Morphological and Molecular Identification of Fusarium ipomoeae as the Causative Agent of Leaf Spot Disease in Tobacco from China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation
2.2. Morphology
2.3. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Pathogenicity Test
3. Results
3.1. Serious Leaf Spot and Blight Disease Was Observed on Field Tobacco Plants
3.2. Morphology Characterization Indicated a Fusarium spp.
3.3. Phylogenetic Analyses Identified a Fusarium ipomoeae Agent
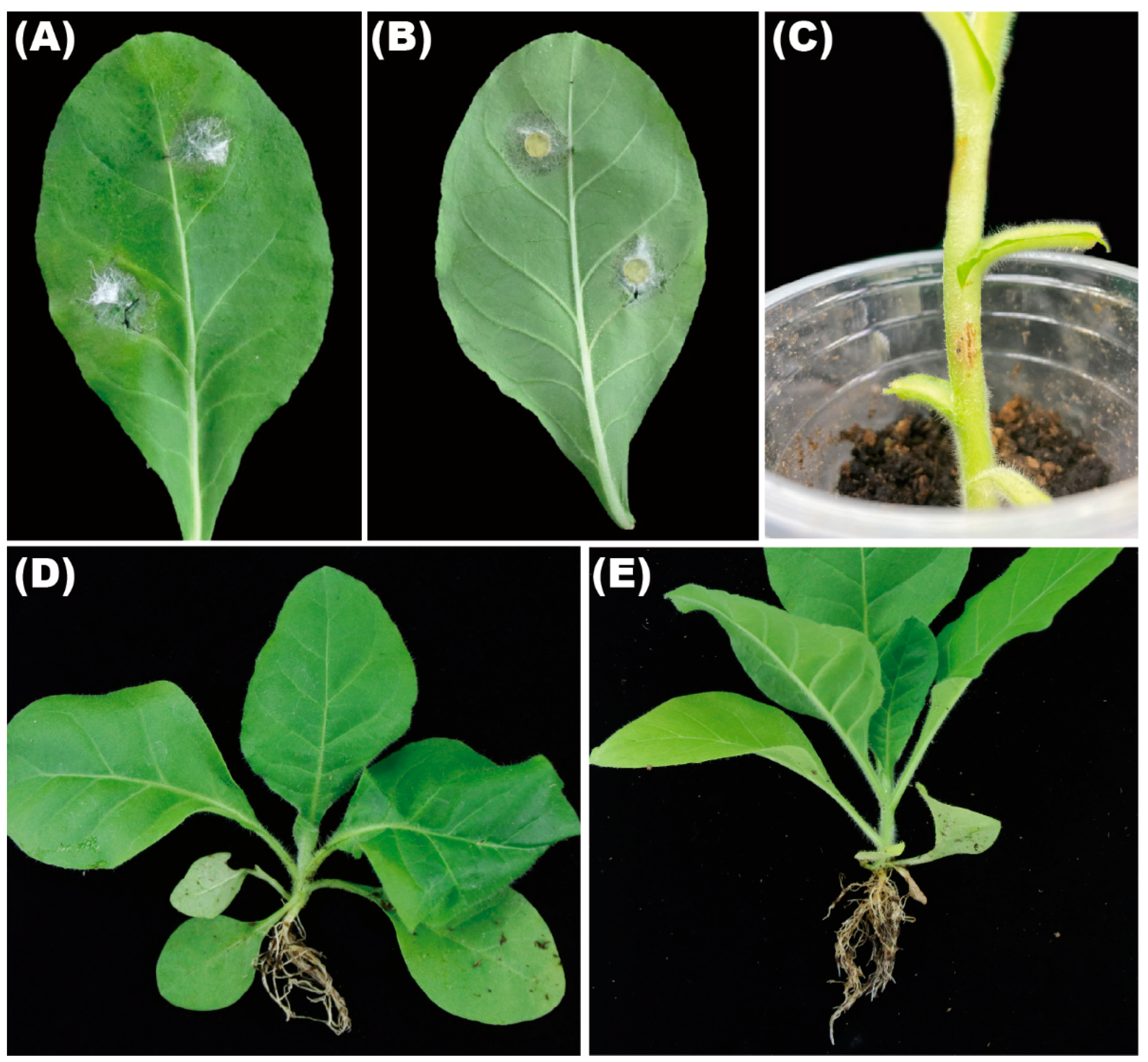
3.4. F. ipomoeae Showed Pathogenicity on Leaf and Stem
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Cao, P.; Wang, H.; Yin, J. Stem-end Rot Caused by Lasiodiplodia brasiliense on Tobacco in China. Plant Dis. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, K.E. The Economics of Tobacco: Myths and Realities. Tob. Control 2000, 1, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins–da–Silva, A.S.; Torales, J.; Becker, R.F.V.; Moura, H.F. Tobacco growing and tobacco use. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2022, 1, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Xie, H.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xiang, L.; Yu, Z.; Yang, X. Leaf Spot Caused by Didymella segeticola on Tobacco in China. Plant Dis. 2019, 5, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Wang, M.S.; Xia, H.Q.; Yang, S.J.; Shi, J.X. First Report of Fusarium Wilt of Tobacco Caused by Fusarium kyushuense in China. Plant Dis. 2013, 3, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, F.; Ding, Y.; Wei, D.; Reddy, M.S.; Du, B. Genetic Diversity and Phylogeny of Antagonistic Bacteria against Phytophthora nicotianae Isolated from Tobacco Rhizosphere. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 5, 3055–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaMondia, J.A. Fusarium wilt of tobacco. Crop Prot. 2015, 1, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, C.; Chao, F.; Kong, F. Occurrence and pathogen isolation of tobacco Fusarium root rot in main tobacco production regions of Shandong province. In Proceedings of the 2011 6th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Beijing, China, 21–23 June 2011; pp. 2637–2639. [Google Scholar]
- Gurdaswani, V.; Ghag, S.B. Toxins from Fusarium species and their role in animal and plant diseases. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 7–27. [Google Scholar]
