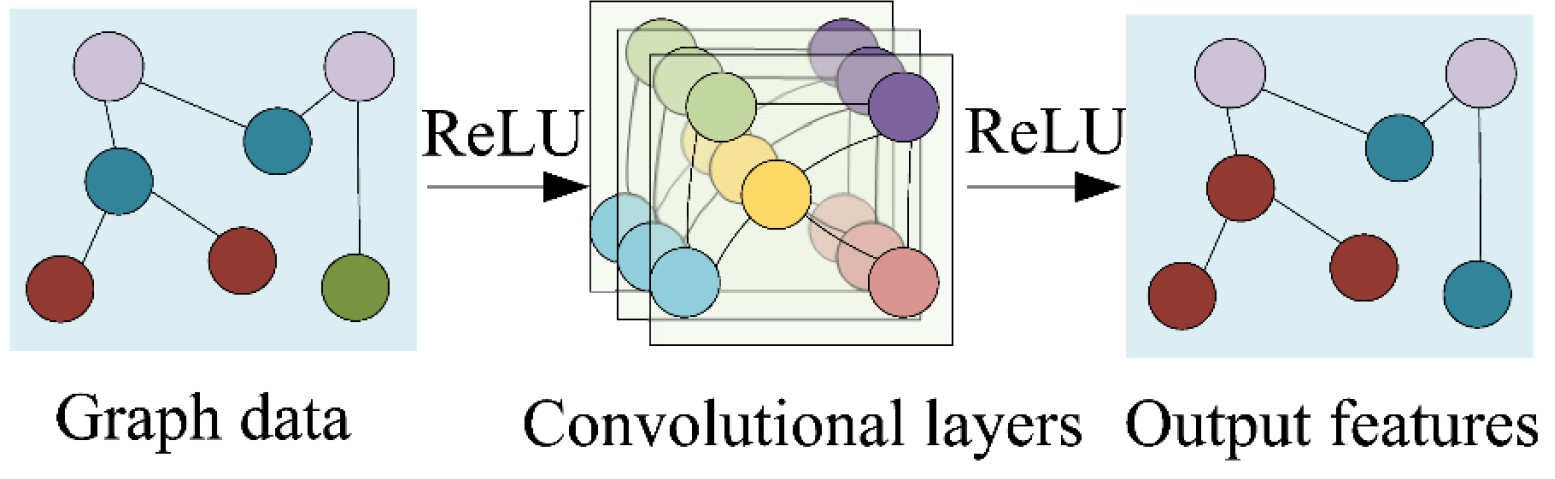
Figure 1.
The network diagram of GCN with graph data, convolutional layers, and output features.
Figure 1.
The network diagram of GCN with graph data, convolutional layers, and output features.
