A Heat-Killed Probiotic Mixture Regulates Immune T Cells Balance and IgE Production in House Dust Mite Extraction-Induced Atopic Dermatitis Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacteria Preparation
2.2. Anti-Allergic Potential Strains Screening Strategy
2.3. Animals
2.4. Sensitization and Bacterial Treatment
2.5. Histological Section
2.6. Total Serum IgE Analysis
2.7. Cytokine Production in Mesenteric Lymph Nodes (MLN)
2.8. The Measurement of T Cell Staining
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Lactobacillus Strains Isolated from Fermented Milk on Inflammatory Cytokine Secretion In Vitro
3.2. A Mixture of Heat-Killed MP01 and MP02 Strains Alleviated Skin Lesions in HDM Extraction-Induced AD Mice
3.3. A Mixture of Heat-Killed MP01 and MP02 Strains Regulated the Number of Th1 and Th2 Cells in the Spleen of HDM-Extraction-Induced AD Mice
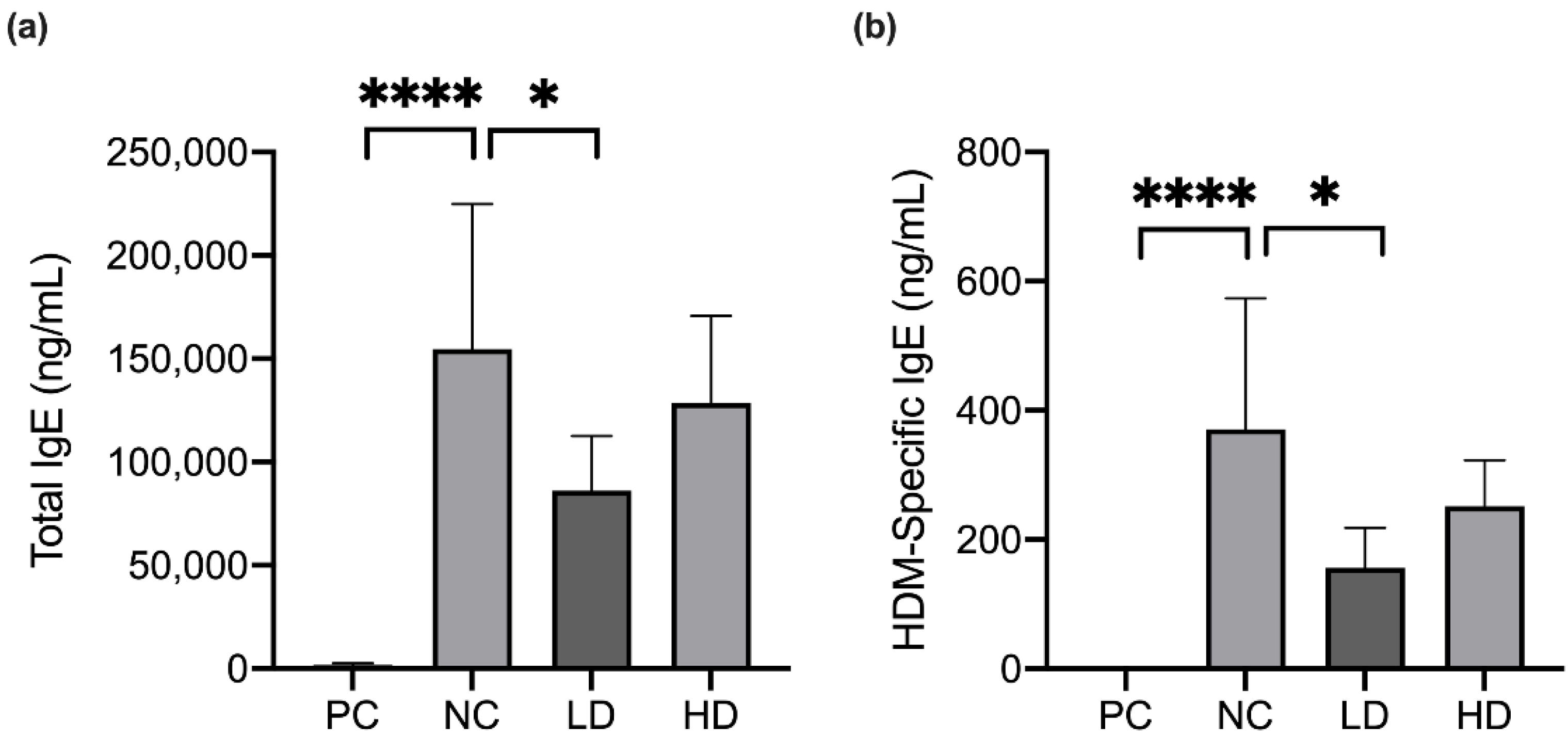
3.4. A Mixture of Heat-Killed MP01 and MP02 Strains Decreased the Level of HDM-Specific IgE in HDM-Extraction-Induced AD Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nutten, S. Atopic dermatitis: Global epidemiology and risk factors. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 66, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, C.N.A.; Irvine, A.D.; Terron-Kwiatkowski, A.; Zhao, Y.; Liao, H.; Lee, S.P.; Goudie, D.R.; Sandilands, A.; Campbell, L.E.; Smith, F.J.D.; et al. Common loss-of-function variants of the epidermal barrier protein filaggrin are a major predisposing factor for atopic dermatitis. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flohr, C.; Yeo, L. Atopic Dermatitis and the Hygiene Hypothesis Revisited. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2011, 41, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Yang, T.; Wu, Z.; Zhong, J.; Huang, Y.; Huang, T.; Zheng, E. Differentiation of T-helper cells in distinct phases of atopic dermatitis involves Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2017, 15, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenfield, L.F.; Ahluwalia, J.; Waldman, A.; Borok, J.; Udkoff, J.; Boguniewicz, M. Current guidelines for the evaluation and management of atopic dermatitis: A comparison of the Joint Task Force Practice Parameter and American Academy of Dermatology guidelines. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, S49–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lee, E.; Park, Y.M.; Hong, S.J. Microbiome in the Gut-Skin Axis in Atopic Dermatitis. Allergy. Asthma Immunol. Res. 2018, 10, 354–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, I.A.; Bajpai, V.K.; Kumar, S.; Lim, J.; Paek, W.K.; Park, Y.-H. Probiotics and Atopic Dermatitis: An Overview. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Lu, W.; Chen, W. Gut Microbiota, Probiotics, and Their Interactions in Prevention and Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: A Review. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 720393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majamaa, H.; Isolauri, E. Probiotics: A novel approach in the management of food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1997, 99, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeldt, V.; Benfeldt, E.; Nielsen, S.D.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Jeppesen, D.L.; Valerius, N.H.; Paerregaard, A. Effect of probiotic Lactobacillus strains in children with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.-Y.; Kim, Y.-H.; Oh, S.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Chun, T. Anti-inflammatory potential of a heat-killed Lactobacillus strain isolated from Kimchi on house dust mite-induced atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothari, D.; Patel, S.; Kim, S.-K. Probiotic supplements might not be universally-effective and safe: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kang, M.-J.; Seo, J.-H.; Kim, H.-Y.; Jeong, S.K.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, J.-M.; Hong, S.-J. A novel mouse model of atopic dermatitis with epicutaneous allergen sensitization and the effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; He, R.; Oyoshi, M.; Geha, R.S. Animal models of atopic dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumbacea, R.S.; Corcea, S.L.; Ali, S.; Dinica, L.C.; Fanfaret, I.S.; Boda, D. Mite allergy and atopic dermatitis: Is there a clear link? (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 3554–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.D.; Smythies, L.E.; Shen, R.; Greenwell-Wild, T.; Gliozzi, M.; Wahl, S.M. Intestinal macrophages and response to microbial encroachment. Mucosal Immunol. 