- Mincuzzi, A.; Sanzani, S.M.; Palou, L.; Ragni, M.; Ippolito, A. Postharvest Rot of Pomegranate Fruit in Southern Italy: Characterization of the Main Pathogens. J. Fungi 2022, 5, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhao, L.; Wei, X.; Liu, X.; Gao, G.; Deng, J.; Li, M. Alternaria species causing leaf spot on hemp (Cannabis sativa) in Northern China. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. Vol. 2022, 4, 957–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, J.; Liao, J.; Yi, J.; Ma, D.; Deng, J. Grafted twig rot on Citrus sinensis caused by a member of the Fusarium solani species complex. Can. J. Plant Pathol. Rev. Can. Phytopathol. 2020, 42, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenis, J.L. Rapid extraction of fungal DNA for PCR amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 9, 2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, K.; Cigelnik, E.; Nirenberg, H.I. Molecular systematics and phylogeography of the Gibberella fujikuroi species complex. Mycologia 1998, 3, 465–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, K.; Nirenberg, H.I.; Aoki, T.; Cigelnik, E. A Multigene phylogeny of the Gibberella fujikuroi species complex: Detection of additional phylogenetically distinct species. Mycoscience 2000, 1, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, K. Phylogenetic analyses of RPB1 and RPB2 support a middle Cretaceous origin for a clade comprising all agriculturally and medically important Fusaria. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2013, 3, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirghasempour, S.A.; Studholme, D.J.; Chen, W.; Zhu, W.; Mao, B. Molecular and Pathogenic Characterization of Fusarium Species Associated with Corm Rot Disease in Saffron from China. J. Fungi 2022, 5, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignassa, M.; Meile, J.C.; Chiroleu, F.; Soria, C.; Leneveu–Jenvrin, C.; Schorr–Galindo, S.; Chillet, M. Pineapple Mycobiome Related to Fruitlet Core Rot Occurrence and the Influence of Fungal Species Dispersion Patterns. J. Fungi 2021, 3, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Cheng, H.; Htun, A.A.; Ge, H.; Xia, Z.Z. Phylogeny and taxonomy of two new Alternaria (Ascomycota: Pleosporaceae) species in section Gypsophilae