Genomic Profiling of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolates from Surface Water of Agricultural Drainage in North-Western Mexico: Detection of the International High-Risk Lineages ST410 and ST617
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)
2.3. DNA Extraction, Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS), and Read Preprocessing
2.4. Genome Assembly and Annotation
2.5. Serotyping, Phylogrouping, Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST), Virulence, and Antimicrobial Resistance-Associated Genes
2.6. Plasmid Replicons and Prophages Regions
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genome Sequencing
3.2. Phylogroups, Serotype, and Sequence Types
3.3. Virulence-Associated Genes (VAGs)
3.4. Resistance Profile and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes (ARGs)
3.5. Detection of Plasmid Replicons and Prophages
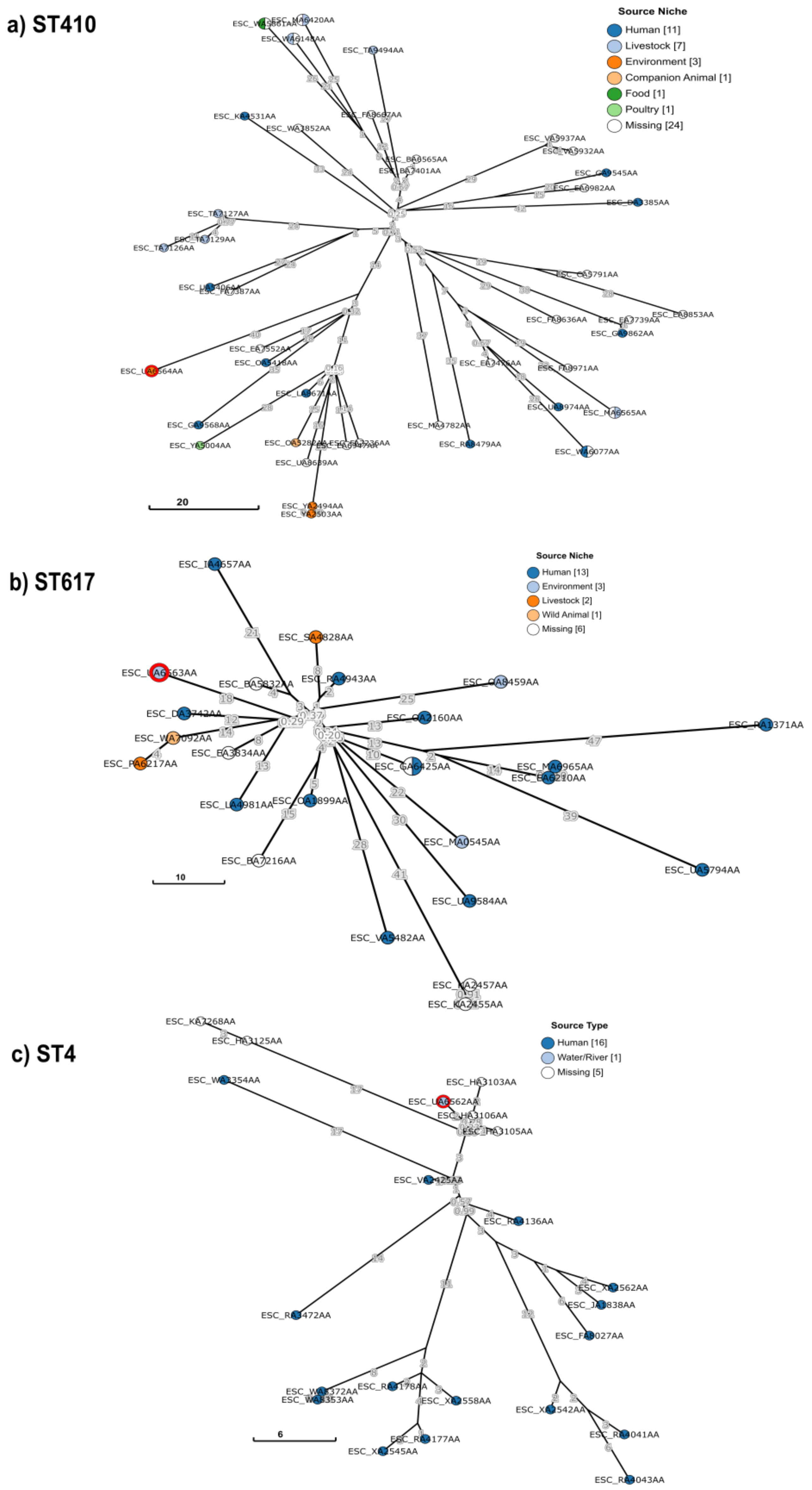
3.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Neill, J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations; HM Government and Wellcome Trust: London, UK, 2016.
