Robust H∞ Control of STMDs Used in Structural Systems by Hardware in the Loop Simulation Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
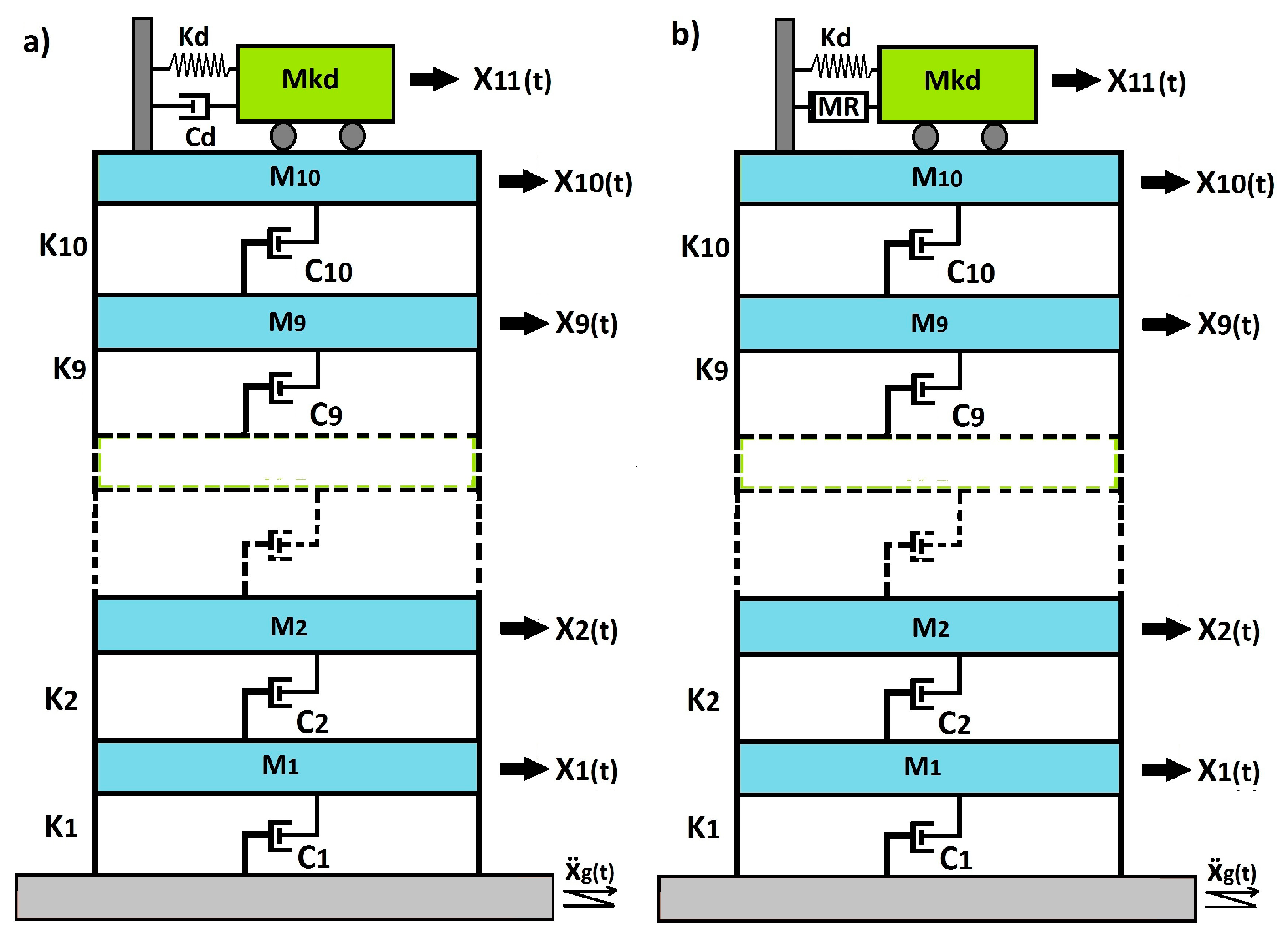
2.1. Motion Equations of Building Models
2.2. Robust Control Design
2.2.1. Defining the System and Model Reduction
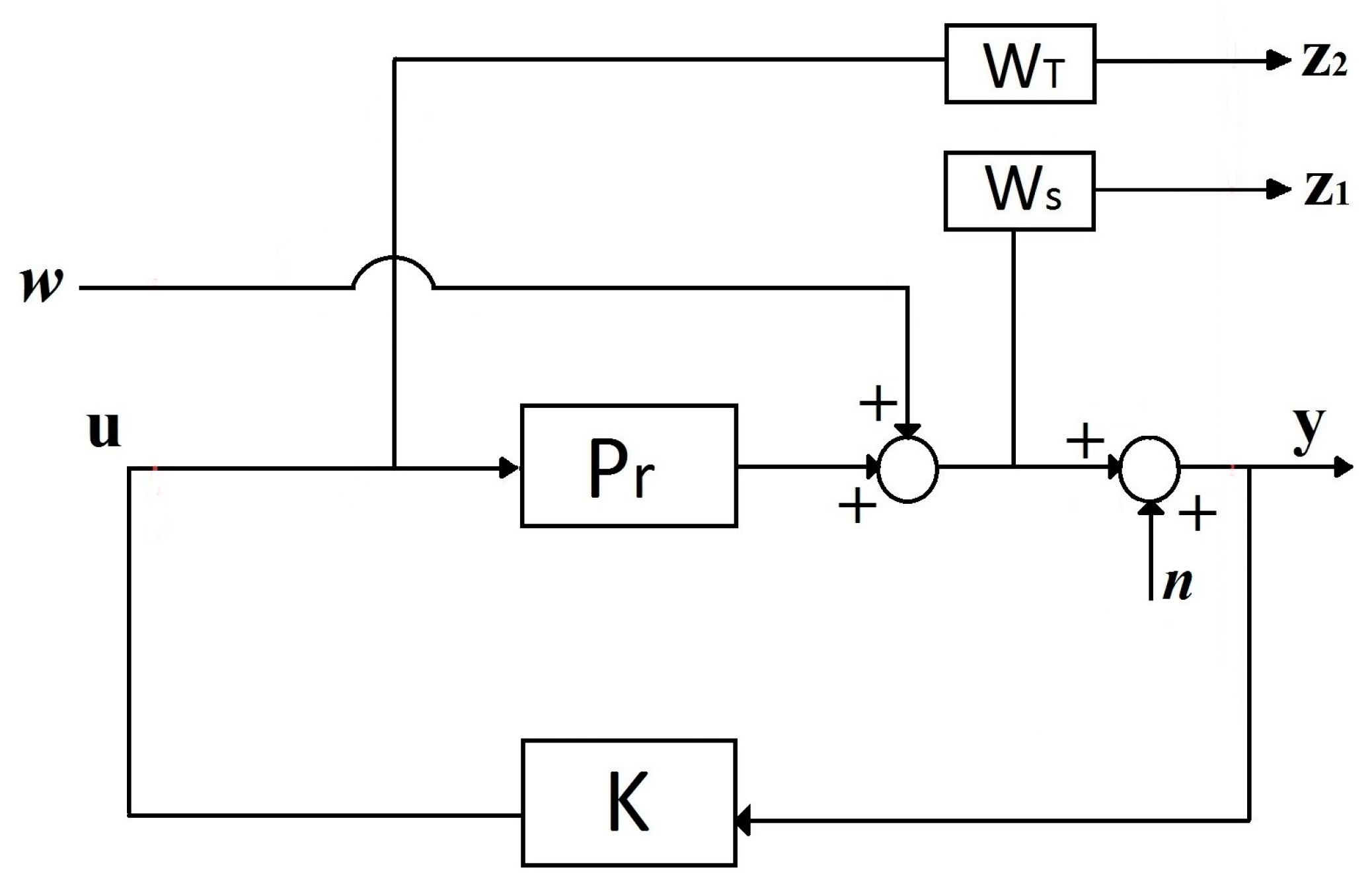
2.2.2. Control Design
2.2.3. Selection of Frequency Shaping Filters and Control in Solution Mixed Sensitivity Structure
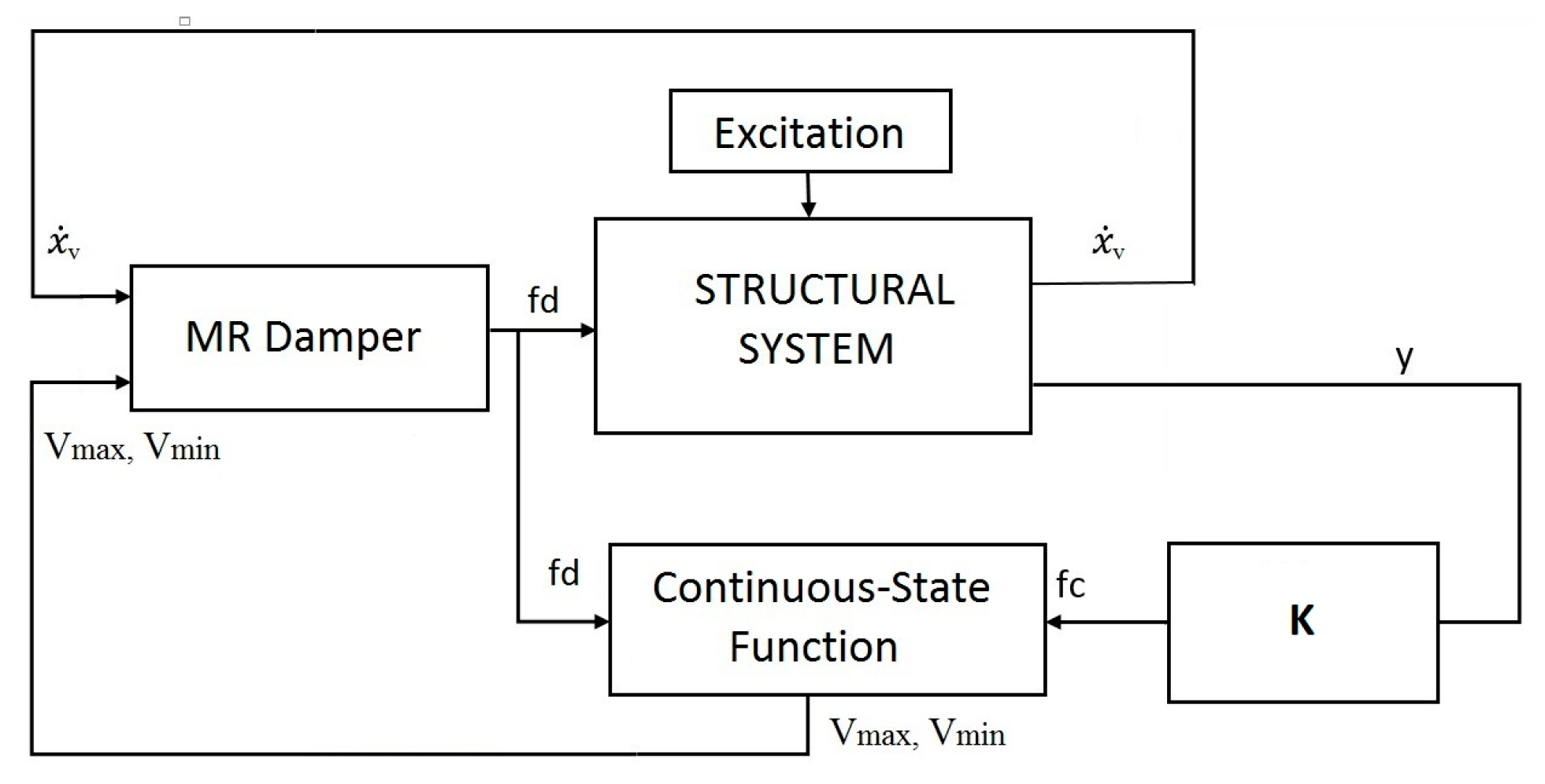
2.3. Application of the Controller to the Semi-Active System
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Performance Analysis and Results with the HILS Method
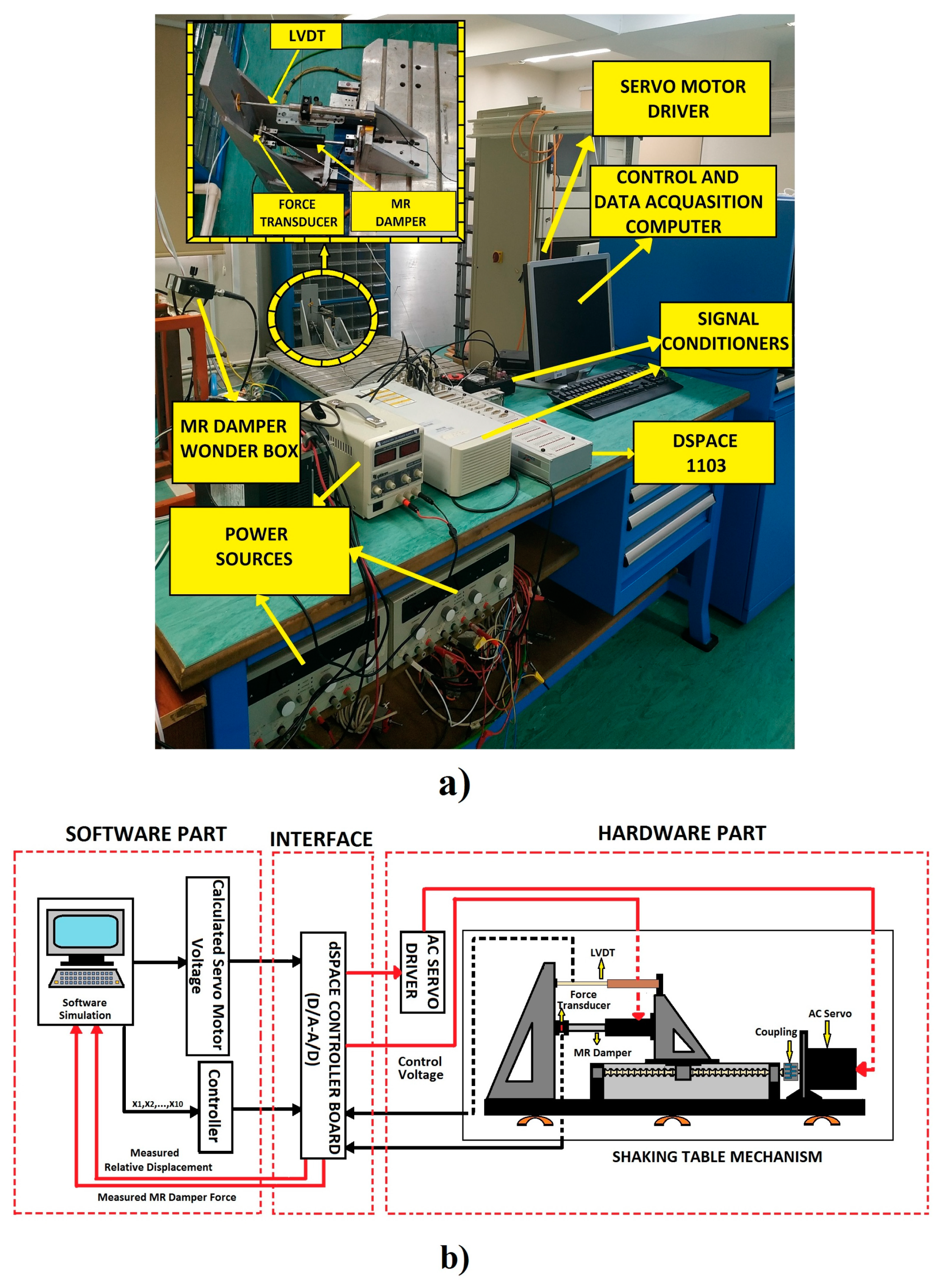
3.1.1. Introduction of the Experimental Setup
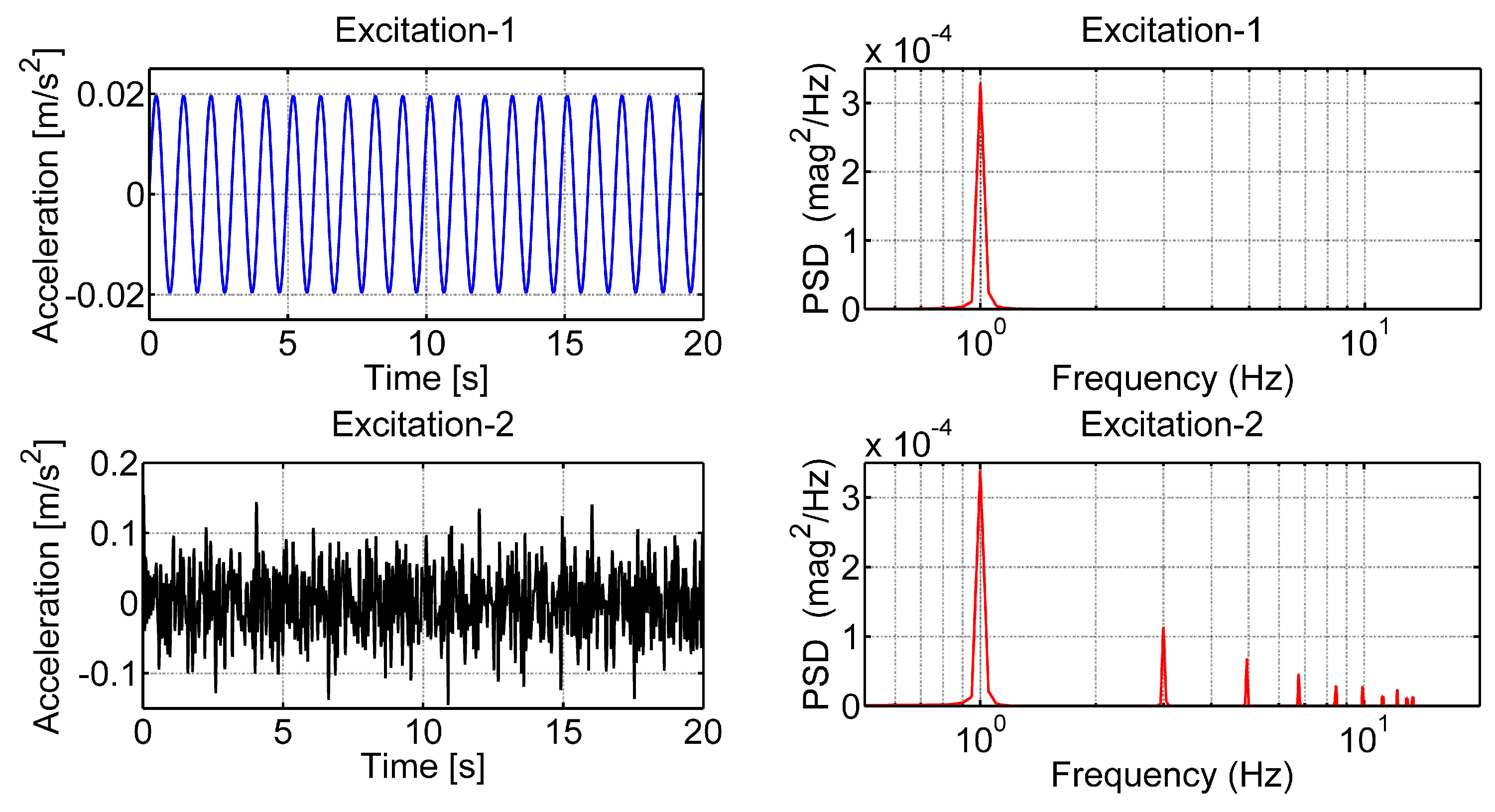
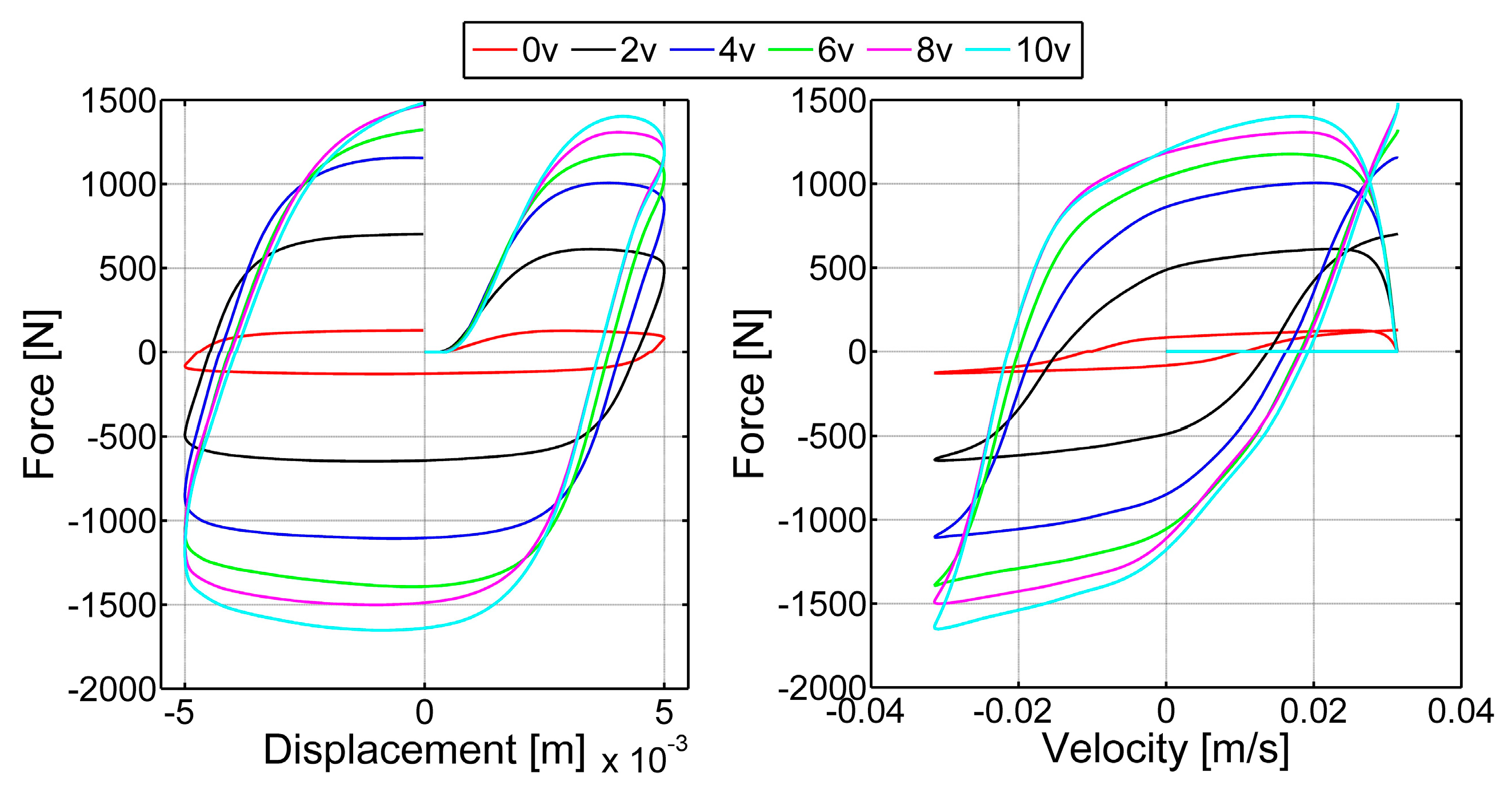
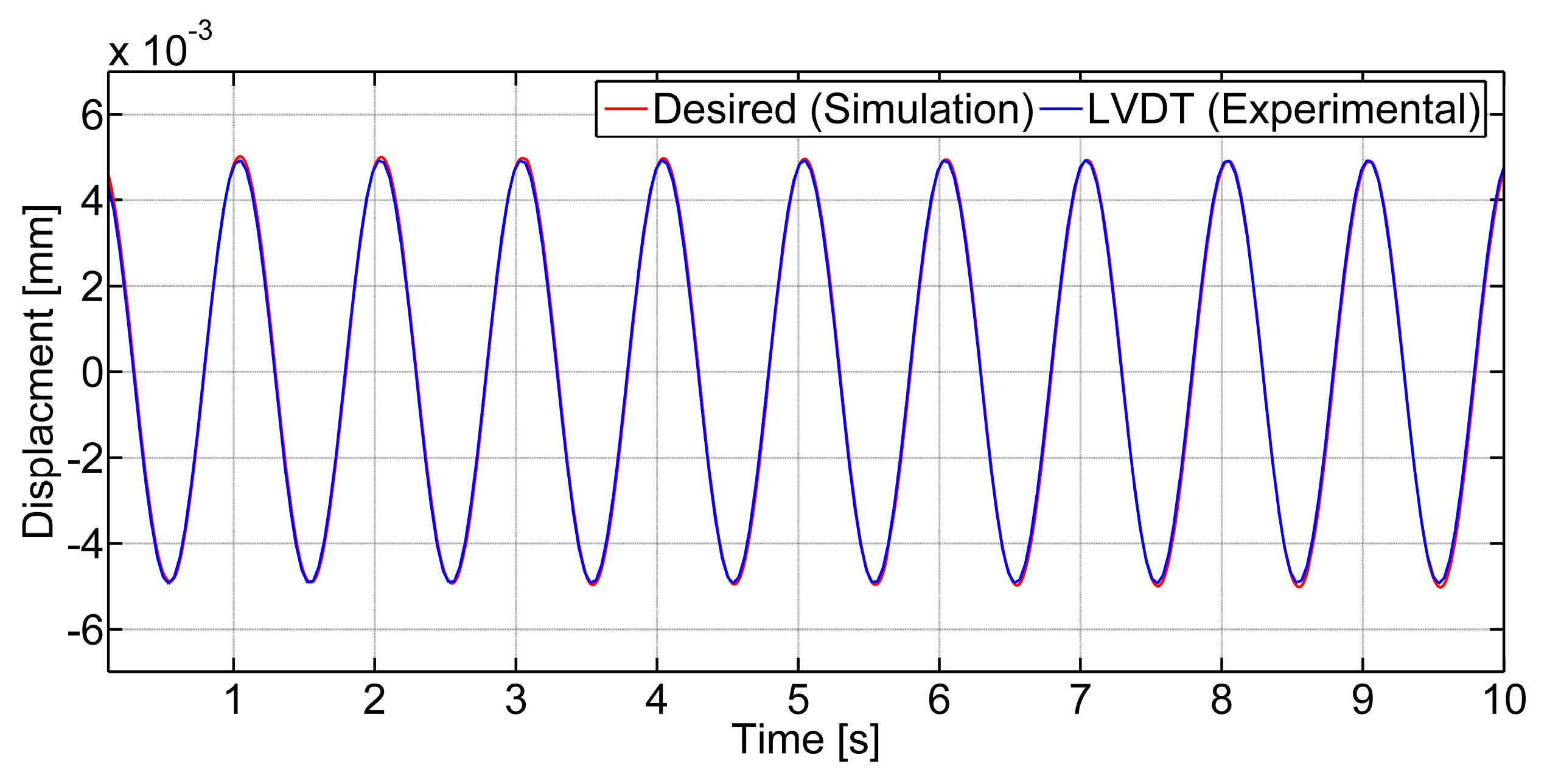
3.1.2. Determination of Parameters
3.2. Application of the Robust Controller
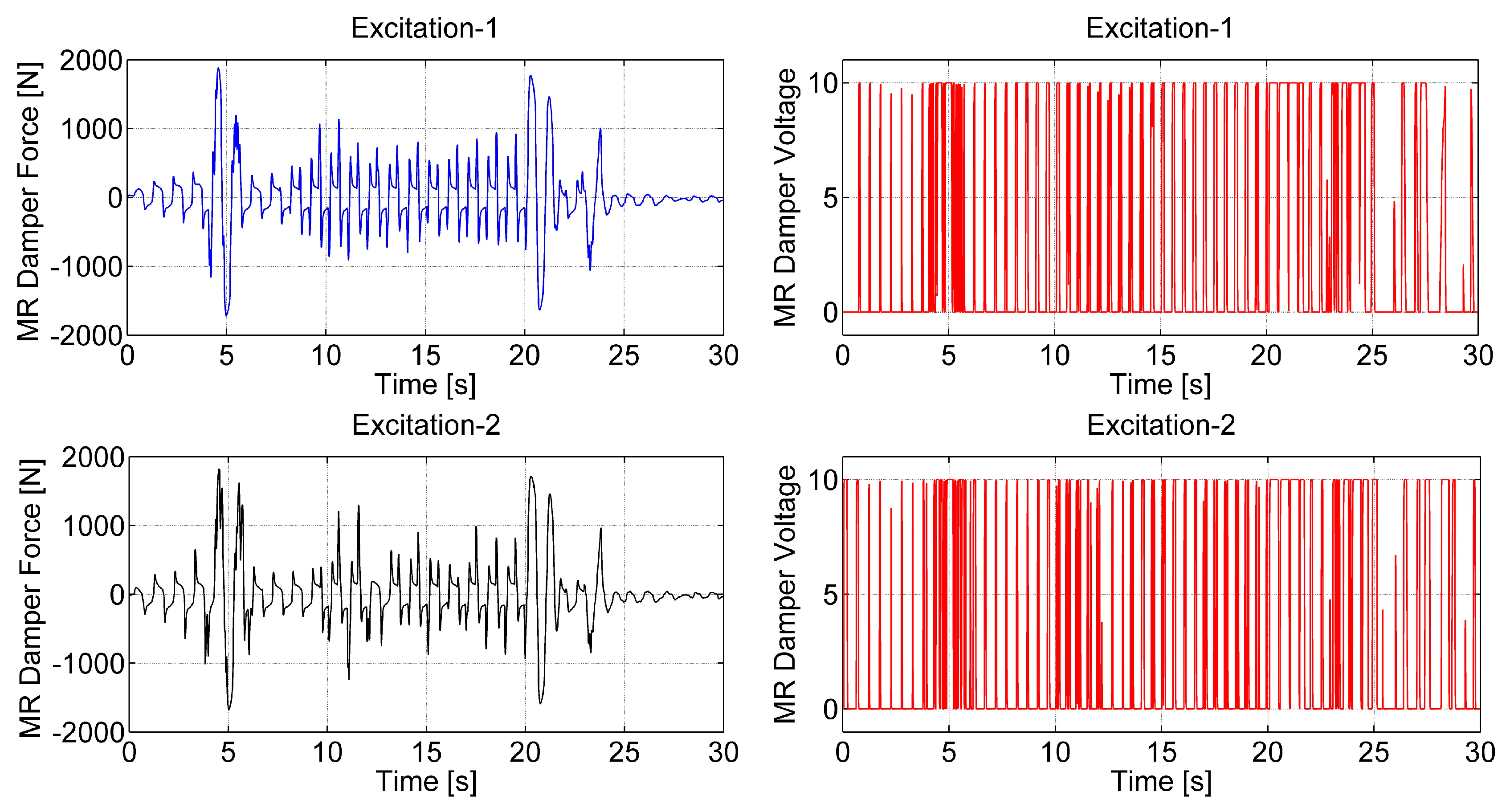
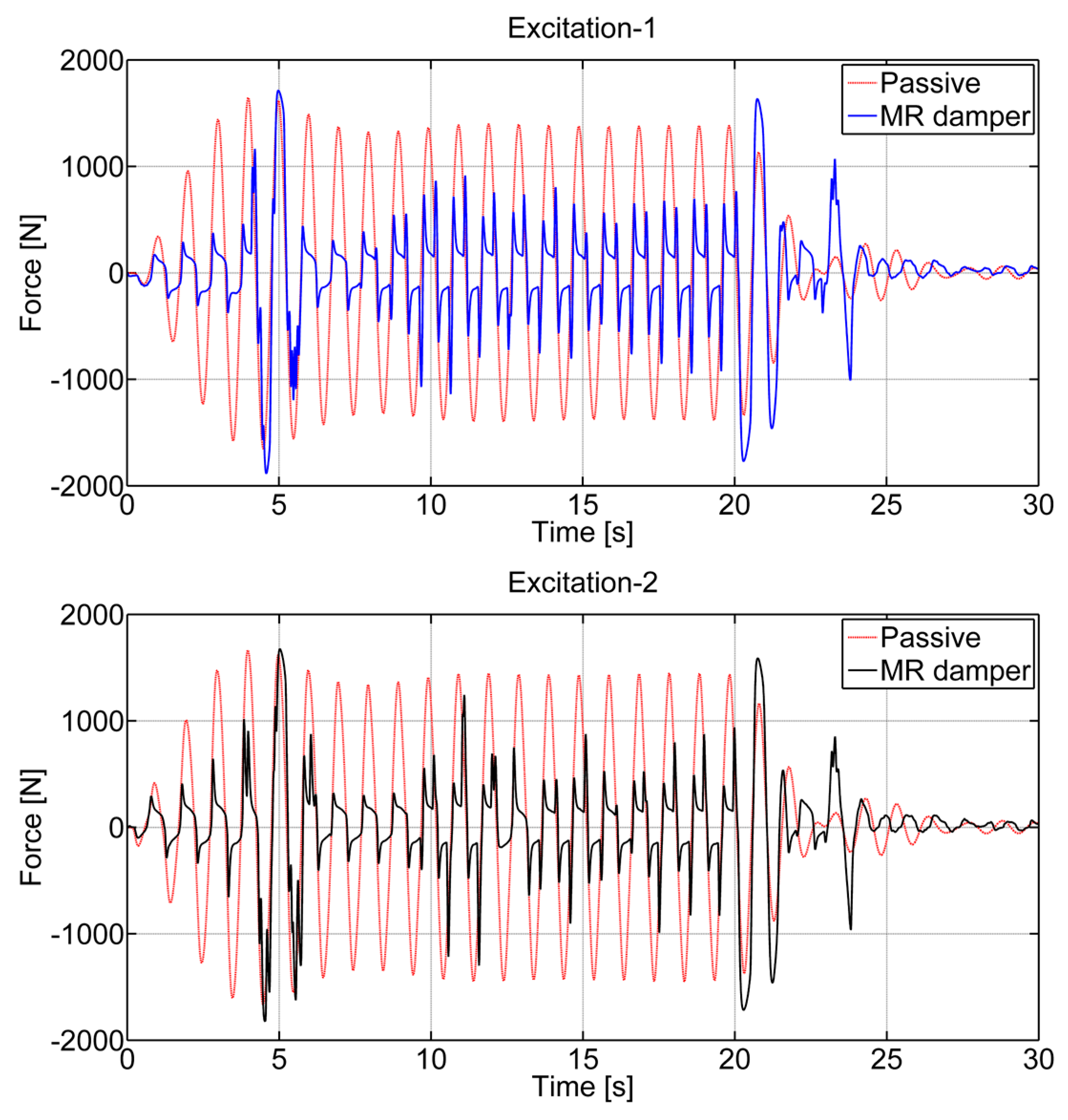
3.2.1. Time Responses
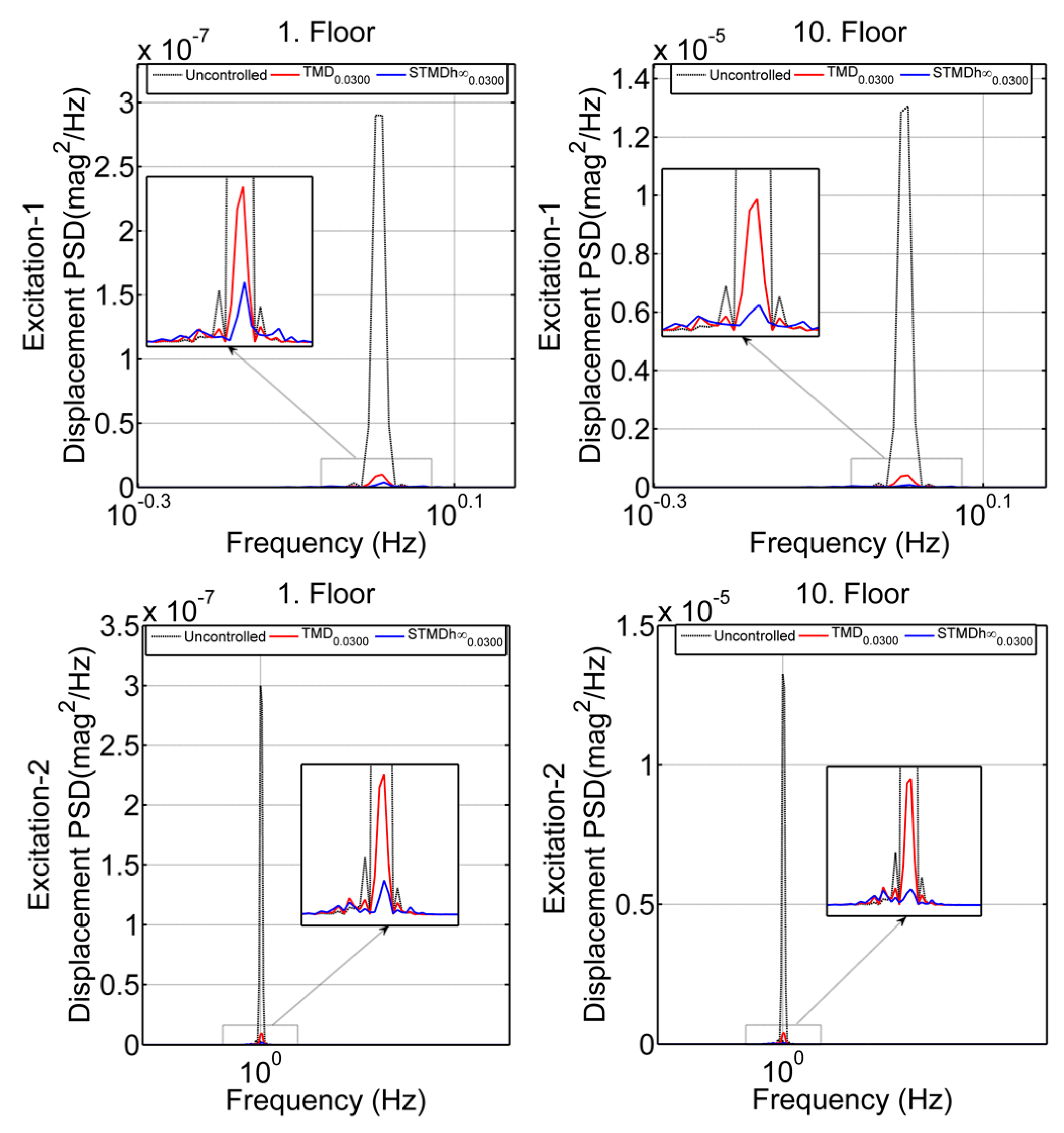
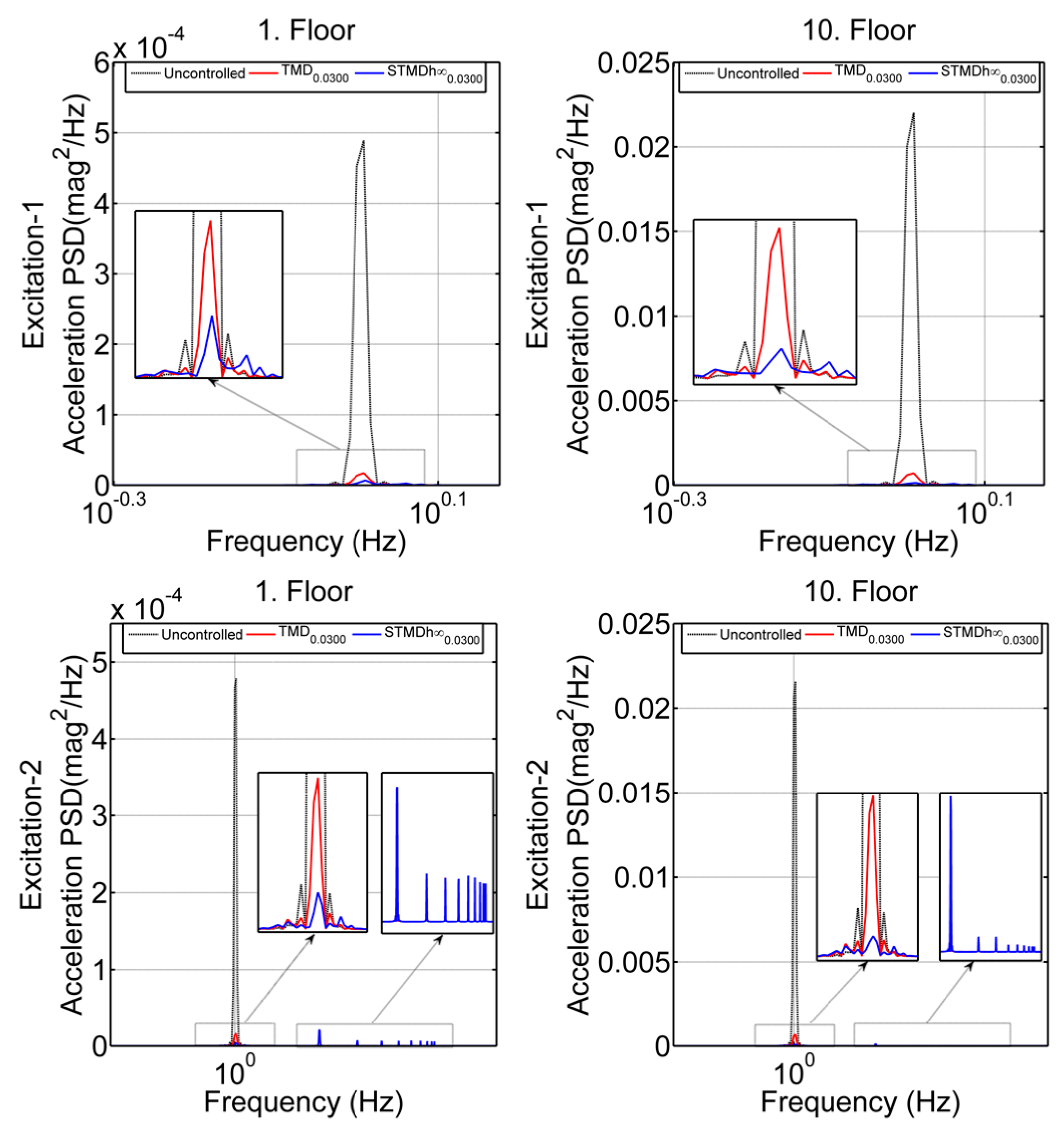
3.2.2. Frequency Analysis
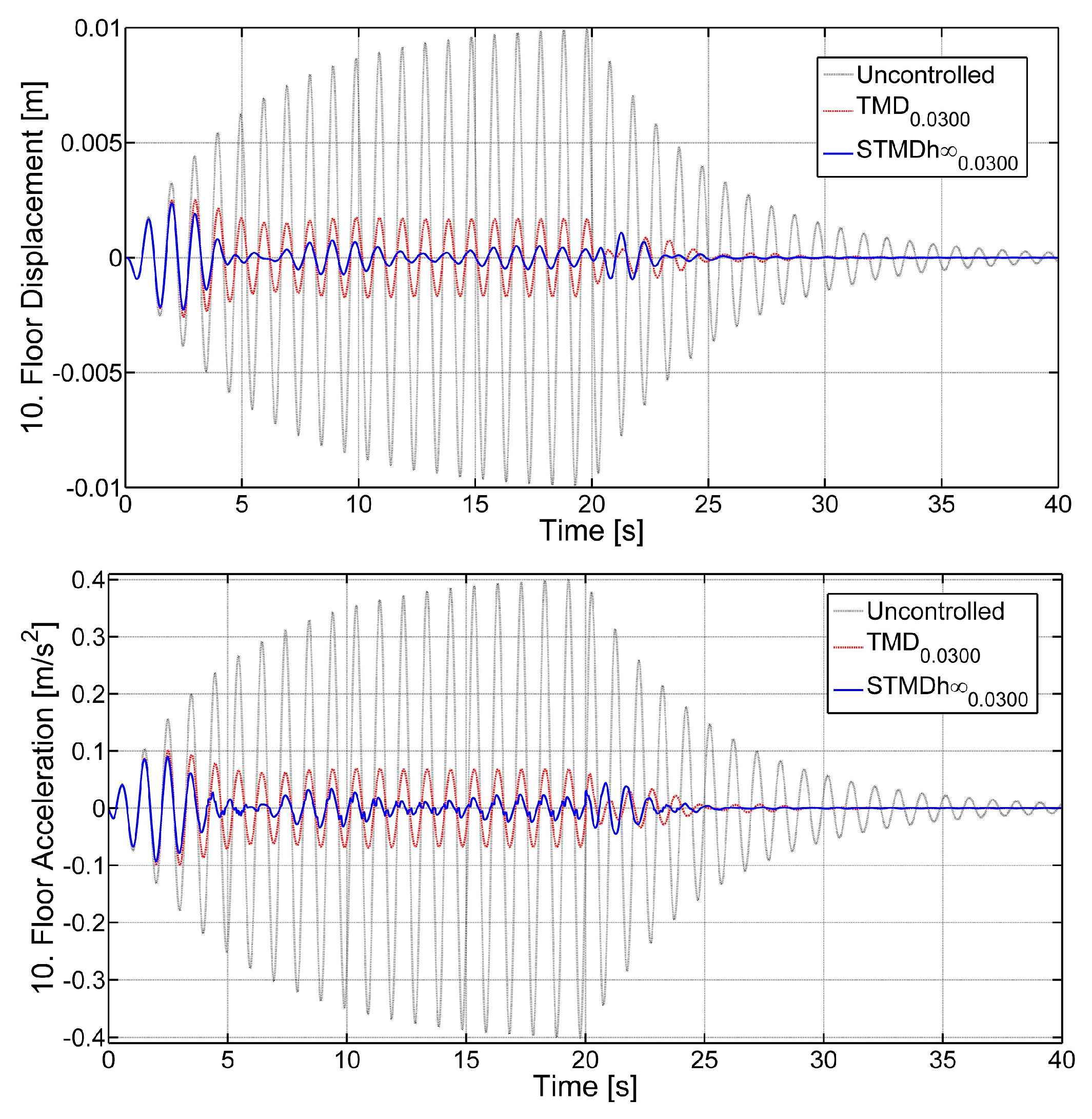
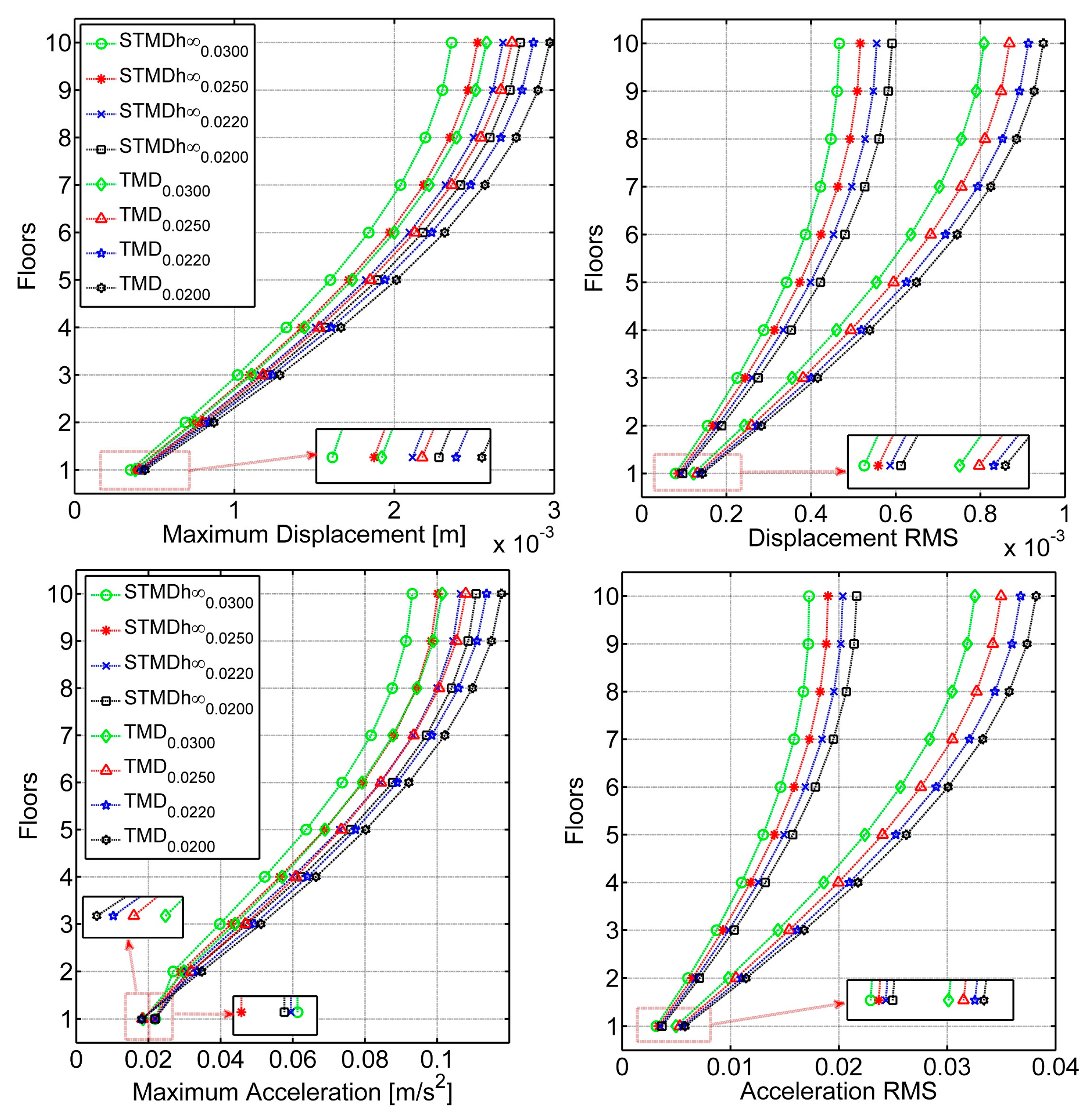
3.3. Structural Vibration Performance Evaluations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| MDOF | Multi degree of freedom |
| SDOF | Single degree of freedom |
| TMD | Tuned mass damper |
| STMD | Semi-active tuned mass damper |
| MR | Magnetorheological |
| HILS | Hardware in the loop simulation |
| RTHS | Real-time hybrid simulation |
| FOM | Full order model |
| ROM | Reduced-order model |
| RMS | Root mean square |
| PSD | Power spectral density |