from China. Mycol. Prog. 2021, 4, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunpapao, A.; Suwannarach, N.; Kumla, J.; Dumhai, R.; Riangwong, K.; Sanguansub, S.; Wanchana, S.; Arikit, S. Morphological and Molecular Identification of Plant Pathogenic Fungi Associated with Dirty Panicle Disease in Coconuts (Cocos nucifera) in Thailand. J. Fungi 2022, 4, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A.; Ludwig, T.; Meier, H. RAxML-III: A fast program for maximum likelihood-based inference of large phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. MODELTEST: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 817–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Chen, Q.; Diao, Y.; Duan, W.; Cai, L. Fusarium incarnatum-equiseti complex from China. Pers. Mol. Phylogeny Evol. Fungi 2019, 1, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.L.; Cai, L.; Wang, H.C.; Cai, L.T. Fungal composition and diversity of the tobacco leaf phyllosphere during curing of leaves. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 554051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Chi, Y. First Report of Fusarium ipomoeae Causing Peanut leaf Spot in China. Plant Dis. 2021, 11, 3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Yang, S.; Wang, S.; Lv, J.; Zhou, H. Identification of Fusarium ipomoeae as the causative agent of leaf spot disease in Bletilla striata in China. Plant Dis. 2021, 4, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, J.F.; Summerell, B.A. The Fusarium Laboratory Manual—Species Concepts in Fusarium; Blackwell Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]


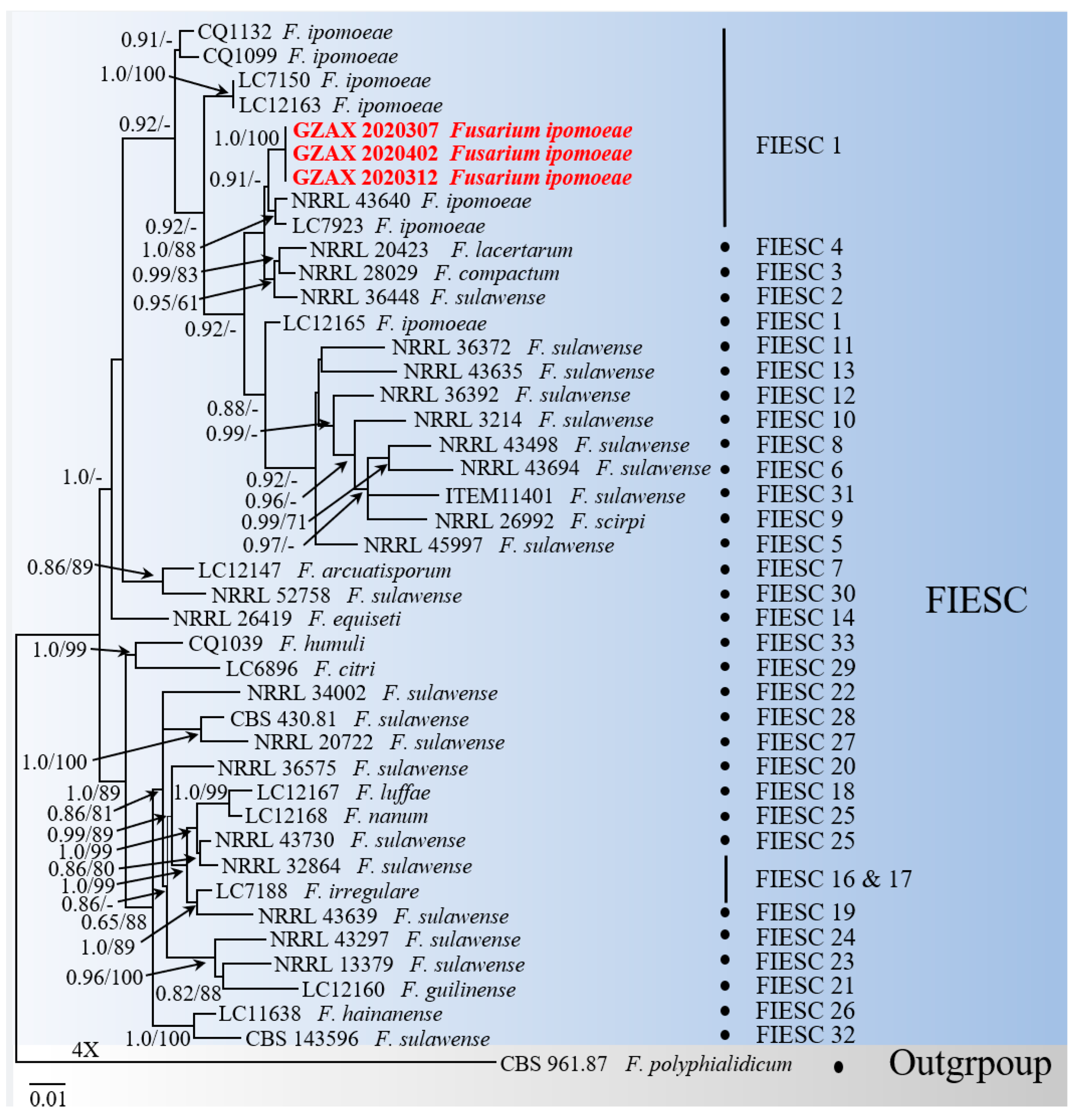
| Species | Phylogenetic Species | Strain | Host | Location | ITS | EF–1 | CAM | RPB2 | RPB1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F. ipomoeae | FIESC 1 | CQ1099 | Rhododendron pulchrum leaf | Jiangsu, China | MK280853 | MK289573 | MK289715 | MK289727 | MK289861 |
| LC7923 | Capsicum sp. | Shandong, China | MK280800 | MK289635 | MK289688 | MK289789 | MK289853 | ||
| CQ1132 | Vinca major leaf | Jiangsu, China | MK280854 | MK289574 | MK289716 | MK289728 | MK289862 | ||
| NRRL 43640 = UTHSC 04–123 | Dog nose | Texas, America | GQ505756 | GQ505667 | GQ505578 | GQ505845 | HM347191 | ||
| LC12165 = CGMCC3.19496 (T) | Ipomoea aquatica leaf | Fujian, China | MK280832 | MK289599 | MK289704 | MK289752 | MK289859 | ||
