1. Introduction
Over the past decade, autonomous driving systems have attracted increasing interest from both industry and research communities. These systems are a cornerstone for reducing traffic accidents, improving traffic efficiency, and enabling new forms of mobility. A key factor in the development of autonomous driving systems is the design of controllers capable of safely and accurately following desired trajectories, especially in complex urban environments [
1].
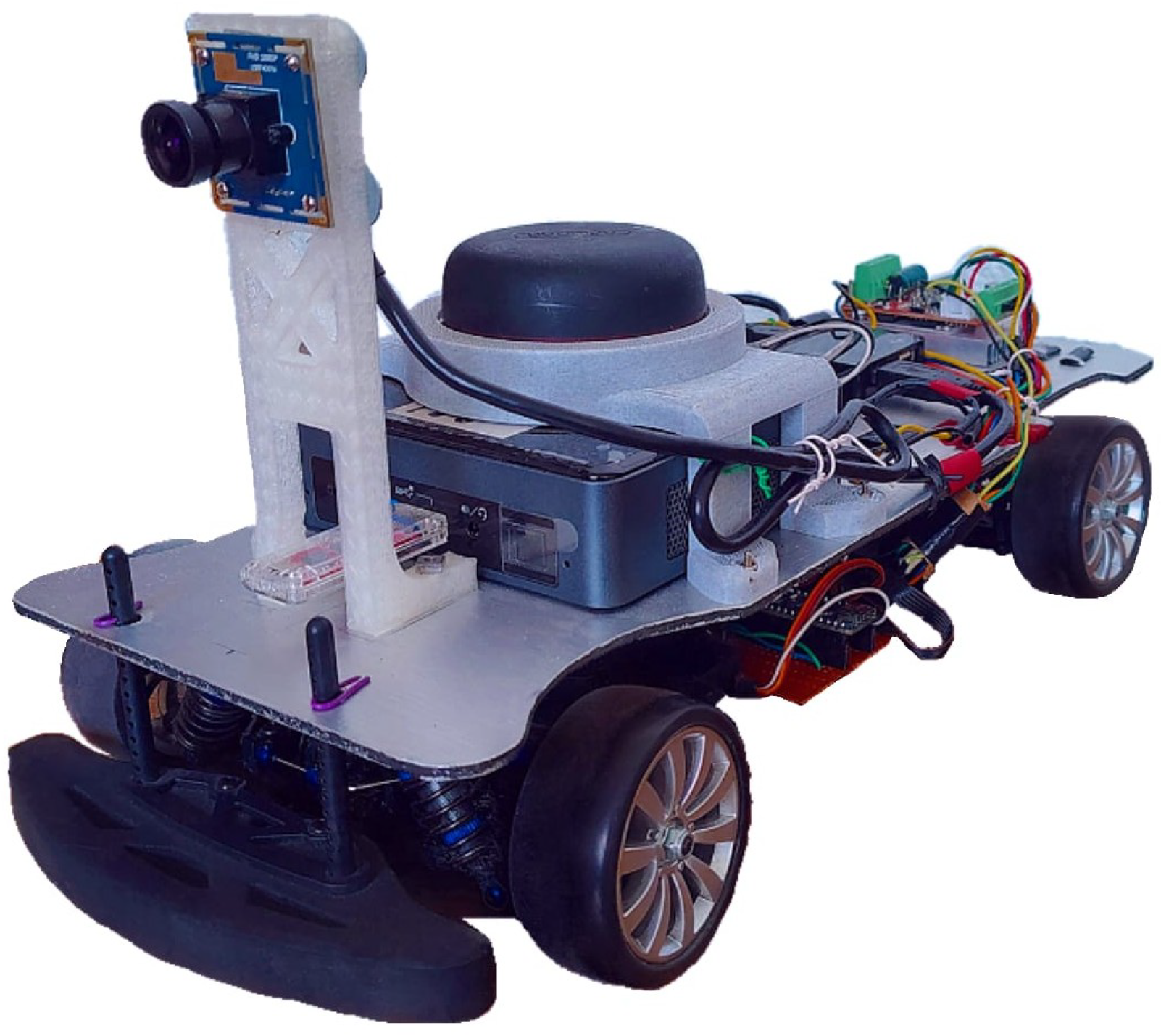
Most of the advances in the development of self-driving vehicles have started as research projects using scale-sized prototypes, as is the case of the project reported in this work, which was developed in academic laboratory conditions using a scale-sized car, where the road surface is flat and there are no adverse atmospheric conditions; this work is focused in the problem of controlling this car to manage the navigation in standard urban intersections.
Intersections are particularly critical points in traffic networks, often leading to delays and accidents. For this reason, Autonomous Intersection Management (AIM) is an active area of research, where path planning is performed for each vehicle in cruising scenarios, and vehicle movements are executed through automation [
2,
3].
Considering the literature reported so far, the research gaps found are the following: (1) Control systems for navigating in intersections require oversimplified models and complex sensing and communication schemes. (2) Several strategies neglect the lower-level vehicle controller implementation details and integration. (3) There is a substantial predominance on simulation-based validation. (4) The use of off-board computing and sensing reduces the reliability on real-world scenarios. (5) The prevalently employed controllers are not capable to handle real-world constraints, such as actuator limits.
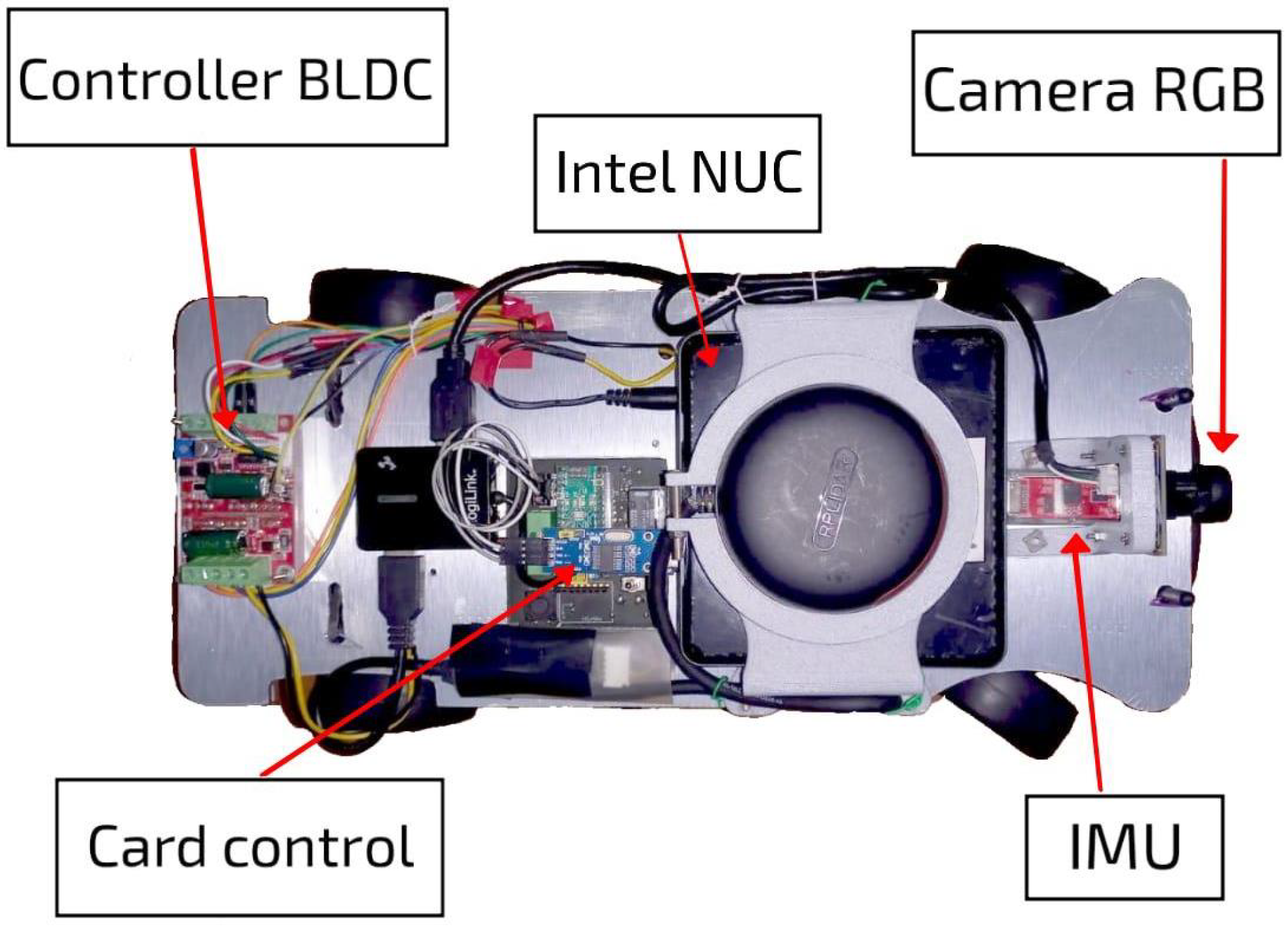
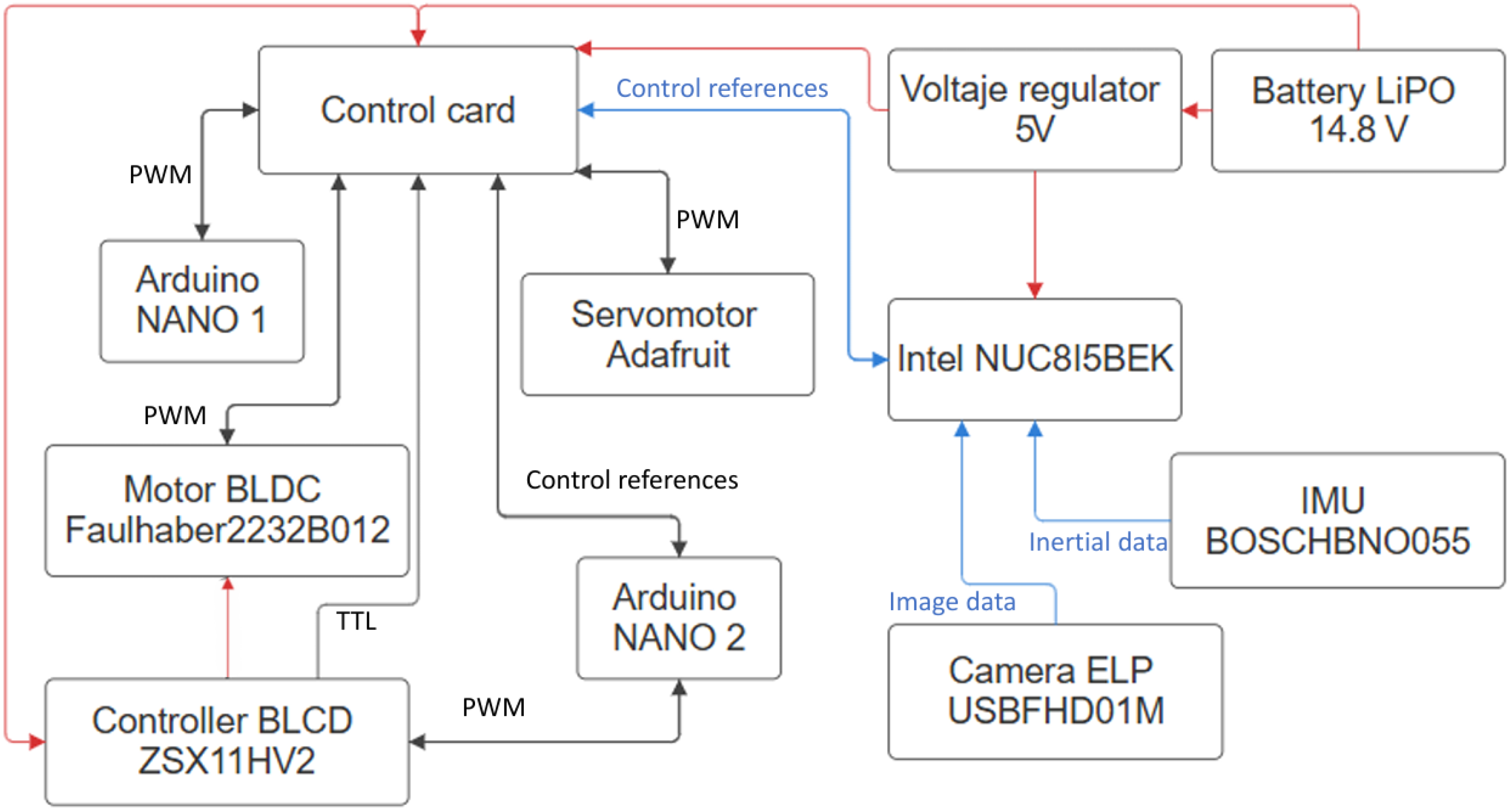
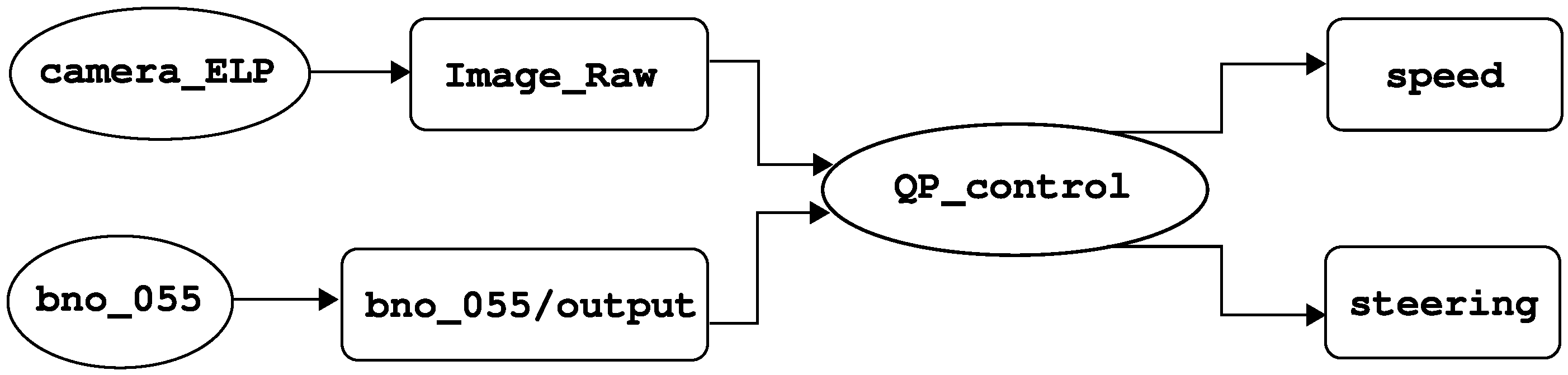
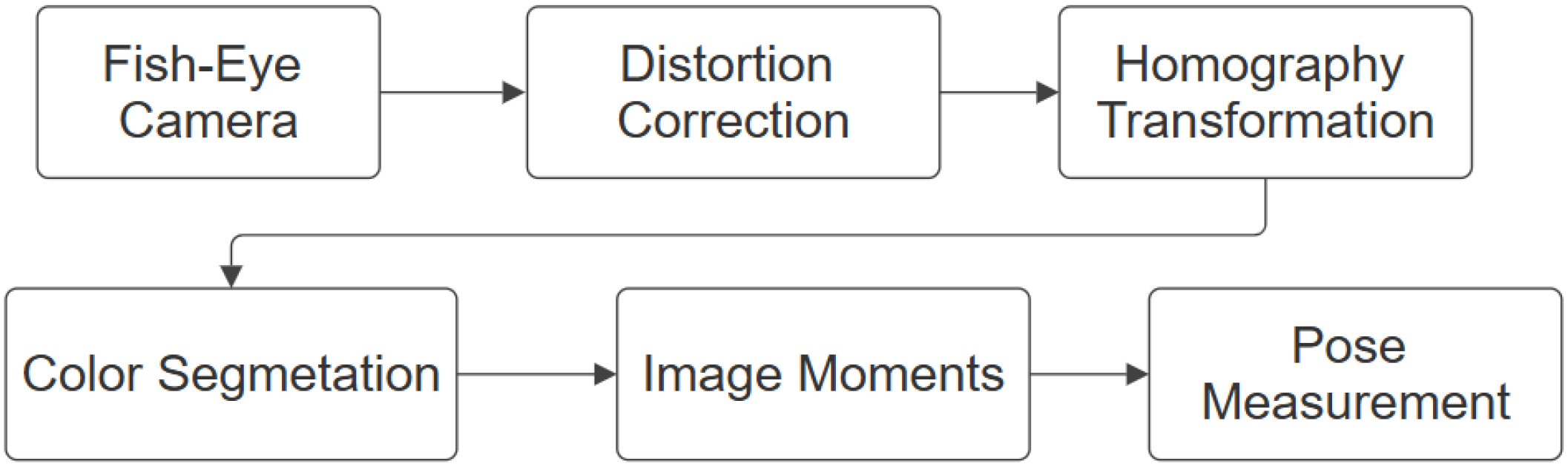
Aiming to fill out the aforementioned research gaps, this work presents an autonomous control architecture that enables lane following and intersection navigation using only an inertial measurement unit (IMU), a monocular camera, and computer vision algorithms. The system integrates visual processing for lane and intersection detection, vehicle state estimation, and a