Magnetic Field Analytical Calculation of No-Load Electromagnetic Performance of Line-Start Explosion-Proof Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Considering Saturation Effect
Abstract
1. Introduction
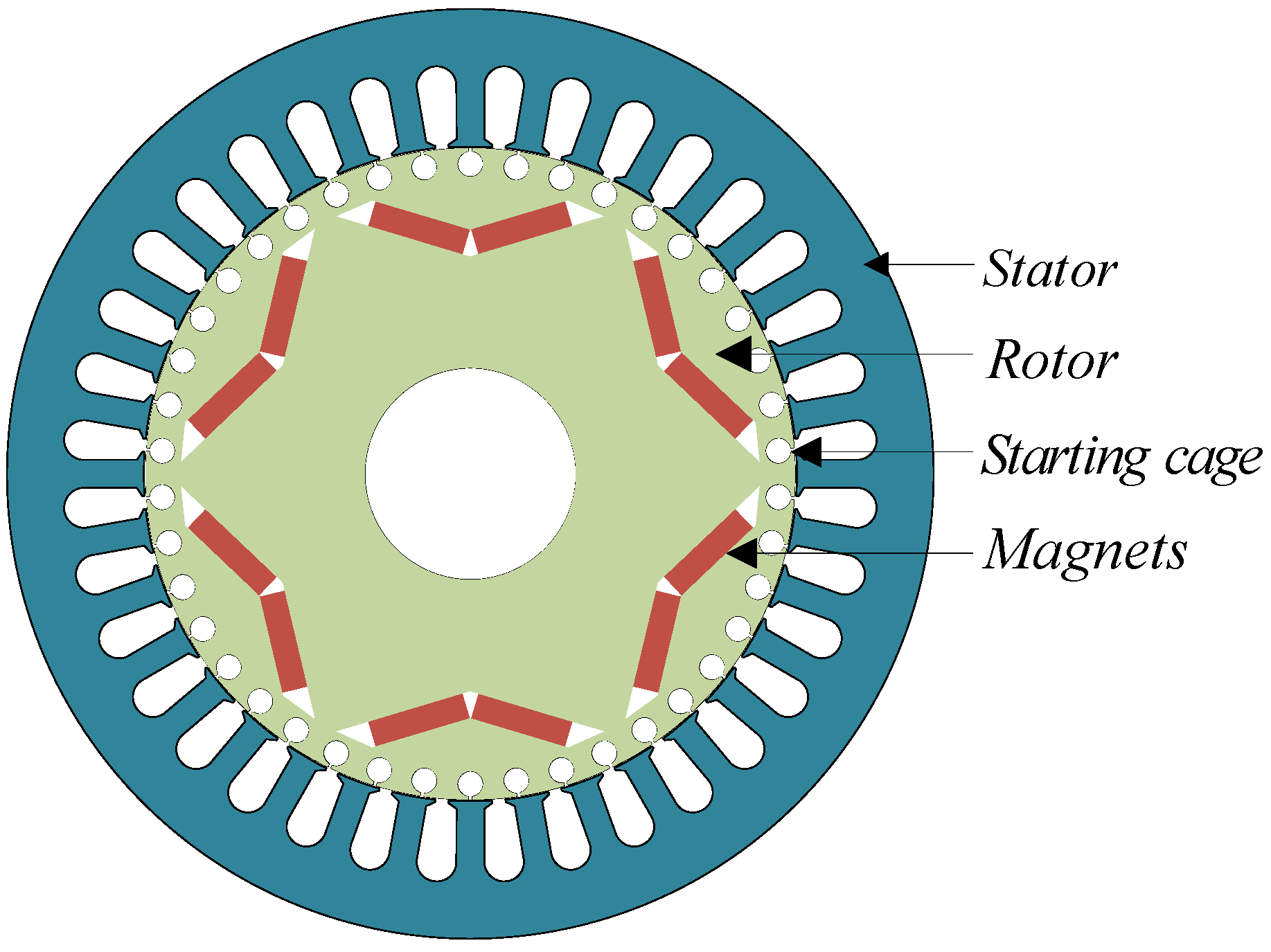
2. Motor Topology and Equivalent Process
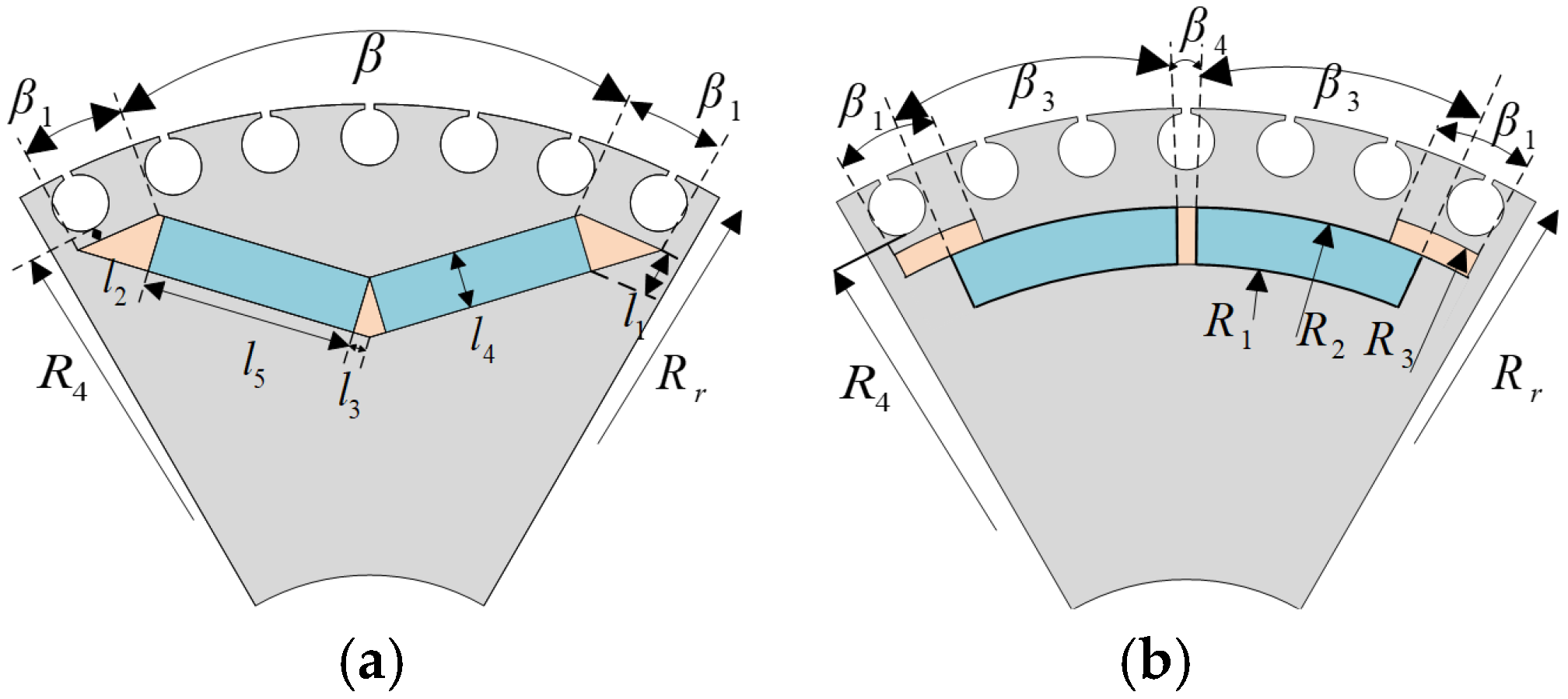
2.1. Simplification of Magnet
- (1)
- The air-gap flux generated by the sector-shaped magnet and the rectangular magnet must be equal.
- (2)