| LC7150 | Bamboo | Jiangxi, China | MK280818 | MK289627 | MK289678 | MK289781 | MK289852 | ||
| LC12163 | Hibiscus syriacus | Fujian, China | MK280790 | MK289597 | MK289700 | MK289750 | MK289857 | ||
| GZAX 402 | Tobacco | Guizhou, China | OP454871 | OP432881 | OP432880 | OP432883 | OP432882 | ||
| GZAX 307 | Tobacco | Guizhou, China | ON961779 | ON982723 | ON982721 | ON962725 | ON962727 | ||
| GZAX 312 | Tobacco | Guangxi, China | ON961780 | ON982724 | ON982722 | ON982726 | ON982728 | ||
| F. sulawense | FIESC 2 | NRRL 36448 = CBS 384.92 | Phaseolus vulgaris seed | Sudan | GQ505741 | GQ505652 | GQ505564 | GQ505830 | – |
| F. compactum | FIESC 3 | NRRL 28029 = CDC B–3335 | Human eye | California, America | GQ505691 | GQ505602 | GQ505514 | GQ505780 | HM347150 |
| F. lacertarum | FIESC 4 | NRRL 20423 = IMI 300797 (T) | Lizard skin | India | GQ505682 | GQ505593 | GQ505505 | GQ505771 | JX171467 |
| F. sulawense | FIESC 5 | NRRL 45997 = UTHSC 04–1902 | Human sinus | Colorado, America | GQ505761 | GQ505672 | GQ505583 | GQ505850 | – |
| NRRL 34035 = UTHSC 91–569 | Human sinus | Colorado, America | GQ505726 | GO505637 | GQ505549 | GQ505815 | – | ||
| F. sulawense | FIESC 6 | NRRL 43694 = CDC 2006743607 | Human eye | Texas, America | GQ505757 | GQ505668 | GQ505579 | GQ505846 | HM347193 |
| F. arcuatisporum | FIESC 7 | LC12147 = CGMCC3.19493 (T) | Brassica campestris pollen | Hubei, China | MK280802 | MK289584 | MK289697 | MK289739 | MK289799 |
| F. sulawense | FIESC 8 | NRRL 43498 | Human eye | Pennsylvania, America | GQ505747 | GQ505658 | —— | GQ505836 | HM347181 |
| F. sulawense | FIESC 30 | NRRL 52758 = ARSEF 4714 | Prosapia nr. bicincta on Cynodon | Costa Rica | JF740925 | JF740833 | —— | JF741159 | —— |
| F. scirpi | FIESC 9 | NRRL 26992 = CBS 610.95 | Soil | France | GQ505681 | GQ505592 | GQ505504 | GQ505770 | —— |
| F. sulawense | FIESC 31 | ITEM11401 | Avena sativa | Canada | —— | LN901578 | LN901594 | LN901611 | —— |
| F. sulawense | FIESC 10 | NRRL 3214 = FRC R–6054, 7.13 MRC | Unknown | Unknown | GQ505676 | GQ5O5587 | GQ505499 | GQ505765 | —— |
| F. sulawense | FIESC 13 | NRRL 43635 = UTHSC 06–638 | Horse | Nebraska | GQ505751 | GQ505662 | GQ505573 | GQ505840 | HM347188 |
| F. sulawense | FIESC 12 | NRRL 36392 = CBS 259.54 | Unknown plant seedling | Germany | GQ505739 | GQ505650 | GQ505562 | GQ505828 | —— |
