Distinguishing Kingella kingae from Pyogenic Acute Septic Arthritis in Young Portuguese Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Kingella kangas
3.2. Comparing Data between K. kingae and Pyogenic SA
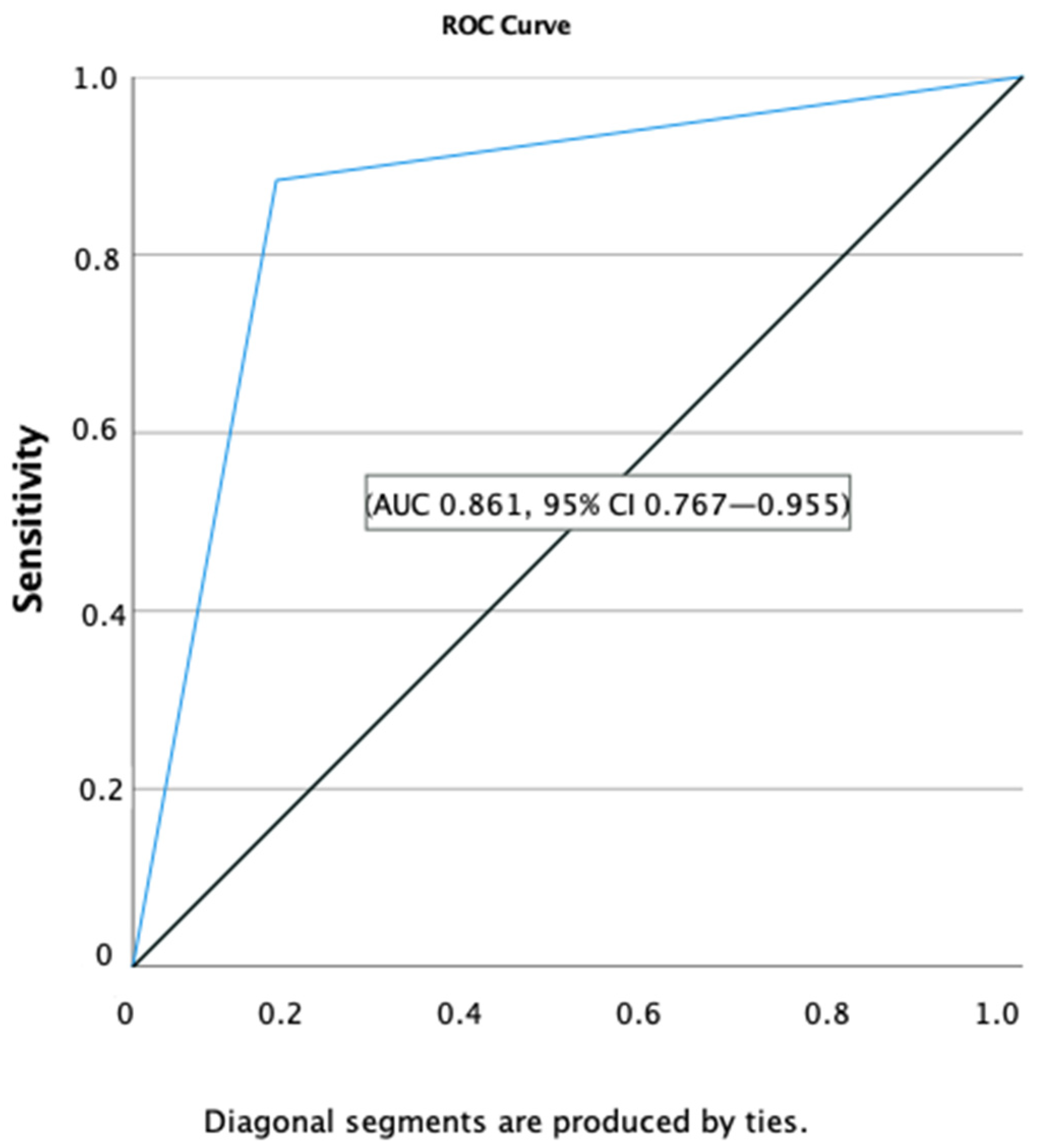
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ceroni, D.; Dubois-Ferrière, V.; Cherkaoui, A.; Lamah, L.; Renzi, G.; Lascombes, P.; Wilson, B.; Schrenzel, J. 30 Years of Study of Kingella kingae: Post Tenebras, Lux. Future Microbiol. 2013, 8, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ceroni, D.; Kampouroglou, G.; della Llana, R.A.; Salvo, D. Osteoarticular Infections in Young Children: What Has Changed over the Last Years? Swiss Med. Wkly. 2014, 144, w13971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samara, E.; Spyropoulou, V.; Tabard-Fougère, A.; Merlini, L.; Valaikaite, R.; Dhouib, A.; Manzano, S.; Juchler, C.; Dayer, R.; Ceroni, D. Kingella kingae and Osteoarticular Infections. Pediatrics 2019, 144, e20191509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bréhin, C.; Claudet, I.; Dubois, D.; Sales de Gauzy, J.; Vial, J.; Chaix, Y.; Grouteau, E. Assessing the Management of Pediatric Bone and Joint Infections According to French Guidelines. Med. Mal. Infect. 2019, 50, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Rupérez, M.B.; Suárez-Arrabal, M.D.C.; Villa-García, Á.; Zarzoso-Fernández, S.; Navarro-Gómez, M.; Santos-Sebastián, M.D.M.; García-Martín, A.; Marín, M.; González-Martínez, F.; Narbona-Cárceles, J.; et al. Kingella kingae as the Main Cause of Septic Arthritis: Importance of Molecular Diagnosis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, C.; Duarte, M.; Norte, S.; Arcangelo, J.; Pinto, M.; Correia, C.; Simões, M.J.; Canhão, H.; Tavares, D. Kingella kingae Displaced S. Aureus as the Most Common Cause of Acute Septic Arthritis in Children of All Ages. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2021, 40, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagupsky, P. Kingella kingae: From Medical Rarity to an Emerging Paediatric Pathogen. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2004, 4, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basmaci, R.; Lorrot, M.; Bidet, P.; Doit, C.; Vitoux, C.; Penneçot, G.; Mazda, K.; Bingen, E.; Ilharreborde, B.; Bonacorsi, S. Comparison of Clinical and Biologic Features of Kingella Kingae and Staphylococcus aureus Arthritis at Initial Evaluation. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2011, 30, 902–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juchler, C.; Spyropoulou, V.; Wagner, N.; Merlini, L.; Dhouib, A.; Manzano, S.; Tabard-Fougère, A.; Samara, E.; Ceroni, D. The Contemporary Bacteriologic Epidemiology of Osteoarticular Infections in Children in Switzerland. J. Pediatr. 2018, 194, 190–196.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.C.; Bradley, J.S. Osteoarticular Infections in Children. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 29, 557–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra-Lozano, J.; Falup-Pecurariu, O.; Faust, S.N.; Girschick, H.; Hartwig, N.; Kaplan, S.; Lorrot, M.; Mantadakis, E.; Peltola, H.; Rojo, P.; et al. Bone and Joint Infections. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagupsky, P. Antibiotic Susceptibility of Kingella kingae Isolates from Children with Skeletal System Infections. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2012, 31, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Bayer, A.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Daum, R.S.; Fridkin, S.K.; Gorwitz, R.J.; Kaplan, S.L.; Karchmer, A.W.; Levine, D.P.; Murray, B.E.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America for the Treatment of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infections in Adults and Children. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, e18–e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gij On, M.; Bellusci, M.; Petraitiene, B.; Noguera-Julian, A.; Zilinskaite, V.; Sanchez Moreno, P.; Saavedra-Lozano, J.; Glikman, D.; Daskalaki, M.; Kaiser-Labusch, P.; et al. Factors Associated with Severity in Invasive Community-Acquired Staphylococcus aureus Infections in Children: A Prospective European Multicentre Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 643.e1–643.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceroni, D.; Cherkaoui, A.; Combescure, C.; François, P.; Kaelin, A.; Schrenzel, J. Differentiating Osteoarticular Infections Caused by Kingella Kingae from Those Due to Typical Pathogens in Young Children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2011, 30, 906–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basmaci, R.; Ilharreborde, B.; Lorrot, M.; Bidet, P.; Bingen, E.; Bonacorsi, S. Predictive Score to Discriminate Kingella kingae from Staphylococcus aureus Arthritis in France. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2011, 30, 1120–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehours, P.; Freydière, A.M.; Richer, O.; Burucoa, C.; Boisset, S.; Lanotte, P.; Prère, M.F.; Ferroni, A.; Lafuente, C.; Vandenesch, F.; et al. The RtxA Toxin Gene of Kingella kingae: A Pertinent Target for Molecular Diagnosis of Osteoarticular Infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moumile, K.; Merckx, J.; Glorion, C.; Berche, P.; Ferroni, A. Osteoarticular Infections Caused by Kingella Kingae in Children: Contribution of Polymerase Chain Reaction to the Microbiologic Diagnosis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2003, 22, 837–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravel, J.; Ceroni, D.; Lacroix, L.; Renaud, C.; Grimard, G.; Samara, E.; Cherkaoui, A.; Renzi, G.; Schrenzel, J.; Manzano, S. Association between Oropharyngeal Carriage of Kingella Kingae and Osteoarticular Infection in Young Children: A Case-Control Study. Cmaj 2017, 