Effect of Optimal Placement of Permanent Magnets on the Electromagnetic Force in the Horizontal Direction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
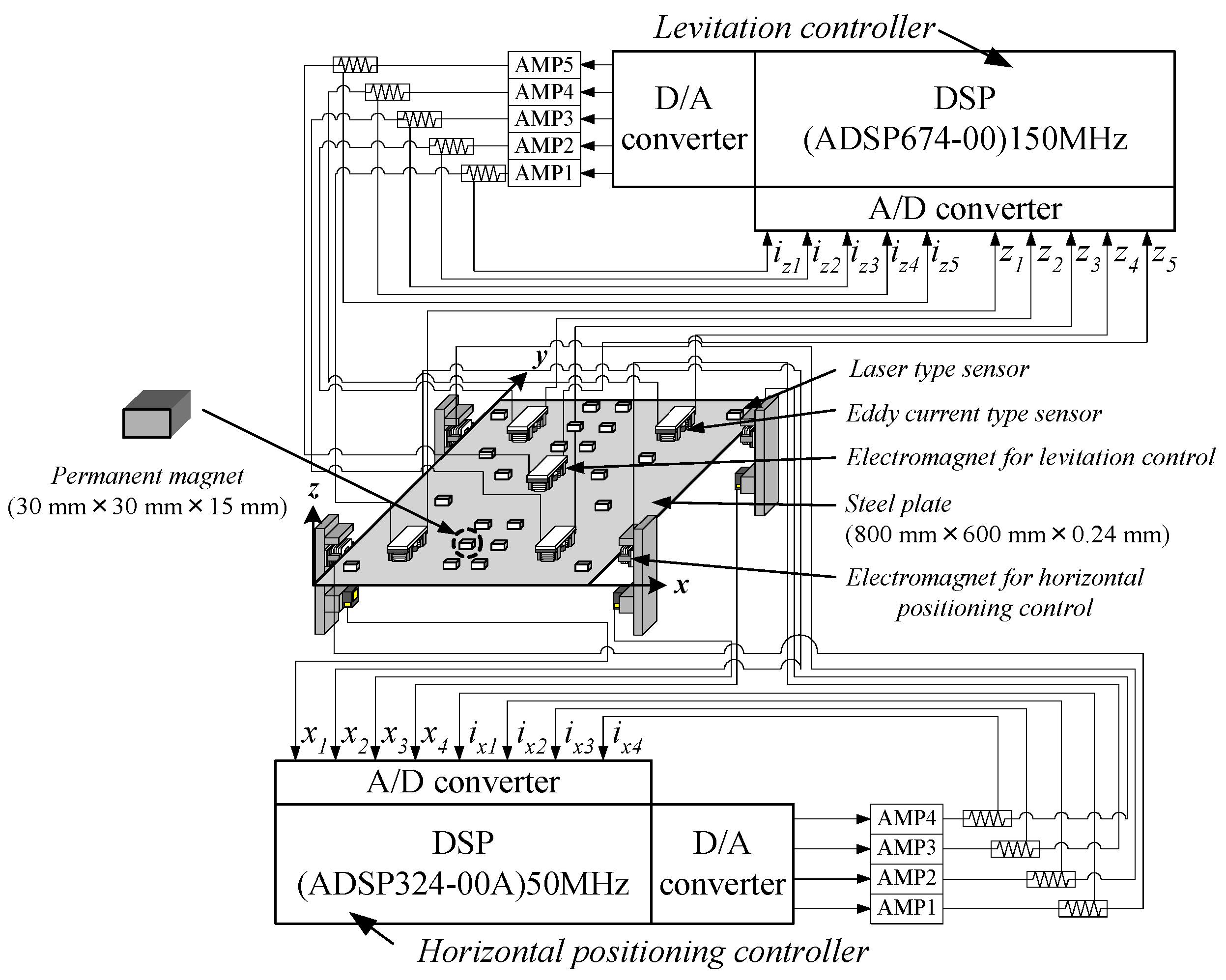
2. Outline of the Electromagnetic Levitation System Integrating Permanent Magnets and the Horizontal Positioning Control System
3. Control Model
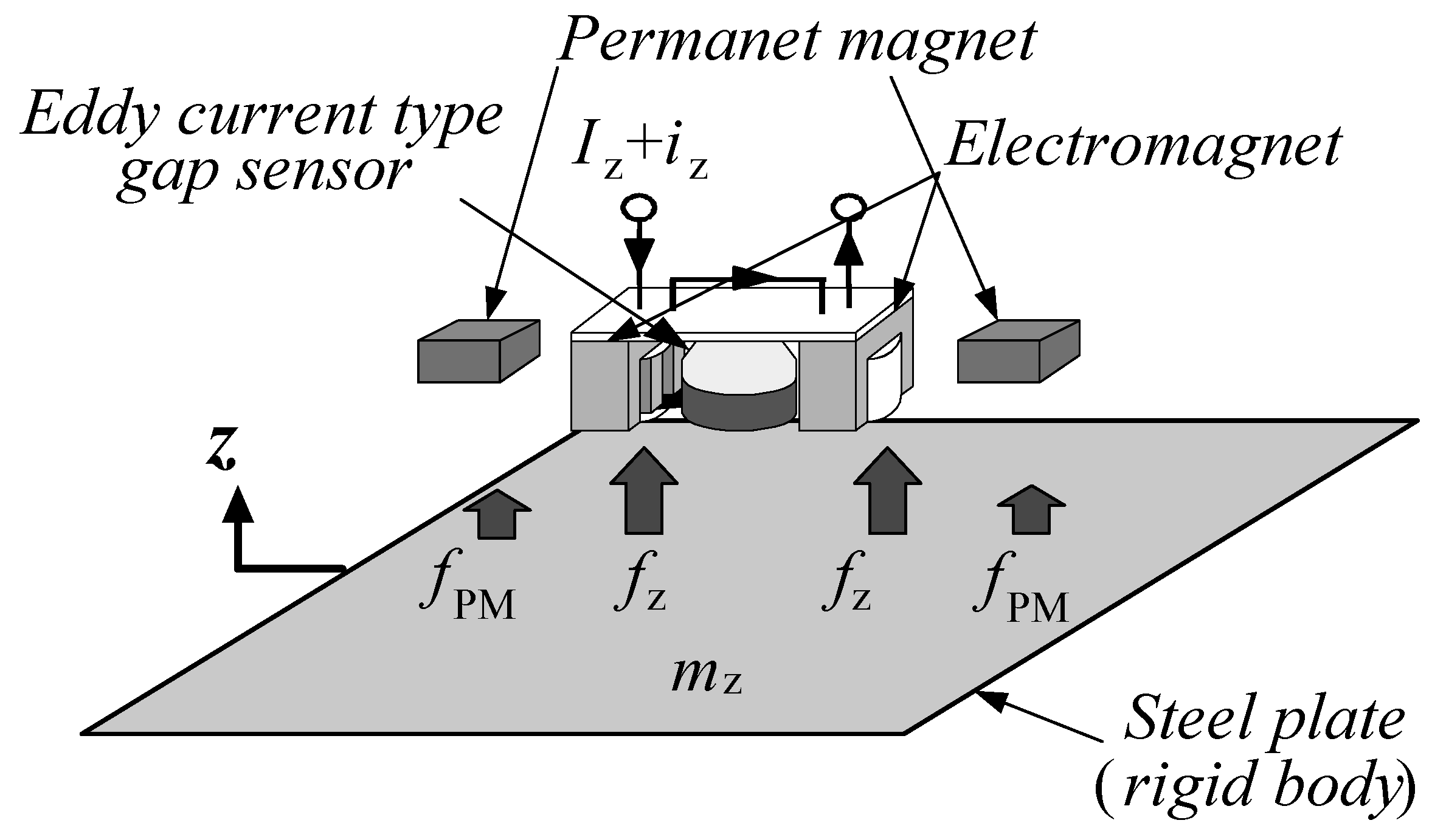
3.1. Electromagnetic Levitation Control System
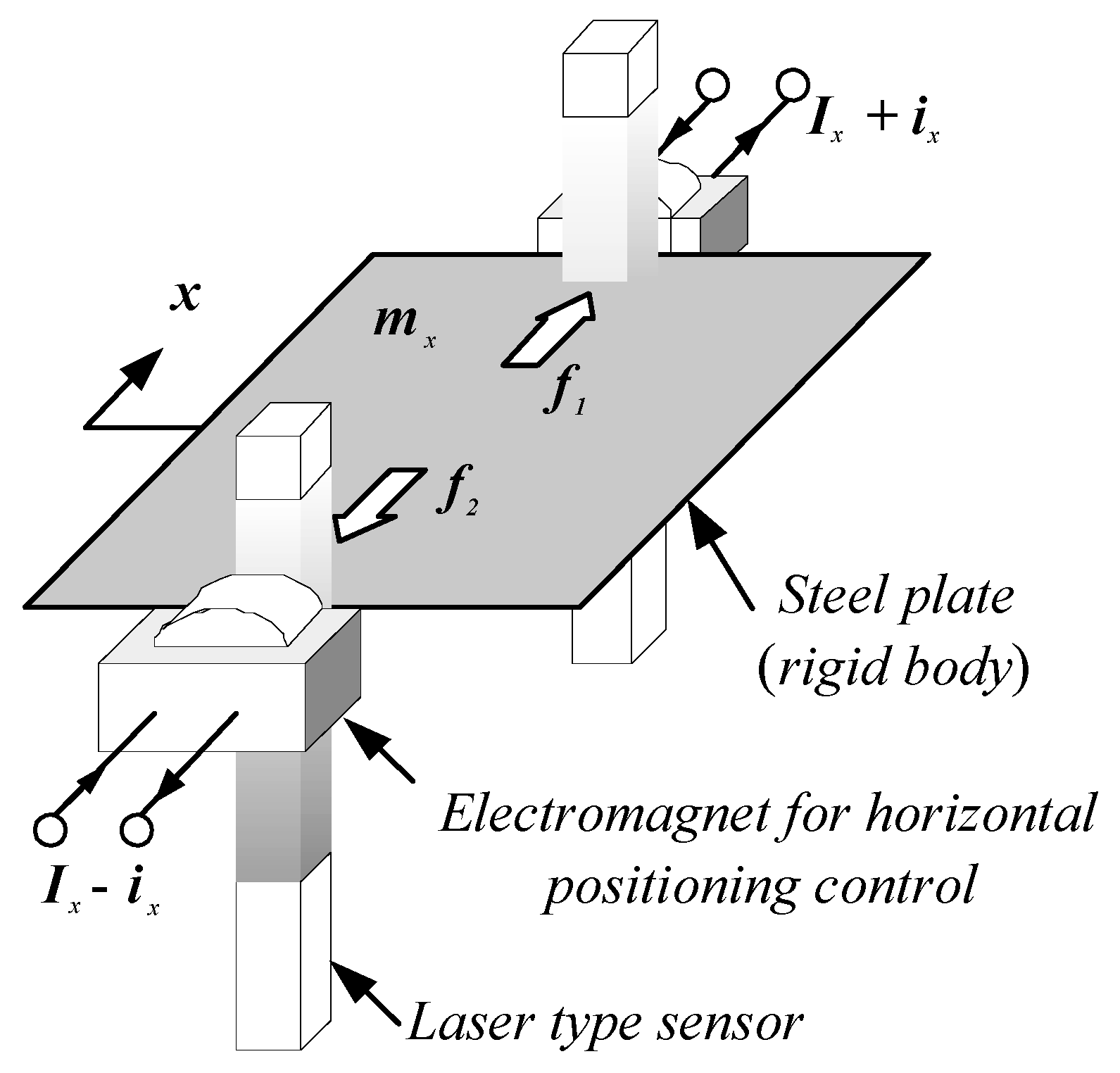
3.2. Horizontal Positioning Control System
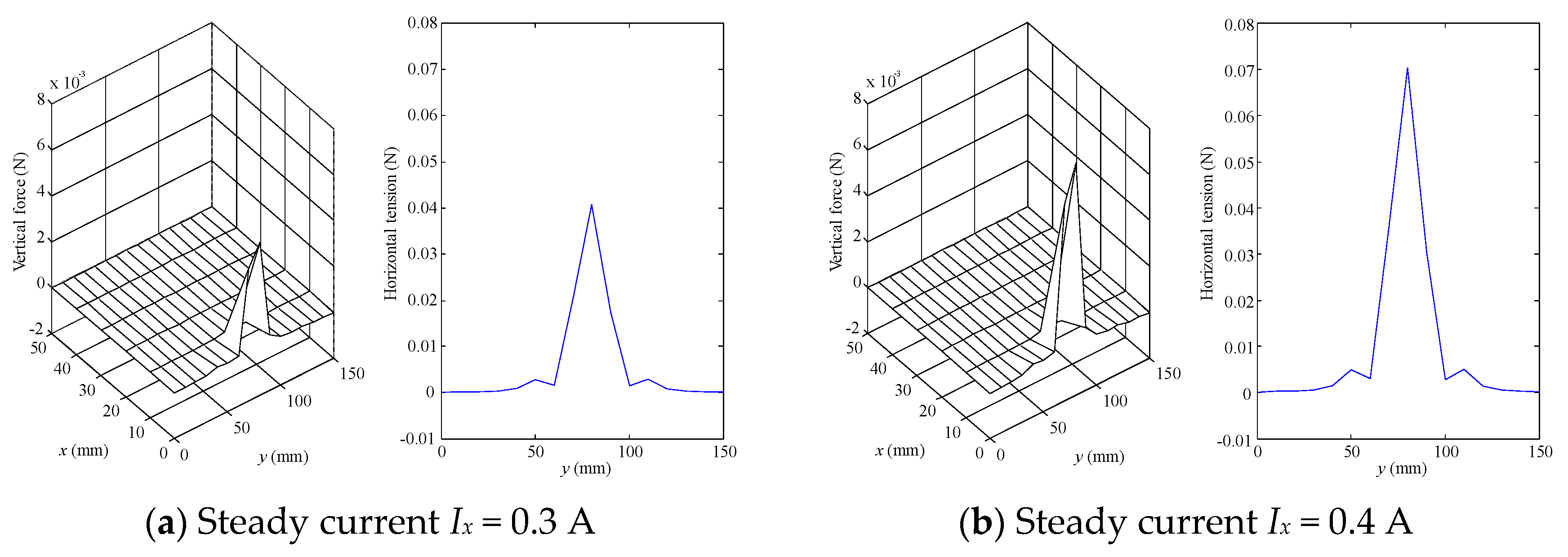
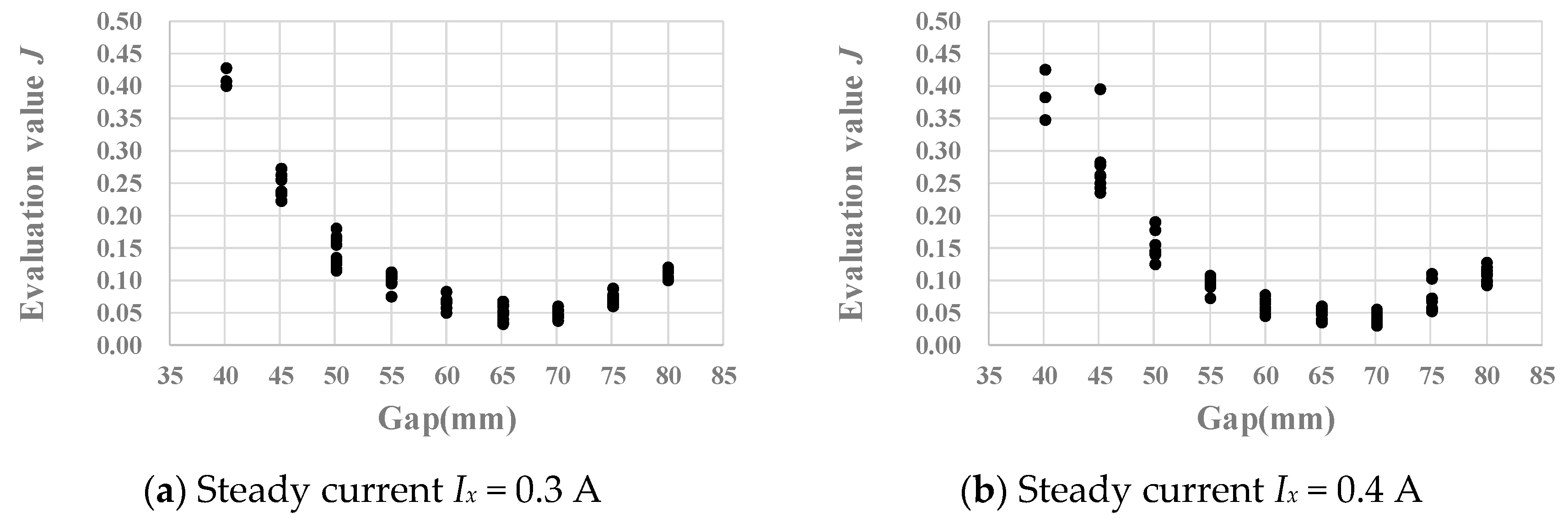
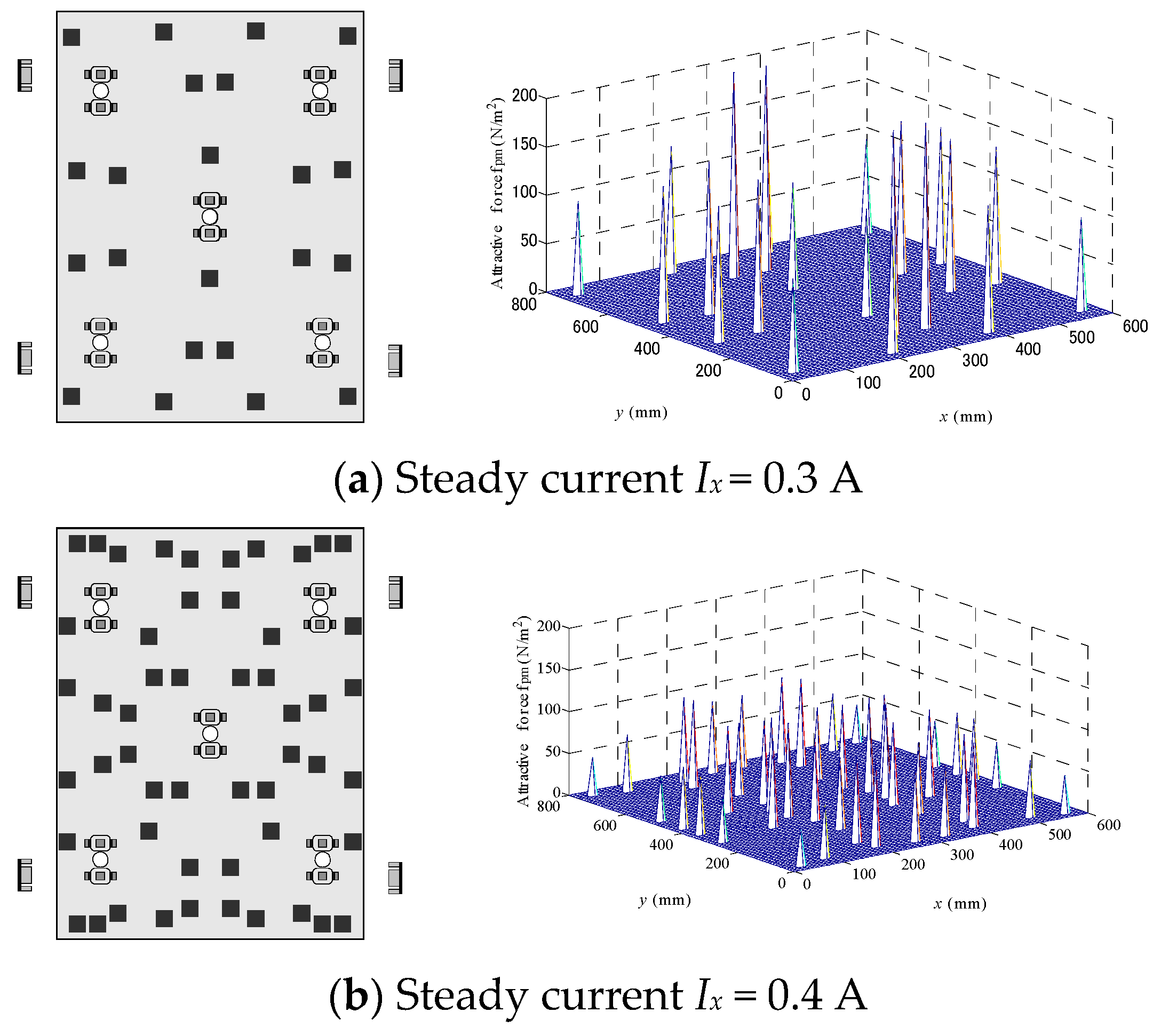
4. Determination of Optimal Placement
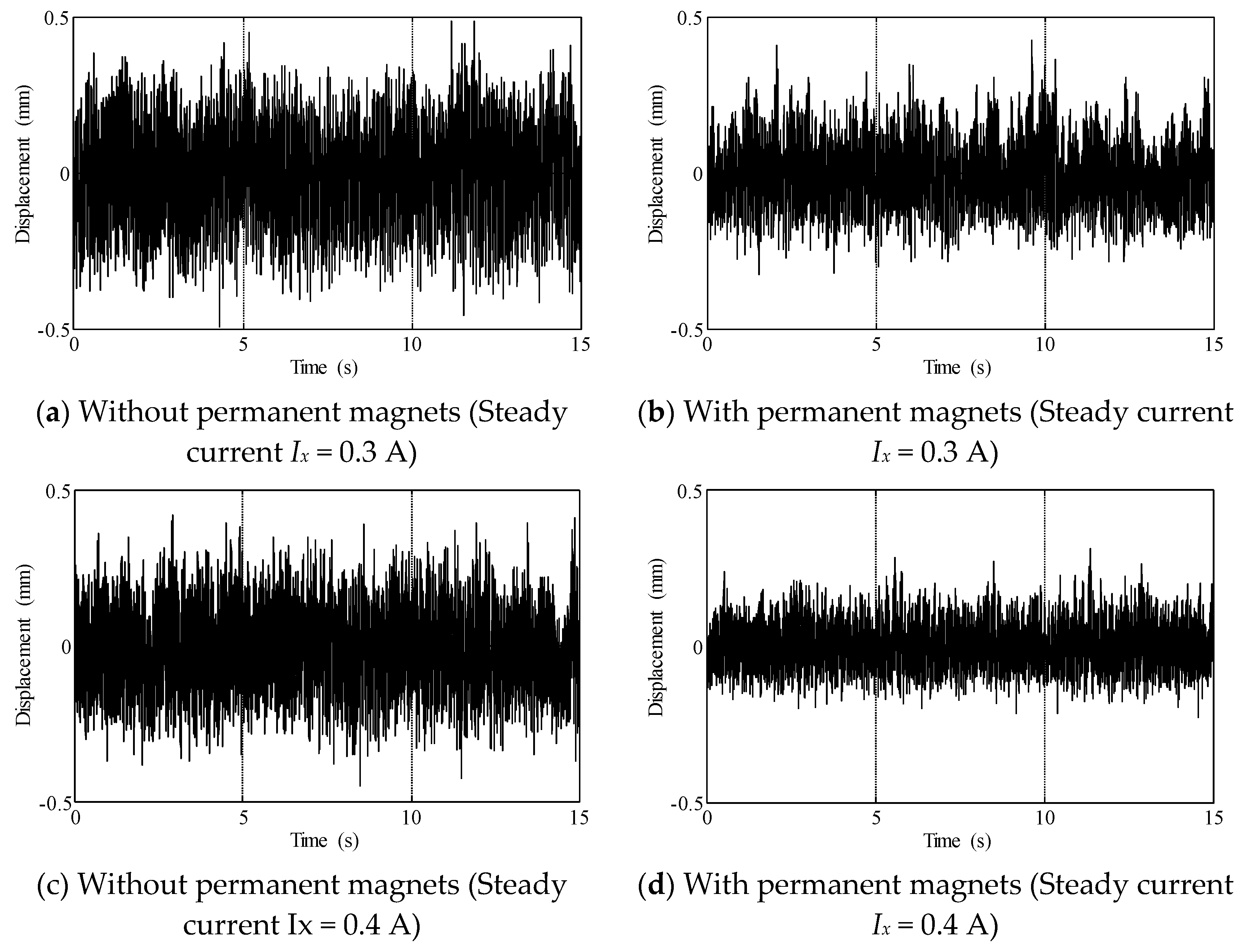
5. Magnetic Levitation Experiment Using Optimal Placement
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| E | Young’s modulus of the thin steel plate (N/m2) |
