Recent Structure Development of Poly(vinylidene fluoride)-Based Piezoelectric Nanogenerator for Self-Powered Sensor
Abstract
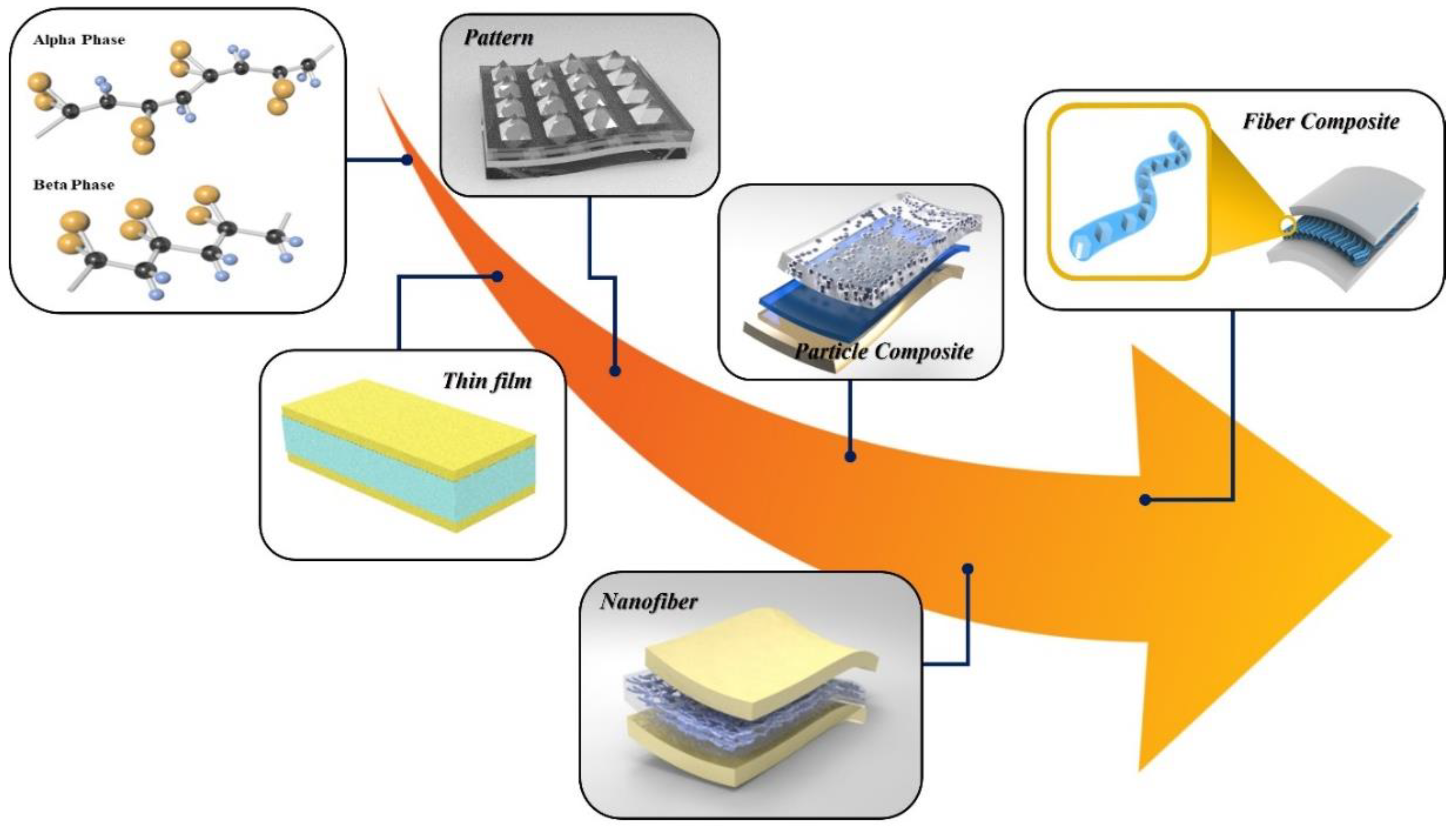
1. Introduction
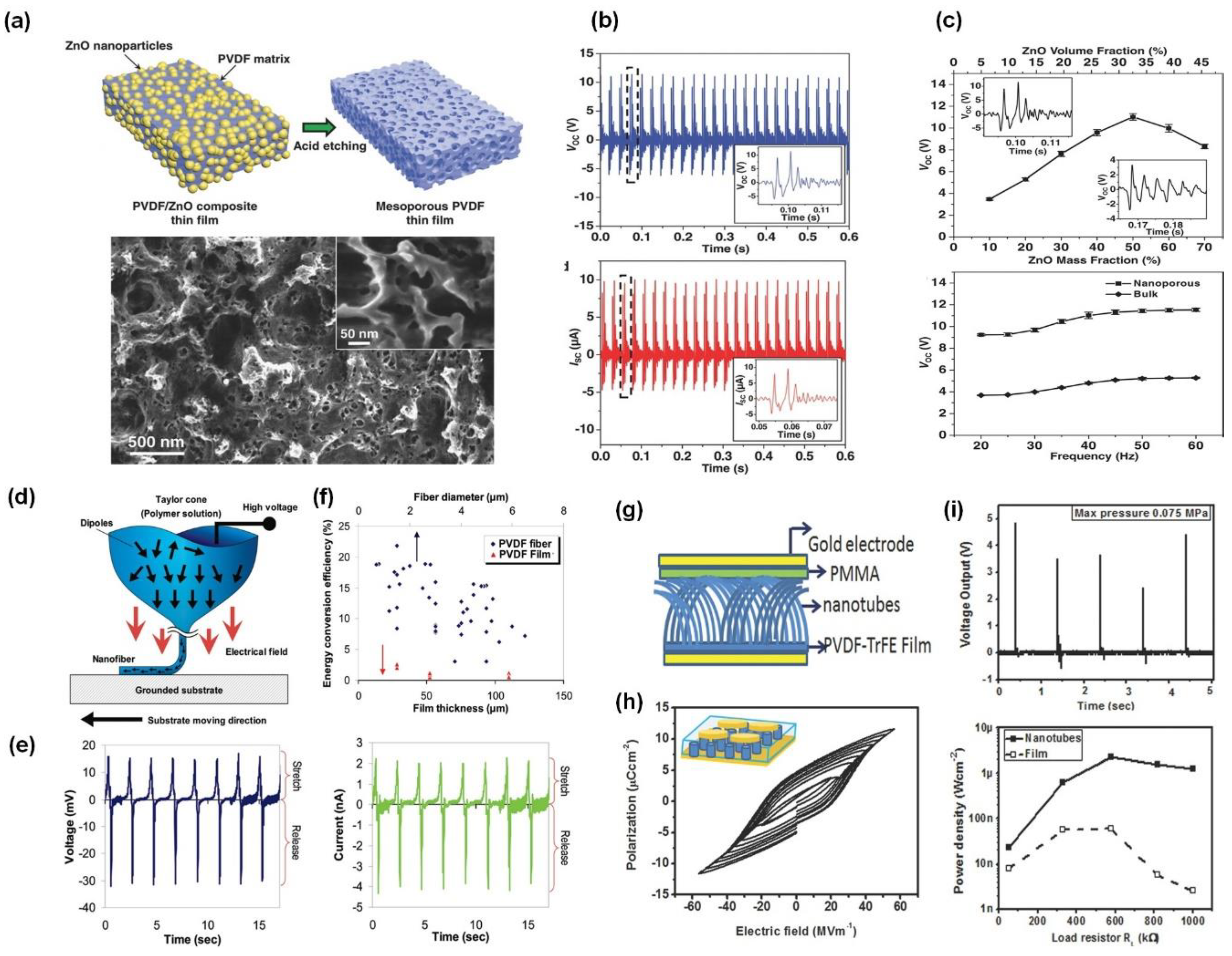
2. Thin Film PVDF Structure
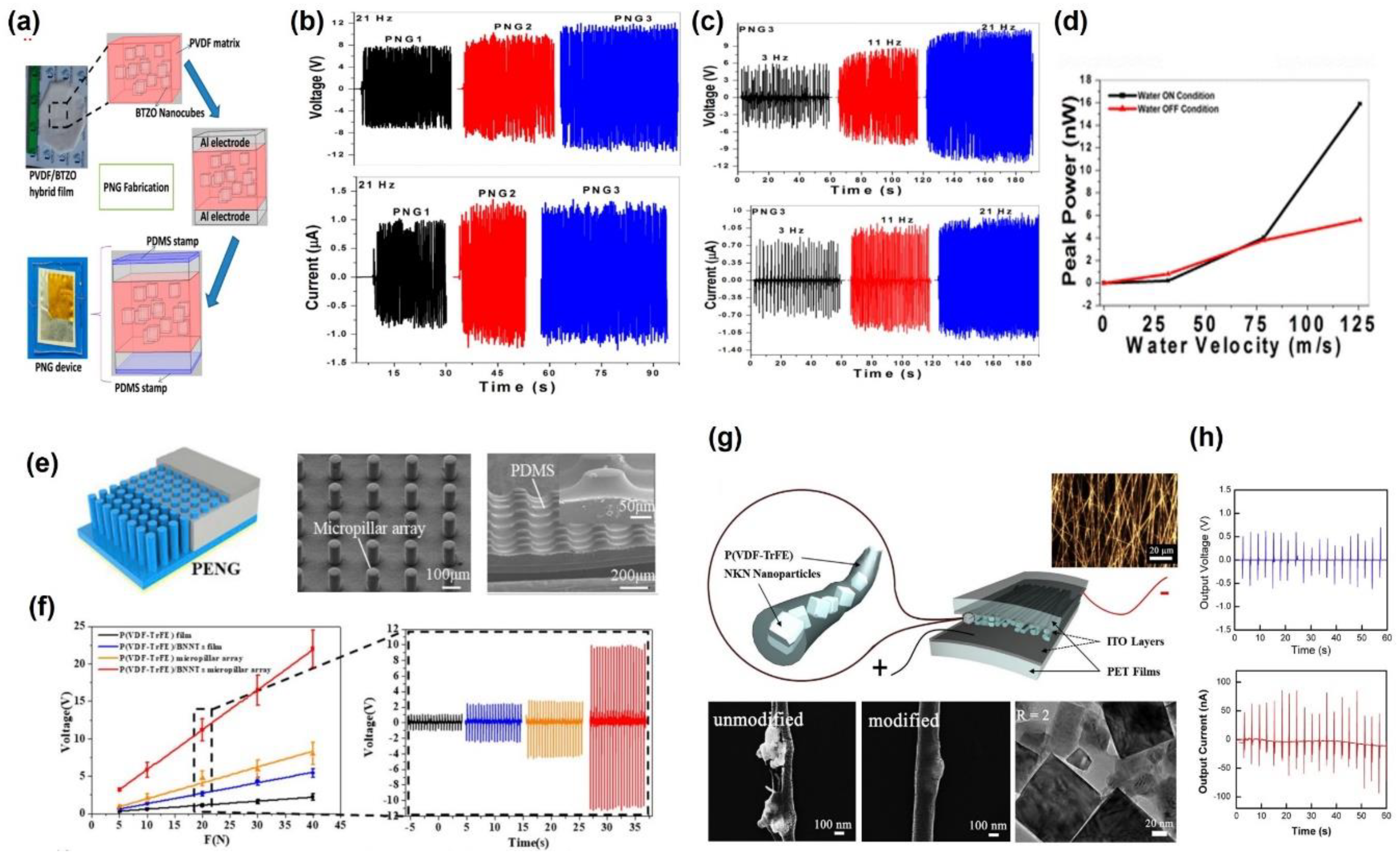
3. Micro Scale PVDF Structure
4. Nano Scale PVDF Structure
5. PVDF Nanocomposite
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anton, S.R.; Sodano, H.A. A review of power harvesting using piezoelectric materials (2003–2006). Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeder, M.D.; Damjanovic, D.; Setter, N. Lead free piezoelectric materials. J. Electroceram. 2004, 13, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.; Kell, R.; Taylor, R.; Thomas, L. Piezoelectric materials, a review of progress. IRE Trans. Compon. Parts 1962, 9, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodano, H.A.; Inman, D.J.; Park, G. A review of power harvesting from vibration using piezoelectric materials. Shock Vib. Dig. 2004, 36, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, K.Y.; Gupta, M.K.; Majumder, S.; Kim, S.-W. Self-compensated insulating ZnO-based piezoelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 6949–6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Song, J.; Xu, S.; Yang, R.; Gao, Z.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.L. Growth of ZnO nanotube arrays and nanotube based piezoelectric nanogenerators. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 9260–9264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.L. Direct-current nanogenerator driven by ultrasonic waves. Science 2007, 316, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.; Lee, C.; Park, H.; Lee, J.-H. Direct-current flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators based on two-dimensional ZnO nanosheet. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 509, 145328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Bae, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.-H.; Yoon, G.C.; Gupta, M.K.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Park, J.; Kim, S.-W. Depletion width engineering via surface modification for high performance semiconducting piezoelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2014, 8, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, S.-W. Two-dimensional vanadium-doped ZnO nanosheet-based flexible direct current nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8932–8939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Yao, N.; Shi, Y. 1.6 V nanogenerator for mechanical energy harvesting using PZT nanofibers. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2133–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Kim, J.; Nguyen, T.D.; Lisko, B.; Purohit, P.K.; McAlpine, M.C. Enhanced piezoelectricity and stretchability in energy harvesting devices fabricated from buckled PZT ribbons. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.I.; Son, J.H.; Hwang, G.T.; Jeong, C.K.; Ryu, J.; Koo, M.; Choi, I.; Lee, S.H.; Byun, M.; Wang, Z.L. Highly-efficient, flexible piezoelectric PZT thin film nanogenerator on plastic substrates. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2514–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Jia, W.; Qian, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.; Hou, X.; Mu, J.; Geng, W.; Cho, J.; He, J. High-performance PZT-based stretchable piezoelectric nanogenerator. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 7, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiat, J.-M.; Uesu, Y.; Dkhil, B.; Matsuda, M.; Malibert, C.; Calvarin, G. Monoclinic structure of unpoled morphotropic high piezoelectric PMN-PT and PZN-PT compounds. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 064106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yeh, Y.-W.; Poirier, G.; McAlpine, M.C.; Register, R.A.; Yao, N. Flexible piezoelectric PMN–PT nanowire-based nanocomposite and device. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2393–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.T.; Park, H.