Overview of Actuated Arm Support Systems and Their Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
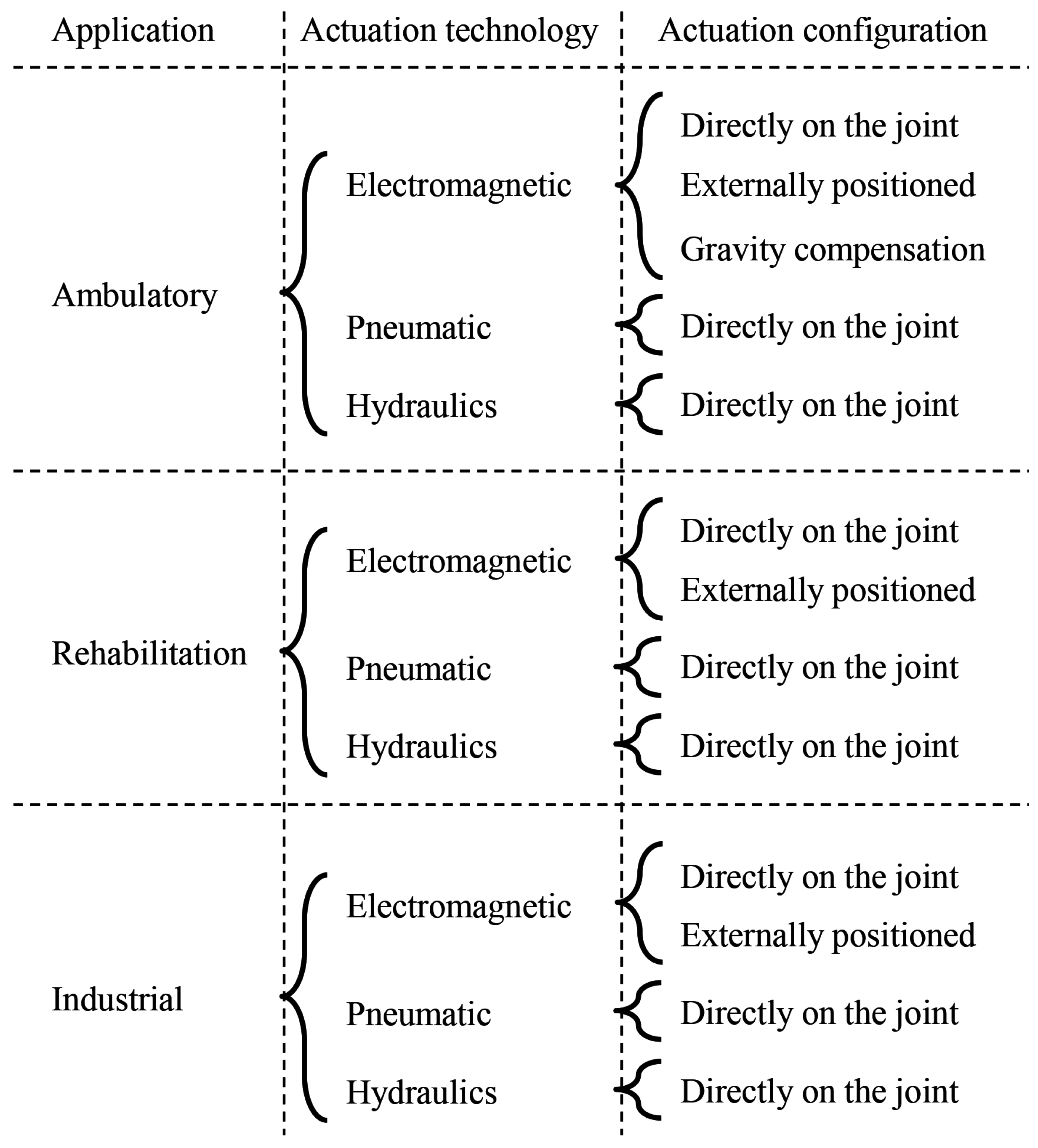
2. Applications
2.1. Ambulatory
2.2. Rehabilitation
2.3. Industrial
3. Actuation Principle
3.1. Electromagnetic Actuators
3.2. Pneumatic Actuators
3.3. Hydraulic Actuators
3.4. Semi-Active Damping
4. Compliant and Back-Drivable Actuation
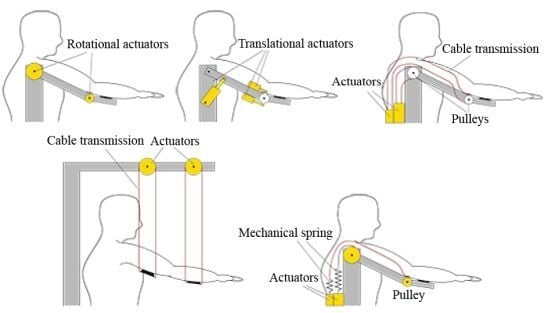
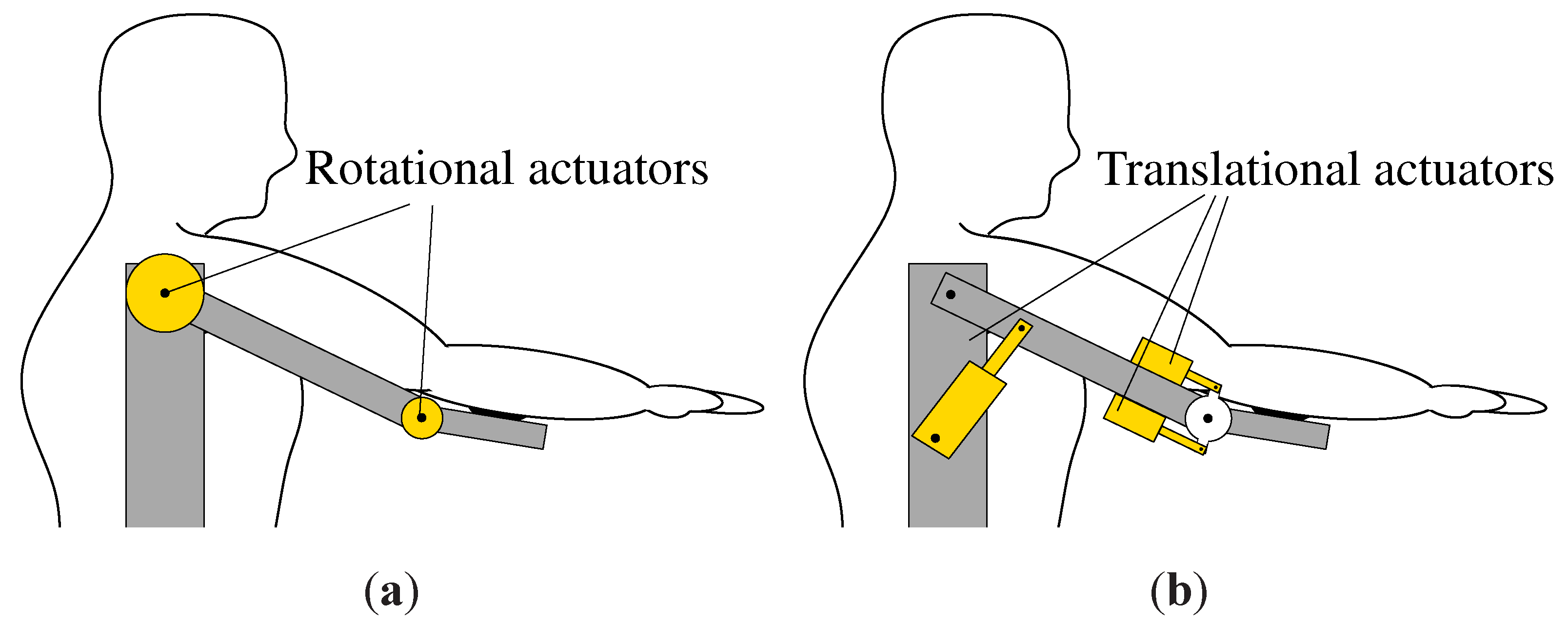
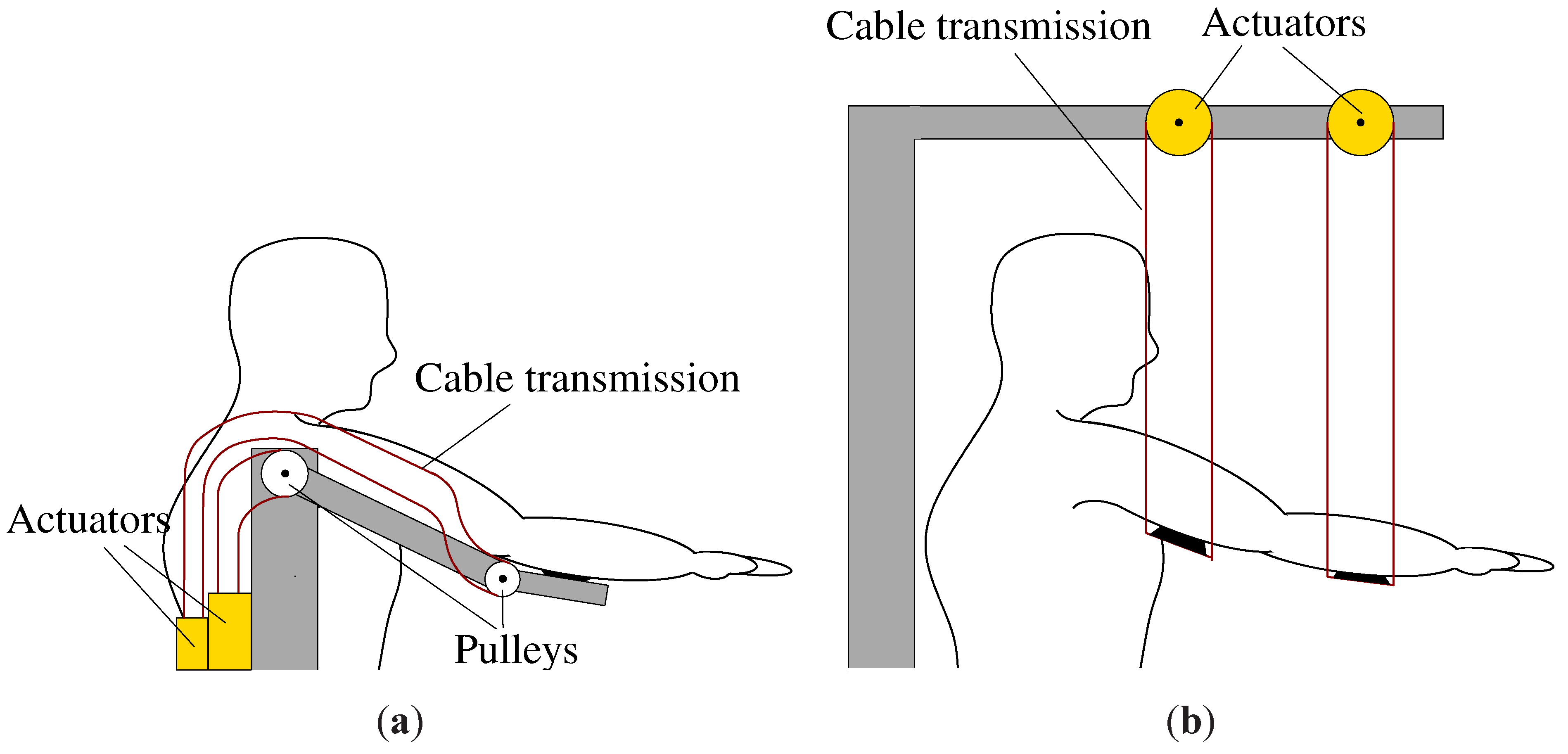
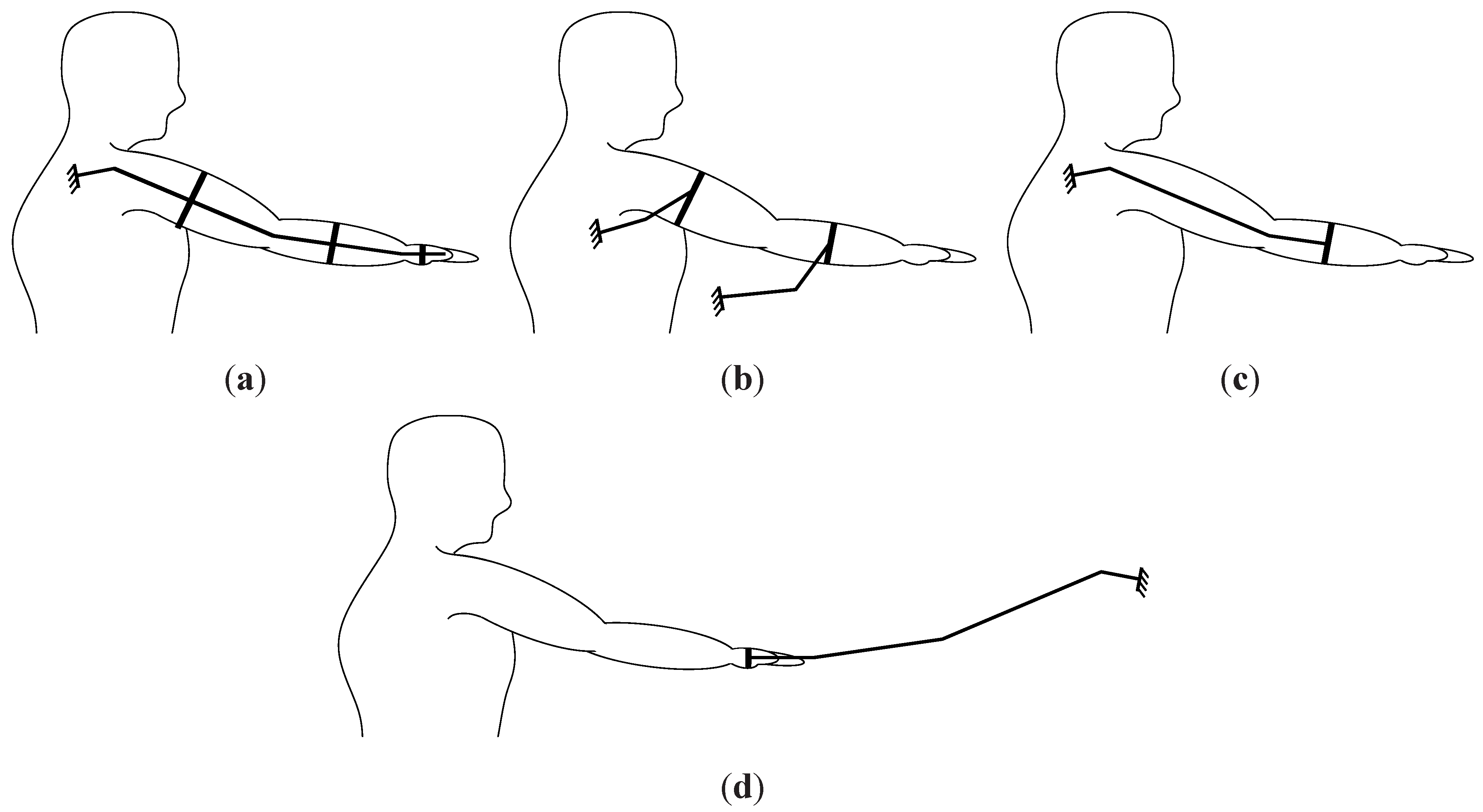
5. Actuator Configuration
5.1. Configurations
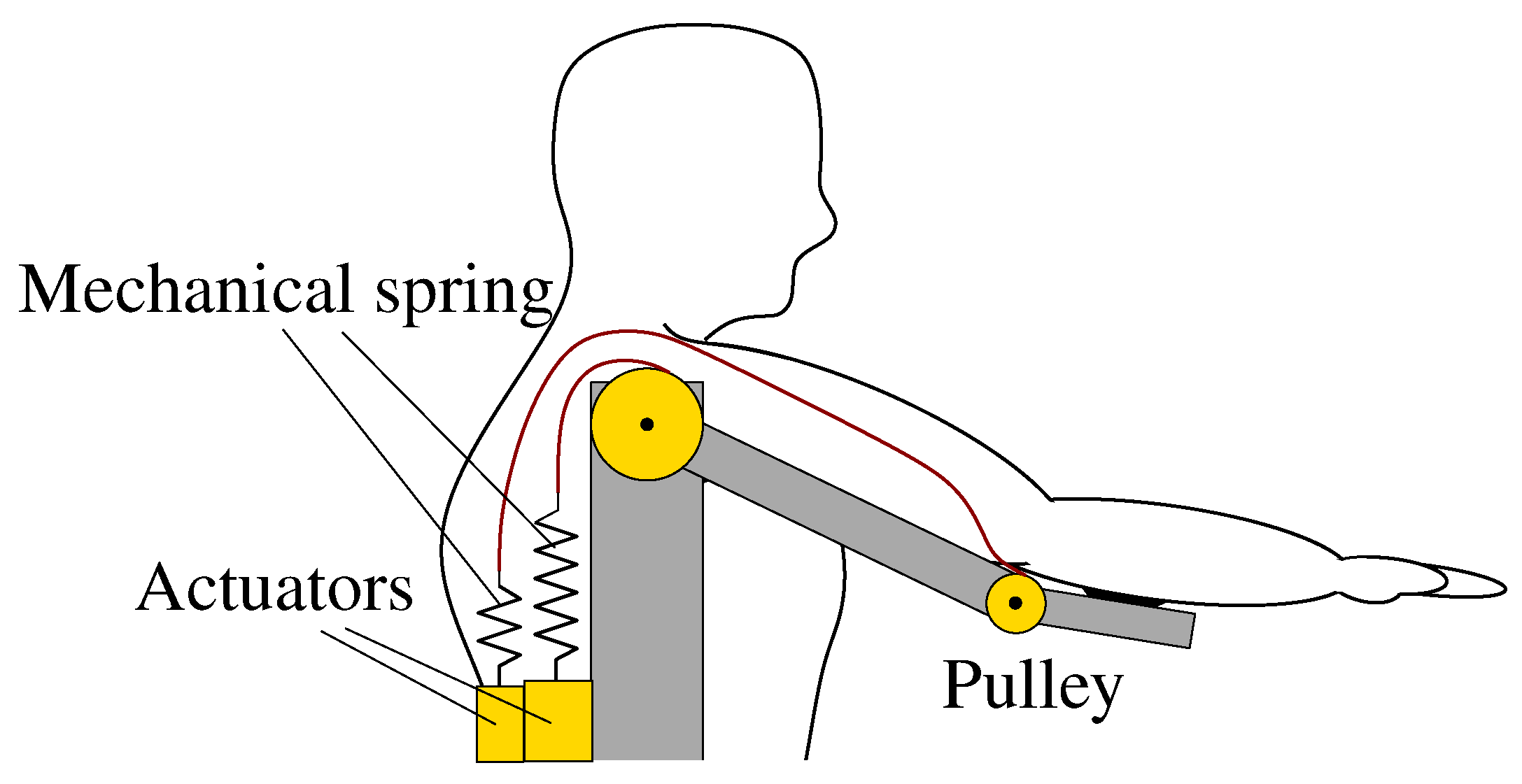
5.2. Inertia
5.3. Bandwidth
5.4. Degrees of Freedom
5.5. Exoskeleton versus End-Effector
6. Comparison
| Actuation Technology | Actuator Configuration | [Nm] | [N] | Speed | Power [W] | Reference | Publication Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder | Elbow | |||||||
| Electromagnetic actuators | Directly on the joint | 23 | 23 | - | 48/s | 19 | [78] | 1969 |
| 15 | 7.2 | - | 75/s | 19.6 | [51] | 2001 | ||
| External positioned | 98 | 28.4 | - | 95/s | 185 | [79] | 2008 | |
| Gravity compensation | - | - | 45 | 0 | 0 | [1] | 2006 | |
| - | - | 50 | 0 | 0 | [60] | 2007 | ||
| Pneumatic | Directly on the joint | - | - | 220 | 1.1m/s | 242 | [42] | 2006 |
| Hydraulic | Directly on the joint | 63.6 | 89 | - | - | - | [33] | 2009 |
| Actuation Technology | Actuator Configuration | [Nm] | [N] | Speed | Power [W] | Reference | Publication Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder | Elbow | |||||||
| Electromagnetic actuators | Directly on the joint | - | 28 | 151 | - | 150 | [77] | 2006 |
| - | - | 12 | - | - | [70] | 2007 | ||
| 20 | - | - | 1146/s | 400 | [54] | 2008 | ||
| Externally positioned | - | - | 50 | - | 312 | [55] | 2007 | |
