Dual Halbach Array Compact Linear Actuator with Thrust Characteristics Part I Simulation Result
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
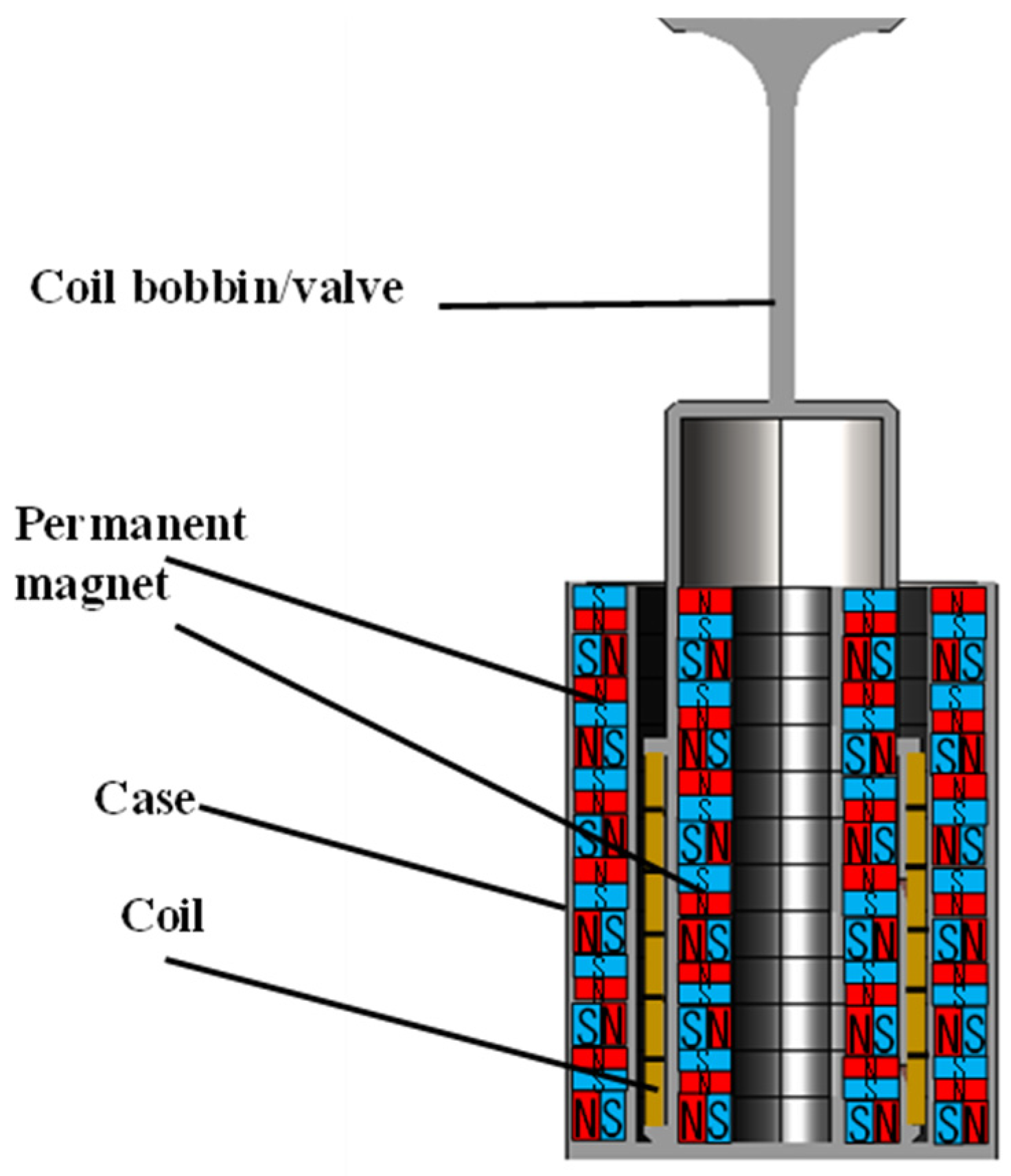