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, S.; Park, K.I.; Byun, M.; Park, H.; Ahn, G.; Jeong, C.K.; No, K. Self-powered cardiac pacemaker enabled by flexible single crystalline PMN-PT piezoelectric energy harvester. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4880–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, T.; Maruyama, K.-I.; Sakata, K. (Bi1/2Na1/2) TiO3-BaTiO3 system for lead-free piezoelectric ceramics. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 30, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaki, T.; Yan, K.; Miyamoto, T.; Adachi, M. Lead-free piezoelectric ceramics with large dielectric and piezoelectric constants manufactured from BaTiO3 nano-powder. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 46, L97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-I.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Hwang, G.-T.; Kang, S.-J.L.; Wang, Z.L.; Lee, K.J. Piezoelectric BaTiO3 thin film nanogenerator on plastic substrates. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4939–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.H.; Ryu, H.; Lee, J.H.; Khan, U.; Kim, H.; Kwak, S.S.; Kim, S.-W. High-Performance Piezoelectric, Pyroelectric, and Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on P (VDF-TrFE) with Controlled Crystallinity and Dipole Alignment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Ryu, H.; Kim, T.Y.; Kwak, S.S.; Yoon, H.J.; Kim, T.H.; Seung, W.; Kim, S.-W. Thermally Induced Strain-Coupled Highly Stretchable and Sensitive Pyroelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1500704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Lee, K.Y.; Kumar, B.; Tien, N.T.; Lee, N.-E.; Kim, S.-W. Highly sensitive stretchable transparent piezoelectric nanogenerators. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, A.; Choi, Y.S.; Chalmers, E.; Ou, C.; Kar-Narayan, S. Piezoelectric Nylon-11 Nanowire Arrays Grown by Template Wetting for Vibrational Energy Harvesting Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.-Q.; Tang, Y.-Y.; Li, P.-F.; You, Y.-M.; Xiong, R.-G. Competitive halogen bond in the molecular ferroelectric with large piezoelectric response. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 3975–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Han, S.A.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, S.W. Biomolecular Piezoelectric Materials: From Amino Acids to Living Tissues. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J.H.; Xiao, J.; Desai, M.S.; Zhang, X.; Lee, S.-W. Vertical self-assembly of polarized phage nanostructure for energy harvesting. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 2661–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Heo, K.; Schulz-Schönhagen, K.; Lee, J.H.; Desai, M.S.; Jin, H.-E.; Lee, S.-W. Diphenylalanine peptide nanotube energy harvesters. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 8138–8144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, X.-X.; Song, W.-Z.; Qiu, H.-J.; Zhang, J.; Fan, Z.; Yu, M.; Long, Y.-Z. Wireless Single-Electrode Self-Powered Piezoelectric Sensor for Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 8288–8295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.K.; Hyeon, D.Y.; Hwang, G.-T.; Lee, G.-J.; Lee, M.-K.; Park, J.-J.; Park, K.-I. Nanowire-percolated piezoelectric copolymer-based highly transparent and flexible self-powered sensors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 25481–25489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuh, Y.-K.; Chen, P.-C.; Huang, Z.-M.; Ho, H.-C. Self-powered sensing elements based on direct-write, highly flexible piezoelectric polymeric nano/microfibers. Nano Energy 2015, 11, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachan, V.K.; Imam, S.A.; Beg, M. Energy-efficient communication methods in wireless sensor networks: A critical review. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2012, 39, 35–48. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, B.; Yousefi, A.A.; Bellah, S.M. Effect of tensile strain rate and elongation on crystalline structure and piezoelectric properties of PVDF thin films. Polym. Test. 2007, 26, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, V.; Mahapatra, D.R.; Jain, A.; Gayathri, A. Characterization of a large-area PVDF thin film for electro-mechanical and ultrasonic sensing applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2010, 163, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, N.I.; Ab Rahim, R.; Ralib, A.A.M. Flexible PVDF thin film as piezoelectric energy harvester. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2019, 8, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, M.; Tian, B.; Xiang, P.; Zhong, N.; Lin, H.; Luo, C.; Peng, H.; Duan, C.G. Transparent PVDF-TrFE/Graphene Oxide Ultrathin Films with Enhanced Energy Harvesting Performance. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 7951–7955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saygh, A.; Ponnamma, D.; AlMaadeed, M.A.; Vijayan, P.; Karim, A.; Hassan, M.K. Flexible pressure sensor based on PVDF nanocomposites containing reduced graphene oxide-titania hybrid nanolayers. Polymers 2017, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, H.; Gao, T.; Li, C.; Shi, G. A small graphene oxide sheet/polyvinylidene fluoride bilayer actuator with large and rapid responses to multiple stimuli. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 17465–17470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystrov, V.S.; Bdikin, I.K.; Silibin, M.; Karpinsky, D.; Kopyl, S.; Paramonova, E.V.; Goncalves, G. Molecular modeling of the piezoelectric properties of ferroelectric composites containing polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and either graphene or graphene oxide. J. Mol. Model. 2017, 23, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, C. An integrated flexible harvester coupled triboelectric and piezoelectric mechanisms using PDMS/MWCNT and PVDF. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2015, 24, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusarova, E.; Viala, B.; Plihon, A.; Gusarov, B.; Gimeno, L.; Cugat, O. Flexible screen-printed piezoelectric P (VDF-TrFE) copolymer microgenerators for energy harvesting. In Proceedings of the 2015 Transducers-2015 18th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (TRANSDUCERS), Anchorage, AK, USA, 21–25 June 2015; pp. 1901–1904. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, H.; Xia, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, H.; Wu, H.; Lin, S. Graphene-piezoelectric material heterostructure for harvesting energy from water flow. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Towfeeq, I.; Dong, Y.; Gorman, S.; Rao, A.M.; Koley, G. P (VDF-TrFE) film on PDMS substrate for energy harvesting applications. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wen, C.; Zhang, Z.-B.; Wu, D. Flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator made of poly (vinylidenefluoride-co-trifluoroethylene)(PVDF-TrFE) thin film. Nano Energy 2014, 7, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Gupta, M.K.; Kim, T.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Oh, J.; Ryu, C.; Yoo, W.J.; Kang, C.Y.; Yoon, S.J. Highly stretchable piezoelectric-pyroelectric hybrid nanogenerator. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavanasi, V.; Kumar, V.; Parida, K.; Wang, J.; Lee, P.S. Enhanced piezoelectric energy harvesting performance of flexible PVDF-TrFE bilayer films with graphene oxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoshi, T.; Chen, H.; Soldani, G.; Galletti, P.M.; Goddard, M. Microporous small diameter PVDF-TrFE vascular grafts fabricated by a spray phase inversion technique. ASAIO J. 1992, 38, M201–M206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwansumpan, D.; Manuspiya, H.; Laoratanakul, P.; Bhalla, A. Induced Internal Bubble Shapes Affected Piezoelectric Behaviors of PVDF Films; Advanced Materials Research, Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2008; pp. 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, V.F.; Botelho, G.