- The pole arc angle, determined by the width angle of the magnet, should be consistent between the sector-shaped magnet and the rectangular magnet.
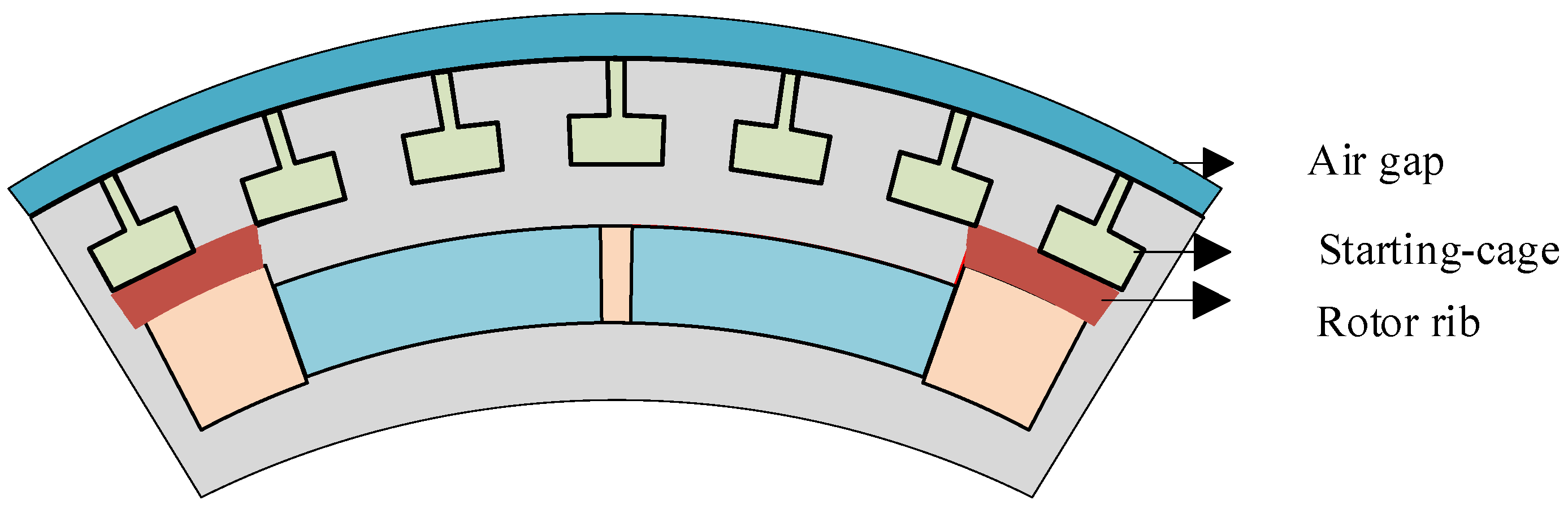
2.2. Simplification of Squirrel Cage Slots
2.3. Magnetic Bridge Saturation
3. Subdomain Model
3.1. Assumptions
- The entire structure stator and rotor (except the bridge) have infinite permeance, and saturation is considered only in the rotor magnetic bridge
- The effect of the end windings is neglected.