2.1. Magnetic Field with Dual Halbach Array
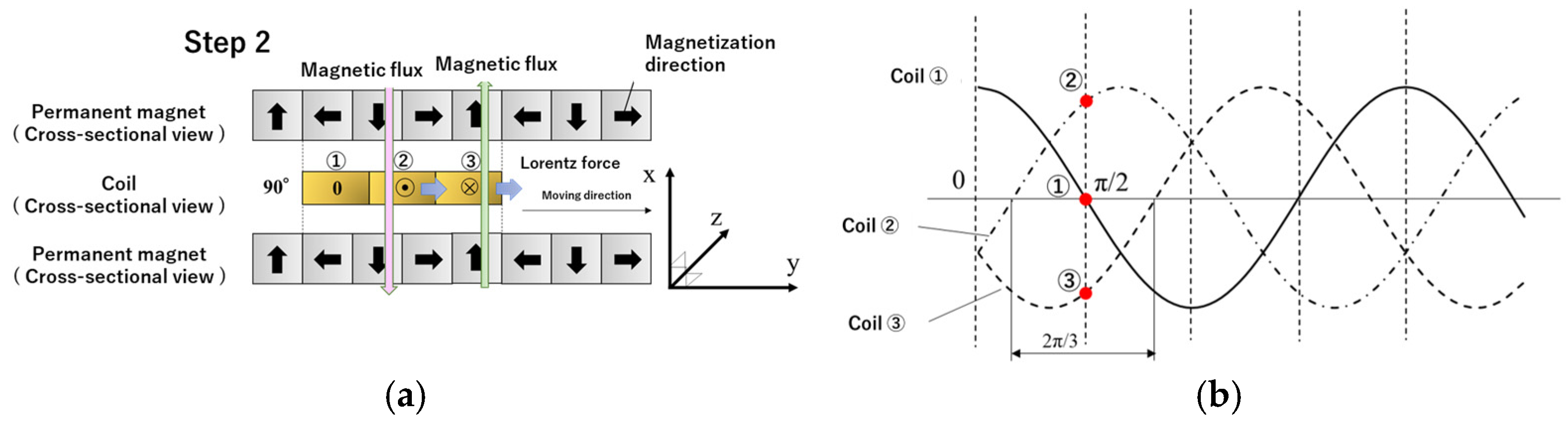
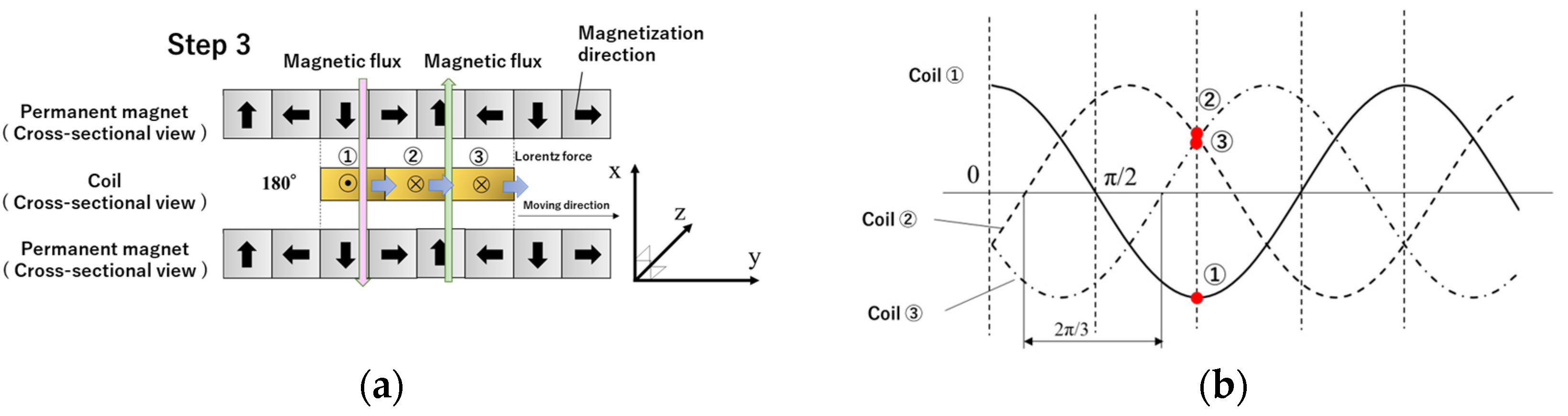
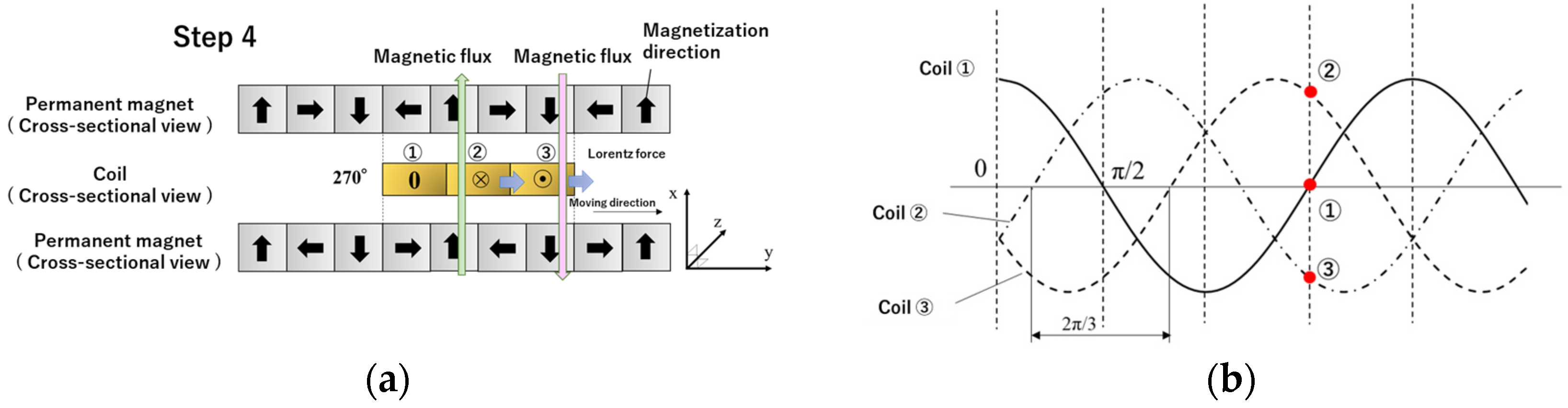
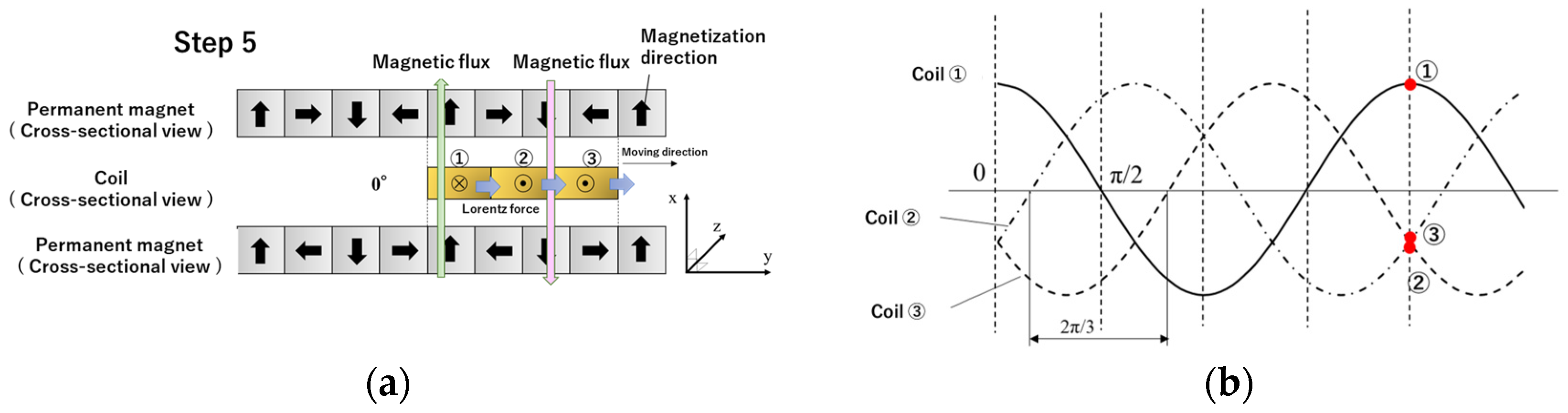