| Ms | Mass matrix of the structural system |
| Cs | Stiffness matrix of the structural system |
| Ks | Damping matrix of the structural system |
| L | The seismic input vector |
| The placement of control units | |
| Acceleration vector | |
| Velocity vector | |
| Displacement vector | |
| f(t) | The damping force of MR damper |
| The earthquake ground acceleration | |
| i th floor displacement | |
| H∞ | H infinity control |
| State-space matrices for the full order model | |
| State-space matrices for the reduced-order model | |
| Modal transformation vector | |
| / | The state vectors of the full-order/reduced-order system model |
| / | The output vectors of the full-order/reduced-order system model |
| Pf (s) | Full order model of the system |
| Pr (s) | Reduced-order model of the system |
| Cy | Locations of the measurements of the system |
| ƞ | Modal space of the system |
| w | The input excitation |
| K | Controller of the system |
| u | The control signal of the system |
| y | The measured response of the system |
| z1, z2 | They are regulating outputs of frequency shaping filters. |
| n | The noise of the measurement |
| The transfer function of the mixed sensitivity structure | |
| The damping ratio of last controlled mode | |
| The damping ratio of first uncontrolled mode | |
| Frequency of the last controlled mode | |
| Frequency of the first uncontrolled mode | |
| Minimum voltage in the MR damper | |
| The maximum voltage in the MR damper | |
| The force necessary for system | |
| The system measures force | |
| WT, WM | Filters |
| S(s) | Sensitivity transfer function |
| T(s) | The complementary sensitivity transfer function |
| Additive uncertainty of the system | |
| Maximum singular value of the S(s) | |
