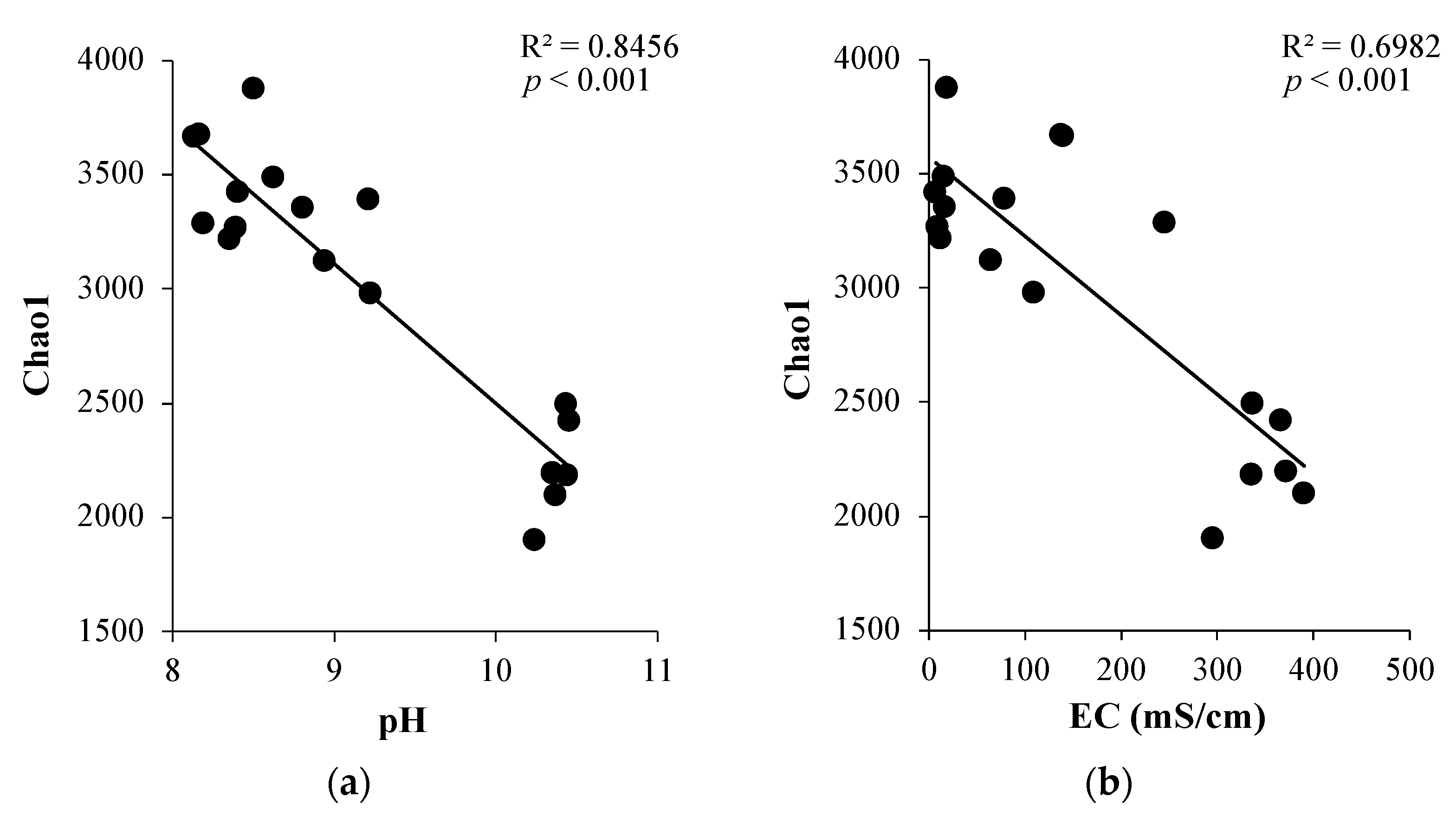
3.2. Soil Bacterial Community Diversity and Association with Soil Characteristics
3.3. Soil Bacterial Community Composition
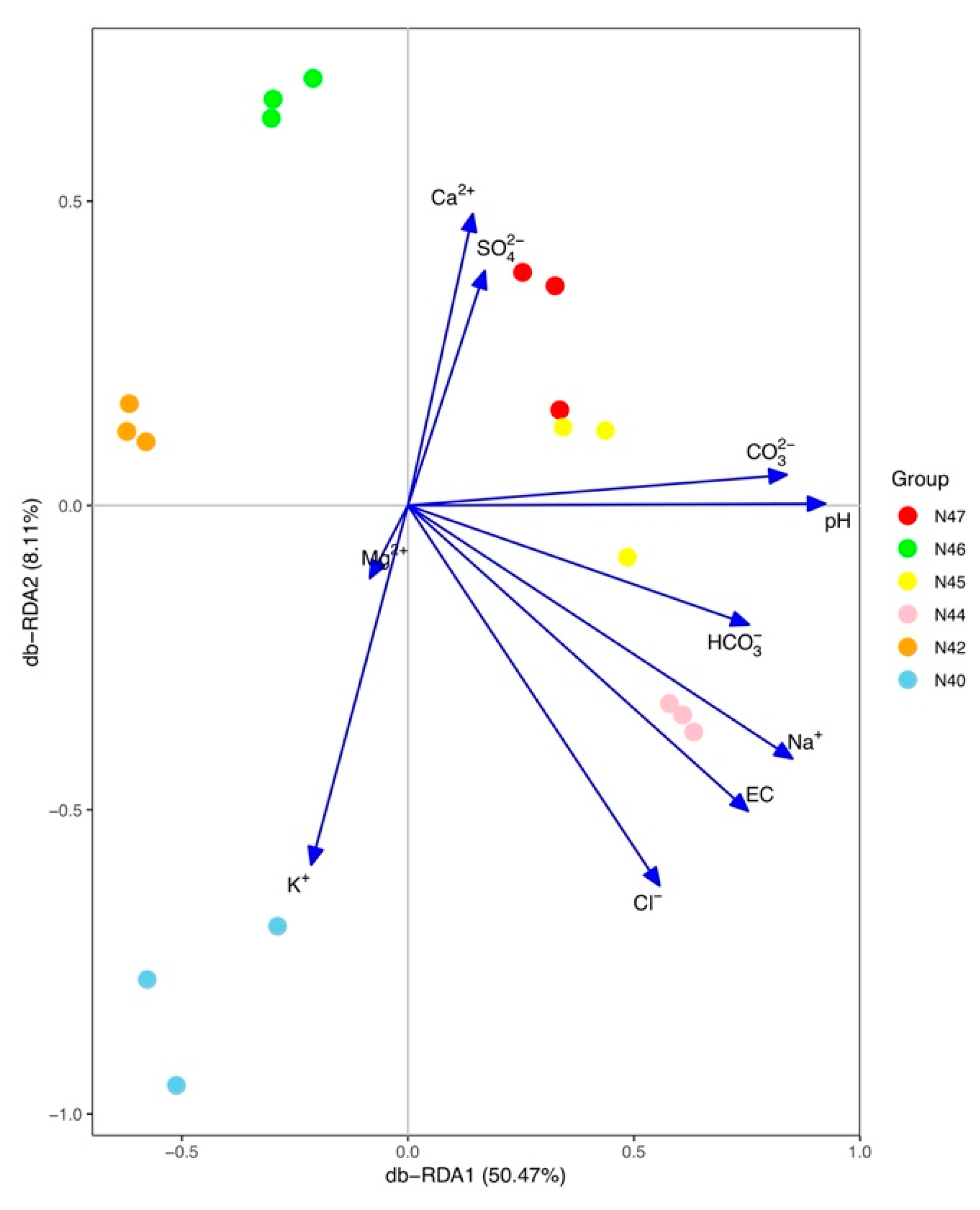
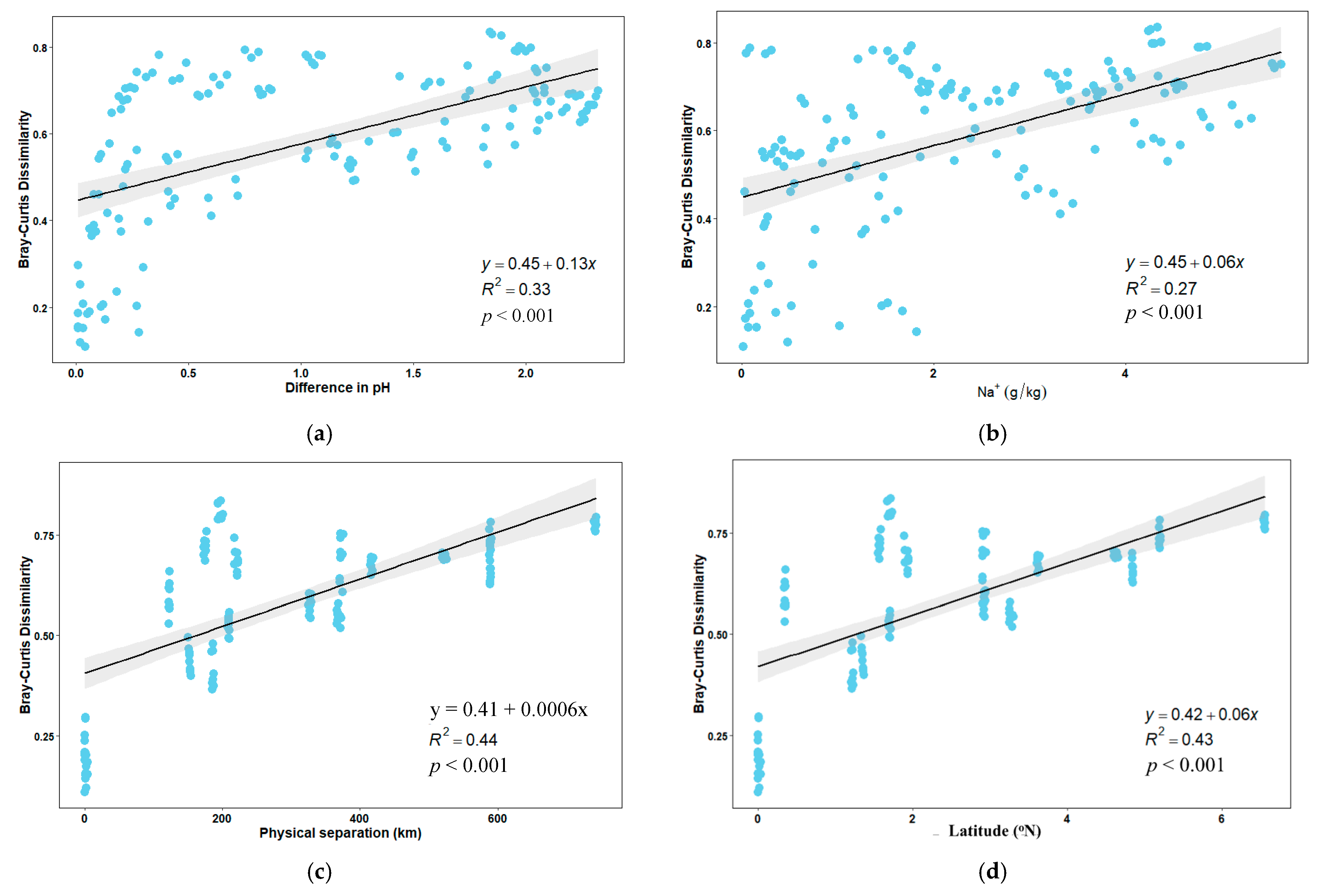
3.4. Impacts of Soil Characteristics on Bacterial Community Composition
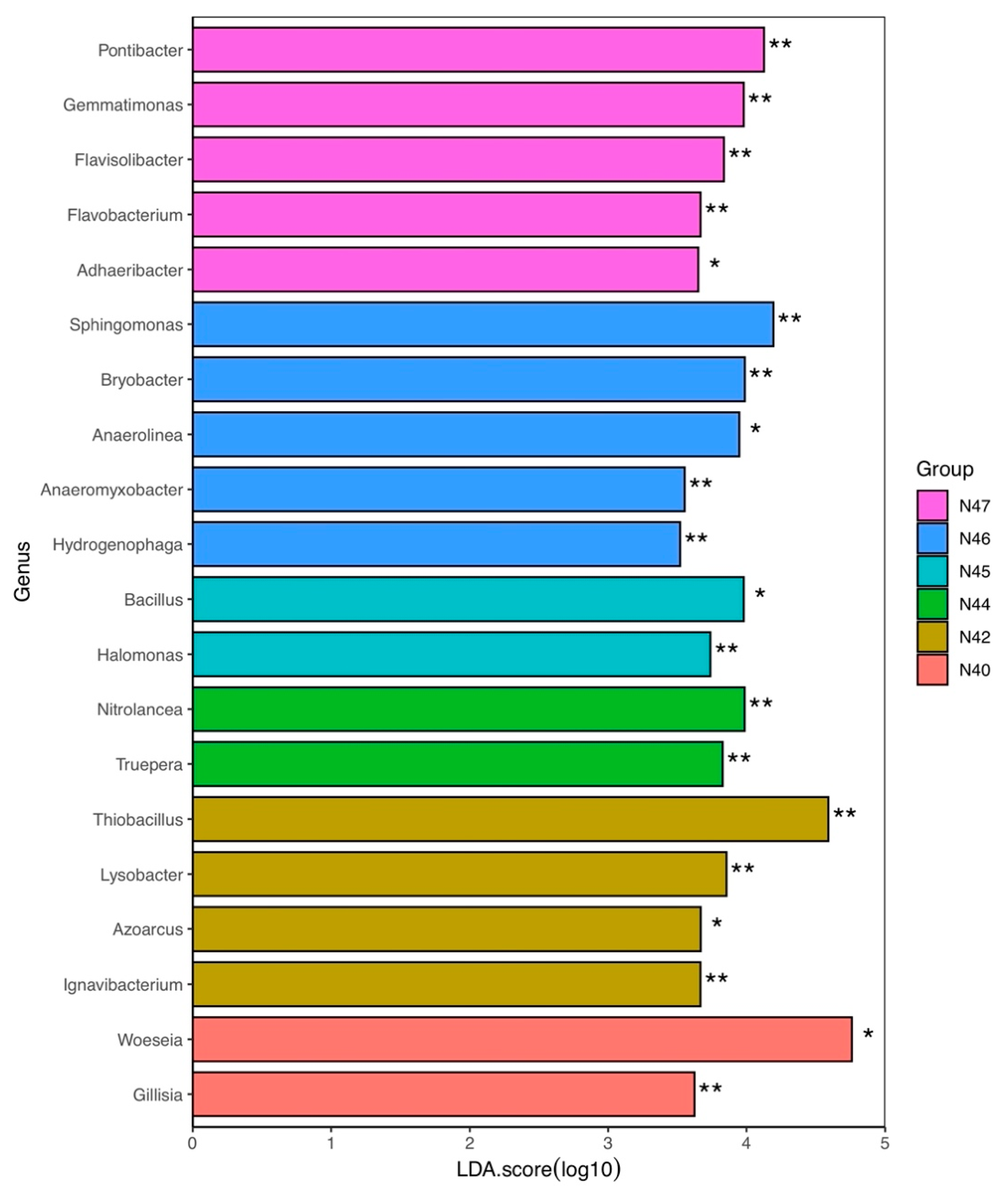
3.5. Major Bacterial Genera Accounting for Community Composition Differences
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, X.; Pu, L.; Zhu, M.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X. Linkage between soil salinization indicators and physicochemical properties in a long-term intensive agricultural coastal reclamation area, Eastern China. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 3699–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litalien, A.; Zeeb, B. Curing the earth: A review of anthropogenic soil salinization and plant-based strategies for sustainable mitigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Pu, L.; Han, M.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, R.; Xiang, Y. Soil salinization research in China: Advances and prospects. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 943–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, S.; Ghadiri, H.; Chen, C.; Marschner, P. Salt-affected soils, reclamation, carbon dynamics, and biochar: A review. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, R.; Tian, Y.; Guo, K.; Sun, H.; Liu, X.; Chu, H.; Liu, B. Long-term phytoremediation of coastal saline soil reveals plant species-specific patterns of microbial community recruitment. mSystems 2020, 5, e00741-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.N.; Srivastava, S.; Khare, S.K.; Prakash, V. Extremophiles: An overview of microorganism from extreme environment. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Biotechnol. 2014, 7, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Radosevich, M.; Löffler, F.; Schaeffer, S.M.; Zhuang, J. Impact of microbial iron oxide reduction on the transport of diffusible tracers and non-diffusible nanoparticles in soils. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, K.; Gao, F.; Liu, X. Petroleum depletion property and microbial community shift after bioremediation using Bacillus halotolerans T-04 and Bacillus cereus 1-1. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, X.U.; Pei, G.; Xia, Z.; Peng, B.O.; Sun, L.; Wang, J.; Gao, D.; Chen, S.; Liu, D.; et al. Stabilization of microbial residues in soil organic matter after two years of decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 141, 107687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Bradford, M.A. Soil-carbon response to warming dependent on microbial physiology. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Jackson, R.D.; DeLucia, E.H.; Tiedje, J.M.; Liang, C. The soil microbial carbon pump: From conceptual insights to empirical assessments. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 6032–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Gao, D.; Zhao, C.; Wang, C.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bai, E. Improved model simulation of soil carbon cycling by representing the microbially derived organic carbon pool. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2248–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Miao, F.; Li, Z.; Tang, W.; Sun, J. Assessing the effect of soil salinization on soil microbial respiration and diversities under incubation conditions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 155, 103671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Jiang, N.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Bello, A.; Yang, W. Disentangling the role of salinity-sodicity in shaping soil microbiome along a natural saline-sodic gradient. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.C.; Li, Z.Z.; Liu, H.; Gao, M.; Zhang, Y.Y. Microbial biomass and activity in salt affected soils under arid conditions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2007, 35, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egamberdieva, D.; Wirth, S.; Bellingrath-Kimura, S.D.; Mishra, J.; Arora, N.K. Salt-tolerant plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for enhancing crop productivity of saline soils. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, H.; Yan, B. Unraveling bacterial community structure and function and their links with natural salinity gradient in the Yellow River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Tebbe, C.C.; Zhao, Q.; Jia, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Yu, L. Salinity controls soil microbial community structure and function in coastal estuarine wetlands. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 1020–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, J.; Banerjee, S.; Zhou, N.