Characterization and Public Health Insights of the New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacterales from Laying Hens in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Identification
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.3. Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS) and Identification of the SNPs, STs, and ARGs
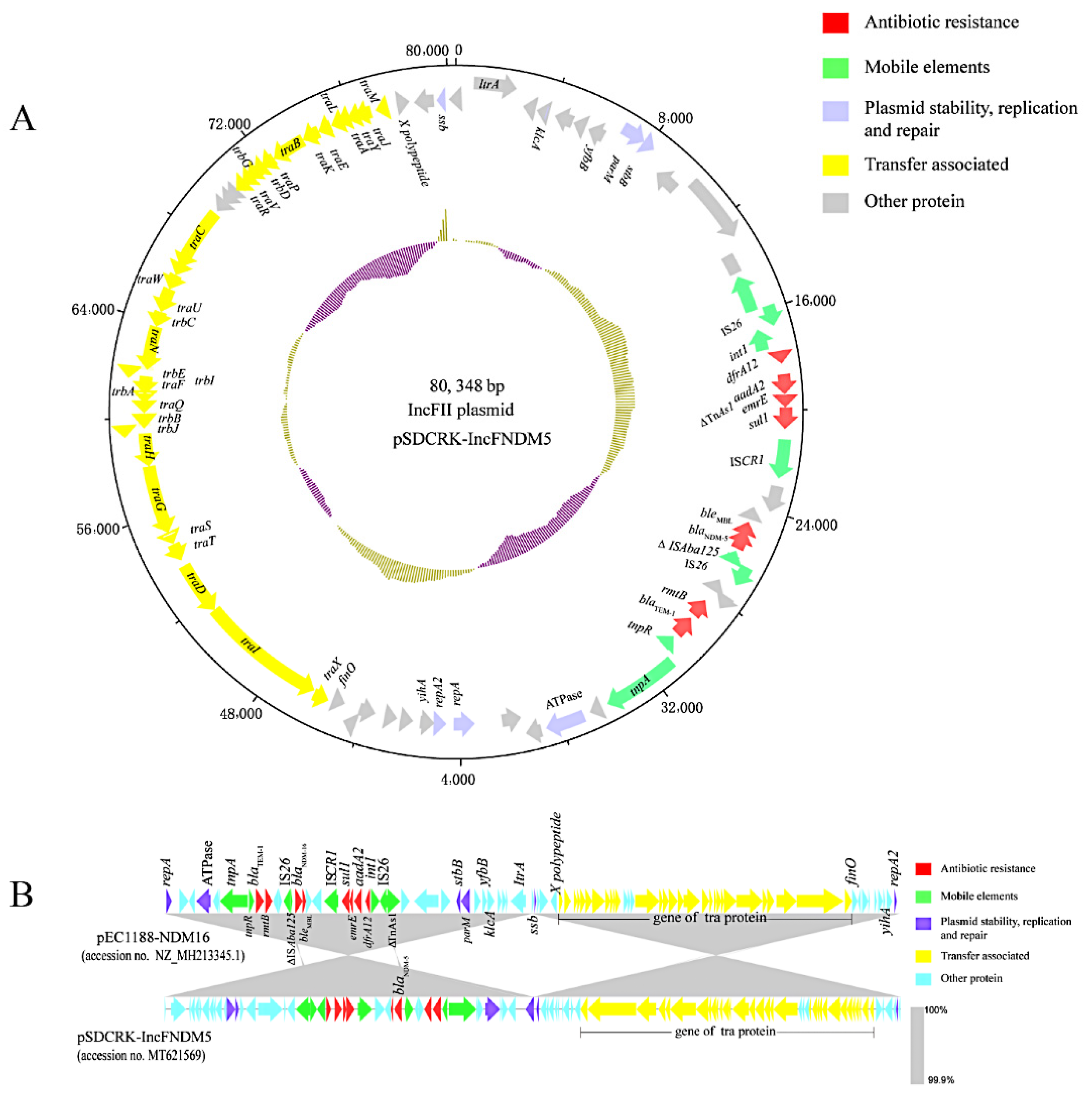
2.4. Identification of Plasmids and blaNDM Gene Location and Environment
2.5. Conjugation Transfer Experiment
2.6. Determination of Growth Curves
2.7. Growth Competition Experiment
2.8. The blaNDM-Positive Plasmid Stability
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Antibiotic-Resistant Phenotype of the blaNDM Gene Carrying Bacteria
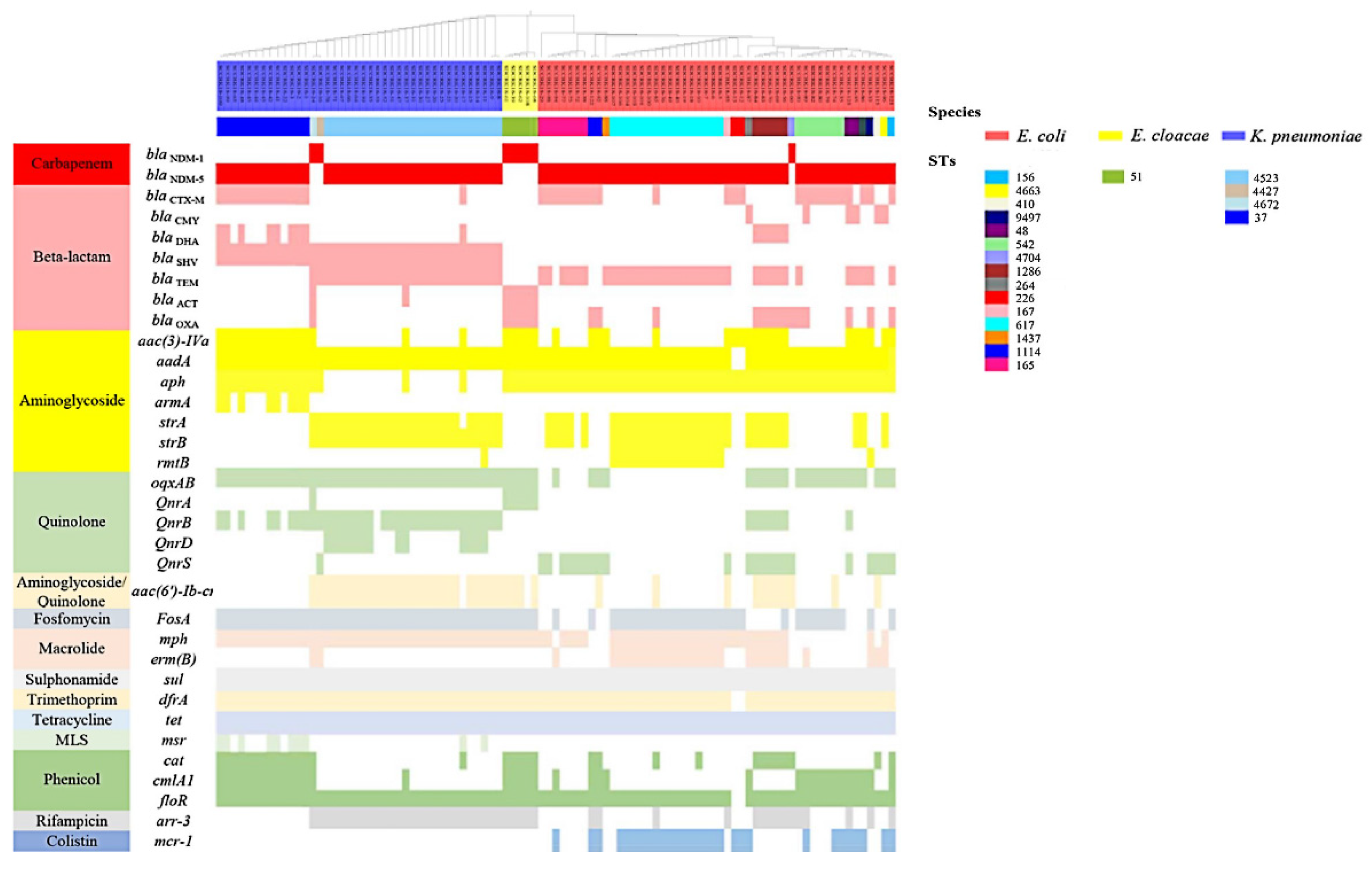
3.2. Co-Existence of Other Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARGs) and blaNDM in Isolates
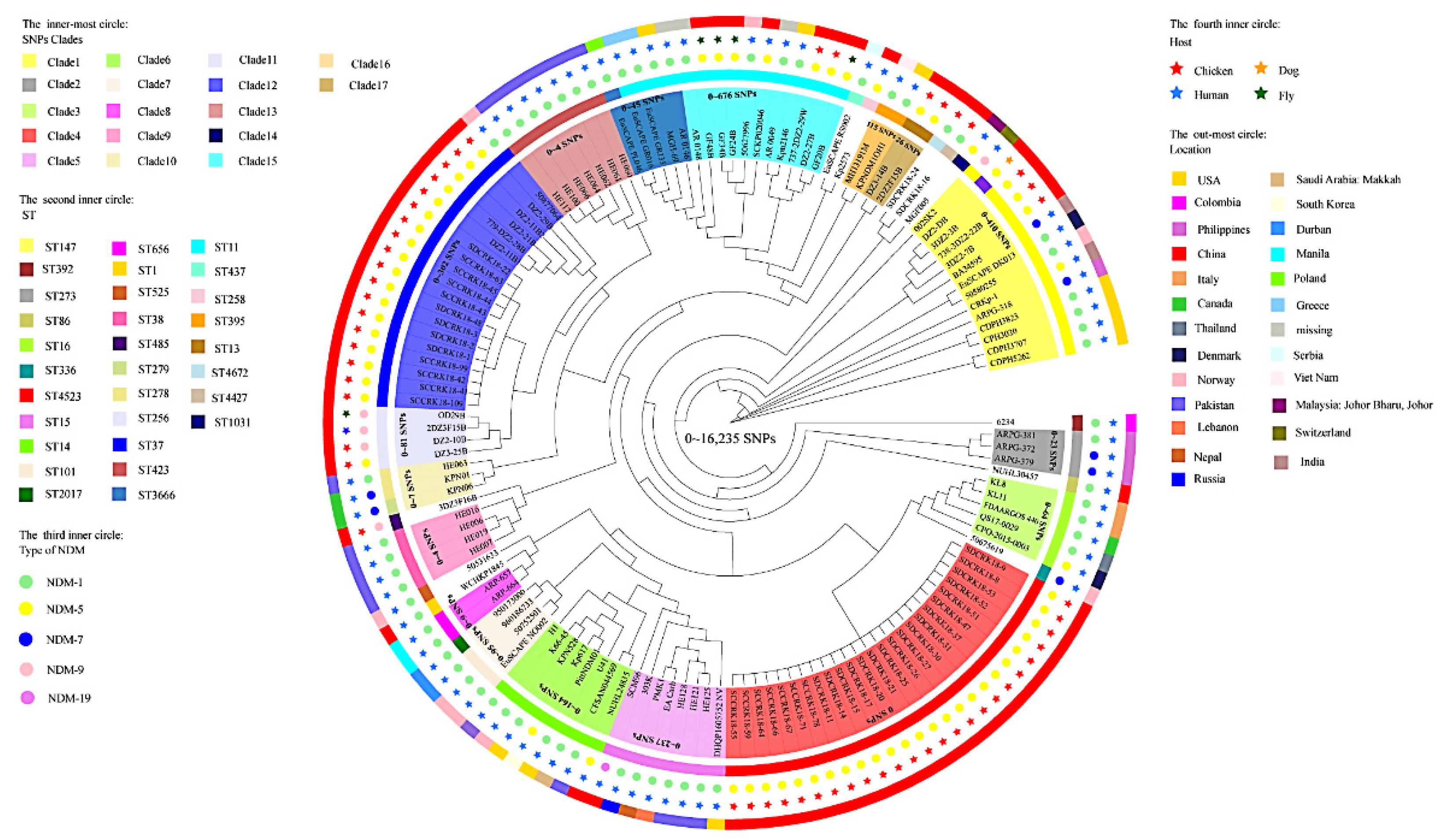
3.3. Genomic Diversity Characteristics of the NDM-Positive Enterobacterales
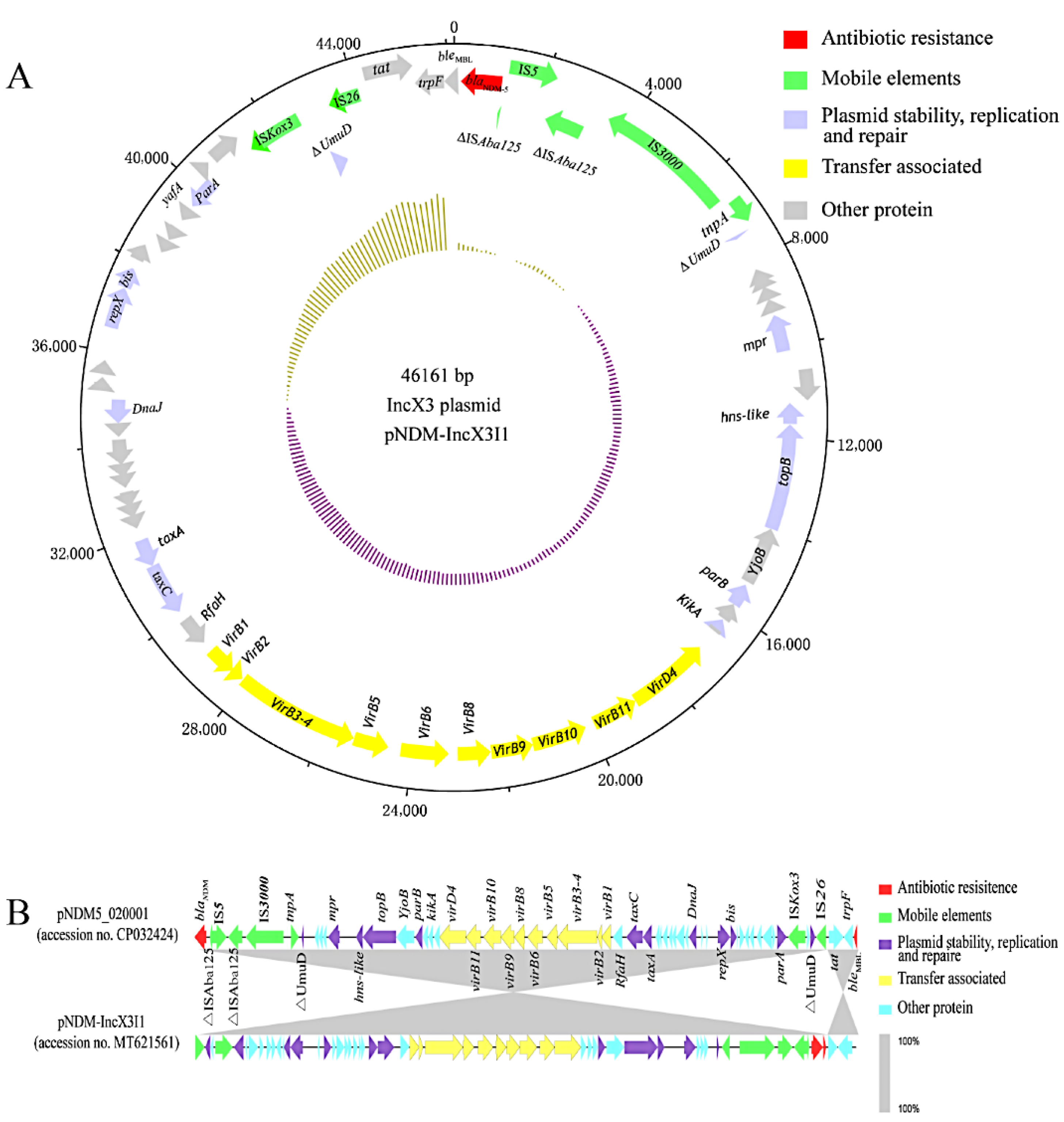
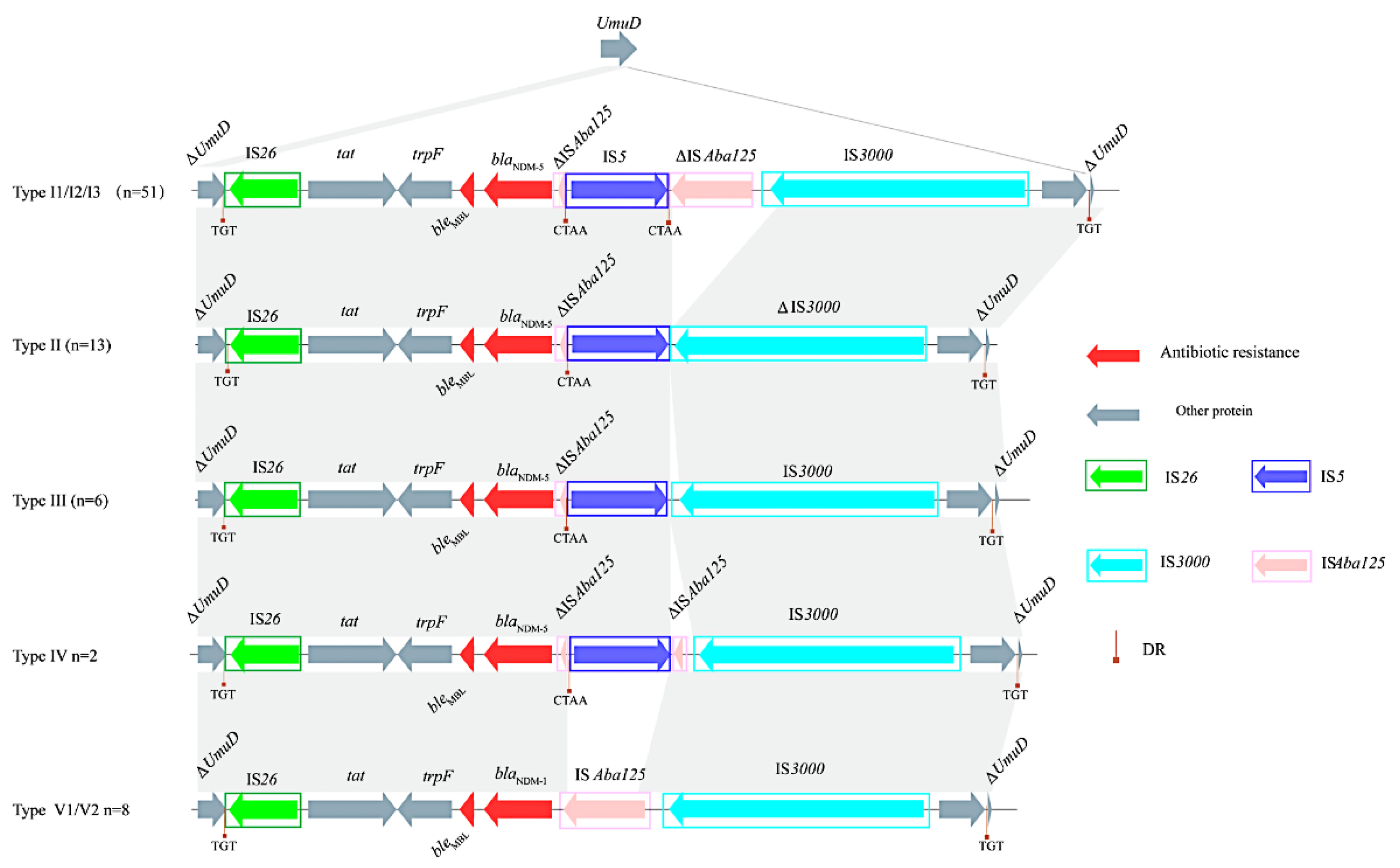
3.4. blaNDM-Harboring Plasmids and Genetic Context of blaNDM
3.5. Fitness and Genetic Stability of the blaNDM-Carrying Plasmids
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. WHO Pathogens Priority List Working Group. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulthurst, S.J.; Barnard, A.M.; Salmond, G.P. Regulation and biosynthesis of carbapenem antibiotics in bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornaglia, G.; Giamarellou, H.; Rossolini, G.M. Metallo-β-lactamases: A last frontier for β-lactams? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Duin, D.; Doi, Y. The global epidemiology of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Virulence 2017, 8, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, L.K.; Weinstein, R.A. The Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae: The Impact and Evolution of a Global Menace. