Improvement of Zn (II) and Cd (II) Biosorption by Priestia megaterium PRJNA526404 Isolated from Agricultural Waste Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Characterization of Bacteria
2.2. DNA Extraction, Sequencing, and Phylogenetic Analysis
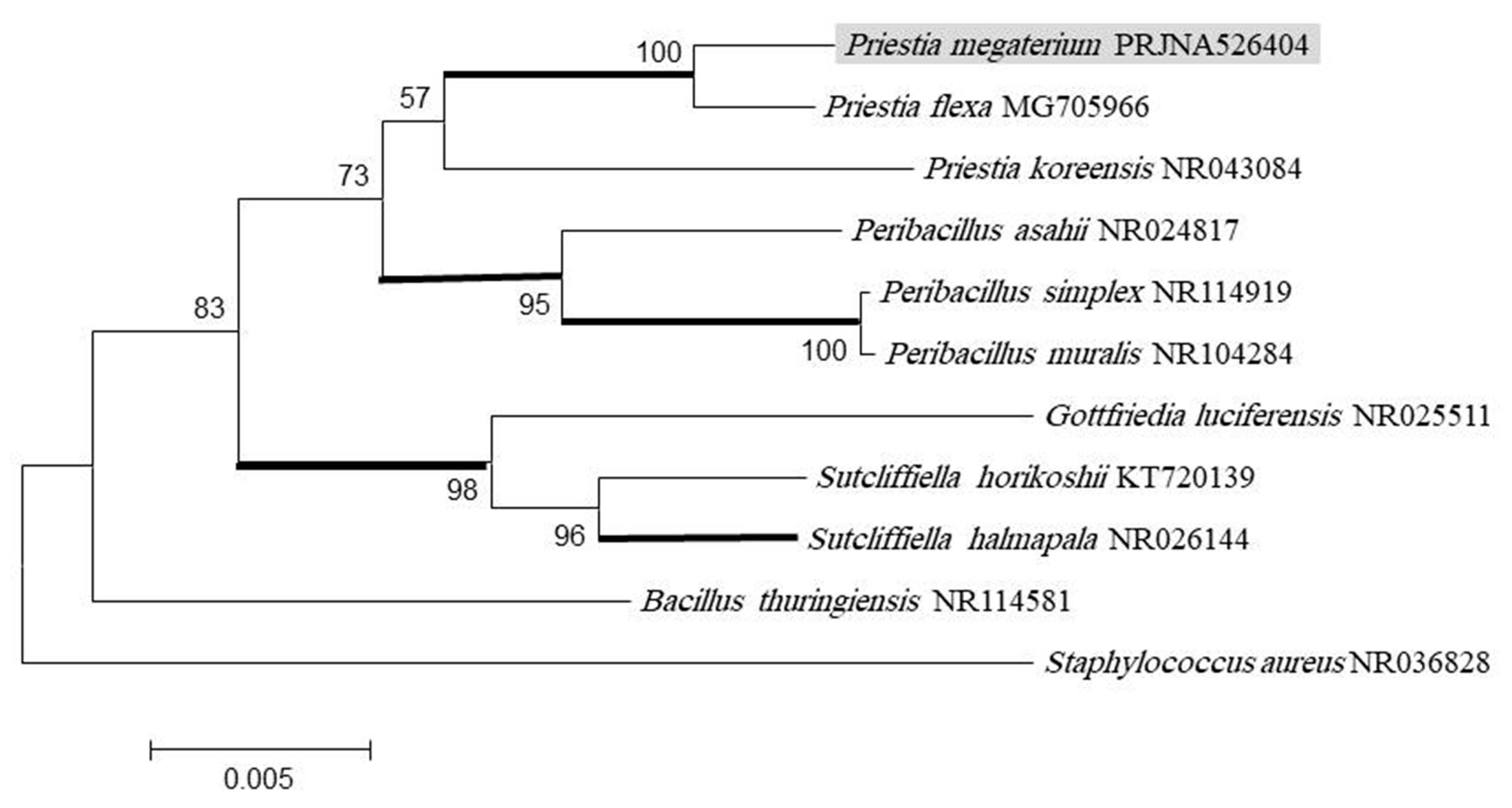
2.3. DNA Sequencing and Phylogenetic Tree
2.4. Preparation of Priestia Megaterium PRJNA526404 Biomass
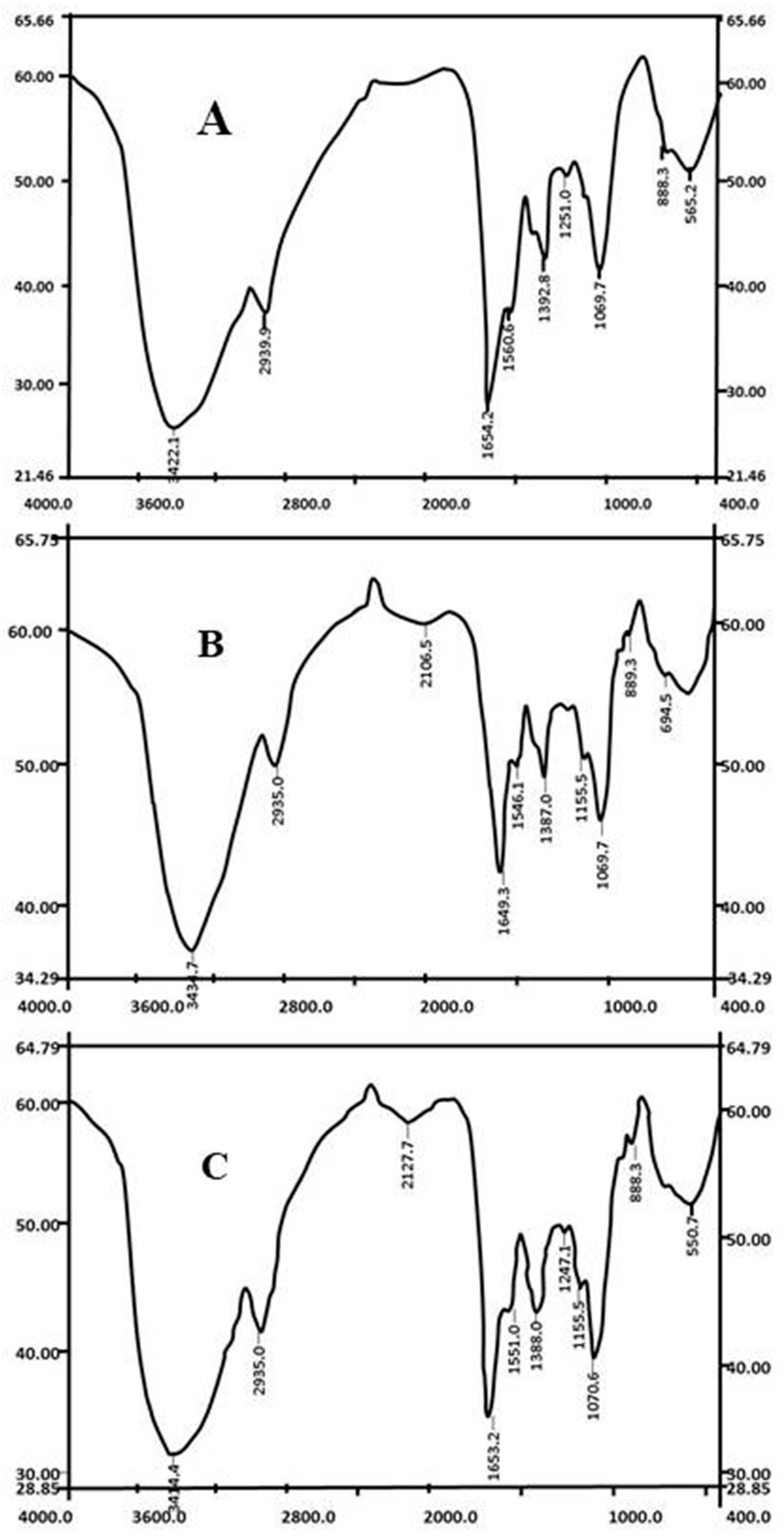
2.5. FTIR Spectroscopy
2.6. Effect of pH and Time on Biosorption
2.7. Adsorption Procedure
2.8. Evaluation of Data
2.9. Adsorption Isotherms
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Isolation and Identification of Bacteria
3.2. Cell Surface Change by FTIR Analysis
3.3. Effect of pH on Biosorption
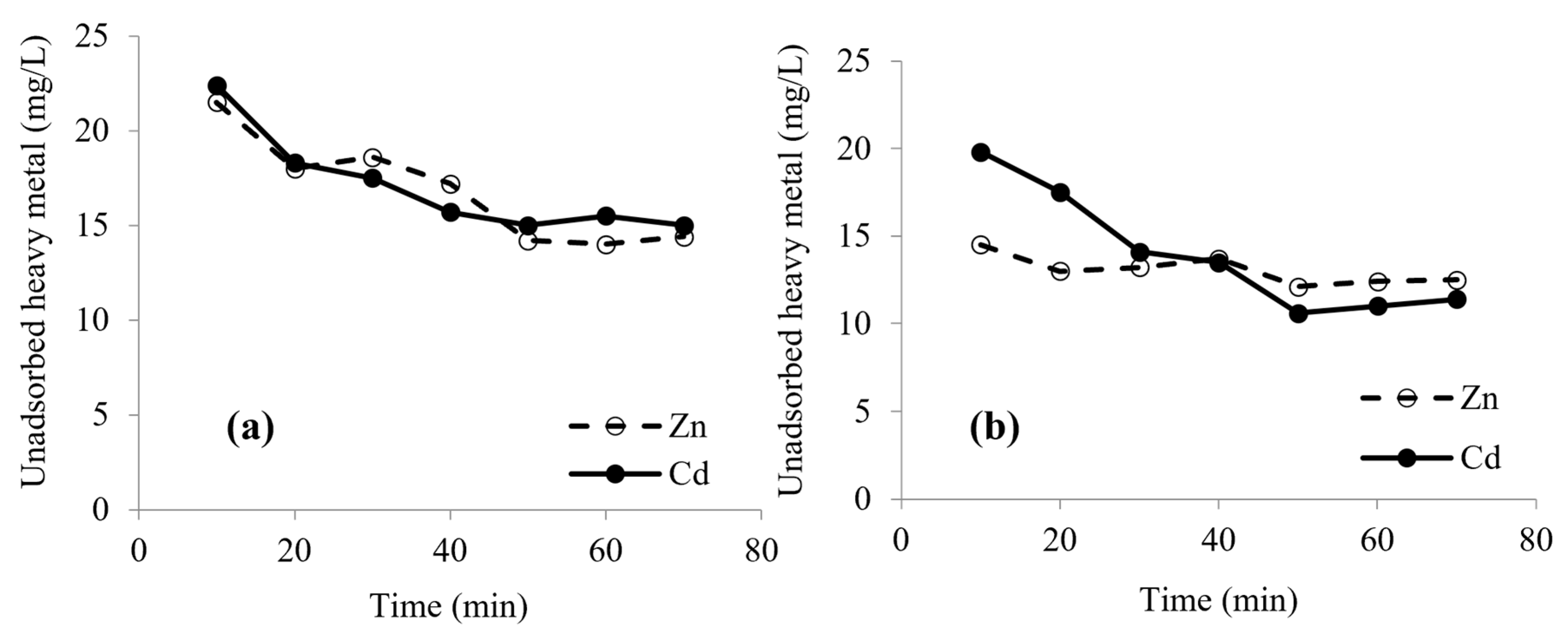
3.4. Effect of Contact Time on Biosorption
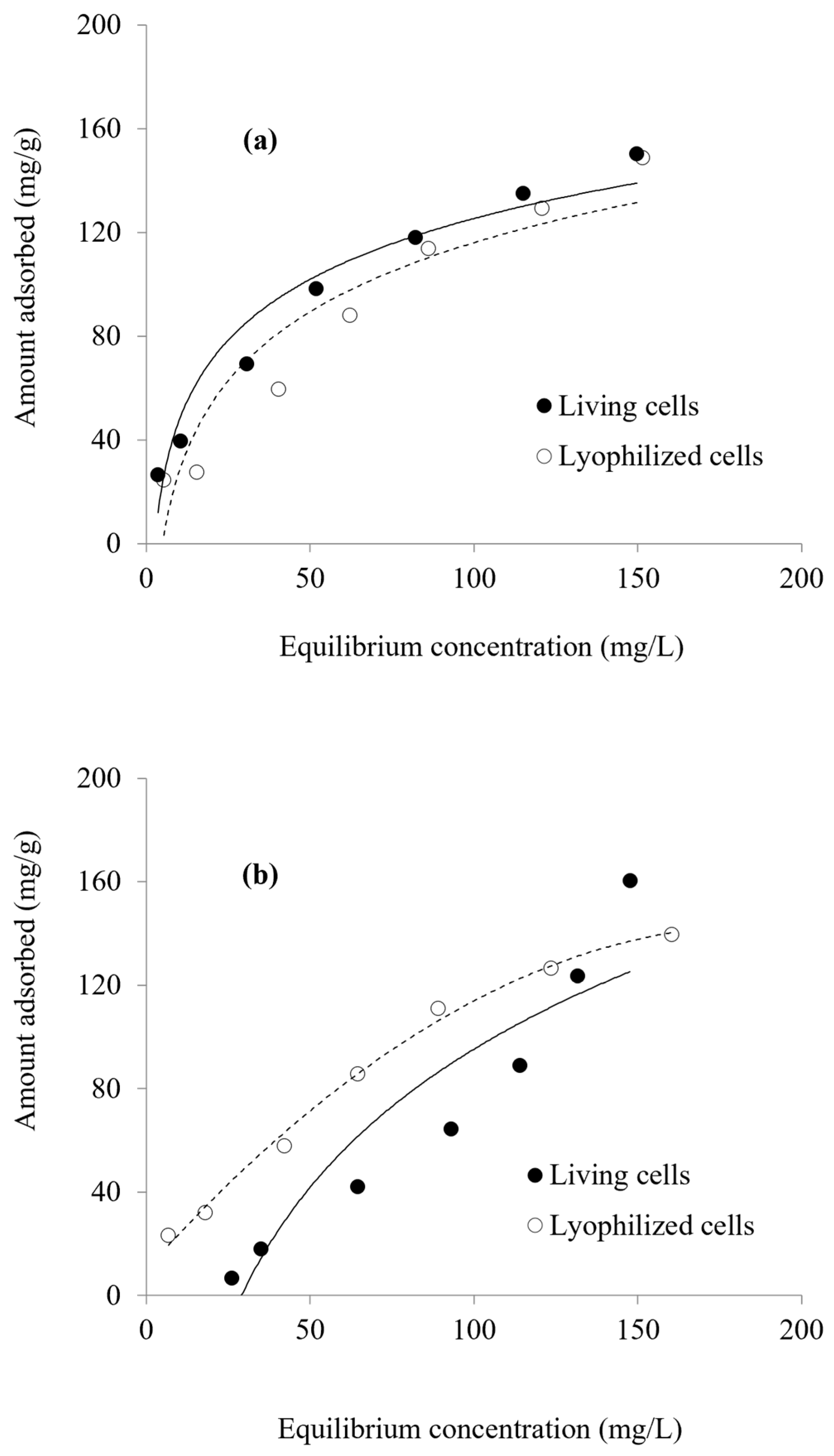
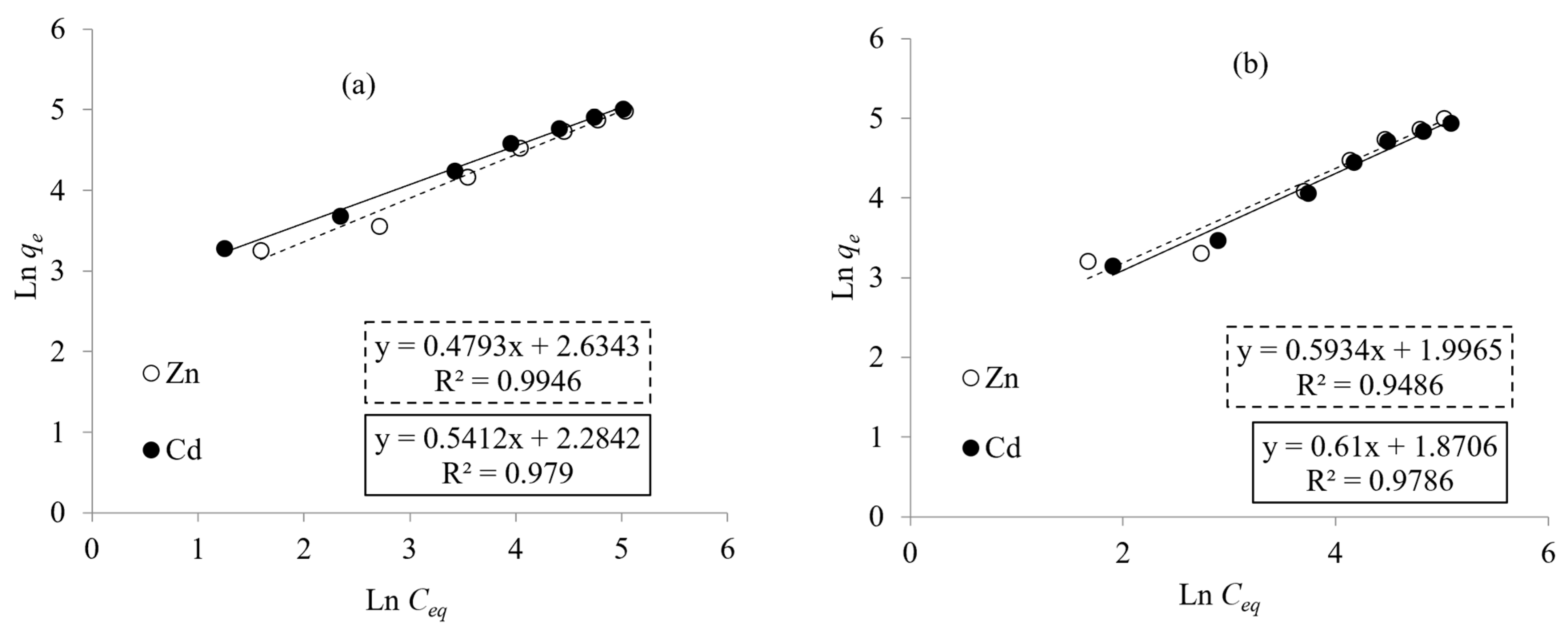
3.5. Adsorption Isotherms
3.6. Effect of Pretreatment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grégorio, C.; Lichtfouse, E. Green Adsorbents for Pollutant Removal Fundamentals and Design; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulyman, M.; Namiesnik, J.; Gierak, A. Low-cost Adsorbents Derived from Agricultural By-products/Wastes for Enhancing Contaminant Uptakes from Wastewater: A Review. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 479–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, S.; Toorisakaa, E.; Hirataa, M.; Hano, T. Adsorption and toxicity of heavy metals on activated sludge. Sci. Asia 2010, 36, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmey, A.; Aboseidah, A.; Youssef, A. Application of Langmuir and Freundlich Isotherm Models on Biosorption of Pb2+ by Freez-dried Biomass of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Egypt. J. Microbiol. 2018, 53, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, C.; Qi, P.; Liu, Y. Adsorption of aquatic Cd2+ using a combination of bacteria and modified carbon fiber. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Karim, M. Metallothionein: A Potential Link in the Regulation of Zinc in Nutritional Immunity. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 182, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Khan, M.; Majid, T.; Sheikh, M.; Mumtaz, M.; Chohan, T.; Shamim, S.; Liu, Y. Zinc Essentiality, Toxicity, and Its Bacterial Bioremediation: A Comprehensive Insight. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 900740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, P.; Ting, Y.; Chen, J.; Hong, L. Sorption of lead, copper, cadmium, zinc and nickel by marine algal biomass: Characterization of biosorptive capacity and investigation of mechanisms. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, S.; Ahmed, H.; Ehab, A.; Mohammad, F. Optimization of Cadmium, Zinc and Copper biosorption in an aqueous solution by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Am. Sci. 2010, 6, 597–604. [Google Scholar]
- Komy, Z.; Gabr, R.; Shoriet, A.; Mohammed, R. Characterization of acidic sites of Pseudomonas biomass capable of binding protons and cadmium and removal of cadmium via biosorption. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 22, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flora, S.; Megha, M.; Ashish, M. Heavy metal induced oxidative stress and its possible reversal by chelation therapy. Indian J. Med. Res. 2008, 128, 501–523. [Google Scholar]
- Ojuederie, O.; Babalola, O. Microbial and plant-assisted bioremediation of heavy metal polluted environments: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, R.S.; Shiau, R.C. Metal removal from aqueous solutions using chitosan-enhanced membrane filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 165, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, P.; Asghari, B.; Mohammadi, F. Biosorption of Ni(II), Cu(II) and Pb(II) by Punica geranatum from Aqueous Solutions. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2010, 2, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šuránek, M.; Melichová, Z.; Kureková, V.; Kljajević, L.; Nenadović, S. Removal of Nickel from Aqueous Solutions by Natural Bentonites from Slovakia. Materials 2021, 14, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, D.; Jain, C.; Yadav, A. Removal of heavy metals from emerging cellulosic low-cost adsorbents: A review. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2113–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourest, E.; Roux, J. Heavy metal biosorption by fungal mycelial by-products: Mechanisms and influence of pH. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1992, 37, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haferburg, G.; Kothe, E. Microbes and metals: Interactions in the environment. J. Basic Microbiol. 2007, 47, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Nurgul, R.; Dong, M. Isolation and identification of an exopolysaccharide-producing lactic acid bacterium strain from Chinese Paocai and biosorption of Pb(II) by its exopolysaccharide. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, T111–T117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergeay, M. Heavy metal resistance in microbial ecosystems. Mol. Microb. Ecol. Mannual 1995, 6, 7–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, R.; Smyth, D.; Blowes, D.; Spink, L.; Wilkin, R.; Jewett, D.; Weisener, C. Treatment of arsenic, heavy metals, and acidity using a mixed ZVI-compost PRB. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1970–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; Gibson, T.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D. The ClustalX windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swofford, D. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (and Other Methods); Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein, J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: A maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 1981, 17, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K. Modeltest: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 817–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrière, G.; Gouy, M. WWW-query An on-line retrieval system for biological sequence banks. Biochimie 1996, 78, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puranik, P.; Paknikar, K. Influence of Co Cations on Biosorption of Lead and Zinc: A Comparative Evaluation in Binary and Multimetal Systems. Bioresour. Technol. 