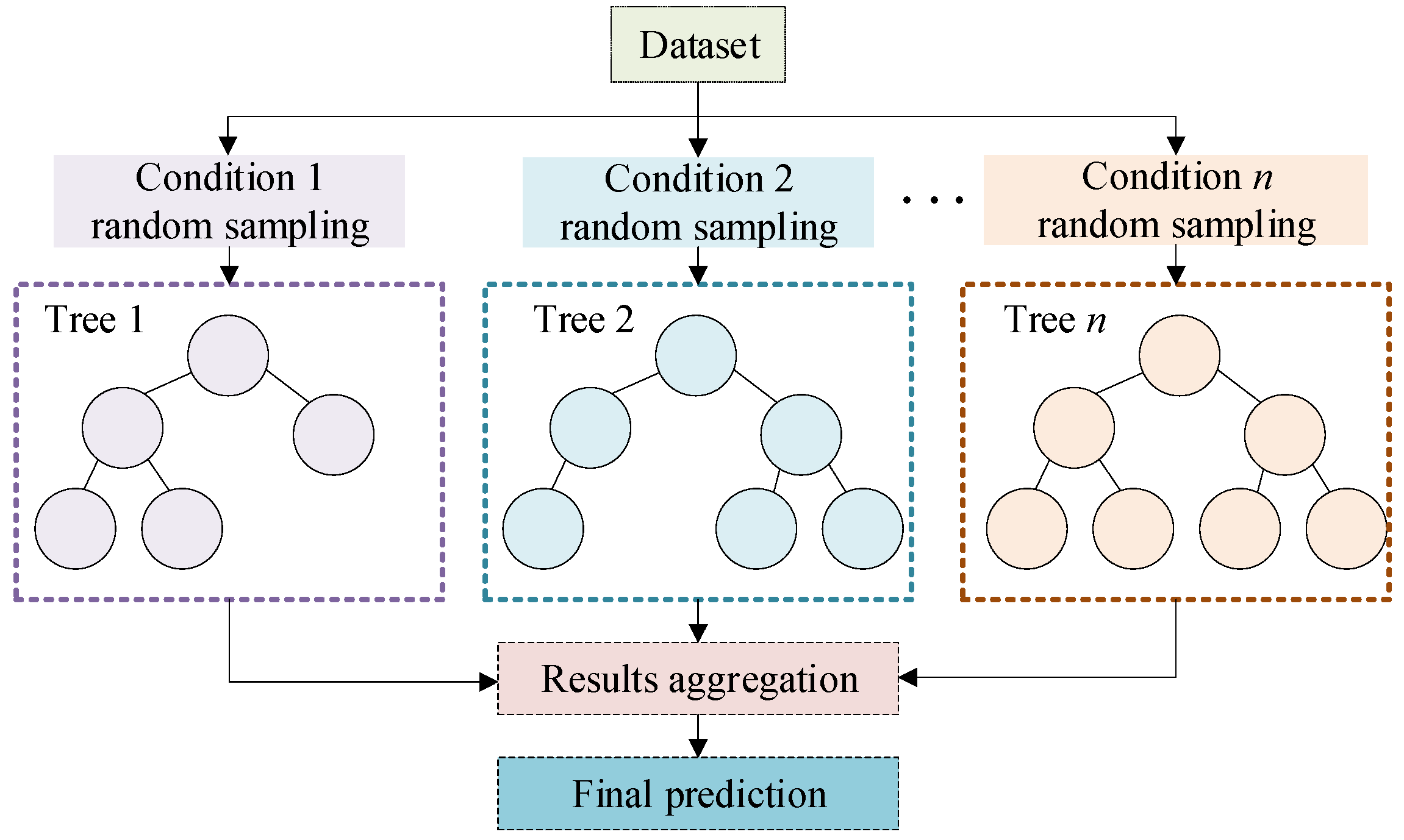
Figure 2.
RF network architecture diagram with random sampling, decision tree construction, results aggregation, and final prediction.
Figure 2.
RF network architecture diagram with random sampling, decision tree construction, results