A Sporulation-Specific sRNA Bvs196 Contributing to the Developing Spore in Bacillus velezensis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains, Plasmids, and Growth Conditions
2.2. Spore Resistance Assay
2.3. RNA Extraction
2.4. Generation of Mutants and Overexpression Strains
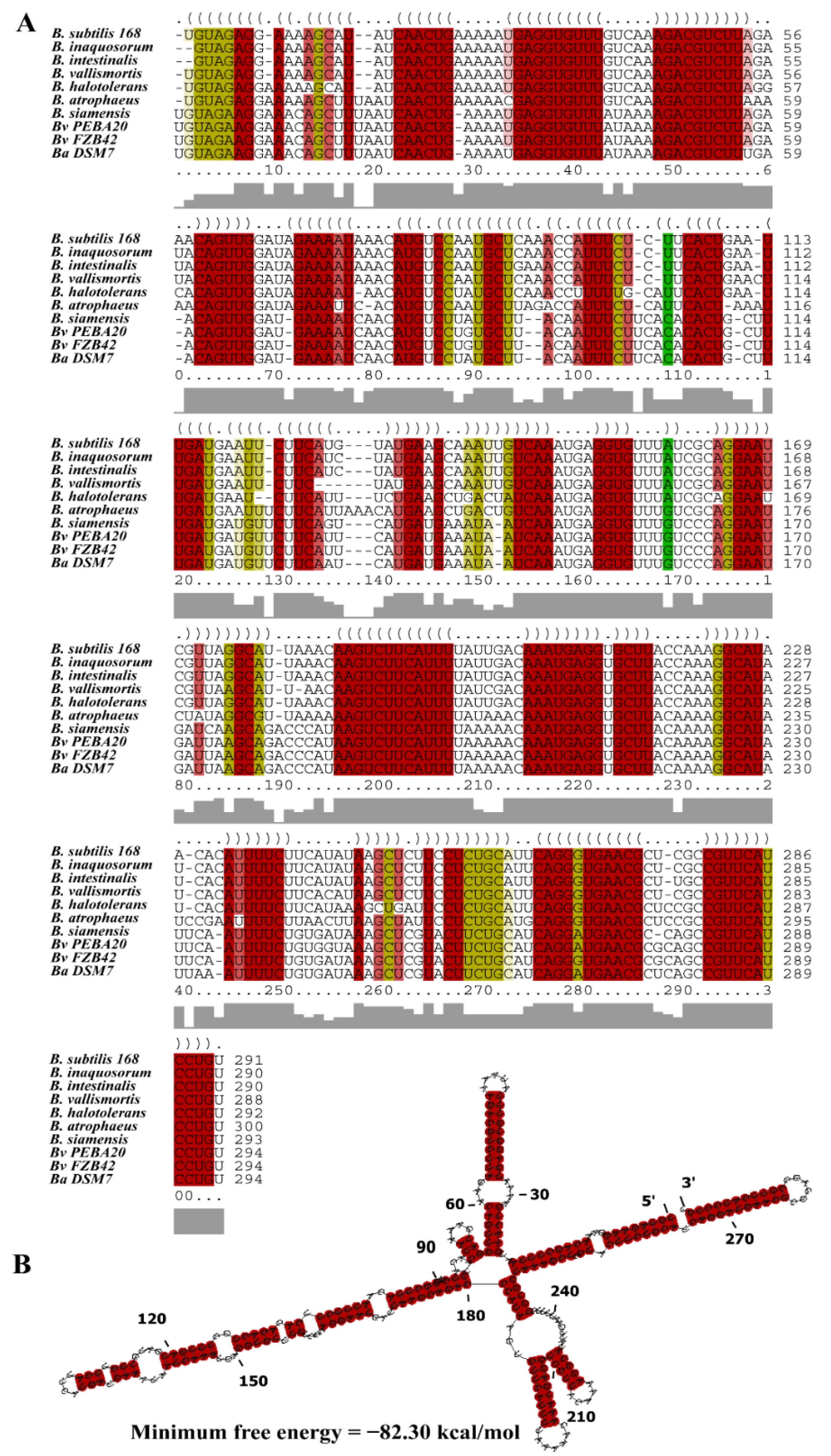
2.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.6. qRT-PCR Analysis
2.7. Northern Blot
2.8. Fluorescence Microscopy
2.9. Microscale Thermophoresis (MST) Assay
3. Results
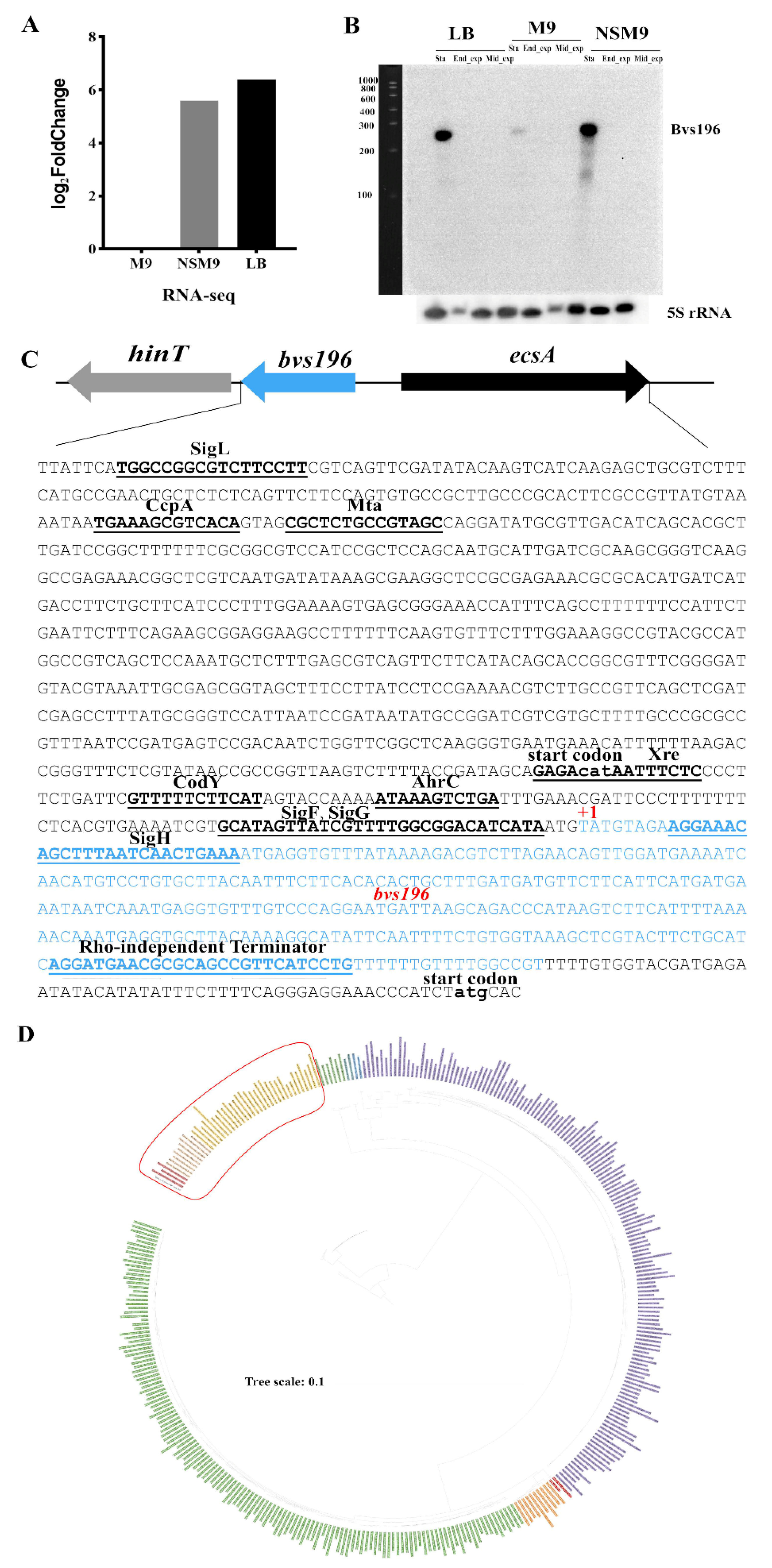
3.1. Characterization of the sRNA Bvs196
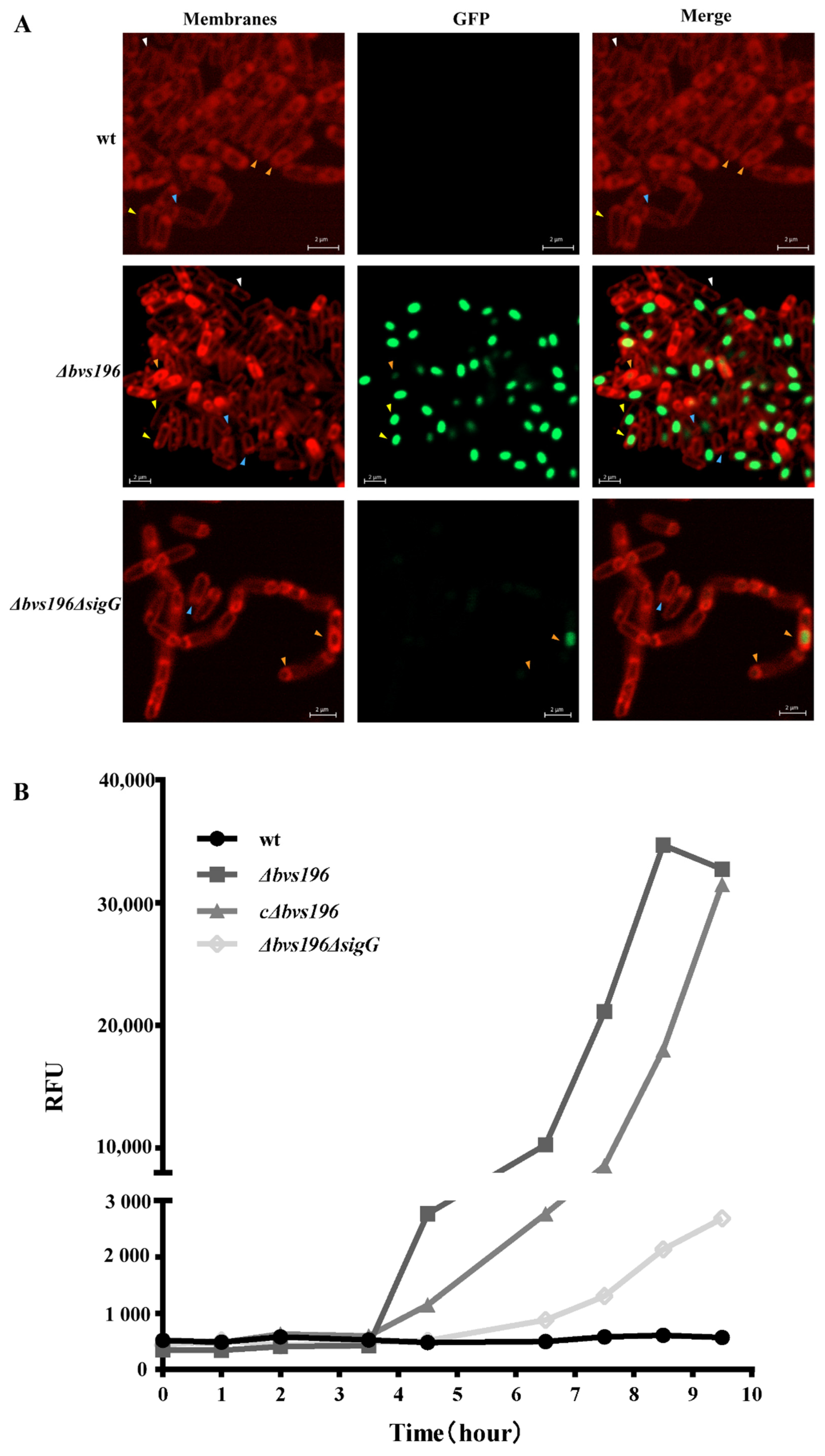
3.2. Bvs196 Is a Forespore-Specific sRNA
3.3. Bvs196 Contributes to Resistance of PEBA20
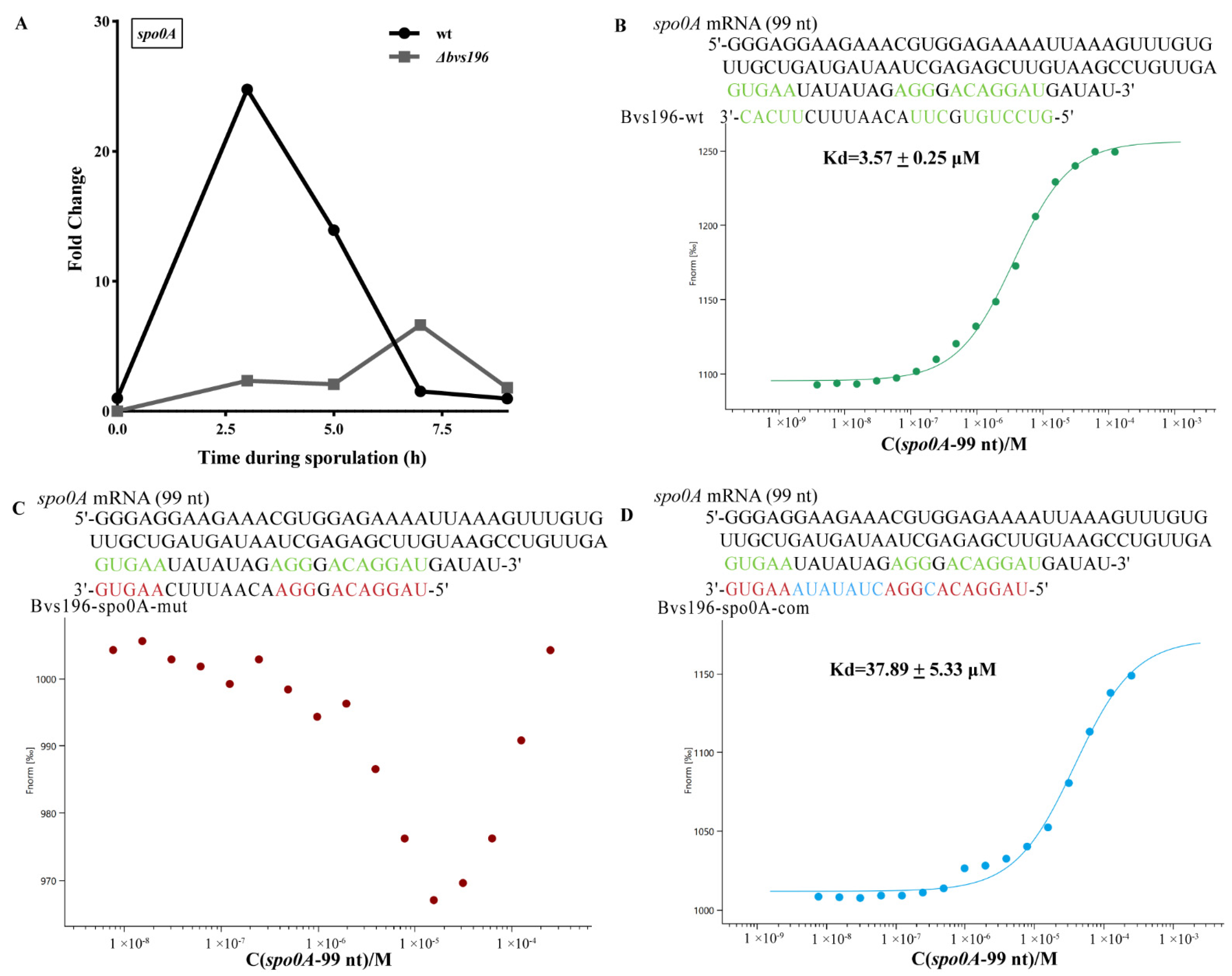
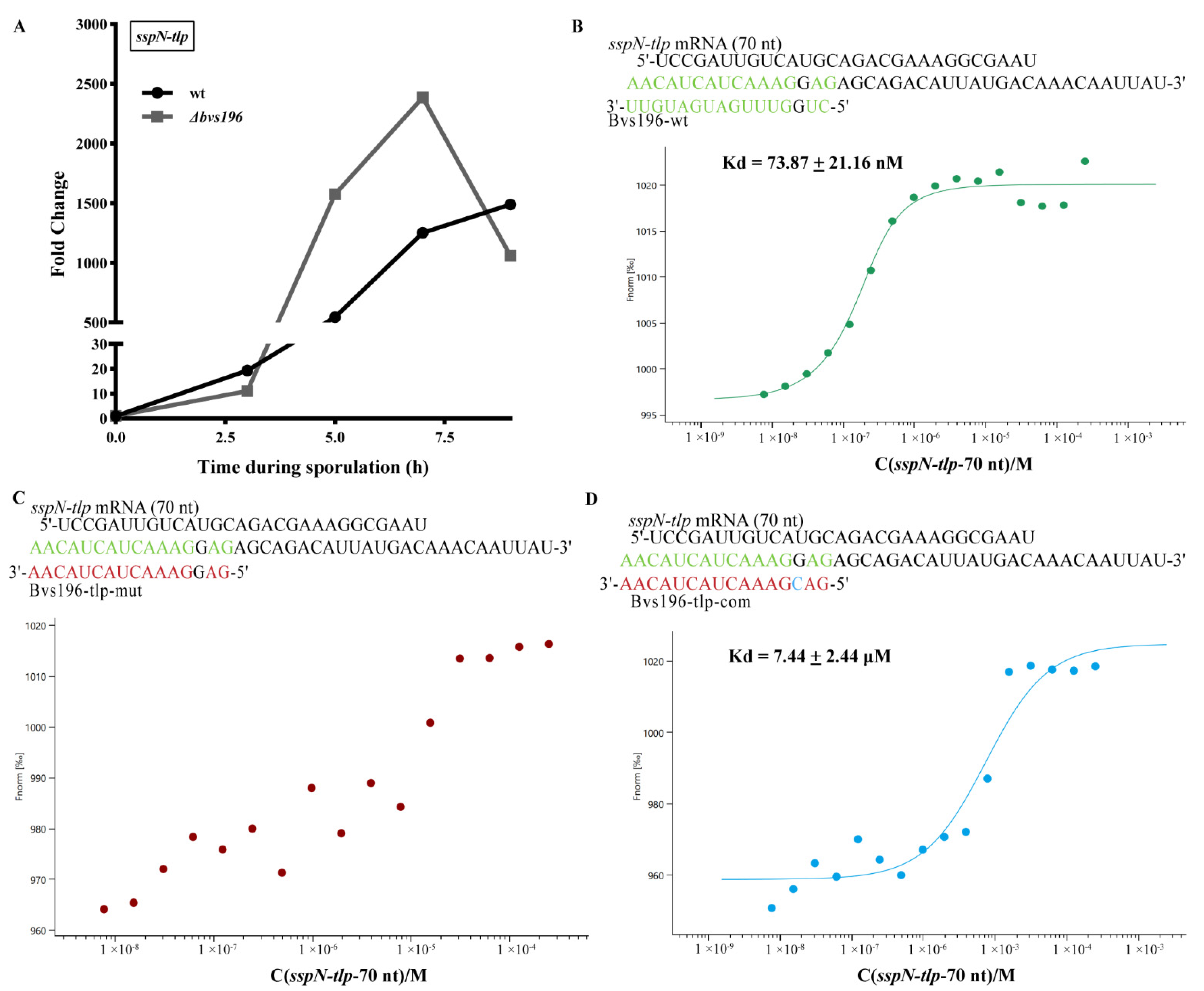
3.4. spo0A and sspN-tlp mRNA Are Direct Targets of Bvs196
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Earl, A.M.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Ecology and genomics of Bacillus subtilis. Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buescher, J.M.; Liebermeister, W.; Jules, M.; Uhr, M.; Muntel, J.; Botella, E.; Hessling, B.; Kleijn, R.J.; Le Chat, L.; Lecointe, F.; et al. Global network reorganization during dynamic adaptations of Bacillus subtilis metabolism. Science 2012, 335, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Hoon, M.J.L.; Eichenberger, P.; Vitkup, D. Hierarchical evolution of the bacterial sporulation network. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, R735–R745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arrieta-Ortiz, M.L.; Hafemeister, C.; Bate, A.R.; Chu, T.; Greenfield, A.; Shuster, B.; Barry, S.N.; Gallitto, M.; Liu, B.; Kacmarczyk, T.; et al. An experimentally supported model of the Bacillus subtilis global transcriptional regulatory network. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2015, 11, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, M.G.; Pettersen, J.S.; Kallipolitis, B.H. sRNA-mediated control in bacteria: An increasing diversity of regulatory mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2020, 1863, 194504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, D.; Cheung, M.K.; Nong, W.; Huang, Q.; Kwan, H.S. BSRD: A repository for bacterial small regulatory RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D233–D238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kröger, C.; Dillon, S.C.; Cameron, A.D.S.; Papenfort, K.; Sivasankaran, S.K.; Hokamp, K.; Chao, Y.; Sittka, A.; Hébrard, M.; Händler, K.; et al. The transcriptional landscape and small RNAs of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1277–E1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raghavan, R.; Groisman, E.A.; Ochman, H. Genome-wide detection of novel regulatory RNAs in E. coli. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 1487–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brantl, S.; Müller, P. Cis- and Trans-Encoded Small Regulatory RNAs in Bacillus subtilis. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Li, L.; Chao, Y.; Förstner, K.; Vogel, J.; Borriss, R.; Wu, X.-Q. dRNA-Seq Reveals Genomewide TSSs and Noncoding RNAs of Plant Beneficial Rhizobacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silvaggi, J.M.; Perkins, J.B.; Losick, R. Genes for small, noncoding RNAs under sporulation control in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmalisch, M.; Maiques, E.; Nikolov, L.; Camp, A.H.; Chevreux, B.; Muffler, A.; Rodriguez, S.; Perkins, J.; Losick, R. Small genes under sporulation control in the Bacillus subtilis genome. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 5402–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicolas, P.; Mäder, U.; Dervyn, E.; Rochat, T.; Leduc, A.; Pigeonneau, N.; Bidnenko, E.; Marchadier, E.; Hoebeke, M.; Aymerich, S.; et al. Condition-dependent transcriptome reveals high-level regulatory architecture in Bacillus subtilis. Science 2012, 335, 1103–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchais, A.; Duperrier, S.; Durand, S.; Gautheret, D.; Stragier, P. CsfG, a sporulation-specific, small non-coding RNA highly conserved in endospore formers. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavanagh, A.T.; Wassarman, K.M. 6S-1 RNA function leads to a delay in sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 2079–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thüring, M.; Ganapathy, S.; Schlüter, M.A.C.; Lechner, M.; Hartmann, R.K. 6S-2 RNA deletion in the undomesticated B. subtilis strain NCIB 3610 causes a biofilm derepression phenotype. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidrich, N.; Chinali, A.; Gerth, U.; Brantl, S. The small untranslated RNA SR1 from the Bacillus subtilis genome is involved in the regulation of arginine catabolism. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 62, 520–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Haq, I.; Brantl, S.; Müller, P. A new role for SR1 from Bacillus subtilis: Regulation of sporulation by inhibition of kinA translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 10589–10603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mars, R.A.T.; Nicolas, P.; Denham, E.L.; van Dijl, J.M. Regulatory RNAs in Bacillus subtilis: A Gram-Positive Perspective on Bacterial RNA-Mediated Regulation of Gene Expression. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 1029–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaeffer, P.; Millet, J.; Aubert, J.P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1965, 54, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sterlini, J.M.; Mandelstam, J. Commitment to sporulation in Bacillus subtilis and its relationship to development of actinomycin resistance. Biochem. J. 1969, 113, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholson, W.L.; Setlow, P. Sporulation, germination and outgrowth. Mol. Biol. Methods Bacillus 2001, 537–548. [Google Scholar]
- Luu, J.; Mott, C.M.; Schreiber, O.R.; Giovinco, H.M.; Betchen, M.; Carabetta, V.J. Nε-Lysine Acetylation of the Histone-Like Protein HBsu Regulates the Process of Sporulation and Affects the Resistance Properties of Bacillus subtilis Spores. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 782815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irnov, I.; Winkler, W.C. A regulatory RNA required for antitermination of biofilm and capsular polysaccharide operons in Bacillales. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaud, M.; Chastanet, A.; Débarbouillé, M. New vector for efficient allelic replacement in naturally nontransformable, low-GC-content, gram-positive bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 6887–6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Will, S.; Joshi, T.; Hofacker, I.L.; Stadler, P.F.; Backofen, R. LocARNA-P: Accurate boundary prediction and improved detection of structural RNAs. RNA 2012, 18, 900–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernhart, S.H.; Hofacker, I.L.; Will, S.; Gruber, A.R.; Stadler, P.F. RNAalifold: Improved consensus structure prediction for RNA alignments. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertels, F.; Silander, O.K.; Pachkov, M.; Rainey, P.B.; van Nimwegen, E. Automated reconstruction of whole-genome phylogenies from short-sequence reads. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kery, M.B.; Feldman, M.; Livny, J.; Tjaden, B. TargetRNA2: Identifying targets of small regulatory RNAs in bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W124–W129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, P.R.; Richter, A.S.; Papenfort, K.; Mann, M.; Vogel, J.; Hess, W.R.; Backofen, R.; Georg, J. Comparative genomics boosts target prediction for bacterial small RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E3487–E3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Backofen, R.; Engelhardt, J.; Erxleben, A.; Fallmann, J.; Grüning, B.; Ohler, U.; Rajewsky, N.; Stadler, P.F. RNA-bioinformatics: Tools, services and databases for the analysis of RNA-based regulation. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 261, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerabek-Willemsen, M.; Wienken, C.J.; Braun, D.; Baaske, P.; Duhr, S. Molecular interaction studies using microscale thermophoresis. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2011, 9, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jerabek-Willemsen, M.; André, T.; Wanner, R.; Roth, H.M.; Duhr, S.; Baaske, P.; Breitsprecher, D. MicroScale Thermophoresis: Interaction analysis and beyond. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1077, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bressuire-Isoard, C.; Broussolle, V.; Carlin, F. Sporulation environment influences spore properties in Bacillus: Evidence and insights on underlying molecular and physiological mechanisms. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujita, M.; Losick, R. Evidence that entry into sporulation in Bacillus subtilis is governed by a gradual increase in the level and activity of the master regulator Spo0A. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 2236–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujita, M.; González-Pastor, J.E.; Losick, R. High- and low-threshold genes in the Spo0A regulon of Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 1357–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujita, M.; Losick, R. The master regulator for entry into sporulation in Bacillus subtilis becomes a cell-specific transcription factor after asymmetric division. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Setlow, P. Small, acid-soluble spore proteins of Bacillus species: Structure, synthesis, genetics, function, and degradation. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1988, 42, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setlow, P. Mechanisms for the prevention of damage to DNA in spores of Bacillus species. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1995, 49, 29–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Hernandez, A.; Setlow, P. Analysis of the regulation and function of five genes encoding small, acid-soluble spore proteins of Bacillus subtilis. Gene 2000, 248, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.C.; Tipper, D.J. Acid-soluble spore proteins of Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 1981, 146, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cabrera-Hernandez, A.; Sanchez-Salas, J.L.; Paidhungat, M.; Setlow, P. Regulation of four genes encoding small, acid-soluble spore proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Gene 1999, 232, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korza, G.; Camilleri, E.; Green, J.; Robinson, J.; Nagler, K.; Moeller, R.; Caimano, M.J.; Setlow, P. Analysis of the mRNAs in Spores of Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, e00007-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Setlow, P. Spores of Bacillus subtilis: Their resistance to and killing by radiation, heat and chemicals. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutlu, A.; Kaspar, C.; Becker, N.; Bischofs, I.B. A spore quality-quantity tradeoff favors diverse sporulation strategies in Bacillus subtilis. ISME J. 2020, 14, 2703–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, T.; Li, X.; Chen, K.; Qin, H.; Yi, Z.; Meng, Y.; Liu, Z. A Sporulation-Specific sRNA Bvs196 Contributing to the Developing Spore in Bacillus velezensis. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10051015
Xu T, Li X, Chen K, Qin H, Yi Z, Meng Y, Liu Z. A Sporulation-Specific sRNA Bvs196 Contributing to the Developing Spore in Bacillus velezensis. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(5):1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10051015
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Tingting, Xiangying Li, Kerong Chen, Haoxin Qin, Zhengkai Yi, Yuan Meng, and Zhenyu Liu. 2022. "A Sporulation-Specific sRNA Bvs196 Contributing to the Developing Spore in Bacillus velezensis" Microorganisms 10, no. 5: 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10051015
APA StyleXu, T., Li, X., Chen, K., Qin, H., Yi, Z., Meng, Y., & Liu, Z. (2022). A Sporulation-Specific sRNA Bvs196 Contributing to the Developing Spore in Bacillus velezensis. Microorganisms, 10(5), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10051015