| 62 | 33 | - | - | - | [2] | 2007 | ||
| 200 | 32 | - | 35/s | 122 | [62] | 2008 | ||
| - | 45 | - | - | [56] | 2012 | |||
| Pneumatic | Directly on the joint | 30 | 6 | - | 64/s | 33.5 | [45] | 2003 |
| 15 | 15 | - | 50/s | 13 | [44] | 2007 | ||
| Hydraulic | Directly on the joint | - | 15 | - | 469 /s | 123 | [34] | 2011 |
| Actuation Technology | Actuator Configuration | [Nm] | [N] | Speed | Power [W] | Reference | Publication Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder | Elbow | |||||||
| Electromagnetic actuators | Directly on the joint | 20 | 10 | - | - | - | [4] | 1994 |
| Externally positioned | 19.3 | 4.5 | - | 150 | [64] | 2011 | ||
| Pneumatic | Directly on the joint | - | 200 | 10/s | - | [80] | 1999 | |
6.1. AAS Systems
6.2. RAS Systems
6.3. IAS Systems
7. Future Trends
| Developers Location | References | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| USA | [2,5,11,14,26,27,36,42,44,54,56,59,62,63,72,74,78,89] | 18 |
| Japan | [33,40,41,52,53,66,79,80,82,90,91,92] | 12 |
| UK | [7,32,45,51,58,65,70,73] | 8 |
| The Netherlands | [1,17,19,35,60,64] | 6 |
| Italy | [3,4,34,55] | 4 |
| Switzerland | [6,77,87,93] | 4 |
| Spain | [12,24,94] | 3 |
| Belgium | [48,88] | 2 |
| Canada | [29,76] | 2 |
| China | [31,67] | 2 |
| New-Zealand | [9,95] | 2 |
| Austria | [96] | 1 |
| Brazil | [57] | 1 |
| France | [25] | 1 |
| Hungary | [71] | 1 |
| Poland | [69] | 1 |
| Romania | [22] | 1 |
| Slovenia | [47] | 1 |
| S. Korea | [28] | 1 |
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Conflict of Interest
References