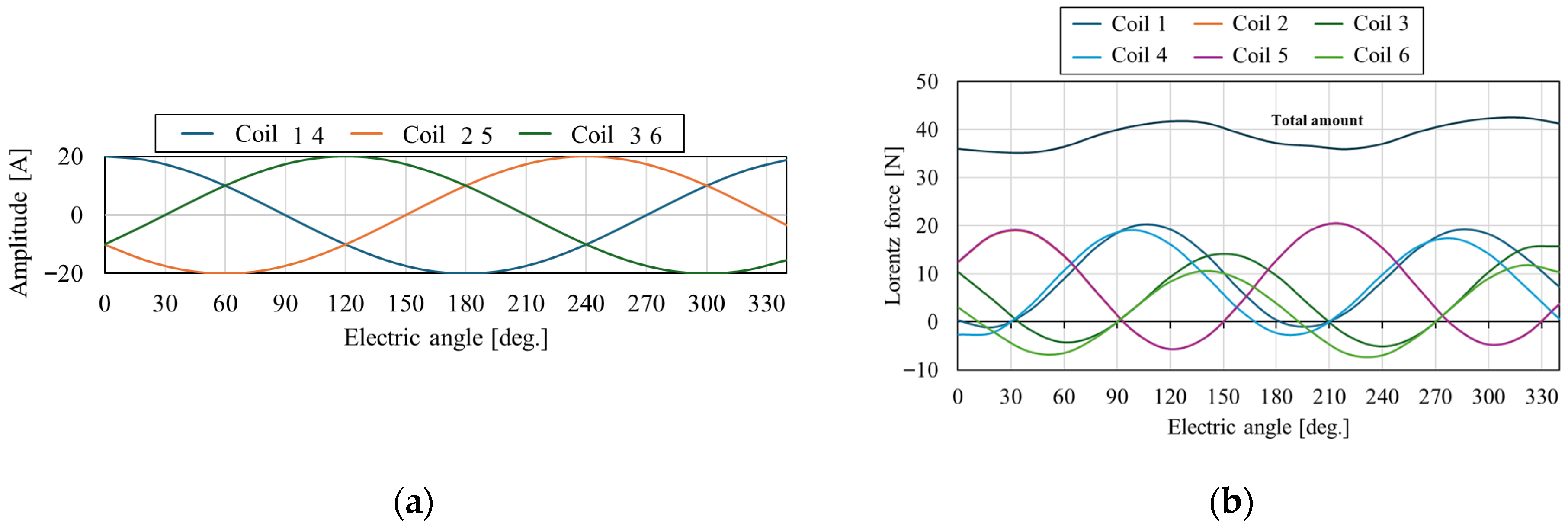
2.2. Principle of Operating a Linear Actuator with Three-Phase Alternating Current
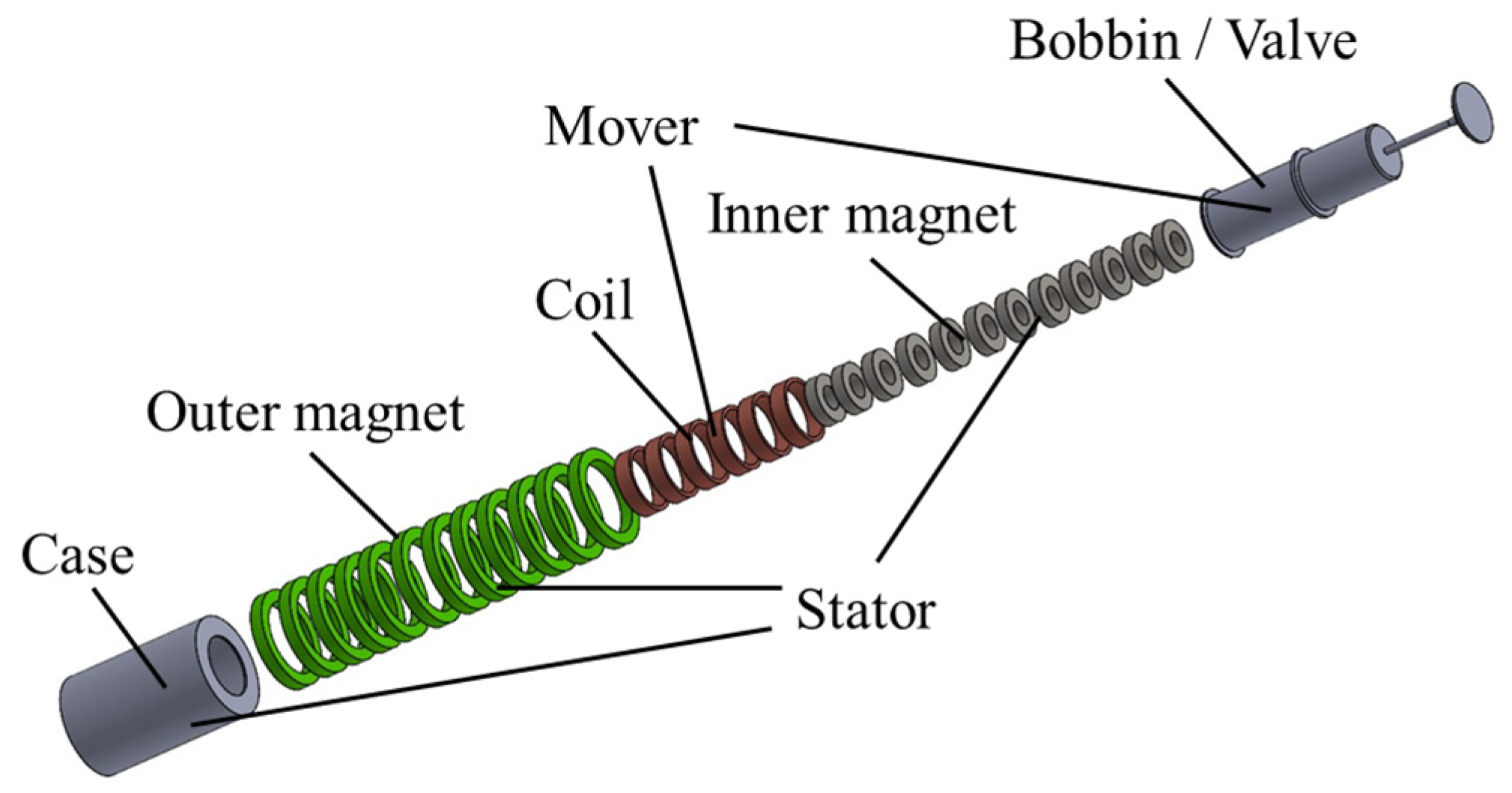