| F. sulawense | FIESC 11 | NRRL 36372 = CBS 235.79 | Air | Antilles, Netherlands | GQ505738 | GQ505649 | GQ505561 | GQ505827 | —— |
| F. equiseti | FIESC 14 | NRRL 26419 = CBS 307.94, BBA 68556 (NT) | Soil | Germany | GQ505688 | GQ505599 | GQ505511 | GQ505777 | —— |
| F. irregulare | FIESC 15 | LC7188 = CGMCC3.19489 (T) | Bamboo | Guangdong, China | MK280829 | MK289629 | MK289680 | MK289783 | MK289863 |
| F. sulawense | FIESC 16 & 17 | NRRL 32864 = FRC R–7245 | Human | Texas, America | GQ505702 | GQ505613 | GQ505525 | GQ505791 | HM347160 |
| NRRL 43730 = CDC 2006743605 | Contact lens | Mississippi, America | EF453193 | GQ505669 | GQ505580 | GQ505847 | —— | ||
| F. luffae | FIESC 18 | LC12167 = CGMCC3.19497 (T) | Luffa aegyptiaca | Fujian, China | MK280852 | MK289569 | MK289711 | MK289723 | MK289870 |
| F. sulawense | FIESC 19 | NRRL 43639 = UTHSC 04–135 | Manatee | Florida, America | GQ505755 | GQ505666 | GQ505577 | GQ505844 | HM347190 |
| F. sulawense | FIESC 20 | NRRL 36575 = CBS 976.97 | Juniperus chinensis leaf | Hawaii, America | GQ505745 | GQ505656 | GQ505568 | GQ505834 | —— |
| F. sulawense | FIESC 22 | NRRL 34002 = UTHSC 95–1545 | Human ethmoid sinus | Texas, America | GQ505715 | GQ505626 | GQ505538 | GQ505804 | HM347165 |
| F. sulawense | FIESC 23 | NRRL 13379 = FRC R–5198, BBA 62200 | Oryza sativa | India | GQ505680 | GQ505591 | GQ505503 | GQ505769 | —— |
| F. sulawense | FIESC 24 | NRRL 43297 = W. Elmer 22 | Spartina rhizomes | Connecticut, America | GQ505746 | GQ505657 | GQ505569 | GQ505835 | —— |
| F. sulawense | FIESC 27 | NRRL 20722 = IMI 190455 | Chrysanthemum sp. | Kenya | GQ505684 | GQ505595 | GQ505507 | GQ505773 | —— |
| F. guilinense | FIESC 21 | LC12160 = CGMCC3.19495 (T) | Musa nana leaf | Guangxi, China | MK280837 | MK289594 | MK289652 | MK289747 | MK289831 |
| F. sulawense | FIESC 28 | CBS 430.81 = NRRL 28577 | Grave stone | Romania | GQ505692 | GQ505603 | GQ505515 | GQ505781 | —— |
| F. sulawense | FIESC 32 | CBS 143596 | Stereum irsutum | Iran | LT970815 | LT970779 | LT970732 | LT970751 | —— |
| F. nanum | FIESC 25 | LC12168 = CGMCC3.19498 (T) | Musa nana leaf | Guangxi, China | GQ505697 | GQ505608 | GQ505520 | GQ505786 | —— |
| F. hainanense | FIESC 26 | LC11638 = CGMCC3.19478 (T) | Oryza sp. stem | Hainan, China | MK280836 | MK289581 | MK289657 | MK289735 | MK289833 |
