Bacterial Succession during Vermicomposting of Silver Wattle (Acacia dealbata Link)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Silver Wattle (Acacia Dealbata)
2.2. Vermicomposting Setup and Sampling Design
2.3. Microbial Activity
2.4. DNA Sequencing and Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Earthworm Density and Microbial Activity during Vermicomposting
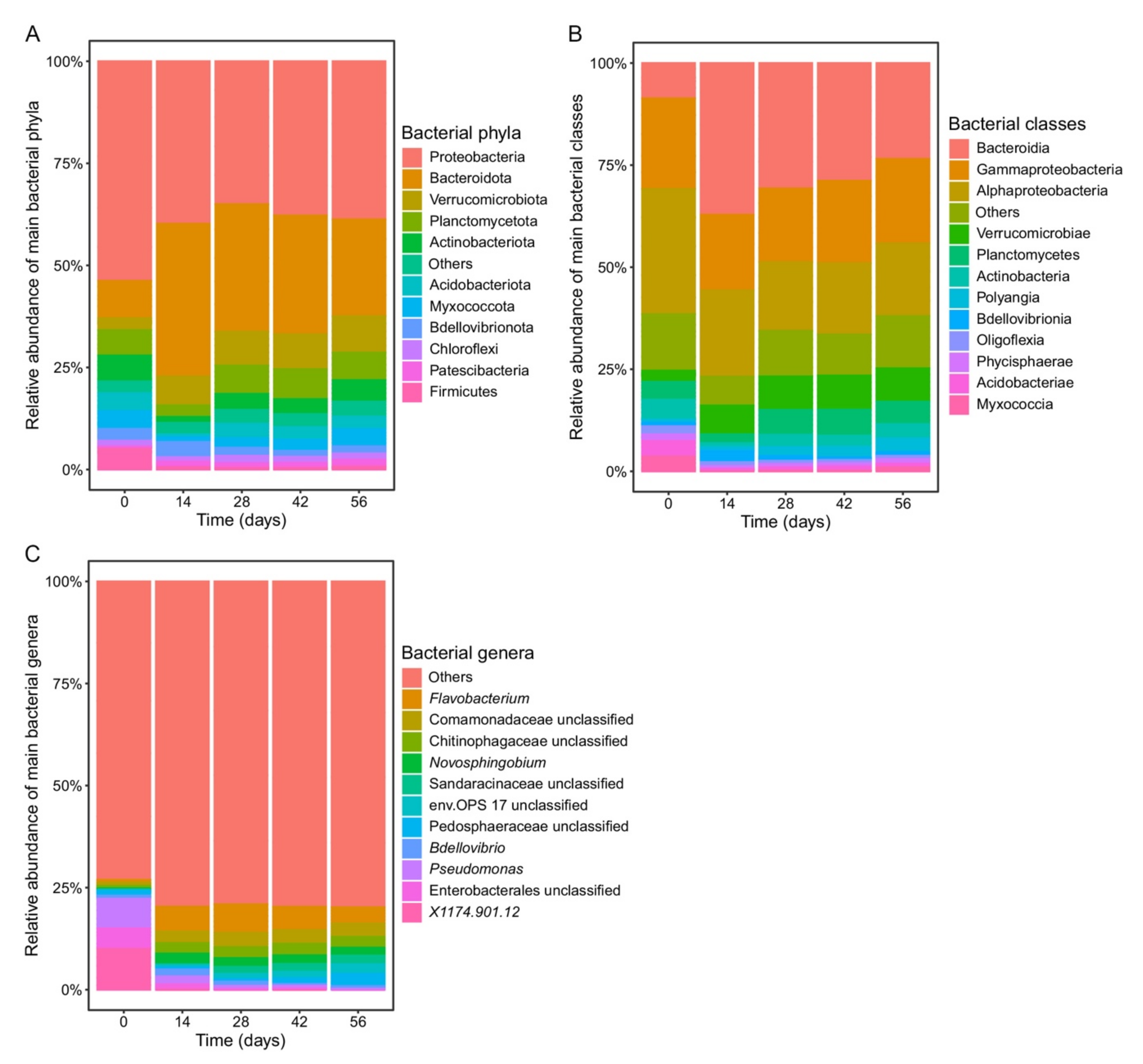
3.2. Changes in Bacterial Community Composition during Vermicomposting
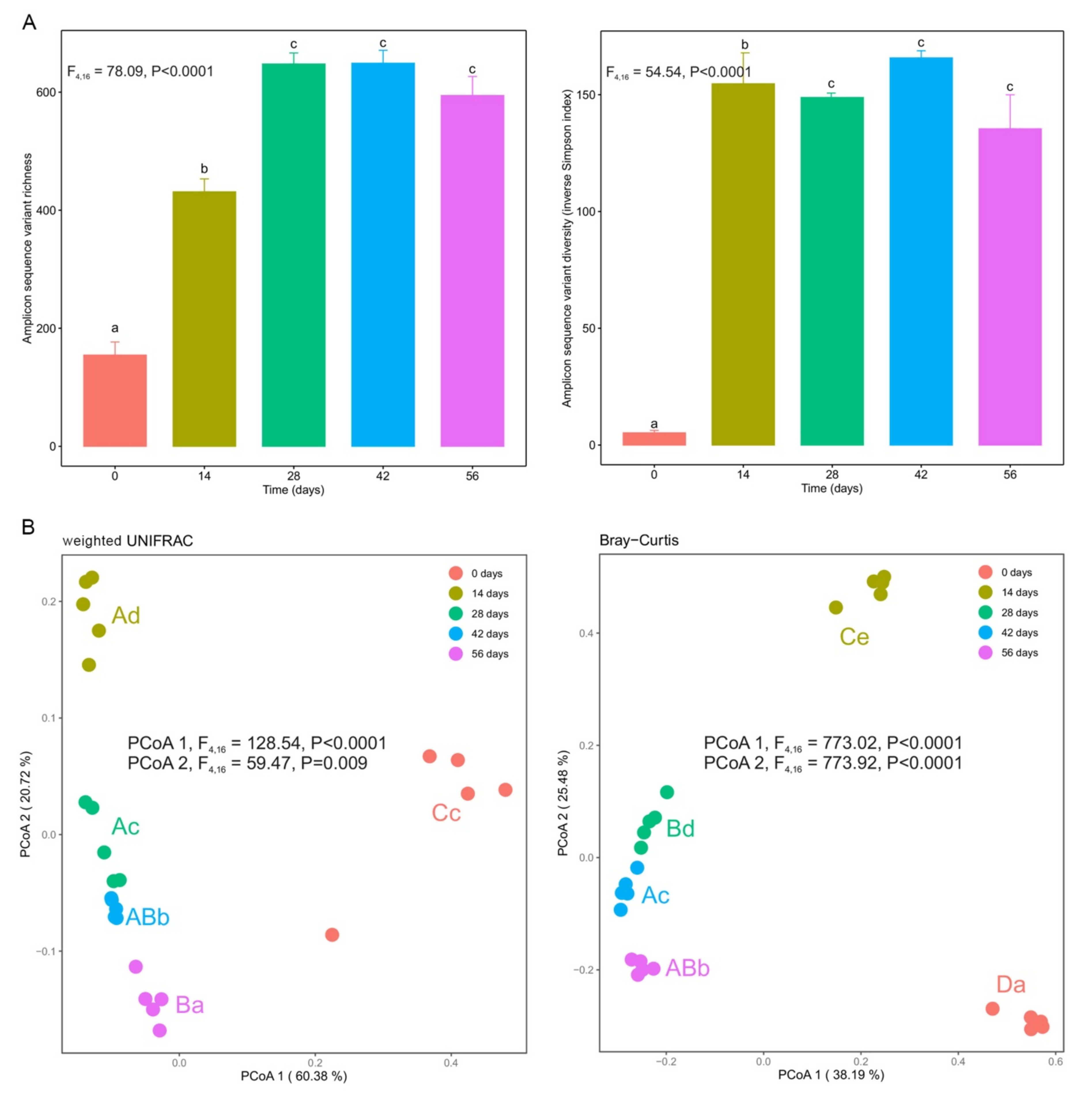
3.3. Changes in α- and β-Diversity during Vermicomposting
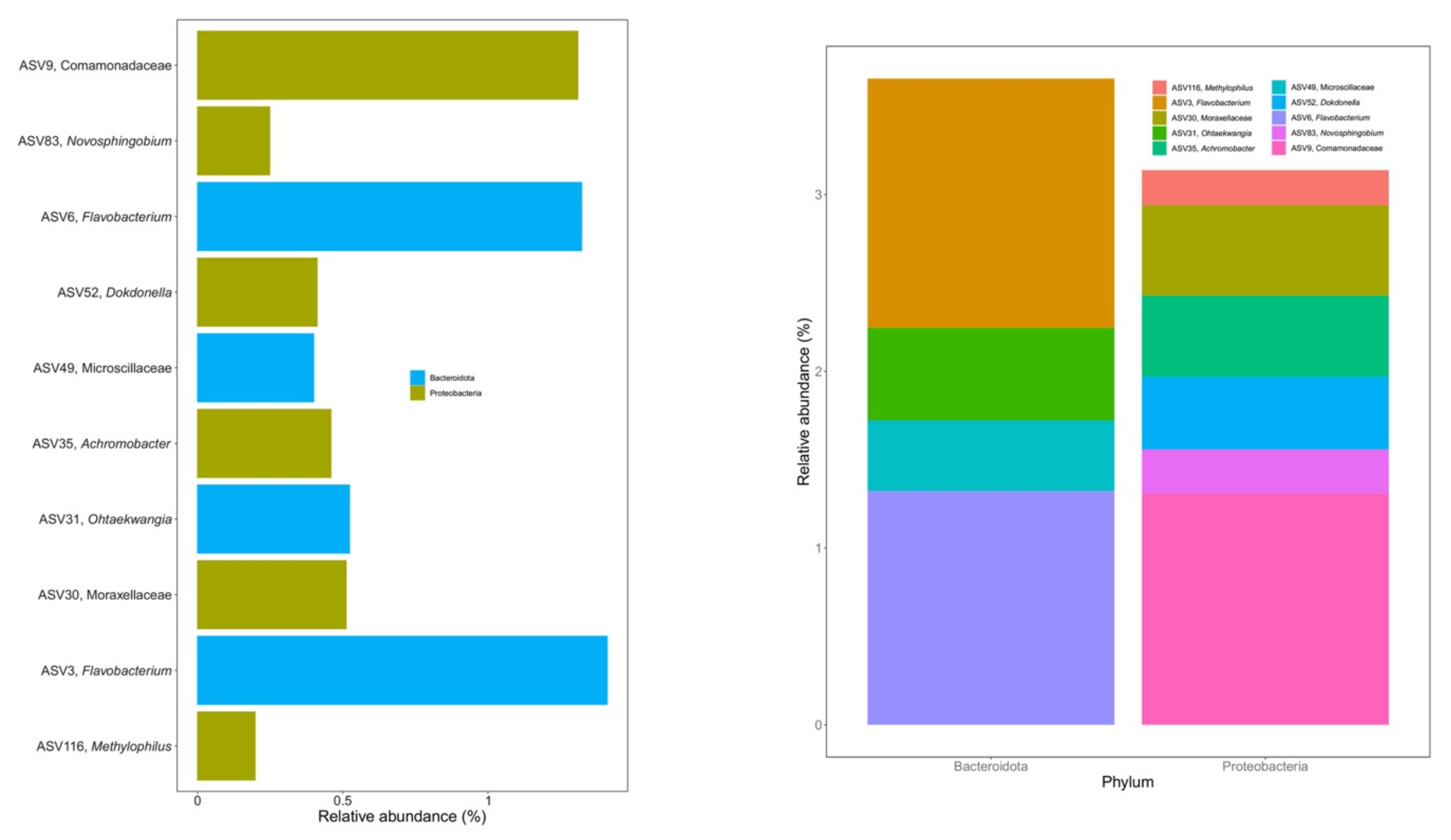
3.4. Core Microbiome during Vermicomposting
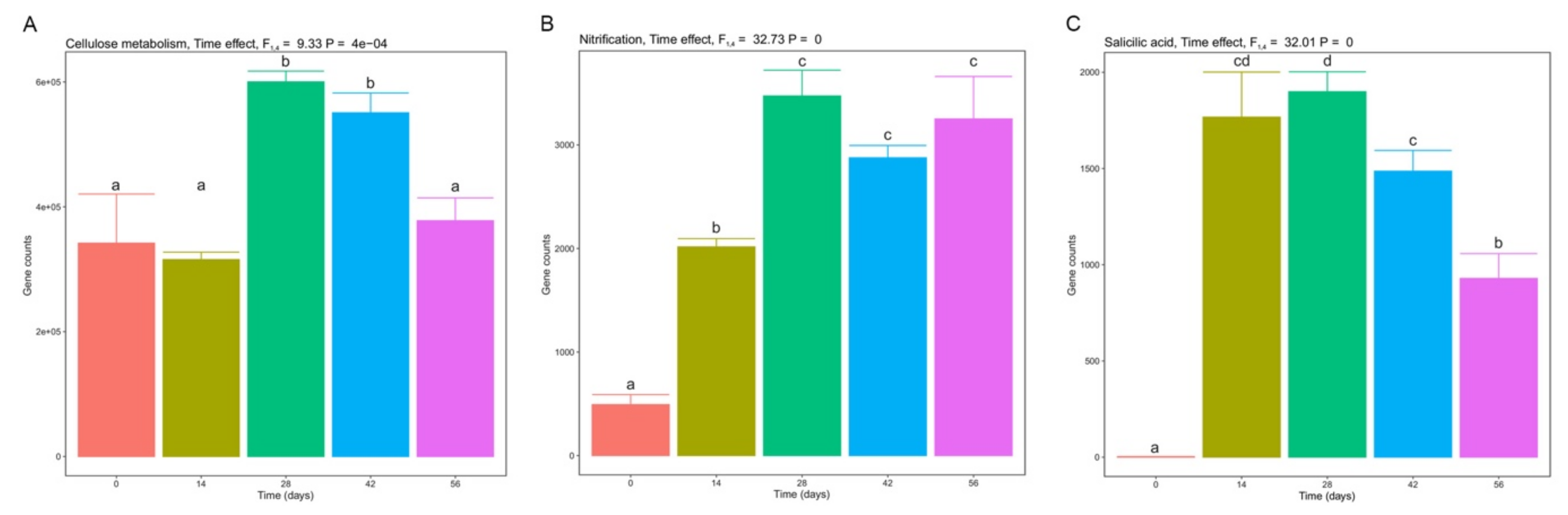
3.5. Functional Diversity during Vermicomposting
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Domínguez, J.; Aira, M.; Gómez-Brandón, M. Microbes at work. In Microbes at Work; Insam, H., Franke-Whittle, I., Goberna, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 93–114. [Google Scholar]
- Domínguez, J.; Gómez-Brandón, M. Vermicomposting: Composting with earthworms to recycle organic wastes. In Management of Organic Waste; Kumar, S., Bharti, A., Eds.; Intech Open Science: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 29–48. [Google Scholar]
- Drake, H.L.; Horn, M.A. As the Worm Turns: The Earthworm Gut as a Transient Habitat for Soil Microbial Biomes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 61, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Nemergut, D.; Knight, R.; Craine, J.M. Changes through time: Integrating microorganisms into the study of succession. Res. Microbiol. 2010, 161, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, P.J.; Shade, A. Trait-based patterns of microbial dynamics in dormancy potential and heterotrophic strategy: Case studies of resource-based and post-press succession. ISME J. 2018, 12, 2575–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aira, M.