Effects of Root Zone Aeration on Soil Microbes Species in a Peach Tree Rhizosphere and Root Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
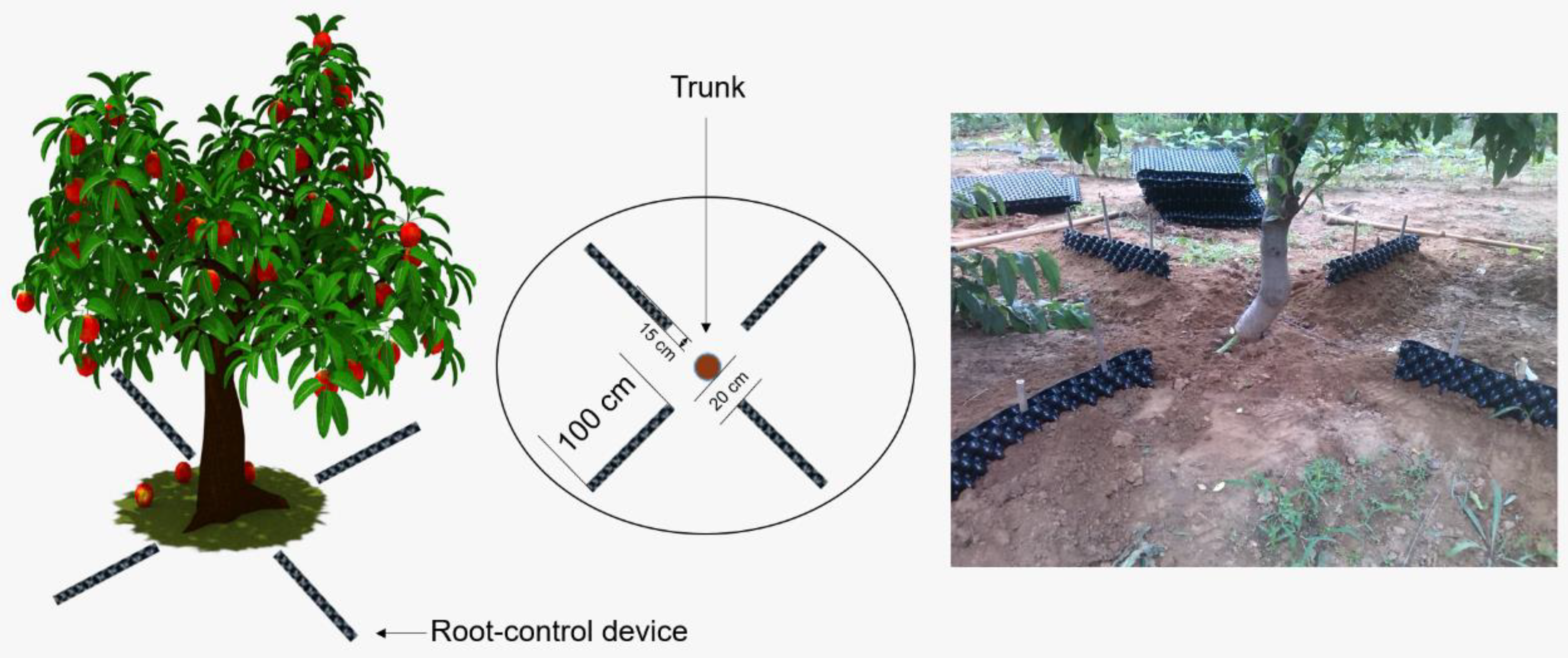
2.1. Experimental Sites, Plant Materials, and Sampling Time
2.2. Determination of the Soil Oxygen Content
2.3. Determination of the Soil Nutrient Content
2.4. High-Throughput Sequencing Method for the Microbial Community
2.5. Determination of Indicators Related to Root System Architecture
2.6. Determination of the Contents of Total Nitrogen and Total Potassium in Plants
2.7. Determination of Plant Growth Indicators
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Root-Zone Aeration on the Soil Oxygen and Nutrient Contents
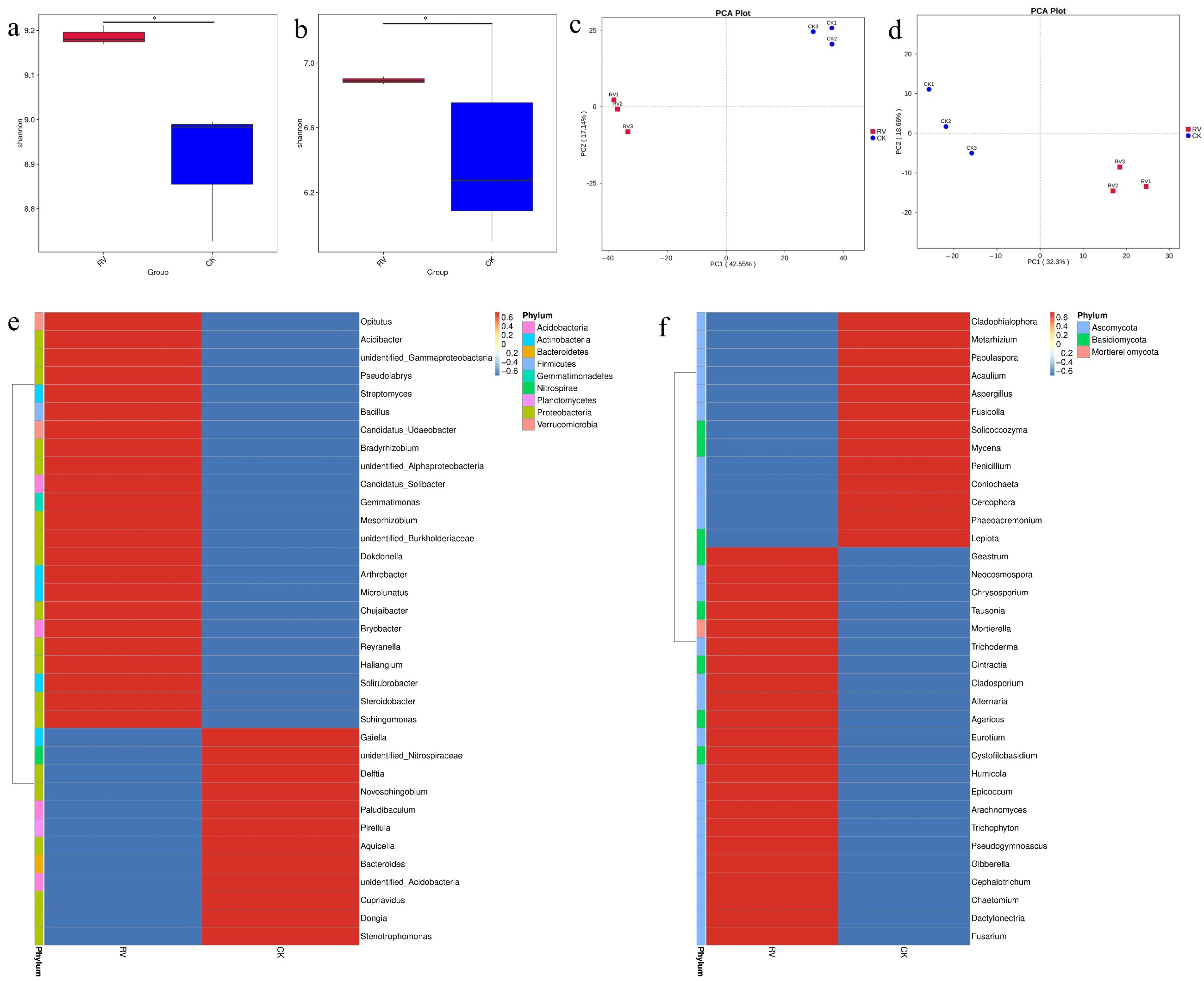
3.2. Effects of Root-Zone Aeration on the Alpha Diversity Index, PCA Plot, and Species Abundance Clustering Heatmap
3.3. Effects of Root-Zone Aeration on LDA Effect Size and Genus-Level t-Test
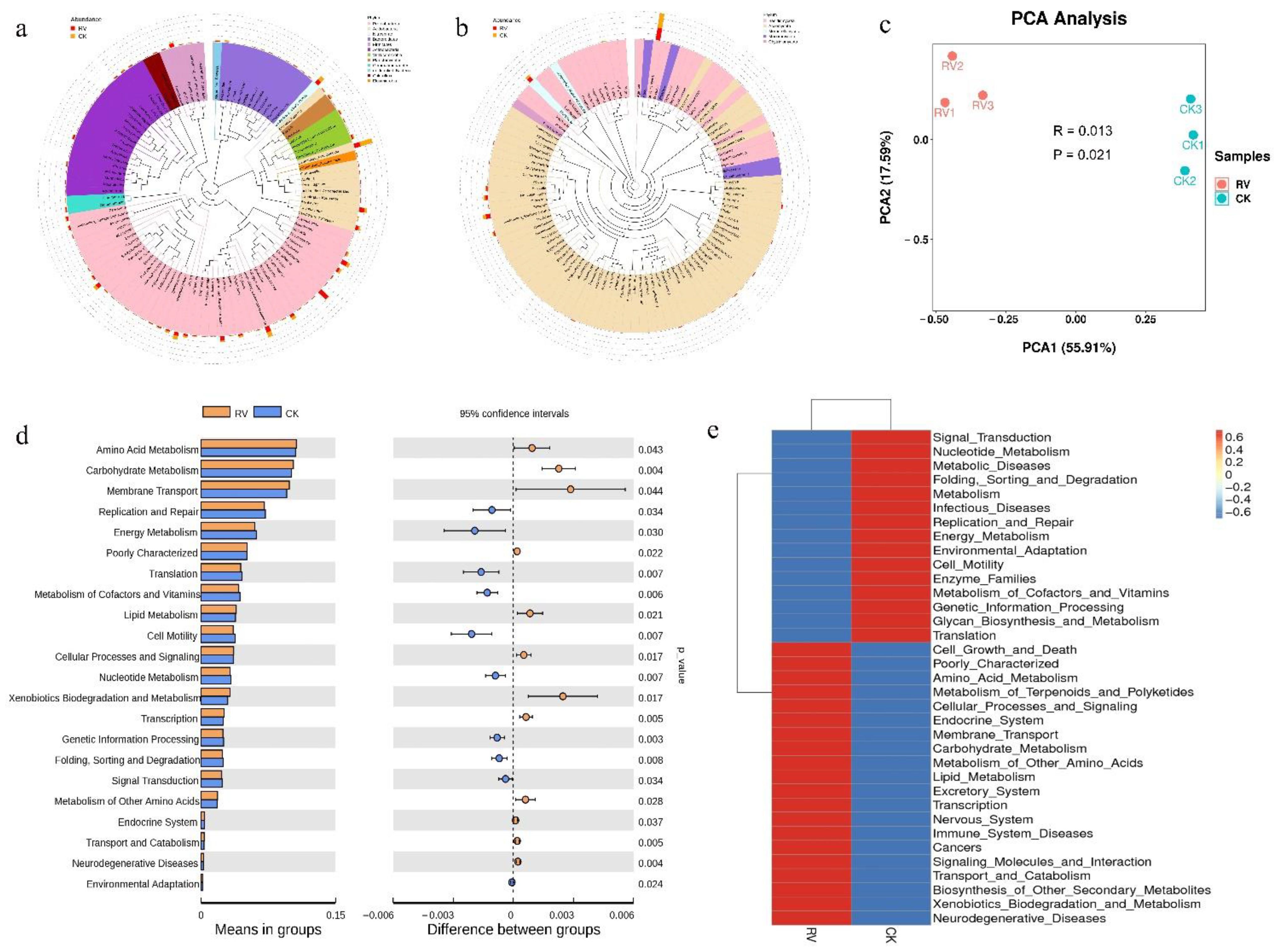
3.4. Effects of Root-Zone Aeration on Genus-Level Evolutionary Trees and Functional Annotation of Relative Abundance
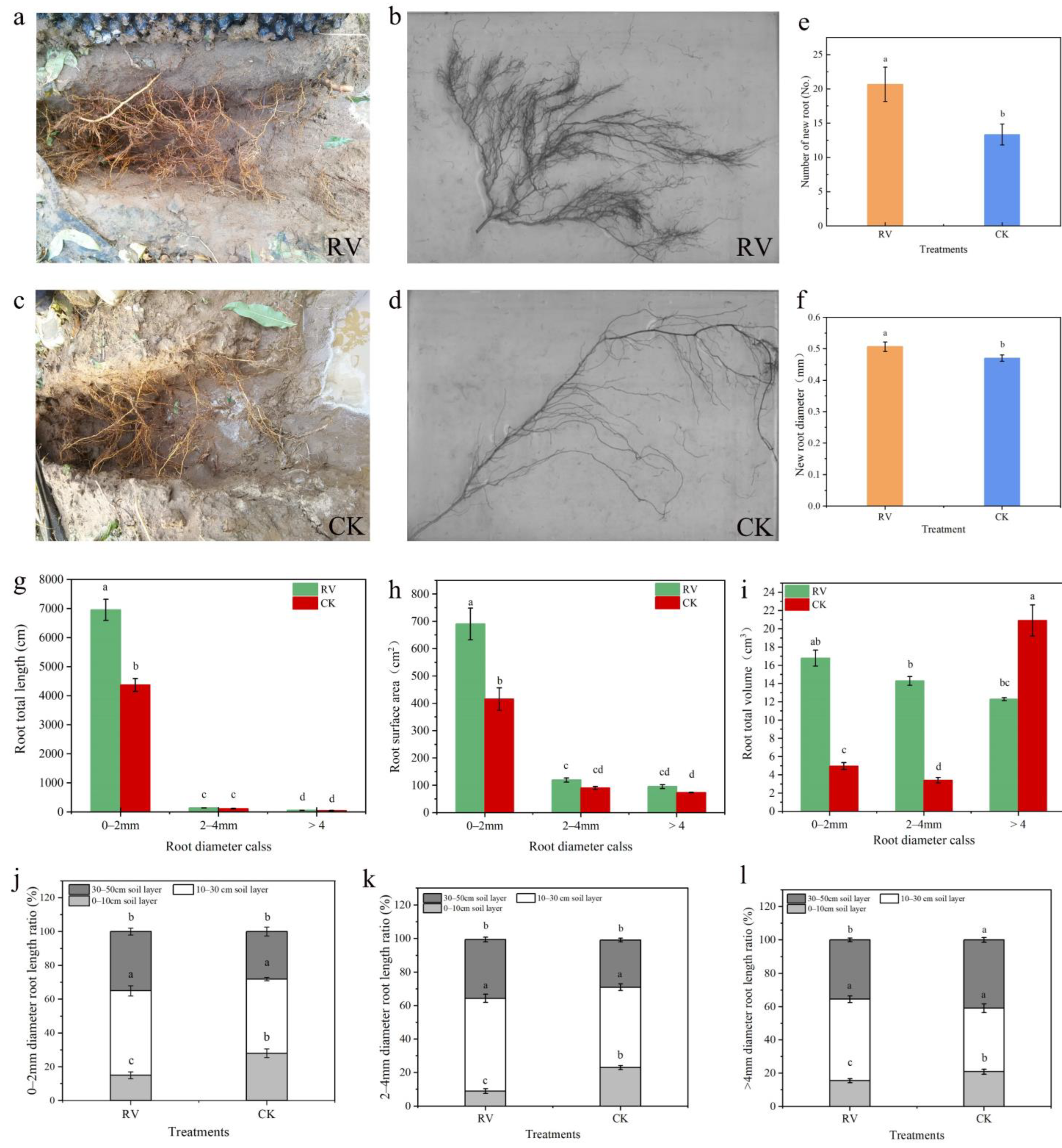
3.5. Effects of Root-Zone Aeration on the Root Growth and Root System Architecture of Peach Trees
3.6. Analysis of Root and Twig Growth’s Correlation with the Genus-Level Microbial Community
3.7. Effects of Root-Zone Aeration on Potassium and Nitrogen Uptake and the Potassium–nitrogen Ratio in Peach Trees
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manganaris, G.A.; Minas, I.; Cirilli, M.; Torres, R.; Bassi, D.; Costa, G. Peach for the future: A specialty crop revisited. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 305, 111390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.R. Physiology of Fruit Tree Cultivation; Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 1993; Volume 93, pp. 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Chen, L.; Chen, S.; Chu, G.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X. Effects of rhizosphere oxygen concentration on root physiological characteristics and anatomical structure at the tillering stage of rice. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2020, 177, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Hayat, S.; Hayat, Q.; Afroz, S.; Ahmad, A. Physiological and biochemical changes in plants under waterlogging. Protoplasma 2010, 241, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.Q.; Jia, Z.X.; Zhang, X.; Shao, H.B. Effects of soil rhizosphere aeration on the root growth and water absorption of tomato. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 2012, 40, 1364–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolini, L. Injecting air into the soil with buried fertirrigation equipment. Inf. Agrar. 2005, 61, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, H. Effect of simulated aeration, leaching and ground water on selected chemical characteristics of pyritic marine sediments. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 2001, 49, 354–357. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, Y. Response of tomato root systems to environmental stress under soilless culture. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. JARQ 2007, 41, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Tian-lai, L.; Zhou-ping, S. Effects of substrate-aeration cultivation pattern on tomato growth. Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao 2010, 21, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen-Quan, N.; Chao, G.; Hongbo, S.; Pute, W. Effects of different rhizosphere ventilation treatment on water and nutrients absorption of maize. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 949–959. [Google Scholar]
- Goorahoo, D.; Carstensen, G.; Zoldoske, D.; Norum, E.; Mazzei, A. Using air in sub-surface drip irrigation(SDI) to increase yields in bell peppers. Int. Water Irrig. 2002, 22, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Vyrlas, P.; Sakellariou-Makrantonaki, M. Soil aeration through subsurface drip irrigation. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Vol. B—Poster Presentations, Rhodes, Greece, 1–3 September 2005; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero, P.; Dec, J.; Bollag, J. Soil as a catalytic system. Soil Biochem. 1996, 9, 79–122. [Google Scholar]
- Gianfreda, L.; Bollag, J. Influence of natural and anthropogenic factors on enzyme activity in soil. Soil Biochem. 1996, 9, 123–193. [Google Scholar]
- Parmar, P.; Sindhu, S. Potassium solubilization by rhizosphere bacteria: Influence of nutritional and environmental conditions. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 3, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Archana, D.; Nandish, M.; Savalagi, V.; Alagawadi, A. Characterization of potassium solubilizing bacteria (KSB) from rhizosphere soil. Bioinfolet-A Q. J. Life Sci. 2013, 10, 248–257. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.; Liu, X.; Tang, J.; Hu, S.; Jiang, P.; Li, W.; Xu, L. Characterization and potassium-solubilizing ability of Bacillus Circulans Z 1–3. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2012, 10, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, J.P.; Yadav, J.; Tiwari, K.N.; Kumar, A. Effect of indigenous Mesorhizobium spp. and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on yields and nutrients uptake of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) under sustainable agriculture. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 51, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, P.; Kandeler, E.; Marschner, B. Structure and function of the soil microbial community in a long-term fertilizer experiment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Peng, F.; Dang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shu, H. Influence of rhizosphere ventilation on soil nutrient status, root architecture and the growth of young peach trees. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2015, 61, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, W.-H. Genetic approaches for improvement of the crop potassium acquisition and utilization efficiency. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 25, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J. Potassium control of plant functions: Ecological and agricultural implications. Plants 2021, 10, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, H. Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lester, G.E.; Jifon, J.L.; Makus, D.J. Impact of potassium nutrition on postharvest fruit quality: Melon (Cucumis melo L.) case study. Plant Soil 2010, 335, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, B.; Song, H.; Ma, R.; Yan, J.; Wang, C. Effect of potassium fertilizer application on fruit quality and vegetative growth of flat peach. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2015, 35, 2273–2279. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Meng, Y.; Jia, X.; Chen, Q.; Xu, X.; Han, Z. Effects of nitrogen applied rate on fruit yield, quality and leaf nutrient content of ‘Bayuecui’ peach. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci 2006, 12, 918–921. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Hou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J.; Wei, G.; Lin, Y. Soil microbial diversity during 30 years of grassland restoration on the Loess Plateau, China: Tight linkages with plant diversity. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1172–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, L.; He, X.; Chen, X.; Cui, Z. Long-term optimization of crop yield while concurrently improving soil quality. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jia, Z.; Niu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M. Effect of post-infiltration soil aeration at different growth stages on growth and fruit quality of drip-irrigated potted tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Niu, W.; Dyck, M.; Wang, J.; Zou, X. Yields and nutritional of greenhouse tomato in response to different soil aeration volume at two depths of subsurface drip irrigation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Zhuang, S.; Gao, J.; Tang, L.; Harindintwali, J.D.; Wang, F. Aeration increases soil bacterial diversity and nutrient transformation under mulching-induced hypoxic conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 153017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Niu, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z. Artificial soil aeration increases soil bacterial diversity and tomato root performance under greenhouse conditions. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 1443–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000; Volume 30, (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, G.T.; Bates, S.T.; Eilers, K.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Caporaso, J.G.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. The under-recognized dominance of Verrucomicrobia in soil bacterial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1450–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findley, K.; Oh, J.; Yang, J.; Conlan, S.; Deming, C.; Meyer, J.A.; Schoenfeld, D.; Nomicos, E.; Park, M.; Kong, H.H. Topographic diversity of fungal and bacterial communities in human skin. Nature 2013, 498, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierret, A.; Moran, C.J. Plant roots and soil structure. In Encyclopedia of Agrophysics; Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series; Glinski, J., Horabik, J., Lipiec, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Discussion on the soil enzyme activity and soil fertility. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 1989, 4, 190–192. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, G.; Yuan, L.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, F.; Ren, H. Influences of different water and nitrogen supplies on soil biological environment in solar greenhouse. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2005, 21, 124–127. [Google Scholar]