| Positive design parameter | |
| G(s) | The augmented system structure |
| The state vector of the augmented system model | |
| The state vector of the controller | |
| The MR damper controller gain | |
| Optimum frequency ratio of TMD | |
| The optimum damping ratio of TMD | |
| μ | Mass ratio |
| Wni | The natural frequency of the system model |
| The velocity of the floor to which the MR damper was connected in the system | |
| g | The acceleration of gravity |
| Jn | Performance indices of the system |
| hi | Distance between floors |
| di | Displacement between floors |
| (t) | Absolute acceleration without the controller |
References
- Frahm, H. Device for Damping Vibrations of Bodies. U.S. Patent 989958A, 18 April 1911. [Google Scholar]
- Den Hartog, J.P.; Ormondroyd, J. Theory of the dynamic vibration absorber. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 1928, 50, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Den Hartog, J.P. Mechanical Vibrations; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Connor, J.J. Structural Motion Control; Pearson Education Inc.: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Guclu, R.; Sertbas, A. Evaluation of Sliding Mode and Proportional-Integral-Derivative Controlled Structures with an Active Mass Damper. J. Vib. Control 2005, 11, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guclu, R.; Yazici, H. Vibration control of a structure with ATMD against earthquake using fuzzy logic controllers. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 318, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran-Carbajal, F.; Silva-Navarro, G. Output feedback dynamic control for trajectory tracking and vibration suppression. Appl. Math. Model. 