| F. citri | FIESC 29 | LC6896 = CGMCC3.19467 (T) | Citrus reticulata leaf | Hunan, China | MK280803 | MK289617 | MK289668 | MK289771 | MK289828 |
| F. humuli | FIESC 33 | CQ1039 = CGMCC3.19374 (T) | Humulus scandens leaf | Jiangsu, China | MK280845 | MK289570 | MK289712 | MK289724 | MK289840 |
| F. polyphialidicum | —— | CBS 961.87 | Plant debris | South Africa | GQ505763 | GQ505674 | GQ505585 | GQ505852 | —— |
| Species (Strain) | Location | Colonies (mm) | Conidia | Pathogenicity on Tobacco Leaf (mm) | On Stem (mm) | On Root (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body (μm) | Septa | Wounded | Unwounded | Wounded | Unwounded | ||||
| F. ipomoeae (GZAX 307) | Zheng’an in Guizhou province | 61.5 ± 0.5 | 44–118 × 4–11 | 4–6 | 37 ± 2 | 34 ± 3 | 18 ± 2 | 12 ± 6 | — |
| F. ipomoeae (GZAX 312) | Shanglin in Guangxi Zhuang autonomous region | 62 ± 1 | 47–123 × 2–9 | 4–6 | 35 ± 1 | 32 ± 2 | 20 ± 4 | 11 ± 5 | — |
| F. ipomoeae (GZAX 402) | Fenggang in Guizhou province | 62.5 ± 1 | 42–120 × 4–14 | 4–6 | 33 ± 4 | 34 ± 3 | 17 ± 2 | 10 ± 5 | — |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Cai, L.; Meng, J.; Xia, G.; Yin, J.; Liu, X. Morphological and Molecular Identification of Fusarium ipomoeae as the Causative Agent of Leaf Spot Disease in Tobacco from China. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101890
Wang H, Li Y, Li W, Cai L, Meng J, Xia G, Yin J, Liu X. Morphological and Molecular Identification of Fusarium ipomoeae as the Causative Agent of Leaf Spot Disease in Tobacco from China. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(10):1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101890
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hancheng, Yiting Li, Wenhong Li, Liuti Cai, Jianyu Meng, Gen Xia, Junliang Yin, and Xi Liu. 2022. "Morphological and Molecular Identification of Fusarium ipomoeae as the Causative Agent of Leaf Spot Disease in Tobacco from China" Microorganisms 10, no. 10: 1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101890
APA StyleWang, H., Li, Y., Li, W., Cai, L., Meng, J., Xia, G., Yin, J., & Liu, X. (2022). Morphological and Molecular Identification of Fusarium ipomoeae as the Causative Agent of Leaf Spot Disease in Tobacco from China. Microorganisms, 10(10), 1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101890