| f | vertical static magnetic force applied to the plate, which is generated by the permanent magnets (N/m2) |
| fz | dynamic magnetic force (N) |
| Fx | magnetic force of the coupled magnets in the equilibrium state (N) |
| Fz | magnetic force of the coupled magnets in the equilibrium state (N) |
| g | acceleration due to gravity (m/s2) |
| h | plate thickness (m) |
| iz | dynamic current of the coupled electromagnets (A) |
| ix | dynamic current of the coupled magnets (A) |
| Ix | current of the coupled magnets in the equilibrium state (A) |
| Iz | current of the coupled electromagnets in the equilibrium state (A) |
| JD | evaluation function of the maximum deflection (m) |
| Jz | evaluation function of the average absolute deflection (m) |
| Llea | leakage inductance of one magnet coil (H) |
| Lx | inductance of one magnet coil in the equilibrium state (H) |
| Lxlea | leakage inductance of one magnet coil (H) |
| Lxeff/X0 | effective inductance of one magnet coil (H) |
| Lz | inductance of one electromagnet coil in the equilibrium state (H) |
| mz | virtually divided steel plate (kg) |
| N | the total number of analysis points |
| Rx | resistance of the coupled magnet coils (Ω) |
| Rz | resistance of the coupled magnet coils (Ω) |
| Ts | sampling time (s) |
| ν | Poisson ratio |
| vx | dynamic voltage of the coupled magnets (V) |
| vz | dynamic voltage of the coupled magnets (V) |
| x | coordinates in the width direction (m) |
| X0 | gap between the steel plate and electromagnet in the equilibrium state (m) |
| y | coordinates in the longitudinal direction (m) |
| z | vertical displacement from the equilibrium state (m) |
| zi | displacement at each analysis point on the thin steel plate (m) |