2020, 79, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guclu, R.; Yazici, H. Seismic-vibration mitigation of a nonlinear structural system with an ATMD through a fuzzy PID controller. Nonlinear Dyn. 2009, 58, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guclu, R.; Yazici, H. Self-tuning fuzzy logic control of a non-linear structural system with ATMD against earthquake. Nonlinear Dyn. 2009, 56, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldemir, U. Optimal control of structures with semiactive-tuned mass dampers. J. Sound Vib. 2003, 266, 847–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.Y.; Chung, L.L.; Loh, C.H. Semiactive Control of Building Structures with Semiactive Tuned Mass Damper. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2005, 20, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, K.T.; Kwok, K.C.S.; Hitchcock, P.A.; Samali, B.; Huang, M.F. Vibration control of a wind-excited benchmark tall building with complex lateral-torsional modes of vibration. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2007, 10, 283–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Kang, J.-W. Semi-active fuzzy control of a wind-excited tall building using multi-objective genetic algorithm. Eng. Struct. 2012, 41, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S. Seismic response control of adjacent buildings coupled by semi-active shared TMD. Int. J. Steel Struct. 2016, 16, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathaei, A.; Zahrai, S.M.; Ramezani, M. Semi-active seismic control of an 11-DOF building model with TMD+MR damper using type-1 and -2 fuzzy algorithms. J. Vib. Control 2018, 24, 2938–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, A.M. Control of wind-induced motion in high-rise buildings with hybrid TM/MR dampers. Wind Struct. 