Quadratic Programming (QP)-based controller that determines the vehicle’s actions in real time, which in contrast to standard optimal controllers such as the linear quadratic regulator (LQR) or predictive algorithms, allows the handling of inequality constraints with less computational burden, directly computing the control input without a prediction horizon, as is presented in [
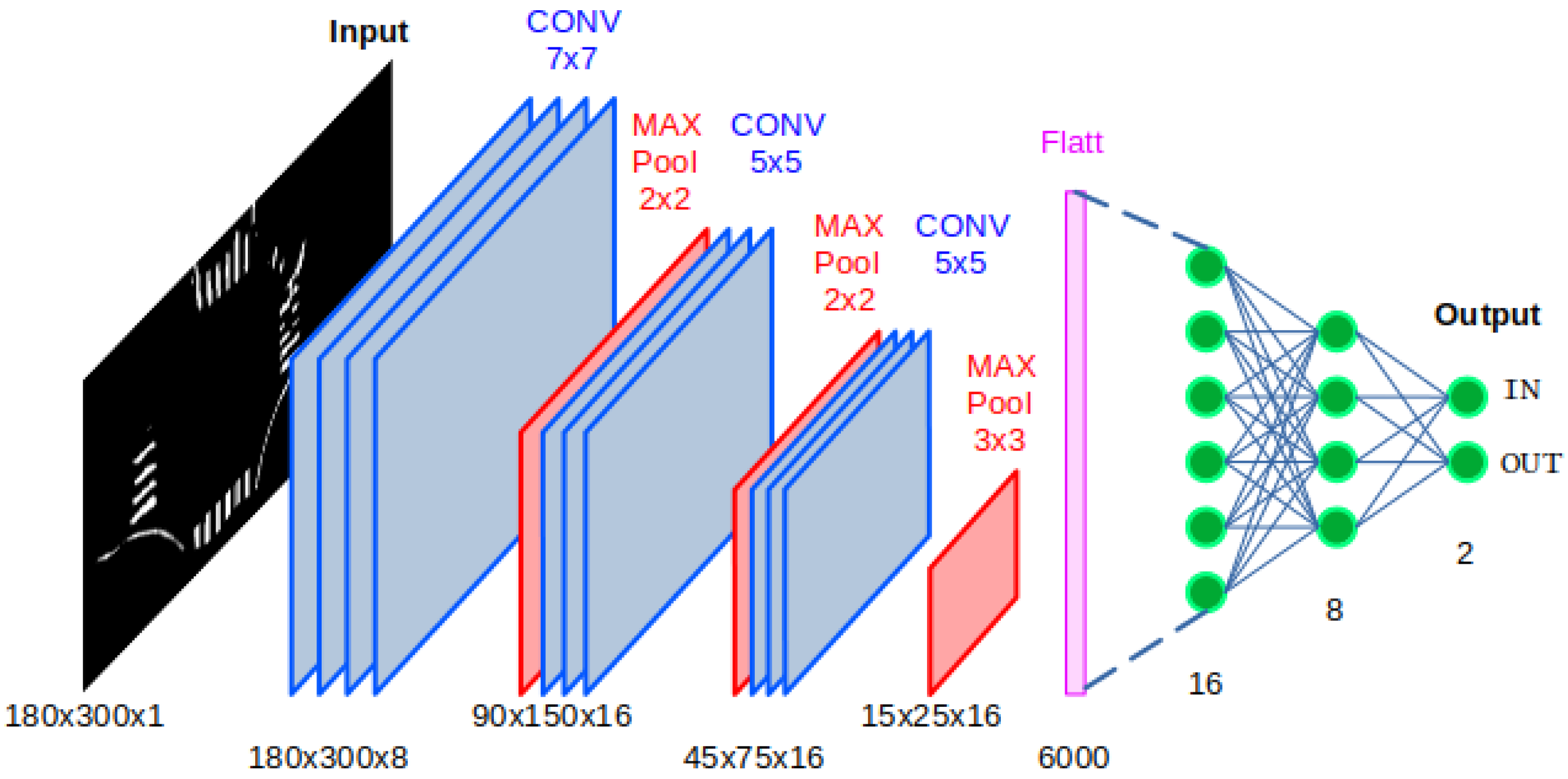
4]. The proposed architecture consists of several modules: a visual perception module that processes images captured by a forward-facing camera to identify lane markings; a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to detect cruising scenarios; a state estimation module that interprets visual and inertial data to define the vehicle’s current and desired states; and a switching controller module that implements an optimal control scheme based on QP to compute steering and velocity commands, enabling the vehicle to achieve navigation objectives while satisfying the imposed actuator constraints.
This paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 presents the related work, while
Section 3 presents dynamic model of the vehicle and the hardware/software architecture employed.
Section 4 details the visual feedback pipeline, covering road perspective correction, state estimation, and CNN-based scene classification.
Section 5 describes the proposed QP controller and its stability.
Section 6 reports the experimental results obtained in real-world navigation scenarios, comparing the proposed QP controller against LQR and Model-Predictive Control (MPC) baselines. Finally,
Section 7 summarizes the main conclusions and outlines future research directions.
2. Related Work
The navigation control of autonomous vehicles is taken for granted in navigation scenarios, so most research is instead dedicated to traffic monitoring and control, thereby leaving aside the potential implications of the lower-level controller implementation. Nonetheless, some authors have attempted to solve the navigation in intersections control problem, so diverse schemes have been reported in the literature so far, such as PID, Optimal Control, and MPC. However, most studies in the literature develop control laws based on overly simplified models, requiring a constant communication between vehicles and others agents, also assuming that many vehicle states are measured. In addition, a substantial majority of these results are obtained solely through numerical simulations, leaving aside the feedback state measurement or estimation algorithms [
