The Evaluation of Bacterial Abundance and Functional Potentials in the Three Major Watersheds, Located in the Hot Spring Zone of the Tatun Volcano Group Basin, Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
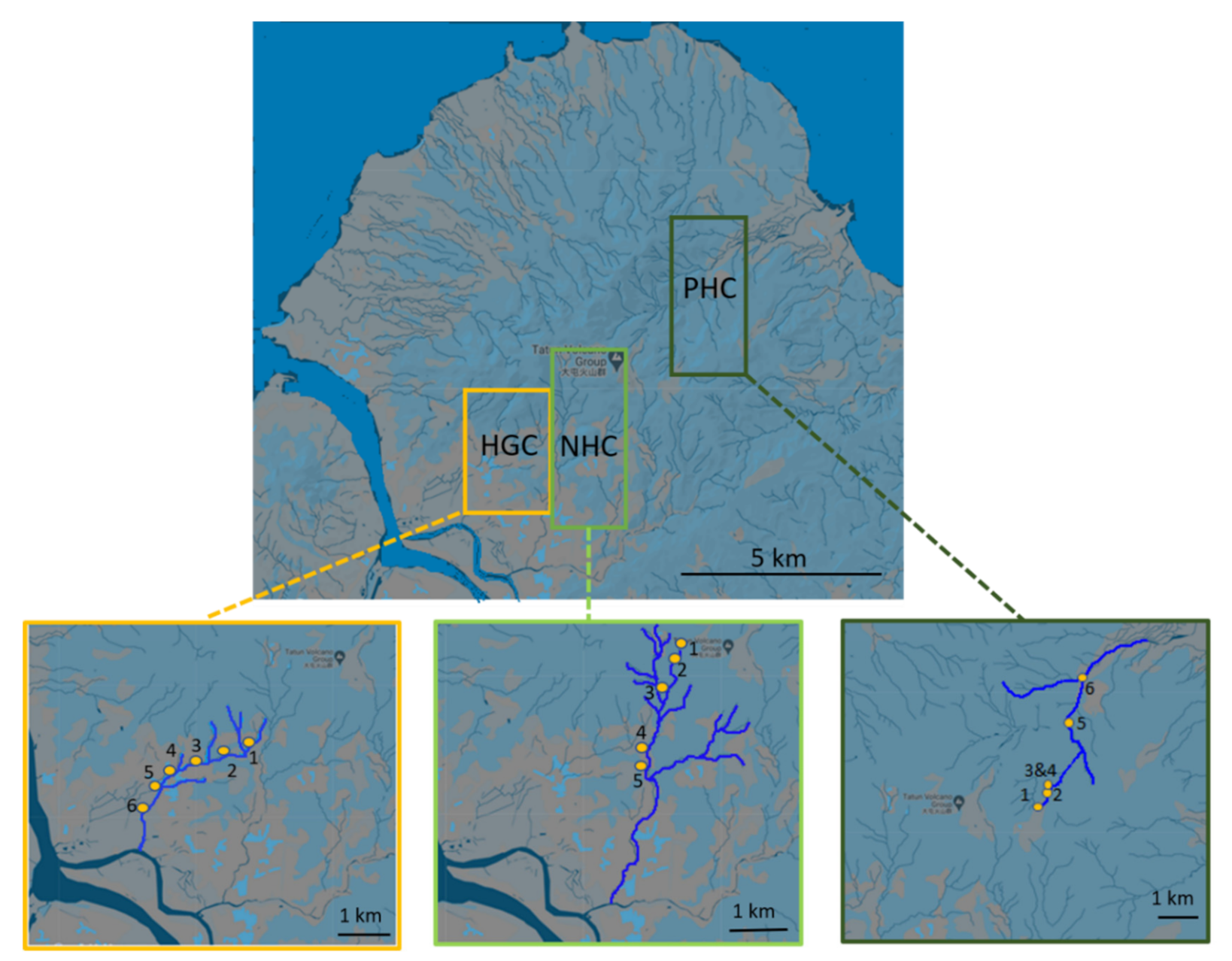
2.1. Sample Site Description and Sampling Details
2.2. Physicochemical Properties of the Sampling Sites
2.3. Microbial DNA Extraction
2.4. 16S rRNA Amplicon Sequencing, Library Construction, and Data Analyses
2.5. Metabolic Functional Prediction of the Bacterial Communities
3. Results
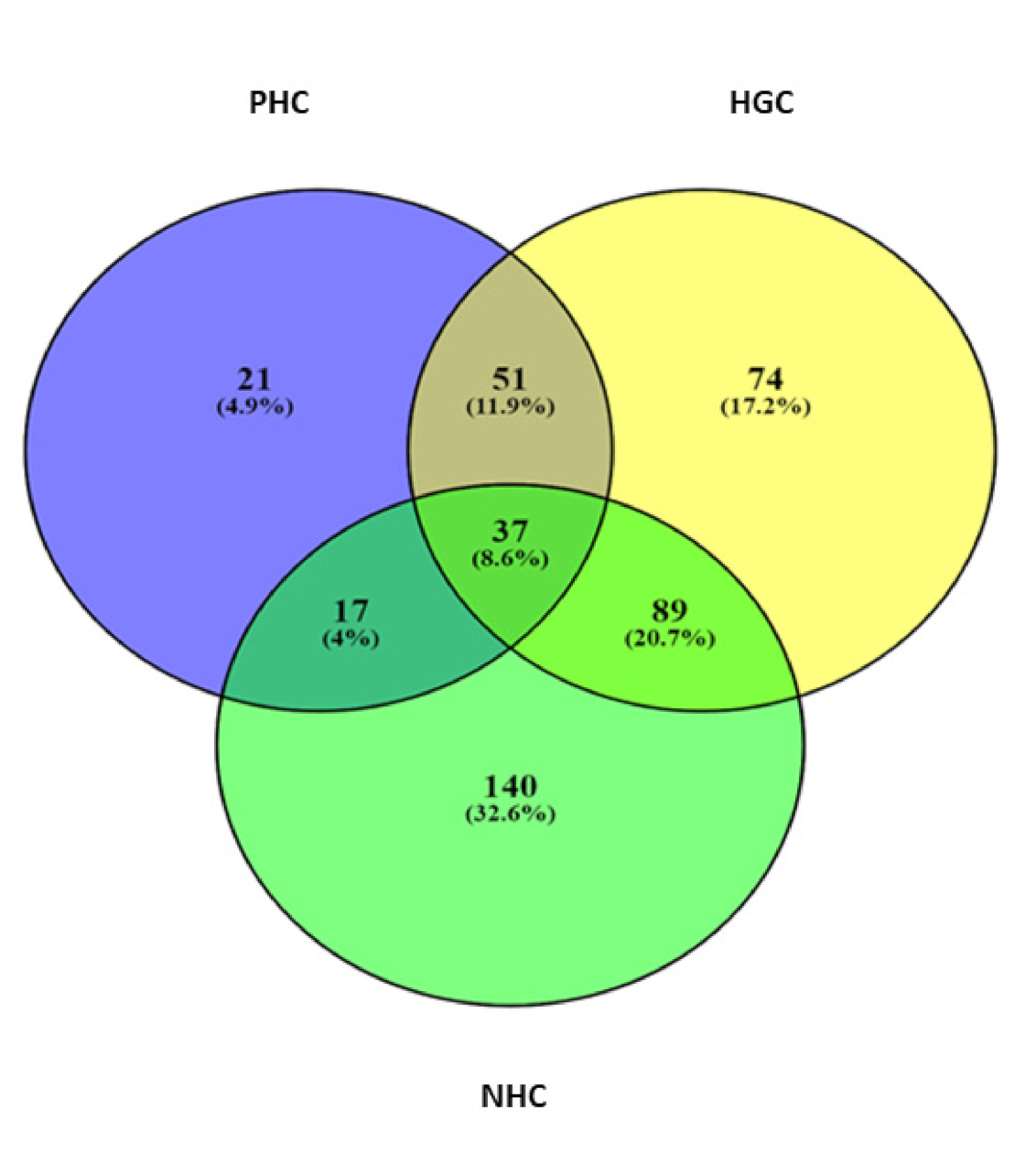
3.1. Sequence Depth, ASV Analysis, and Bacterial Diversity
3.2. Bacterial Abundance Based on 16SrRNA Gene Amplicons
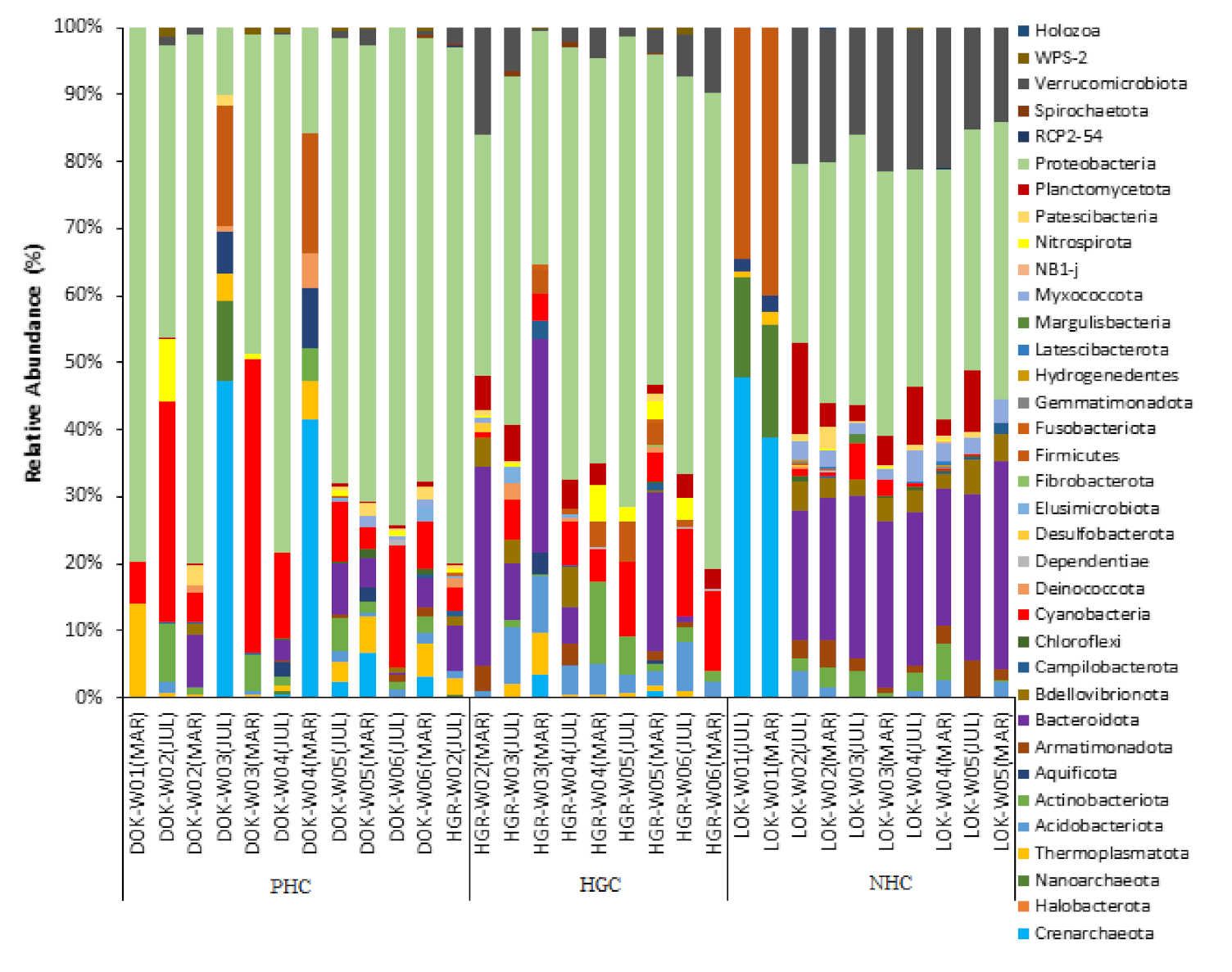
3.2.1. Phylum Level Bacterial Abundance
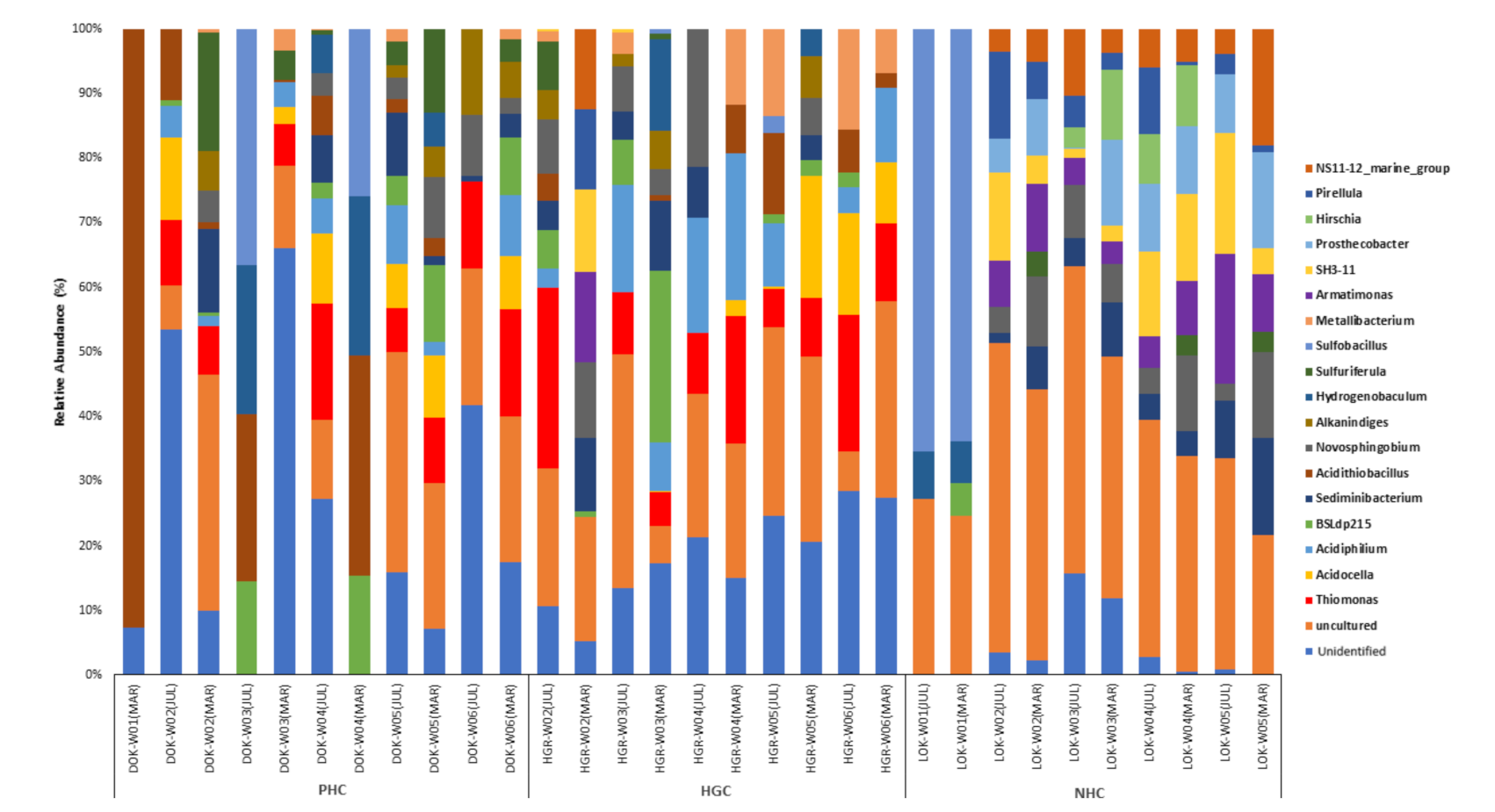
3.2.2. Genus Level Bacterial Abundance
3.2.3. LEfSe Analysis of Differential Bacterial Abundance
3.3. Metabolic Functional Prediction of the Bacterial Community
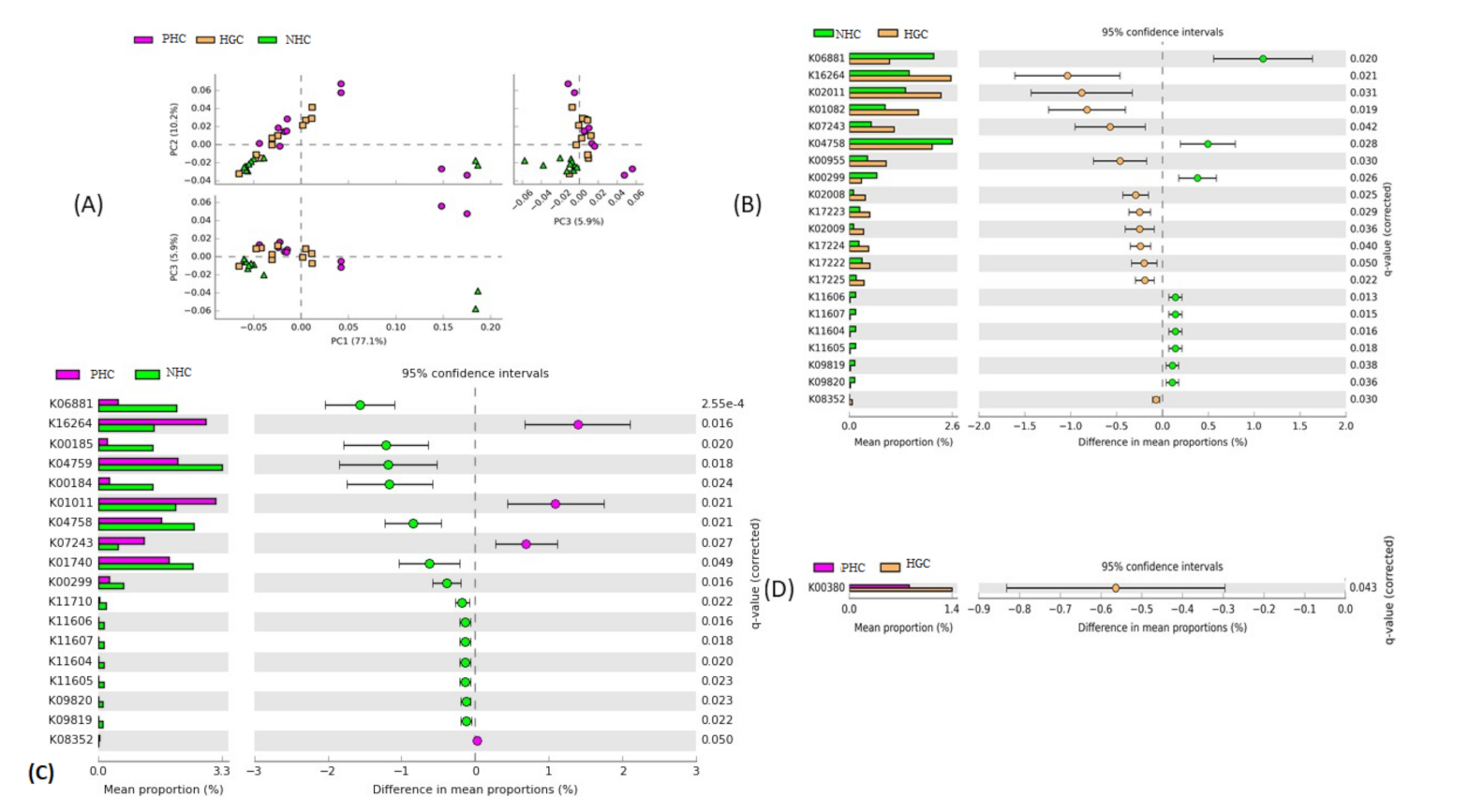
3.3.1. PCA and Shift Analysis
3.3.2. Correlation between the Significant Bacterial Genera and Predicted Metabolic Functions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brock, T.D. The value of basic research: Discovery of Thermus aquaticus and other extreme thermophiles. Genetics 1997, 146, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, E.; Higashi, K.; Mori, H.; Suda, K.; Nakamura, H.; Omori, S.; Maruyama, S.; Hongoh, Y.; Kurokawa, K. The relationship between microbial community structures and environmental parameters revealed by metagenomic analysis of hot spring water in the Kirishima Area, Japan. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirajno, F. Subaerial hot springs and near-surface hydrothermal mineral systems past and present, and possible extraterrestrial analogues. Geosci. Front. 2020, 11, 1549–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Des Marais, D.J.; Walter, M.R. Terrestrial hot spring systems: Introduction. Astrobiology 2019, 19, 1419–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podar, P.T.; Yang, Z.; Björnsdóttir, S.H.; Podar, M. Comparative analysis of microbial diversity across temperature gradients in hot springs from yellowstone and Iceland. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousk, J.; Bengtson, P. Microbial regulation of global biogeochemical cycles. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, M.C.; Aitchison, J.C.; Pointing, S.B. Bacterial community composition in thermophilic microbial mats from five hot springs in central Tibet. Extremophiles 2009, 13, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.S.; Albrecht, H.L.; Dawson, K.S.; Schaperdoth, I.; Freeman, K.H.; Pi, Y.; Pearson, A.; Macalady, J.L. Community genomic analysis of an extremely acidophilic sulfur-oxidizing biofilm. ISME J. 2012, 6, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Shoji, J.; Ohsawa, S.; Mishima, T.; Hata, M.; Honda, H.; Fujii, M.; Taniguchi, M. Hot spring drainage impact on fish communities around temperate estuaries in southwestern Japan. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 11, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburto-Medina, A.; Shahsavari, E.; Cohen, M.; Mantri, N.; Ball, A.S. Analysis of the microbiome (bathing biome) in geothermal waters from an Australian Balneotherapy Centre. Water 2020, 12, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanatani, J.