189, E1107–E1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceroni, D.; Dubois-Ferriere, V.; Cherkaoui, A.; Gesuele, R.; Combescure, C.; Lamah, L.; Manzano, S.; Hibbs, J.; Schrenzel, J. Detection of Kingella kingae Osteoarticular Infections in Children by Oropharyngeal Swab PCR. Pediatrics 2013, 131, e230–e235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Houmami, N.; Bzdrenga, J.; Pons, J.; Minodier, P.; Durand, G.; Oubraham, A.; Ceroni, D.; Yagupsky, P.; Raoult, D.; Bidet, P.; et al. A Modified Multilocus Sequence Typing Protocol to Genotype Kingella Kingae from Oropharyngeal Swabs without Bacterial Isolation. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dubnov-Raz, G.; Scheuerman, O.; Chodick, G.; Finkelstein, Y.; Samra, Z.; Garty, B.Z. Invasive Kingella kingae Infections in Children: Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics. Pediatrics 2008, 122, 1305–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo-Marquez, M.A.; Hulten, K.G.; Hammerman, W.; Mason, E.O.; Kaplan, S.L. USA300 Is the Predominant Genotype Causing Staphylococcus aureus Septic Arthritis in Children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2009, 28, 1076–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhinai, Z.; Elahi, M.; Park, S.; Foo, B.; Lee, B.; Chapin, K.; Koster, M.; Sánchez, P.J.; Michelow, I.C. Prediction of Adverse Outcomes in Pediatric Acute Hematogenous Osteomyelitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, e454–e464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athey, A.G.; Mignemi, M.E.; Gheen, W.T.; Lindsay, E.A.; Jo, C.H.; Copley, L.A. Validation and Modification of a Severity of Illness Score for Children with Acute Hematogenous Osteomyelitis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2019, 39, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copley, L.A.B.; Barton, T.; Garcia, C.; Sun, D.; Gaviria-Agudelo, C.; Gheen, W.T.; Browne, R.H. A Proposed Scoring System for Assessment of Severity of Illness in Pediatric Acute Hematogenous Osteomyelitis Using Objective Clinical and Laboratory Findings. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2014, 33, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| TOTAL N = 75 | K. kingae N = 44 | Typical Pathogens N = 31 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, months, median (IQR) | 16.8 (12–24) | 15.3 (12–24) | 18 (9.6–36) | 0.623 |
| Age < 36 months, n (%) | 64 (85.3) | 41 (93.2) | 23 (74.2) | 0.043 |
| Male gender, n (%) | 52 (69.3) | 32 (72.7) | 20 (64.5) | 0.448 |
| Symptom duration at admission, days, median (IQR) | 3 (2–5) | 3 (2–5) | 2 (1–6) | 0.220 |
| Fever duration, n (%) | 0.5 (0–2) | 0 (0–2) | 2 (0.75–7.5) | <0.001 |
| Fever at admission, n (%) | 42/74 (56.8) | 16/43 (37.2) | 26 (83.9) | <0.001 |
| Fever > 48 h of antibiotics, n (%) | 7/64 (10.9) | 0 (0) | 7/23 (30.4) | <0.001 |
| Septic look, n (%) | 6/71(8.4) | 0 (0) | 6/28 (21.4) | 0.003 |