- Magnets have linear demagnetization properties and are fully magnetized in the direction of magnetization.
3.2. Partial Differential Equations
3.3. General Solutions
3.4. Boundary Conditions
3.5. No-Load Electromagnetic Performance
4. Calculation Results and Analysis
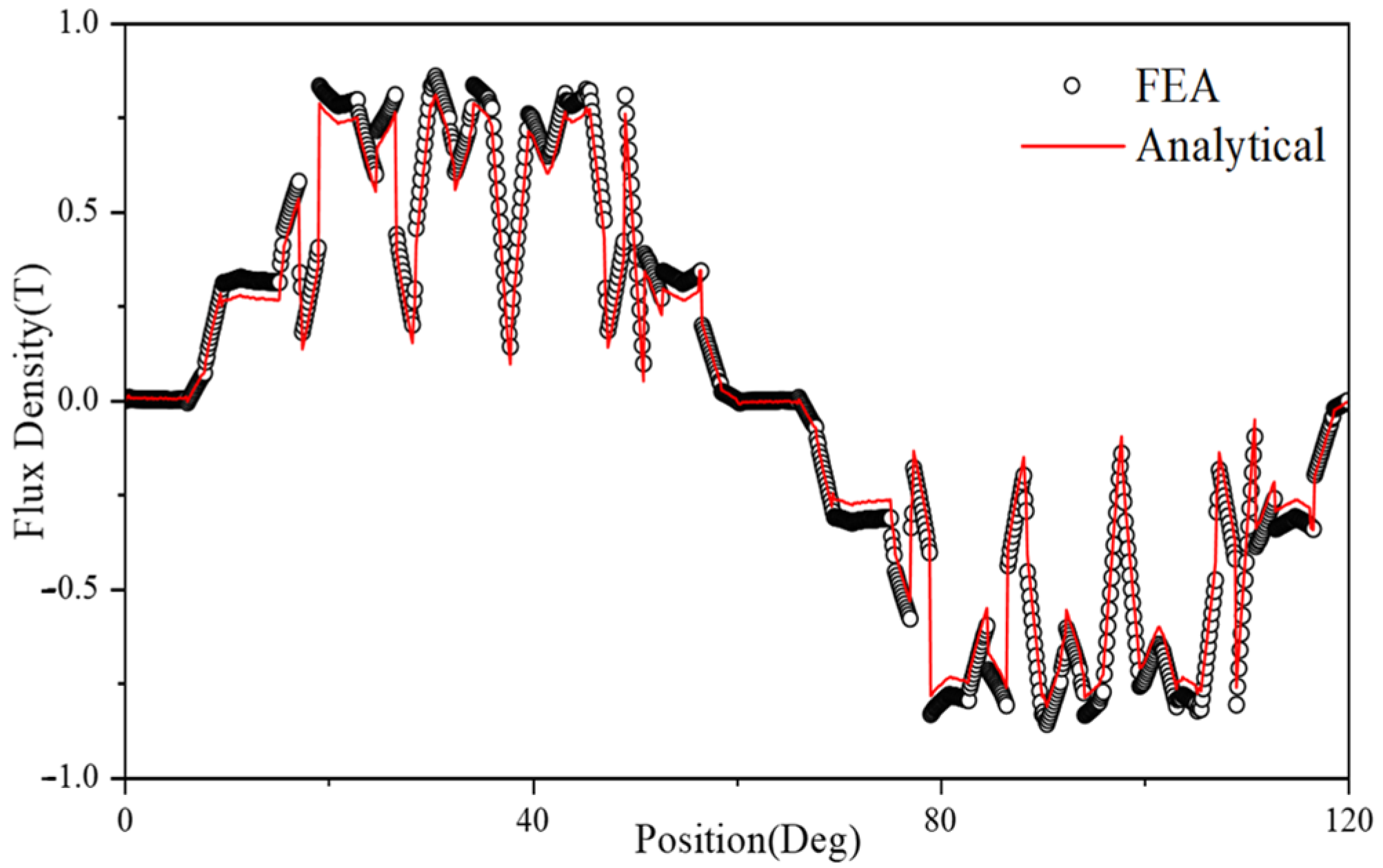
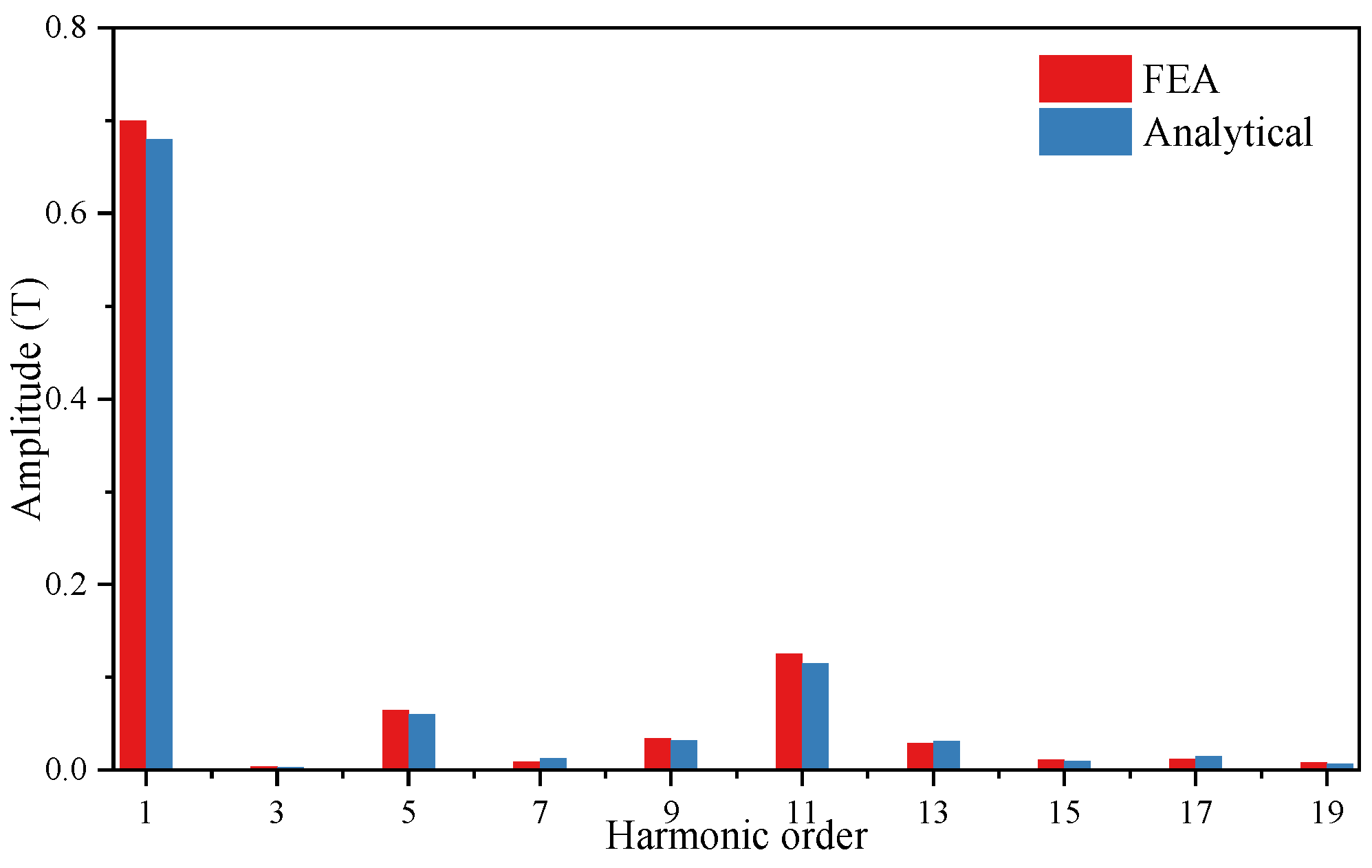
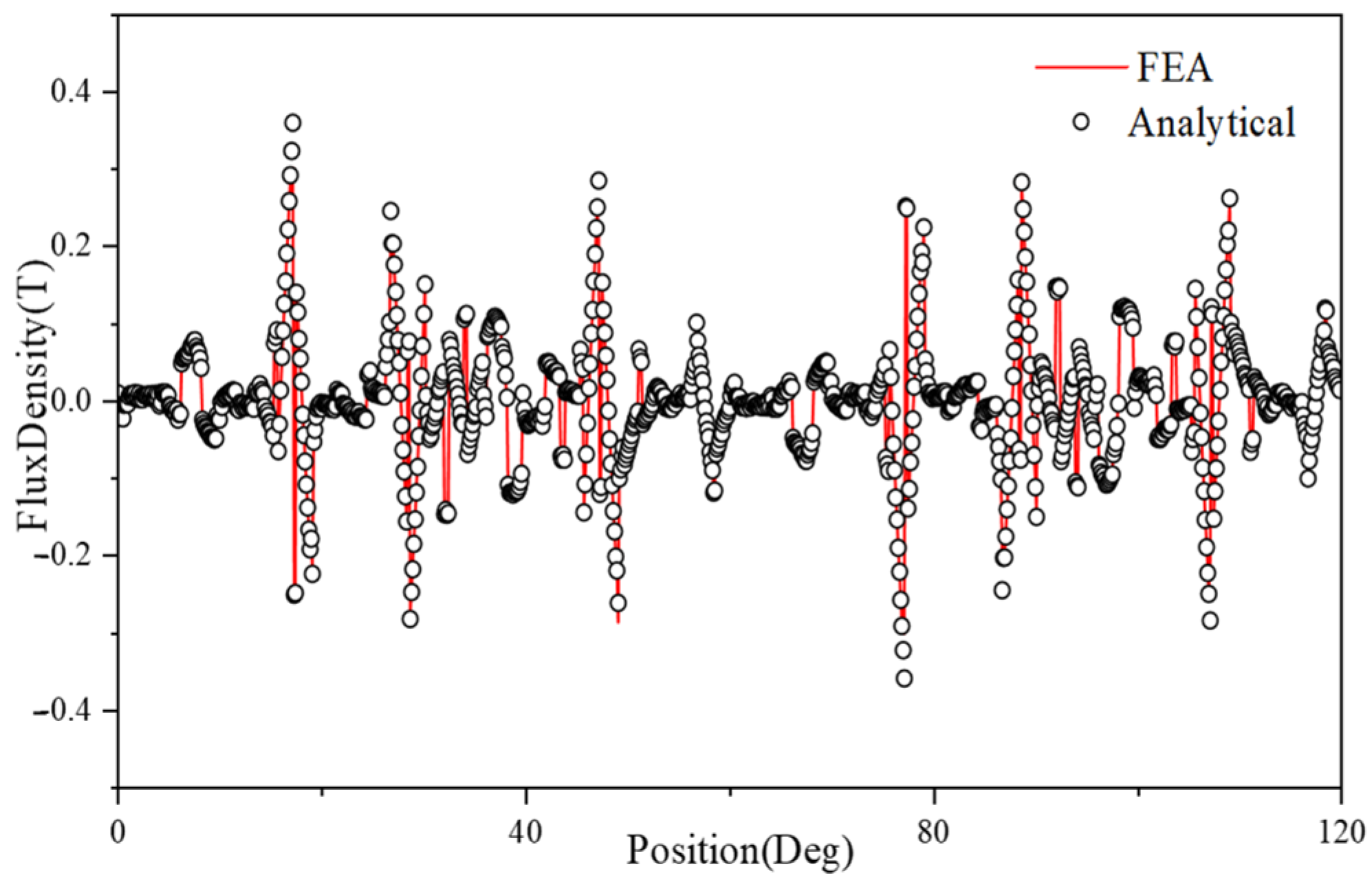
4.1. Air-Gap Flux Density
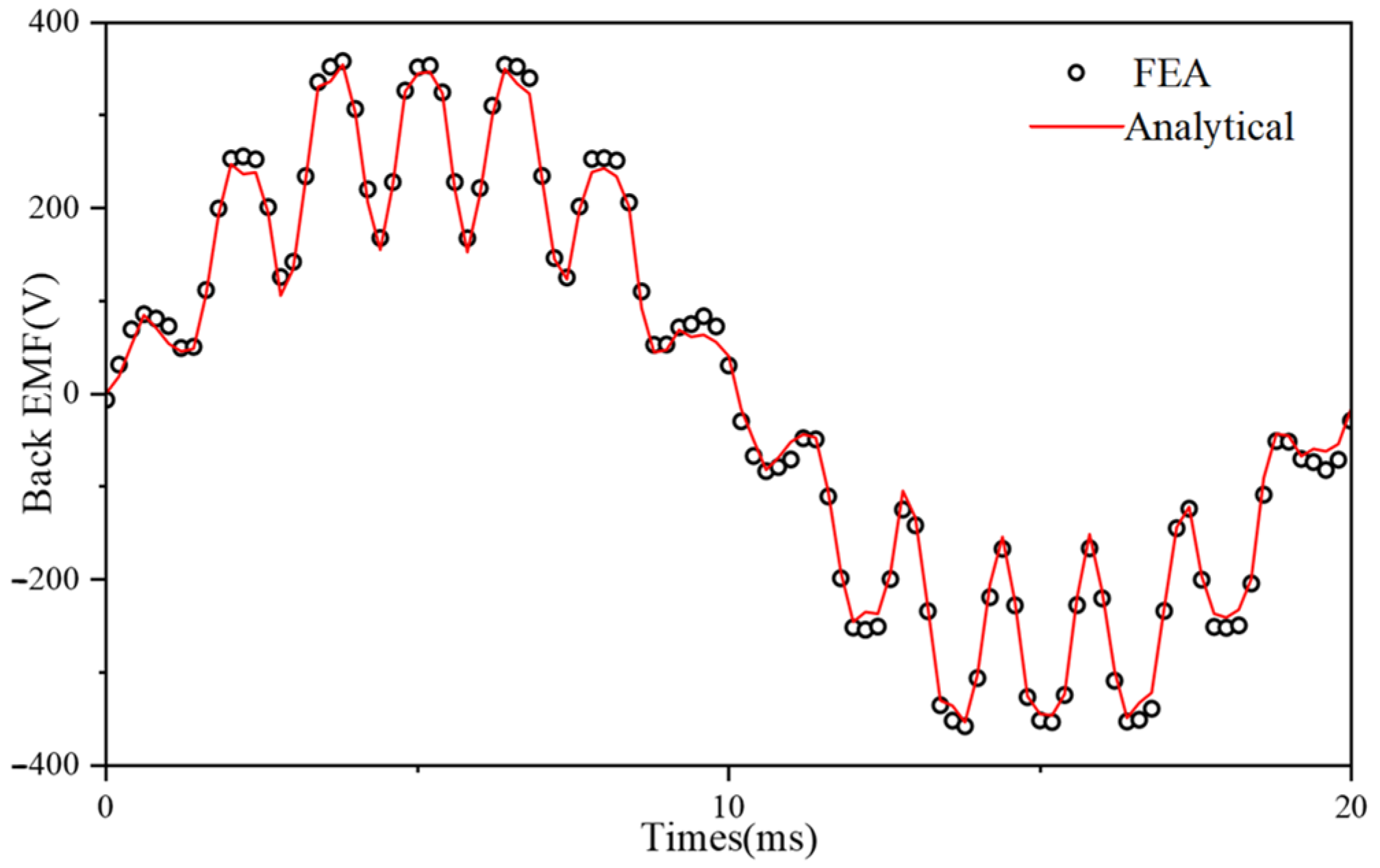
4.2. Flux Linkage and Back EMF
4.3. Computational Time
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Palangar, M.F.; Soong, W.L.; Bianchi, N.; Wang, R.-J. Design and Optimization Techniques in Performance Improvement of Line-Start Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, W.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Tao, W. Research on the Bearingless Brushless DC Motor Structure with Like-Tangential Parallel-Magnetization Interpolar Magnetic Poles and Its Air-Gap Magnetic Field Analytical Calculation. Actuators 2025, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhao, P.; Goh, H.; Carbone, G.; Niu, S.; Ding, J.; Shu, S.; Zhao, Z. An Efficient and High-Precision Electromagnetic–Thermal Bidirectional Coupling Reduced-Order Solution Model for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. Actuators 2023, 12, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, B.; Xu, H.; Liu, B.; Dai, M.; Zhu, C.; Li, S. Novel Magnetic Circuit Topology of Linear Force Motor for High Energy Utilization of Permanent Magnet: Analytical Modelling and Experiment. Actuators 2021, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Wang, D.; Yu, Z.