Biomimetic Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Ethyl Acetate Extract of Urtica diocia Leaves; Characterizations and Emerging Antimicrobial Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Preparation of Plant leaves
2.2. UD Leaf Extraction
2.3. Preparation of UD-AgNPs
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Antimicrobial Evaluation
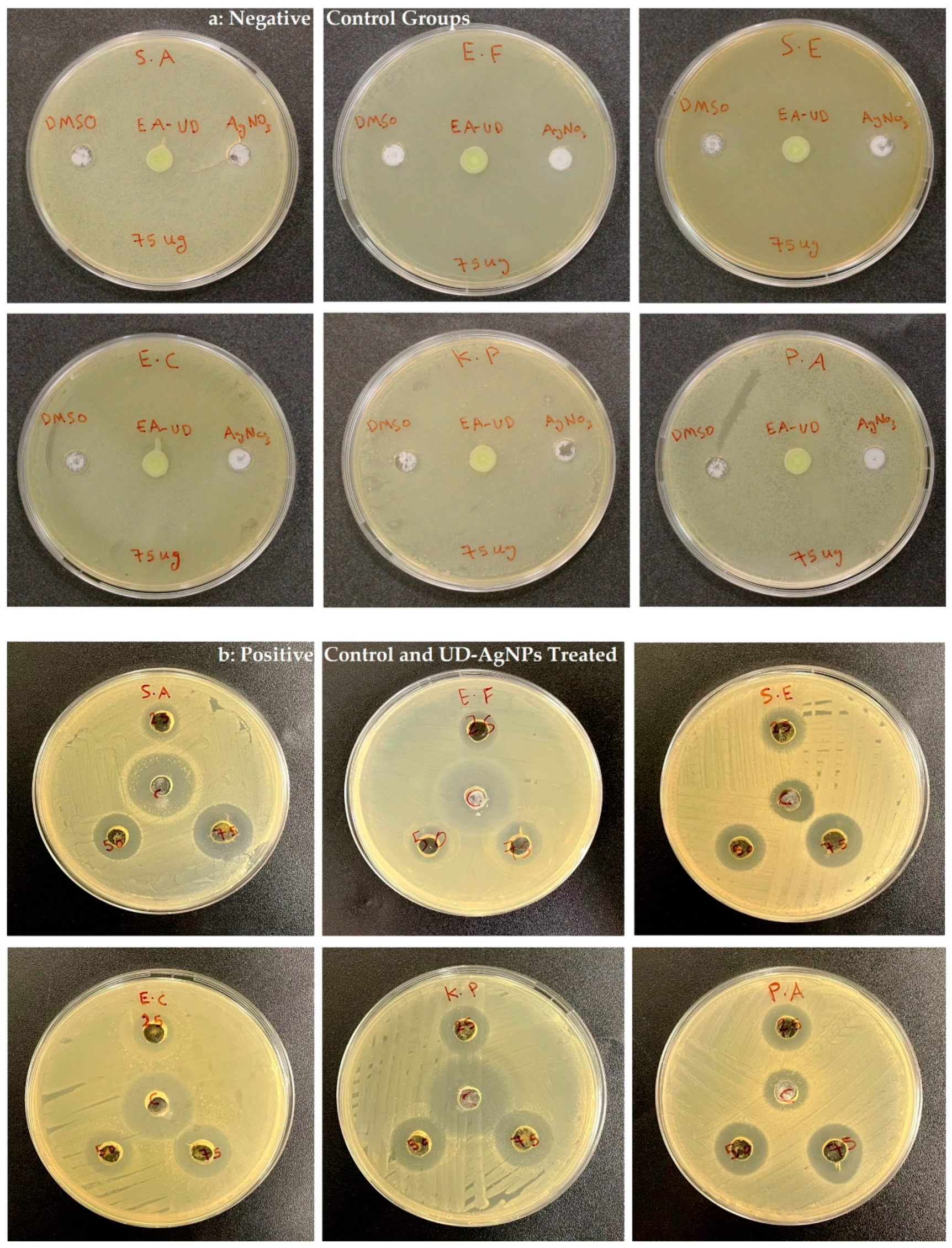
2.5.1. Inhibition Study
2.5.2. MIC
2.5.3. MBC
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterizations
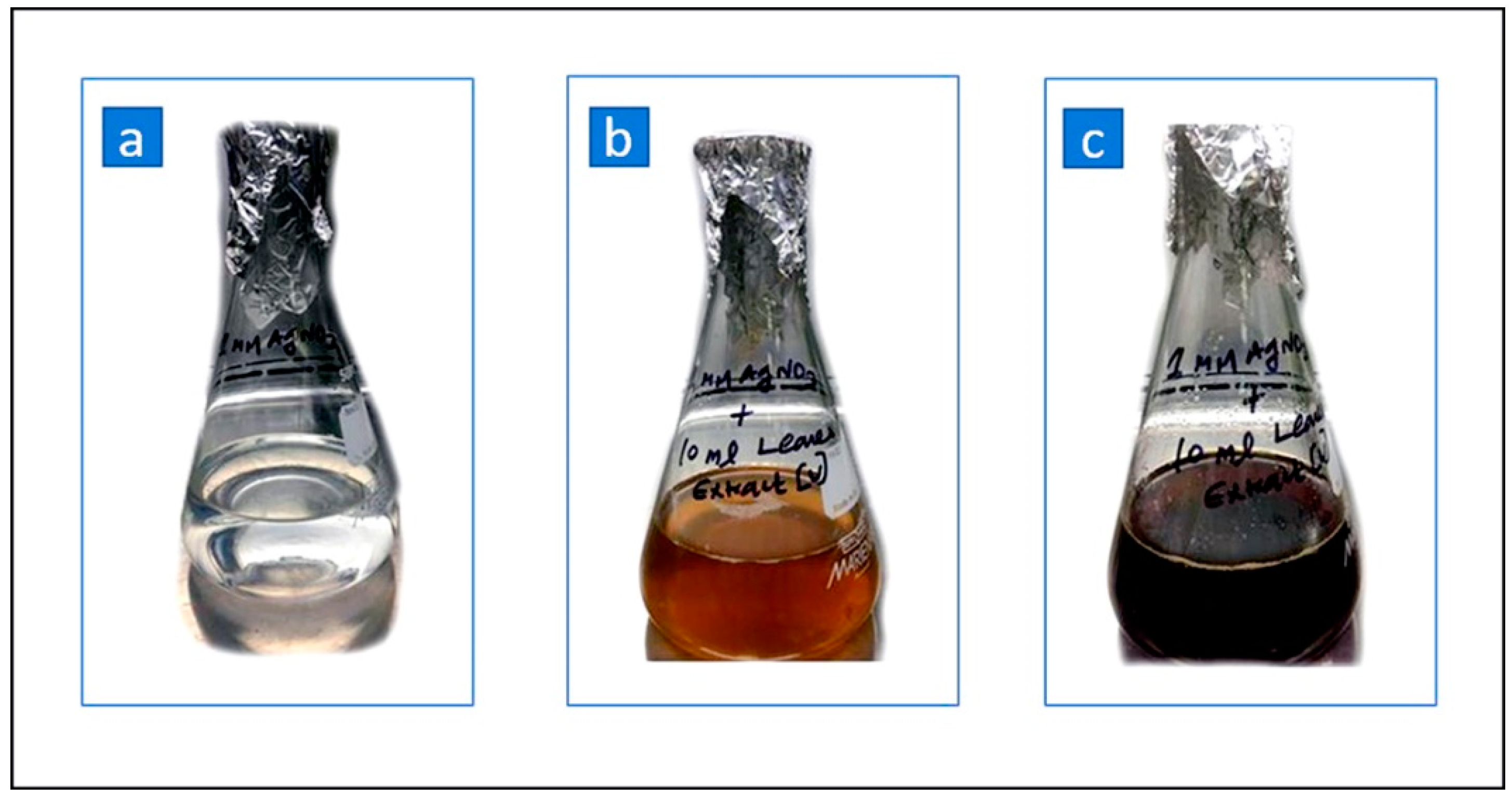
3.1.1. Visual Observation
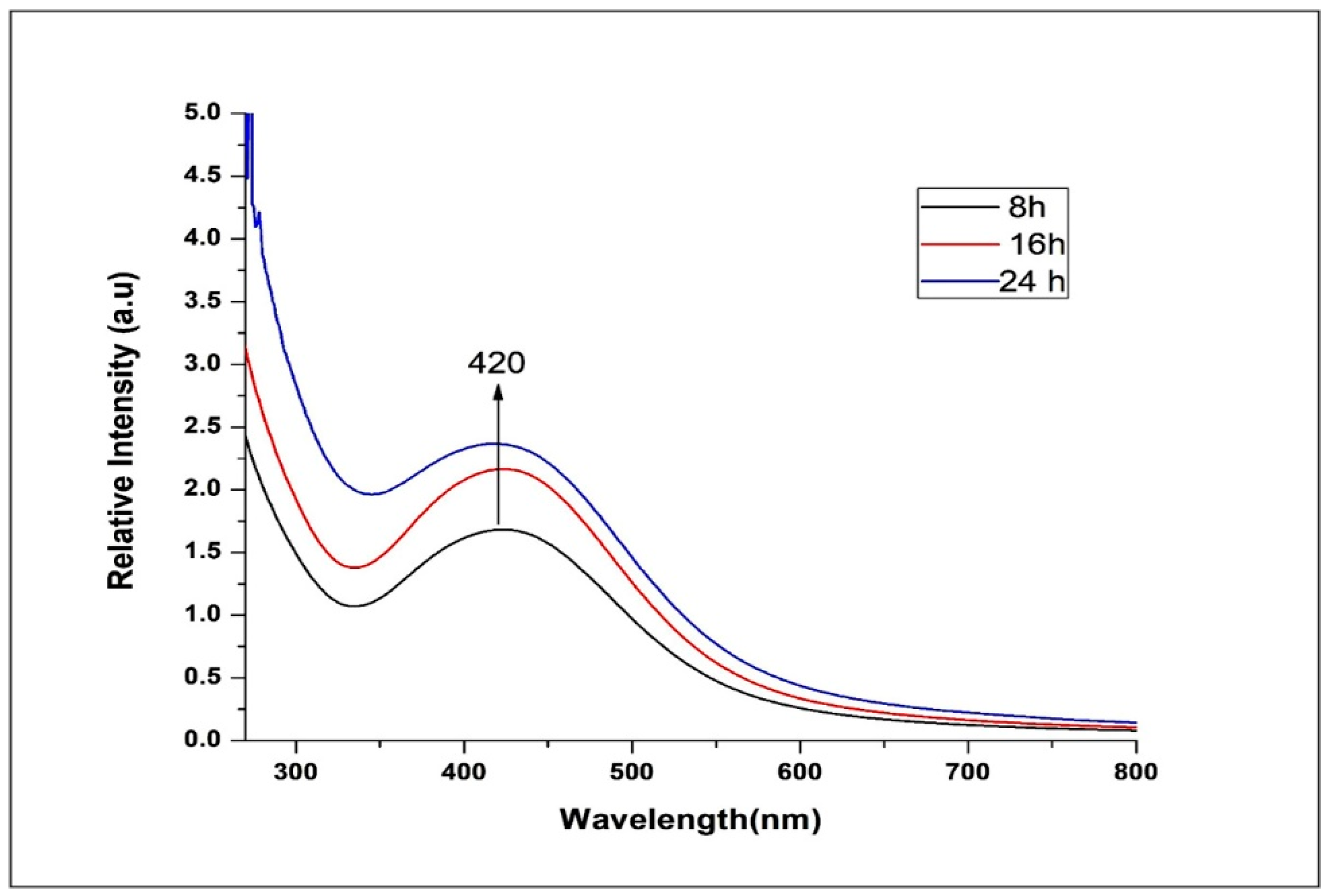
3.1.2. UV–vis Spectral Study
3.1.3. FTIR Spectroscopy
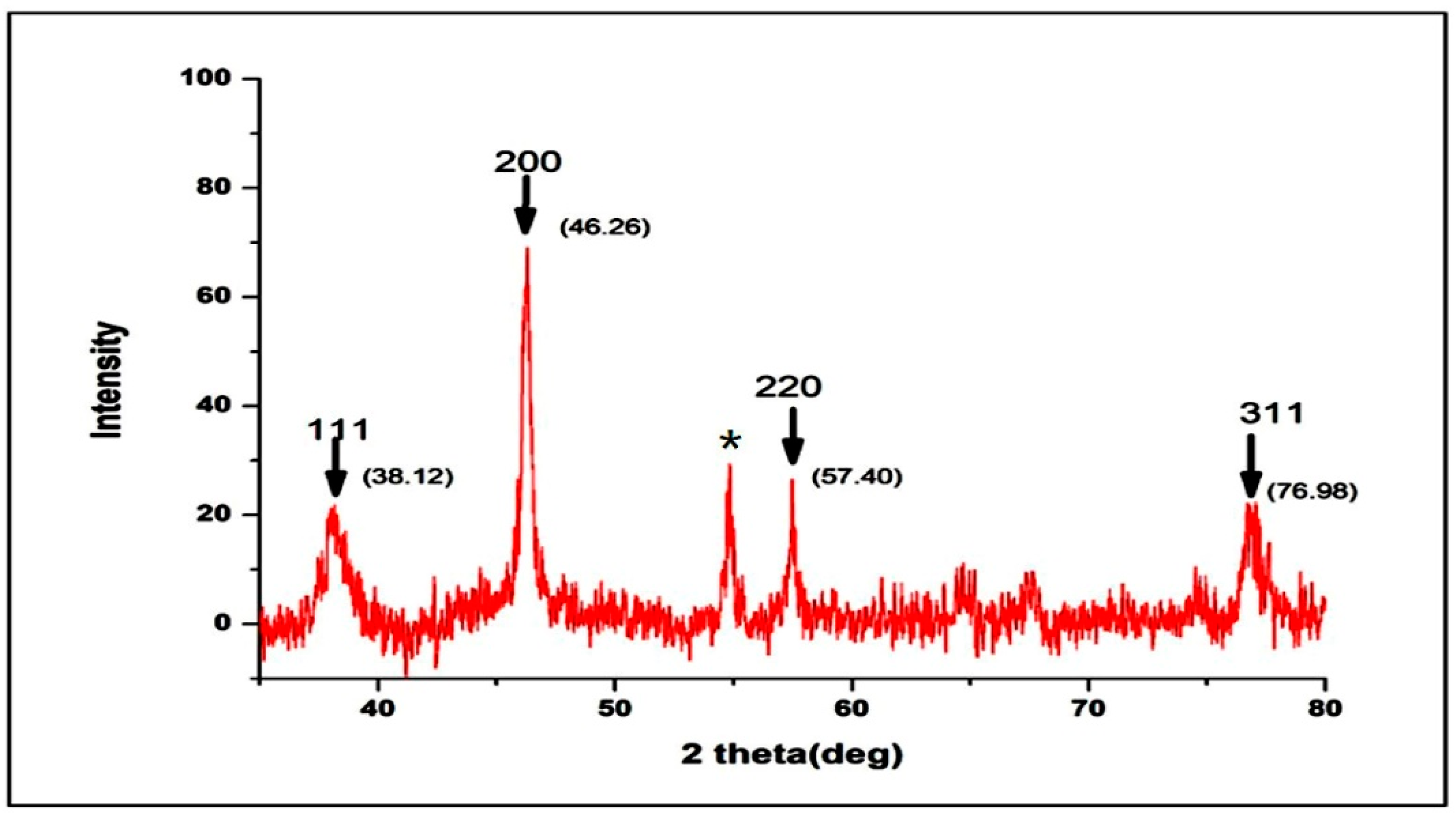
3.1.4. XRD Pattern
3.1.5. DLS Analysis
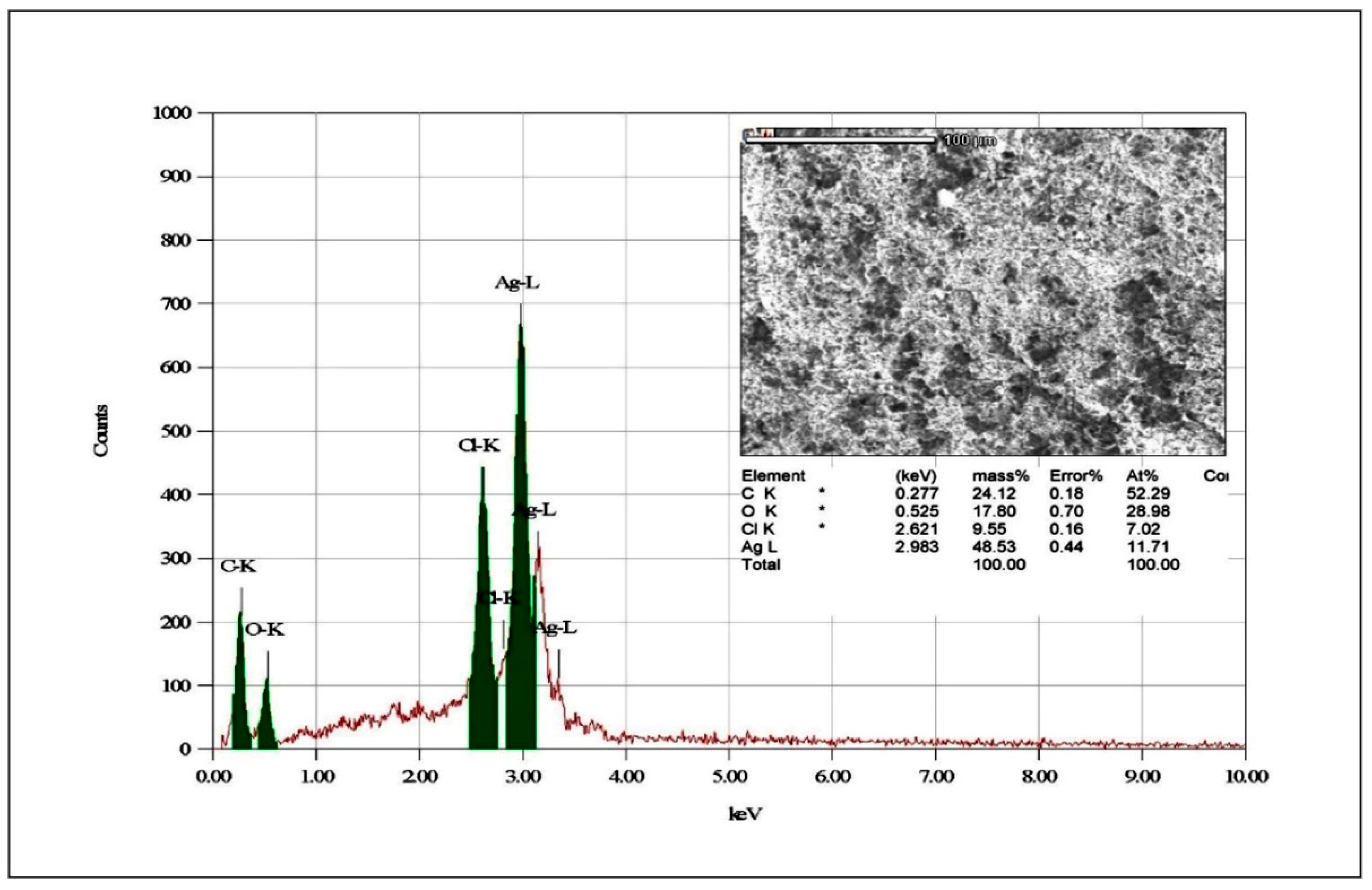
3.1.6. EDAX Analysis
3.1.7. SEM and TEM Images
3.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility
3.2.1. MIC Analysis
3.2.2. MBC Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dar, S.A.; Ganai, F.A.; Yousuf, A.R.; Balkhi, M.-u.-H.; Bhat, T.M.; Sharma, P. Pharmacological and toxicological evaluation of Urtica dioica. Pharm. Biol. 2013, 51, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shonte, T.T.; Duodu, K.G.; de Kock, H.L. Effect of drying methods on chemical composition and antioxidant activity of underutilized stinging nettle leaves. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nallan Chakravartula, S.S.; Moscetti, R.; Farinon, B.; Vinciguerra, V.; Merendino, N.; Bedini, G.; Neri, L.; Pittia, P.; Massantini, R. Stinging Nettles as Potential Food Additive: Effect of Drying Processes on Quality Characteristics of Leaf Powders. Foods 2021, 10, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grauso, L.; de Falco, B.; Lanzotti, V.; Motti, R. Stinging nettle, Urtica dioica L.: Botanical, phytochemical and pharmacological overview. Phytochem. Rev. 2020, 19, 1341–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaei, R.; Foshati, S.; Hadi, A.; Kermani, M.A.H.; Ghavami, A.; Clark, C.C.; Tarrahi, M.J. The effect of nettle (Urtica dioica) supplementation on the glycemic control of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Dar, S.; Sharma, P. Antibacterial activity and toxicological evaluation of semi purified hexane extract of Urtica dioica leaves. Res. J. Med. Plants 2012, 6, 123–135. [Google Scholar]