| Osteoarthritis, n (%) | 10 (13.3) | 4 (9.1) | 6 (19.4) | 0.3 |
| Disseminated infection, n (%) | 3 (4) | 0 (0) | 3 (9.6) | 0.067 |
| Abscesses, n (%) | 3 (4) | 1 (2.3) | 2 (6.5) | 0.566 |
| Myositis, n (%) | 10/73 (13.7) | 4/43 (9.3) | 6/30 (20) | 0.3 |
| WBC count, cells/mm3, median (IQR) | 13,900 (10,800–18,200) | 12,700 (10,300–17,100) | 15,200 (11,300–19,700) | 0.58 |
| WBC < 14,000/mm3, n (%) | 38/71 (53.5) | 24/40 (60) | 14 (41.9) | 0.214 |
| Platelet’s count, cells/mm3, median (IQR) | 505,000 (363,000–571,100) | 474,500 (376,000–530,500) | 554,000 (346,000 690,000) | 0.133 |
| CRP peak, mg/L, median (IQR) | 61.6 (30–147) | 40.5 (18–69) | 162 (93.7–215) | <0.001 |
| CRP < 100, mg/L, n (%) | 47 (62.7) | 39 (88.6) | 8 (25.8) | <0.001 |
| CRP at 48–96 h, median (IQR) | 27.4 (9.7–79) | 16.3 (5–29) | 73.3 (30–150) | <0.001 |
| ESR peak, mm/h, median (IQR) | 61 (42–79) | 54 (39–68.5) | 68 (59–94) | 0.003 |
| Admitted to ICU, (%) | 3 (4) | 0 (0) | 3 (9.7) | 0.067 |
| ≥2 surgeries, n (%) | 16 (21.3) | 7 (15.9) | 9 (29) | 0.172 |
| Days of IV antibiotic, median (IQR) | 10 (5–15) | 6 (4–10) | 16(13–27) | <0.001 |
| Days of total antibiotic, median (IQR) | 25 (21–32.5) | 21 (21–26) | 32 (26–44) | <0.001 |
| LOS, days, median (IQR) | 10 (5–16) | 6 (4–11) | 16 (11–23) | <0.001 |
| Complications, n (%) | 15 (20) | 5 (11.4) | 10 (32.3) | 0.026 |
| Sequelae at 6 months, n (%) | 3/73(4.1) | 0/43 | 3/30 (10) | 0.065 |
| Predicted K. kingae | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed | No | yes | % Correct | |
| K. kingae | No | 26 | 5 | 83.9 |
| Yes | 5 | 38 | 88.4 | |
| 86.5 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gouveia, C.; Subtil, A.; Norte, S.; Arcangelo, J.; Santos, M.A.; Corte-Real, R.; Simões, M.J.; Canhão, H.; Tavares, D. Distinguishing Kingella kingae from Pyogenic Acute Septic Arthritis in Young Portuguese Children. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061233
Gouveia C, Subtil A, Norte S, Arcangelo J, Santos MA, Corte-Real R, Simões MJ, Canhão H, Tavares D. Distinguishing Kingella kingae from Pyogenic Acute Septic Arthritis in Young Portuguese Children. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(6):1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061233
Chicago/Turabian StyleGouveia, Catarina, Ana Subtil, Susana Norte, Joana Arcangelo, Madalena Almeida Santos, Rita Corte-Real, Maria João Simões, Helena Canhão, and Delfin Tavares. 2022. "Distinguishing Kingella kingae from Pyogenic Acute Septic Arthritis in Young Portuguese Children" Microorganisms 10, no. 6: 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061233
APA StyleGouveia, C., Subtil, A., Norte, S., Arcangelo, J., Santos, M. A., Corte-Real, R., Simões, M. J., Canhão, H., & Tavares, D. (2022). Distinguishing Kingella kingae from Pyogenic Acute Septic Arthritis in Young Portuguese Children. Microorganisms, 10(6), 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061233