-i.; Isobe, J.; Norimoto, S.; Kimata, K.; Mitsui, C.; Amemura-Maekawa, J.; Kura, F.; Sata, T.; Watahiki, M. Prevalence of Legionella species isolated from shower water in public bath facilities in Toyama Prefecture, Japan. J. Infect. Chemother. 2017, 23, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, K.Y.; Lin, K.C.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, T.-K.; Wang, M.K. Arsenic and lead (beudantite) contamination of agricultural rice soils in the Guandu Plain of northern Taiwan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.-H.; Yeh, H.-F. Factors Controlling of thermal water hydrogeochemical characteristics in Tatun Volcano Group, Taiwan. Water 2020, 12, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.-C.; Pi, J.-L.; You, C.-F.; Shieh, Y.-T.; Lu, H.-Y.; Huang, K.-F.; Liu, H.-C.; Chung, C.-H. Hydrogeology constrained by multi-isotopes and volatiles geochemistry of hot springs in Tatun Volcanic Group, Taiwan. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.-H.; Wang, S.-W.; Maji, S.K.; Liu, C.-W.; Wang, P.-L.; Chang, F.-J.; Liao, C.-M. Hydrochemical, mineralogical and isotopic investigation of arsenic distribution and mobilization in the Guandu wetland of Taiwan. J. Hydrol. 2013, 498, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Konstantinou, K.; Liang, W.; Pu, H.; Lin, Y.; You, S.; Huang, Y. Preliminary analysis of volcanoseismic signals recorded at the Tatun Volcano Group, northern Taiwan. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L10313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, B. Preliminary Study of Heavy Metal Pollution from Fe-Al Oxides in Peihuang Creek, North Taiwan. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–7 December 2012; p. H43E-1391. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.-Y. Application of water chemistry as a hydrological tracer in a volcano catchment area: A case study of the Tatun Volcano Group, North Taiwan. J. Hydrol. 2014, 511, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-Y. Using Pb Isotope as an indicator of the source of Arsenic Pollution. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria, 4–13 April 2018; p. 2129. [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao, Y.H. Hydrochemical Study of Huanggang Creek and South Huangg Creek Using Rare Earth Elements as a Natural Tracer; National Chung Cheng University: Minxiong, Taiwan, 2015. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, H.-C.; Chen, J.-S.; Nagarajan, V.; Hussain, B.; Huang, S.-W.; Rathod, J.; Hsu, B.-M. Assessment of temporal effects of a mud volcanic eruption on the cacterial community and their predicted metabolic functions in the mud volcanic sites of Niaosong, Southern Taiwan. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, B.; Chen, J.-S.; Hsu, B.-M.; Chu, I.; Koner, S.; Chen, T.