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, Y. Strength Analysis and Design of a Multi-Bridge V-Shaped Rotor for High-Speed Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. Actuators 2025, 14, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jigyasu, R.; Shrivastava, V.; Singh, S. Deep optimal feature extraction and selection-based motor fault diagnosis using vibration. Electr. Eng. 2024, 106, 6339–6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Ma, T. Analytical Model for Evaluating Unbalanced Electromagnetic Forces in Switched Reluctance Hub Motors Under Air-Gap Eccentricity. In Proceedings of the WCX SAE World Congress Experience, Detroit, MI, USA, 16–18 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhang, P. Analysis and Optimization Design of Moving Magnet Linear Oscillating Motors. Actuators 2025, 14, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Shi, T.; Guo, L.; Wang, H.; Xia, C. Accurate Analytical Method for Magnetic Field Calculation of Interior PM Motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Geng, W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z. 3-D Equivalent Magnetic Network Modeling and FEA Verification of a Novel Axial-Flux Hybrid-Excitation In-wheel Motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghods, M.; Faiz, J.; Gorginpour, H.; Bazrafshan, M.A.; Nøland, J.K. Equivalent Magnetic Network Modeling of Variable-Reluctance Fractional-Slot V-Shaped Vernier Permanent Magnet Machine Based on Numerical Conformal Mapping. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 9, 3880–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MGhods, M.; Gorginpour, H.; Faiz, J.; Bazrafshan, M.A.; Toulabi, M.S. Design and Enhanced Equivalent Magnetic Network Modeling of a Fractional-Slot Spoke-Array Vernier PM Machine with Rotor Flux Barriers. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers 2022, 38, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Ma, C.; Zhang, N.; Guo, Y.; Degano, M.; Gerada, C.; Bu, F.; Yin, X.; Li, Q.; Zhou, S. Calculation Model of Armature Reaction Magnetic Field of Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Segmented Skewed Poles. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers 2022, 37, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ni, R.; Zhu, W.; Liu, Y. Modified Approach to Inductance Calculation of Variable Reluctance Resolver Based on Segmented Winding Function Method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 5900–5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D.; Bolte, E.; Ackermann, B. Instantaneous Magnetic Field Distribution in Brushless Permanent Magnet DC motors. I. Open-circuit Field. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1993, 29, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdinjak, M.; Miljavec, D. Analytical Calculation of the Magnetic Field Distribution in Slotless Brushless Machines with U-Shaped Interior Permanent Magnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2020, 67, 6721–6731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, D. Magnetic Field Prediction for Line-Start Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor via Incorporating Geometry Approximation and Finite Difference Method into Subdomain Model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 2843–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Wei, H.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, X. Prediction of Electromagnetic Performance for IPMSM Based on Improved Analytical Model Considering Saturation Effects. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 1128–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahfarokhi, M.M.; Faradonbeh, V.Z.; Amiri, E.; Bafrouei, S.M.M.; Aliabad, A.D.; Boroujeni, S.T. Computationally Efficient Analytical Model of Interior Permanent Magnet Machines Considering Stator Slotting Effects. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 4587–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Chai, F.; Yu, Y.; Chen, L. Analytical Model of a Spoke-Type Permanent Magnet Synchronous In-Wheel Motor With Trapezoid Magnet Accounting for Tooth Saturation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Sun, Y. A Novel Analytical Model for On-Load Performance Prediction of Delta-Type IPM Motors Based on Rotor Simplification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 71, 6841–6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tong, W.; Hou, M.; Wu, S.; Tang, R. Analytical Model for No-Load Electromagnetic Performance Prediction of V-Shape IPM Motors considering Nonlinearity of Magnetic Bridges. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 37, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