- Aslam, B.; Wang, W.; Arshad, M.I.; Khurshid, M.; Muzammil, S.; Nisar, M.A.; Alvi, R.F.; Aslam, M.A.; Qamar, M.U.; Salamat, M.K.F.; et al. Antibiotic resistance: A rundown of a global crisis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglund, B. Environmental dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes and correlation to anthropogenic contamination with antibiotics. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2015, 5, 28564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwu, C.D.; Korsten, L.; Okoh, A.I. The incidence of antibiotic resistance within and beyond the agricultural ecosystem: A concern for public health. Microbiol. Open 2020, 9, e1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyi-Loh, C.; Mamphweli, S.; Meyer, E.; Okoh, A. Antibiotic Use in Agriculture and Its Consequential Resistance in Environmental Sources: Potential Public Health Implications. Molecules 2018, 23, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance 2014; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Castanheira, M.; Simner, P.J.; Bradford, P.A. Extended-spectrum β-lactamases: An update on their characteristics, epidemiology and detection. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 3, dlab092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaper, J.B.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L.T. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxen, M.; Finlay, B.B. Molecular mechanisms of Escherichia coli pathogenicity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leimbach, A.; Hacker, J.; Dobrindt, U. E. coli as an All-Rounder: The Thin Line Between Commensalism and Pathogenicity. In Between Pathogenicity and Commensalism; Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 358, pp. 3–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, S.; Ksoll, W.B.; Hicks, R.E.; Sadowsky, M.J. Presence and Growth of Naturalized Escherichia coli in Temperate Soils from Lake Superior Watersheds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymensen, L.; Pyrdok, F.; Coles, D.; Koning, W.; McAllister, T.A.; Jokinen, C.; Dowd, S.; Neumann, N. Comparative accessory gene fingerprinting of surface water Escherichia coli reveals genetically diverse naturalized population. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, F.Y.R.; González, F.J.A.; Garneau, P.; Díaz, F.M.; Barrera, A.L.G.; Harel, J. Presence of multi-drug resistant pathogenic Escherichia coli in the San Pedro River located in the State of Aguascalientes, Mexico. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, I.; Salinas, E.; Martínez, L.; Cruz-Córdova, A.; González-Pedrajo, B.; Espinosa, N.; Amábile-Cuevas, C.F. Characterization of Escherichia coli Isolates from an Urban Lake Receiving Water from a Wastewater Treatment Plant in Mexico City: Fecal Pollution and Antibiotic Resistance. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 71, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Gardea, M.C.E.; Tamez-Guerra, P.; Gomez-Flores, R.; De La Serna, F.J.Z.-D.; La Vega, G.E.-D.; Nevárez-Moorillón, G.V.; Pérez-Recoder, M.C.; Sánchez-Ramírez, B.; Gonzalez-Horta, C.; Infante-Ramírez, R. Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria Isolated from Surface Water in Bassaseachic Falls National Park, Mexico. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Orgániz, Á.; Garza-Ramos, U.; Sampedro-Rosas, M.L.; González-González, J.; Nava-Faustino, G.; Toribio-Jiménez, J. Patotipos y Resistencia a Antibióticos de Escherichia coli en Agua Residual. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2020, 36, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amábile-Cuevas, C.; Arredondo-García, J.; Cruz, A.; Rosas, I. Fluoroquinolone resistance in clinical and environmental isolates of Escherichia coli in Mexico City. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaidez, C.; Soto, M.; Martinez, C.; Keswick, B. Drinking water microbiological survey of the Northwestern State of Sinaloa, Mexico. J. Water Health 2008, 6, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cuevas, O.L.; Félix, J.L.; Edeza, M.J.; Quiroz, C.C. Detección y resistencia a antibióticos de Escherichia coli y Salmonella en agua y suelo agrícola. Rev. Fitotec. Mex. 2009, 32, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Ahumada-Santos, Y.P.; Báez-Flores, M.E.; Díaz-Camacho, S.P.; Uribe-Beltrán, M.D.J.; López-Angulo, G.; Vega-Aviña, R.; Chávez-Duran, F.A.; Montes-Avila, J.; Carranza-Díaz, O.; Möder, M.; et al. Spatiotemporal distribution of the bacterial contamination of agricultural and domestic wastewater discharged to a drainage ditch (Sinaloa, Mexico). Cienc. Mar. 2014, 40, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Canizalez-Roman, A.; Velazquez-Roman, J.; Valdez-Flores, M.A.; Flores-Villaseñor, H.; Vidal, J.E.; Muro-Amador, S.; Guadrón-Llanos, A.M.; Gonzalez-Nuñez, E.; Medina-Serrano, J.; Tapia-Pastrana, G.; et al. Detection of antimicrobial-resistance diarrheagenic Escherichia coli strains in surface water used to irrigate food products in the northwest of Mexico. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 304, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeder, M.; Carranza-Diaz, O.; López-Angulo, G.; Vega-Aviña, R.; Chávez-Durán, F.A.; Jomaa, S.; Winkler, U.; Schrader, S.; Reemtsma, T.; Delgado-Vargas, F. Potential of vegetated ditches to manage organic pollutants derived from agricultural runoff and domestic sewage: A case study in Sinaloa (Mexico). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI Standard M02; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests. 13th ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018; ISBN 1-56238-834-7.
- CLSI Supplement M100; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. 31st ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-68440-104-8.
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data; Babraham Institute: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasman, H.; Saputra, D.; Sicheritz-Ponten, T.; Lund, O.; Svendsen, C.A.; Frimodt-Møller, N.; Aarestrup, F.M. Rapid Whole-Genome Sequencing for Detection and Characterization of Microorganisms Directly from Clinical Samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosi, E.; Donati, B.; Galardini, M.; Brunetti, S.; Sagot, M.-F.; Lió, P.; Crescenzi, P.; Fani, R.; Fondi, M. MeDuSa: A multi-draft based scaffolder. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2443–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid Prokaryotic Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensen, K.G.; Tetzschner, A.M.; Iguchi, A.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Scheutz, F. Rapid and Easy in Silico Serotyping of Escherichia coli Isolates by Use of Whole-Genome Sequencing Data. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2410–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, T.; Falush, D.; Lan, R.; Colles, F.; Mensa, P.; Wieler, L.H.; Karch, H.; Reeves, P.R.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Ochman, H.; et al. Sex and virulence in Escherichia coli: An evolutionary perspective. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 60, 1136–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M.V.; Cosentino, S.; Rasmussen, S.; Friis, C.; Hasman, H.; Marvig, R.L.; Jelsbak, L.; Sicheritz-Ponten, T.; Ussery, D.W.; Aarestrup, F.M.; et al. Multilocus Sequence Typing of Total-Genome-Sequenced Bacteria. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensen, K.G.; Scheutz, F.; Lund, O.; Hasman, H.; Kaas, R.S.; Nielsen, E.M.; Aarestrup, F.M. Real-Time Whole-Genome Sequencing for Routine Typing, Surveillance, and Outbreak Detection of Verotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clermont, O.; Dixit, O.; Vangchhia, B.; Condamine, B.; Dion, S.; Bridier-Nahmias, A.; Denamur, E.; Gordon, D. Characterization and rapid identification of phylogroup G in Escherichia coli, a lineage with high virulence and antibiotic resistance potential. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 3107–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghain, J.; Bridier-Nahmias, A.; Le Nagard, H.; Denamur, E.; Clermont, O. ClermonTyping: An easy-to-use and accurate in silico method for Escherichia genus strain phylotyping. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; Garcìa-Fernández, A.; Larsen, M.V.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Hasman, H. In Silico Detection and Typing of Plasmids using PlasmidFinder and Plasmid Multilocus Sequence Typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, D.; Grant, J.R.; Marcu, A.; Sajed, T.; Pon, A.; Liang, Y.; Wishart, D.S. PHASTER: A better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W16–W21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.