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Nonsolvent induced phase separation preparation of poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-chlorotrifluoroethylene) membranes with tailored morphology, piezoelectric phase content and mechanical properties. Mater. Des. 2015, 88, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Hang, M.; Chen, K.; Brown, K.; Zhang, J.X. Piezoelectric PVDF thin films with asymmetric microporous structures for pressure sensing. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE SENSORS, Busan, Korea, 1–4 November 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, J.X. Microporous polyvinylidene fluoride film with dense surface enables efficient piezoelectric conversion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 193901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, D.M.; Ribeiro, C.; Sencadas, V.; Vikingsson, L.; Gasch, M.O.; Ribelles, J.G.; Botelho, G.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Strategies for the development of three dimensional scaffolds from piezoelectric poly (vinylidene fluoride). Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Kang, Y.S.; Park, C. Micropatterning of semicrystalline poly (vinylidene fluoride)(PVDF) solutions. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 1002–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, P.-M.; Lee, S.; Gorton, A.; Schulz, M.J.; Ahn, C.H. Flexible dome and bump shape piezoelectric tactile sensors using PVDF-TrFE copolymer. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2008, 17, 334–341. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Nakagawa, Y.; Takai, Y.; Kikuchi, K.; Tsuchitani, S. PVdf film micro fabrication for the robotics skin sensor having flexibility and high sensitivity. In Proceedings of the 2011 Fifth International Conference on Sensing Technology, Palmerston North, New Zealand, 28 November–1 December 2011; pp. 603–606. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, W.; Ke, C.; Lim, P.; Kuarm, A.; Zeng, K.; Ho, G.W. Direct stamping and capillary flow patterning of solution processable piezoelectric polyvinylidene fluoride films. Polymer 2013, 54, 5330–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sümer, B.; Koc, I.M. Fabrication of a flexible tactile sensor with micro-pillar array. Procedia Eng. 2015, 120, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zabek, D.; Taylor, J.; Boulbar, E.L.; Bowen, C.R. Micropatterning of flexible and free standing polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) films for enhanced pyroelectric energy transformation. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1401891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, X.; Zhu, P.; Zeng, W.; Hu, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, R.; Wong, C.-P. Highly sensitive flexible pressure sensor based on silver nanowires-embedded polydimethylsiloxane electrode with microarray structure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 26314–26324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Du, X.; Gao, R.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Yu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Tai, H. Self-polarization of PVDF film triggered by hydrophilic treatment for pyroelectric sensor with ultra-low piezoelectric noise. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, D.; Ferrell, N.J.; Hansford, D.J. Fabrication of piezoelectric polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) microstructures by soft lithography for tissue engineering and cell biology applications. MRS Online Proc. Libr. Arch. 2007, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Dapino, M.J.; Gallego-Perez, D.; Hansford, D. Microphone based on polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) micro-pillars and patterned electrodes. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2009, 153, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavese, G.; Stassi, S.; Cauda, V.; Verna, A.; Motto, P.; Chiodoni, A.; Marasso, S.L.; Demarchi, D. Different scale confinements of PVDF-TrFE as functional material of piezoelectric devices. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 2237–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shao, J.; Tian, H.; Li, X.; Tian, Y.; Wang, C. Flexible three-axial tactile sensors with microstructure-enhanced piezoelectric effect and specially-arranged piezoelectric arrays. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 025018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariy, I.; Ivanova, A.; Shvartsman, V.; Lupascu, D.; Sukhorukov, G.; Surmeneva, M.; Surmenev, R. Poling and annealing of piezoelectric Poly (Vinylidene fluoride) micropillar arrays. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 239, 122035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuh, Y.-K.; Chen, S.-Y.; Ye, J.-C. Massively parallel aligned microfibers-based harvester deposited via in situ, oriented poled near-field electrospinning. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 033114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuh, Y.-K.; Ye, J.-C.; Chen, P.-C.; Huang, Z.-M. A highly flexible and substrate-independent self-powered deformation sensor based on massively aligned piezoelectric nano-/microfibers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 16101–16106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Bian, J.; Su, Y.; Zhou, J.; Duan, Y.; Yin, Z. Hyper-stretchable self-powered sensors based on electrohydrodynamically printed, self-similar piezoelectric nano/microfibers. Nano Energy 2017, 40, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabriani, F.; Chinnam, K.C.; Casalotti, A.; Lanzara, G. Effect of Electrospun PVDF-Fibers Orientation for Vibration Sensing; IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; p. 012056. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Dai, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z. Highly Stretchable Piezoelectric Strain Sensor with Dual Wavy Structures of PVDF Microfibers. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 4th Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (ITNEC), Chongqing, China, 12–14 June 2020; pp. 2418–2422. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Sharma, T.; Zhang, J.X. Mesoporous surface control of PVDF thin films for enhanced piezoelectric energy generation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 216, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Yoon, H.J.; Kim, T.Y.; Gupta, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Seung, W.; Ryu, H.; Kim, S.-W. Micropatterned P (VDF-TrFE) film-based piezoelectric nanogenerators for highly sensitive self-powered pressure sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3203–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-Y.; Yun, T.G.; Qaiser, N.; Paik, H.; Roh, H.S.; Hong, J.; Hong, S.; Han, S.M.; No, K. Vertically aligned P (VDF-TrFE) core-shell structures on flexible pillar arrays. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tian, H.; Li, X.; Shao, J.; Ding, Y.; An, N.; Zhou, Y. A high performance P (VDF-TrFE) nanogenerator with self-connected and vertically integrated fibers by patterned EHD pulling. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 11536–11544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, H.; Ku, J.; Sohn, J.I.; Park, Y.J.; Song, B.G.; Jung, M.H.; Lee, E.K.; Choi, B.L. Porous PVDF as effective sonic wave driven nanogenerators. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 5142–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauda, V.; Stassi, S.; Bejtka, K.; Canavese, G. Nanoconfinement: An effective way to enhance PVDF piezoelectric properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6430–6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Wang, X.; Shi, X.; Ran, X. The induction of poly (vinylidene fluoride) electroactive phase by modified anodic aluminum oxide template nanopore surface. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 87429–87436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, S.; Kadlec, A. Piezoelectric and dielectric properties of nanoporous polyvinylidence fluoride (PVDF) films. In Behavior and Mechanics of Multifunctional Materials and Composites 2016, Proceedings of the SPIE Smart Structures and Materials + Nondestructive Evaluation and Health Monitoring, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 21–23 March 2016; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; p. 98000P. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, H.; Tong, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; An, Q. A self-powered porous ZnS/PVDF-HFP mechanoluminescent composite film that converts human movement into eye-readable light. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 5489–5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Tran, V.H.; Wang, J.; Fuh, Y.-K.; Lin, L. Direct-write piezoelectric polymeric nanogenerator with high energy conversion efficiency. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Ren, G.; Zhang, P.; Xu, C. A flexible piezoelectric force sensor based on PVDF fabrics. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 045009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadimani, R.L.; Bayramol, D.V.; Sion, N.; Shah, T.; Qian, L.; Shi, S.; Siores, E. Continuous production of piezoelectric PVDF fibre for e-textile applications. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 075017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuh, Y.-K.; Ye, J.-C.; Chen, P.-C.; Ho, H.-C.; Huang, Z.-M. Hybrid energy harvester consisting of piezoelectric fibers with largely enhanced 20 V for wearable and muscle-driven applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 16923–16931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, F.; Latifi, M.; Shamshirsaz, M. Electrospinning/electrospray of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF): Piezoelectric nanofibers. J. Text. Inst. 2016, 107, 1037–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, B.; Sarkar, M.D. PVDF based Piezoelectric Nanogenerator as a new kind of device for generating power from renewable resources. IOSR J. Polym. Text. Eng. (IOSR-JPTE) 2017, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serairi, L.; Gu, L.; Qin, Y.; Lu, Y.; Basset, P.; Leprince-Wang, Y. Flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators based on PVDF-TrFE nanofibers. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 80, 30901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaman, M.; Khudiyev, T.; Ozgur, E.; Kanik, M.; Aktas, O.; Ozgur, E.O.; Deniz, H.; Korkut, E.; Bayindir, M. Arrays of indefinitely long uniform nanowires and nanotubes. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, W.H.; Mirshekarloo, M.S.; Chen, S.; Yao, K.; Tay, F.E.H. Nanoconfinement induced crystal orientation and large piezoelectric coefficient in vertically aligned P (VDF-TrFE) nanotube array. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 09790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.-T.; Yen, C.-K.; Wang, S.-Y.; Lai, Y.-C.; Lin, L.; Huang, J.; Kuo, S.-W. Near-field electrospinning enhances the energy harvesting of hollow PVDF piezoelectric fibers. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 85073–85081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-M.; Chou, M.-H.; Zeng, W.-Y. Piezoelectric response of aligned electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride/carbon nanotube nanofibrous membranes. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Zhao, P.; McConohy, G.; Yang, H.; Tong, Y.; Wang, X. Sponge-like piezoelectric polymer films for scalable and integratable nanogenerators and self-powered electronic systems. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1301624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavanasi, V.; Kusuma, D.Y.; Lee, P.S. Polarization Orientation, Piezoelectricity, and Energy Harvesting Performance of Ferroelectric PVDF-TrFE Nanotubes Synthesized by Nanoconfinement. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1400723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Chung, G.-S. Synthesis of PVDF-graphene nanocomposites and their properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 581, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hazmi, F.S.; de Leeuw, D.M.; Al-Ghamdi, A.; Shokr, F. Synthesis and characterization of novel Cu2O/PVDF nanocomposites for flexible ferroelectric organic electronic memory devices. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2017, 17, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinya, I.; Pal, A.; Sen, S. Polyglycolated zinc ferrite incorporated poly (vinylidene fluoride)(PVDF) composites with enhanced piezoelectric response. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 722, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Achaby, M.; Arrakhiz, F.; Vaudreuil, S.; Essassi, E.; Qaiss, A. Piezoelectric β-polymorph formation and properties enhancement in graphene oxide–PVDF nanocomposite films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 7668–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silibin, M.; Bystrov, V.; Karpinsky, D.; Nasani, N.; Goncalves, G.; Gavrilin, I.; Solnyshkin, A.; Marques, P.; Singh, B.; Bdikin, I. Local mechanical and electromechanical properties of the P (VDF-TrFE)-graphene oxide thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 421, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Chen, C.Y.; Wang, S.; Cha, S.N.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, J.M.; Chou, L.J.; Wang, Z.L. A hybrid piezoelectric structure for wearable nanogenerators. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Hou, Y.; Gao, X.; Zheng, M.; Zhu, M. Highly durable piezoelectric energy harvester based on a PVDF flexible nanocomposite filled with oriented BaTi2O5 nanorods with high power density. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, H.; Kishor, R.; Xiao, J.; Gao, F.; Zeng, K.; Chen, X.; Sun, X.W. High-performance piezoelectric nanogenerators composed of formamidinium lead halide perovskite nanoparticles and poly (vinylidene fluoride). Nano Energy 2017, 37, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Fernando, T.; Li, M.; Lin, Y.; Tseng, T.-L.B. Fabrication and characterization of 3D printed BaTiO3/PVDF nanocomposites. J. Compos. Mater. 2018, 52, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, L.; Hu, N.; Qiu, J.; Chang, C.; Atobe, S.; Fukunaga, H.; Watanabe, T.; Liu, Y.; Ning, H. Evaluation of piezoelectric property of reduced graphene oxide (rGO)–poly (vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposites. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7250–7255. [Google Scholar]
- Harstad, S.; D’Souza, N.; Soin, N.; El-Gendy, A.A.; Gupta, S.; Pecharsky, V.K.; Shah, T.; Siores, E.; Hadimani, R.L. Enhancement of β-phase in PVDF films embedded with ferromagnetic Gd5Si4 nanoparticles for piezoelectric energy harvesting. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 056411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.H.; Singh, S.; Khare, N. Enhanced β-phase in PVDF polymer nanocomposite and its application for nanogenerator. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Guo, H.; He, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, H.; Volkov, A.V.; He, T. Unprecedented scaling/fouling resistance of omniphobic polyvinylidene fluoride membrane with silica nanoparticle coated micropillars in direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 117819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-Y.; Kim, H.; Li, H.-M.; Jang, A.-R.; Lim, Y.-D.; Cha, S.N.; Park, Y.J.; Kang, D.J.; Yoo, W.J. Hybrid energy harvester based on nanopillar solar cells and PVDF nanogenerator. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 175402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melilli, G.; Gorse, D.; Galifanova, A.; Oral, O.; Balanzat, E.; Doare, D.; Tabellout, M.; Bechelany, M.; Lairez, D.; Je, W. Enhanced Piezoelectric Response in Nanostructured Ni/PVDF Films. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, İ.M.; Akça, E. Design of a piezoelectric based tactile sensor with bio-inspired micro/nano-pillars. Tribol. Int. 2013, 59, 321–331. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi-Khojin, A.; Jalili, N. A comprehensive model for load transfer in nanotube reinforced piezoelectric polymeric composites subjected to electro-thermo-mechanical loadings. Compos. Part B Eng. 2008, 39, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Sun, B.; Huang, X.; Jiang, P. Synergistic effect of graphene nanosheet and BaTiO3 nanoparticles on performance enhancement of electrospun PVDF nanofiber mat for flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khudiyev, T.; Ozgur, E.; Yaman, M.; Bayindir, M. Structural coloring in large scale core–shell nanowires. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 4661–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasipour, M.; Khajavi, R.; Yousefi, A.A.; Yazdanshenas, M.E.; Razaghian, F. The piezoelectric response of electrospun PVDF nanofibers with graphene oxide, graphene, and halloysite nanofillers: A comparative study. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 15942–15952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, S.; Kang, H.; Kim, H.; Son, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Shin, H.J.; Kim, S.W.; Cho, J.H. High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride–Silver Nanowire Composite Nanofibers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1703778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, B.; Sarkar, M.D. Gold nanoparticle doped PVDF nanofiber preparation of concurrently harvesting light and mechanical energy. IOSR J. Appl. Phys. (IOSR-JAP) 2017, 9, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.H.; Cho, J.H.; Jeong, Y.H.; Paik, J.-H.; Do Yun, J.; Yun, J.S. Flexible lead-free piezoelectric nanofiber composites based on BNT-ST and PVDF for frequency sensor applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 247, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafqi, M.S.S.; Bagherzadeh, R.; Latifi, M. Fabrication of composite PVDF-ZnO nanofiber mats by electrospinning for energy scavenging application with enhanced efficiency. J. Polym. Res. 2015, 22, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garain, S.; Jana, S.; Sinha, T.K.; Mandal, D. Design of in situ poled Ce3+-doped electrospun PVDF/graphene composite nanofibers for fabrication of nanopressure sensor and ultrasensitive acoustic nanogenerator. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4532–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alluri, N.R.; Saravanakumar, B.; Kim, S.-J. Flexible, Hybrid Piezoelectric Film (BaTi(1–x)ZrxO3)/PVDF Nanogenerator as a Self-Powered Fluid Velocity Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 9831–9840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S.; Cheng, C.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Hu, H.; Tian, H.; Li, X.; Ma, L. High-performance piezoelectric nanogenerator based on microstructured P (VDF-TrFE)/BNNTs composite for energy harvesting and radiation protection in space. Nano Energy 2019, 60, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.B.; Han, C.S.; Pyun, J.C.; Ryu, W.H.; Kang, C.-Y.; Cho, Y.S. (Na, K) NbO3 nanoparticle-embedded piezoelectric nanofiber composites for flexible nanogenerators. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 111, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, C.; Park, H.; Lee, J.-H. Recent Structure Development of Poly(vinylidene fluoride)-Based Piezoelectric Nanogenerator for Self-Powered Sensor. Actuators 2020, 9, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/act9030057
Lee C, Park H, Lee J-H. Recent Structure Development of Poly(vinylidene fluoride)-Based Piezoelectric Nanogenerator for Self-Powered Sensor. Actuators. 2020; 9(3):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/act9030057
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Cheoljae, Hyosik Park, and Ju-Hyuck Lee. 2020. "Recent Structure Development of Poly(vinylidene fluoride)-Based Piezoelectric Nanogenerator for Self-Powered Sensor" Actuators 9, no. 3: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/act9030057
APA StyleLee, C., Park, H., & Lee, J.-H. (2020). Recent Structure Development of Poly(vinylidene fluoride)-Based Piezoelectric Nanogenerator for Self-Powered Sensor. Actuators, 9(3), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/act9030057