- Zehraw, H.M.; Taleb, Z.M.M.; Mukhlif, B.; Al-Jabbar, S.A. Extraction and evaluation the activity of Urtica dioica as bleeding stop material. Iraqi J. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Zouari Bouassida, K.; Bardaa, S.; Khimiri, M.; Rebaii, T.; Tounsi, S.; Jlaiel, L.; Trigui, M. Exploring the Urtica dioica leaves hemostatic and wound-healing potential. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1047523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modarresi-Chahardehi, A.; Ibrahim, D.; Fariza-Sulaiman, S.; Mousavi, L. Screening antimicrobial activity of various extracts of Urtica dioica. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2012, 60, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.; Moore, L.; Sundsfjord, A.; Steinba, M.; Regmi, S.; Karey, A.; Guerin, P.J.; Piddoc, L.J.V. Understanding the mechanisms and drivers of antimicrobial resistance. Lancet 2016, 387, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabi, R.; Momtaz, H. Virulence factors and antibiotic resistance properties of the Staphylococcus epidermidis strains isolated from hospital infections in Ahvaz, Iran. Trop. Med. Health 2019, 47, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, D.; Daima, H.K.; Kachhwaha, S.; Kothari, S. Synthesis of plant-mediated silver nanoparticles using papaya fruit extract and evaluation of their anti-microbial activities. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2009, 4, 557–563. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Raouf, N.; Al-Enazi, N.M.; Ibraheem, I.B. Green biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using Galaxaura elongata and characterization of their antibacterial activity. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3029–S3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikshit, P.K.; Kumar, J.; Das, A.K.; Sadhu, S.; Sharma, S.; Singh, S.; Gupta, P.K.; Kim, B.S. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles: Applications and Limitations. Catalysts 2021, 11, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanesan, S.; AlSalhi, M.S. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using the Flower Extract of Abelmoschus esculentus for Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial Studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSalhi, M.S.; Devanesan, S.; Alfuraydi, A.A.; Vishnubalaji, R.; Munusamy, M.A.; Murugan, K.; Nicoletti, M.; Benelli, G. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Pimpinella anisum seeds: Antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity on human neonatal skin stromal cells and colon cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanesan, S.; Ponmurugan, K.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Al-Dhabi, N.A. Cytotoxic and antimicrobial efficacy of silver nanoparticles synthesized using a traditional phytoproduct, asafoetida gum. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakal, T.C.; Kumar, A.; Majumdar, R.S.; Yadav, V. Mechanistic basis of antimicrobial actions of silver nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Han, J.W.; Kwon, D.-N.; Kim, J.-H. Enhanced antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities of silver nanoparticles against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Bai, Y.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Xing, X.; Wang, C.; Gao, L.; Yogi, M.; Swamy, M.K. Anticancer and Antibacterial Activities of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) Synthesized from Cucumis melo L. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 4143–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.; Patra, J.K.; Nagaraj Basavegowda, C.N.V.; Shin, H.-S. Comparative study on antidiabetic, cytotoxicity, antioxidant and antibacterial properties of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using outer peels of two varieties of Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salleh, A.; Naomi, R.; Utami, N.D.; Mohammad, A.W.; Mahmoudi, E.; Mustafa, N.; Fauzi, M.B. The potential of silver nanoparticles for antiviral and antibacterial applications: A mechanism of action. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadczak, P.; Kulpa, D.; Drozd, R.; Przewodowski, W.; Przewodowska, A. Effect of AuNPs and AgNPs on the Antioxidant System and Antioxidant Activity of Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia Mill.) from In Vitro Cultures. Molecules 2020, 25, 5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanlalveni, C.; Lallianrawna, S.; Biswas, A.; Selvaraj, M.; Changmai, B.; Rokhum, S.L. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant extracts and their antimicrobial activities: A review of recent literature. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 2804–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laouini, S.E.; Bouafia, A.; Soldatov, A.V.; Algarni, H.; Tedjani, M.L.; Ali, G.A.; Barhoum, A. Green synthesized of Ag/Ag2O nanoparticles using aqueous leaves extracts of phoenix dactylifera L. And their azo dye photodegradation. Membranes 2021, 11, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meretoudi, A.; Banti, C.N.; Raptis, P.K.; Papachristodoulou, C.; Kourkoumelis, N.; Ikiades, A.A.; Zoumpoulakis, P.; Mavromoustakos, T.; Hadjikakou, S.K. Silver Nanoparticles from Oregano Leaves’ Extracts as Antimicrobial Components for Non-Infected Hydrogel Contact Lenses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, M.; Aldujaili, A.; Homady, M. Assessment of hepatoprotective role of phenolic extract of Urtica dioica and silver nanoparticles in male rat induced by carbon tetra-chloride. Rasayan J. Chem. 2017, 10, 305–312. [Google Scholar]
- Nassar, A.M. Research Article Effectiveness of Silver Nano-particles of Extracts of Urtica urens (Urticaceae) Against Root-knot Nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Asian J. Nematol. 2016, 5, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyoti, K.; Baunthiyal, M.; Singh, A. Characterization of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Urtica dioica Linn. leaves and their synergistic effects with antibiotics. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2016, 9, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.C.; Kumar, V.; Singh, A.; Singh, R. Characterisations, Antimicrobial activities and Biological synthesis of silver (Ag) nanoparticles using the leaf extract of Urtica dioica. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2019, 12, 4429–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, J.; Franus, W.; Panek, R.; Szymańska-Chargot, M.; Flieger, W.; Flieger, M.; Kołodziej, P. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Natural Extracts with Proven Antioxidant Activity. Molecules 2021, 26, 4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanam, R.; Prasuna, R.G. Comparison of extraction methods and solvents for total phenolics from dairy waste. Asian J. Dairy Food Res. 2017, 36, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Joshi, D.R.; Adhikari, N. An overview on common organic solvents and their toxicity. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2019, 28, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thouri, A.; Chahdoura, H.; El Arem, A.; Omri Hichri, A.; Ben Hassin, R.; Achour, L. Effect of solvents extraction on phytochemical components and biological activities of Tunisian date seeds (var. Korkobbi and Arechti). BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadou, A.; Al-Shahwany, A.W. Biogenic Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Some Medical Plants and Evaluation of Their Antibacterial and Toxicity Potential. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 1905–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Tang, H.; Lyles, J.; Pineau, R.; Mashwani, Z.R.; Quave, C.L. Antibacterial properties of medicinal plants from Pakistan against multidrug-resistant ESKAPE pathogens. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, Y.Y.; Rukayadi, Y.; Nor-Khaizura, M.-A.-R.; Kuan, C.H.; Chieng, B.W.; Nishibuchi, M.; Radu, S. In vitro antimicrobial activity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles against selected gram-negative foodborne pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfuraydi, A.A.; Devanesan, S.; Al-Ansari, M.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Ranjitsingh, A.J. Eco-friendly green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from the sesame oil cake and its potential anticancer and antimicrobial activities. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 192, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zou, J.; Chen, X.; Zheng, H.; Jin, Z.; Li, F.; Piao, J.-G. The Effect of Size on the Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering Property of SiO2@PDA@AgNP Core-Shell-Satellite Nanocomposite. Chem. Lett. 2020, 49, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Ijaz, M.; Ali, S.; Haider, J.; Imran, M.; Majeed, H.; Shahzadi, I.; Ali, M.M.; Khan, J.A.; Ikram, M. Green synthesized phytochemically (Zingiber officinale and Allium sativum) reduced nickel oxide nanoparticles confirmed bactericidal and catalytic potential. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, E.O. Silver nanoparticles: Mechanism of action and probable bio-application. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rama, P.; Baldelli, A.; Vignesh, A.; Altemimi, A.B.; Lakshmanan, G.; Selvam, R.; Arunagirinathan, N.; Murugesan, K.; Pratap-Singh, A. Antimicrobial, antioxidant, and angiogenic bioactive silver nanoparticles produced using Murraya paniculata (L.) jack leaves. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanesan, S.; Jayamala, M.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Umamaheshwari, S.; Ranjitsingh, A.J.A. Antimicrobial and Anticancer properties of Carica papaya leaves derived di-methyl flubendazole mediated silver nanoparticles. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallehudin, T.A.T.; Seman, M.N.A.; Chik, S.M.S.T. Preparation and Characterization Silver Nanoparticle Embedded Polyamide Nanofiltration (NF) Membrane. ATEC Web Conf. 2018, 150, 02003. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, P.M.; Felício, M.R.; Santos, N.C.; Gonçalves, S.; Domingues, M.M. Application of light scattering techniques to nanoparticle characterization and development. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahdar, A.; Amini, N.; Askari, F.; Susan, M.; Hasan, A.B. Dynamic light scattering: A useful technique to characterize nanoparticles. J. Nanoanal. 2019, 6, 80–89. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, A.; Liu, Q.; Griffin, S.; Nicholls, A.; Regalbuto, J. Synthesis of ultrasmall, homogeneously alloyed, bimetallic nanoparticles on silica supports. Science 2017, 358, 1427–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomelí-Rosales, D.A.; Zamudio-Ojeda, A.; Reyes-Maldonado, O.K.; López-Reyes, M.E.; Basulto-Padilla, G.C.; Lopez-Naranjo, E.J.; Zuñiga-Mayo, V.M.; Velázquez-Juárez, G. Green Synthesis of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Capsicum chinense Plant. Molecules 2022, 27, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, S.T.; Sadat, S.; Walliser, M.; Haddadi, A. Targeted therapeutic nanoparticles: An immense promise to fight against cancer. J. Drug Deliv. 2017, 2017, 9090325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurj, A.; Braicu, C.; Pop, L.-A.; Tomuleasa, C.; Gherman, C.D.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. The new era of nanotechnology, an alternative to change cancer treatment. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scimeca, M.; Bischetti, S.; Lamsira, H.K.; Bonfiglio, R.; Bonanno, E. Energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX) microanalysis: A powerful tool in biomedical research and diagnosis. Eur. J. Histochem. EJH 2018, 62, 2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, H.; Sami, M.A.; Sadaf, S.; Hassan, U. Salvadora persica mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antimicrobial