- Herder, J.; Vrijlandt, N.; Antonides, T.; Cloosterman, M.; Peter L., M. Principle and design of a mobile arm support for people with muscular weakness. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2006, 43, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, J.; Rosen, J.; Burns, S. Upper-limb powered exoskeleton design. Trans. Mechatron. (ASME) 2007, 12, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamasco, M.; Salsedo, F.; Marcheschi, S.; Lucchesi, N. A Novel Actuation Module for Wearable Robots. In Advances in Robot Kinematics: Motion in Man and Machine; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamasco, M.; Allotta, B.; Bosio, L.; Ferretti, L.; Parrini, G.; Prisco, G.; Salsedo, F.; Sartini, G. An Arm Exoskeleton System for Teleoperation and Virtual Environments Applications. In Proceedings International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Diego, CA, USA, 8–13 May 1994; Volume 2, pp. 1449–1454.
- Reinkensmeyer, D.; Lum, P.; Winters, J. Emerging Technologies for Improving Access to Movement Therapy following Neurologic Injury. In Emerging and Accessible Telecommunications, Information and Healthcare Technologies; RESNA Press: Arlington, VA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Riener, R.; Nef, T.; Colombo, G. Robot-aided neurorehabilitation of the upper extremities. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2005, 43, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loureiro, R.; Harwin, W.; Nagai, K.; Johnson, M. Advances in upper limb stroke rehabilitation: A technology push. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2011, 49, 1103–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Heide, L.; van Ninhuijs, B.; Bergsma, A.; Gelderblom, G.; van der Pijl, D.; de Witte, L. An overview and categorization of dynamic arm supports for people with decreased arm function. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2013, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.S.; Xie, S.Q. Exoskeleton robots for upper-limb rehabilitation: State of the art and future prospects. Med. Eng. Phys. 2012, 34, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guizzo, E.; Goldstein, H. The rise of the body bots [robotic exoskeletons]. Spectr. IEEE 2005, 42, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchal-Crespo, L.; Reinkensmeyer, D.J. Review of control strategies for robotic movement training after neurologic injury. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2009, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, A.; Forner-Cordero, A.; Rocon, E.; Pons, J.L. Exoskeletons for Rehabilitation and Motor Control. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, (BioRob), Pisa, Italy, 20–22 February 2006; pp. 601–606.
- Gopura, R.A.R.C.; Kiguchi, K. Mechanical Designs of Active Upper-limb Exoskeleton Robots: State-of-the-Art and Design Difficulties. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Kyoto, Japan, 23–26 June 2009; pp. 178–187.
- Koo, B.; Montes, J.; Gamarnik, V.; Yeager, K.; Marra, J.; Dunaway, S.; Montgomery, M.; de Vivo, D.; Strauss, N.; Konofagou, E.; Kaufmann, P.; Morrison, B. Design and Evaluation of a Hybrid Passive and Active Gravity Neutral Orthosis (GNO). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009; pp. 1573–1576.
- Van der Smagt, P.; Grebenstein, M.; Urbanek, H.; Fligge, N.; Strohmayr, M.; Stillfried, G.; Parrish, J.; Gustus, A. Robotics of human movements. J. Physiol. Paris 2009, 103, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesar, D. Overview of the long term objectives of the journal actuators. Actuators 2012, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastenbroek, B.; de Haan, E.; van den Berg, M.; Herder, J. Development of a Mobile Arm Support (Armon): Design Evolution and Preliminary User Experience. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 13–15 June 2007; pp. 1114–1120.