2015, 21, 565–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.; Distl, H.; Fischer, S.; Braun, C. MR Damper Controlled Vibration Absorber for Enhanced Mitigation of Harmonic Vibrations. Actuators 2016, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setareh, M.; Ritchey, J.K.; Murray, T.M.; Koo, J.-H.; Ahmadian, M. Semiactive Tuned Mass Damper for Floor Vibration Control. J. Struct. Eng. 2007, 133, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.-Y.; Lin, T.-K.; Hwang, J.-S. A semi-active mass damping system for low- and mid-rise buildings. Earthq. Struct. 2013, 4, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paksoy, M.; Metin, M. Nonlinear semi-active adaptive vibration control of a half vehicle model under unmeasured road input. J. Vib. Control 2019, 25, 2453–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, B.M.; Spencer, B.F. Model-Based Feedforward-Feedback Actuator Control for Real-Time Hybrid Simulation. J. Struct. Eng. 2013, 139, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggumus, H.; Cetin, S. Experimental investigation of semiactive robust control for structures with magnetorheological dampers. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2018, 37, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Zhang, N. Active vibration control of structures subject to parameter uncertainties and actuator delay. J. Vib. Control 2008, 14, 689–709. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, L.; Song, G.; Li, H.; Grigoriadis, K. Robust control design of active structural vibration suppression using an active mass damper. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 17, 015021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y. Robust finite frequency H∞ static-output-feedback control with application to vibration active control of structural systems. Mechatronics 2014, 24, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.-W.; Petkov, P.H.; Konstantinov, M.M. Robust Control Design with MATLAB®, 2nd ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sivrioglu, S.; Tanaka, N.; Yuksek, I. Acoustic power suppression of a panel structure using H∞ output feedback control. J. Sound Vib. 2002, 249, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kafafy, M.; El-Demerdash, S.M.; Rabeih, A.-A.M. Automotive ride comfort control using MR fluid damper. Engineering 2012, 4, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lam, A.H.-F.; Liao, W.-H. Semi-active control of automotive suspension systems with magneto-rheological dampers. Int. J. Veh. Des. 2003, 33, 50–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, G.B. Optimum absorber parameters for various combinations of response and excitation parameters. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1982, 10, 381–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.P.; Matheu, E.E.; Suarez, L.E. Active and Semi-Active Control of Structures Under Seismic Excitation. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1997, 26, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, M.N.; Arfiadi, Y. Optimum design of absorber for MDOF structures. J. Struct. Eng. 1998, 124, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtori, Y.; Christenson, R.E.; Spencer, B.F., Jr.; Dyke, S.J. Benchmark control problems for seismically excited nonlinear buildings. J. Eng. Mech. 2004, 130, 366–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, S.; Zergeroglu, E.; Sivrioglu, S.; Yuksek, I. A