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Domínguez, J. Microbiome dynamics during cast ageing in the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 139, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aira, M.; Bybee, S.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Domínguez, J. Feeding on microbiomes: Effects of detritivory on the taxonomic and phylogenetic bacterial composition of animal manures. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Brandón, M.; Aira, M.; Lores, M.; Domínguez, J. Epigeic Earthworms Exert a Bottleneck Effect on Microbial Communities through Gut Associated Processes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pathma, J.; Sakthivel, N. Microbial diversity of vermicompost bacteria that exhibit useful agricultural traits and waste management potential. Springerplus 2012, 1, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Domínguez, J.; Aira, M.; Kolbe, A.R.; Gómez-Brandón, M.; Pérez-Losada, M. Changes in the composition and function of bacterial communities during vermicomposting may explain beneficial properties of vermicompost. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lorenzo, P.; González, L.; Reigosa, M.J. The genus Acacia as invader: The characteristic case of Acacia dealbata Link in Europe. Ann. For. Sci. 2010, 67, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Hortas, L.; Rodríguez-González, I.; Díaz-Reinoso, B.; Torres, M.D.; Moure, A.; Domínguez, H. Tools for a multiproduct biorefinery of Acacia dealbata biomass. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 169, 113655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Alonso, P.; Puig, C.G.; Pedrol, N.; Freitas, H.; Rodríguez-Echeverría, S.; Lorenzo, P. Exploring the use of residues from the invasive Acacia sp. for weed control. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2020, 35, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, M.; Gómez, I.; Fernández-Boy, E.; Díaz, M.-J. Effects of Sewage Sludge and Acacia dealbata Composts on Soil Biochemical and Chemical Properties. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2014, 45, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the miseq illumina sequencing platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S.P. Exact sequence variants should replace operational taxonomic units in marker-gene data analysis. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2639–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langille, M.G.I.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Smith, D.K.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y.; Lam, T.T.-Y. ggtree: An r package for visualization and annotation of phylogenetic trees with their covariates and other associated data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Waste Not, Want Not: Why Rarefying Microbiome Data Is Inadmissible. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2–Approximately Maximum-Likelihood Trees for Large Alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faith, D.P. Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity. Biol. Conserv. 1992, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; DebRoy, S. R Core Team nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models. R Package Version 3.1153. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=nlme (accessed on 26 December 2021).
- Hothorn, T.; Bretz, F.; Westfall, P.; Heiberger, R. Simultaneous Inference in General Parametric Models. Biom. J. 2008, 50, 346–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Brandón, M.; Aira, M.; Domínguez, J. Vermicomposts Are Biologically Different: Microbial and Functional Diversity of Green Vermicomposts. In Earthworm Assisted Remediation of Effluents and Wastes; Bhat, S.A., Vig, A.P., Li, F., Ravindran, B., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 125–140. [Google Scholar]
- Kolbe, A.R.; Aira, M.; Gómez-Brandón, M.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Domínguez, J. Bacterial succession and functional diversity during vermicomposting of the white grape marc Vitis vinifera v. Albariño. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Gong, X.; Sun, X.; Li, S.; Yu, X. Comparison of chemical and microbiological changes during the aerobic composting and vermicomposting of green waste. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fierer, N.; Bradford, M.A.; Jackson, R.B. Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 2007, 88, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedini, A.; Mercy, L.; Schneider, C.; Franken, P.; Lucic-Mercy, E. Unraveling the Initial Plant Hormone Signaling, Metabolic Mechanisms and Plant Defense Triggering the Endomycorrhizal Symbiosis Behavior. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rivas-San Vicente, M.; Plasencia, J. Salicylic acid beyond defence: Its role in plant growth and development. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 3321–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vlot, A.C.; Dempsey, D.A.; Klessig, D.F. Salicylic Acid, a Multifaceted Hormone to Combat Disease. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2009, 47, 177–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Domínguez, J.; Gómez-Brandón, M. The influence of earthworms on nutrient dynamics during the process of vermicomposting. Waste Manag. Res. 2013, 31, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke-Whittle, I.H.; Knapp, B.A.; Fuchs, J.; Kaufmann, R. Application of COMPOCHIP Microarray to Investigate the Bacterial Communities of Different Composts. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 57, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Mondéjar, R.; Zühlke, D.; Becher, D.; Riedel, K.; Baldrian, P. Cellulose and hemicellulose decomposition by forest soil bacteria proceeds by the action of structurally variable enzymatic systems. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, S.; Tiago, I.; Pires, A.L.; Da Costa, M.S.; Veríssimo, A. Dokdonella fugitiva sp. nov., a Gammaproteobacterium isolated from potting soil. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 29, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Xing, M.; Yang, J. Exploring the effects of earthworms on bacterial profiles during vermicomposting process of sewage sludge and cattle dung with high-throughput sequencing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 12528–12537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, Z.; Yang, J.; Xing, M.; Yu, F.; Guo, M. Effect of earthworms on the performance and microbial communities of excess sludge treatment process in vermifilter. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 117, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Zhen, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhong, L.; Hu, H.; Luo, C.; Bai, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D. The impact on the soil microbial community and enzyme activity of two earthworm species during the bioremediation of pentachlorophenol-contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 301, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Z.; Zhen, Z.; Ren, L.; Yang, J.; Luo, C.; Zhong, L.; Hu, H.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D. Effects of two ecological earthworm species on atrazine degradation performance and bacterial community structure in red soil. Chemosphere 2018, 196, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Firestone, M.K. Biological Denitrification. In Nitrogen in Agricultural Soils; Stevenson, F.J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1982; pp. 289–326. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Q.; Li, X.; Jiang, H.; Wu, H.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; et al. Ammonia removal through combined methane oxidation and nitrification-denitrification and the interactions among functional microorganisms. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Miao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, L.; Peng, Y. Enhancing sewage nitrogen removal via anammox and endogenous denitrification: Significance of anaerobic/oxic/anoxic operation mode. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 289, 121665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mandal, S.; Mathipi, V.; Muthukumaran, R.B.; Gurusubramanian, G.; Lalnunmawii, E.; Kumar, N.S. Amplicon sequencing and imputed metagenomic analysis of waste soil and sediment microbiome reveals unique bacterial communities and their functional attributes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, J.; Cerniglia, C.; Pritchard, P. Bioremediation of environments contaminated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. In Bioremediation: Principles and Applications; Crawford, R., Crawford, D., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996; pp. 125–194. [Google Scholar]
- Vives-Peris, V.; Gómez-Cadenas, A.; Pérez-Clemente, R.M. Salt stress alleviation in citrus plants by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria Pseudomonas putida and Novosphingobium sp. Plant Cell Rep. 2018, 37, 1557–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo Diaz, J.M.; Delgado-Moreno, L.; Núñez, R.; Nogales, R.; Romero, E. Enhancing pesticide degradation using indigenous microorganisms isolated under high pesticide load in bioremediation systems with vermicomposts. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosado, D.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Aira, M.; Domínguez, J. Bacterial Succession during Vermicomposting of Silver Wattle (Acacia dealbata Link). Microorganisms 2022, 10, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10010065
Rosado D, Pérez-Losada M, Aira M, Domínguez J. Bacterial Succession during Vermicomposting of Silver Wattle (Acacia dealbata Link). Microorganisms. 2022; 10(1):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10010065
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosado, Daniela, Marcos Pérez-Losada, Manuel Aira, and Jorge Domínguez. 2022. "Bacterial Succession during Vermicomposting of Silver Wattle (Acacia dealbata Link)" Microorganisms 10, no. 1: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10010065
APA StyleRosado, D., Pérez-Losada, M., Aira, M., & Domínguez, J. (2022). Bacterial Succession during Vermicomposting of Silver Wattle (Acacia dealbata Link). Microorganisms, 10(1), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10010065