aggregation, and final prediction.
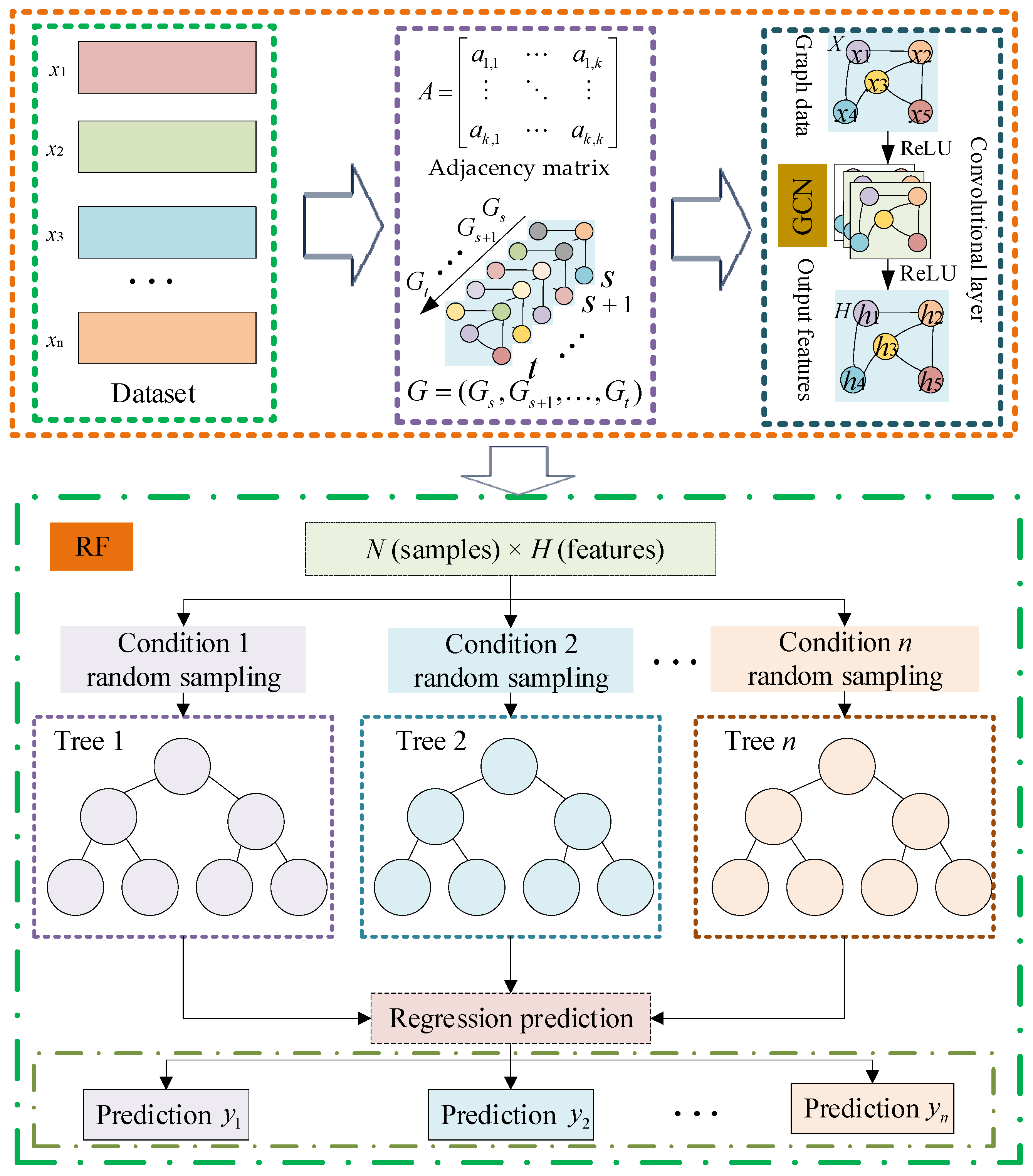
Figure 3.
GCN–RF architecture diagram with graph data feature extraction and regression prediction.
Figure 3.
GCN–RF architecture diagram with graph data feature extraction and regression prediction.