1,
3,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9].
For example, Vitale et al. [
9], propose a centralized control method to manage traffic at road intersections. Their scheme solves an optimization problem where the states include the position and velocity of the vehicles, and the output is an acceleration profile for each vehicle within the intersection. They present simulation results showing that vehicles can cross safely without collisions, maintaining a safety distance of six meters. However, their system requires constant and perfect communication between vehicles, and the model assumes that vehicles cannot make turns. These limitations hinder its applicability in real-world environments.
Another strategy is presented by Ding et al. [
8], where a control system for autonomous vehicles is used to perform turning maneuvers at intersections. In their work, vehicles communicate with Road Side Units and with each other to obtain the position and velocity of nearby vehicles. Using a Model-Predictive Control (MPC) scheme, each vehicle calculates its acceleration and steering angle to execute left turns, right turns, or U-turns while cruising—adjusting its speed accordingly and maintaining a safe distance. Nevertheless, this system relies on a communication infrastructure that is subject to latency, data loss, and limited coverage. Additionally, high precision in vehicle positioning is required.
Similarly, Meng and Cassandras [
7] propose a real-time optimal control method for autonomous vehicles approaching signalized intersections under free-flow conditions. The goal is to minimize both energy consumption and travel time while avoiding idle stops. By leveraging vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication, their algorithm dynamically adjusts vehicle speed profiles to enable non-stop intersection crossings. The control formulation assumes a single autonomous vehicle operating in free-flow mode, excluding interaction effects, lateral maneuvers, and lane constraints. The framework also depends on precise V2I signal timing, and potential discomfort caused by acceleration spikes near the onset of green lights may require additional buffering strategies. Furthermore, the method assumes straight-line motion without turns, and does not address the feasibility of lane changes.