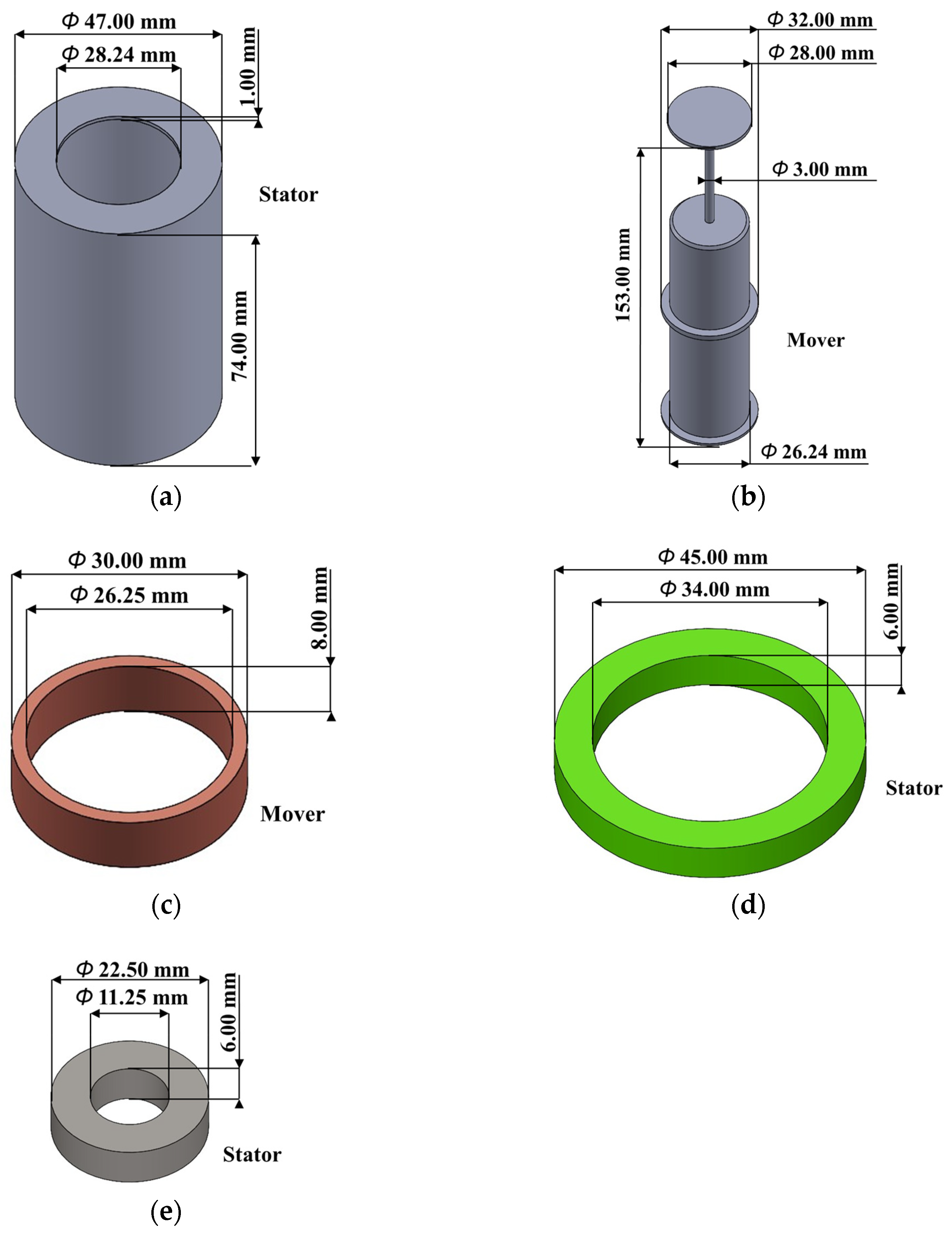
2.3. Geometry and Dimensions of the 3D Model
2.4. Finite Element Analysis Model and Analysis Conditions
2.5. Theoretical Background and Governing Equations