-F.; Mohamed, K.; Fan, Y.; the Agama Study Group; Achtman, M. The EnteroBase user’s guide, with case studies on Salmonella transmissions, Yersinia pestis phylogeny, and Escherichia core genomic diversity. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.-F.; Sergeant, M.J.; Luhmann, N.; Vaz, C.; Francisco, A.P.; Carriço, J.A.; Achtman, M. GrapeTree: Visualization of core genomic relationships among 100,000 bacterial pathogens. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mageiros, L.; Méric, G.; Bayliss, S.C.; Pensar, J.; Pascoe, B.; Mourkas, E.; Calland, J.K.; Yahara, K.; Murray, S.; Wilkinson, T.S.; et al. Genome evolution and the emergence of pathogenicity in avian Escherichia coli. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, R.J.; Dallman, T.J.; Allen, H.; De Silva, P.M.; Stenhouse, G.; Pulford, C.V.; Bennett, R.J.; Jenkins, C.; Baker, K.S. Accessory Genome Dynamics and Structural Variation of Shigella from Persistent Infections. mBio 2021, 12, e00254-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodford, N.; Turton, J.; Livermore, D.M. Multiresistant Gram-negative bacteria: The role of high-risk clones in the dissemination of antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 736–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petty, N.K.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Stanton-Cook, M.; Skippington, E.; Totsika, M.; Forde, B.M.; Phan, M.-D.; Moriel, D.G.; Peters, K.M.; Davies, M.; et al. Global dissemination of a multidrug resistant Escherichia coli clone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5694–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoesser, N.; Sheppard, A.; Pankhurst, L.; De Maio, N.; Moore, C.; Sebra, R.; Turner, P.; Anson, L.W.; Kasarskis, A.; Batty, L.; et al. Evolutionary History of the Global Emergence of the Escherichia coli Epidemic Clone ST131. mBio 2016, 7, e02162-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaufler, K.; Semmler, T.; Wieler, L.H.; Wöhrmann, M.; Baddam, R.; Ahmed, N.; Müller, K.; Kola, A.; Fruth, A.; Ewers, C.; et al. Clonal spread and interspecies transmission of clinically relevant ESBL-producing Escherichia coli of ST410—Another successful pandemic clone? FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiv155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falgenhauer, L.; Imirzalioglu, C.; Ghosh, H.; Gwozdzinski, K.; Schmiedel, J.; Gentil, K.; Bauerfeind, R.; Kämpfer, P.; Seifert, H.; Michael, G.B.; et al. Circulation of clonal populations of fluoroquinolone-resistant CTX-M-15-producing Escherichia coli ST410 in humans and animals in Germany. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 47, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roer, L.; Overballe-Petersen, S.; Hansen, F.; Schønning, K.; Wang, M.; Røder, B.L.; Hansen, D.S.; Justesen, U.S.; Andersen, L.P.; Fulgsang-Damgaard, D.; et al. Escherichia coli Sequence Type 410 Is Causing New International High-Risk Clones. mSphere 2018, 3, e00337-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, P.; Machado, J.; Peixe, L. Dissemination of sul3-Containing Elements Linked to Class 1 Integrons with an Unusual 3′ Conserved Sequence Region among Salmonella Isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáenz, Y.; Vinué, L.; Ruiz, E.; Somalo, S.; Martínez, S.; Rojo-Bezares, B.; Zarazaga, M.; Torres, C. Class 1 integrons lacking qacE∆1 and sul1 genes in Escherichia coli isolates of food, animal and human origins. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 144, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, R.A.; Holt, K.E.; Hall, R.M. pCERC3 from a commensal ST95 Escherichia coli: A ColV virulence-multiresistance plasmid carrying a sul3-associated class 1 integron. Plasmid 2016, 84–85, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Vo, H.-N.; Tran, P.T.-B.; Le, L.; Matsumoto, Y.; Motooka, D.; Nakamura, S.; Jones, J.W.; Iida, T.; Cao, V. Complex Class 1 Integron in a Clinical Escherichia coli Strain from Vietnam Carrying Both mcr-1 and blaNDM–1. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingali, T.; Reid, C.J.; Chapman, T.A.; Gaio, D.; Liu, M.; Darling, A.E.; Djordjevic, S.P. Whole Genome Sequencing Analysis of Porcine Faecal Commensal Escherichia coli Carrying Class 1 Integrons from Sows and Their Offspring. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Báez, J.; Hernández-García, M.; Guamparito, C.; Díaz, S.; Olave, A.; Guerrero, K.; Cantón, R.; Baquero, F.; Gahona, J.; Valenzuela, N.; et al. Molecular Characterization and Genetic Diversity of ESBL-Producing Escherichia coli Colonizing the Migratory Franklin’s Gulls (Leucophaeus pipixcan) in Antofagasta, North of Chile. Microb. Drug Resist. 2015, 21, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha-Gracia, R.C.; Cortés-Cortés, G.; Lozano-Zarain, P.; Bello, F.; Martínez-Laguna, Y.; Torres, C. Faecal Escherichia coli isolates from healthy dogs harbour CTX-M-15 and CMY-2 β-lactamases. Vet. J. 2015, 203, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, Z.; Fenn, S.; Connor, C.; Feng, Y.; McNally, A. Complete genomic characterization of two Escherichia coli lineages responsible for a cluster of carbapenem-resistant infections in a Chinese hospital. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 2340–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, T.; Cantamessa, R.; Melo, L.; Fernandes, M.R.; Fraga, E.; Dropa, M.; Sato, M.I.; Cerdeira, L.; Lincopan, N. International high-risk clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae KPC-2/CC258 and Escherichia coli CTX-M-15/CC10 in urban lake waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, D.F.; Sellera, F.P.; Fernandes, M.R.; Moura, Q.; Landgraf, M.; Lincopan, N. Genome Sequencing of an Escherichia coli Sequence Type 617 Strain Isolated from Beach Ghost Shrimp (Callichirus major) from a Heavily Polluted Ecosystem Reveals a Wider Resistome against Heavy Metals and Antibiotics. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e01471-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snesrud, E.; Ong, A.C.; Corey, B.; Kwak, Y.I.; Clifford, R.; Gleeson, T.; Wood, S.; Whitman, T.J.; Lesho, E.P.; Hinkle, M.; et al. Analysis of Serial Isolates of mcr-1-Positive Escherichia coli Reveals a Highly Active IS Apl1 Transposon. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00056-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zając, M.; Sztromwasser, P.; Bortolaia, V.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Cavaco, L.M.; Ziȩtek-Barszcz, A.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Wasyl, D. Occurrence and Characterization of mcr-1-Positive Escherichia coli Isolated from Food-Producing Animals in Poland, 2011–2016. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Yoon, K.-B.; Jeon, D.-Y.; Oh, S.-S.; Oh, K.-H.; Chung, G.T.; Kim, S.W.; Cho, S.-H. Consecutive Outbreaks of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli O6 in Schools in South Korea Caused by Contamination of Fermented Vegetable Kimchi. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2016, 13, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattabiraman, V.; Katz, L.S.; Chen, J.C.; McCullough, A.E.; Trees, E. Genome wide characterization of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli serogroup O6 isolates from multiple outbreaks and sporadic infections from 1975–2016. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartsev, N.N.; Fursova, N.K.; Pachkunov, D.M.; Bannov, V.A.; Eruslanov, B.V.; Svetoch, E.A.; Dyatlov, I.A. Molecular Characterization of Enterotoxin-Producing Escherichia coli Collected in 2011–2012, Russia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kwon, T.; Chung, S.-Y.; Jung, Y.-H.; Jung, S.-J.; Roh, S.-G.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, C.-H.; Kim, W.; Bak, Y.-S.; Cho, S.-H. Comparative genomic analysis and characteristics of NCCP15740, the major type of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in Korea. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadashi, M.; Sameni, F.; Bostanshirin, N.; Yaslianifard, S.; Khosravi-Dehaghi, N.; Nasiri, M.J.; Goudarzi, M.; Hashemi, A.; Hajikhani, B. Global prevalence and molecular epidemiology of mcr-mediated colistin resistance in Escherichia coli clinical isolates: A systematic review. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldaña-Ahuactzi, Z.; Cruz-Córdova, A.; Rodea, G.E.; Porta, H.; Navarro-Ocaña, A.; Eslava-Campos, C.; Cevallos, M.A.; Xicohtencatl-Cortes, J. Genome Sequence of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Strain FMU073332. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e01600-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Escherichia coli | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ADD147 | ADD167 | ADD183 | |