- MicroGravity. Armon. 2012. Available online: http://www.mginside.eu (accessed on 27 September 2013).
- Stienen, A.H.A.; McPherson, J.; Schouten, A.; Dewald, J.P.A. The ACT-4D: A Novel Rehabilitation Robot for the Quantification of Upper Limb Motor Impairments following Brain Injury. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Zurich, Switzerland, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 1–6.
- Jansen, M.; Burgers, J.; Jannink, M.; van Alfen, N.; de Groot, I.J. Functional deterioration in wheelchair-dependent boys with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy may be delayed by arm-support and assisted training. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2013, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrholz, J.; Platz, T.; Kugler, J.; Pohl, M. Electromechanical and robot-assisted arm training for improving arm function and activities of daily living after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alutei, A.; Vaida, A.; Mandru, D.; Tatar, M. Development of an Active Upper-Limb Orthosis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advancements of Medicine and Health Care through Technology, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 23–26 September 2009; Volume 26, pp. 405–408.
- Van Peppen, R.; van der Pijl, D.; Feys, P. Robotgeassisteerde arm revalidatie bij cliënten na een CVA. Wetenschappelijk Tijdschrift voor Ergotherapie 2011, 4, 4–13. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, F.; Retolaza, I.; Pujana-Arrese, A.; Cenitagoya, A.; Basurko, J.; Landaluze, J. Design of a Five Actuated DoF Upper Limb Exoskeleton Oriented to Workplace Help. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 19–22 October 2008; pp. 169–174.