1999, 70, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, Z.; Donmez, G. Comparison of copper (II) biosorptive properties of live and treated Candida sp. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2001, 36, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, H.; Suzuki, A.; Mitsueda, S. Biosorption of heavy metal ions on Rhodobacter sphaeroides and Alcaligenes eutrophus H16. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 197, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.; Sartaj, M.; Mohammadian, A.; Qiblawey, H. Biosorption of Pb and Cu using fixed and suspended bacteria. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1663–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shroff, K.; Vaidya, V. Kinetics and equilibrium studies on biosorption of nickel from aqueous solution by dead fungal biomass of Mucor hiemalis. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Mosa, K.; Saadoun, I.; Kumar, K.; Helmy, M.; Dhankher, O. Potential biotechnological strategies for the cleanup of heavy metals and metalloids. Front. Plant. Sci. 2016, 7, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarekegn, M.; Salilih, F.; Ishetu, A. Microbes used as a tool for bioremediation of heavy metal from the environment. Cogent Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1783174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, R.; Hassan, S.; Shoreit, A. Biosorption of Lead and Nickel by Living and Non-living Cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ASU 6a. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2008, 62, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giotta, L.; Mastrogiacomo, D.; Italiano, F.; Milano, F.; Agostiano, A.; Nagy, K.; Valli, L.; Trotta, M. Reversible binding of metal ions onto bacterial layers revealed by protonation-induced ATR-FTIR difference spectroscopy. Langmuir 2011, 27, 3762–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oves, M.; Khan, M.; Zaidi, A. Biosorption of heavy metals by Bacillus thuringiensis strain OSM29 originating from industrial effluent contaminated north Indian soil. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 20, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Yan, Z.; Ao, Y. Adsorption of cadmium by live and dead biomass of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 33523–33533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honghui, M. Cadmium Adsorption Characterization of Cadmium-resistant Fungal Strain Paecilomyces lilacinus. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhenggang, X.; Yi, D.; Huimin, H.; Liang, W.; Yunlin, Z.; Guiyan, Y. Biosorption Characteristics of Mn (II) by Bacillus cereus Strain HM-5 Isolated from Soil Contaminated by Manganese Ore. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edris, G.; Alhamed, Y.; Alzahrani, A. Cadmium and lead biosorption by Chlorella vulgaris. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth International Water Technology Conference, Istanbul, Turkey, 7–10 May 2012; Volume 16, pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Okbah, M.; El-Gammal, M.; Ibrahim, M.; El-Mabrouk, K. A Study on the Removal Characteristics of Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution by Low Cost Biosorbent (Ulva lactuca). Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2022, 26, 159–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babak, L.; Šupinova, P.; Zichova, M.; Burdychova, R.; Vitova, E. Biosorption of Cu, Zn and Pb by thermophilic bacteria—Effect of biomass concentration on biosorption capacity. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2012, 60, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameen, M.; Moustafa, A.; Mofeed, M.; Hasnaoui, M.; Olanrewaju, O.; Lazzaro, U.; Aryal, M. A comprehensive study on the bacterial biosorption of heavy metals: Materials, performances, mechanisms, and mathematical modellings. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 715–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzba, S. Biosorption of lead (II), zinc(II) and nickel(II) from industrial wastewater by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Bacillus subtilis. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2015, 17, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Gao, H.; Sun, J.; Cai, F. Experimental probation on the binding kinetics and thermodynamics of Au (III) onto Bacillus subtilis. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Q.; Shi, J.; Wu, W.; Chen, Y. Biosorption of copper (II) and zinc (II) from aqueous solution by Pseudomonas putida CZ1. Colloid Surface B 2005, 46, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katircioğlu, H.; Aslim, B.; Tunçeli, A. Chromium (VI) Biosorption from Aqueous Solutions by Free and Immobilized Biomass of Oscillatoria sp. H1 Isolated from freshwater. ISIJ Int. 2012, 52, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kariuki, Z.; Kiptoo, J.; Onyancha, D. Biosorption studies of lead and copper using rogers mushroom biomass ‘Lepiota hystrix’. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 23, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Luo, X.; Ding, L.; Luo, S. Application of Nanotechnology in the Removal of Heavy Metal From Water. Micro Nano Technol. 2019, 83–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lin, Y.; Guan, W.; Chang, J.; Xu, L.; Guo, J.; Wei, G. Biosorption of Zn (II) by live and dead cells of Streptomyces ciscaucasicus strain CCNWHX 72–14. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Xu, R.; Yang, Y.; Yin, H.; Jin, S.; Jiang, T. Potentiality of phosphorus-accumulating organisms biomasses in biosorption of Cd(II), Pb(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) from aqueous solutions: Behaviors and mechanisms. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohapatra, R.; Parhi, P.; Pandey, S.; Bindhani, B.; Thatoi, H.; Panda, C. Active and passive biosorption of Pb(II) using live and dead biomass of marine bacterium Bacillus xiamenensis PbRPSD202: Kinetics and isotherm studies. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 247, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavasant, P.; Apiratikul, R.; Sungkhum, V.; Suthiparinyanont, P.; Wattanachira, S.; Marhaba, T. Biosorption of Cu2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, and Zn2+ using dried marine green macroalga Caulerpa lentillifera. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 2321–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limcharoensuk, T.; Sooksawat, N.; Sumarnrote, A.; Awutpet, T.; Kruatrachue, M.; Pokethitiyook, P.; Auesukaree, C. Bioaccumulation and biosorption of Cd2+ and Zn2+ by bacteria isolated from a zinc mine in Thailand. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramya, D.; Thatheyusa, A.; Juliana, S.; Kiruba, N.; Selvam, D. Physical characterization and kinetic studies of Zn (II) biosorption by Morganella morganii ACZ05. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 970–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.; Rehman, A.; Hussain, S.; Nisar, M.; Zulfiqar, S. Cadmium resistance and uptake by bacterium, Salmonella enterica 43C, isolated from industrial effluent. AMB Express 2016, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunali, S.; Akar, T.; Ozcan, A.; Kiran, I.; Ozcan, A. Equilibrium and kinetics of biosorption of lead (II) from aqueous solutions by Cephalosporium aphidicola. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 47, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.; Kim, J.; Chang, S.; Chung, W. Bacterial Biosorbents, an Efficient Heavy Metals Green Clean-Up Strategy: Prospects, Challenges, and Opportunities. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics Observed | Tests Employed |
|---|---|
| +ve | Gram stain |
| bacilli | Morphology |
| pairs, chains | Arrangement |
| +ve | Endospore |
| +ve | Starch hydrolysis |
| +ve | Catalase |
| −ve | Oxidase |
| +ve | Acid from glucose |
| −ve | VP |
| +ve | Citrate |
| +ve | Urease |
| −ve | Nitrate reduction |
| +ve | Glucose |
| +ve | Lipase production |
| +ve | Growth on 7% NaCl |
| Obligate aerobe | O/F |
| Living Cells | Lyophilized Cells | |
|---|---|---|
| Zn2+ Cd2+ | Zn2+ Cd2+ | |