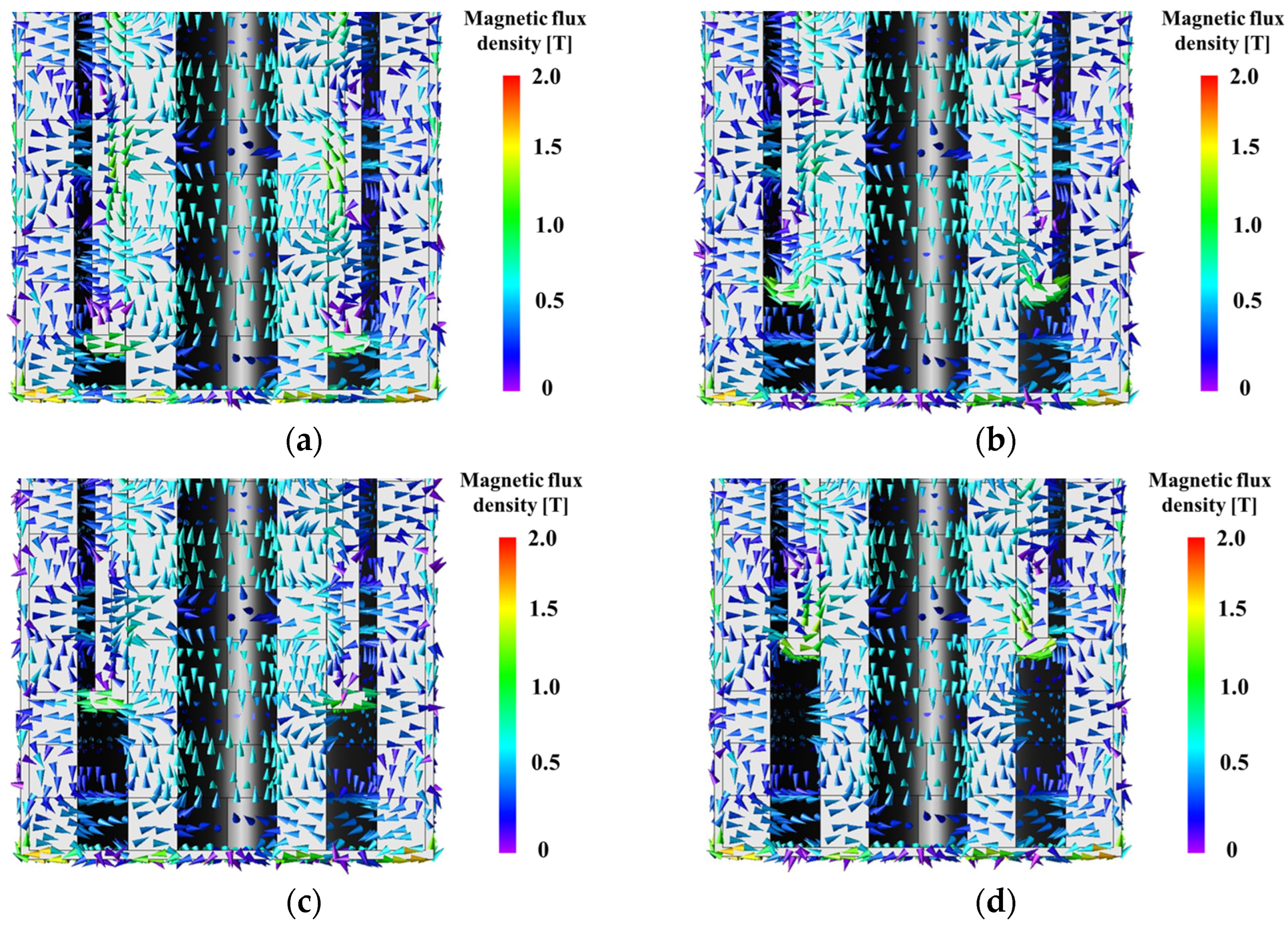
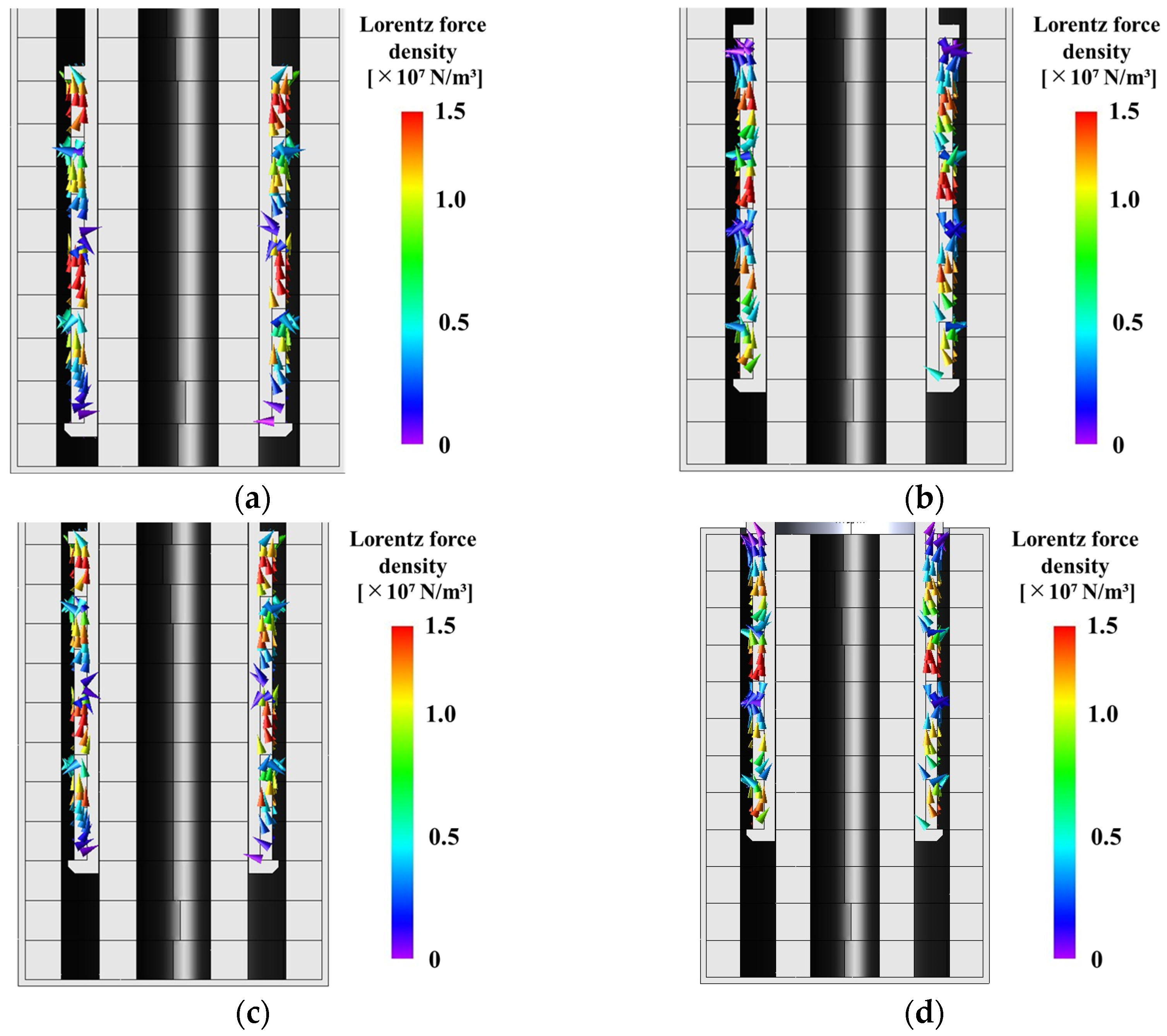
3. Basic Electromagnetic Behavior of Dual Halbach Array Linear Actuators
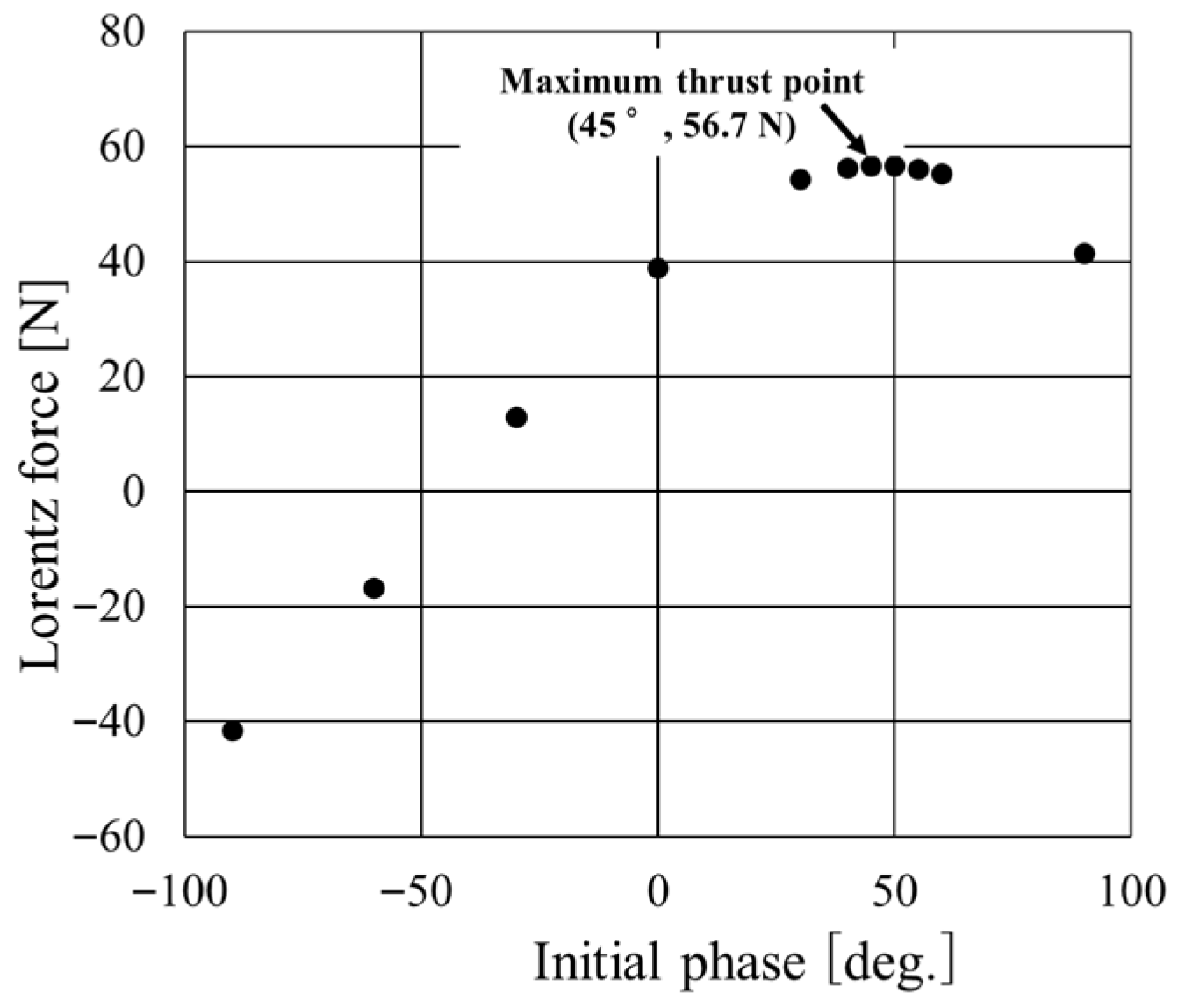
