Resistome Analysis of Campylobacter jejuni Strains Isolated from Human Stool and Primary Sterile Samples in Croatia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparing the Bacterial Isolates
2.1.1. Campylobacter Isolates
2.1.2. DNA Extraction
2.1.3. Species Confirmation/Identification
2.1.4. MLST
2.1.5. Whole Genome Sequencing
2.2. Genomics
2.2.1. Whole Genome Sequencing
2.2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.2.3. Genotypic–Phenotypic Comparisons
3. Results
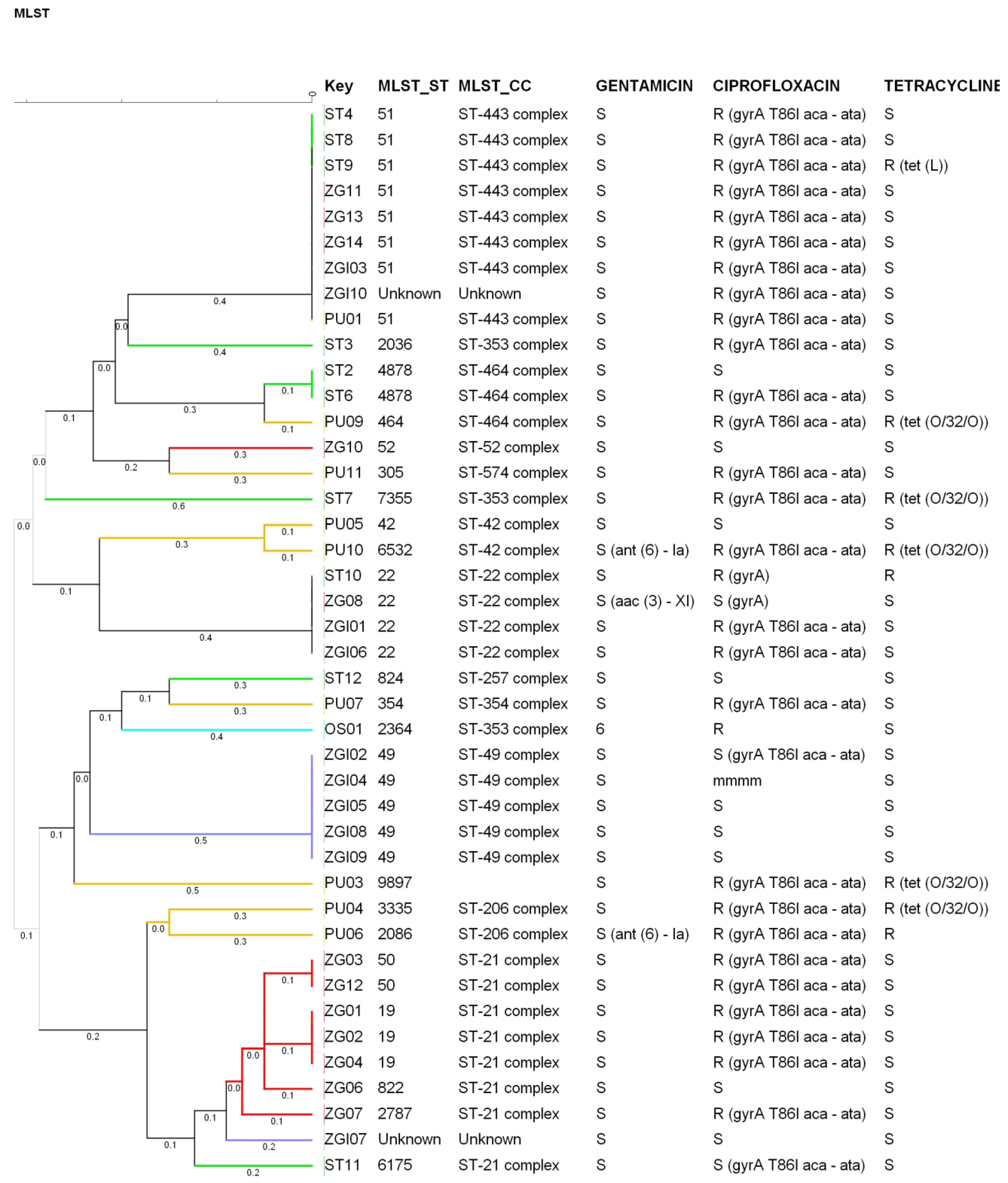
3.1. PCR Identification and Epidemiological Relatedness
3.2. Genotypic Determination of AMR
3.3. Comparison between Phenotypic and Genotypic AMR
3.3.1. Resistance to Macrolides
3.3.2. Resistance to Fluoroquinolones
3.3.3. Resistance to Tetracyclines
3.3.4. Resistance to Aminoglycosides
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (EFSA and ECDC). The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2017. EFSA J. 2018, 16, 5500. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (EFSA and ECDC). The European Union One Health 2020 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2021, 19, 6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Estimates of the Global Burden of Foodborne Diseases: Foodborne Disease Burden Epidemiology Reference Group 2007–2015; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/199350 (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Blaser, M.J. Epidemiologic and Clinical Features of Campylobacter jejuni Infections. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 176, S103–S105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auwaerter, P. Campylobacter Jejuni. Johns Hopkins ABX Guide; The Johns Hopkins University: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ban, M.A. Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Campylobacter Infection. UpToDate. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-manifestations-diagnosis-and-treatment-of-campylobacter-infection (accessed on 23 March 2022).
- Alfredson, D.A.; Korolik, V. Antibiotic resistance and resistance mechanisms in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 277, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieczorek, K.; Osek, J. Antimicrobial resistance mechanisms among Campylobacter. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 340605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Same, R.G.; Tamma, P.D. Campylobacter Infections in Children. Pediatr. Rev. 2018, 39, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusulja, M.; Santini, M.; Margetić, K.; Guzvinec, M.; Šoprek, S.; Butić, I.; Tambić Andrašević, A. Meningitis caused by Campylobacter jejuni: A case presentation and literature review. Acta Clin. Belg. 2021, 76, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, L.M.; Vazquez-Pertejo, M.T. Campylobacter and Related Infections; MSD Manual Professional Edition; Merck & Co, Inc.: Rahway, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Endtz, H.P.; Ruijs, G.J.; Van Klingeren, B.; Jansen, W.H.; Van der Reyden, T.; Mouton, R.P. Quinolone resistance in Campylobacter isolated from man and poultry following the introduction of fluoroquinolones in veterinary medicine. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1991, 27, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payot, S.; Bolla, J.-M.; Corcoran, D.; Fanning, S.; Mégraud, F.; Zhang, Q. Mechanisms of fluo-roquinolone and macrolide resistance in Campylobacter spp. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 1967–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engberg, J.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Taylor, D.E.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Nachamkin, I. Quinolone and macrolide resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli: Resistance mechanisms and trends in human isolates. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, B.; Muraoka, W.; Sahin, O.; Zhang, Q. Role of Cj1211 in natural transformation and transfer of antibiotic resistance determinants in Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 2699–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payot, S.; Avrain, L.; Magras, C.; Praud, K.; Cloeckaert, A.; Chaslus-Dancla, E. Relative contribution of target gene mutation and efflux to fluoro-quinolone and erythromycin resistance, in French poultry and pig isolates of Campylo-bacter coli. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2004, 23, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagliero, C.; Mouline, C.; Cloeckaert, A.; Payot, S. Synergy between efflux pump CmeABC and modifications in ribosomal proteins L4 and L22 in conferring macrolide resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 3893–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.E.; de Grandis, S.A.; Karmali, M.A.; Fleming, P.C. Transmissible plasmids from Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1981, 19, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkhill, J.; Wren, B.W.; Mungall, K.; Ketley, J.M.; Churcher, C.; Basham, D.; Chillingworth, T.; Davies, R.M.; Feltwell, T.; Holroyd, S.; et al. The genome sequence of the food-borne pathogen Campylobacter jejuni reveals hypervariable sequences. Nature 2000, 403, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfredson, D.A.; Korolik, V. Isolation and expression of a novel molecular class D β-lactamase, OXA-61, from Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2515–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucain, C.; Goossens, H.; Pechere, J.C. Beta-lactamases in Campylobacter jejuni. In Campylobacter III; Pearson, A.D., Skirrow, M.B., Lior, H., Rowe, B., Eds.; Public Health Laboratory Service: London, UK, 1985; Volume 5, pp. 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Overbye Michel, L.; Zhang, Q.J. CmeABC functions as a multidrug efflux system in Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2124–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumbwe, L.; Piddock, L.J.V. Identification and molecular characterisation of CmeB, a Campylobacter jejuni multidrug efflux pump. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 206, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Plummer, J. Mechanism of antibiotic resistance in Campylobacter. In Campylobacter; Nachamkin, I., Szymanski, C.M., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 263–276. [Google Scholar]
- Llano-Sotelo, B.; Azucena, E.F.; Kotra, L.P.; Mobashery, S.; Chow, C.S. Aminoglycosides modified by resistance enzymes display diminished binding to the bacterial ribosomal aminoacyl-tRNA site. Chem. Biol. 2002, 9, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engberg, J.; Keelan, M.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Taylor, D.E. Antimicrobial resistance in Campylobacter. In Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria of Animal Origin; Aarestrup, F.M., Ed.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; pp. 269–291. [Google Scholar]
- Connell, S.R.; Trieber, C.A.; Dinos, G.P.; Einfeldt, E.; Taylor, D.E.; Nierhaus, K.H. Mechanism of Tet(O)-mediated tetracycline resistance. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.E.; Garner, R.S.; Allan, B.J. Characterization of tetracycline resistance plasmids from Campylo-bacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1983, 24, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibreel, A.; Tracz, D.M.; Nonaka, L.; Ngo, T.M.; Connell, S.R.; Taylor, D.E. Incidence of antibiotic resistance in Campylobacter jejuni isolated in Alberta, Canada, from 1999 to 2002, with special reference to tet(O)-mediated tetracycline resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3442–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, S.; Kehrenberg, C.; Doublet, B.; Cloeckaert, A. Molecular basis of bacterial re-sistance to chloramphenicol and florfenicol. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 28, 519–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Clark, C.G.; Taylor, T.M.; Pucknell, C.; Barton, C.; Price, L.; Woodward, D.L.; Rodgers, F.G. Colony multiplex PCR assay for identification and differentiation of Campylobacter jejuni, C. coli, C. lari, C. upsaliensis, and C. fetus subsp. Fetus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 4744–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MIC and Zone Distributions and ECOFFs. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/mic_distributions_and_ecoffs/ (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- EFSA. Technical report on the methodological approach used for the assessment of the control measures for Category A diseases in the context of the new Animal Health Law. EFSA J. 2020, 17, EN-1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ResFinder. Available online: https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/ResFinder/ (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- Ohno, H.; Wachino, J.I.; Saito, R.; Jin, W.; Yamada, K.; Kimura, K.; Arakawa, Y. A Highly Macrolide-Resistant Campylobacter jejuni Strain with Rare A2074T Mutations in 23S rRNA Genes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2580–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibreel, A.; Kos, V.N.; Keelan, M. Macrolide resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli: Molecular mechanism and stability of the resistance phenotype. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2753–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Luo, N.; Sahin, O.; Lin, J.; Michel, L.O.; Zhang, Q. In vivo selection of Campylobacter isolates with high levels of fluoroquinolone resistance associated with gyrA mutations and the function of the CmeABC efflux pump. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.L.; Cribb, D.M.; Bulach, D.M.; Ingle, D.J.; Joensen, K.G.; Nielsen, E.M.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Stingl, K.; Kirk, M.D. Campylobacter jejuni ST50, a pathogen of global importance: A comparative genomic analysis of isolates from Australia, Europe and North America. Zoonoses Public Health 2021, 68, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carev, M.E. Epidemiološke i Mikrobiološko-Molekularne Značajke Kampilobakterioze u Splitsko- Dalmatinskoj Županiji: 2007–2012. Epidemiological and Microbiological-Molecular Characteristics of Campylobacteriosis in Split-Dalmatia County: 2007–2012. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Medicine, University of Split, Split, Croatia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- The Croatian Academy of Medical Sciences. Antibiotic Resistance in Croatia. 2020. Section 1 Antibiotic Resistance in 2020. pp. 117–119. Available online: https://iskra.bfm.hr/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/Knjiga-2020.-za-web_novo.pdf (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Welcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo-Díaz, J.F.; González Del Río, P.; Álvarez-Ordóñez, A. Whole Resistome Analysis in Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli Genomes Available in Public Repositories. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 662144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieczorek, K.; Wołkowicz, T.; Osek, J. MLST-based genetic relatedness of Campylobacter jejuni isolated from chickens and humans in Poland. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinueza-Burgos, C.; Wautier, M.; Martiny, D.; Cisneros, M.; Van Damme, I.; De Zutter, L. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance and genetic diversity of Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni in Ecuadorian broilers at slaughter age. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 2366–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohishi, T.; Aoki, K.; Ishii, Y.; Usui, M.; Tamura, Y.; Kawanishi, M.; Ohnishi, K.; Tateda, K. Molecular epidemiological analysis of human- and chicken-derived isolates of Campylobacter jejuni in Japan using next-generation sequencing. J. Infect. Chemother. 2017, 23, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramonaite, S.; Tamuleviciene, E.; Alter, T.; Kasnauskyte, N.; Malakauskas, M. MLST genotypes of Campylobacter jejuni isolated from broiler products, dairy cattle and human campylobacteriosis cases in Lithuania. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, I.; Miller, W.G.; Uyttendaele, M.; Houf, K.; De Zutter, L. Clonal population structure and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni in chicken meat from Belgium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 4264–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.N.; Sheppard, S.K.; McCarthy, N.D.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Ingmer, H.; Krogfelt, K.A. MLST clustering of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from patients with gastroenteritis, reactive arthritis and Guillain–Barre´ syndrome. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärenlampii, R.; Rautelin, H.; Schönberg-Norio, D.; Paulin, L.; Hänninen, M.L. Longitudinal study of Finnish Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli isolates from humans, using multilocus sequence typing, including comparison with epidemiological data and isolates from poultry and cattle. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullner, P.; Spencer, S.E.; Wilson, D.J.; Jones, G.; Noble, A.D.; Midwinter, A.C.; Collins-Emerson, J.M.; Carter, P.; Hathaway, S.; French, N.P. Assigning the source of human campylobacteriosis in New Zealand: A comparative genetic and epidemiological approach. Infect. Gen. Evol. 2009, 9, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickan, L.; Doyle, R.; Valcanis, M.; Dingle, K.E.; Unicomb, L.; Lanser, J. and the Australian Campylobacter Subtyping Study Group. Multilocus sequence typing of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from New South Wales, Australia. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Mou, K.; Sahin, O.; Zhang, Q. Genomic insights into Campylobacter jejuni virulence and population genetics. Infect. Dis. Transl. Med. 2016, 2, 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Dearlove, B.L.; Cody, A.J.; Pascoe, B.; Meric, G.; Wilson, D.J.; Sheppard, S.K. Rapid host switching in generalist Campylobacter strains erodes the signal for tracing human infections. ISME J. 2016, 10, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiedoruk, K.; Daniluk, T.; Rozkiewicz, D.; Oldak, E.; Prasad, S.; Swiecicka, I. Whole-genome comparative analysis of Campylobacter jejuni strains isolated from patients with diarrhea in northeastern Poland. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| SAMPLE Nr. | MLST_ST | MLST_CC | aspA | glnA | gltA | glyA | pgm | tkt | uncA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OS01 | 2364 | ST-353 complex | 14 | 249 | 5 | 2 | 11 | 3 | 6 |
| PU01 | 51 | ST-443 complex | 7 | 17 | 2 | 15 | 23 | 3 | 12 |
| PU03 | 9897 | / | 2 | 21 | 12 | 62 | 11 | 67 | 6 |
| PU04 | 3335 | ST-206 complex | 62 | 4 | 5 | 10 | 2 | 1 | 5 |
| PU05 | 42 | ST-42 complex | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 9 | 3 |
| PU06 | 2086 | ST-206 complex | 2 | 4 | 5 | 25 | 11 | 1 | 5 |
| PU07 | 354 | ST-354 complex | 8 | 10 | 2 | 2 | 11 | 12 | 6 |
