Abstract
This study implemented an innovative system that trains a speech recognition model based on the DeepSpeech2 architecture using Python for voice control of a robot on the LabVIEW platform. First, a speech recognition model based on the DeepSpeech2 architecture was trained using a large speech dataset, enabling it to accurately transcribe voice commands. Then, this model was integrated with the LabVIEW graphical user interface and the myRIO controller. By leveraging LabVIEW’s graphical programming environment, the system processed voice commands, translated them into control signals, and directed the robot’s movements accordingly. Experimental results demonstrate that the system not only accurately recognizes various voice commands, but also controls the robot’s behavior in real time, showing high practicality and reliability. This study addresses the limitations inherent in conventional voice control methods, demonstrates the potential of integrating deep learning technology with industrial control platforms, and presents a novel approach for robotic voice control.
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Motivation
With the rapid advancement of technology, voice recognition systems and remote control technologies have shown significant potential in various fields, including smart homes, autonomous driving, and medical robotics. Voice recognition technology allows for more natural and intuitive human–machine interactions, while mobile control systems enhance the autonomy and flexibility of robots. The combination of these two technologies creates opportunities for more efficient and intelligent systems, addressing the growing demand for smart living environments.
Despite the advancements, current voice control systems predominantly rely on proprietary software and hardware, leading to high costs and limited flexibility in customization and development. This creates a significant barrier for broader adoption and innovation. LabVIEW, a powerful graphical programming tool, stands out as an ideal solution. It offers ease of learning, rich hardware integration, and extensive control capabilities. By leveraging LabVIEW in combination with voice recognition technology, this research aims to develop a low-cost, highly flexible mobile control system with extensive applications.
1.2. Research Background
1.2.1. Voice Recognition Technology
Voice recognition technology converts human speech into corresponding text or commands. In recent years, advancements in deep learning and big data technologies have significantly improved the accuracy and responsiveness of voice recognition systems. Widely used voice assistants like Google Speech-to-Text, Amazon Alexa, and Apple Siri have become integral to daily life, and their applications are expanding into smart homes, automotive systems, and mobile devices, reflecting the growing prominence of voice recognition across various sectors.
1.2.2. Mobile Control Systems
Mobile control systems represent a key area within robotics, involving the precise control of robotic movements, including path planning, obstacle avoidance, and position and posture control. With ongoing advancements in sensor technology and control algorithms, modern mobile control systems can achieve a high degree of autonomy and precision, making them essential in applications such as autonomous vehicles and logistics robots.
1.2.3. LabVIEW
LabVIEW 2018 (64-bit) (Laboratory Virtual Instrument Engineering Workbench), developed by National Instruments (NI), is a graphical programming language and integrated development environment (IDE) tailored for engineering and scientific applications. LabVIEW’s distinctive feature lies in its use of the “Virtual Instrument” (VI) concept, which simplifies complex tasks such as data acquisition, instrument control, and automated testing through a graphical interface. This user-friendly programming method lowers the development barrier, enabling users without extensive programming experience to quickly create powerful applications.
LabVIEW supports integration with a wide range of hardware, including data acquisition cards, sensors, and robotics. It offers comprehensive libraries that cover signal processing, data analysis, and control system design, making it a widely adopted tool in industries such as industrial automation, medical devices, and scientific research. LabVIEW’s ability to build stable and efficient systems quickly makes it invaluable in these fields [1].
1.3. Research Objectives
The primary objective of this study was to explore the design and implementation of a mobile control system that integrates LabVIEW with voice recognition technology. By conducting experiments, this research sought to evaluate the feasibility, advantages, and limitations of the proposed system, with the aim of providing valuable insights for further development in areas such as smart homes, medical robotics, and autonomous driving. The specific research objectives are as follows:
- (a)
- To develop an AI model for voice recognition and optimize its speed and accuracy;
- (b)
- To design a robotic mobile mechanism and control program;
- (c)
- To integrate the voice recognition model with the robotic control system;
- (d)
- To test and evaluate the results, identifying strengths, weaknesses, and potential improvements.
1.4. Research Methods and Procedures
This research followed the methodology and steps outlined in Figure 1. First, existing voice recognition technologies and related literature were reviewed to establish the focus of the study. A new voice recognition model was then designed and trained using deep learning algorithms, followed by extensive testing to validate its performance. In the mobile control section, LabVIEW was employed for programming, with NI myRIO-1900 controllers (National Instruments, Austin, TX, USA) connected via WIFI to achieve mobile control. Finally, the voice recognition model was integrated with LabVIEW, and the system’s performance was measured through a human–machine interface. The results, including robot movement, voice recognition accuracy, and task completion rates, were analyzed. Based on these findings, suggestions for improvement and directions for future research are proposed.
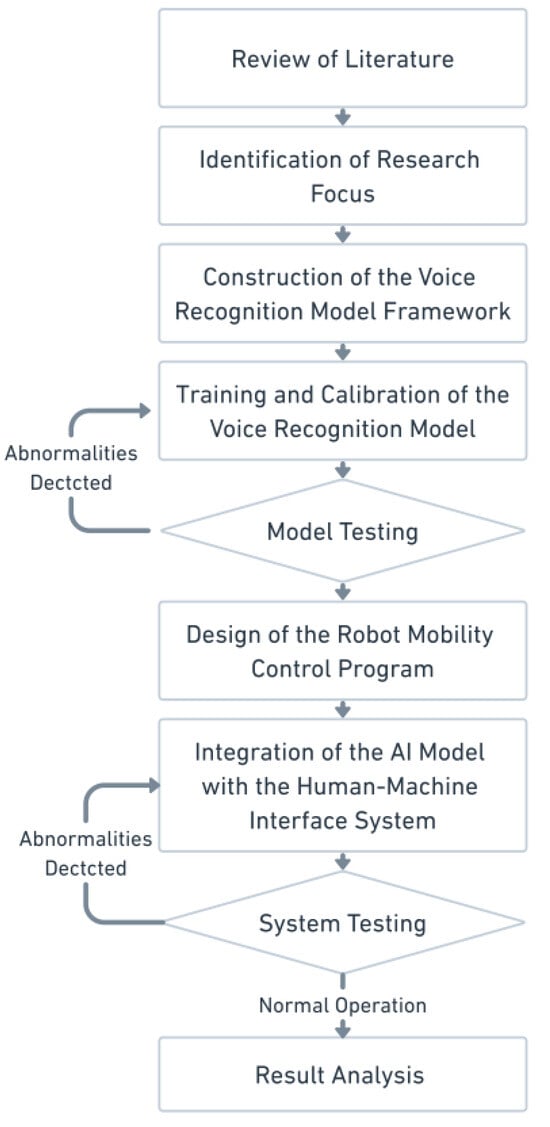
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the research steps.
2. Literature Review
Voice recognition technology is a critical research direction in the fields of artificial intelligence and language processing, aiming to convert human speech signals into readable text. Since its inception in the mid-20th century, this technology has significantly improved in terms of accuracy and practicality, particularly with advancements in computing power and the application of deep learning techniques.