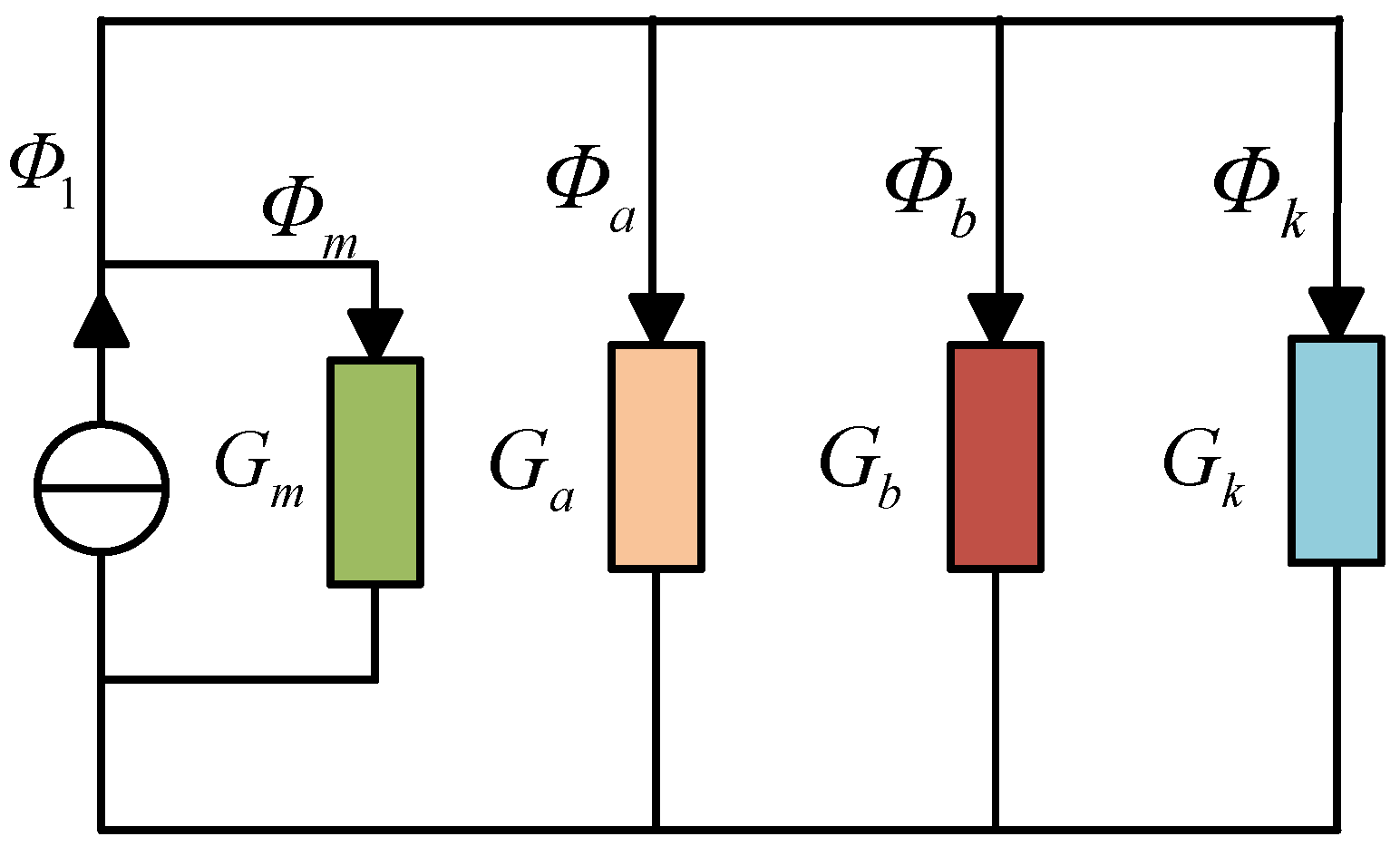





| Advantages | Shortcomings | |
|---|---|---|
| FEA | High calculation accuracy | Calculates long-time consumption, not easy to parameterize. |
| MEC | Calculates the saturation effects of each part of the iron core accurately | The calculation accuracy depends on the number of magnetic resistance divisions, the difficulty of dynamic magnetic field calculation, and the difficulty of dynamic magnetic field calculation. |
| Sub + MEC | High calculation accuracy, considers the influence of slotting and core saturation simultaneously | The applicability of the model is average. |
| Parameter | Symbol | Value (Unit) |
|---|---|---|
| Number of pole pairs | p | 3 (/) |
| Number of stator slots | Ns | 36 (/) |
| Number of rotor slots | Nr | 42 (/) |
| Inner radius of stator | RS | 147 (mm) |
| Outer radius of rotor | Rr | 148 (mm) |
| Outer diameter of stator slot | R7 | 149 (mm) |
| Inner diameter of stator slot | R6 | 184 (mm) |
| Inner diameter of cage slot | R4 | 134 (mm) |
| Width of magnet | l5 | 22.5 (mm) |
| Thickness of the magnet | l4 | 6 (mm) |
| permeance of air | 4π × 10−7 (H/m) | |
| Axial length | L | 110 (mm) |
| Span angle of the magnet | 0.73 (rad) | |
| Length of the air gap at the outer edge of the magnet | l1 | 4 (mm) |
| Length of the air gap at the inner edge of the magnet | l3 | 1.5 (mm) |
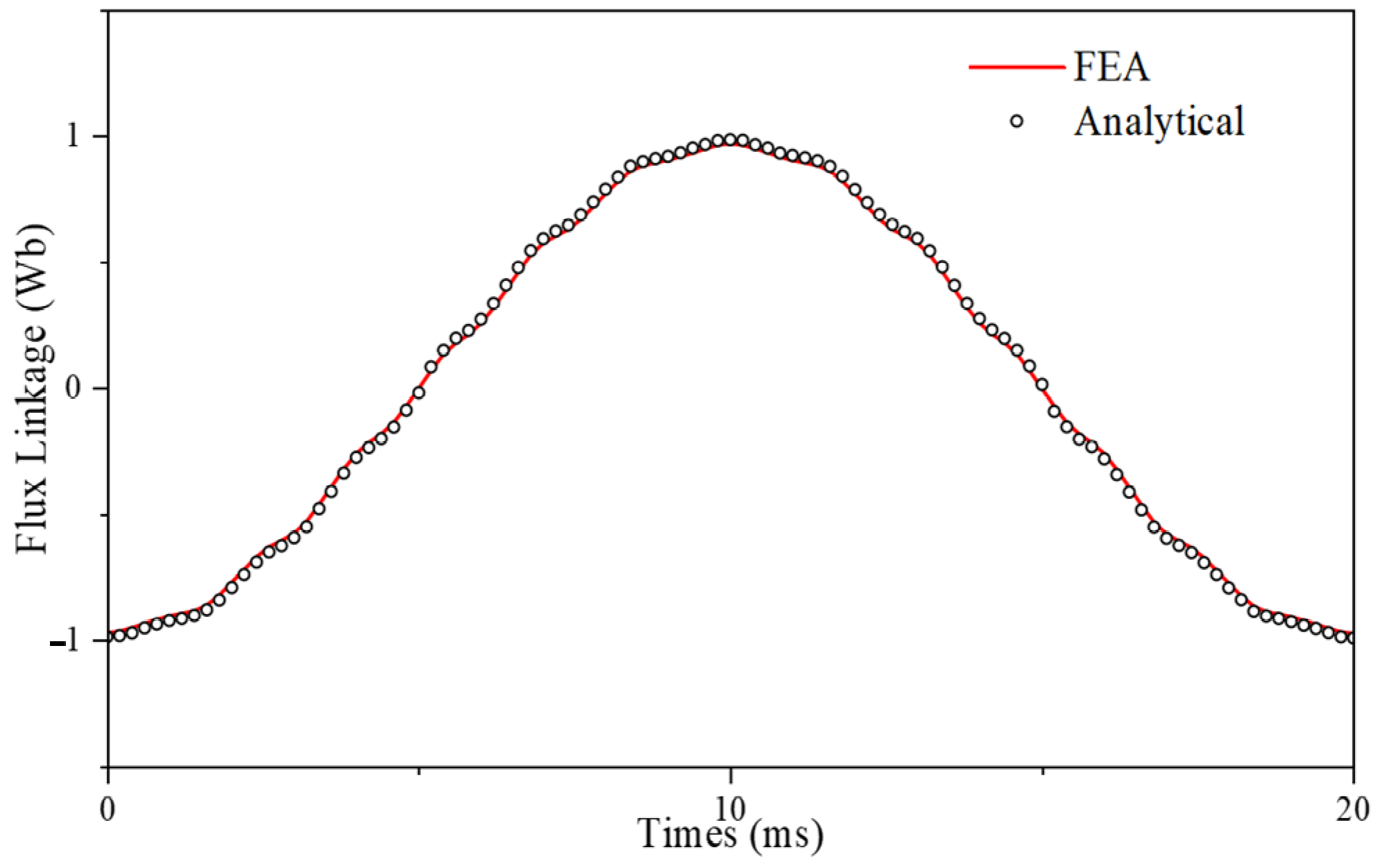
| Item | FEA | Analytical | Errors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flux Linkage (Wb) | 0.97 | 0.98 | 1% |
| Back EMF (V) | 353 | 357 | 1.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Shi, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M. Magnetic Field Analytical Calculation of No-Load Electromagnetic Performance of Line-Start Explosion-Proof Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Considering Saturation Effect. Actuators 2025, 14, 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14060294
Liu J, Shi Y, Zheng Y, Wang M. Magnetic Field Analytical Calculation of No-Load Electromagnetic Performance of Line-Start Explosion-Proof Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Considering Saturation Effect. Actuators. 2025; 14(6):294. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14060294
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jinhui, Yunbo Shi, Yang Zheng, and Minghui Wang. 2025. "Magnetic Field Analytical Calculation of No-Load Electromagnetic Performance of Line-Start Explosion-Proof Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Considering Saturation Effect" Actuators 14, no. 6: 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14060294
APA StyleLiu, J., Shi, Y., Zheng, Y., & Wang, M. (2025). Magnetic Field Analytical Calculation of No-Load Electromagnetic Performance of Line-Start Explosion-Proof Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Considering Saturation Effect. Actuators, 14(6), 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14060294