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, K.; Hu, M.; Tian, C. Biogeographical distribution of bacterial communities in saline agricultural soil. Geoderma 2020, 361, 114095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Yu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Smith, P. Dynamics of pedogenic carbonate in the cropland of the North China Plain: Influences of intensive cropping and salinization. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 292, 106820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setia, R.; Marschner, P.; Baldock, J.; Chittleborough, D.; Verma, V. Relationships between carbon dioxide emission and soil properties in salt-affected landscapes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayment, G.E.; Higginson, F.R. Australian Laboratory Handbook of Soil and Water Chemical Methods; Inkata Press Pty Ltd.: Sydney, NSW, Australia, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, T.C.; Walsh, K.A.; Harris, J.A.; Moffett, B.F. Using ecological diversity measures with bacterial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2003, 43, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chessel, D.; Dufour, A.B.; Thioulouse, J. The ade4 package-I-One-table methods. R News 2004, 4, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Jackson, R.B. The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, R.I.; Thomson, B.C.; James, P.; Bell, T.; Bailey, M.; Whiteley, A.S. The bacterial biogeography of British soils. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1642–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasternak, Z.; Al-Ashhab, A.; Gatica, J.; Gafny, R.; Avraham, S.; Minz, D.; Gillor, O.; Jurkevitch, E. Spatial and temporal biogeography of soil microbial communities in arid and semiarid regions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahram, M.; Hildebrand, F.; Forslund, S.K.; Anderson, J.L.; Soudzilovskaia, N.A.; Bodegom, P.M.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Anslan, S.; Coelho, L.P.; Harend, H.; et al. Structure and function of the global topsoil microbiome. Nature 2018, 560, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Wu, L.; Liu, W.; Ge, Y.; Mu, T.; Zhou, T.; Li, Z.; Zhou, J.; Sun, X.; Luo, Y.; et al. Biogeography and diversity patterns of abundant and rare bacterial communities in rice paddy soils across China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; He, J.Z.; Zhu, Y.G.; Zhang, J.B.