2.1. Development of Voice Recognition Technology
2.1.1. Early Research and Techniques
Voice recognition technology initially developed from template-matching methods and gradually transitioned to statistical methods based on Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) [2,3]. In 1976, Jelinek et al. proposed a continuous speech recognition method using statistical techniques, employing HMMs to model the statistical properties of speech [4]. HMM is a tool capable of handling the data sequences of varying lengths, where hidden “states” are used to understand temporal relationships in the data. Each state follows a rule to generate or analyze sequences, allowing HMMs to process sequences of various lengths based on these hidden states and rules.
Subsequently, Bahl et al. introduced a continuous speech recognition method based on Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE), which improved recognition accuracy by maximizing the probability of observed data to estimate model parameters [5]. Early systems also employed Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) algorithms to effectively align and recognize speech signals of varying lengths [6,7,8].
2.1.2. The Era of Machine Learning
In the 21st century, machine learning techniques such as Support Vector Machines (SVMs) and Gaussian Mixture Models (GMMs) were applied to voice recognition [9,10,11]. These methods achieved some success in processing complex speech signals, but they also had limitations, particularly in handling large-scale data and variable-length sequences [12,13,14,15].
2.2. Applications of Deep Learning in Voice Recognition
2.2.1. Deep Neural Networks (DNNs)
In 2012, Hinton et al. introduced the Deep Neural Networks (DNN) approach, ushering in a new era for voice recognition technology [16]. Their paper demonstrated the superior performance of DNNs in acoustic modeling, particularly in handling complex speech data, which significantly improved the accuracy of voice recognition.
2.2.2. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), which have achieved remarkable success in image processing, were subsequently applied to voice recognition [17,18]. CNNs demonstrated their ability to effectively capture spatial features when processing spectrograms, showing an advantage in feature extraction for voice recognition tasks [16,19].
2.2.3. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are particularly well-suited for processing time-series data due to their ability to handle dependencies across sequences. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) improves upon traditional RNNs by addressing the issue of long-term dependencies, capturing more contextual information from speech sequences and thus improving recognition accuracy [20,21,22,23]. In 2013, Graves et al. proposed a multi-layer RNN architecture based on LSTM units, which overcame the gradient vanishing problem associated with traditional RNNs when processing long-term dependencies. Their study showed that the use of LSTM combined with the Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) loss function significantly outperformed traditional models like HMM-GMM in speech recognition tasks [24].
2.3. Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC)
2.3.1. Basic Principles
The Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) loss function was introduced by Graves et al. to solve sequence labeling problems, especially when the input and output sequence lengths do not match (see Figure 2) [24]. CTC allows RNNs to handle variable–length sequences without the need for prior segmentation or alignment of the input. By introducing a “blank” label, CTC enables the insertion of an arbitrary number of blanks between input and output sequences, thus achieving alignment.
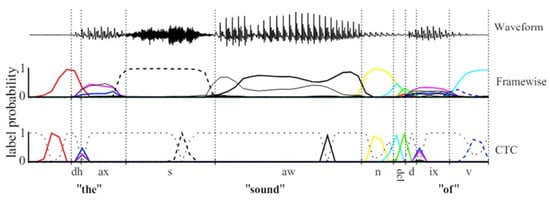
Figure 2.
Frame-by-frame network and CTC network for classifying speech signals.
Through CTC (Connectionist Temporal Classification), each frame in a time series of speech can be automatically aligned with the transcribed text sequence, eliminating the need to explicitly annotate the start and end times of each word or phoneme. This enables the model to classify the speech signal directly on the time series, thereby simplifying the complex alignment steps required in traditional speech recognition systems.
2.3.2. Loss Calculation
CTC uses Dynamic Programming (DP) to compute the probability of all possible alignment paths. Given an input sequence X and a target sequence Y, each path represents a possible alignment between the input and output sequences.
The CTC loss is calculated by summing the probabilities of all alignment paths. The overall loss is expressed by the following formula:
The CTC loss is defined as the negative logarithm of this probability:
In summary, CTC loss measures the model’s performance in recognizing speech sequences by computing the total probability of all possible alignment paths and taking its negative logarithm. This loss function allows the model to automatically learn how to handle variable–length sequence alignment issues and optimize itself during training to improve recognition accuracy.
2.3.3. Application Example
In speech recognition, CTC loss is often used to train models that do not require precise alignment, such as in the DeepSpeech V2 framework, further validating its effectiveness in large-scale speech recognition tasks [25,26].
2.4. The DeepSpeech2 Model
DeepSpeech2 is a speech recognition model developed using deep learning, as illustrated in Figure 3. Created by Baidu Research’s Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, this model is trained end-to-end and has demonstrated exceptional performance in multilingual speech recognition tasks. Compared to traditional speech recognition systems, DeepSpeech2 exhibits greater flexibility, accuracy, and scalability [25,27,28].
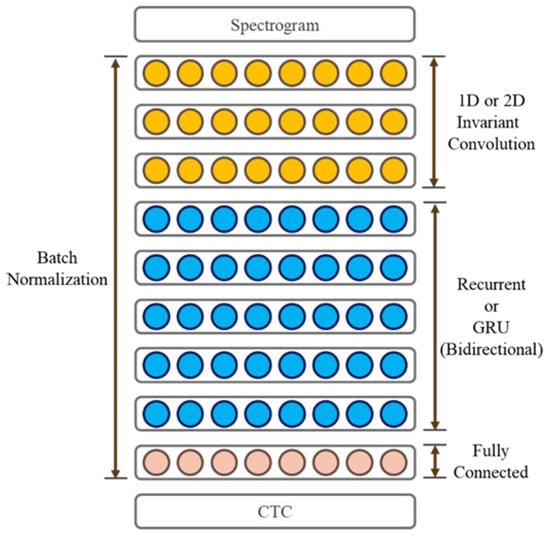
Figure 3.
DeepSpeech2 speech recognition model architecture.
3. System Architecture
This chapter is divided into three sections to describe the system’s software, hardware devices, and the architecture of the speech recognition model (Refer to Figure 4). The first section introduces the AI model training for speech recognition and the equipment used. The second section presents the robot’s mobile control devices, and the third section explains the integration of the LabVIEW-based speech recognition model with the mobile control system.
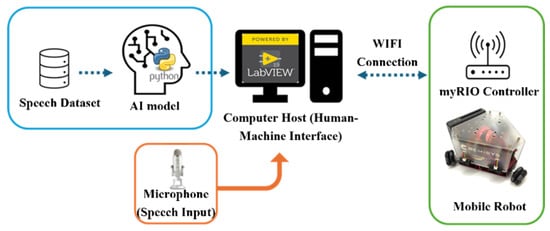
Figure 4.
Architecture of the LabVIEW-integrated speech recognition model for mobile control system.