In contrast, the navigation of autonomous vehicles in cruising scenarios without external communication systems has been less explored in the literature [
10,
11,
12,
13]. For example, Pourjafari et al. [
13] propose a predictive scheme for navigating unsignalized road intersections. Their objective is to predict the behavior of other vehicles, determine the order of passage at collision points, and compute an acceleration profile for the ego vehicle. The proposed control method considers multiple constraints, while the states of other vehicles are estimated using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and Graph Neural Networks. Ultimately, they present simulation results based on 250 real-world scenarios, demonstrating that the vehicle can navigate safely and, in some cases, outperform human drivers. However, the method relies heavily on the precision of neural network data and has not been experimentally validated.
On the other hand, Zannatha et al. [
12,
14] have presented a modular navigation system for scaled autonomous vehicles operating in urban environments. Their approach integrates route planning using Dijkstra’s algorithm, geometric trajectory generation adapted to intersection geometry, and a hybrid navigation controller that combines odometry-based Stanley steering with trapezoidal velocity profiling. All modules were validated in a ROS–Gazebo simulator within a 2D urban environment featuring 90° intersections and a uniform road layout. However, the method assumes idealized urban geometry—excluding roundabouts, diagonal roads, or variable curvatures. Only a single vehicle is considered, with no dynamic agents or multi-agent coordination. Their controller relies heavily on odometry, and lane perception is limited to geometric assumptions.
Sezer et al. [
11] present a decision-making system for autonomous vehicles that infers the intentions of other drivers and makes safe and efficient decisions to cross or merge at unsignalized T-intersections. To achieve this, they use a probabilistic model known as a Mixed Observability Markov Decision Process (MOMDP). The system was implemented on an autonomous vehicle (a modified golf cart) and tested at a real intersection on the campus of the National University of Singapore. In their experiments, the system successfully detected changes in the intentions of aggressive drivers, avoided collisions, and chose safe actions. However, the model assumes that the positions of both the autonomous and human-driven vehicles are perfectly observable, which may not hold in practice due to sensor errors, occlusions, or adverse conditions. Additionally, the approach is computationally expensive.
Additionally, control strategies based on Quadratic Programming are attractive because they yield optimal solutions while simultaneously accounting for state and control input constraints. However, this approach has been primarily used for trajectory tracking [
15,
16,
17,
18,
19], and mostly present only simulation results. In Lee [
19], a soft-constrained variant of the constrained iterative Linear Quadratic Regulator (CILQR) algorithm is proposed for lane-keeping control in autonomous vehicles. The controller introduces slack variables to relax state and input constraints within a barrier-function-based optimization framework, aiming to suppress steering jitter without relying on external filters. Performance is validated through numerical simulations and vision-based experiments in perturbed environments.
Similarly, Yuan and Zhao [
17] present a hierarchical trajectory-tracking controller for autonomous vehicles that couples lateral and longitudinal dynamics using a hybrid Linear LQR and MPC framework. The architecture integrates an Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) observer to estimate driving states (e.g., velocity and yaw rate), aiming to improve accuracy under state uncertainty. The framework is validated using CarSim–Simulink co-simulation across various speed scenarios and benchmarked against a classical MPC-only control scheme. However, the EKF’s accuracy depends on well-tuned noise parameters, which may vary across scenarios.
Considering the published results regarding autonomous vehicles control in intersections so far, this paper presents a low-level control system that only uses on-board sensors and computers to accurately navigate in intersections, avoiding communication between agents and external sensing in contrast to the works found in the literature. Moreover, the proposed control scheme takes into account actuator constraints and it is implemented on a real scale-model vehicle, which are clear advantages over the state of the art.
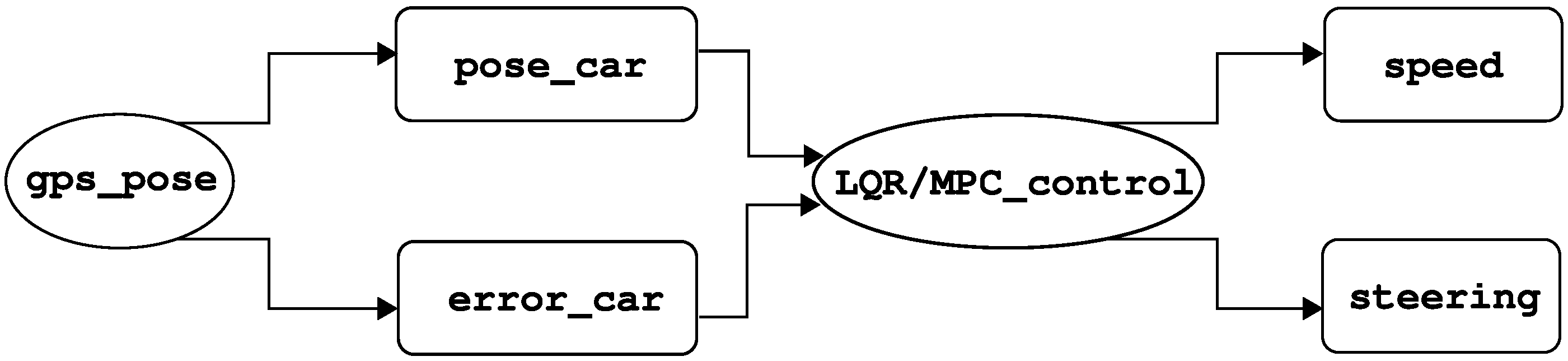
5. Quadratic-Programming Control
Quadratic Programming (QP) is a type of mathematical optimization problem in which the objective function is quadratic and the constraints are linear. It is a widely used control strategy because it allows for the explicit handling of constraints on system dynamics, states, and actuator limits, which cannot be directly handled by traditional optimal control approaches like the Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR). The objective function typically reflects goals such as minimizing control effort or tracking error, while the constraints can include the system dynamics, actuator saturation, state bounds, and safety requirements.
Considering the error dynamics (
6), and the control problem of leading to zero the states, a cost objective function can be defined as
where
is a positive definite diagonal matrix and
are positive scalars. The penalty constant
is obtained by varying its value while solving the optimization problem in simulation, it can be later implemented in the real vehicle. Moreover,
is a differentiable quadratic function that penalizes violations of the actuator constraints. This approach is referred to as a soft constraint [
21,
22], which introduces a weighted penalty whenever the control input
exceeds the admissible range, which in this case is
, resulting from the admissible values of the ROS topic
steering, which in turn maps the corresponding PWM value to move the servomotor within a
to
radians or
to
deg (0 deg steering corresponds to 90 deg servomotor shaft).
