Circulation of SARS-CoV-2 Variants among Children from November 2020 to January 2022 in Trieste (Italy)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. RNA Isolation from NPS and SARS-CoV-2 Detection
2.3. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Real-Time PCR (RT–qPCR)
2.4. Sanger Sequencing of the SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain (RBD) Genomic Region
2.5. Next Generation Sequencing
2.6. Variation Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Whole Genome Sequencing
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.8. Cell Culture
2.9. Virus Isolation
2.10. Plaque Reduction Assay
2.11. Variant Strain Growth Curves: Kinetics of Infection
2.12. Tissue Culture Infectious Dose Assay
2.13. Microneutralization Assay
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Data of Study Children
3.2. Sequencing of the SARS-CoV-2 RBD Spike Region
3.3. Full Genome Sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.258 (∆H69/∆V70) and B.1.617.2+AY.43 by Next-Generation Sequencing
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
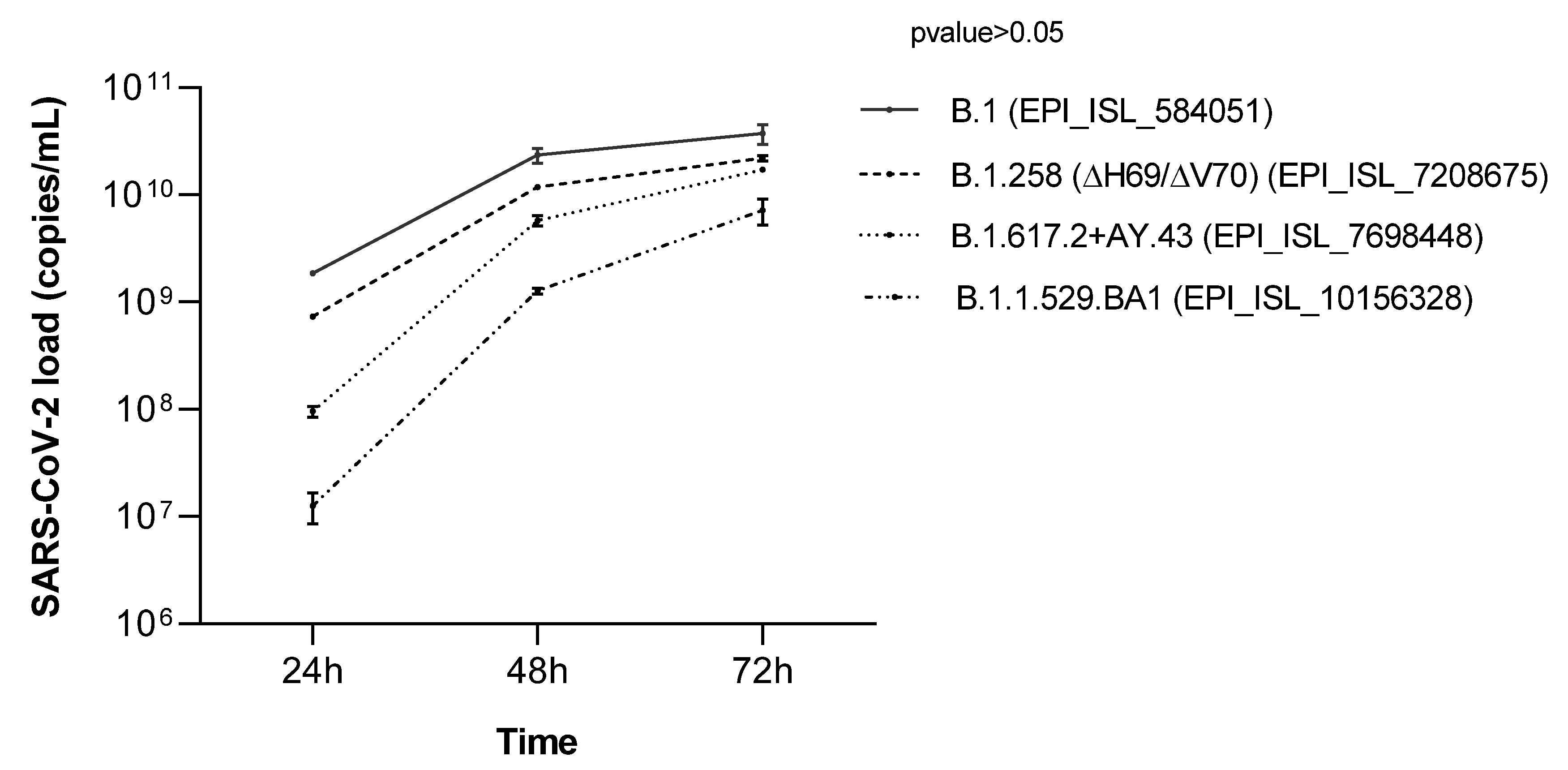
3.5. SARS-CoV-2 Isolates Growth Curves
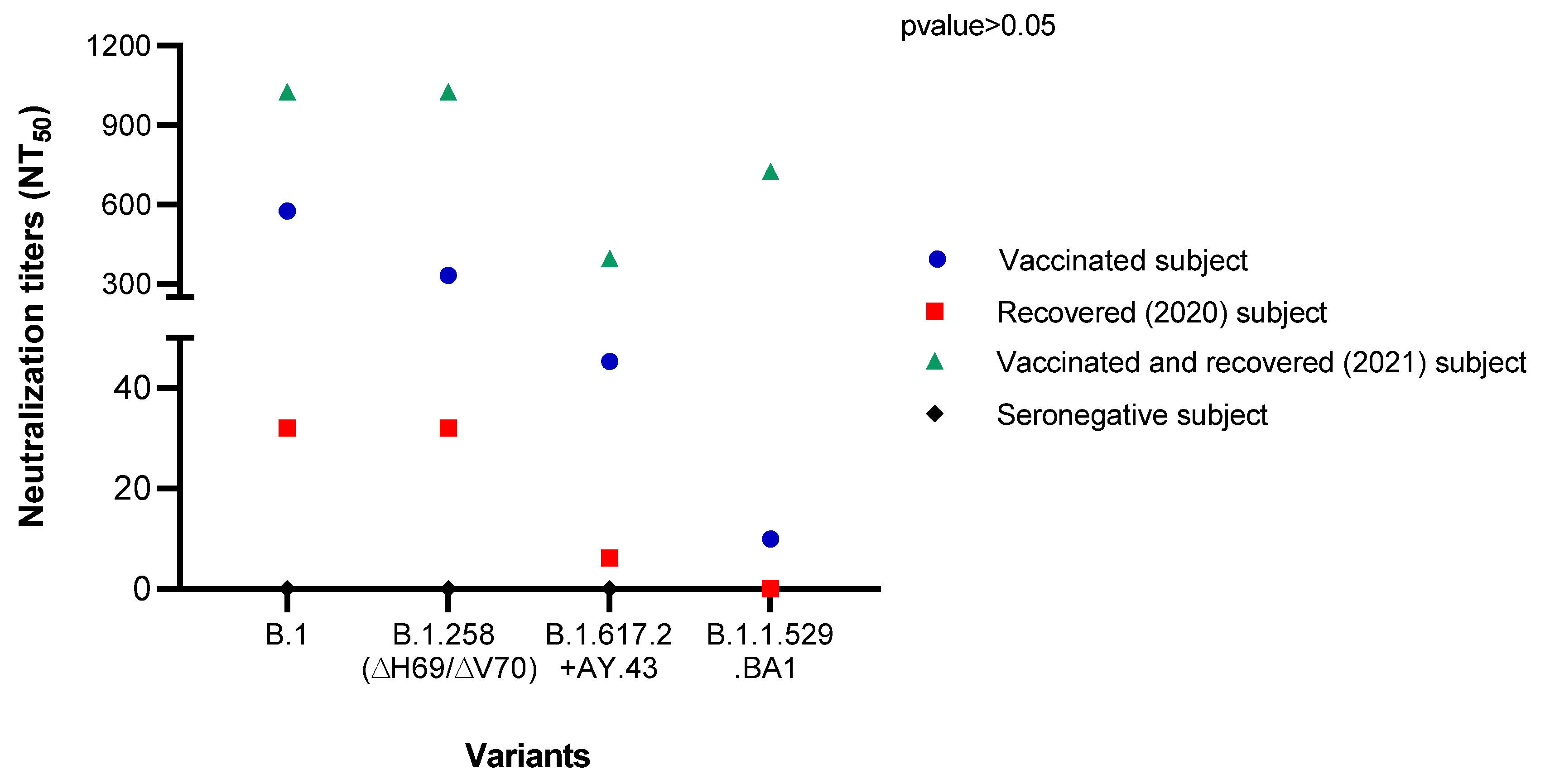
3.6. Microneutralization Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, H.; Wei, L.; Niu, P. The novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. Glob. Health Res. Policy 2020, 5, 2019–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, J. SARS-coV-2: An emerging coronavirus that causes a global threat. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1678–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajapakse, N.; Dixit, D. Human and novel coronavirus infections in children. Paediatr. Int. Child Health 2021, 41, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irfan, O.; Muttalib, F.; Tang, K.; Jiang, L.; Lassi, Z.S.; Bhutta, Z. Clinical characteristics, treatment and outcomes of paediatric COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2021, 106, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastin, C.; Eastin, T. Epidemiological characteristics of 2143 pediatric patients with 2019 coronavirus disease in China. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 58, 712–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunyavanich, S.; Do, A.; Vicencio, A. Nasal Gene Expression of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 in Children and Adults. JAMA 2020, 323, 2427–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percivalle, E.; Cambie, G.; Cassaniti, I.; Nepita, E.V.; Maserati, R.; Ferrari, A.; Di’Martino, R.; Isernia, P.; Mojoli, F.; Bruno, R.; et al. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 specific neutralising antibodies in blood donors from the Lodi Red Zone in Lombardy, Italy, as at 6 April 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2001031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Information for Pediatric Healthcare Providers. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/pediatric-hcp.html (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- Götzinger, F.; Santiago-Garcia, B.; Nogera-Julian, A.; Lanaspa, M.; Lancella, L.; Calo Carducci, F.I.; Gabrovska, N.; Velizarova, S.; Prunk, P.; Osterman, V.; et al. COVID-19 in children and adolescents in Europe: A multinational, multicentre cohort study. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Evaluation and Management Considerations for Neonates At Risk for COVID-19. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/caring-for-newborns.html (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Sinaci, S.; Ocal, D.F.; Seven, B.; Anuk, A.T.; Besimoglu, B.; Keven, M.C.; Ayhan, S.G.; Akin, M.S.; Tayman, C.; Keskin, H.L. Vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A prospective cross-sectional study from a tertiary center. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 5864–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhu, F.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Lu, X.; Ma, J.; et al. Children Infected With SARS-CoV-2 From Family Clusters. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somekh, I.; Stein, M.; Karakis, I.; Simões, E.A.F.; Somekh, E. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Israeli Children during the Circulation of Different SARS-CoV-2 Variants. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2124343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaythorpe, K.A.M.; Bhatia, S.; Mangal, T.; Unwin, H.J.U.; Imai, N.; Cuomo-Dannenburg, G.; Walters, C.E.; Jauneikaite, E.; Bayley, H.; Kont, M.D.; et al. Children’s role in the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review of early surveillance data on susceptibility, severity, and transmissibility. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Science Brief: Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in K-12 Schools and Early Care and Education Programs–Updated. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/science/science-briefs/transmission_k_12_schools.html (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Yonker, L.M.; Boucau, J.; Regan, J.; Choudhary, M.C.; Burns, M.D.; Young, N.; Farkas, E.J.; Davis, J.P.; Moschovis, P.P.; Kinane, T.B.; et al. Virologic features of SARS-CoV-2 infection in children. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard-Jones, A.R.; Bowen, A.C.; Danchin, M.; Koirala, A.; Sharma, K.; Yeoh, D.K.; Burgner, D.P.; Crawford, N.W.; Goeman, E.; Gray, P.E.; et al. COVID-19 in children: I. Epidemiology, prevention and indirect impacts. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2021, 58, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Available online: https://www.who.int/ (accessed on 22 February 2022).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/ (accessed on 23 February 2022).