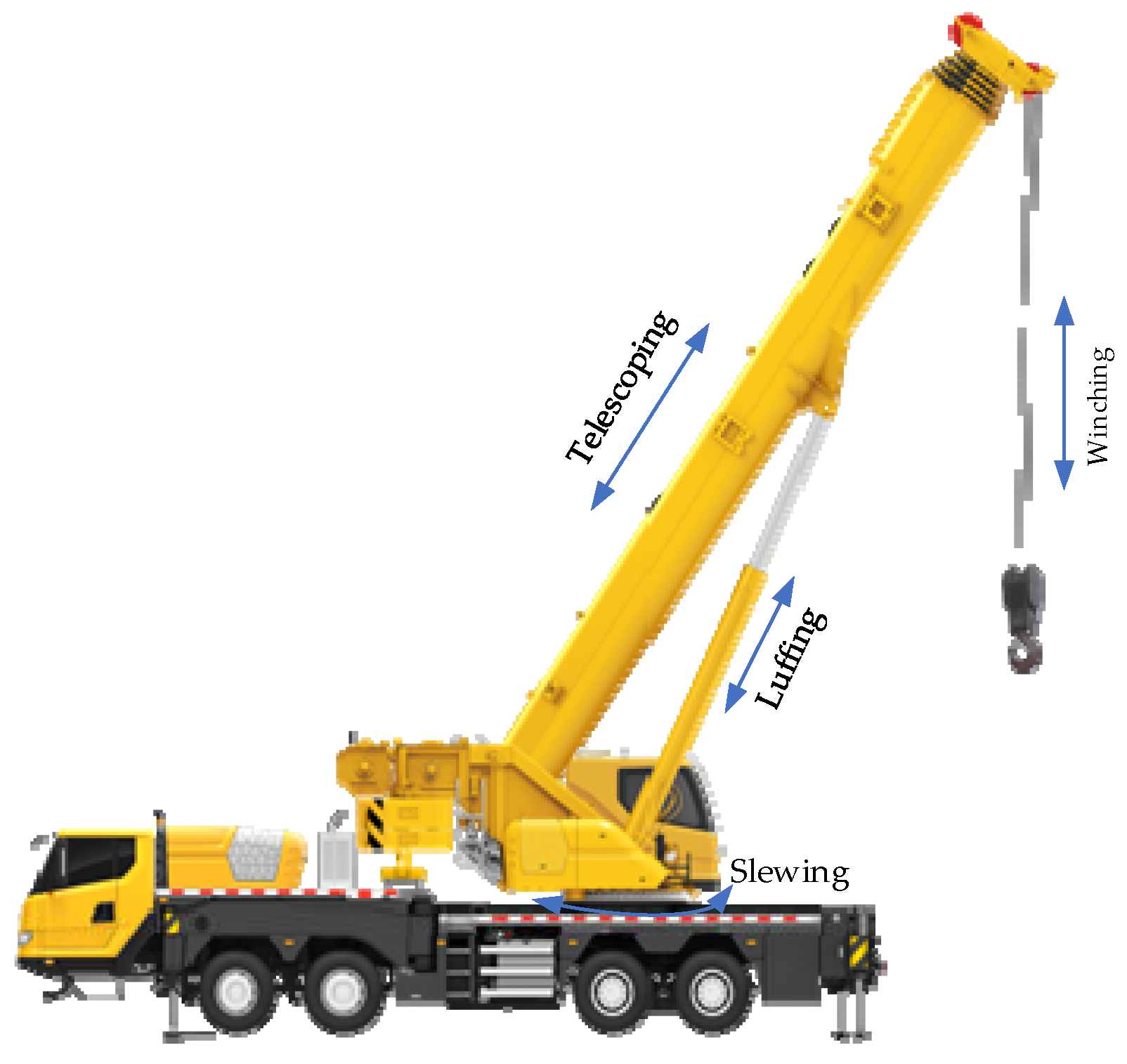
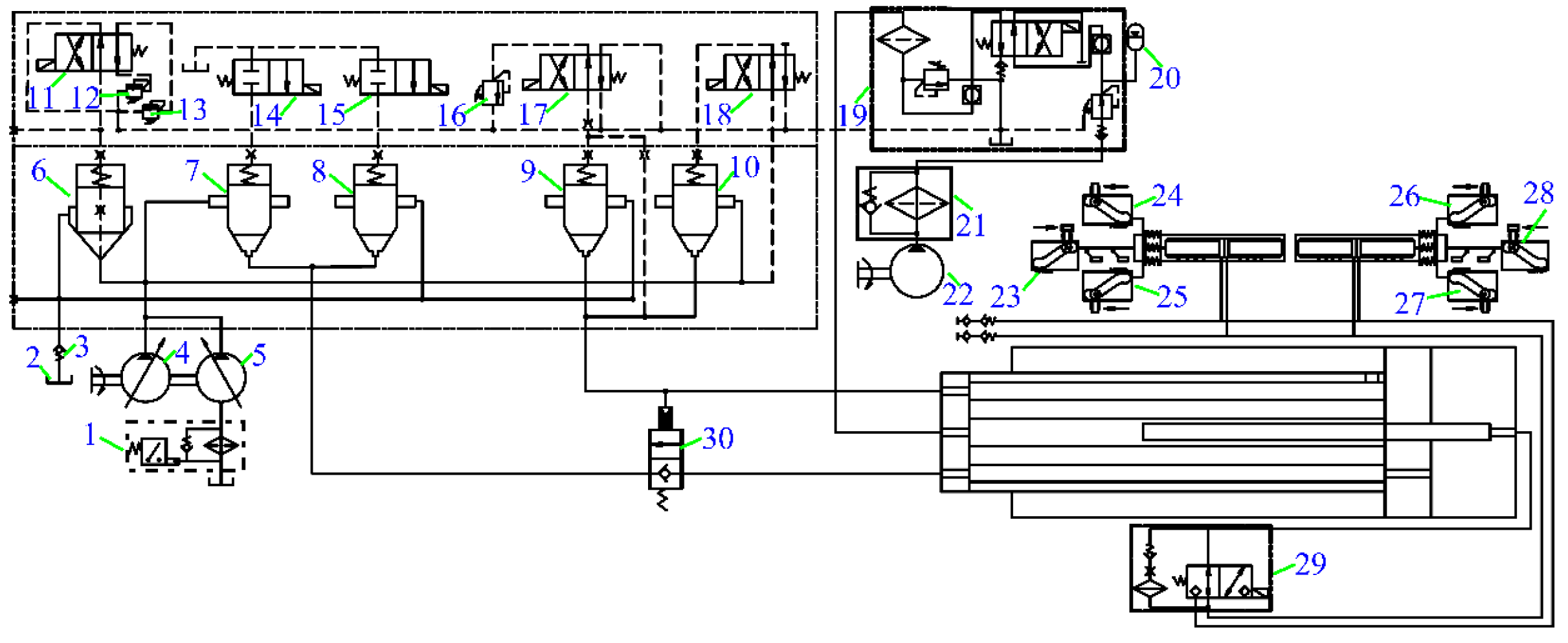
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of the truck crane working systems: luffing, slewing, telescoping, and winching systems.