3.1. Speech Recognition System
A speech recognition system (SRS) is a technology that converts human speech into text or commands. It is widely used in smart devices, voice assistants, and voice control systems. With the advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning, the accuracy and application range of speech recognition systems have expanded significantly. The speech recognition system developed in this study consists of several main components: speech signal input, database, data preprocessing, model training and inference, post-processing, and output. The AI model training equipment features a Windows 10 Pro 64-bit operating system, an i7-10870H processor (Intel Corporation, Santa Clara, CA, USA), 16 GB of RAM (8 GB × 2), a 500 GB SSD for storage, and utilizes Python version 3.6.
3.1.1. Front-End Processing
The primary objective of front-end processing is to enhance the quality of the speech signal, providing high-quality data for subsequent feature extraction and model training. The system captures the speech signal using a microphone, which is critical for the accuracy of the speech recognition system. The microphone’s sensitivity range and directionality directly impact recognition accuracy. The audio input device used is a Blue Yeti Microphone, operating at 5 V 150 mA, with a 48 kHz sampling rate, 16-bit bit rate, and a frequency response of 20 Hz–20 kHz. The microphone supports multiple polar patterns, and Cardioid mode was selected for this study. The maximum SPL is 120 dB (THD: 0.5% at 1 kHz).
A microphone is a device that converts sound waves into electrical signals. It is mainly composed of a diaphragm, sensor, and amplifier. Sound waves cause the diaphragm to vibrate, generating electrical signals, which can then be processed for analysis and recognition [16]. Based on their operating principles, microphones can be classified into dynamic, condenser, and electret types. Condenser microphones, known for their high sensitivity and wide frequency response, are widely used in speech recognition systems. This is one of the reasons why a condenser microphone was selected for this study.
Additionally, the microphone’s directivity affects the quality of recordings and the accuracy of subsequent processing. Depending on the directivity, microphones can optimize sound capture from specific directions or ranges, thereby improving the effectiveness of speech recognition. Below are the four types of directivity available with the microphone used in this study, with the polar pattern diagrams illustrated in Figure 5:
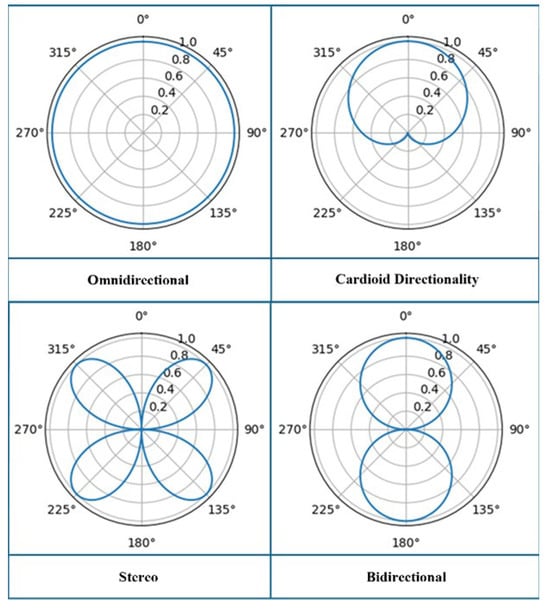
Figure 5.
Microphone polar patterns.
- (a)
- Omnidirectional
An omnidirectional microphone has equal sensitivity in all directions, capturing all sound signals from the surrounding environment. It is suitable for situations requiring broad sound capture, such as conference recordings and outdoor recordings. However, it is susceptible to noise and environmental interference.
- (b)
- Cardioid Directionality
A cardioid microphone has a directional sensitivity focused on one side, primarily capturing sound from the front while reducing noise from the rear and sides. It is ideal for high-quality recordings in studios and auditoriums, where minimal background noise is required.
- (c)
- Bidirectional
Bidirectional microphones are sensitive to sounds from the front and rear, making them suitable for recording conversations in face-to-face interviews. However, if the sound sources are too close, distortion, such as popping sounds, can occur.
- (d)
- Stereo
Stereo microphones are designed to capture spatial information about sound, providing a more realistic and natural auditory experience that mimics human hearing.
3.1.2. Speech Databases
As speech recognition technology rapidly advances, high-quality, large-scale speech datasets have become essential for training and evaluating models. The LibriSpeech dataset was created in this context to provide a valuable resource for the research community. Released by Vassil Panayotov et al. in 2015, the dataset includes approximately 1000 h of English speech recordings sourced from public domain audiobooks on LibriVox website version [17]. The dataset is divided based on recording quality and background noise levels, including high-quality “clean” datasets and noisier “other” datasets. These are further divided into training, validation, and testing subsets, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Composition of the LibriSpeech dataset.
The LibriSpeech dataset offers a diverse and challenging speech data resource to meet the demands of different speech recognition tasks. Its high-quality recordings and strict data curation standards make it a popular choice for training deep learning models and serve as one of the standard datasets for speech recognition research. Below are the key features and contents of the LibriSpeech dataset:
- (a)
- Text Annotations: Each audio file is accompanied by corresponding text annotations, which include the transcribed text of the audiobook passages;
- (b)
- Audio Format: All audio files are 16 kHz mono WAV files;
- (c)
- Speaker Diversity: The dataset includes recordings from multiple speakers, with varying backgrounds and accents, helping to train models with better generalization capabilities.
3.1.3. Data Preprocessing
Before training the model, the speech signals need to be preprocessed for use in model training and evaluation. The preprocessing steps include converting audio into a Mel spectrogram, applying masking techniques to enhance the model’s generalization capability, converting text into integer sequences, and padding sequences for batch processing. The following outlines the process in detail:
- (a)
- Audio Processing:
Convert waveforms into feature representations (Mel spectrogram and masking);
Compress and transpose the Mel spectrogram to fit the model input format.
- (b)
- Text Processing:
Convert text sequences into integer sequences and vice versa;
Compute the lengths of input spectrograms and labels for CTC loss calculation.
- (c)
- Sequence Padding:
Pad all spectrograms to the same length to create a batch input;
Similarly, pad label sequences to the same length;
These steps ensure the model can effectively learn and process the speech data.
3.1.4. Model Training and Inference
The speech recognition model in this study is trained based on the DeepSpeech2 architecture. Below is a detailed description of its design:
- (a)
- Convolutional Layer (CNN): Responsible for capturing local features of the audio signal and reducing data size to decrease the computational burden of subsequent layers.
- (b)
- Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): These layers handle “memory and comprehension” and use Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs) to capture long-term dependencies and contextual information in speech, enabling the model to understand the meaning of entire sentences.
- (c)
- Fully Connected Layer (FC): Transforms the RNN output into a probability distribution for each character, essentially translating the speech signal into text.
- (d)
- CTC Loss Function: This function allows the model to learn how to align audio and text sequences. Even if their lengths are not the same, the model can directly learn from unaligned audio-text pairs.
- (e)
- Learning Rate: The learning rate is dynamically adjusted using the OneCycleLR scheduler in PyTorch v2.2.0. This scheduler gradually increases the learning rate to a maximum value and then decreases it to a very low value (Refer to Figure 6). This strategy helps the model quickly explore the parameter space while stabilizing at a good solution in the later stages, accelerating convergence and improving final model performance.