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. Available online: https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 23 February 2022).
- BioEdit: A User-Friendly Biological Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Program for Windows 95/98/NT. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/2034992/BioEdit_a_user_friendly_biological_sequence_alignment_editor_and_analysis_program_for_Windows_95_98_NT (accessed on 23 February 2022).
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- GISAID. Available online: https://platform.gisaid.org/epi3/ (accessed on 23 February 2022).
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence Limits on Phylogenies: An Approach Using the Bootstrap. Int. J. Org. Evol. 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, M.A. Determination of 50% endpoint titer using a simple formula. World J. Virol. 2016, 5, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariën, J.; Ceulemans, A.; Michiels, J.; Heyndrickx, L.; Kerkhof, K.; Foque, N.; Widdowson, M.-A.; Mortgat, L.; Duysburgh, E.; Desombere, I.; et al. Evaluating SARS-CoV-2 spike and nucleocapsid proteins as targets for antibody detection in severe and mild COVID-19 cases using a Luminex bead-based assay. J. Virol. Methods 2021, 288, 114025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- cov-lineages.org. Pangolin. Available online: https://cov-lineages.org/resources/pangolin.html (accessed on 23 February 2022).
- Delbue, S.; D’Alessandro, S.; Signorini, L.; Dolci, M.; Pariani, E.; Bianchi, M.; Fattori, S.; Modenese, A.; Galli, C.; Eberini, I.; et al. Isolation of SARS-CoV-2 strains carrying a nucleotide mutation, leading to a stop codon in the ORF 6 protein. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern as of 24 February 2022. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/covid-19/variants-concern (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- European Medicines Agency. Comirnaty COVID-19 Vaccine: EMA Recommends Approval for Children Aged 5 to 11. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/comirnaty-covid-19-vaccine-ema-recommends-approval-children-aged-5-11 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Lai, A.; Bergna, A.; Menzo, S.; Zehender, G.; Caucci, S.; Ghisetti, V.; Rizzo, F.; Maggi, F.; Cerutti, F.; Giurado, G.; et al. Circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants in Italy, October 2020–March 2021. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.J.; Chiba, S.; Halfmann, P.; Ehre, C.; Kuroda, M.; Dinnon, K.H., III; Leist, S.R.; Schafer, A.; Nakajima, N.; Takahashi, K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 D614G variant exhibits efficient replication ex vivo and transmission in vivo. Science 2020, 370, 1464–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurkovetskiy, L.; Wang, X.; Pascal, K.E.; Tomkins-Tinch, C.; Nyalile, T.P.; Wang, Y.; Baum, A.; Diehl, W.E.; Dauphin, A.; Carbone, C. Structural and Functional Analysis of the D614G SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Variant. SSRN Electron. J. 2020, 183, 729–751. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, W.T.; Carabelli, A.; Jackson, B.; Gupta, R.; Thomson, E.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Ludden, C.; Reeve, R.; Rambaut, A.; Peacock, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, E.C. Circulating SARS-CoV-2 spike N439K variants maintain fitness while evading antibody-mediated immunity. Cell 2021, 184, 1171–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Q. Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2. Science 2020, 367, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piccoli, L.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Czudnochowski, N.; Walls, A.C.; Beltramello, M.; Silacci-Fregni, C.; Pinto, D.; Rosen, L.E.; Bowen, J.E.; et al. Mapping Neutralizing and Immunodominant Sites on the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain by Structure-Guided High-Resolution Serology. Cell 2020, 183, 1024–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brejová, B.; Boršová, K.; Hodorová, V.; Čabanová, V.; Reizigová, L.; Paul, E.D.; Čekan, P.; Klempa, B.; Nosek, J.; Vinař, T. A SARS-CoV-2 mutant from B.1.258 lineage with ∆H69/∆V70 deletion in the Spike protein circulating in Central Europe in the fall 2020. Virus Genes 2021, 57, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Plante, K.S.; Plante, J.A.; Xie, X.; Zhang, X.; Ku, Z.; An, Z.; Scharton, D.; Schindewolf, C.; et al. The N501Y spike substitution enhances SARS-CoV-2 infection and transmission. Nature 2021, 602, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, B.; Kemp, S.A.; Papa, G.; Datir, R.; Ferreira, I.A.; Marelli, S.; Harvey, W.T.; Lytras, S.; Mohamed, A.; Gallo, G.; et al. Recurrent emergence of SARS-CoV-2 spike deletion H69/V70 and its role in the Alpha variant B.1.1.7. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, Y.; Kimura, I.; Uriu, K.; Fukushi, M.; Irie, T.; Koyanagi, Y.; Sauter, D.; Gifford, R.J.; USFQ-COVID19 Consortium; Nakagawa, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 ORF3b Is a Potent Interferon Antagonist Whose Activity Is Increased by a Naturally Occurring Elongation Variant. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Dong, X.; Ma, R.; Wang, W.; Xiao, X.; Tian, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Ren, L.; et al. Activation and evasion of type I interferon responses by SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, C.; Smulian, S.A.; Rasmussen, M.D. Evasion of Type I Interferon by SARS-CoV-2. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Nemudryi, A.; Nemudraia, A.; Wiegand, T.; Nichols, J.; Snyder, D.T.; Hedges, J.F.; Cicha, C.; Lee, H.; Vanderwood, K.K.; Bimczok, D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 genomic surveillance identifies naturally occurring truncation of ORF7a that limits immune suppression. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodcroft, E.B.; Zuber, M.; Nadeau, S.; Vaughan, T.G.; Crawford, K.H.D.; Althaus, C.L.; Reichmuth, M.L.; Bowen, J.E.; Walls, A.C.; Corti, D.; et al. Spread of a SARS-CoV-2 variant through Europe in the summer of 2020. Nature 2021, 595, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genomic Epidemiology of Novel Coronavirus–Global Subsampling. Available online: https://nextstrain.org/ncov/gisaid/global?c=gt-S_477&gmax=24271&gmin=22482 (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Greaney, A.J.; Loes, A.N.; Crawford, K.H.D.; Starr, T.N.; Malone, K.D.; Chu, H.Y.; Bloom, J.D. Comprehensive mapping of mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain that affect recognition by polyclonal human plasma antibodies. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortorici, M.A.; Beltramello, M.; Lempp, F.A.; Pinto, D.; Dang, H.V.; Rosen, L.E.; McCallum, M.; Bowen, J.; Minola, A.; Jaconi, S.; et al. Ultrapotent human antibodies protect against SARS-CoV-2 challenge via multiple mechanisms. Science 2020, 370, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. What You Need to Know About Variants. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/variants/variant.html (accessed on 23 February 2022).