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, S28–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yong, D.; Toleman, M.A.; Giske, C.G.; Cho, H.S.; Sundman, K.; Lee, K.; Walsh, T.R. Characterization of a new metallo-beta-lactamase gene, bla(NDM-1), and a novel erythromycin esterase gene carried on a unique genetic structure in Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 14 from India. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 5046–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mills, M.C.; Lee, J. The threat of carbapenem-resistant bacteria in the environment: Evidence of widespread contamination of reservoirs at a global scale. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255 Pt 1, 113143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchar Mahamat, O.; Kempf, M.; Lounnas, M.; Tidjani, A.; Hide, M.; Benavides, J.A.; Carrière, C.; Bañuls, A.L.; Jean-Pierre, H.; Ouedraogo, A.S.; et al. Epidemiology and prevalence of extended-spectrum β-lactamase- and carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in humans, animals and the environment in West and Central Africa. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2021, 57, 106203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, R.; Fu, B.; Shi, X.; Sun, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Shen, Z.; Walsh, T.R.; Cai, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. Contaminated in-house environment contributes to the persistence and transmission of NDM-producing bacteria in a Chinese poultry farm. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadziabdic, S.; Fischer, J.; Borowiak, M.; Malorny, B.; Juraschek, K.; Kaesbohrer, A.; Guerra, B.; Deneke, C.; Gonzalez-Zorn, B.; Szabo, I. The blaNDM-1-Carrying IncA/C2 Plasmid Underlies Structural Alterations and Cointegrate Formation In Vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00380-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamza, E.; Dorgham, S.M.; Hamza, D.A. Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in broiler poultry farming in Egypt. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2016, 7, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyas, S.; Rasool, M.H.; Arshed, M.J.; Qamar, M.U.; Aslam, B.; Almatroudi, A.; Khurshid, M. The Escherichia coli Sequence Type 131 Harboring Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases and Carbapenemases Genes from Poultry Birds. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Feng, Y.; Tang, G.; Qiao, F.; McNally, A.; Zong, Z. NDM Metallo-β-Lactamases and Their Bacterial Producers in Health Care Settings. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00115-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.W.; Chen, T.L.; Chen, Y.T.; Lauderdale, T.L.; Liao, T.L.; Lee, Y.T.; Chen, C.P.; Liu, Y.M.; Lin, A.C.; Chang, Y.H.; et al. Copy Number Change of the NDM-1 sequence in a multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolate. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, L.L.; Zhang, Y.F.; Doi, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.F.; Zeng, K.J.; Shen, C.; Patil, S.; Xing, Y.; Zou, Y.; et al. Coproduction of MCR-1 and NDM-1 by Colistin-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolated from a Healthy Individual. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 61, e01962-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, D.; Xie, M.; Li, R.; Chen, K.; Chan, E.W.; Chen, S. IncFII Conjugative Plasmid-Mediated Transmission of blaNDM-1 Elements among Animal-Borne Escherichia coli Strains. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 61, e02285-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Yin, W.; Schwarz, S.; Tyrrell, J.M.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Shen, Z.; et al. Comprehensive resistome analysis reveals the prevalence of NDM and MCR-1 in Chinese poultry production. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 16260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Gu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, K. Swine waste: A reservoir of high-risk blaNDM and mcr-1. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 683, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: An online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2016, 44, W242–W245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernández, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Møller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, R.; Kong, Z.; Qian, H.; Jiang, F.; Kang, H.; Gu, B.; Ma, P. High Prevalence of blaNDM Variants Among Carbapenem-Resistant Escherichia coli in Northern Jiangsu Province, China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, Y.; Shintani, M.; Takase, N.; Kazo, Y.; Kawamura, F.; Hara, H.; Nishida, H.; Okada, K.; Yamane, H.; Nojiri, H. Modulation of primary cell function of host Pseudomonas bacteria by the conjugative plasmid pCAR1. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 134–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Hu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Hu, F.; Zhou, H.; Shu, L.; Ma, T.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Emerging Carriage of NDM-5 and MCR-1 in Escherichia coli from Healthy People in Multiple Regions in China: A Cross Sectional Observational Study. EClinicalMedicine 2018, 6, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, L.; Zhou, H.; Chan, E.W.; Li, J.; Fang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liao, K.; Chen, S. Nationwide Surveillance of Clinical Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) Strains in China. EBioMedicine 2017, 19, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, L.H.; Lei, C.W.; Ma, S.Z.; Jiang, W.; Liu, B.H.; Wang, Y.X.; Guan, R.; Men, S.; Yuan, Q.W.; Cheng, G.Y.; et al. Various Sequence Types of Escherichia coli Isolates Coharboring blaNDM-5 and mcr-1 Genes from a Commercial Swine Farm in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02167-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.T.; Song, F.J.; Zou, M.; Zhang, Q.D.; Shan, H. High Incidence of Escherichia coli Strains Coharboring mcr-1 and blaNDM from Chickens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02347-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zurfluh, K.; Stevens, M.J.A.; Stephan, R.; Nüesch-Inderbinen, M. Complete and assembled genome sequence of an NDM-5- and CTX-M-15-producing Escherichia coli sequence type 617 isolated from wastewater in Switzerland. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 15, 105–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, B.; Tada, T.; Shimada, K.; Shrestha, S.; Ohara, H.; Pokhrel, B.M.; Sherchand, J.B.; Kirikae, T. Emergence of Various NDM-Type-Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Clinical Isolates in Nepal. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01425-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, B.; Chang, J.; Cao, L.; Luo, Q.; Xu, H.; Lyu, W.; Qian, M.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xia, X.; et al. Characterization of an NDM-5 carbapenemase-producing Escherichia coli ST156 isolate from a poultry farm in Zhejiang, China. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, D.; Pan, F.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H. Resistance phenotype and clinical molecular epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae among pediatric patients in Shanghai. Infect. Drug. Resist. 2018, 11, 1935–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Sun, L.; Ding, B.; Yang, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, W.; Zhu, D.; Yang, F.; Zhang, H.; Hu, F. Outbreak of NDM-1-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST76 and ST37 isolates in neonates. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Bi, Z.; Ma, S.; Chen, B.; Cai, C.; He, J.; Schwarz, S.; Sun, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, J.; et al. Inter-host Transmission of Carbapenemase-Producing Escherichia coli among Humans and Backyard Animals. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 107009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Xie, L.; Wang, X.; Han, L.; Guo, X.; Ni, Y.; Qu, H.; Sun, J. Further Spread of bla NDM-5 in Enterobacteriaceae via IncX3 Plasmids in Shanghai, China. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sugawara, Y.; Akeda, Y.; Hagiya, H.; Sakamoto, N.; Takeuchi, D.; Shanmugakani, R.K.; Motooka, D.; Nishi, I.; Zin, K.N.; Aye, M.M.; et al. Spreading Patterns of NDM-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Clinical and Environmental Settings in Yangon, Myanmar. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01924-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Lv, L.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Lu, J.; Liu, E.; Wan, M.; Xun, H.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Rapid Increase in Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Retail Meat Driven by the Spread of the blaNDM-5-Carrying IncX3 Plasmid in China from 2016 to 2018. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00573-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poirel, L.; Schrenzel, J.; Cherkaoui, A.; Bernabeu, S.; Renzi, G.; Nordmann, P. Molecular analysis of NDM-1-producing enterobacterial isolates from Geneva, Switzerland. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 1730–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Fu, Y.; Shen, M.; Huang, D.; Du, X.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; Yu, Y. Dissemination of blaNDM-5 gene via an IncX3-type plasmid among non-clonal Escherichia coli in China. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2018, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Mu, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, D.; Ji, J.; Quan, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Y. Detection and characterization of a clinical Escherichia coli ST3204 strain coproducing NDM-16 and MCR-1. Infect. Drug. Resist. 2018, 11, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, W.; Schwarz, S.; Wang, C.; Yang, Q.; Luan, T.; Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W. Characterization of a blaNDM-1-carrying IncHI5 plasmid from Enterobacter cloacae complex of food-producing animal origin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porse, A.; Schønning, K.; Munck, C.; Sommer, M.O. Survival and Evolution of a Large Multidrug Resistance Plasmid in New Clinical Bacterial Hosts. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 2860–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liakopoulos, A.; van der Goot, J.; Bossers, A.; Betts, J.; Brouwer, M.S.M.; Kant, A.; Smith, H.; Ceccarelli, D.; Mevius, D. Genomic and functional characterisation of IncX3 plasmids encoding blaSHV-12 in Escherichia coli from human and animal origin. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Antibiotics | Number of Resistant Isolates | Resistance Rate (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | K. peneumoniae | E. cloacae | E. coli | K. peneumoniae | E. cloacae | |
| MEN | 50 | 40 | 5 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| IPM | 50 | 40 | 5 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| CAZ | 50 | 40 | 5 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| CTX | 50 | 40 | 5 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| FOX | 50 | 40 | 5 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| SXT | 50 | 40 | 5 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| TET | 50 | 40 | 5 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| ATM | 15 | 1 | 0 | 30 | 2.5 | 0 |
| TGC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| GEN | 30 | 13 | 0 | 60 | 32.5 | 0 |
| CIP | 39 | 16 | 0 | 78 | 40 | 0 |
| FOS | 28 | 40 | 5 | 56 | 100 | 100 |
| PB | 29 | 0 | 0 | 58 | 0 | 0 |
| FFC | 48 | 40 | 5 | 96 | 100 | 100 |
| Type I1 | Type I2 | Type I3 | Type II | Type III | Type IV | Type V1 | Type V2 | Location | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2325 (C-T) | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | IS5 |
| 10232 (A-G) | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | non-coding region |
| 12470 (C-T) | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | topB |
| 13038 (G-A) | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | topB |
| 13627 (A-G) | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | topB |