Given a control horizon
, at iteration
k, it is possible to estimate future states
by applying (
6) iteratively. Then, the estimated immediate cost from time step
k is
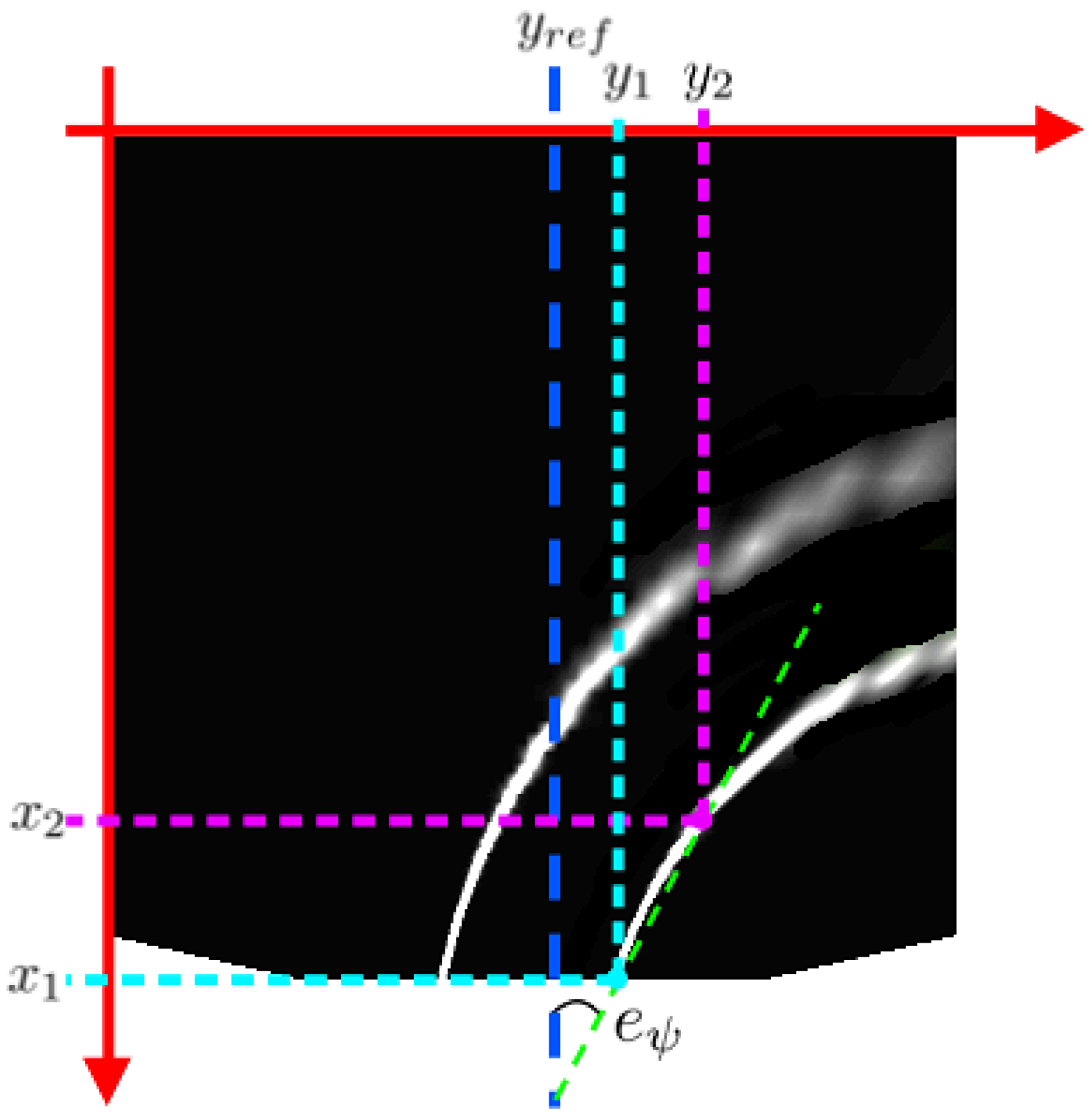
In practice, two types of controllers are used for navigation. The first is a vision-based controller for lane keeping, using the lane markings as reference. From the images captured by the on-board camera, it is possible to measure the states
and
(as detailed in
Section 4.4). In general, this is sufficient to follow the road. However, at an intersection, there are three possible paths and insufficient floor markings to reliably estimate the vehicle’s position and orientation. For this reason, a second controller with IMU-based feedback was designed. This controller records the vehicle’s yaw angle
just before entering the cruise and computes the orientation error
as follows:
After computing
and
by minimizing the immediate cost in (
12), a controller switching strategy was implemented as follows:
where
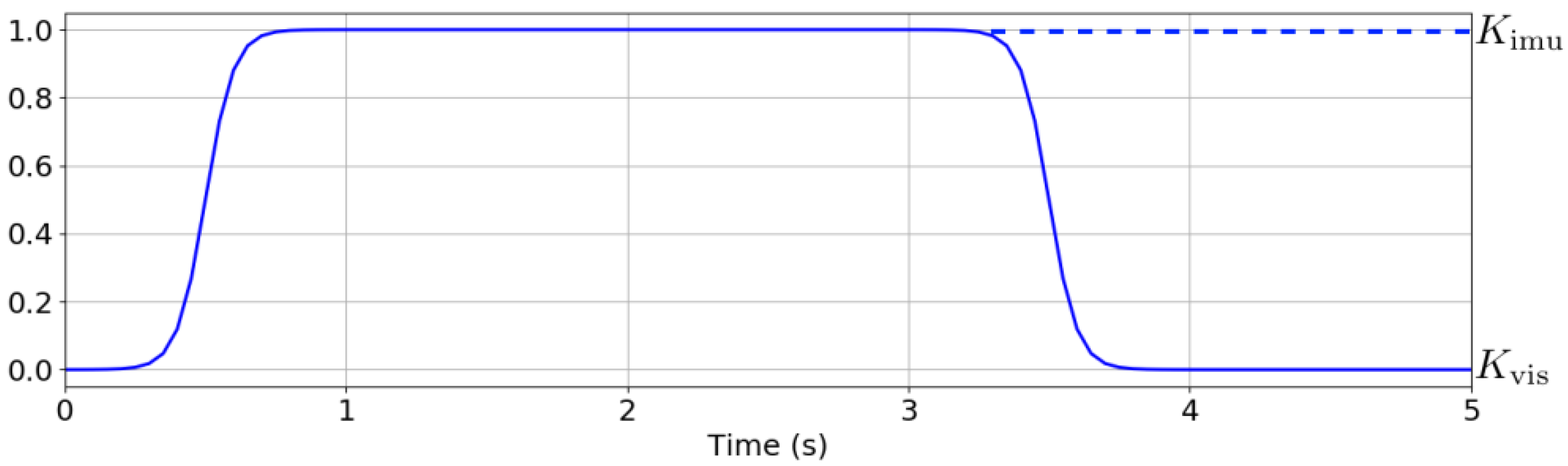
. Such a function is defined as the difference between two sigmoid functions, as shown in
Figure 14. When
, the vision-based controller dominates, whereas when
, the IMU-based controller takes over the steering.
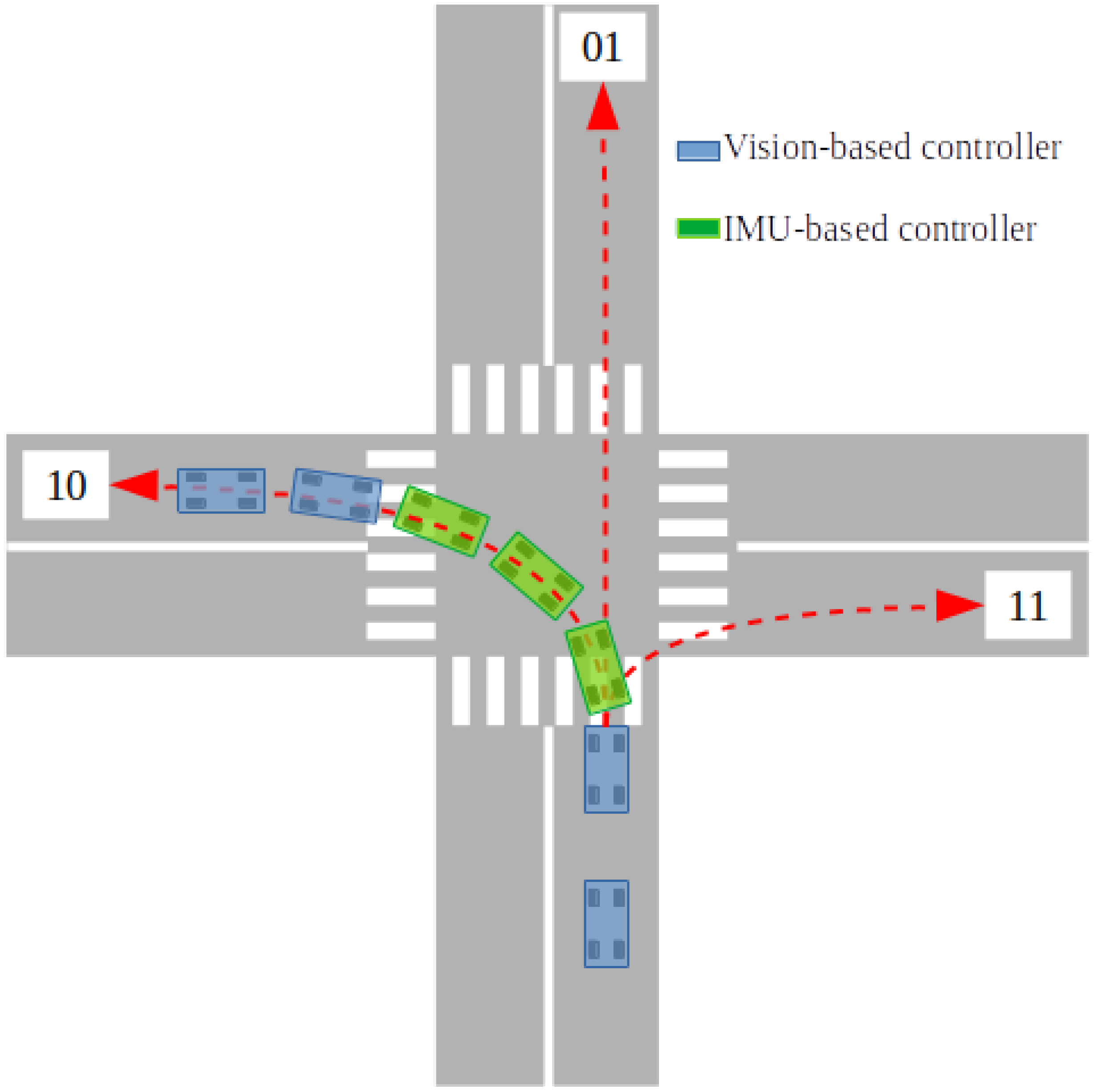
Figure 15 illustrates the controller switching strategy and how each path in the cruise is labeled.