new semiactive nonlinear adaptive controller for structures using MR damper: Design and experimental validation. Nonlinear Dyn. 2011, 66, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mass Ratio | Abbreviations of the TMD | Abbreviations of the STMD | G Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.09 | |||
| 0.05 | |||
| 0.01 | |||
| 0.01 |
| Abbreviations | Excitation-1 | Excitation-2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MR Damper Forces | MR Damper Voltage | MR Damper Forces | MR Damper Voltage | |||||
| Maximum | RMS | Maximum | RMS | Maximum | RMS | Maximum | RMS | |
| 1910.60 | 328.51 | 10 | 2.52 | 1906.78 | 344.02 | 10 | 3.82 | |
| 1840.27 | 330.10 | 10 | 2.58 | 1948.94 | 340.36 | 10 | 3.67 | |
| 1847.94 | 348.74 | 10 | 3.57 | 1886.71 | 348.59 | 10 | 4.92 | |
| 1883.10 | 359.30 | 10 | 4.06 | 1821.12 | 355.17 | 10 | 4.84 | |
| Abbreviations | Excitation-1 | Excitation-2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | RMS | Maximum | RMS | |
| 1307.03 | 490.19 | 1288.10 | 487.57 | |
| 1387.54 | 518.96 | 1369.70 | 516.06 | |
| 1497.22 | 559.94 | 1478.27 | 556.62 | |
| 1662.28 | 623.44 | 1652.36 | 619.38 | |
| Abbreviations (TMD and STMD) | Maximum Relative Displacement [m] | Maximum Displacement [m] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excitation-1 | Excitation-2 | Excitation-1 | Excitation-2 | |
| 0.01636 | 0.01663 | 0.01699 | 0.01655 | |
| 0.01507 | 0.01538 | 0.01577 | 0.01531 | |
| 0.01356 | 0.01385 | 0.01423 | 0.01374 | |
| 0.01164 | 0.01197 | 0.01227 | 0.01184 | |
| 0.02499 | 0.02543 | 0.02548 | 0.02492 | |
| 0.02324 | 0.02369 | 0.02355 | 0.02309 | |
| 0.02114 | 0.02085 | 0.02111 | 0.02062 | |