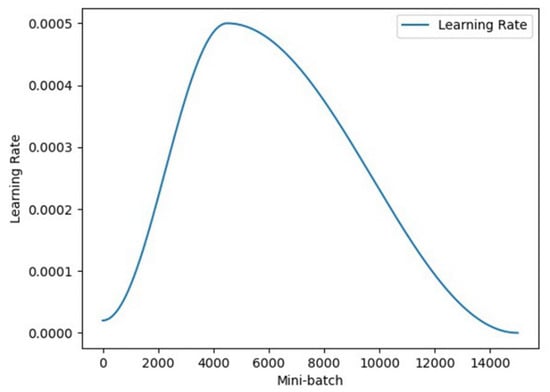 Figure 6. Speech recognition model learning rate curve.
Figure 6. Speech recognition model learning rate curve.
3.1.5. Post-Processing and Output
- (a)
- Post-processing
In the speech recognition system developed in this study, the model’s output undergoes further processing to improve readability and accuracy. The steps are as follows:
- Decoding: Greedy decoding is used to convert the probability distribution output by the model into the most likely character sequence. Greedy decoding selects the most probable character at each time step, quickly generating the most likely character sequence.
- Evaluation Metrics: Word Error Rate (WER) is used to evaluate model performance. This metric measures the difference between the model output and the ground truth label.
WER is calculated using the formula
S (Substitutions) refers to the number of words in the hypothesis (model output) that are incorrectly transcribed compared to the reference (ground truth). D (Deletions) represents the number of words that are present in the reference but missing in the hypothesis. I (Insertions) indicates the number of extra words in the hypothesis that do not appear in the reference. N is the total number of words in the reference transcription. A lower WER value indicates better performance of the speech recognition system.
In addition to WER, this study evaluates the model using word-level accuracy metrics, including precision, recall, and the F1 score. Precision is defined as the number of correctly recognized words divided by the total number of words predicted by the model (Precision = True Positives/(True Positives + False Positives)). Recall is the number of correctly recognized words divided by the total number of words in the ground truth (Recall = True Positives/(True Positives + False Negatives)). The F1 score, which is the harmonic mean of precision and recall, is calculated as F1 = 2 × (Precision × Recall)/(Precision + Recall). Higher values of these metrics reflect better model performance. The performance of the speech recognition model was tested across five different acoustic scenarios: quiet environment, indoor background noise, outdoor noise, multi-speaker background, and mechanical noise interference (see Table 2).

Table 2.
Motor driver pin configuration.
The speech recognition model demonstrates high effectiveness in quiet environments, with performance gradually degrading in noisier or more complex acoustic scenarios. Despite reduced recall and F1 scores in adverse conditions, the model still maintains relatively high precision, indicating its potential reliability. These findings underscore the importance of incorporating noise reduction preprocessing for improved performance in real-world applications.
- (b)
- Result Output
The program outputs include the model’s training and evaluation results. Figure 7 shows the loss value curve during each training and testing epoch, while Figure 8 shows the word error rate (WER) curve.
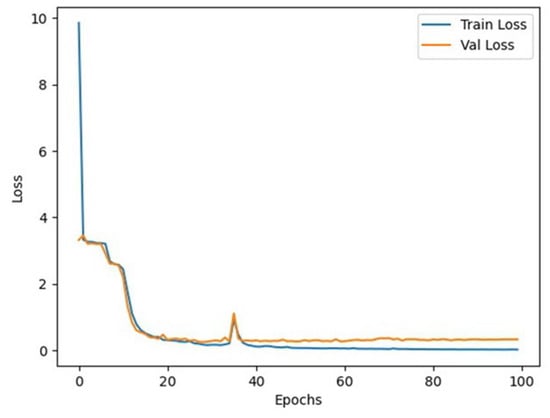
Figure 7.
Model loss curve.
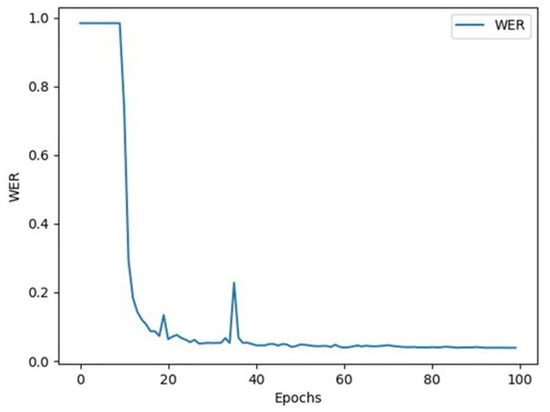
Figure 8.
Word error rate (WER) curve.
3.2. Mobile Control Robot
The physical structure and design of the mobile robot are illustrated in Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11. This study utilized LabVIEW, connected via Wi-Fi, to remotely control the robot. The equipment and control programs used will be explained in sequence in this section.

Figure 9.
Front view of the mobile control robot integrated with the LabVIEW speech recognition model.

Figure 10.
Right-side view of the mobile control robot integrated with the LabVIEW speech recognition model.
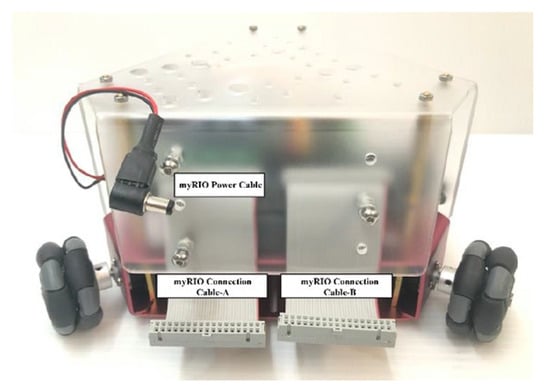
Figure 11.
Rear view of a motion-controlled robot with an integrated LabVIEW speech recognition model.
3.2.1. Mobile Robot Hardware Architecture
The mobile robot in this study uses the NI myRIO-1900 (National Instruments) controller from National Instruments (NI) as the main controller, as shown in Figure 12. Through a Wi-Fi connection and with the use of sensors and motors, it executes remote control commands from the monitoring system.