- Molteni, E.; Sudre, C.H.; Canas, L.S.; Bhopal, S.S.; Hughes, R.C.; Chen, L.; Deng, J.; Murray, B.; Kerfoot, E.; Antonelli, M.; et al. Illness characteristics of COVID-19 in children infected with the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planas, D.; Veyer, D.; Baidaliuk, A.; Staropoli, I.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Rajah, M.M.; Planchais, C.; Porrot, F.; Robillard, N.; Puech, J.; et al. Reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta to antibody neutralization. Nature 2021, 596, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planas, D.; Saunders, N.; Maes, P.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Planchais, C.; Buchrieser, J.; Bolland, W.H.; Porrot, F.; Staropoli, I.; Lemoine, F.; et al. Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to antibody neutralization. Nature 2021, 602, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muik, A.; Lui, B.G.; Wallisch, A.K.; Bacher, M.; Mühl, J.; Reinholz, J.; Ozhelvaci, O.; Beckmann, N.; Güimil Garcia, R.C.; Poran, A.; et al. Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron by BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine-elicited human sera. Science 2022, 375, 678–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, G.; Yuan, C.; Yang, Y.; Ling, G.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, T.; Lin, W.; Lin, Z. Progress in the diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19 in children: A review. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 8097–8108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, K.L.; Yang, Y.H.; Jiang, R.M.; Wang, T.Y.; Zhao, D.C.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, X.X.; Jin, R.M.; Zheng, Y.J.; Xu, B.P.; et al. Updated diagnosis, treatment and prevention of COVID-19 in children: Experts ’ consensus statement (condensed version of the second edition). World J. Pediatr. 2020, 16, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Primer | Position * | Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| SARS-CoV-2 S-F5 | 22775-22801 | GATGAAGTCAGACAAATCGCTCCAGG |
| SARS-CoV-2 S-R6 | 23641-23668 | TGCCTACACTATGTCACTTGGTGCAGAA |
| Patient | Gender | Age | Clinical Symptoms | Viral Load (Copies/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | F | 13 years | Fever | 2.50 × 107 |
| #2 | F | 11 years | Fever | 2.50 × 106 |
| #3 | M | 8 months | Neutropenic fever | 2.50 × 108 |
| #4 | M | 15 months | Fever | 2.50 × 107 |
| #5 | F | 14 months | Fever | 2.50 × 107 |
| #6 | F | 1 month | Fever | 2.50 × 107 |
| #7 | F | 21 months | Fever | 2.50 × 106 |
| #8 | F | 7 months | Fever | 2.50 × 107 |
| #9 | M | 8 months | Fever, rhinitis | 2.50 × 105 |
| #10 | F | 5 months | Fever | 2.50 × 108 |
| #11 | M | 20 months | Fever | 2.50× 105 |
| #12 | F | 13 months | Fever | 2.50 × 105 |
| #13 | M | 11 months | Fever | 2.50 × 104 |
| #14 | M | 4 months | Fever | 2.50 × 105 |
| #15 | F | 8 years | Fever, pharyngodynia | 2.50 × 108 |
| #16 | M | 2 months | Fever | 2.50 × 107 |
| #17 | M | 13 years | Fever | 2.50 × 108 |
| #18 | M | 10 years | Fever | 2.50 × 107 |
| #19 | F | 10 years | Fever | 2.50 × 107 |
| #20 | F | 13 years | Fever, headache | 2.50 × 107 |
| #21 | F | 11 years | Fever | 2.50 × 108 |
| #22 | F | 10 years | Fever, headache | 2.50 × 108 |
| #23 | M | 13 years | Fever, vomit | 2.50 × 107 |
| #24 | F | 13 years | Fever | 2.50 × 108 |
| #25 | M | 7 years | Fever | 2.50 × 108 |