- Vessey, J.K. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria as biofertilizers. Plant Soil 2003, 255, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungria, M.; Franchini, J.; Campo, R.; Graham, P. The importance of nitrogen fixation to soybean cropping in South America. In Nitrogen Fixation in Agriculture, Forestry, Ecology, and the Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 25–42. [Google Scholar]
- Miljaković, D.; Marinković, J.; Tamindžić, G.; Đorđević, V.; Tintor, B.; Milošević, D.; Ignjatov, M.; Nikolić, Z. Bio-priming of soybean with Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Bacillus megaterium: Strategy to improve seed germination and the initial seedling growth. Plants 2022, 11, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraud, E.; Moulin, L.; Vallenet, D.; Barbe, V.; Cytryn, E.; Avarre, J.-C.; Jaubert, M.; Simon, D.; Cartieaux, F.; Prin, Y. Legumes symbioses: Absence of Nod genes in photosynthetic bradyrhizobia. Science 2007, 316, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouws, L.F.M.; Leite, J.; de Matos, G.F.; Zilli, J.E.; Coelho, M.R.R.; Xavier, G.R.; Fischer, D.; Hartmann, A.; Reis, V.M.; Baldani, J.I. Endophytic Bradyrhizobium spp. isolates from sugarcane obtained through different culture strategies. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2014, 6, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, S.; Morikawa, T.; Wasai, S.; Kasahara, Y.; Koshiba, T.; Yamazaki, K.; Fujiwara, T.; Tokunaga, T.; Minamisawa, K. Identification of nitrogen-fixing Bradyrhizobium associated with roots of field-grown sorghum by metagenome and proteome analyses. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smercina, D.N.; Evans, S.E.; Friesen, M.L.; Tiemann, L.K. To fix or not to fix: Controls on free-living nitrogen fixation in the rhizosphere. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02546-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaintreuil, C.; Giraud, E.; Prin, Y.; Lorquin, J.; Bâ, A.; Gillis, M.; De Lajudie, P.; Dreyfus, B. Photosynthetic bradyrhizobia are natural endophytes of the African wild rice Oryza breviligulata. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 5437–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piromyou, P.; Greetatorn, T.; Teamtisong, K.; Tittabutr, P.; Boonkerd, N.; Teaumroong, N. Potential of rice stubble as a reservoir of bradyrhizobial inoculum in rice-legume crop rotation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01488-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greetatorn, T.; Hashimoto, S.; Sarapat, S.; Tittabutr, P.; Boonkerd, N.; Uchiumi, T.; Teaumroong, N. Empowering rice seedling growth by endophytic Bradyrhizobium sp. SUTN 9-2. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesch, L.F.W.; Camargo, F.A.; Bento, F.M.; Triplett, E.W. Biodiversity of diazotrophic bacteria within the soil, root and stem of field-grown maize. Plant Soil 2008, 302, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terakado-Tonooka, J.; Fujihara, S.; Ohwaki, Y. Possible contribution of Bradyrhizobium on nitrogen fixation in sweet potatoes. Plant Soil 2013, 367, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues Coelho, M.R.; De Vos, M.; Carneiro, N.P.; Marriel, I.E.; Paiva, E.; Seldin, L. Diversity of nifH gene pools in the rhizosphere of two cultivars of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) treated with contrasting levels of nitrogen fertilizer. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 279, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaweenut, N.; Hachisuka, Y.; Ando, S.; Yanagisawa, S.; Yoneyama, T. Two seasons’ study on nifH gene expression and nitrogen fixation by diazotrophic endophytes in sugarcane (Saccharum spp. hybrids): Expression of nifH genes similar to those of rhizobia. Plant Soil 2011, 338, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, D.; Pfitzner, B.; Schmid, M.; Simões-Araújo, J.L.; Reis, V.M.; Pereira, W.; Ormeño-Orrillo, E.; Hai, B.; Hofmann, A.; Schloter, M. Molecular characterisation of the diazotrophic bacterial community in uninoculated and inoculated field-grown sugarcane (Saccharum sp.). Plant Soil 2012, 356, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, S.; Zehner, S.; Hempel, J.; Lang, K.; Göttfert, M. Genetic organization and functional analysis of the type III secretion system of Bradyrhizobium elkanii. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 295, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-M.; Moulin, L.; Bontemps, C.; Vandamme, P.; Béna, G.; Boivin-Masson, C. Legume Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation byβ-Proteobacteria Is Widespread inNature. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 7266–7272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diep, C.N.; Hieu, T.N. Phosphate and potassium solubilizing bacteria from weathered materials of denatured rock mountain, Ha Tien, Kiên Giang province Vietnam. Am. J. Life Sci. 2013, 1, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, E.; El-Shamma, M.; El-Shazly, S.; El-Gazzar, A.; Abdel-Hak, R. Efficiency of rock-feldspar combined with silicate dissolving bacteria on yield and fruit quality of Valencia orange fruits in reclaimed soils. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 8, 4504–4510. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhong, N. The relationship between root system growth and soil physical property. Agric. Mechan. Res. 2007, 8, 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Niu, W. Effects of rhizosphere ventilation on growth and root activity of potted maize. Zhongguo Shengtai Nongye Xuebao/Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2010, 18, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Qi, Z.; Wang, J.; Wu, P.; Zhang, J. Effects of rhizosphere ventilation environment on potted cucumber growth. J. Henan Agric. Univ 2008, 42, 280–283. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, H.T.; Yang, H.Q.; Shen, W.B.; Jiang, Q.Q.; You, S.Z.; Zhang, L. Effect of Nitrogen -deficientand Iron-deficienton Root Architecture of Young Seedlings of Malushupehensis(Pamp) Rehd. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2009, 36, 321–326. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, H.; Tao, J.; Shi, P.; Guo, D.H.; Fan, C.H. Effects of Topdressing Potassium Fertilizer on Fruit Yield and Quality and Tree Nutrition of‘Chongyanghong’Peach before Harvest. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2016, 25, 1–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, M.; Liu, X.; Shi, K.; Peng, F.; Xiao, Y. Effects of Root Zone Aeration on Soil Microbes Species in a Peach Tree Rhizosphere and Root Growth. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101879
Sun M, Liu X, Shi K, Peng F, Xiao Y. Effects of Root Zone Aeration on Soil Microbes Species in a Peach Tree Rhizosphere and Root Growth. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(10):1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101879
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Maoxiang, Xiaolong Liu, Kaiwu Shi, Futian Peng, and Yuansong Xiao. 2022. "Effects of Root Zone Aeration on Soil Microbes Species in a Peach Tree Rhizosphere and Root Growth" Microorganisms 10, no. 10: 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101879
APA StyleSun, M., Liu, X., Shi, K., Peng, F., & Xiao, Y. (2022). Effects of Root Zone Aeration on Soil Microbes Species in a Peach Tree Rhizosphere and Root Growth. Microorganisms, 10(10), 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101879