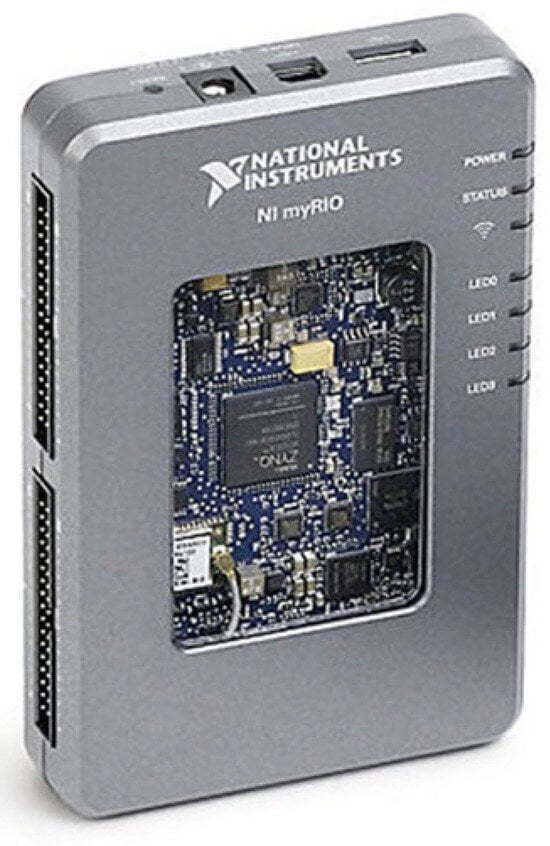

Figure 12.
NI myRIO-1900 controller.
The NI myRIO-1900 is equipped with an Xilinx Z-7010 FPGA (Xilinx, San Jose, CA, USA) and a 667 MHz ARM Cortex-A9 processor (AMD, Santa Clara, CA, USA), making it highly efficient in performing complex calculations and data processing, capable of handling a variety of embedded applications. In terms of I/O interfaces, the myRIO-1900 provides 10 analog inputs, 6 analog outputs, and 40 digital I/Os. It also supports pulse–width modulation (PWM) output and includes interfaces such as I2C, SPI, and UART, facilitating communication with various sensors and peripherals.
The myRIO-1900 also includes 256 MB of DDR3 RAM and 512 MB of non-volatile memory for storing applications and data. For wireless connectivity, the myRIO-1900 supports Wi-Fi, which enables wireless data transmission and remote control, enhancing its usability.
Figure 13 illustrates the arrangement and function of the components on the NI myRIO-1900. Figure 14 and Figure 15 show the main/auxiliary signal connection ports on the controller, with Figure 14 displaying areas A and B, and Figure 15 displaying area C.
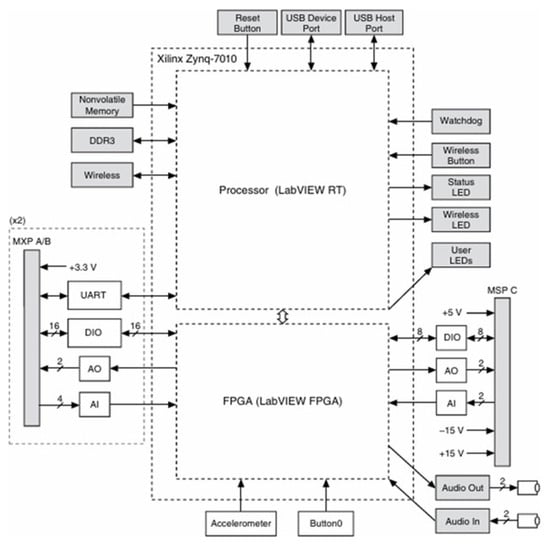
Figure 13.
NI myRIO-1900 hardware framework.
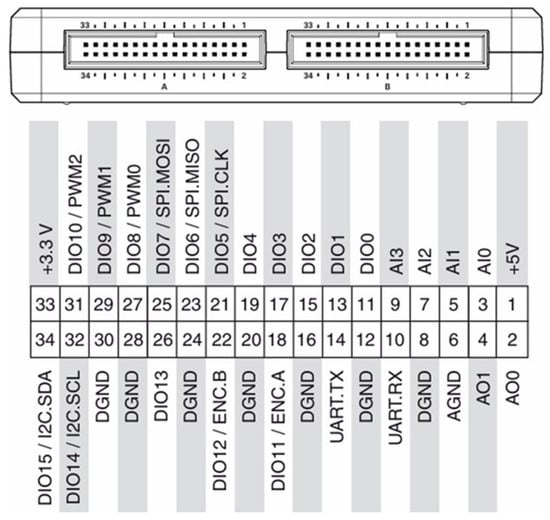
Figure 14.
Main/auxiliary signal connection ports (Areas A and B) on the NI myRIO-1900 controller.
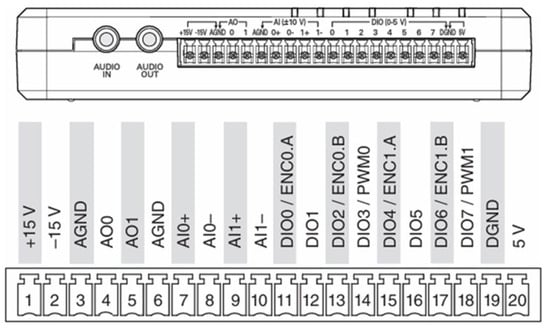
Figure 15.
Main/auxiliary signal connection ports (Area C) on the NI myRIO-1900 controller.
In this study, the main controller of the NI myRIO-1900 had to be connected via cables A and B, as shown in Figure 11. Once connected, it linked to the robot’s control board, as illustrated in the pin configuration diagram Figure 16. The front of the robot chassis was equipped with two infrared distance sensors, which used two analog inputs, as shown in the pin configuration diagram Figure 17 and Table 3. Three servo motors were controlled by PWM, DIR, and ENA pins, as indicated in Figure 18 and Table 4.
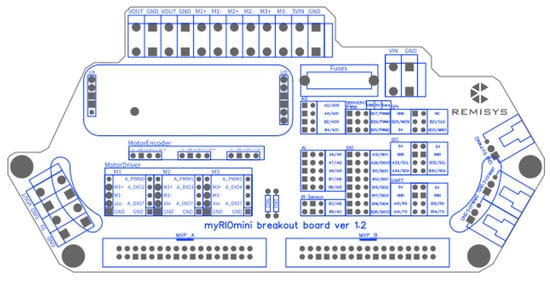
Figure 16.
myRIO robot motherboard pin configuration.
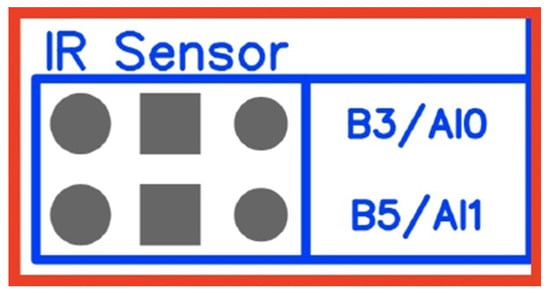
Figure 17.
Infrared distance sensor pin configuration.

Table 3.
Analog input pins for the infrared distance sensors.
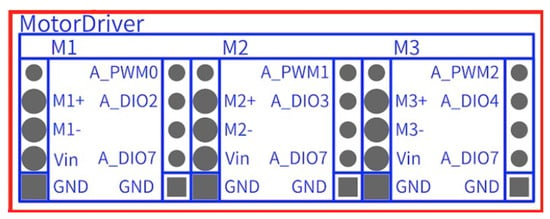
Figure 18.
Motor driver pin configuration.