| 19367 (G-T) | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | virB11 |
| 21112 (A-G) | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | virB10 |
| 25945 (C-T) | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | virB3-4 |
| 26374 (C-A) | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | virB3-4 |
| 35556 (G-A) | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | non-coding region |
| 36080 (T-C) | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | non-coding region |
| NO. Strains | 9 | 25 | 17 | 13 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 7 | — |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, H.; Kong, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhou, C.; Li, C.; Ma, B.; Li, C.; Lei, C.; et al. Characterization and Public Health Insights of the New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacterales from Laying Hens in China. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10040800
Wei H, Kong L, Wang Y, Huang Z, Yang X, Zhou C, Li C, Ma B, Li C, Lei C, et al. Characterization and Public Health Insights of the New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacterales from Laying Hens in China. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(4):800. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10040800
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Hongcheng, Linghan Kong, Yulong Wang, Zheren Huang, Xue Yang, Changyu Zhou, Chao Li, Boheng Ma, Cui Li, Changwei Lei, and et al. 2022. "Characterization and Public Health Insights of the New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacterales from Laying Hens in China" Microorganisms 10, no. 4: 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10040800
APA StyleWei, H., Kong, L., Wang, Y., Huang, Z., Yang, X., Zhou, C., Li, C., Ma, B., Li, C., Lei, C., & Wang, H. (2022). Characterization and Public Health Insights of the New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacterales from Laying Hens in China. Microorganisms, 10(4), 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10040800