| zmax | maximum deflection of the thin steel plate (m) |
| Z0 | gap between the steel plate and electromagnet in the equilibrium state (m) |
| ρ | plate density (kg/m3) |
References
- Onuki, T.; Toda, Y. Optimal design of hybrid magnet in maglev system with both permanent and electromagnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1993, 29, 1783–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, K.; Higuchi, T. 3 Degree of freedom maglev system with actuators and permanent magnets. IEEJ Trans. Ind. Appl. 1995, 115, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, M.; Ito, H. The self-gap-detecting zero power controlled electromagnetic suspension system. IEEJ Trans. Ind. Appl. 2006, 126, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamijo, Y.; Ito, H.; Maruyama, Y. Structure and characteristic of magnetic bearing with zero power controlled electromagnetic suspension. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng. Ser. C 2013, 79, 4963–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshinoya, Y.; Ishibashi, K. Development of electromagnetic levitation control device for a rectangular sheet steel. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng. Ser. C 2001, 661, 2855–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.E. Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization, and Machine Learning; Addison-Wesley Professional: Boston, MA, USA, 1989; ISBN 978-0201157675. [Google Scholar]
- Mallik, S.; Mallik, K.; Barman, A.; Maiti, D.; Biswas, S.K.; Deb, N.K.; Basu, S. Efficiency and cost optimized design of an induction motor using genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 9854–9863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, Y.; Tominaga, Y.; Wakao, S.; Sato, S. Topology