Stability
Consider the discrete error dynamics (
6). The control problem is to lead
also during the transition between controllers, so the QP controller (
15) is proposed, ensuring a smooth transition. Thus the following is assumed:
- A1.
The longitudinal velocity satisfies , hence the pair is controllable.
- A2.
The QP is convex, despite the linear constraints, since the cost function is convex, so all the solutions are feasible.
- A3.
The states are always measured at a higher rate than the discrete dynamics and the vehicle has enough power to perform the control action.
- A4.
The AutoMINY vehicle navigates in a flat surface, so roll and pitch angles are neglected.
- A5.
The road is always within the camera field of view.
The closed-loop system composed by the error dynamics and the proposed controller can be expressed as
The following theorem proves the stability of its solutions .
Theorem 1. Under Assumptions A1 to A5, the solutions of the state equations describing the closed-loop system are stable, i.e., the solutions are stable.
Proof. To demonstrate the stability of the solutions for the differences Equation (
16), the QP optimization problem must be analyzed. Firstly, it is worth remembering that the cost function matrix
Q in (
13) is symmetric and a positive definite. Afterwards, from the definition of optimal control (Pontryagin’s Maximum Principle), one component of the Hamiltonian’s gradient yields the optimal controller
where
R is the same proposed in the cost function (
13), and
is symmetric and positive definite, which is obtained, by
The solution of this finite-horizon problem is obtained by recursively solving the QP as
is obtained; thus, the following Lyapunov candidate function is proposed
whose difference equation is
Since is negative definite, then the stability of the trajectories of is guaranteed. □
6. Experimental Results
In order to assess the performance of the controller (
15) developed in this work, a series of experiments were conducted in which the car followed one of three possible paths in an intersection scenario. For each path, the initial pose of the car was varied. Ten experiments were carried out in total, and during each trial, the Root Mean Square (RMSE) of the lateral error
, the Integral Square Error (ISE) of the heading error
, and the Total Control Effort (TCE) of
were computed using the following:
where
h is the sampling period.
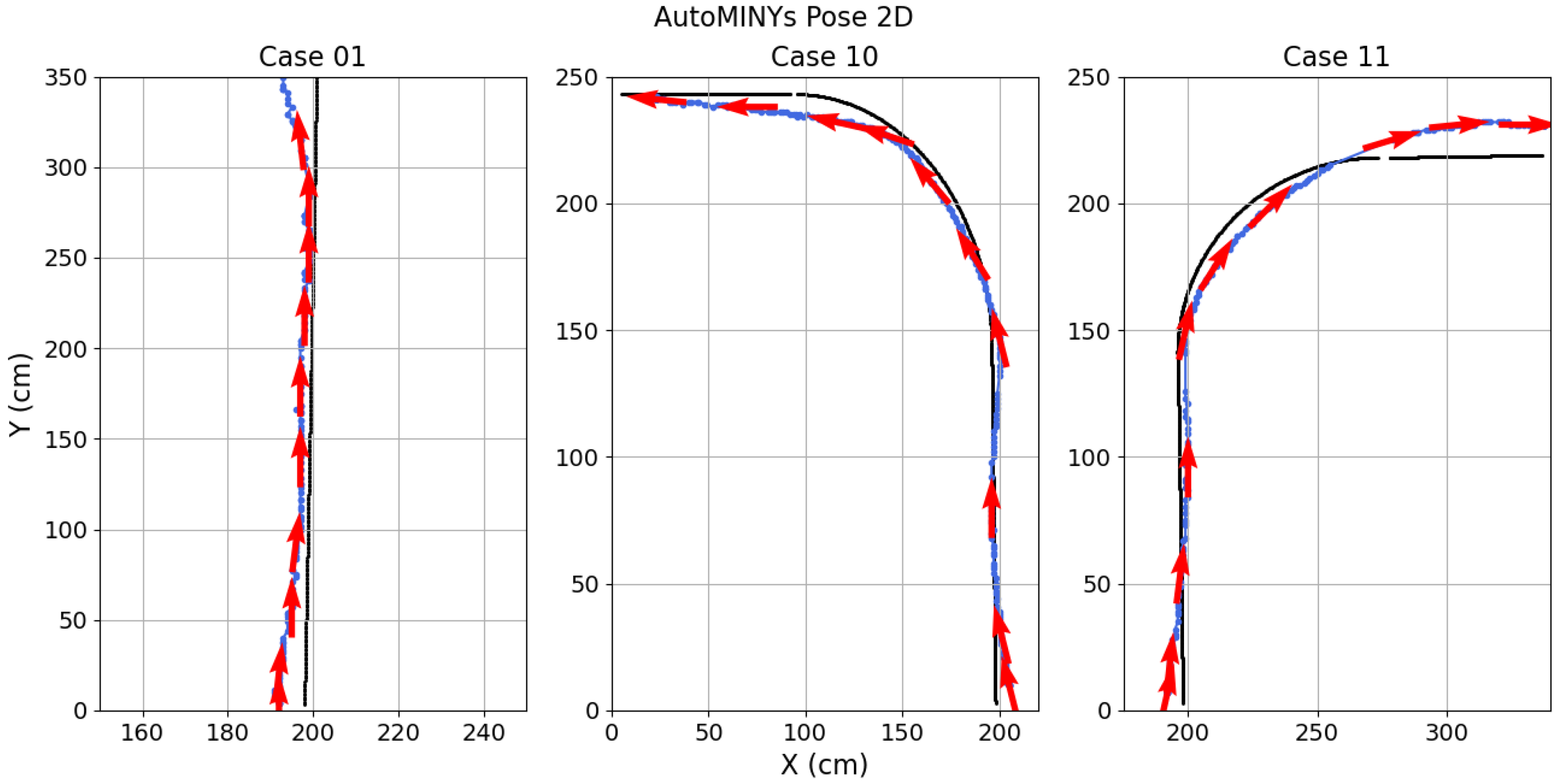
Figure 16 shows both the reference trajectory and the mean trajectory followed by the car during the 10 trials using the proposed controller (
15), where it can be shown that the trajectories were tracked with a few centimeters error, which is acceptable for a prototype scaled vehicle. A video of the experiments is available at
https://youtu.be/Tnf-_E8l6jo?si=pVEqnw_1i7ZdY6mW (accessed on 30 July 2025).
In order to compare the performance of this controller with other approaches, LQR and MPC controllers were also implemented to follow the ideal trajectory based on ground-truth information. As before, ten experiments were carried out for each case, the initial pose of the car was varied in each trial, and the RMSE of
, the ISE of
, and the TCE of
were measured. It is worth mentioning that both LQR and MPC require the use of ground-truth data to be implemented; in contrast, QP control is exclusively fedback with the on-board sensors.