-H.; Rathod, J.; Chan, M.W. Deciphering bacterial community structure, functional prediction and food safety assessment in fermented fruits using next-generation 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G. PICRUSt2: An improved and customizable approach for metagenome inference. BioRxiv 2020, 8, 672295. [Google Scholar]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribe-Lorío, L.; Brenes-Guillén, L.; Hernández-Ascencio, W.; Mora-Amador, R.; González, G.; Ramírez-Umaña, C.J.; Díez, B.; Pedrós-Alió, C. The influence of temperature and pH on bacterial community composition of microbial mats in hot springs from Costa Rica. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Qi, S.; Du, Z.; Zhang, H. Assessing heavy metal contamination and ecological risk in Poyang Lake area, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, R.; Dhakan, D.B.; Mittal, P.; Waiker, P.; Chowdhury, A.; Ghatak, A.; Sharma, V.K. Metagenomic analysis of hot springs in Central India reveals hydrocarbon degrading thermophiles and pathways essential for survival in extreme environments. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.S.; Chan, K.-G.; Tay, Y.-L.; Chua, Y.-H.; Goh, K.M. Diversity of thermophiles in a Malaysian hot spring determined using 16S rRNA and shotgun metagenome sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Briggs, B.R.; Wang, S.; Hou, W.; Li, G.; Wu, G.; Solis, R.; Arcilla, C.A.; Abrajano, T. Archaeal and bacterial diversity in acidic to circumneutral hot springs in the Philippines. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 85, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, H.; Huber, R.; Stetter, K. Thermoproteales. In The Prokaryotes; Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Schleifer, K.H., Stackebrandt, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 10–22. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, S.C.; Delong, E.F.; Pace, N.R. Phylogenetic and ecological perspectives on uncultured Crenarchaeota and Korarchaeota. Prokaryotes 2006, 3, 281–289. [Google Scholar]
- Stetter, K. Diversity of extremely thermophilic archaebacteria. In The thermophiles: General, molecular and applied microbiology; Brock, T.D., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 39–74. [Google Scholar]
- Munson-McGee, J.H.; Field, E.K.; Bateson, M.; Rooney, C.; Stepanauskas, R.; Young, M.J. Nanoarchaeota, their Sulfolobales host, and Nanoarchaeota virus distribution across Yellowstone National Park hot springs. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 7860–7868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshahed, M.S.; Youssef, N.H.; Luo, Q.; Najar, F.Z.; Roe, B.A.; Sisk, T.M.; Bühring, S.I.; Hinrichs, K.-U.; Krumholz, L.R. Phylogenetic and metabolic diversity of Planctomycetes from anaerobic, sulfide-and sulfur-rich Zodletone Spring, Oklahoma. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4707–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshahed, M.S.; Senko, J.M.; Najar, F.Z.; Kenton, S.M.; Roe, B.A.; Dewers, T.A.; Spear, J.R.; Krumholz, L.R. Bacterial diversity and sulfur cycling in a mesophilic sulfide-rich spring. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5609–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbieta, M.S.; González-Toril, E.; Bazán, Á.A.; Giaveno, M.A.; Donati, E. Comparison of the microbial communities of hot springs waters and the microbial biofilms in the acidic geothermal area of Copahue (Neuquén, Argentina). Extremophiles 2015, 19, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, A.K.; Bisht, S.S.; De Mandal, S.; Kumar, N.S. Bacterial and archeal community composition in hot springs from Indo-Burma region, North-east India. Amb. Express 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badhai, J.; Ghosh, T.S.; Das, S.K. Taxonomic and functional characteristics of microbial communities and their correlation with physicochemical properties of four geothermal springs in Odisha, India. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.S.; Lali, R. Molecular signatures for the phylum Aquificae and its different clades: Proposal for division of the phylum Aquificae into the emended order Aquificales, containing the families Aquificaceae and Hydrogenothermaceae, and a new order Desulfurobacteriales ord. nov., containing the family Desulfurobacteriaceae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2013, 104, 349–368. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrera, I.; Banta, A.B.; Reysenbach, A.-L. Spatial patterns of Aquificales in deep-sea vents along the Eastern Lau Spreading Center (SW Pacific). Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 37, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reysenbach, A.-L.; Gotz, D.; Banta, A.; Jeanthon, C.; Fouquet, Y. Expanding the distribution of the Aquificales to the deep-sea vents on Mid-Atlantic Ridge and Central Indian Ridge. CBM Cah. De Biol. Mar. 2002, 43, 425–428. [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Matsuzawa, H.; Muramatsu, M.; Meng, X.-Y.; Hanada, S.; Mori, K.; Kamagata, Y. Armatimonas rosea gen. nov., sp. nov., of a novel bacterial phylum, Armatimonadetes phyl. nov., formally called the candidate phylum OP10. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 1442–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochetkova, T.V.; Toshchakov, S.V.; Zayulina, K.S.; Elcheninov, A.G.; Zavarzina, D.G.; Lavrushin, V.Y.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A.; Kublanov, I.V. Hot in cold: Microbial life in the hottest springs in permafrost. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, C.; Samudrala, R.; Anderson, I.; Hedlund, B.P.; Petroni, G.; Michailova, N.; Pinel, N.; Overbeek, R.; Rosati, G.; Staley, J.T. Genes for the cytoskeletal protein tubulin in the bacterial genus Prosthecobacter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 17049–17054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwan, N.; Lambert, C.; Sharma, A.; Gupta, V.; Khurana, P.; Khurana, J.P.; Sockett, R.E.; Gilbert, J.A.; Lal, R. Arsenic rich Himalayan hot spring metagenomics reveal genetically novel predator–prey genotypes. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2015, 7, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sar, T.; Umeh, E.; Akosu, D. Occurrence, detection and isolation of Bdellovibrio spps. from some fresh water bodies in Benue State, Nigeria. Microbiol. J. 2015, 5, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fry, J.; Staples, D. The occurrence and role of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus in a polluted river. Water Res. 1974, 8, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iebba, V.; Santangelo, F.; Totino, V.; Nicoletti, M.; Gagliardi, A.; De Biase, R.V.; Cucchiara, S.; Nencioni, L.; Conte, M.P.; Schippa, S. Higher prevalence and abundance of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus in the human gut of healthy subjects. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61608. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, K.-H.; Liao, B.-Y.; Chang, H.-W.; Huang, S.-W.; Chang, T.-Y.; Yang, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-B.; Lin, Y.-T.K.; Wu, Y.-W.; Tang, S.-L. Metabolic characteristics of dominant microbes and key rare species from an acidic hot spring in Taiwan revealed by metagenomics. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruneel, O.; Personné, J.C.; Casiot, C.; Leblanc, M.; Elbaz-Poulichet, F.; Mahler, B.; Le Fleche, A.; Grimont, P. Mediation of arsenic oxidation by Thiomonas sp. in acid-mine drainage (Carnoulès, France). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-F.; Yang, T.F.; Lan, T.F.; Chen, C.-H.; Song, S.-R.; Tsao, S. Temporal variations of gas compositions of fumaroles in the Tatun Volcano Group, northern Taiwan. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2008, 178, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akob, D.M.; Hallenbeck, M.; Beulig, F.; Fabisch, M.; Küsel, K.; Keffer, J.L.; Woyke, T.; Shapiro, N.; Lapidus, A.; Klenk, H.-P. Mixotrophic iron-oxidizing Thiomonas isolates from an acid mine drainage-affected creek. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01420–e01424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.G.; Geng, A.L.; Yan, R.; Gould, W.; Ng, Y.L.; Liang, D. Isolation and characterization of sulphur-oxidizing Thiomonas sp. and its potential application in biological deodorization. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 39, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duquesne, K.; Lieutaud, A.; Ratouchniak, J.; Muller, D.; Lett, M.C.; Bonnefoy, V. Arsenite oxidation by a chemoautotrophic moderately acidophilic Thiomonas sp.: From the strain isolation to the gene study. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, D.J.; Andreote, F.D.; Chaves, D.; Montaña, J.S.; Osorio-Forero, C.; Junca, H.; Zambrano, M.M.; Baena, S. Structural and functional insights from the metagenome of an acidic hot spring microbial planktonic community in the Colombian Andes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajan, R.; Sibanda, T.; Venkatachalam, S.; Kamika, I.; Nel, W.A. Industrial wastewaters harbor a unique diversity of bacterial communities revealed by high-throughput amplicon analysis. Ann. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.-S.; Huang, C.-H.; Ikeyama, N.; Lee, A.-Y.; Chen, I.-C.; Blom, J.; Chen, C.-C.; Chen, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-C.; Hsieh, S.-Y. Prevotella hominis sp. nov., isolated from human faeces. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 4767–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.-Y.; Huang, T.-Y.; Chen, J.-S.; Chen, W.-J.; Lin, C.-Y.; Hsu, B.-M. Metagenomics insight into effects of a heavy metal resistance in hot spring environments adjacent to Huang-gang Creek. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria, 8–13 April 2018; p. 11514. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Sardari, R.R.; Jasilionis, A.; Böök, O.; Öste, R.; Rascón, A.; Heyman-Lindén, L.; Holst, O.; Karlsson, E.N. Cultivation of the gut bacterium Prevotella copri DSM 18205T using glucose and xylose as carbon sources. Microbiol. Open 2021, 10, e1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakao, N.; Yasuda, T.; Jojima, Y.; Yamanaka, S.; Hiraishi, A. Enhanced growth of Acidocella facilis and related acidophilic bacteria at high concentrations of aluminum. Microbes Environ. 2002, 17, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massello, F.L.; Chan, C.S.; Chan, K.-G.; Goh, K.M.; Donati, E.; Urbieta, M.S. Meta-Analysis of microbial communities in hot springs: Recurrent taxa and complex shaping factors beyond PH and temperature. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.E.; Lu, W.-m.; Huang, H.-I.; Huang, W.-k. Environmental survey of Legionella pneumophila in hot springs in Taiwan. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2006, 70, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, B.-M.; Chen, C.-H.; Wan, M.-T.; Cheng, H.-W. Legionella prevalence in hot spring recreation areas of Taiwan. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3267–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Kojima, H.; Fukui, M. Sulfuriferula thiophila sp. nov., a chemolithoautotrophic sulfur-oxidizing bacterium, and correction of the name Sulfuriferula plumbophilusWatanabe, Kojima and Fukui 2015 to Sulfuriferula plumbiphila corrig. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 2041–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, T.; Gupta, G.; Sharma, A.; Kaur, B.; El-Sheikh, M.A.; Alyemeni, M.N. Metagenomic analysis exploring taxonomic and functional diversity of bacterial communities of a Himalayan urban fresh water lake. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello-Yeves, P.J.; Zemskaya, T.I.; Zakharenko, A.S.; Sakirko, M.V.; Ivanov, V.G.; Ghai, R.; Rodriguez-Valera, F. Microbiome of the deep Lake Baikal, a unique oxic bathypelagic habitat. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 65, 1471–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, W.A.; Jin, Z.; Youngblut, N.; Wallace, J.G.; Sutter, J.; Zhang, W.; González-Peña, A.; Peiffer, J.; Koren, O.; Shi, Q. Large-scale replicated field study of maize rhizosphere identifies heritable microbes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7368–7373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurgel, S.N.; Douglas, G.M.; Dusault, A.; Percival, D.; Langille, M.G. Dissecting community structure in wild blueberry root and soil microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, M.J.; Subramanian, G.; Nguyen, T.-T.; Robert, C.; Mediannikov, O.; Fournier, P.-E.; Raoult, D. Genome sequence of Diplorickettsia massiliensis, an emerging Ixodes ricinus-associated human pathogen. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mediannikov, O.; Sekeyová, Z.; Birg, M.-L.; Raoult, D. A novel obligate intracellular gamma-proteobacterium associated with ixodid ticks, Diplorickettsia massiliensis, Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedrich, S.; Schippers, A. Distribution of acidophilic microorganisms in natural and man-made acidic enviroments. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 40, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Liang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Li, L.; Luo, Y.; Shah, M.M.R.; Daroch, M. Temperature-controlled thermophilic bacterial communities in hot springs of western Sichuan, China. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, W.-D.; Li, M.-M.; Salam, N.; Ding, Y.-P.; Zhou, E.-M.; Yin, Y.-R.; Liu, L.; Xiao, M.; Li, W.-J. Novosphingobium meiothermophilum sp. nov., isolated from a hot spring. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najar, I.N.; Sherpa, M.T.; Das, S.; Das, S.; Thakur, N. Microbial ecology of two hot springs of Sikkim: Predominate population and geochemistry. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637, 730–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.S.; Chan, K.-G.; Ee, R.; Hong, K.-W.; Urbieta, M.S.; Donati, E.R.; Shamsir, M.S.; Goh, K.M. Effects of physiochemical factors on prokaryotic biodiversity in Malaysian circumneutral hot springs. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yli-Hemminki, P.; Jørgensen, K.S.; Lehtoranta, J. Iron–manganese concretions sustaining microbial life in the Baltic Sea: The structure of the bacterial community and enrichments in metal-oxidizing conditions. Geomicrobiol. J. 2014, 31, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovely, D.R. Dissimilatory Fe(III) and Mn(IV) reduction. Microbiol. Rev. 1991, 55, 259–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tebo, B.; Rosson, R.; Nealson, K. Potential for Manganese (II) Oxidation and Manganese (IV) Reduction to Co-Occur in the Suboxic Zone of the Black Sea. In Black Sea Oceanography; Izdar, E., Murray, J.W., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 173–185. [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki, T. Iron-sulfur world in aerobic and hyperthermoacidophilic archaea Sulfolobus. Archaea 2010, 2010, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusi, E.; Patrissi, T.; Guarascio, P. Nickel-resistant bacteria isolated in human microbiome. New Microbes New Infect. 2017, 19, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ercal, N.; Gurer-Orhan, H.; Aykin-Burns, N. Toxic metals and oxidative stress part I: Mechanisms involved in metal-induced oxidative damage. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2001, 1, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, E.Y.; Braz, V.S.; Guzzo, C.; Marques, M.V. Two RND proteins involved in heavy metal efflux in Caulobacter crescentus belong to separate clusters within proteobacteria. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.M.; Ahn, B.-E.; Lee, J.-H.; Roe, J.-H. Regulation of a nickel–cobalt efflux system and nickel homeostasis in a soil actinobacterium Streptomyces coelicolor. Metallomics 2015, 7, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huertas, M.J.; López-Maury, L.; Giner-Lamia, J.; Sánchez-Riego, A.M.; Florencio, F.J. Metals in cyanobacteria: Analysis of the copper, nickel, cobalt and arsenic homeostasis mechanisms. Life 2014, 4, 865–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lin, J.-Q.; Liu, X.-M.; Pang, X.; Zhang, C.-J.; Yang, C.-L.; Gao, X.-Y.; Lin, C.-M.; Li, Y.-Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Sulfur oxidation in the acidophilic autotrophic Acidithiobacillus spp. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelán-Sánchez, H.G.; Meza-Rodríguez, P.M.; Carrillo, E.; Ríos-Vázquez, D.I.; Liñan-Torres, A.; Batista-García, R.A.; Pérez-Rueda, E.; Rojas-Ruíz, N.E.; Dávila-Ramos, S. The microbial composition in circumneutral thermal springs from Chignahuapan, Puebla, Mexico reveals the presence of particular sulfur-oxidizing bacterial and viral communities. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyushkina, A.; Bulaev, A.; Belyi, A.V. Unraveling the central role of sulfur-oxidizing Acidiphilium multivorum LMS in industrial bioprocessing of gold-bearing sulfide concentrates. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Adams, M. Sulfide dehydrogenase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus: A new multifunctional enzyme involved in the reduction of elemental sulfur. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 6509–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrandt, T.M.; Grieshaber, M.K. Three enzymatic activities catalyze the oxidation of sulfide to thiosulfate in mammalian and invertebrate mitochondria. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 3352–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.-J.; Stockdreher, Y.; Koch, T.; Sun, S.-T.; Fan, Z.; Josten, M.; Sahl, H.-G.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Y.-M.; Liu, S.-J. Thiosulfate transfer mediated by DsrE/TusA homologs from acidothermophilic sulfur-oxidizing archaeon Metallosphaera cuprina. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 26949–26959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipollone, R.; Ascenzi, P.; Visca, P. Common themes and variations in the rhodanese superfamily. IUBMB Life 2007, 59, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagarajan, V.; Tsai, H.-C.; Chen, J.-S.; Hussain, B.; Fan, C.-W.; Asif, A.; Hsu, B.-M. The Evaluation of Bacterial Abundance and Functional Potentials in the Three Major Watersheds, Located in the Hot Spring Zone of the Tatun Volcano Group Basin, Taiwan. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030500
Nagarajan V, Tsai H-C, Chen J-S, Hussain B, Fan C-W, Asif A, Hsu B-M. The Evaluation of Bacterial Abundance and Functional Potentials in the Three Major Watersheds, Located in the Hot Spring Zone of the Tatun Volcano Group Basin, Taiwan. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(3):500. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030500
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagarajan, Viji, Hsin-Chi Tsai, Jung-Sheng Chen, Bashir Hussain, Cheng-Wei Fan, Aslia Asif, and Bing-Mu Hsu. 2022. "The Evaluation of Bacterial Abundance and Functional Potentials in the Three Major Watersheds, Located in the Hot Spring Zone of the Tatun Volcano Group Basin, Taiwan" Microorganisms 10, no. 3: 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030500
APA StyleNagarajan, V., Tsai, H.-C., Chen, J.-S., Hussain, B., Fan, C.-W., Asif, A., & Hsu, B.-M. (2022). The Evaluation of Bacterial Abundance and Functional Potentials in the Three Major Watersheds, Located in the Hot Spring Zone of the Tatun Volcano Group Basin, Taiwan. Microorganisms, 10(3), 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030500