optimization of rotor core combined with identification of current phase angle in IPM motor using multistep genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 725–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, T.; Hasegawa, S.; Oshinoya, Y. Optimal placement of permanent magnets in a hybrid magnetic levitation system for thin steel plate (experimental consideration on levitation probability). Proc. Sch. Eng. Tokai Univ. 2013, 38, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Narita, T.; Hasegawa, S.; Oshinoya, Y. Hybrid electromagnetic levitation system for thin steel plates using permanent magnets. J. Magn. Soc. Jpn. 2013, 37, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Narita, T.; Kato, H. Hybrid magnetic levitation system for thin steel plate by electromagnets and permanent magnets (basic study on optimal placement search considering the interaction of the magnetic field). J. Jpn. Soc. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2016, 24, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, A.; Fukao, T.; Ichikawa, O.; Oshima, M.; Takemoto, M.; Dorrell, D.G. Magnetic Bearings and Bearingless Drives; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2005; p. 20. ISBN 9780750657273. [Google Scholar]
- Timoshenko, S.P.; Woinowsky-Krieger, S. Theory of Plate and Shells; McGraw-Hill Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]


| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| m | 0.864 kg |
| E | 206 GPa |
| ν | 0.3 |
| Z0 | 5 × 10−3 m |
| Rn | 21.0 Ω |
| Leff | 2.55 × 10−4 Hm |
| Llea | 0.090 H |
| Ts | 0.001 s |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ito, Y.; Oda, Y.; Narita, T.; Kato, H. Effect of Optimal Placement of Permanent Magnets on the Electromagnetic Force in the Horizontal Direction. Actuators 2018, 7, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/act7030054
Ito Y, Oda Y, Narita T, Kato H. Effect of Optimal Placement of Permanent Magnets on the Electromagnetic Force in the Horizontal Direction. Actuators. 2018; 7(3):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/act7030054
Chicago/Turabian StyleIto, Yasuaki, Yoshiho Oda, Takayoshi Narita, and Hideaki Kato. 2018. "Effect of Optimal Placement of Permanent Magnets on the Electromagnetic Force in the Horizontal Direction" Actuators 7, no. 3: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/act7030054
APA StyleIto, Y., Oda, Y., Narita, T., & Kato, H. (2018). Effect of Optimal Placement of Permanent Magnets on the Electromagnetic Force in the Horizontal Direction. Actuators, 7(3), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/act7030054