| #26 | M | 1 day | Fever | 2.50 × 103 |
| #27 | F | 3 months | Fever | 2.50 × 107 |
| #28 | M | 11 years | Fever | 2.50 × 107 |
| #29 | M | 18 months | Fever | 2.50 × 107 |
| #30 | M | 2 months | Fever | 2.50 × 107 |
| #31 | F | 9 years | Fever | 2.50 × 107 |
| #32 | M | 12 years | Asymptomatic | 2.50 × 107 |
| Sequence ID | Nucleotide Mutations | Amino Acid Mutations | GISAID ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | C22987T, A23403G | Synon, D614G | EPI_ISL_1589116 |
| #2 | G22992A, A23403G | S477N, D614G | EPI_ISL_1589117 |
| #3 | A23403G | D614G | EPI_ISL_1589118 |
| #4 | A23403G | D614G | EPI_ISL_1589119 |
| #5 | A23403G | D614G | EPI_ISL_1589120 |
| #6 | C22987T, Ins C (23056) A23403G | Synon, - D614G | EPI_ISL_1589121 |
| #7 | A23403G | D614G | EPI_ISL_1589122 |
| #8 | T23047C, A23403G | Synon, D614G | EPI_ISL_1589123 |
| #9 | C22879A, A23403G | N439K, D614G | EPI_ISL_1589124 |
| #10 | C22879A, A23403G | N439K, D614G | EPI_ISL_1589125 |
| #11 | A23403G | D614G | EPI_ISL_1589126 |
| #12 | C22987T, A23403G | Synon, D614G | EPI_ISL_1589127 |
| #13 | C23230T, A23403G | Synon, D614G | EPI_ISL_1589128 |
| #14 | A23403G | D614G | EPI_ISL_1589129 |
| #15 | A23403G | D614G | EPI_ISL_1589130 |
| #16 | A23403G | D614G | EPI_ISL_1589131 |
| #17 | A23403G | D614G | EPI_ISL_1589133 |
| #18 | A23403G | D614G | EPI_ISL_1589135 |
| #19 | T22831C, A23403G | Synon, D614G | EPI_ISL_1589134 |
| #20 | A23403G | D614G | EPI_ISL_1589132 |
| #21 | A23403G | D614G | EPI_ISL_1589136 |
| #22 | A23403G | D614G | EPI_ISL_1589138 |
| #23 | A23403G | D614G | EPI_ISL_1589137 |
| #24 | C22747T, C22879A A23403G | Synon, N439K D614G | EPI_ISL_1589139 |
| #25 | T22917G, C22995A A23403G, C23604G | L452R, T478K D614G, P681R | EPI_ISL_5409853 |
| #26 | T22917G, C22995A A23403G, C23604G | L452R, T478K D614G, P681R | EPI_ISL_8063575 |
| #27 | T22917G, C22995A A23403G, C23604G | L452R, T478K D614G, P681R | EPI_ISL_8063576 |
| #28 | T22917G, C22995A A23403G, C23577T, C23604G | L452R, T478K D614G, A672V P681R | EPI_ISL_8063573 |
| #29 | T22917G, C22995A A23403G, C23604G | L452R, T478K D614G, P681R | EPI_ISL_8063479 |
| #30 | T22917G, C22995A A23403G, C23604G | L452R, T478K D614G, P681R | EPI_ISL_8063577 |
| #31 | T22917G, C22995A A23403G, C23604G | L452R, T478K D614G, P681R | EPI_ISL_8063577 |
| #32 | T22882G, G22898A G22992A, C22995A A23013C, A23040G G23048A, A23055G A23063T, T23075C C23202A, A23403G C23525T, T23599G C23604A | N440K, G446S S477N, T478K E484A, Q493R G496S, Q498R N501Y, Y505H T547K, D614G H655Y, N679K P681H | EPI_ISL_10156328 |
| Nucleotide Position | EPI_ISL_7208675 | Reference NC_045512 | Gene | Variant Type | Amino Acid Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 241 | C | T | Intergenic | Non coding | |
| 885 | G | A | ORF1ab | Non syn | R207H |
| 3037 | C | T | ORF1ab | Syn | F924 |
| 5950 | G | T | ORF1ab | Non syn | K1895N |
| 7767 | T | C | ORF1ab | Non syn | I2501T |
| 8047 | C | T | ORF1ab | Syn | Y2594 |
| 12,988 | G | T | ORF1ab | Non syn | M4241I |
| 14,064 | T | C | ORF1ab | Syn | D4600 |
| 14,408 | C | T | ORF1ab | Non syn | P4715L |
| 15,598 | G | A | ORF1ab | Non syn | V5112I |
| 17,104 | C | T | ORF1ab | Non syn | H5614Y |
| 18,028 | G | T | ORF1ab | Non syn | A5922S |
| 19,032 | C | T | ORF1ab | Syn | D6256 |
| 20,268 | A | G | ORF1ab | Syn | L6668 |
| 21,764 | ATACATG | A | S | Deletion | H69Δ, V70Δ |
| 21,786 | G | T | S | Non syn | G75V |
| 22,747 | C | T | S | Syn | V395 |
| 22,879 | C | A | S | Non syn | N439K |
| 23,403 | A | G | S | Non syn | D614G |