| Length (bp) | 4,748,629 | 4,637,520 | 4,865,392 |
| GC (%) | 50.74 | 50.94 | 50.77 |
| Coverage depth (×) | 60 | 60 | 44 |
| Contigs | 594 | 523 | 504 |
| Scaffolds (>300 bp) | 47 | 22 | 6 |
| No. coding sequence (CDS) | 4440 | 4278 | 4553 |
| Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) | 8 | 8 | 11 |
| Transfer RNA (tRNA) | 81 | 81 | 80 |
| Serotype | ONT:H9 a | O101:H10 | O6:H16 |
| Phylogroup | C | A | A |
| Sequence type (ST) | ST410 | ST617 | ST4 |
| Clonal complex (CC) | CC23 | CC10 | CC10 |
| Isolate | Antimicrobial Resistance Profile a | Acquired Antimicrobial Resistance Genes b | QRDR Mutations b | Plasmid Replicons c | Virulence Genes d | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-lactams | Aminoglycosides | Lincosamides | Multidrug Efflux System | Phenicols | Sulfonamides | Tetracycline | Trimethoprim | |||||
| ADD147 | AM, CB, CPF, CL, GE, NET, NOF, STX | blaTEM-1B | aadA1, aadA2, aph(3′)-Ia, aac(3)-IId | lnu(F) | mdf(A) | floR, cmlA1 | sul2, sul3 | tet(A) | dfrA12 | gyrA-S83L+D87N; parC-S80I; parE-S458A | Col(pHAD28), IncFIB(AP001918), IncFIC(FII), IncX1 | gad, hra, lpfA, papC, terC |
| ADD167 | AM, CB, CF, CFX, CPF, GE, NF, NOF, STX | blaCTX-M-15 | aac(3)-IIa, aadA5, aph(3″)-Ib, aph(6)-Id | - | mdf(A) | - | sul1, sul2 | tet(B) | dfrA17 | gyrA-S83L+D87N; parC-S80I; parE-S458A | Col(MG828), Col(pHAD28) | astA, capU, gad, iss |
| ADD183 | CPF | - | - | - | mdf(A) | - | - | - | - | gyrA-S83L | ColRNAI, IncFII(pCoo) | astA, capU, eatA, gad, iss, kpsE, kpsM_K15, ltcA, ompT, terC, traT |
| Isolate | Region | Length (kbp) | GC% | CDS | Phage (Hit Genes Counts) a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADD147 | 1 | 11.5 | 48.4 | 18 | Enterobacteria phage VT2phi_272 (2) |
| ADD167 | 1 | 40.4 | 50.6 | 50 | Enterobacteria phage BP-4795 (9) |
| 2 | 15.1 | 54.5 | 21 | Escherichia phage pro483 (18) | |
| ADD183 | 1 | 40.2 | 49.9 | 44 | Enterobacteria phage P88 (21) |
| 2 | 53.7 | 51.6 | 45 | Enterobacteria phage P88 (27) | |
| 3 | 25.6 | 49.8 | 22 | Enterobacteria phage P4 (9) | |
| 4 | 10.3 | 54.2 | 15 | Escherichia phage SH2026Stx1 (3) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magaña-Lizárraga, J.A.; Gómez-Gil, B.; Rendón-Maldonado, J.G.; Delgado-Vargas, F.; Vega-López, I.F.; Báez-Flores, M.E. Genomic Profiling of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolates from Surface Water of Agricultural Drainage in North-Western Mexico: Detection of the International High-Risk Lineages ST410 and ST617. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030662
Magaña-Lizárraga JA, Gómez-Gil B, Rendón-Maldonado JG, Delgado-Vargas F, Vega-López IF, Báez-Flores ME. Genomic Profiling of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolates from Surface Water of Agricultural Drainage in North-Western Mexico: Detection of the International High-Risk Lineages ST410 and ST617. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(3):662. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030662
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagaña-Lizárraga, José Antonio, Bruno Gómez-Gil, José Guadalupe Rendón-Maldonado, Francisco Delgado-Vargas, Inés Fernando Vega-López, and María Elena Báez-Flores. 2022. "Genomic Profiling of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolates from Surface Water of Agricultural Drainage in North-Western Mexico: Detection of the International High-Risk Lineages ST410 and ST617" Microorganisms 10, no. 3: 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030662
APA StyleMagaña-Lizárraga, J. A., Gómez-Gil, B., Rendón-Maldonado, J. G., Delgado-Vargas, F., Vega-López, I. F., & Báez-Flores, M. E. (2022). Genomic Profiling of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolates from Surface Water of Agricultural Drainage in North-Western Mexico: Detection of the International High-Risk Lineages ST410 and ST617. Microorganisms, 10(3), 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030662