| PU09 | 464 | ST-464 complex | 24 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 3 | 1 |
| PU10 | 6532 | ST-42 complex | 346 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 9 | 3 |
| PU11 | 305 | ST-574 complex | 9 | 53 | 2 | 10 | 11 | 3 | 3 |
| ST10 | 22 | ST-22 complex | 1 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| ST11 | 6175 | ST-21 complex | 2 | 1 | 5 | 10 | 608 | 1 | 5 |
| ST12 | 824 | ST-257 complex | 9 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 11 | 5 | 6 |
| ST2 | 4878 | ST-464 complex | 7 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 3 | 1 |
| ST3 | 2036 | ST-353 complex | 7 | 17 | 52 | 10 | 11 | 3 | 6 |
| ST4 | 51 | ST-443 complex | 7 | 17 | 2 | 15 | 23 | 3 | 12 |
| ST6 | 4878 | ST-464 complex | 7 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 3 | 1 |
| ST7 | 7355 | ST-353 complex | 8 | 17 | 5 | 2 | 10 | 59 | 23 |
| ST8 | 51 | ST-443 complex | 7 | 17 | 2 | 15 | 23 | 3 | 12 |
| ST9 | 51 | ST-443 complex | 7 | 17 | 2 | 15 | 23 | 3 | 12 |
| ZG01 | 19 | ST-21 complex | 2 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 5 |
| ZG02 | 19 | ST-21 complex | 2 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 5 |
| ZG03 | 50 | ST-21 complex | 2 | 1 | 12 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 5 |
| ZG04 | 19 | ST-21 complex | 2 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 5 |
| ZG06 | 822 | ST-21 complex | 2 | 1 | 79 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 5 |
| ZG07 | 2787 | ST-21 complex | 2 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 340 | 1 | 5 |
| ZG08 | 22 | ST-22 complex | 1 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| ZG10 | 52 | ST-52 complex | 9 | 25 | 2 | 10 | 22 | 3 | 6 |
| ZG11 | 51 | ST-443 complex | 7 | 17 | 2 | 15 | 23 | 3 | 12 |
| ZG12 | 50 | ST-21 complex | 2 | 1 | 12 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 5 |
| ZG13 | 51 | ST-443 complex | 7 | 17 | 2 | 15 | 23 | 3 | 12 |
| ZG14 | 51 | ST-443 complex | 7 | 17 | 2 | 15 | 23 | 3 | 12 |
| ZGI01 | 22 | ST-22 complex | 1 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| ZGI02 | 49 | ST-49 complex | 3 | 1 | 5 | 17 | 11 | 11 | 6 |
| ZGI03 | 51 | ST-443 complex | 7 | 17 | 2 | 15 | 23 | 3 | 12 |
| ZGI04 | 49 | ST-49 complex | 3 | 1 | 5 | 17 | 11 | 11 | 6 |
| ZGI05 | 49 | ST-49 complex | 3 | 1 | 5 | 17 | 11 | 11 | 6 |
| ZGI06 | 22 | ST-22 complex | 1 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| ZGI07 | Unknown | Unknown | 2 | 1 | 79 | 3 | 23 | 1 | 5 |
| ZGI08 | 49 | ST-49 complex | 3 | 1 | 5 | 17 | 11 | 11 | 6 |
| ZGI09 | 49 | ST-49 complex | 3 | 1 | 5 | 17 | 11 | 11 | 6 |
| ZGI10 | Unknown | Unknown | / | / | / | 15 | / | / | 12 |
| Isolate Nr. | Antimicrobial Agent (Class) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chloramphenicol (Amphenicol) | Erythromycin (Macrolide) | Gentamicin (Aminoglycoside) | Ciprofloxacin (Fluoroquinolone) | Tetracycline (Tetracycline) | Ertapenem (Beta-Lactam) | |||||||
| 16 mg/L | RD | 8 mg/L | RD | 2 mg/L | RD | 0.5 mg/L | RD | 1 mg/L | RD | 1 mg/L | RD | |
| OS1 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | W | W | - | ||
| PU01 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| PU03 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | NW | tet (O/32/O) | W | - |
| PU04 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | NW | tet (O/32/O) | W | - |
| PU05 | W | - | W | - | W | - | W | W | W | - | ||
| PU06 | W | - | W | - | W | ant (6)-Ia | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | NW | W | - | |
| PU07 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| PU09 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | NW | tet (O/32/O) | W | - |
| PU10 | W | - | W | - | W | ant (6)-Ia | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | NW | tet (O/32/O) with mutation | W | - |