efficacy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareek, V.; Devineau, S.; Sivasankaran, S.K.; Bhargava, A.; Panwar, J.; Srikumar, S.; Fanning, S. Silver nanoparticles induce a triclosan-like antibacterial action mechanism in multi-drug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, A.S.H.; Karthikeyan, C.; Ahamed, A.P.; Thajuddin, N.; Alharbi, N.S.; Alharbi, S.A.; Ravi, G. In vitro antibacterial activity of ZnO and Nd doped ZnO nanoparticles against ESBL producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, P.V.; McCusker, M.P.; Carvalho, A.; Ferreira, D.A.; Mohan, N.M.; Martins, M.; Fernandes, A.R. Nano-strategies to fight multidrug resistant bacteria—“A Battle of the Titans”. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Monk, I.; Goncalves da Silva, A.; Seemann, T.; Chua, K.Y.L.; Kearns, A.; Hill, R.; Woodford, N.; Bartels, M.D.; Strommenger, B.; et al. Global spread of three multidrug-resistant lineages of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brayner, R.; Ferrari-Iliou, R.; Brivois, N.; Djediat, S.; Benedetti, M.F.; Fiévet, F. Toxicological impact studies based on Escherichia coli bacteria in ultrafine ZnO nanoparticles colloidal medium. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panpaliya, N.P.; Dahake, P.T.; Kale, Y.J.; Dadpe, M.V.; Kendre, S.B.; Siddiqi, A.G.; Maggavi, U.R. In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial property of silver nanoparticles and chlorhexidine against five different oral pathogenic bacteria. Saudi Dent. J. 2019, 31, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizaj, S.M.; Lotfipour, F.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Zarrintan, M.H.; Adibkia, K. Antimicrobial activity of the metals and metal oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 44, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun’an Qing, L.C.; Li, R.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Qin, Y. Potential antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and the optimization of orthopedic implants by advanced modification technologies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Shen, C.; Ji, Q.; An, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Z. Food storage material silver nanoparticles interfere with DNA replication fidelity and bind with DNA. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 085102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Zone of Inhibition (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | 25 uL (Mean ± SD) | 50 uL (Mean ± SD) | 75 uL (Mean± SD) | Control |
