A Wearable Wrist Rehabilitation Device with Vacuum-Actuated Artificial Muscles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structure Design and Test
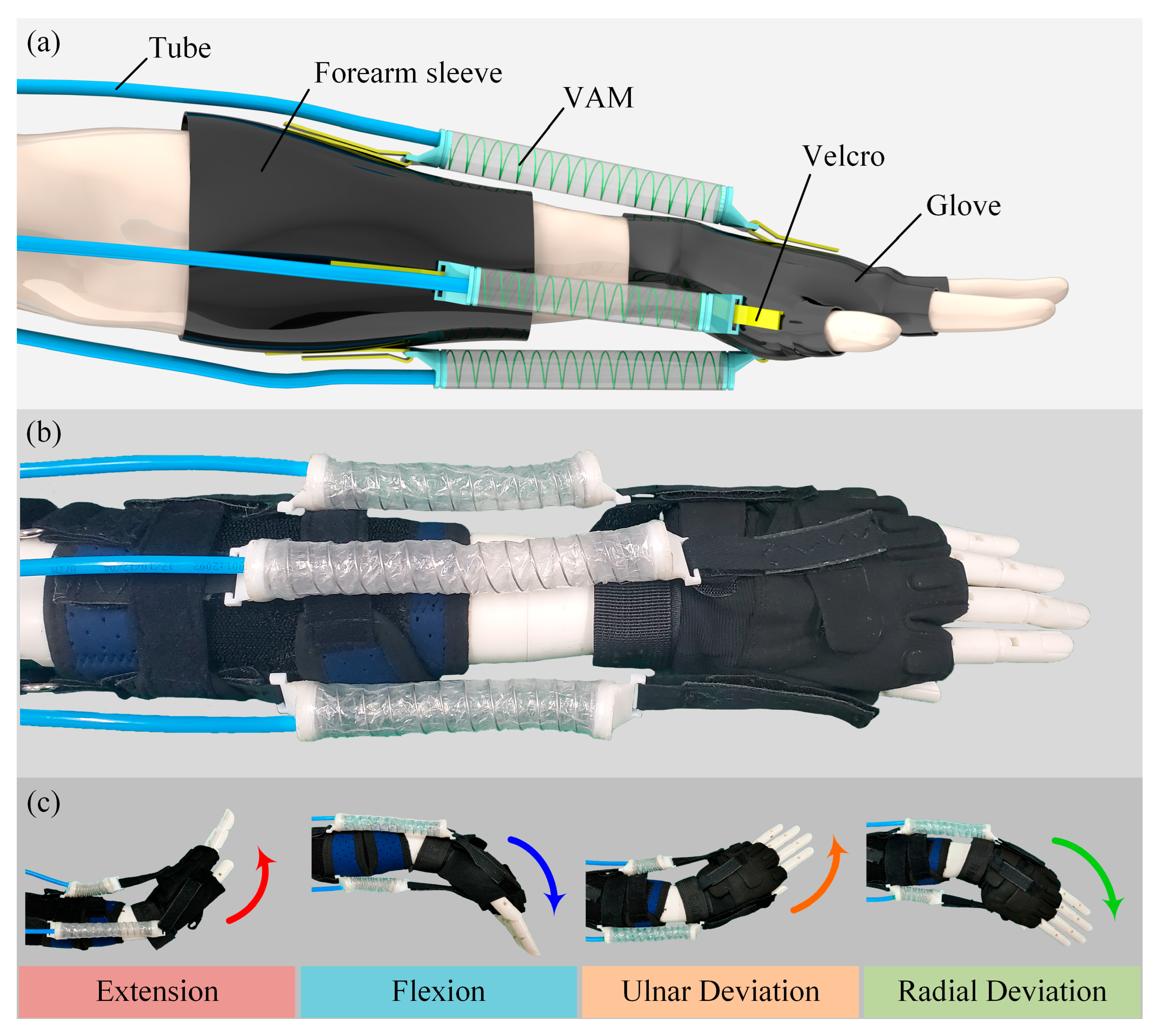
2.1. Design of the WWRD
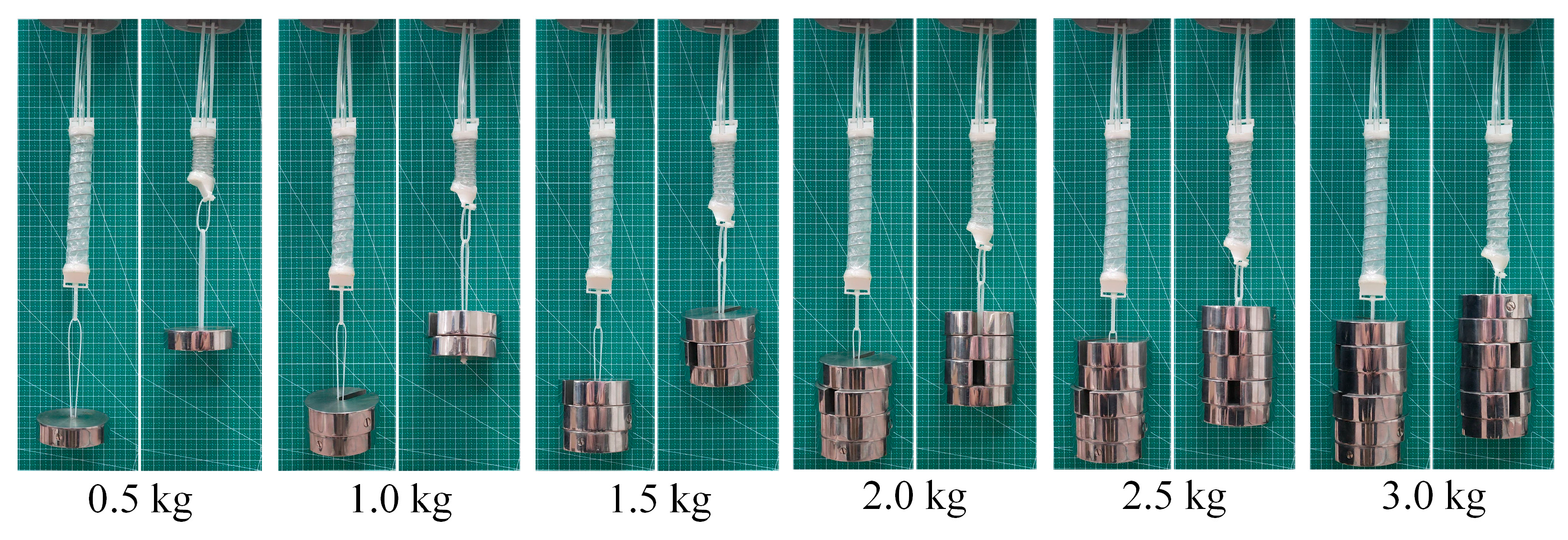
2.2. Design of VAM
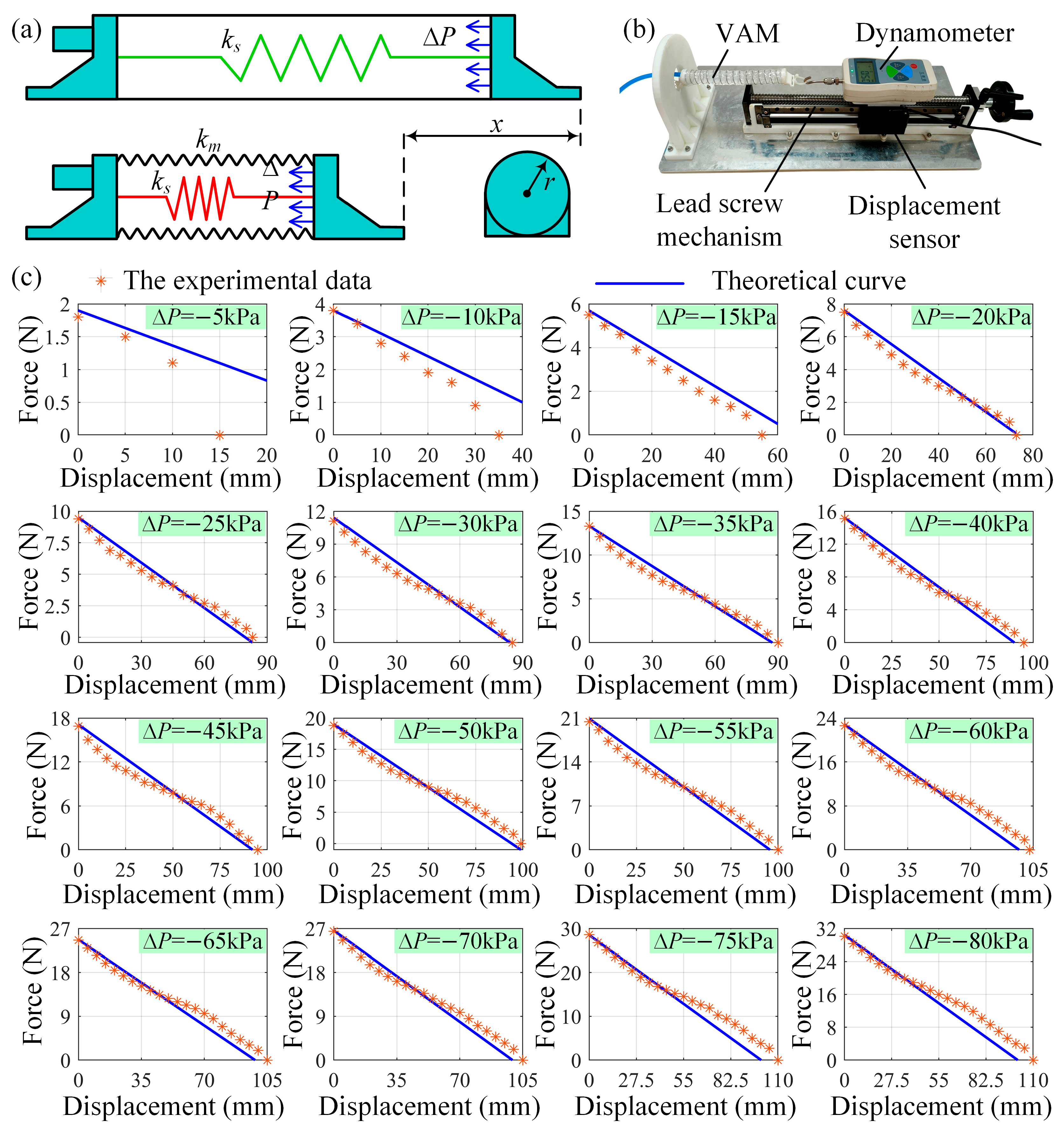
2.3. The Statics Analysis of the VAM
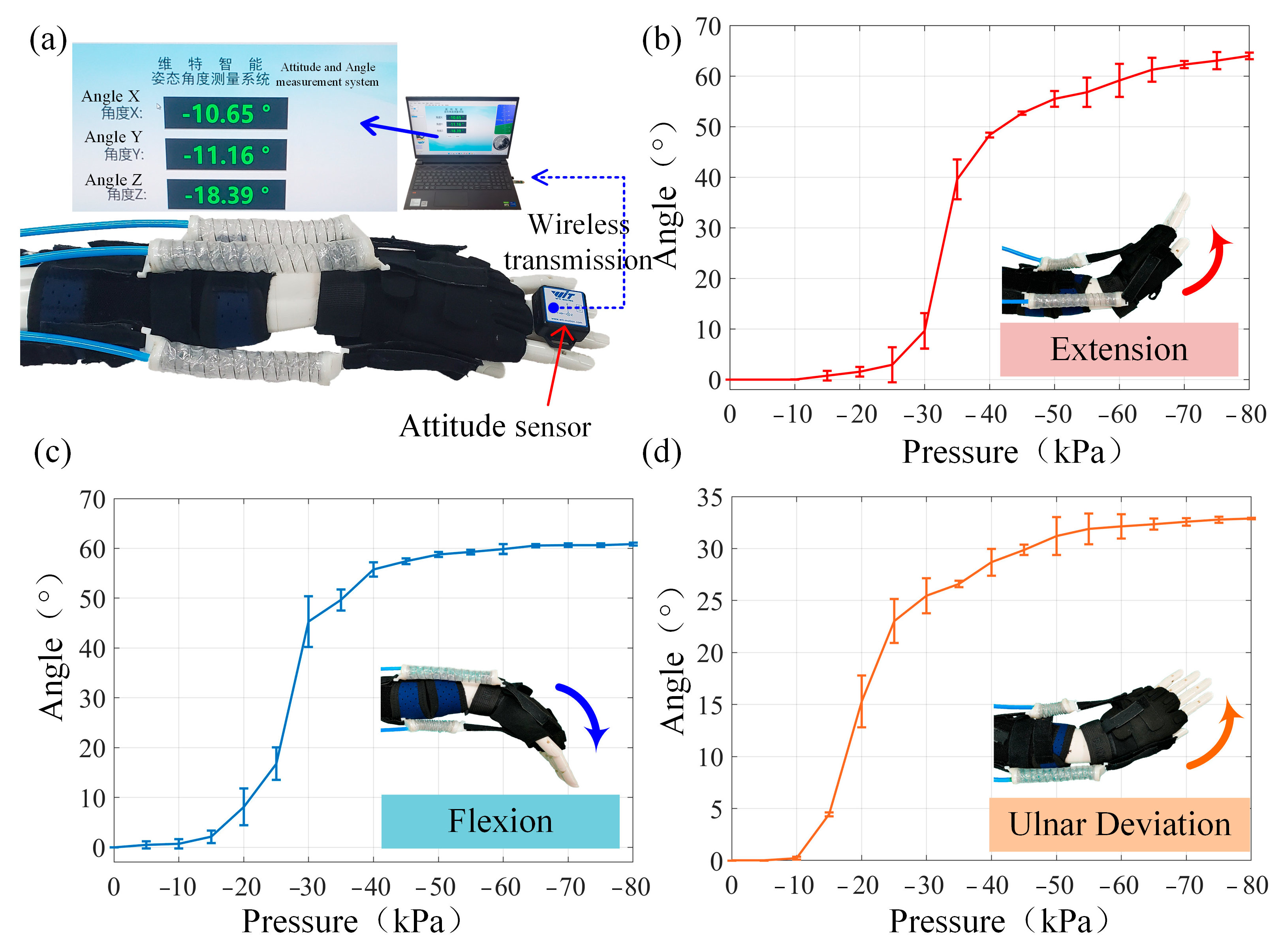
3. Motion Analysis of the WWRD
3.1. Analysis of Multidirectional Wrist Motions: Ulnar Deviation, Radial Deviation, Extension, and Flexion
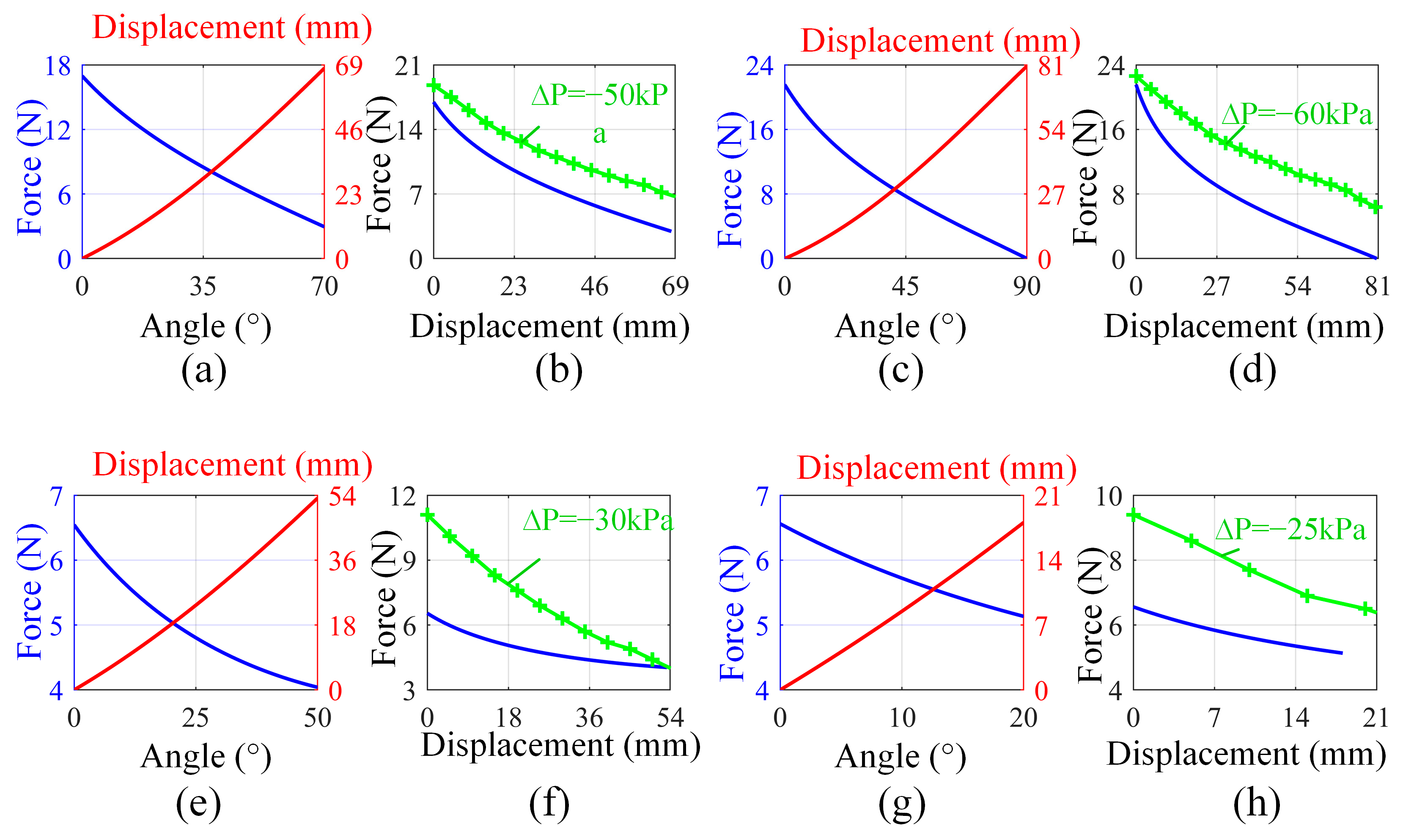
3.2. The Mechanical Analysis of Wrist Extension and Flexion Motions
3.3. The Mechanical Analysis of Wrist Ulnar Deviation and Radial Deviation Motions
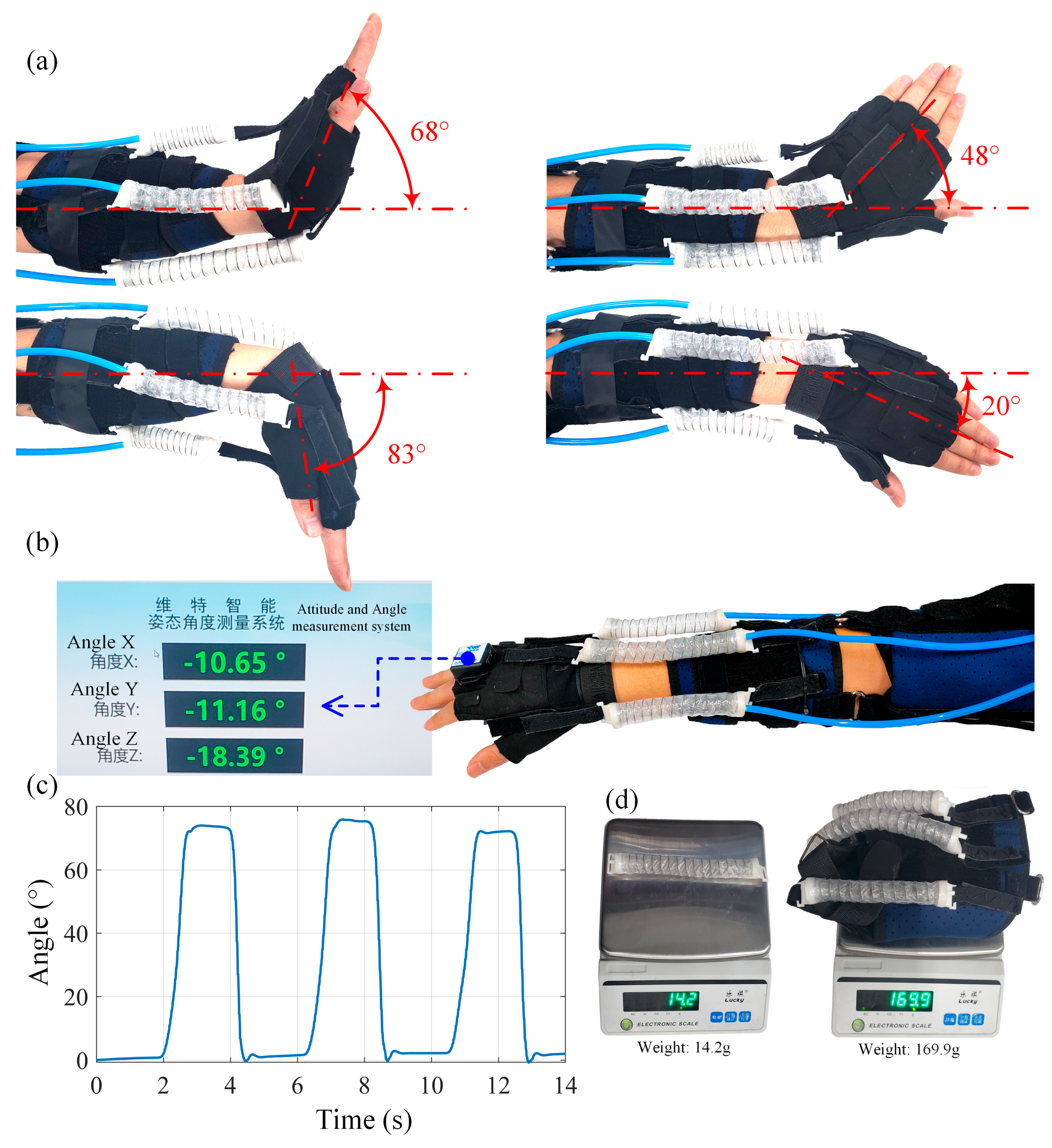
4. Wearing Experiments of WWRD
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, B.; Li, M.; Mei, T.; McCoul, D.; Qin, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, J. Wearable Stretch Sensors for Motion Measurement of the Wrist Joint Based on Dielectric Elastomers. Sensors 2017, 17, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caumes, M.; Goislard de Monsabert, B.; Hauraix, H.; Berton, E.; Vigouroux, L. Complex Couplings between Joints, Muscles and Performance: The Role of the Wrist in Grasping. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuelcken, M.; Mellifont, D.; Gorman, A.; Sayers, M. Wrist Injuries in Tennis Players: A Narrative Review. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, H.T.; Van Limbeek, J.; Geurts, A.C.; Zwarts, M.J. Motor Recovery after Stroke: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, B.R.; McDowell, S.K.; Worthen-Chaudhari, L.C. Poststroke Upper Extremity Rehabilitation: A Review of Robotic Systems and Clinical Results. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2007, 14, 22–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okita, S.; Schwerz De Lucena, D.; Reinkensmeyer, D.J. Movement Diversity and Complexity Increase as Arm Impairment Decreases After Stroke: Quality of Movement Experience as a Possible Target for Wearable Feedback. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2024, 32, 2961–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjuan, J.D.; Castillo, A.D.; Padilla, M.A.; Quintero, M.C.; Gutierrez, E.E.; Sampayo, I.P.; Hernandez, J.R.; Rahman, M.H. Cable Driven Exoskeleton for Upper-Limb Rehabilitation: A Design Review. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2020, 126, 103445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerasa, A.; Pignolo, L.; Gramigna, V.; Serra, S.; Olivadese, G.; Rocca, F.; Perrotta, P.; Dolce, G.; Quattrone, A.; Tonin, P. Exoskeleton-Robot Assisted Therapy in Stroke Patients: A Lesion Mapping Study. Front. Neuroinform. 2018, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Jamwal, P.K.; Van Vliet, P.; Ghayesh, M.H. State-of-the-Art Robotic Devices for Wrist Rehabilitation: Design and Control Aspects. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2020, 50, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertani, R.; Melegari, C.; De Cola, M.C.; Bramanti, A.; Bramanti, P.; Calabrò, R.S. Effects of Robot-Assisted Upper Limb Rehabilitation in Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Gasperina, S.; Roveda, L.; Pedrocchi, A.; Braghin, F.; Gandolla, M. Review on Patient-Cooperative Control Strategies for Upper-Limb Rehabilitation Exoskeletons. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 8, 745018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, U.; Van Hedel, H.J.A.; Klamroth-Marganska, V.; Riener, R. ChARMin: The First Actuated Exoskeleton Robot for Pediatric Arm Rehabilitation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 21, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Wu, H. Development of a Minimal-Intervention-Based Admittance Control Strategy for Upper Extremity Rehabilitation Exoskeleton. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2018, 48, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.-Y.; Su, Y.-Y.; Yu, Y.-L.; Lin, C.-H.; Lan, C.-C. A 5-Degrees-of-Freedom Lightweight Elbow-Wrist Exoskeleton for Forearm Fine-Motion Rehabilitation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 2684–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiano, L.; Di Pino, G.; Di Biase, L.; Tombini, M.; Tagliamonte, N.L.; Formica, D. PDMeter: A Wrist Wearable Device for an at-Home Assessment of the Parkinson’s Disease Rigidity. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopura, R.A.R.C.; Bandara, D.S.V.; Kiguchi, K.; Mann, G.K.I. Developments in Hardware Systems of Active Upper-Limb Exoskeleton Robots: A Review. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2016, 75, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.; Choi, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, G.; Han, C.; Ji, Y.; Shin, D.; Hwang, S.; Yun, D.; Jang, H.; et al. Feasibility of Rehabilitation Training with a Newly Developed, Portable, Gait Assistive Robot for Balance Function in Hemiplegic Patients. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 41, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Wu, H. Development of an RBFN-Based Neural-Fuzzy Adaptive Control Strategy for an Upper Limb Rehabilitation Exoskeleton. Mechatronics 2018, 53, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Q. Design and Testing of a Soft Parallel Robot Based on Pneumatic Artificial Muscles for Wrist Rehabilitation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fei, Y.; Chen, W. Integration, Sensing, and Control of a Modular Soft-Rigid Pneumatic Lower Limb Exoskeleton. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zuo, J.; Zhu, C.; Xie, S.Q. Design and Control of Soft Rehabilitation Robots Actuated by Pneumatic Muscles: State of the Art. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 113, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Yasir, I.B.; Han, J.; Park, C.H.; Bok, S.-K.; Kyung, K.-U. Design of Shape Memory Alloy-Based Soft Wearable Robot for Assisting Wrist Motion. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copaci, D.; Cano, E.; Moreno, L.; Blanco, D. New Design of a Soft Robotics Wearable Elbow Exoskeleton Based on Shape Memory Alloy Wire Actuators. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2017, 2017, 1605101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Yuan, J.; Wang, M.; Xiao, L.; Yang, J.; Lin, Z.; Xu, P.; Hou, L. Novel Accordion-Inspired Foldable Pneumatic Actuators for Knee Assistive Devices. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veale, A.J.; Staman, K.; van der Kooij, H. Soft, Wearable, and Pleated Pneumatic Interference Actuator Provides Knee Extension Torque for Sit-to-Stand. Soft Robot. 2021, 8, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polygerinos, P.; Wang, Z.; Galloway, K.C.; Wood, R.J.; Walsh, C.J. Soft Robotic Glove for Combined Assistance and At-Home Rehabilitation. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2015, 73, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fang, Z.; Liu, J.; Tang, K.; Luo, J.; Yi, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, Z. A Compact Soft Robotic Wrist Brace with Origami Actuators. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 8, 614623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, B.W.K.; Yeow, C.-H. Design and Modeling of a High Force Soft Actuator for Assisted Elbow Flexion. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3731–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, C.T.; McCann, C.M.; Hohimer, C.J.; Bertoldi, K.; Walsh, C.J. Unfolding Textile-Based Pneumatic Actuators for Wearable Applications. Soft Robot. 2021, 9, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.; Park, J.-H.; Ku, S.; Jeong, Y.; Paik, N.-J.; Park, Y.-L. A Soft Wearable Robotic Ankle-Foot-Orthosis for Post-Stroke Patients. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 2547–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, N.W.; Lyau, V.; Raiford, W.A.; Holland, D.; Gafford, J.B.; Ellis, T.D.; Walsh, C.J. A Soft Robotic Orthosis for Wrist Rehabilitation. J. Med. Devices 2015, 9, 030918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrikopoulos, G.; Nikolakopoulos, G.; Manesis, S. Design and Development of an Exoskeletal Wrist Prototype via Pneumatic Artificial Muscles. Meccanica 2015, 50, 2709–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-P.; Hannaford, B. Measurement and Modeling of McKibben Pneumatic Artificial Muscles. IEEE Trans. Robot. Automat. 1996, 12, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, F.; Walsh, C.J.; Bertoldi, K. Automatic Design of Fiber-Reinforced Soft Actuators for Trajectory Matching. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Vogt, D.M.; Rus, D.; Wood, R.J. Fluid-Driven Origami-Inspired Artificial Muscles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13132–13137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Mosadegh, B.; Ainla, A.; Lee, B.; Khashai, F.; Suo, Z.; Bertoldi, K.; Whitesides, G.M. Buckling of Elastomeric Beams Enables Actuation of Soft Machines. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6323–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Verma, M.S.; So, J.-H.; Mosadegh, B.; Keplinger, C.; Lee, B.; Khashai, F.; Lossner, E.; Suo, Z.; Whitesides, G.M. Buckling Pneumatic Linear Actuators Inspired by Muscle. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2016, 1, 1600055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulasekera, A.L.; Arumathanthri, R.B.; Chathuranga, D.S.; Gopura, R.A.R.C.; Lalitharatne, T.D. A thin-walled vacuum actuator (thinvac) and the development of multifilament actuators for soft robotic applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 332, 113088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawk, C.; In Het Panhuis, M.; Spinks, G.M.; Alici, C. Bioinspired 3d printable soft vacuum actuators for locomotion robots, grippers and artificial muscles. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, P.; Morita, L.; Sun, X.; Sameoto, D. R3VAMPs—Fully recyclable, reconfigurable, and recoverable vacuum actuated muscle-inspired pneumatic structures. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 5th International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Edinburgh, UK, 4–8 April 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 577–582. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 37704-2019; National Technical Committee 13 on Special Service Robots of Standardization Administration of China. General Specifications for Sports Rehabilitation Training Robots. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Xu, Y.Q.; Zhong, S.Z.; Zhu, Q.A.; Zhao, W.D.; Li, Z.H.; Li, Z.Y. Experimental study on kinematics of normal wrist joints. Chin. J. Clin. Anat. 2003, 2, 173–175. [Google Scholar]
- Behrens, M.; Husmann, F.; Mau-Moeller, A.; Schlegel, J.; Reuter, E.-M.; Zschorlich, V.R. Neuromuscular Properties of the Human Wrist Flexors as a Function of the Wrist Joint Angle. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merritt, W.H.; Wong, A.L.; Lalonde, D.H. Recent Developments Are Changing Extensor Tendon Management. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 145, 617e–628e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Fahaam, H.; Davis, S.; Nefti-Meziani, S. Wrist Rehabilitation Exoskeleton Robot Based on Pneumatic Soft Actuators. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference for Students on Applied Engineering (ISCAE), Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 20–21 October 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 491–496. [Google Scholar]



| Parameter | Extension | Flexion | Ulnar Deviation | Radial Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOA (mm) | 144 | 143 | 133 | 151 |
| LOB (mm) | 69 | 63 | 77 | 71 |
| α (°) | 8.5 | 12 | 16 | 12 |
| β (°) | 36 | 25 | 40 | 45 |
| G (N) | 11.5 | 11.5 | 11.5 | 11.5 |
| LOC (mm) | 51.6 | 51.6 | 51.6 | 51.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Zhu, K.; He, F.; Gao, W.; Yao, J. A Wearable Wrist Rehabilitation Device with Vacuum-Actuated Artificial Muscles. Actuators 2025, 14, 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14070304
Chen X, Zhu K, He F, Gao W, Yao J. A Wearable Wrist Rehabilitation Device with Vacuum-Actuated Artificial Muscles. Actuators. 2025; 14(7):304. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14070304
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xinbo, Kunming Zhu, Fengchun He, Weihua Gao, and Jiantao Yao. 2025. "A Wearable Wrist Rehabilitation Device with Vacuum-Actuated Artificial Muscles" Actuators 14, no. 7: 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14070304
APA StyleChen, X., Zhu, K., He, F., Gao, W., & Yao, J. (2025). A Wearable Wrist Rehabilitation Device with Vacuum-Actuated Artificial Muscles. Actuators, 14(7), 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14070304





