A Sporulation-Specific sRNA Bvs196 Contributing to the Developing Spore in Bacillus velezensis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains, Plasmids, and Growth Conditions
2.2. Spore Resistance Assay
2.3. RNA Extraction
2.4. Generation of Mutants and Overexpression Strains
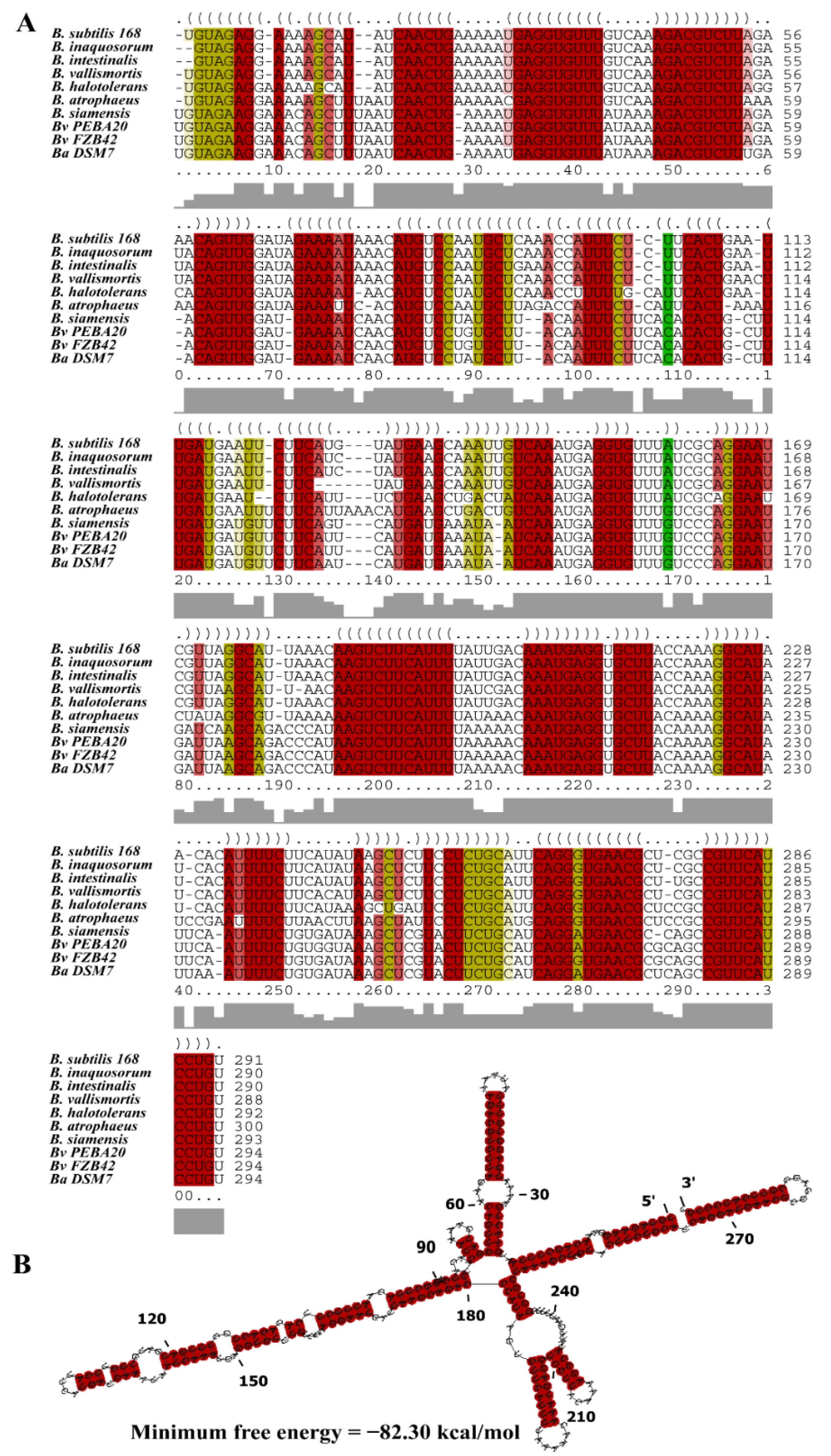
2.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.6. qRT-PCR Analysis
2.7. Northern Blot
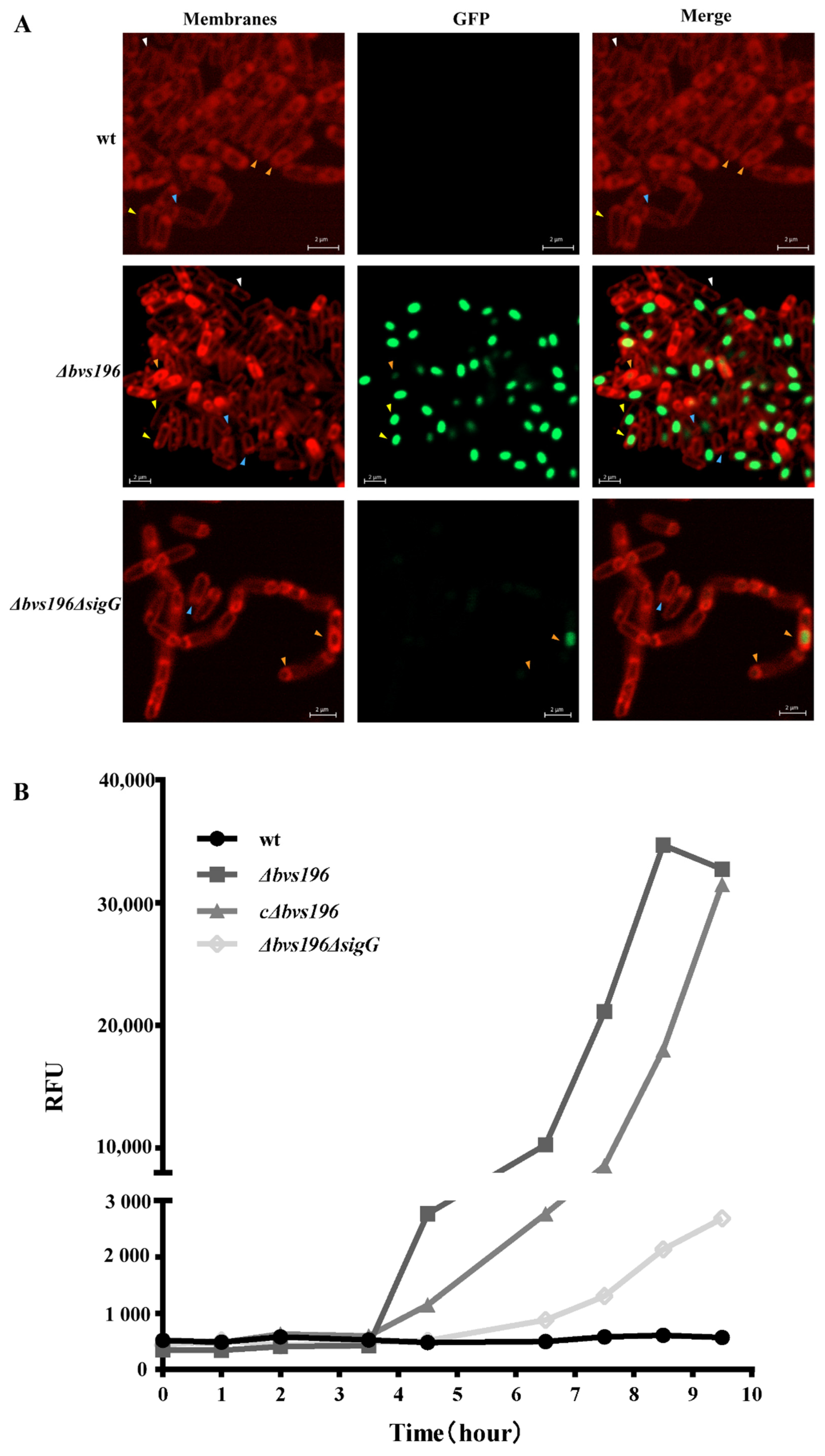
2.8. Fluorescence Microscopy
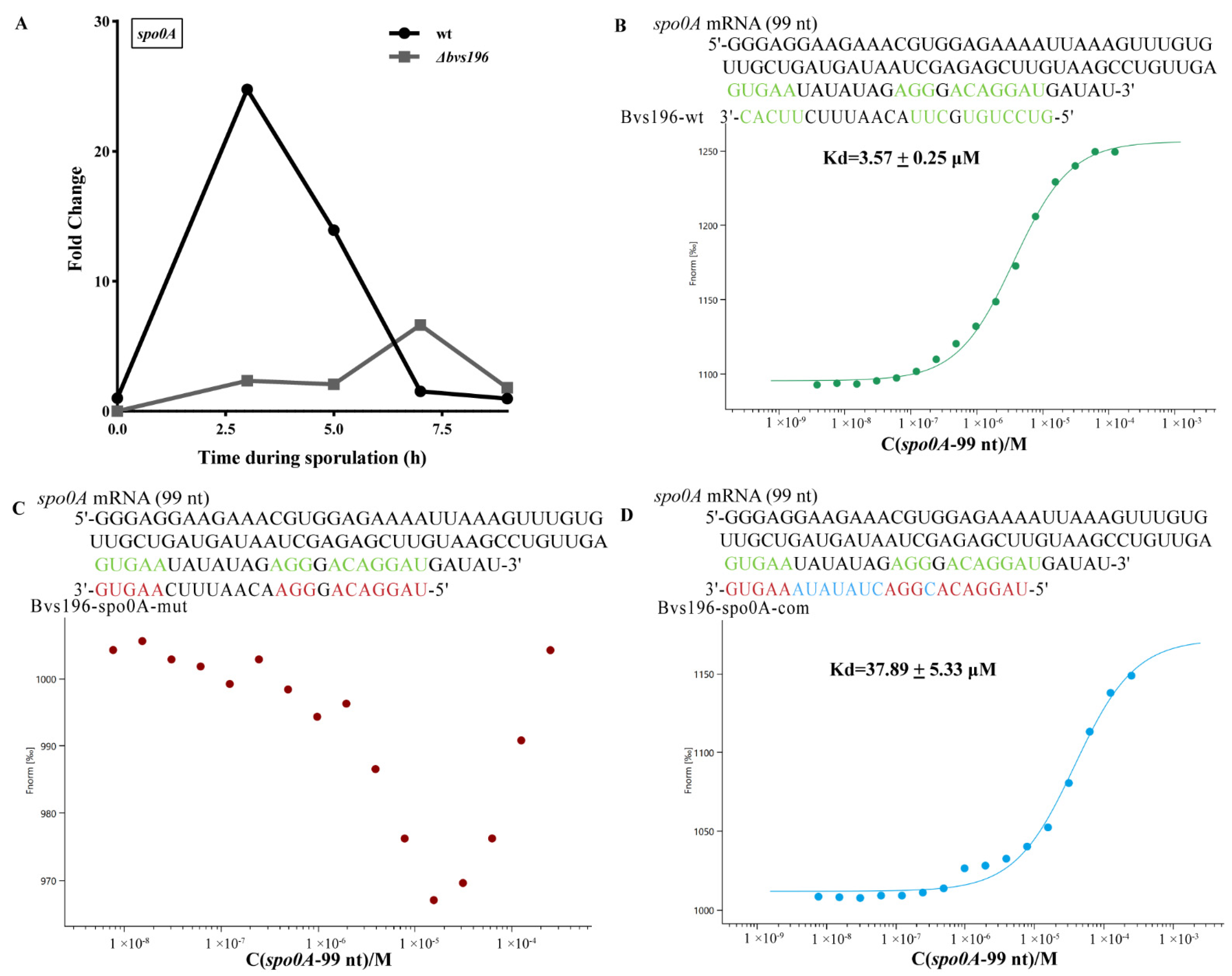
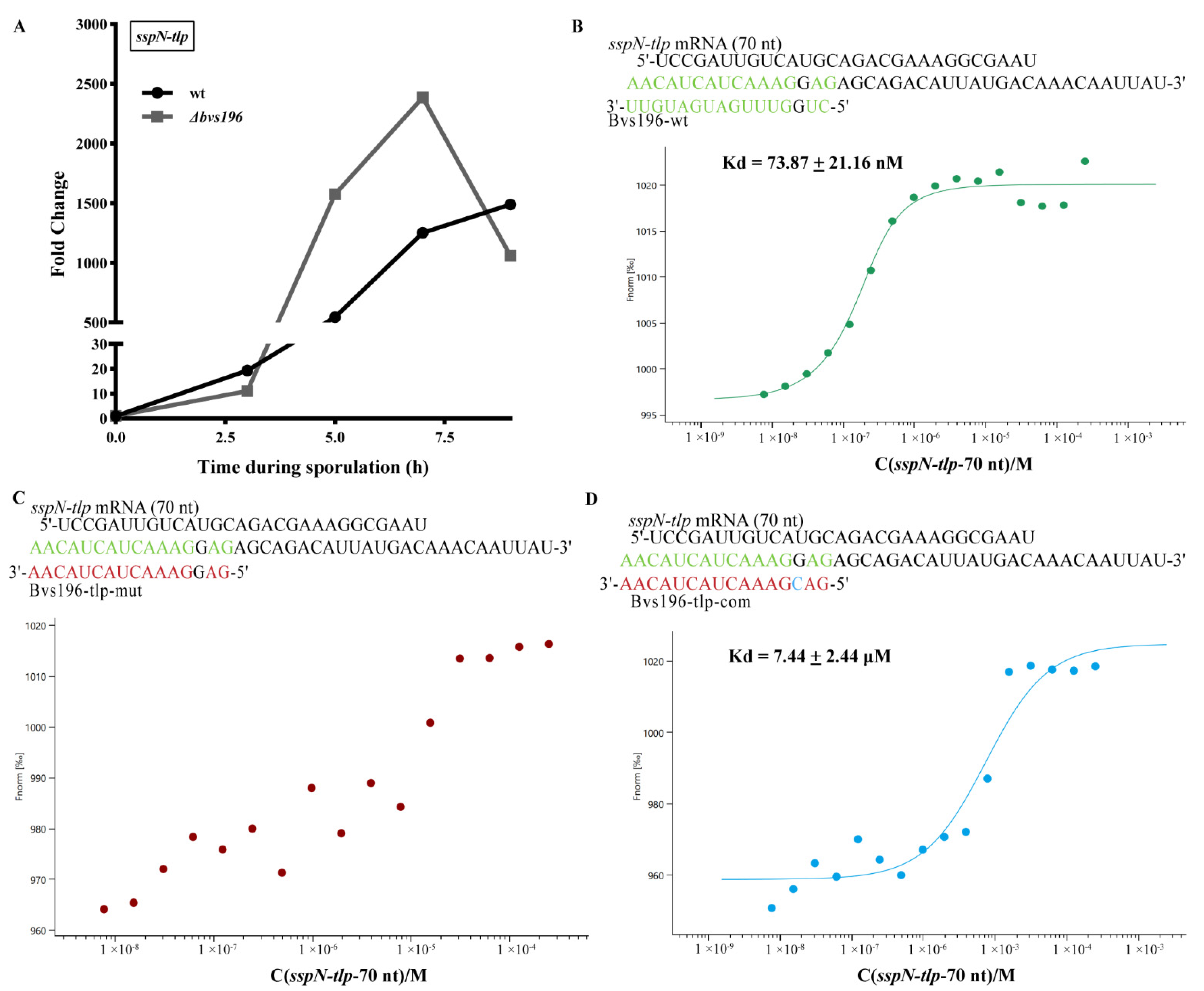
2.9. Microscale Thermophoresis (MST) Assay
3. Results
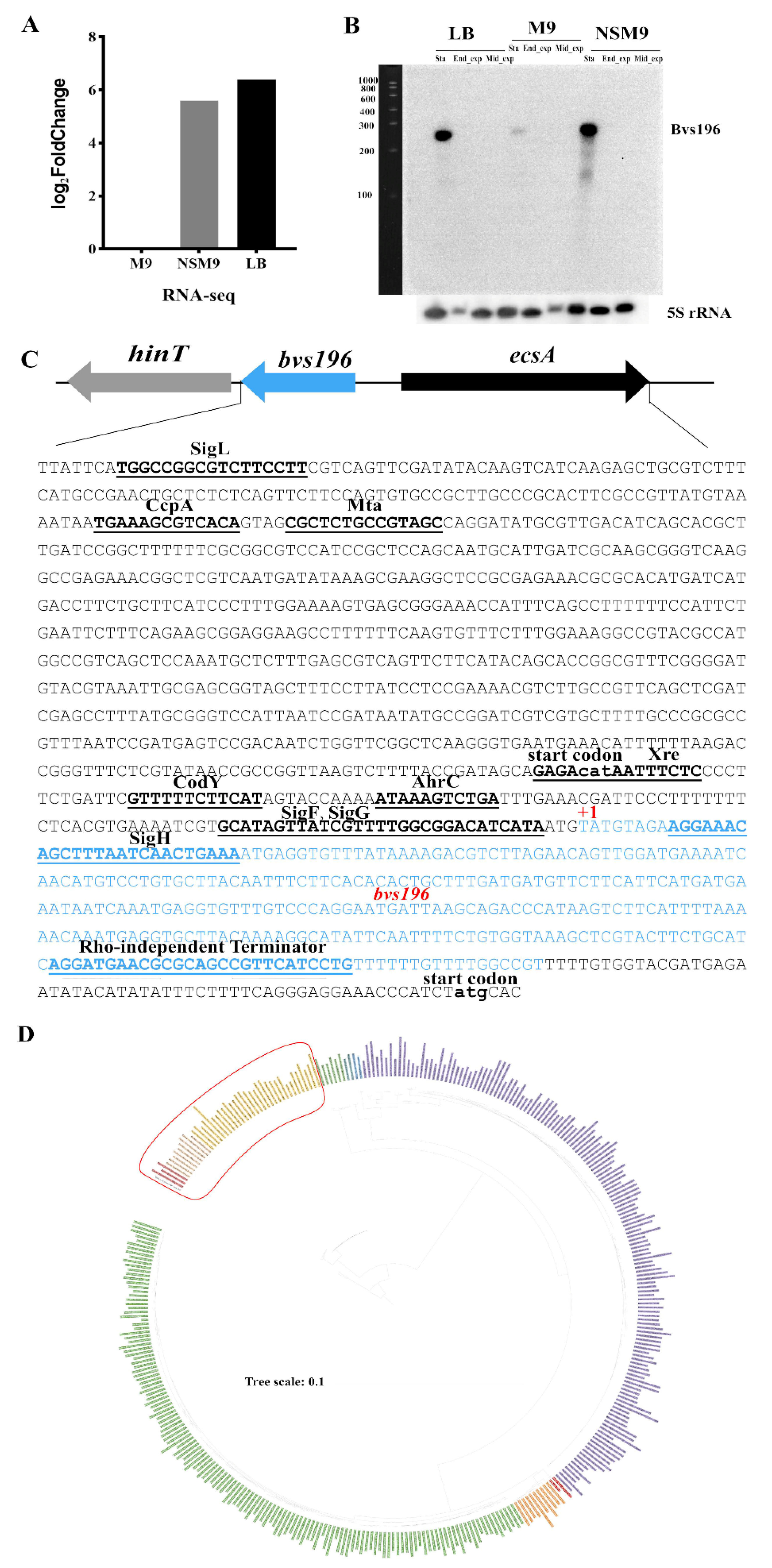
3.1. Characterization of the sRNA Bvs196
3.2. Bvs196 Is a Forespore-Specific sRNA
3.3. Bvs196 Contributes to Resistance of PEBA20
3.4. spo0A and sspN-tlp mRNA Are Direct Targets of Bvs196
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Earl, A.M.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Ecology and genomics of Bacillus subtilis. Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buescher, J.M.; Liebermeister, W.; Jules, M.; Uhr, M.; Muntel, J.; Botella, E.; Hessling, B.; Kleijn, R.J.; Le Chat, L.; Lecointe, F.; et al. Global network reorganization during dynamic adaptations of Bacillus subtilis metabolism. Science 2012, 335, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Hoon, M.J.L.; Eichenberger, P.; Vitkup, D. Hierarchical evolution of the bacterial sporulation network. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, R735–R745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrieta-Ortiz, M.L.; Hafemeister, C.; Bate, A.R.; Chu, T.; Greenfield, A.; Shuster, B.; Barry, S.N.; Gallitto, M.; Liu, B.; Kacmarczyk, T.; et al. An experimentally supported model of the Bacillus subtilis global transcriptional regulatory network. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2015, 11, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, M.G.; Pettersen, J.S.; Kallipolitis, B.H. sRNA-mediated control in bacteria: An increasing diversity of regulatory mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2020, 1863, 194504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, D.; Cheung, M.K.; Nong, W.; Huang, Q.; Kwan, H.S. BSRD: A repository for bacterial small regulatory RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D233–D238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröger, C.; Dillon, S.C.; Cameron, A.D.S.; Papenfort, K.; Sivasankaran, S.K.; Hokamp, K.; Chao, Y.; Sittka, A.; Hébrard, M.; Händler, K.; et al. The transcriptional landscape and small RNAs of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1277–E1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, R.; Groisman, E.A.; Ochman, H. Genome-wide detection of novel regulatory RNAs in E. coli. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 1487–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantl, S.; Müller, P. Cis- and Trans-Encoded Small Regulatory RNAs in Bacillus subtilis. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Li, L.; Chao, Y.; Förstner, K.; Vogel, J.; Borriss, R.; Wu, X.-Q. dRNA-Seq Reveals Genomewide TSSs and Noncoding RNAs of Plant Beneficial Rhizobacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvaggi, J.M.; Perkins, J.B.; Losick, R. Genes for small, noncoding RNAs under sporulation control in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmalisch, M.; Maiques, E.; Nikolov, L.; Camp, A.H.; Chevreux, B.; Muffler, A.; Rodriguez, S.; Perkins, J.; Losick, R. Small genes under sporulation control in the Bacillus subtilis genome. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 5402–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, P.; Mäder, U.; Dervyn, E.; Rochat, T.; Leduc, A.; Pigeonneau, N.; Bidnenko, E.; Marchadier, E.; Hoebeke, M.; Aymerich, S.; et al. Condition-dependent transcriptome reveals high-level regulatory architecture in Bacillus subtilis. Science 2012, 335, 1103–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchais, A.; Duperrier, S.; Durand, S.; Gautheret, D.; Stragier, P. CsfG, a sporulation-specific, small non-coding RNA highly conserved in endospore formers. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, A.T.; Wassarman, K.M. 6S-1 RNA function leads to a delay in sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 2079–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thüring, M.; Ganapathy, S.; Schlüter, M.A.C.; Lechner, M.; Hartmann, R.K. 6S-2 RNA deletion in the undomesticated B. subtilis strain NCIB 3610 causes a biofilm derepression phenotype. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidrich, N.; Chinali, A.; Gerth, U.; Brantl, S. The small untranslated RNA SR1 from the Bacillus subtilis genome is involved in the regulation of arginine catabolism. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 62, 520–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Haq, I.; Brantl, S.; Müller, P. A new role for SR1 from Bacillus subtilis: Regulation of sporulation by inhibition of kinA translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 10589–10603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mars, R.A.T.; Nicolas, P.; Denham, E.L.; van Dijl, J.M. Regulatory RNAs in Bacillus subtilis: A Gram-Positive Perspective on Bacterial RNA-Mediated Regulation of Gene Expression. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 1029–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, P.; Millet, J.; Aubert, J.P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1965, 54, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterlini, J.M.; Mandelstam, J. Commitment to sporulation in Bacillus subtilis and its relationship to development of actinomycin resistance. Biochem. J. 1969, 113, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, W.L.; Setlow, P. Sporulation, germination and outgrowth. Mol. Biol. Methods Bacillus 2001, 537–548. [Google Scholar]
- Luu, J.; Mott, C.M.; Schreiber, O.R.; Giovinco, H.M.; Betchen, M.; Carabetta, V.J. Nε-Lysine Acetylation of the Histone-Like Protein HBsu Regulates the Process of Sporulation and Affects the Resistance Properties of Bacillus subtilis Spores. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 782815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irnov, I.; Winkler, W.C. A regulatory RNA required for antitermination of biofilm and capsular polysaccharide operons in Bacillales. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaud, M.; Chastanet, A.; Débarbouillé, M. New vector for efficient allelic replacement in naturally nontransformable, low-GC-content, gram-positive bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 6887–6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, S.; Joshi, T.; Hofacker, I.L.; Stadler, P.F.; Backofen, R. LocARNA-P: Accurate boundary prediction and improved detection of structural RNAs. RNA 2012, 18, 900–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhart, S.H.; Hofacker, I.L.; Will, S.; Gruber, A.R.; Stadler, P.F. RNAalifold: Improved consensus structure prediction for RNA alignments. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertels, F.; Silander, O.K.; Pachkov, M.; Rainey, P.B.; van Nimwegen, E. Automated reconstruction of whole-genome phylogenies from short-sequence reads. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kery, M.B.; Feldman, M.; Livny, J.; Tjaden, B. TargetRNA2: Identifying targets of small regulatory RNAs in bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W124–W129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.R.; Richter, A.S.; Papenfort, K.; Mann, M.; Vogel, J.; Hess, W.R.; Backofen, R.; Georg, J. Comparative genomics boosts target prediction for bacterial small RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E3487–E3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backofen, R.; Engelhardt, J.; Erxleben, A.; Fallmann, J.; Grüning, B.; Ohler, U.; Rajewsky, N.; Stadler, P.F. RNA-bioinformatics: Tools, services and databases for the analysis of RNA-based regulation. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 261, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerabek-Willemsen, M.; Wienken, C.J.; Braun, D.; Baaske, P.; Duhr, S. Molecular interaction studies using microscale thermophoresis. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2011, 9, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerabek-Willemsen, M.; André, T.; Wanner, R.; Roth, H.M.; Duhr, S.; Baaske, P.; Breitsprecher, D. MicroScale Thermophoresis: Interaction analysis and beyond. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1077, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressuire-Isoard, C.; Broussolle, V.; Carlin, F. Sporulation environment influences spore properties in Bacillus: Evidence and insights on underlying molecular and physiological mechanisms. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Losick, R. Evidence that entry into sporulation in Bacillus subtilis is governed by a gradual increase in the level and activity of the master regulator Spo0A. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 2236–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; González-Pastor, J.E.; Losick, R. High- and low-threshold genes in the Spo0A regulon of Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 1357–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Losick, R. The master regulator for entry into sporulation in Bacillus subtilis becomes a cell-specific transcription factor after asymmetric division. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setlow, P. Small, acid-soluble spore proteins of Bacillus species: Structure, synthesis, genetics, function, and degradation. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1988, 42, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setlow, P. Mechanisms for the prevention of damage to DNA in spores of Bacillus species. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1995, 49, 29–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Hernandez, A.; Setlow, P. Analysis of the regulation and function of five genes encoding small, acid-soluble spore proteins of Bacillus subtilis. Gene 2000, 248, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.C.; Tipper, D.J. Acid-soluble spore proteins of Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 1981, 146, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera-Hernandez, A.; Sanchez-Salas, J.L.; Paidhungat, M.; Setlow, P. Regulation of four genes encoding small, acid-soluble spore proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Gene 1999, 232, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korza, G.; Camilleri, E.; Green, J.; Robinson, J.; Nagler, K.; Moeller, R.; Caimano, M.J.; Setlow, P. Analysis of the mRNAs in Spores of Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, e00007-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setlow, P. Spores of Bacillus subtilis: Their resistance to and killing by radiation, heat and chemicals. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutlu, A.; Kaspar, C.; Becker, N.; Bischofs, I.B. A spore quality-quantity tradeoff favors diverse sporulation strategies in Bacillus subtilis. ISME J. 2020, 14, 2703–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, T.; Li, X.; Chen, K.; Qin, H.; Yi, Z.; Meng, Y.; Liu, Z. A Sporulation-Specific sRNA Bvs196 Contributing to the Developing Spore in Bacillus velezensis. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10051015
Xu T, Li X, Chen K, Qin H, Yi Z, Meng Y, Liu Z. A Sporulation-Specific sRNA Bvs196 Contributing to the Developing Spore in Bacillus velezensis. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(5):1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10051015
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Tingting, Xiangying Li, Kerong Chen, Haoxin Qin, Zhengkai Yi, Yuan Meng, and Zhenyu Liu. 2022. "A Sporulation-Specific sRNA Bvs196 Contributing to the Developing Spore in Bacillus velezensis" Microorganisms 10, no. 5: 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10051015
APA StyleXu, T., Li, X., Chen, K., Qin, H., Yi, Z., Meng, Y., & Liu, Z. (2022). A Sporulation-Specific sRNA Bvs196 Contributing to the Developing Spore in Bacillus velezensis. Microorganisms, 10(5), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10051015