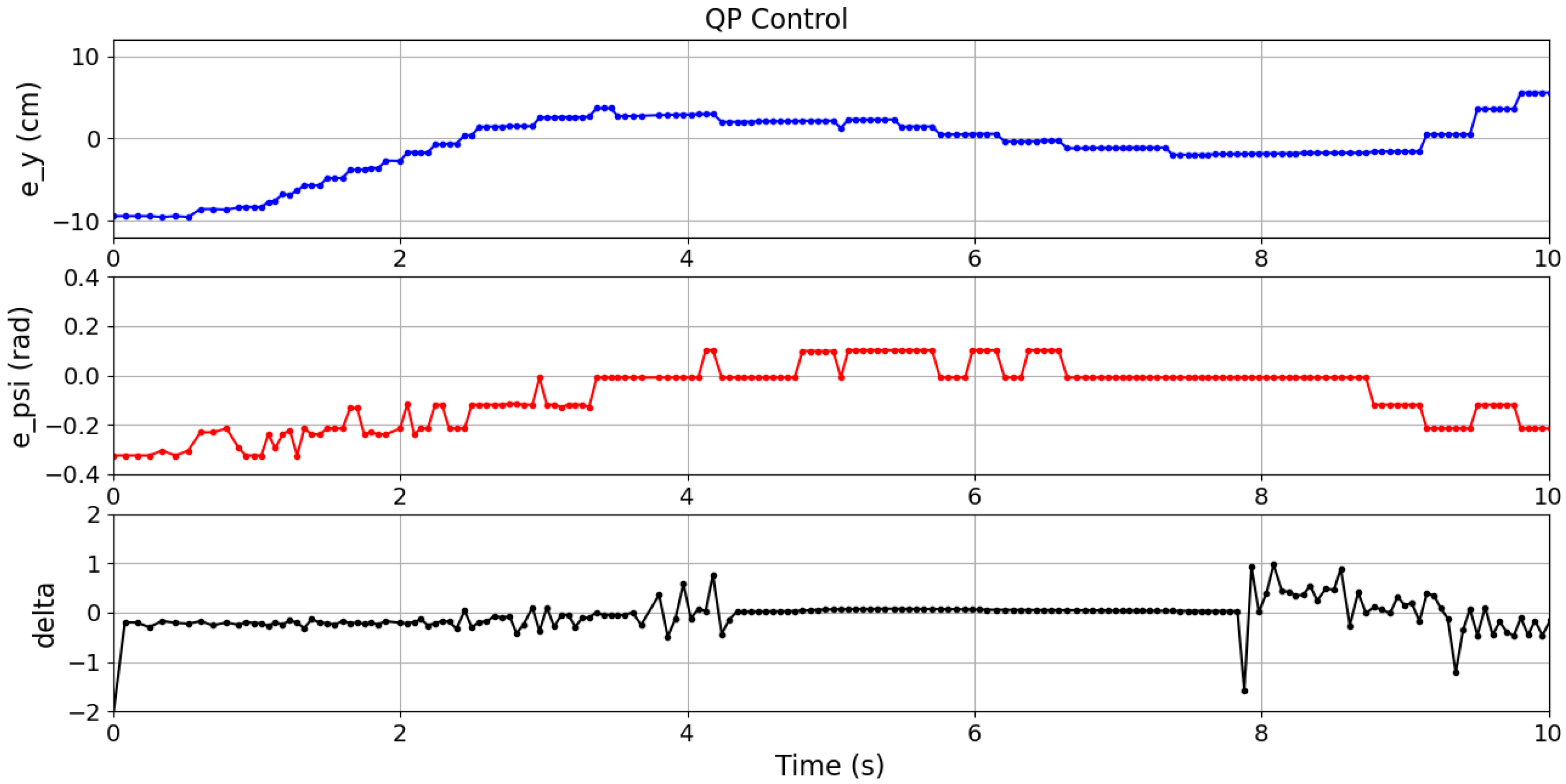
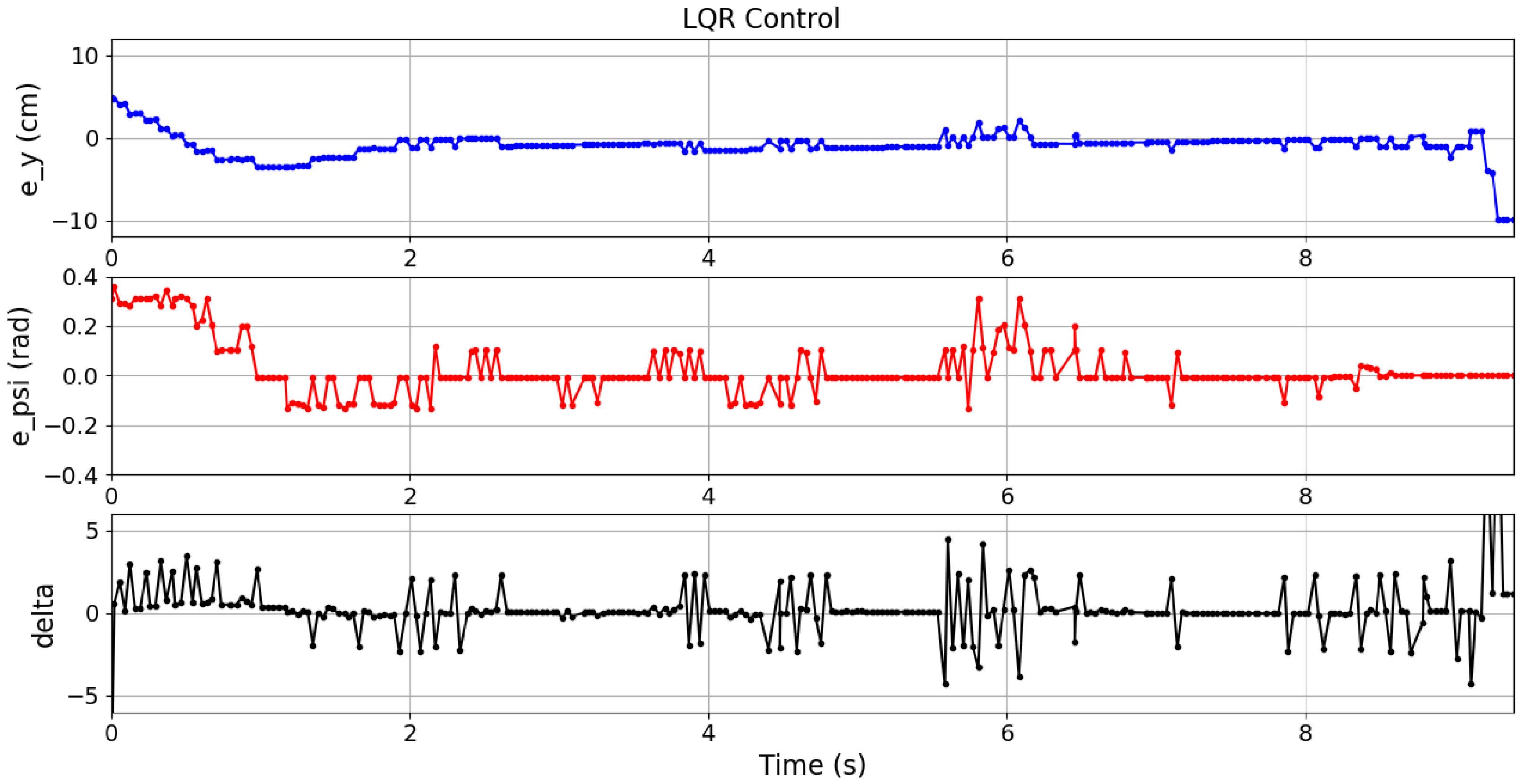
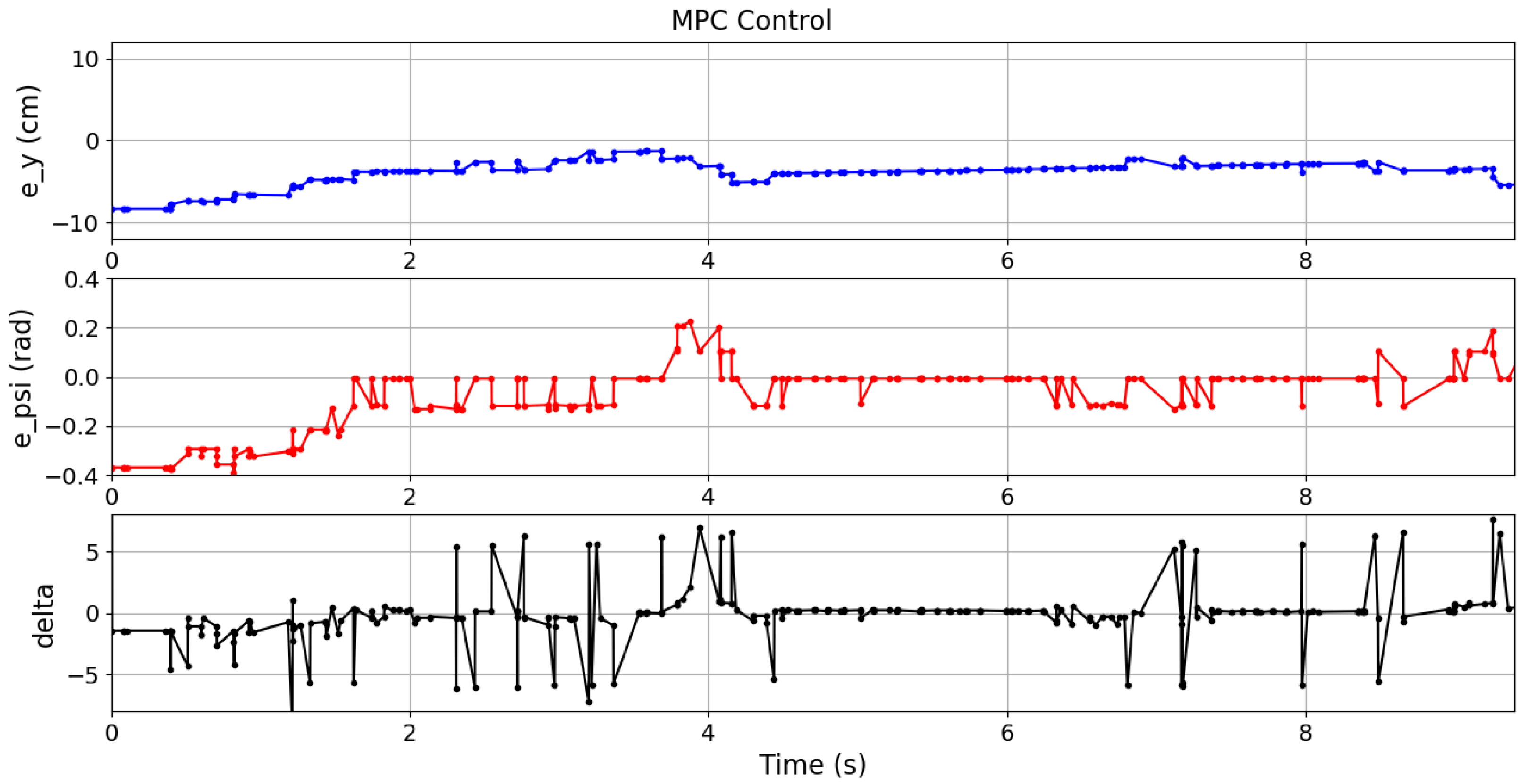
Table 3 reports the mean values of these metrics over ten experiments for each case. In these experiments, the vehicle navigated within an intersection, following the path of the case 01. The different controllers results are plotted as follows: QP control in
Figure 17, LQR control in
Figure 18, and MPC control in
Figure 19.