- Detriche, J. Innovations in dismantling robotics. Nuclear Eng. Design 1998, 182, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, M.; Johnson, D.; Hollerbach, J. Full-Arm Haptics in an Accessibility Task. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment And Teleoperator Systems, Reno, NV, USA, 13–14 March 2008; pp. 405–412.
- Ragonesi, D.; Agrawal, S.; Sample, W.; Rahman, T. Series Elastic Actuator Control of a Powered Exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 3515–3518.
- Ivanova, G.; Bulavintsev, S.; Ryu, J.H.; Poduraev, J. Development of an Exoskeleton System for Elderly and Disabled People. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Science and Applications (ICISA), Jeju Island, South Korea, 26–29 April 2011; pp. 1–7.
- Rahman, M.; K-Ouimet, T.; Saad, M.; Kenne, J.P.; Archambault, P. Nonlinear Control of an Upper-limb Exoskelton Robot. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), Beirut, Lebanon, 11–14 December 2011; pp. 772–775.
- Maxon Program 2010/2011; Maxon motor: Sachseln, Switzerland.
- Xiong, C.; Jiang, X.; Sun, R.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Y. Control methods for exoskeleton rehabilitation robot driven with pneumatic muscles. Ind. Robot Int. J. 2009, 36, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.; Tsagarakis, N.; Caldwell, D. Exoskeletons for human force augmentation. Ind. Robot Int. J. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemura, A.; Saito, Y.; Fujisaki, K. A Study on Power-assisted Rehabilitation Robot Arms Operated by Patient with Upper Limb Disabilities. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Kyoto, Japan, 23–26 June 2009; pp. 451–456.
- Lenzi, T.; Vitiello, N.; de Rossi, S.M.M.; Roccella, S.; Vecchi, F.; Carrozza, M. NEUROExos: A Variable Impedance Powered Elbow Exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 1419–1426.
- Stienen, A.H.A.; Hekman, E.E.G.; ter Braak, H.; Aalsma, A.M.M.; van der Helm, F.C.T.; van der Kooij, H. Design of a rotational hydroelastic actuator for a powered exoskeleton for upper limb rehabilitation. Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, D.; Taheri, B.; Richer, E. Design and characterization of a small-scale magnetorheological damper for tremor suppression. Trans. Mechatron. (ASME) 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulides, J.J.H.; Encica, L.; Lomonova, E.A.; Vandenput, A.J.A. Design considerations for a semi-active electromagnetic suspension system. Trans. Magn. 2006, 42, 3446–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jesus Lozoya-Santos, J.; Tudon-Martinez, J.; Morales-Menendez, R.; Ramirez-Mendoza, R. Comparison of on-off control strategies for a semi-active automotive suspension using HiL. Latin Am. Trans. 2012, 10, 2045–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippi, P.; Tanelli, M.; Corno, M.; Savaresi, S.; Fabbri, L. Semi-active steering damper control in two-wheeled vehicles. Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2011, 19, 1003–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, M.; Kikuchi, T.; Mihara, M.; Hatakenaka, M.; Miyai, I.; Furusho, J. Development of Evaluation System of the Motor Function for Upper Limbs Using 3-D rehabilitation Robot “EMUL” and Near-infrared Spectroscopy “NIRS”. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Kyoto, Japan, 23–26 June 2009.
- Haraguchi, M.; Kikuchi, T.; Jin, Y.; Fukushima, K.; Furusho, J.; Inoue, A.; Oda, K. 3-D Rehabilitation Systems for Upper Limbs Using ER Actuators/Brakes with High Safety: “EMUL”, “Robotherapist” and “PLEMO”. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Reality and Telexistence, Esbjerg, Denmark, 28–30 November 2007.
- Wolbrecht, E.; Leavitt, J.; Reinkensmeyer, D.; Bobrow, J. Control of a Pneumatic Orthosis for Upper Extremity Stroke Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the International Conference of Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, New York, NY, USA, 30 August–3 September 2006.
- Morales, R.; Badesa, F.; Domenech, L.M.; Garcia-Aracil, N.; Sabater, J.; Menchón, M.; Fernandez, E. Design and Control of a Rehabilitation Robot Driven by Pneumatic Swivel Modules. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Tokyo, Japan, 26–29 Sept. 2010; pp. 566–571.
- Sugar, T.; He, J.; Koeneman, E.; Koeneman, J.; Herman, R.; Huang, H.; Schultz, R.; Herring, D.; Wanberg, J.; Balasubramanian, S.; Swenson, P.; Ward, J. Design and Control of RUPERT: A Device for Robotic Upper Extremity Repetitive Therapy. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2007, 15, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsagarakis, N.G.; Caldwell, D.G. Development and control of a soft-actuated exoskeleton for use in physiotherapy and training. Auton. Robot. 2003, 15, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanis, R.; Motoasca, E.; Lomonova, E.A. Trade-offs in the Implementation of Rigid and Intrinsically Compliant Actuators in Biorobotic Applications. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Rome, Italy, 24–27 2012; pp. 100–105.
- Oblak, J.; Cikajlo, I.; Matjai, Z. Haptic Robot for Arm and Wrist Rehabilitation. In IFMBE Proceedings of the World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Munich, Germany, 7–12 September 2009; pp. 20–23.