4. Thrust Enhancement Analysis by Three-Phase AC Initial Phase Optimization
5. Conclusions
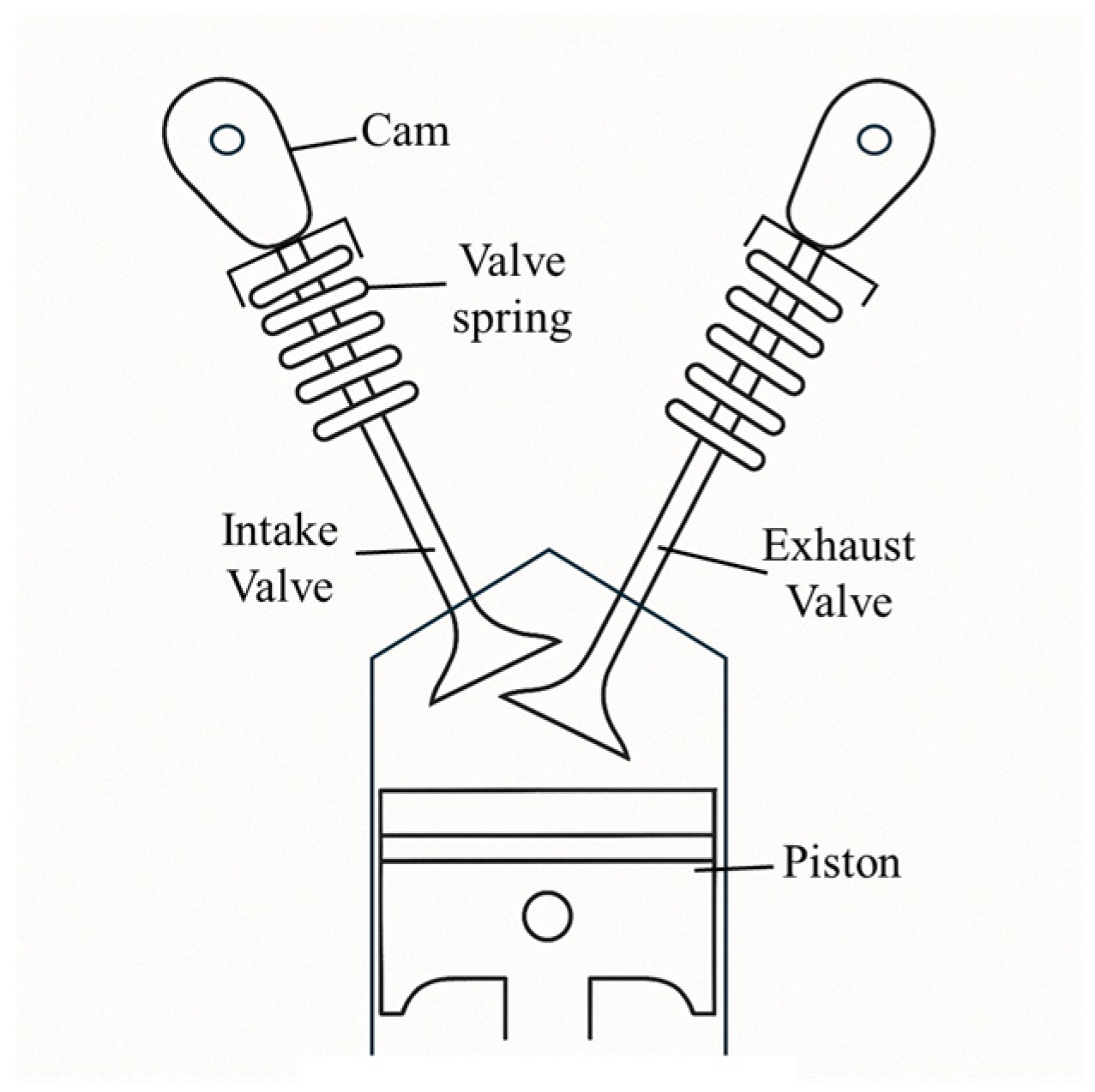
- Architecture for reciprocating use: We propose a compact voice-coil-motor type linear actuator specifically conceived for reciprocating valve motion, employing inner and outer dual Halbach permanent-magnet arrays to focus flux while preserving a small form factor.