Table 4.
Motor driver pin configuration.
3.2.2. Mobile Robot Control Program
The mobile robot control program was developed using LabVIEW’s graphical programming interface. Below are the steps and key components of the control program.
- (a)
- Setting up the LabVIEW Environment
First, ensure that LabVIEW and the associated myRIO toolkit are installed. To wirelessly connect the myRIO controller, ensure it is connected to the same Wi-Fi network or use a data transmission cable. A successful connection will result in a pop-up window as shown in Figure 19.
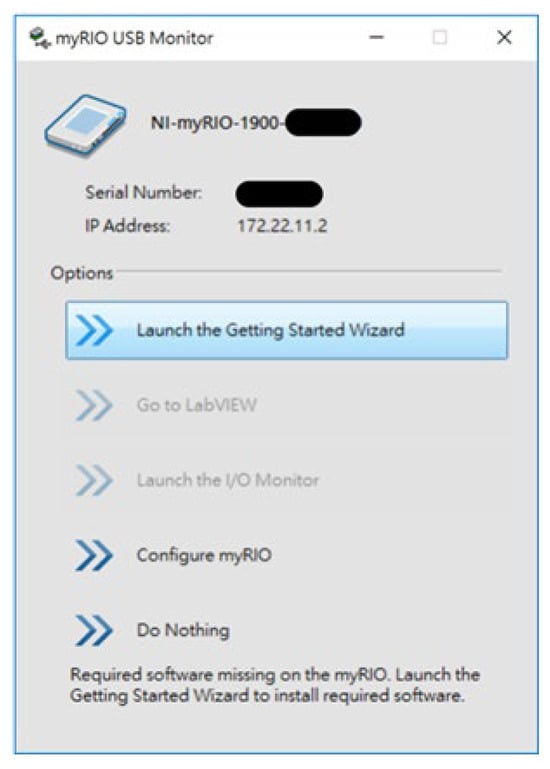
Figure 19.
myRIO controller connection window.
- (b)
- Movement Program
The movement program processes input messages by dividing them into three parts: the received movement command, its value, and the unit. The first step in the speech control program developed for this study is to create a speech-to-value matrix, as shown in Figure 20. Speech commands are converted into corresponding matrix values, which are then managed and executed using LabVIEW’s queue program block. The queue effectively and quickly handles a series of control commands, especially those that need to be executed in a specific sequence.
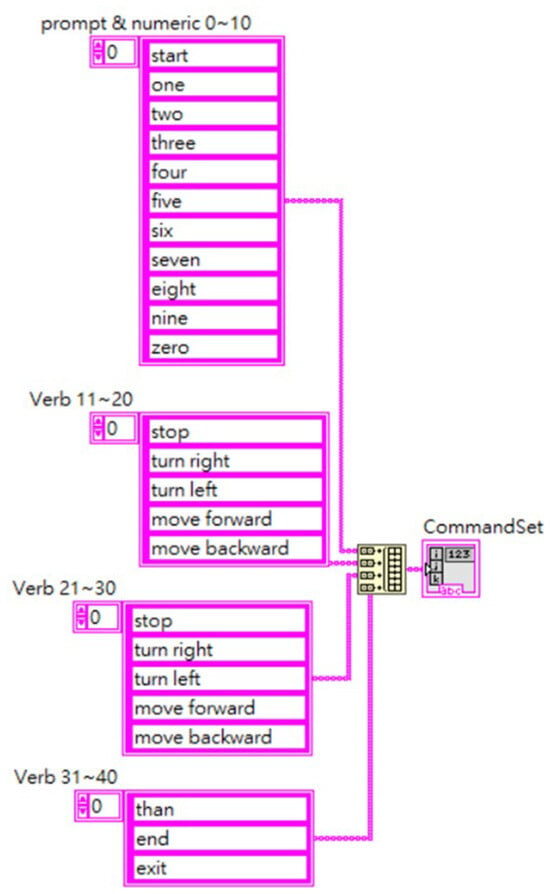
Figure 20.
Speech-to-value matrix.
The queue operation flow is shown in Figure 21. Commands, values, and units are sequentially stored in the queue. If an error in order or command occurs, the queue is cleared. Once the queue receives the complete command, it sends it to the motor for execution, as shown in Figure 22 and Figure 23.
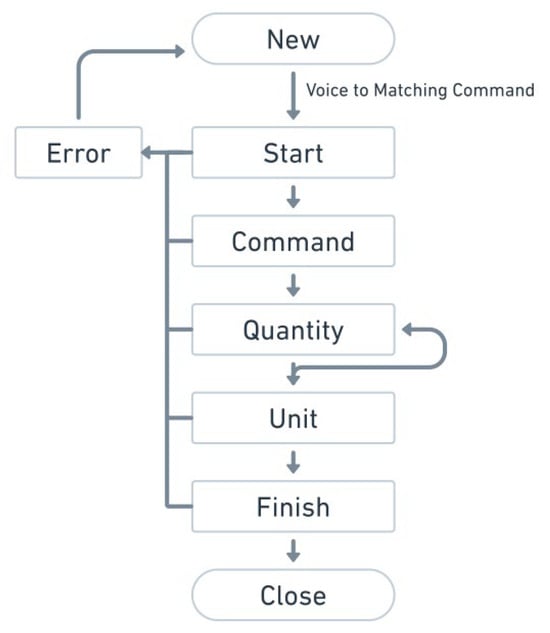
Figure 21.
Queue operation flowchart.
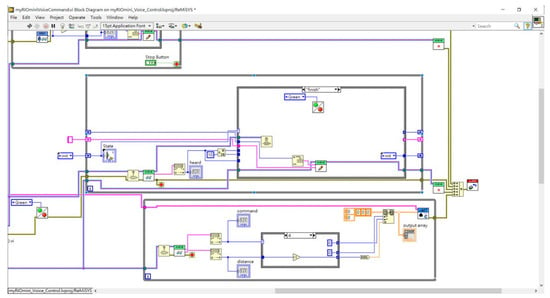
Figure 22.
Queue program block command completion output.
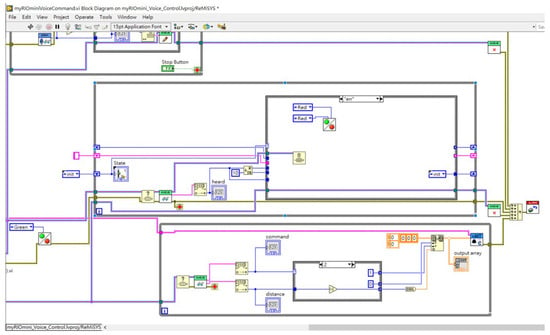
Figure 23.
Queue program block error handling and clearing.
3.3. LabVIEW-Based Integration of the Speech Recognition Model with the Mobile Control System
The integration of LabVIEW and Python can be achieved through various methods. In this study, Python Node functionality in LabVIEW was used to initialize the Python environment and set the path for the Python speech recognition model. Figure 24 shows the three subprograms created using the Python Node after the speech recognition model was imported. These subprograms handle audio input, match the audio with the speech command list, and output the result to the robot’s control unit, displaying the outcome on the human-machine interface (HMI), as shown in Figure 25, before stopping the speech recognition process.