Although the best
was achieved by the LQR controller in all cases, it is important to note that the QP controller (
15) obtained comparable results using only on-board information from the IMU and the camera, which demonstrates its superiority in more realistic sensing conditions. Moreover, the QP controller resulted in the lowest ISE and TCE across all cases. It can also be observed in
Figure 17,
Figure 18 and
Figure 19 where the errors and control signals were plotted. It can be clearly observed that the control signal supplied by the QP control is effectively constrained within the desired range, and also smoother than those obtained through the other compared controllers, which may potentially contribute to improve the passenger comfort and increase the life cycle of actuators.
7. Conclusions
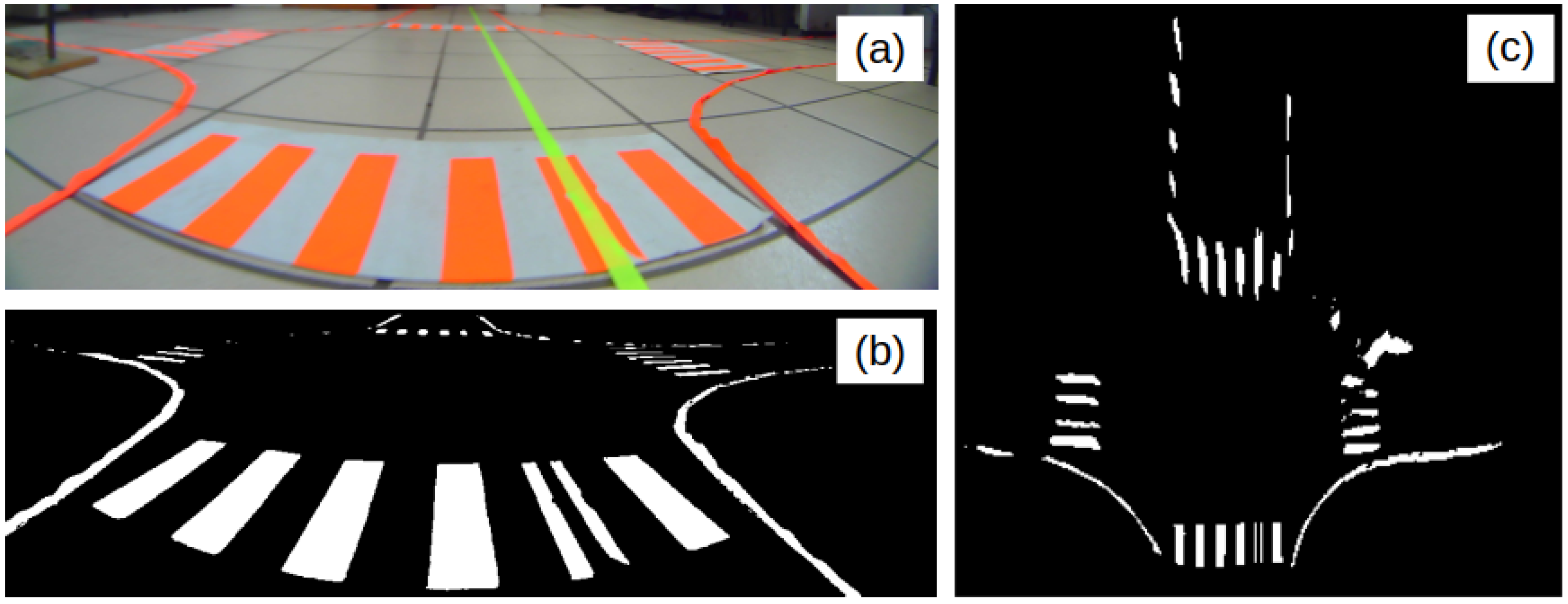
In this work, a Quadratic Programming (QP)-based controller was developed and evaluated for the autonomous navigation of a scale-size autonomous vehicle in intersection scenarios. The execution of the experiments was performed using computer vision techniques, namely the computation of the dynamic states by means of an homography-based estimation. Lane markings were also segmented, enabling accurate measurement of the vehicle’s lateral and heading errors.
A ground-truth system was implemented using a ceiling-mounted camera with colored markers, which proved to be highly useful for validating and quantifying the performance of the controllers. Additionally, a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) was used to detect whether the vehicle was inside or outside an intersection with high accuracy, facilitating the correct switching between straight driving and intersection navigation controllers.
The proposed QP control was validated both mathematically via a Lyapunov method analysis and also experimentally in a real scale-model vehicle. The experimental results showed that the QP controller, which relied solely on on-board sensor information, achieved a competitive performance for lateral lane tracking compared to the LQR and MPC controllers that used ground-truth data. However, the proposed QP controller is significantly more accurate for curve tracking, demonstrating an average 67.0% lower ISE compared to the LQR and an average 53.9% lower ISE compared to the MPC. Moreover, when considering the TCE, the QP controller proved to be significantly more energy-efficient, reducing the required effort by an average of 63.3% compared to the LQR and by an average of 78.4% compared to the MPC, suggesting a less energy consumption and smoother operation, which can be potentially translated into a comfortable passenger experience, actuators preservation, and gentle maneuvers. In addition, it was proved that the control signals supplied by the QP control are correctly constrained to the selected range in contrast to the other compared techniques. These findings validate the feasibility of combining vision-based techniques with QP control for autonomous vehicle applications in controlled environments.
On the one hand, one potential limitation of the proposed controller is that it is designed to work efficiently in flat-surface navigation, so that roll and pitch motions can be negligible. On the other hand, the proposed model excels for scale-sized vehicles, but a more complex model must be implemented for real-sized ones.
As future work, the control system could be extended to more complex scenarios and include additional sensors to improve the controller’s robustness and adaptability. Additionally, the visual perception system can be improved by detecting the lanes and other signals trough semantic segmentation with CNN, which is beneficial to discard disturbing objects on the road, for instance, splashed liquids, garbage, or hail.