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L.M.; Zheng, Y.M. Differences in soil bacterial diversity: Driven by contemporary disturbances or historical contingencies? ISME J. 2008, 2, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, J.L.; Huang, L.N.; Chen, L.X.; Hua, Z.S.; Li, S.J.; Hu, M.; Li, J.T.; Shu, W.S. Contemporary environmental variation determines microbial diversity patterns in acid mine drainage. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yergeau, E.; Newsham, K.K.; Pearce, D.A.; Kowalchuk, G.A. Patterns of bacterial diversity across a range of Antarctic terrestrial habitats. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2670–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, K.N.; Kluepfel, D.A.; Strauss, S.L.; Bokulich, N.A.; Cantu, D.; Steenwerth, K.L. Vineyard soil bacterial diversity and composition revealed by 16S rRNA genes: Differentiation by geographic features. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 91, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruch, Z.; Liddicoat, C.; Cando-Dumancela, C.; Laws, M.; Morelli, H.; Weinstein, P.; Young, J.M.; Breed, M.F. Increased plant species richness associates with greater soil bacterial diversity in urban green spaces. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhuang, J.; Löffler, F.E.; Zhang, Y.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Schaeffer, S.M.; Radosevich, M. Viral and bacterial community responses to stimulated Fe (III)-bioreduction during simulated subsurface bioremediation. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 2043–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Ghosh, D.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Dasgupta, T.; Wommack, K.E.; Liang, X.; Wagner, R.E.; Radosevich, M. Temporal dynamics of soil virus and bacterial populations in agricultural and early plant successional soils. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, L.; Chapuis-Lardy, L.; Razafimbelo, T.; Razafindrakoto, M.; Pablo, A.L.; Legname, E.; Poulain, J.; Brüls, T.; O’donohue, M.; Brauman, A.; et al. Endogeic earthworms shape bacterial functional communities and affect organic matter mineralization in a tropical soil. ISME J. 2012, 6, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wommack, K.E.; Wilhelm, S.W.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Sherfy, A.C.; Zhuang, J.; Radosevich, M. Lysogenic reproductive strategies of viral communities vary with soil depth and are correlated with bacterial diversity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 144, 107767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlawi, S.; Naeem, A.; Rengel, Z.; Naidu, R. Biochar application for the remediation of salt-affected soils: Challenges and opportunities. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 320–335. [Google Scholar]