2011, 4, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ye, Q.; Zeng, X.; Qiao, S. Functions of Macrophages in the Maintenance of Intestinal Homeostasis. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 1512969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorjão, A.L.; de Oliveira, F.E.; Leão, M.V.P.; Carvalho, C.A.T.; Jorge, A.O.C.; de Oliveira, L.D. Live and Heat-Killed Lactobacillus rhamnosus ATCC 7469 May Induce Modulatory Cytokines Profiles on Macrophages RAW 264.7. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 716749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.-S.; Chen, H.-C.; Chen, Y.-P.; Chen, M.-J. Effects of kefir supernatant and lactic acid bacteria isolated from kefir grain on cytokine production by macrophage. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S.S.; Cheng, G. Role of interleukin 10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune disease. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 32, 23–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leung, D.Y.M. Role of IgE in atopic dermatitis. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1993, 5, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollenberg, A.; Thomsen, S.F.; Lacour, J.-P.; Jaumont, X.; Lazarewicz, S. Targeting immunoglobulin E in atopic dermatitis: A review of the existing evidence. World Allergy Organ. J. 2021, 14, 100519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.-T.; Goodarzi, H.; Chen, H.-Y. IgE, Mast Cells, and Eosinophils in Atopic Dermatitis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 41, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Yoon, J.-M.; Kim, Y.-H.; Jeong, D.-G.; Park, S.; Kang, D.-J. Therapeutic effect of tyndallized Lactobacillus rhamnosus IDCC 3201 on atopic dermatitis mediated by down-regulation of immunoglobulin E in NC/Nga mice. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 60, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnani, S. T-cell subsets (Th1 versus Th2). Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2000, 85, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, S.; Howell, M.D. Ruxolitinib Cream Suppresses Th2 Inflammation in Adult Patients With Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, AB128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Park, B.-K.; Park, H.-J.; Park, Y.-H.; Kim, B.-O.; Pyo, S. Atopic dermatitis-mitigating effects of new Lactobacillus strain, Lactobacillus sakei probio 65 isolated from Kimchi. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 115, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Hong, R.; Choi, E.Y.; Yu, K.; Kim, N.; Hyeon, J.Y.; Cho, K.K.; Choi, I.S.; Yun, C.-H. A Probiotic Mixture Regulates T Cell Balance and Reduces Atopic Dermatitis Symptoms in Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-T.; Li, K.-Y.; Huang, H.-W.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chen, M.-J. A Heat-Killed Probiotic Mixture Regulates Immune T Cells Balance and IgE Production in House Dust Mite Extraction-Induced Atopic Dermatitis Mice. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101881
Chen H-Y, Chen Y-T, Li K-Y, Huang H-W, Lin Y-C, Chen M-J. A Heat-Killed Probiotic Mixture Regulates Immune T Cells Balance and IgE Production in House Dust Mite Extraction-Induced Atopic Dermatitis Mice. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(10):1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101881
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hsin-Yu, Yung-Tsung Chen, Kuan-Yi Li, Hsiao-Wen Huang, Yu-Chun Lin, and Ming-Ju Chen. 2022. "A Heat-Killed Probiotic Mixture Regulates Immune T Cells Balance and IgE Production in House Dust Mite Extraction-Induced Atopic Dermatitis Mice" Microorganisms 10, no. 10: 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101881
APA StyleChen, H.-Y., Chen, Y.-T., Li, K.-Y., Huang, H.-W., Lin, Y.-C., & Chen, M.-J. (2022). A Heat-Killed Probiotic Mixture Regulates Immune T Cells Balance and IgE Production in House Dust Mite Extraction-Induced Atopic Dermatitis Mice. Microorganisms, 10(10), 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101881