- Vanderniepen, I.; van Ham, R.; van Damme, M.; Lefeber, D. Design of a Powered Elbow Orthosis for Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Using Compliant Actuation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Scotsdale, AZ, USA, 19–22 October 2008; pp. 801–806.
- Visser, L.; Carloni, R.; Stramigioli, S. Energy-efficient variable stiffness actuators. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2011, 27, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stienen, A.H.A.; Hekman, E.E.G.; Kooij, H.; Ellis, M.D.; Dewald, J.P.A. Aspects of Weight-Support Mechanisms in Rehabilitation Robotics. In IFMBE Proceedings of the World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Munich, Germany, 7–12 September 2009; pp. 392–394.
- Johnson, G.; Carus, D.; Parrini, G.; Scattereggia Marchese, S.; Valeggi, R. The design of a five-degree-of-freedom powered orthosis for the upper limb. Proc. Inst. Mechan. Eng. Part H: J. Eng. Med. 2001, 215, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopura, R.A.R.C.; Kiguchi, K.; Li, Y. SUEFUL-7: A 7DOF Upper-limb Exoskeleton Robot with Muscle-Model-Oriented EMG-Based Control. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–15 October 2009; pp. 1126–1131.
- Hayashi, Y.; Dubey, R.; Kiguchi, K. Torque Optimization for a 7DOF Upper-limb Power-assist Exoskeleton Robot. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Robotic Intelligence In Informationally Structured Spacecarignan (RiiSS), Paris, France, 11–15 April 2011; pp. 49–54.
- Carignan, C.; Naylor, M.; Roderick, S. Controlling Shoulder Impedance in a Rehabilitation Arm Exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2008; pp. 2453–2458.
- Rosati, G.; Gallina, P.; Masiero, S. Design, implementation and clinical tests of a wire-based robot for neurorehabilitation. Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2007, 15, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Agrawal, S. Transition from Mechanical Arm to Human Arm with CAREX: A Cable Driven ARm EXoskeleton (CAREX) for Neural Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Saint Paul, MO, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 2457–2462.
- Nunes, W.; Rodrigues, L.; Oliveira, L.; Ribeiro, J.; Carvalho, J.; Goncalves, R.S. Cable-based Parallel Manipulator for Rehabilitation of Shoulder and Elbow Movements. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Zurich, Germany, 29 June-1 July 2011.
- Loureiro, R.; Smith, T. Design of the ROBIN System: Whole-arm Multi-model Sensorimotor Environment for the Rehabilitation of Brain Injuries While Sitting or Standing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Zurich, Germany, 29 June–1 July 2011.
- Benjuya, N.; Kenney, S. Hybrid arm orthosis. J. Prosthet. Orthot. 1990, 2, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, G.; Romer, G.; Stuyt, H. Design of a Dynamic Arm Support (DAS) for Gravity Compensation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Noodwijk, The Netherlands, 13–15 June 2007; pp. 1042–1048.
- Van Ninhuijs, B.; Motoasca, T.; Gysen, B.; Lomonova, E.A. Modeling of spherical magnet arrays using the magnetic charge model. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 49, 4109–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, L.Q. IntelliArm: An Exoskeleton for Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Neurological Impairments. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 19–22 October 2008; pp. 109–114.
- Brooks, T. Telerobotic Response Requirements. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 4–7 November 1990; pp. 113–120.
- Schiele, A.; Hirzinger, G. A New Generation of Ergonomic Exoskeletons–The High-Performance X-Arm-2 for Space Robotics Telepresence. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 September 2011; pp. 2158–2165.
- Case, D.; Taheri, B.; Richer, E. Biomimetic actuators in prosthetic and rehabilitation applications. Technol. Health Care 2002, 10, 107–120. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, A.; Ohashi, T.; Hashimoto, H. 7 DOF Arm Type Haptic Interface for Teleoperation and Virtual Reality Systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Victoria, TX, USA, 13–17 October 1998; Volume 2, pp. 1266–1271.
- Chou, W.; Wang, T.; Xiao, J. Haptic Interaction with Virtual Environment Using an Arm Type Exoskeleton Device. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation, New Orleans, LA, USA, 26 April–1 May 2004; Volume 2, pp. 1992–1997.
- Seki, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Iijima, H.; Ando, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Fujie, M.; Nagaoka, M. Development of Robotic Upper Limb Orthosis with Tremor Suppressiblity and Elbow Joint Movability. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Anchorage, AK, USA, 9–12 October 2011; pp. 729–735.
- Gmerek, A. The Virtual Reality System Used for Upper Extremity Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Methods and Models in Automation and Robotics, Miedzyzdrojie, Poland, 27–30 August 2012.
- Jackson, A.; Culmer, P.; Makower, S.; Levesley, M.; Richardson, R.; Cozens, A.; Williams, M.; Bhakta, B. Initial Patient Testing of iPAM–a Robotic System for Stroke Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 13–15 June 2007; pp. 250–256.
- Toth, A.; Fazekas, G.; Arz, G.; Jurak, M.; Horvath, M. Passive Robotic Movement Therapy of the Spastic Hemiparetic Arm with REHAROB: Report of the First Clinical Test and the Follow-up System Improvement. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Chicago, IL, USA, 28 June–1 July 2005; pp. 127–130.
- Rahman, T.; Ramanathan, R.; Stroud, S.; Sample, W.; Seliktar, R.; Harwin, W.; Alexander, M.; Scavina, M. Towards the control of a powered orthosis for people with muscular dystrophy. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H: J. Eng. Med. 2001, 215, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, R.; Amirabdollahian, F.; Topping, M.; Driessen, B.; Harwin, W. Upper limb robot mediated stroke therapy–GENTLE/s approach. Auton. Robot. 2003, 15, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, H.; Hogan, N.; Aisen, M.; Volpe, B. Robot-aided neurorehabilitation. Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 1998, 6, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemiadis, P.; Kyriakopoulos, K. EMG-based Position and Force Control of a Robot Arm: Application to Teleoperation and Orthosis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Zurich, Switzerland, 4–7 September 2007.