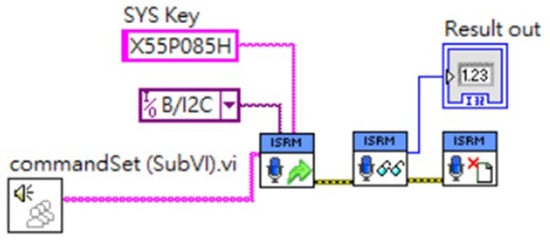
Figure 24.
Importing the speech recognition model using Python Node.
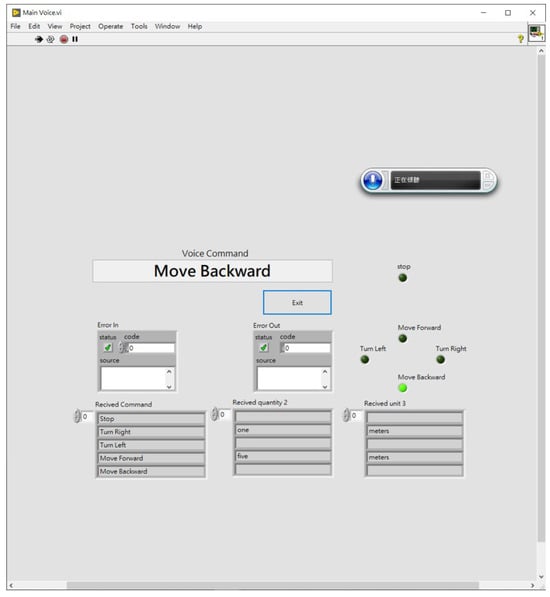
Figure 25.
HMI of the LabVIEW-integrated speech recognition model for the mobile control system.
The performance of the robot’s movement command and control is illustrated in Figure 26. Over 30 trials, the average delay from receiving a speech command to displaying the instruction on the HMI was 1.12 s, and the delay from receiving a speech command to the robot executing the movement was 3.54 s. The delay was reduced to 2.71 s when the robot was connected via a data transmission cable.
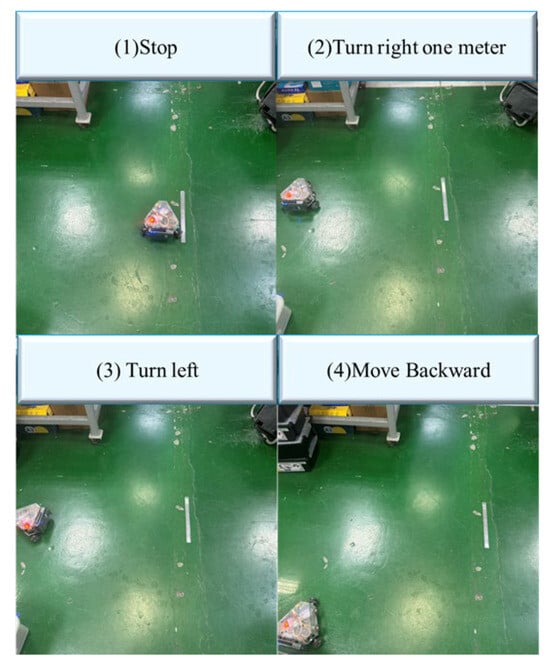
Figure 26.
Robot movement command and control operation.
4. Conclusions and Future Outlook
4.1. Conclusions
This study successfully developed a robot voice control system by integrating speech recognition technology with the LabVIEW graphical programming environment. The system consists of a DeepSpeech2-based speech recognition model, a LabVIEW graphical user interface, a myRIO-1900 controller, and a mobile robot.
The experimental results demonstrated that after training on the LibriSpeech dataset, the speech recognition model exhibited a steady decline in word error rate (WER) on the test set, confirming its accuracy in speech recognition. The adoption of the Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) loss function enabled automatic alignment between input speech sequences and output transcription sequences, thereby improving training efficiency and significantly enhancing the overall model performance.
Traditional baseline models such as GMM-HMM and hybrid HMM-DNN architectures rely on frame-level acoustic modeling and require explicit phoneme alignment, which not only complicates the system design but also limits generalization to variable acoustic environments. In contrast, the DeepSpeech2-based architecture adopts an end-to-end learning framework that directly maps audio inputs to character sequences without the need for intermediate linguistic representations, thereby streamlining the training process and improving robustness. Although Transformer-based ASR models such as Conformer and SpeechTransformer currently represent the state-of-the-art in recognition accuracy, they typically demand significantly higher computational resources and model complexity. This makes them less ideal for deployment in lightweight, real-time embedded systems. Our DeepSpeech2-based system strikes a practical balance between accuracy and computational efficiency, enabling successful integration with the myRIO platform without reliance on high-end GPUs or external cloud services.
In terms of system integration, the trained DeepSpeech2-based speech recognition model was executed externally using a Python runtime environment and connected to the LabVIEW platform through TCP/IP communication. This modular architecture allowed the deep learning model to run independently of the LabVIEW execution thread, ensuring smooth interaction between the speech recognition process and the robot control interface. Within LabVIEW, a graphical user interface was developed to visualize system status and allow for manual override. To handle multiple voice commands efficiently, the LabVIEW Queue function was employed to buffer and sequentially dispatch instructions, ensuring correct execution order and avoiding conflicts during real-time control. During actual deployment, the system demonstrated stable communication and timely command responses. Voice instructions were accurately recognized and transmitted to the myRIO controller, which, in turn, actuated the mobile robot to perform basic movements such as forward, backward, turning left, and turning right. This confirms the feasibility of integrating deep learning-based speech recognition with an embedded robotic system using the LabVIEW graphical programming environment without requiring high-performance computing resources.
This study developed an efficient, accurate, and user-friendly robotic voice control system. The proposed solution provides a feasible technical framework for designing intelligent human–machine interaction systems. These findings contribute to the advancement of voice control applications in robotics, fostering further innovation in smart automation.
4.2. Future Outlook
The present study has demonstrated the feasibility of integrating speech recognition technology with the LabVIEW graphical programming environment. For future research, improvements and expansions are recommended from both technical and user experience perspectives.
- Technical Aspects
Incorporating advanced data augmentation techniques, such as adding background noise and audio distortions, can enhance the model’s recognition accuracy and generalization capability, ensuring stable operation in diverse environments. Further optimization of communication efficiency between LabVIEW and myRIO could reduce latency in voice command transmission and execution, thereby improving the system’s real-time performance. Exploring integration possibilities with other hardware platforms and programming environments would further enhance system flexibility and applicability, allowing for adaptation to a wider range of scenarios and requirements. Additionally, expanding the system’s functionality by introducing more control features, such as adjusting the robot’s speed and executing specific tasks, would increase the practical value of voice command systems. Future applications could extend to more complex robotic control scenarios, including multi-robot collaboration and autonomous navigation in advanced use cases.