| 24,910 | T | C | S | Syn | T1116 |
| 26,972 | T | C | M | Syn | R150 |
| 27,505 | G | T | ORF7a | Stop | G38 * |
| 27,800 | C | A | ORF7b | Syn | A15 |
| 29,734 | G | C | Intergenic | Non coding |
| Nucleotide Position | EPI_ISL_7698448 | Reference NC_045512 | Gene | Variant Type | Amino Acid Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 210 | T | G | Intergenic | Non coding | |
| 241 | T | C | Intergenic | Non coding | |
| 3037 | T | C | ORF1ab | Syn | F924 |
| 4181 | T | G | ORF1ab | Non syn | A1306S |
| 5691 | T | C | ORF1ab | Non syn | A1809V |
| 6402 | T | C | ORF1ab | Non syn | P2046L |
| 7124 | T | C | ORF1ab | Non syn | P2287S |
| 8986 | T | C | ORF1ab | Syn | D2907 |
| 9053 | T | G | ORF1ab | Non syn | V2930L |
| 10,029 | T | C | ORF1ab | Non syn | T3255I |
| 11,201 | G | A | ORF1ab | Non syn | T3646A |
| 11,332 | G | A | ORF1ab | Syn | V3689 |
| 14,408 | T | C | ORF1ab | Non syn | P4715L |
| 15,451 | A | G | ORF1ab | Non syn | G5063S |
| 15,952 | A | C | ORF1ab | Non syn | L5230I |
| 16,466 | T | C | ORF1ab | Non syn | P5401L |
| 19,220 | T | C | ORF1ab | Non syn | A6319V |
| 21,618 | G | C | S | Non syn | T19R |
| 21,987 | A | G | S | Non syn | G142D |
| 22,028 | G | GAGTTCA | S | Deletion | EFR156G F157Δ, R158Δ |
| 22,917 | G | T | S | Non syn | L452R |
| 22,995 | A | C | S | Non syn | T478K |
| 23,403 | G | A | S | Non syn | D614G |
| 23,604 | G | C | S | Non syn | P681R |
| 24,124 | A | G | S | Syn | K854 |
| 24,410 | A | G | S | Non syn | D950N |
| 25,469 | T | C | ORF3a | Non syn | S26L |
| 26,767 | C | T | M | Non syn | I82T |
| 27,638 | C | T | ORF7a | Non syn | V82A |
| 27,752 | T | C | ORF7a | Non syn | T120I |
| 27,874 | T | C | ORF7b | Non syn | T40I |
| 28,002 | C | T | ORF8 | Non syn | C37R |
| 28,247 | A | AGATTTC | ORF8 | Deletion | D119Δ, F120Δ |
| 28,270 | T | TA | Intergenic | Non coding | |
| 28,299 | T | A | N | Non syn | Q9L |
| 28,461 | G | A | N | Non syn | D63G |
| 28,881 | T | G | N | Non syn | R203M |
| 28,916 | T | G | N | Non syn | G215C |
| 29,402 | T | G | N | Non syn | D377Y |
| 29,742 | T | G | Intergenic | Non coding |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dolci, M.; Signorini, L.; Cason, C.; Campisciano, G.; Kunderfranco, P.; Pariani, E.; Galli, C.; Petix, V.; Ferrante, P.; Delbue, S.; et al. Circulation of SARS-CoV-2 Variants among Children from November 2020 to January 2022 in Trieste (Italy). Microorganisms 2022, 10, 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030612
Dolci M, Signorini L, Cason C, Campisciano G, Kunderfranco P, Pariani E, Galli C, Petix V, Ferrante P, Delbue S, et al. Circulation of SARS-CoV-2 Variants among Children from November 2020 to January 2022 in Trieste (Italy). Microorganisms. 2022; 10(3):612. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030612
Chicago/Turabian StyleDolci, Maria, Lucia Signorini, Carolina Cason, Giuseppina Campisciano, Paolo Kunderfranco, Elena Pariani, Cristina Galli, Vincenzo Petix, Pasquale Ferrante, Serena Delbue, and et al. 2022. "Circulation of SARS-CoV-2 Variants among Children from November 2020 to January 2022 in Trieste (Italy)" Microorganisms 10, no. 3: 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030612
APA StyleDolci, M., Signorini, L., Cason, C., Campisciano, G., Kunderfranco, P., Pariani, E., Galli, C., Petix, V., Ferrante, P., Delbue, S., & Comar, M. (2022). Circulation of SARS-CoV-2 Variants among Children from November 2020 to January 2022 in Trieste (Italy). Microorganisms, 10(3), 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030612