| Langmuir qmax (mg/g) | 196.08 178.57 | 227.27 212.777 |
| b (L/mg) | 0.017 0.027 | 0.0113 0.0114 |
| r2 | 0.9391 0.9694 | 0.8348 0.9022 |
| Freundlich Kf (mg/g) | 7.36 6.49 | 13.93 9.82 |
| n (L/mg) | 2.09 1.85 | 1.69 1.64 |
| r2 | 0.9946 0.979 | 0.9486 0.9786 |
| Metal Ion | Biosorbent | qmax (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn2+ | Priestia megaterium PRJNA526404 | 227.27 | The present work |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 3.462 | [9] | |
| Caulerpa lentillif | 40.7 | [53] | |
| P. aeruginosa B237 | 16.75 | [54] | |
| Morganella morganii ACZ05 | 31.24 | [55] | |
| Citrobacter Strain MCM B-181 | 26.38 | [27] | |
| Cd2+ | Priestia megaterium PRJNA526404 | 212.777 | The present work |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 4.73 | [9] | |
| P. aeruginosa B237 | 16.89 | [54] | |
| Exiguobacterium sp. | 15.6 | [55] | |
| Citrobacter Strain MCM B-181 | 66.10 | [27] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alzahrani, O.M.; Abo-Amer, A.E.; Mohamed, R.M. Improvement of Zn (II) and Cd (II) Biosorption by Priestia megaterium PRJNA526404 Isolated from Agricultural Waste Water. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10122510
Alzahrani OM, Abo-Amer AE, Mohamed RM. Improvement of Zn (II) and Cd (II) Biosorption by Priestia megaterium PRJNA526404 Isolated from Agricultural Waste Water. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(12):2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10122510
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlzahrani, Othman M., Aly E. Abo-Amer, and Rehab M. Mohamed. 2022. "Improvement of Zn (II) and Cd (II) Biosorption by Priestia megaterium PRJNA526404 Isolated from Agricultural Waste Water" Microorganisms 10, no. 12: 2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10122510
APA StyleAlzahrani, O. M., Abo-Amer, A. E., & Mohamed, R. M. (2022). Improvement of Zn (II) and Cd (II) Biosorption by Priestia megaterium PRJNA526404 Isolated from Agricultural Waste Water. Microorganisms, 10(12), 2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10122510