- 2.
- User Experience Aspects
Developing a more user-friendly human–machine interaction interface would simplify system operation and configuration, reducing the learning curve and improving usability. Introducing a voice feedback mechanism would enable the robot to provide real-time status updates and execution results, facilitating bidirectional communication between the system and users. This would enhance user engagement and satisfaction.
This study offers new perspectives and methodologies for achieving intelligent and cost-effective robotic control systems. Future research will continue to further advance advancements in speech recognition technology, system functionality, and user experience, promoting the widespread adoption and practical application of the system, and ultimately, voice control technology is expected to become an integral part of everyday life and work environments.
Author Contributions
K.-C.Y., W.-T.H., H.-H.H., T.-Y.C., W.-S.H., J.-S.F. and W.-L.H. contributed meaningfully to this study. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially supported by the National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan, under grant no. NSTC 112-2410-H-018-030-MY3.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from corresponding authors, Teng-Yu Chen and Wei-Sho Ho, upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
This study gratefully acknowledges the technical support provided by the Virtual Instrument Control Center and the Smart Grid Technology and Application Laboratory at the National Changhua University of Education. The authors would also like to express their sincere appreciation to Editor-in-Chief, Academic Editor, editorial staff members and the anonymous reviewers for their thorough evaluation of our manuscript and for their valuable constructive comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Hsi-Huang Hsieh was employed by the company Yaw Shuenn Industrial Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Yao, K.-C.; Huang, W.-T.; Chen, T.-Y.; Wu, C.-C.; Ho, W.-S. Establishing an Intelligent Emotion Analysis System for Long-Term Care Application Based on LabVIEW. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Guo, Z.; Zhu, D.; Yu, H. The research of application of hidden Markov model in the speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Power, Intelligent Computing and Systems (ICPICS), Shenyang, China, 29–31 July 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W. A Hidden Markov Model-Based Performance Recognition System for Marching Wind Bands. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2024, 15, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrouk, E.; Ben Ayed, Y.; Gargouri, F. Hybrid continuous speech recognition systems by HMM, MLP and SVM: A comparative study. Int. J. Speech Technol. 2014, 17, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodland, P.C.; Povey, D. Large scale discriminative training of hidden Markov models for speech recognition. Comput. Speech Lang. 2002, 16, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwana, B.K.; Frinken, V.; Uchida, S. DTW-NN: A novel neural network for time series recognition using dynamic alignment between inputs and weights. Knowl. Based Syst. 2020, 188, 104971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Abdlerazek, S.; El-Henawy, I.M. Development of smart healthcare system based on speech recognition using support vector machine and dynamic time warping. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, M.; Jain, S. Speech recognition employing mfcc and dynamic time warping algorithm. In Innovations in Information and Communication Technologies (IICT-2020), Proceedings of the International Conference on ICRIHE-2020, Delhi, India, 14–15 February 2020; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zakarya, M.A.; Al-Irhaim, Y.F. Unsupervised and Semi-Supervised Speech Recognition System: A Review. AL-Rafidain J. Comput. Sci. Math. 2023, 17, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, T.S.; Aljebory, K.M.; Rasheed, M.A.A.; Al-Ani, M.S.; Sagheer, A.M. Analysis of Methods and Techniques Used for Speaker Identification, Recognition, and Verification: A Study on Quarter-Century Research Outcomes. Iraqi J. Sci. 2021, 62, 3256–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajarajeswari, P.; Anwar Beg, O. An executable method for an intelligent speech and call recognition system using a machine learning-based approach. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2021, 21, 2150055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shaughnessy, D. Recognition and processing of speech signals using neural networks. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 38, 3454–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhavalkar, R.; Hori, T.; Sainath, T.N.; Schlüter, R.; Watanabe, S. End-to-end speech recognition: A survey. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2023, 32, 325–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainath, T.N.; Ramabhadran, B.; Nahamoo, D.; Kanevsky, D.; Van Compernolle, D.; Demuynck, K.; Gemmeke, J.F.; Bellegarda, J.R.; Sundaram, S. Exemplar-based processing for speech recognition: An overview. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2012, 29, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cummins, N.; Schuller, B. Advanced data exploitation in speech analysis: An overview. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2017, 34, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.; Deng, L.; Yu, D.; Dahl, G.E.; Mohamed, A.R.; Jaitly, N.; Senior, A.; Vanhoucke, V.; Nguyen, P.; Sainath, T.N.; et al. Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: The shared views of four research groups. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2012, 29, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hamid, O.; Mohamed, A.R.; Jiang, H.; Deng, L.; Penn, G.; Yu, D. Convolutional neural networks for speech recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2014, 22, 1533–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, G.E.; Sainath, T.N.; Hinton, G.E. Improving deep neural networks for LVCSR using rectified linear units and dropout. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 8609–8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainath, T.N.; Parada, C. Convolutional neural networks for small-footprint keyword spotting. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015; pp. 1478–1482. Available online: https://www.isca-archive.org/interspeech_2015/sainath15b_interspeech.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Abotaleb, M.; Dutta, P.K. Optimizing Long Short-Term Memory Networks for Univariate Time Series Forecasting: A Comprehensive Guide. In Hybrid Information Systems: Non-Linear Optimization Strategies with Artificial Intelligence; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2024; p. 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadiya, J.P. Exploring the use of recurrent neural networks for time series forecasting. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. Technol. 2023, 8, 2023–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mienye, I.D.; Swart, T.G.; Obaido, G. Recurrent Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Review of Architectures, Variants, and Applications. Information 2024, 15, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerakody, P.B.; Wong, K.W.; Wang, G.; Ela, W. A review of irregular time series data handling with gated recurrent neural networks. Neurocomputing 2021, 441, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A.; Mohamed, A.R.; Hinton, G. Speech recognition with deep recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 6645–6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodei, D.; Ananthanarayanan, S.; Anubhai, R.; Bai, J.; Battenberg, E.; Case, C.; Casper, J.; Catanzaro, B.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, G.; et al. Deep speech 2: End-to-end speech recognition in english and mandarin. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; pp. 173–182. Available online: http://proceedings.mlr.press/v48/amodei16.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Hannun, A.; Case, C.; Casper, J.; Catanzaro, B.; Diamos, G.; Elsen, E.; Prenger, R.; Satheesh, S.; Sengupta, S.; Coates, A.; et al. Deep speech: Scaling up end-to-end speech recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.5567. [Google Scholar]
- Panayotov, V.; Chen, G.; Povey, D.; Khudanpur, S. Librispeech: An asr corpus based on public domain audio books. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), South Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 19–24 April 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 5206–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, T.; Hansen, J.H. Microphone array processing for distance speech capture: A probe study on whisper speech detection. In Proceedings of the 2010 Conference Record of the Forty Fourth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grobe, CA, USA, 7–10 November 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1707–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).