- Rath, K.M.; Maheshwari, A.; Bengtson, P.; Rousk, J. Comparative toxicities of salts on microbial processes in soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 2012–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Li, S.; Lei, X.; Sun, X.; Qin, L. Salt stress-induced changes in microbial community structures and metabolic processes result in increased soil cadmium availability. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 147125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Tian, L.; Nasir, F.; Bahadur, A.; Batool, A.; Luo, S.; Yang, F.; Wang, Z.; Tian, C. Response of microbial communities and enzyme activities to amendments in saline-alkaline soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 135, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Shi, Y.; Cui, X.; Yue, P.; Li, K.; Liu, X.; Tripathi, B.M.; Chu, H. Salinity is a key determinant for soil microbial communities in a desert ecosystem. mSystems 2019, 4, e00225-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gao, W.; Zhao, B.; Chen, M.; Ma, L.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, J. Bacterial community composition and assembly along a natural sodicity/salinity gradient in surface and subsurface soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 157, 103731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousk, J.; Bååth, E.; Brookes, P.C.; Lauber, C.L.; Lozupone, C.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratzke, C.; Gore, J. Modifying and reacting to the environmental pH can drive bacterial interactions. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2004248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBruyn, J.M.; Nixon, L.T.; Fawaz, M.N.; Johnson, A.M.; Radosevich, M. Global biogeography and quantitative seasonal dynamics of Gemmatimonadetes in soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6295–6300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmert, E.A.; Geleta, S.B.; Rose, C.M.; Seho-Ahiable, G.E.; Hawkins, A.E.; Baker, K.T.; Evans, A.S.; Harris, M.E.; Mrozinski, A.C.; Folkoff, M.E.; et al. Effect of land use changes on soil microbial enzymatic activity and soil microbial community composition on Maryland’s Eastern Shore. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 161, 103824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, J.R.; Wang, Y.; Jaubert, C.; Nguyen, T.N.; Fernandes, G.R.; DuBow, M.S. The bacterial communities of surface soils from desert sites in the eastern Utah (USA) portion of the Colorado Plateau. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 244, 126664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, R.; Gupta, V.V.; Reith, F.; Bissett, A.; Mele, P.; Franco, C.M. Biogeography and emerging significance of Actinobacteria in Australia and Northern Antarctica soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 146, 107805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, T.; Chan, Y.; Lacap, D.C.; Lau, M.C.; McKay, C.P.; Pointing, S.B. Stochastic and deterministic processes interact in the assembly of desert microbial communities on a global scale. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1406–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, B.M.; Stegen, J.C.; Kim, M.; Dong, K.; Adams, J.M.; Lee, Y.K. Soil pH mediates the balance between stochastic and deterministic assembly of bacteria. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xun, W.; Li, W.; Xiong, W.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Y.; Miao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, N.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R. Diversity-triggered deterministic bacterial assembly constrains community functions. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, B. Biogeographical Patterns and Assembly of Bacterial Communities in Saline Soils of Northeast China. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091787
Liang X, Wang X, Zhang N, Li B. Biogeographical Patterns and Assembly of Bacterial Communities in Saline Soils of Northeast China. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(9):1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091787
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Xiaolong, Xiaoyu Wang, Ning Zhang, and Bingxue Li. 2022. "Biogeographical Patterns and Assembly of Bacterial Communities in Saline Soils of Northeast China" Microorganisms 10, no. 9: 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091787
APA StyleLiang, X., Wang, X., Zhang, N., & Li, B. (2022). Biogeographical Patterns and Assembly of Bacterial Communities in Saline Soils of Northeast China. Microorganisms, 10(9), 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091787