| S. aureus | 13.3 ± 0.7 | 16.6 ± 0.4 | 21.3 ± 0.7 | 24 ± 1 |
| E. faecalis | 12.6 ± 0.4 | 14 ± 1 | 18.6 ± 0.4 | 27 ± 1 |
| S.epidermidis | 14.3 ± 0.7 | 17.6 ± 0.6 | 19 ± 1 | 15.6 ± 0.6 |
| K. pneumoniae | 16.3 ± 0.7 | 17.3 ± 0.7 | 19.6 ± 0.6 | 26 ± 1 |
| P. aeruginosa | 16 ± 1 | 18.6 ± 0.4 | 21.6 ± 0.4 | 16 ± 1 |
| E. coli | 13.6 ± 0.6 | 17 ± 1 | 19.6 ± 0.6 | 24.3 ± 0.7 |
| Bacteria | MIC (µg/mL) (Mean ± SD) | MBC (µg/mL) (Mean ± SD) |
|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | 40 ± 0 | 92 ± 17 |
| S. epidermidis | 38 ± 3 | 233 ± 33 |
| E. faecalis | 42 ± 8 | 83 ± 17 |
| K. pneumoniae | 40 ± 0 | 333 ± 33 |
| P. aeruginosa | 40 ± 0 | 133.± 33 |
| E. coli | 37± 3 | 75 ± 00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Binsalah, M.; Devanesan, S.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Nooh, A.; Alghamdi, O.; Nooh, N. Biomimetic Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Ethyl Acetate Extract of Urtica diocia Leaves; Characterizations and Emerging Antimicrobial Activity. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10040789
Binsalah M, Devanesan S, AlSalhi MS, Nooh A, Alghamdi O, Nooh N. Biomimetic Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Ethyl Acetate Extract of Urtica diocia Leaves; Characterizations and Emerging Antimicrobial Activity. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(4):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10040789
Chicago/Turabian StyleBinsalah, Mohammed, Sandhanasamy Devanesan, Mohamad S. AlSalhi, Abdullrahman Nooh, Osama Alghamdi, and Nasser Nooh. 2022. "Biomimetic Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Ethyl Acetate Extract of Urtica diocia Leaves; Characterizations and Emerging Antimicrobial Activity" Microorganisms 10, no. 4: 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10040789
APA StyleBinsalah, M., Devanesan, S., AlSalhi, M. S., Nooh, A., Alghamdi, O., & Nooh, N. (2022). Biomimetic Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Ethyl Acetate Extract of Urtica diocia Leaves; Characterizations and Emerging Antimicrobial Activity. Microorganisms, 10(4), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10040789