- Average thrust: Under three-phase excitation, an average thrust of 56.7 N was obtained in the valve-actuation direction.
- Initial-phase optimization (hardware-invariant): Without altering the hardware (geometry, materials, or the numbers of magnets and coils), varying only the initial phase of the three-phase current increased the cycle-averaged thrust; sweeping the initial phase from minus 90 to 90° (30° steps, refined to 5° the optimum) revealed a maximum average thrust 45°.
- Continuous propulsion: Despite local reverse components, coordinated excitation of multiple coils maintained a net positive thrust over one electrical cycle.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shiao, Y.; Kantipudi, M.B.; Weng, C.-B. New actuation control for hybrid electromagnetic valve train. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Yin, J.; Lu, Q. Design and analysis of a novel composited electromagnetic linear actuator. Actuators 2022, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yue, H.; Yang, F.; Zhu, J. A high thrust density voice-coil actuator with a new structure of double magnetic circuits for CubeSat deployers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 13305–13315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Wu, G.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Duan, Y.; Chen, Z. Design of a coaxial integrated macro–micro composite actuator with long stroke and high precision. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 43501–43513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, S.; Sadighi, A. Digital tracking control of a cylindrical voice-coil actuator. In Proceedings of the 2022 10th RSI International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (ICRoM), Tehran, Iran, 22–24 November 2022; pp. 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shantiaee Zade, S.M.; Robati, M.; Gilani Nejad, M.; Maleki, S.; Sadighi, A. Optimal design and control of a planar voice-coil actuator for micro-positioning applications. In Proceedings of the 2022 10th RSI International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (ICRoM), Tehran, Iran, 22–24 November 2022; pp. 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-P.; Tsai, M.-C.; Fuh, Y.-K. Tiny piezoelectric multi-layered actuators with application in a compact camera module—Design, fabrication, assembling and testing issues. Micromachines 2022, 13, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, J. Contributed Review: Application of Voice-Coil Motors in High-Precision Positioning Stages with Large Travel Ranges. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2015, 86, 101501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majima, Y.; Kuroda, J.; Suzuki, R.; Narita, T.; Kato, H. Performance improvement of gasoline engines using linear actuator: Fundamental consideration of heat effect on thrust characteristics. Proc. Sch. Eng. Tokai Univ. 2021, 46, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Narita, T.; Kato, H.; Uchida, H.T.; Matsumura, Y. Valve Mechanism for Gasoline Engine with Linear Motor. Proc. Sch. Eng. Tokai Univ. 2019, 44, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Liu, B.; Dong, H. Research on air-gap magnetic-field characteristics of trapezoidal Halbach permanent-magnet linear synchronous motor based on improved equivalent surface-current method. Energies 2023, 16, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Lu, Q.; Li, Y. Design criterion and analysis of hybrid-excited vernier reluctance linear machine with slot Halbach PM arrays. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 70, 5074–5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; He, S.; Shao, J.; Ye, B.; Yang, F.; Wang, L. Design and research of a dual-rotor consequent-pole vernier motor with Halbach array. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 53918–53927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consolo, V.; Musolino, A.; Rizzo, R.; Sani, L. Design of a dual Halbach-array tubular linear motor for long stroke and large force. In Proceedings of the 2020 XXV International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Gothenburg, Sweden, 23–26 August 2020; pp. 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arish, N.; Yaghobi, H. Analysis of a new linear dual-stator consequent-pole Halbach-array flux-reversal machine. Int. J. Eng. 2021, 34, 2002–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Ji, J.; Zeng, T.; Zhao, W. Design optimization and comparison of linear magnetic actuators under different topologies. Chin. J. Electr. 2020, 6, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuroda, J.; Ono, R.; Takayama, T.; Kasamatsu, S.; Kobayashi, I.; Uchino, D.; Ogawa, K.; Kato, T.; Ikeda, K.; Endo, A.; et al. Dual Halbach Array Compact Linear Actuator with Thrust Characteristics Part I Simulation Result. Actuators 2025, 14, 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14100476
Kuroda J, Ono R, Takayama T, Kasamatsu S, Kobayashi I, Uchino D, Ogawa K, Kato T, Ikeda K, Endo A, et al. Dual Halbach Array Compact Linear Actuator with Thrust Characteristics Part I Simulation Result. Actuators. 2025; 14(10):476. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14100476
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuroda, Jumpei, Ryutaro Ono, Takumu Takayama, Shinobu Kasamatsu, Ikkei Kobayashi, Daigo Uchino, Kazuki Ogawa, Taro Kato, Keigo Ikeda, Ayato Endo, and et al. 2025. "Dual Halbach Array Compact Linear Actuator with Thrust Characteristics Part I Simulation Result" Actuators 14, no. 10: 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14100476
APA StyleKuroda, J., Ono, R., Takayama, T., Kasamatsu, S., Kobayashi, I., Uchino, D., Ogawa, K., Kato, T., Ikeda, K., Endo, A., Kato, H., & Narita, T. (2025). Dual Halbach Array Compact Linear Actuator with Thrust Characteristics Part I Simulation Result. Actuators, 14(10), 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14100476