| 0.01743 | 0.01808 | 0.01826 | 0.01778 | |
| Abbreviations (TMD and STMD) | Excitation-1 | Excitation-2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.29636 | 0.30228 | 0.24416 | 0.24497 | 0.34919 | 0.79590 | 0.24969 | 0.76976 | |
| 0.29636 | 0.30228 | 0.23536 | 0.23620 | 0.34919 | 0.79590 | 0.24108 | 0.76841 | |
| 0.27220 | 0.30571 | 0.22414 | 0.22501 | 0.32287 | 0.79296 | 0.23010 | 0.76671 | |
| 0.25577 | 0.30862 | 0.20920 | 0.21013 | 0.30297 | 0.78950 | 0.21548 | 0.76446 | |
| 0.27896 | 0.36409 | 0.14706 | 0.15492 | 0.32710 | 0.76680 | 0.15859 | 0.76293 | |
| 0.26825 | 0.36426 | 0.13966 | 0.14817 | 0.31405 | 0.76188 | 0.15037 | 0.76195 | |
| 0.25257 | 0.36240 | 0.13123 | 0.14094 | 0.29688 | 0.76144 | 0.14378 | 0.76151 | |
| 0.23578 | 0.36444 | 0.12197 | 0.13310 | 0.27372 | 0.76429 | 0.13249 | 0.76131 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aggumus, H.; Guclu, R. Robust H∞ Control of STMDs Used in Structural Systems by Hardware in the Loop Simulation Method. Actuators 2020, 9, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/act9030055
Aggumus H, Guclu R. Robust H∞ Control of STMDs Used in Structural Systems by Hardware in the Loop Simulation Method. Actuators. 2020; 9(3):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/act9030055
Chicago/Turabian StyleAggumus, Huseyin, and Rahmi Guclu. 2020. "Robust H∞ Control of STMDs Used in Structural Systems by Hardware in the Loop Simulation Method" Actuators 9, no. 3: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/act9030055
APA StyleAggumus, H., & Guclu, R. (2020). Robust H∞ Control of STMDs Used in Structural Systems by Hardware in the Loop Simulation Method. Actuators, 9(3), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/act9030055