- Ball, S.; Brown, I.; Scott, S. Performance evaluation of a planar 3DOF robotic exoskeleton for motor assessment. J. Med. Devices 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nef, T.; Mihelj, M.; Colombo, G.; Riener, R. ARMin—Robot for Rehabilitation of the Upper Extremities. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 May 2006; pp. 3152–3157.
- Nickel, V.; Kachak, J.; Allen, J. Electrically powered orthotic systems. J. Bone Joint Surg. 1969, 51-A, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopura, R.; Kiguchi, K. Development of a 6DOF Exoskeleton Robot for Human Upper-Limb Motion Assist. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Automation for Sustainability (ICIAFS), Colombo, Sri Lanka, 12–14 December 2008; pp. 13–18.
- Umetani, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Morizono, T.; Yoshida, T.; Aoki, S. “Skil Mate” Wearable Exoskeleton Robot. In Proceedings International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Tokyo, Japan, 12–15 October 1999; Volume 4, pp. 984–988.
- Kovacs, G.; Lochmatter, P.; Wissler, M. An arm wrestling robot driven by dielectric elastomer actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ino, S.; Sato, M.; Hosono, M.; Izumi, T. Development of a soft metal hydride actuator using a laminate bellows for rehabilitation systems. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2009, 136, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagur-Grodzinski, J. Polymeric gels and hydrogels for biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2010, 21, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.W.; van Lierop, C.M.M.; Lomonova, E.A.; Vandenput, A.J.A. Magnetically levitated planar actuator with moving magnets. Trans. Ind. Appl. 2008, 44, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Chen, I.M.; Yang, G.; Lee, K.M. Analytical and experimental investigation on the magnetic field and torque of a permanent magnet spherical actuator. Trans. Mechatron. (ASME) 2006, 11, 409–419. [Google Scholar]
- Meessen, K.; Paulides, J.J.H.; Lomonova, E.A. Analysis of a novel magnetization pattern for 2-DoF rotary-linear actuators. Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 3867–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staubli, P.; Nef, T.; Klamroth-Marganska, V.; Riener, R. Effects of intersive arm training with the rehabilitation robot ARMin II in chronic stroke patients: Four single-cases. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gijbels, D.; Lamers, I.; Kerkhofs, L.; Alders, G.; Kinppenberg, E.; Feys, P. The Armeo Spring as training tool to improve upper limb functionality in multiple sclerosis: A pilot study. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.L.; Rong Chen, B.; Majidi, C.; Wood, R.; Nagpal, R.; Goldfield, E. Active Modular Elastomer Sleeve for Soft Wearable Assistance Robots. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vilamoura, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012.
- Nagai, K.; Nakanishi, I.; Hanafusa, H.; Kawamura, S.; Makikawa, M.; Tejima, N. Development of an 8 DOF Robotic Orthosis for Assisting Human Upper Limb Motion. In Proceedings International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Leuven, Belgium, 16–20 May 1998; Volume 4, pp. 3486–3491.
- Kobayashi, H.; Uchimura, A.; Shiiba, T. Development on Muscle Suit: Realization of Abduction Motion. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Kobe, Japan, 20–24 July 2003.
- Kobayashi, H.; Hiramatsu, K. Development of Muscle Suit for Upper Limb. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation, New Orleans, LA, USA, 26 April–1 May 2004.
- Staubli, P.; Nef, T.; Klamroth-Marganska, V.; Riener, R. Effects of intensive arm training with the rehabilitation robot ARMin II in chronic stroke patients: Four single-cases. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocon, E.; Belda-Lois, J.; Ruiz, A.; Manto, M.; Moreno, J.; Pons, J. Design and validation of a rehabilitation robotic exoskeleton for tremor assessment and suppression. Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2007, 15, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.K.; Jordan, K.; King, M. Robotic Arm Skate for Stroke Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Zurich, Switzerland, 29 June–1 July 2011.
- Mayr, A.; Kofler, M.; Saltuari, L. An electromechanical robot for upper limb training following stroke. A prospective randomised controlled pilot study. Handchir. Mikrochir. Plast Chir. 2008, 40, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Van Ninhuijs, B.; Van der Heide, L.A.; Jansen, J.W.; Gysen, B.L.J.; Van der Pijl, D.J.; Lomonova, E.A. Overview of Actuated Arm Support Systems and Their Applications. Actuators 2013, 2, 86-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/act2040086
Van Ninhuijs B, Van der Heide LA, Jansen JW, Gysen BLJ, Van der Pijl DJ, Lomonova EA. Overview of Actuated Arm Support Systems and Their Applications. Actuators. 2013; 2(4):86-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/act2040086
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan Ninhuijs, B., L.A. Van der Heide, J.W. Jansen, B.L.J. Gysen, D.J. Van der Pijl, and E.A. Lomonova. 2013. "Overview of Actuated Arm Support Systems and Their Applications" Actuators 2, no. 4: 86-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/act2040086
APA StyleVan Ninhuijs, B., Van der Heide, L. A., Jansen, J. W., Gysen, B. L. J., Van der Pijl, D. J., & Lomonova, E. A. (2013). Overview of Actuated Arm Support Systems and Their Applications. Actuators, 2(4), 86-110. https://doi.org/10.3390/act2040086