| PU11 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ST10 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA | NW | W | - | |
| ST11 | W | - | W | - | W | - | W | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ST12 | W | - | W | - | W | - | W | W | W | - | ||
| ST2 | W | - | W | - | W | - | W | W | W | - | ||
| ST3 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ST4 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ST6 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ST7 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | NW | tet (O/32/O) | W | - |
| ST8 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ST9 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | NW | tet(L) | W | - |
| ZG01 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ZG02 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ZG03 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ZG04 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ZG06 | W | - | W | - | W | - | W | W | W | - | ||
| ZG07 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ZG08 | W | - | W | - | W | aac (3)-XI | W | gyrA | W | W | - | |
| ZG10 | W | - | W | - | W | - | W | W | W | - | ||
| ZG11 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ZG12 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ZG13 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ZG14 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ZGI01 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ZGI02 | W | - | W | - | W | - | W | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ZGI03 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ZGI04 | W | - | W | - | W | - | W | W | W | - | ||
| ZGI05 | W | - | W | - | W | - | W | W | W | - | ||
| ZGI06 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| ZGI07 | W | - | W | - | W | - | W | W | W | - | ||
| ZGI08 | W | - | W | - | W | - | W | W | W | - | ||
| ZGI09 | W | - | W | - | W | - | W | W | W | - | ||
| ZGI10 | W | - | W | - | W | - | NW | gyrA T86I aca-ata | W | W | - | |
| Antimicrobial Agent (Class) | Phenotype Susceptible | Phenotype Resistant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype Resistant | Genotype Susceptible | Genotype Resistant | Genotype Susceptible | |
| Chloramphenicol (amphenicol) | 0 | 42 | 0 | 0 |
| Erythromycin (macrolide) | 0 | 42 | 0 | 0 |
| Gentamicin (aminoglycoside) | 0 | 42 | 0 | 0 |
| Ciprofloxacin (fluoroquinolone) | 3 | 10 | 28 | 1 |
| Tetracycline (tetracycline) | 0 | 34 | 6 | 2 |
| Ertapenem (beta-lactam) | 0 | 42 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šoprek, S.; Duvnjak, S.; Kompes, G.; Jurinović, L.; Tambić Andrašević, A. Resistome Analysis of Campylobacter jejuni Strains Isolated from Human Stool and Primary Sterile Samples in Croatia. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10071410
Šoprek S, Duvnjak S, Kompes G, Jurinović L, Tambić Andrašević A. Resistome Analysis of Campylobacter jejuni Strains Isolated from Human Stool and Primary Sterile Samples in Croatia. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(7):1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10071410
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠoprek, Silvija, Sanja Duvnjak, Gordan Kompes, Luka Jurinović, and Arjana Tambić Andrašević. 2022. "Resistome Analysis of Campylobacter jejuni Strains Isolated from Human Stool and Primary Sterile Samples in Croatia" Microorganisms 10, no. 7: 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10071410
APA StyleŠoprek, S., Duvnjak, S., Kompes, G., Jurinović, L., & Tambić Andrašević, A. (2022). Resistome Analysis of Campylobacter jejuni Strains Isolated from Human Stool and Primary Sterile Samples in Croatia. Microorganisms, 10(7), 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10071410