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of the truck crane working systems: luffing, slewing, telescoping, and winching systems.
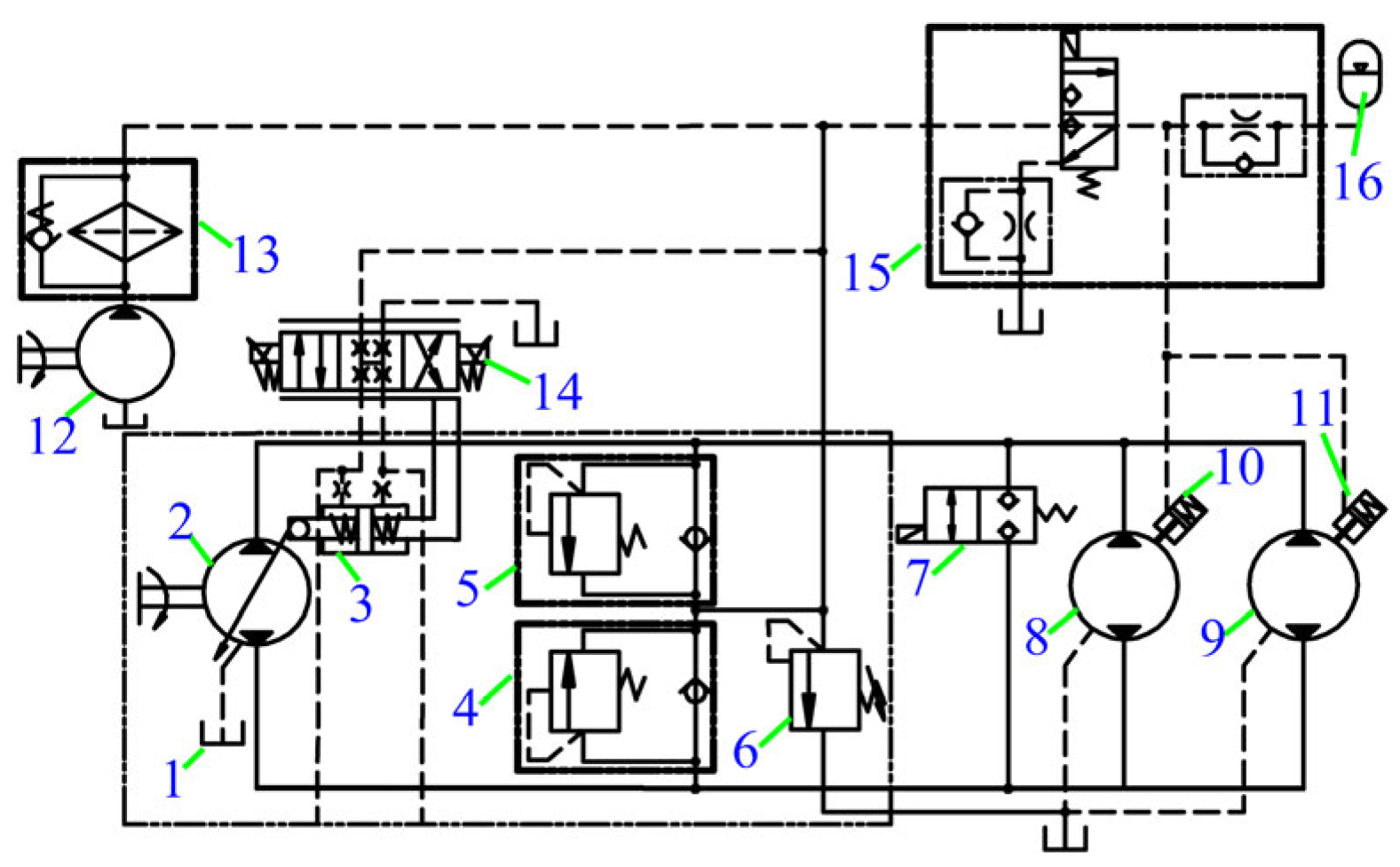
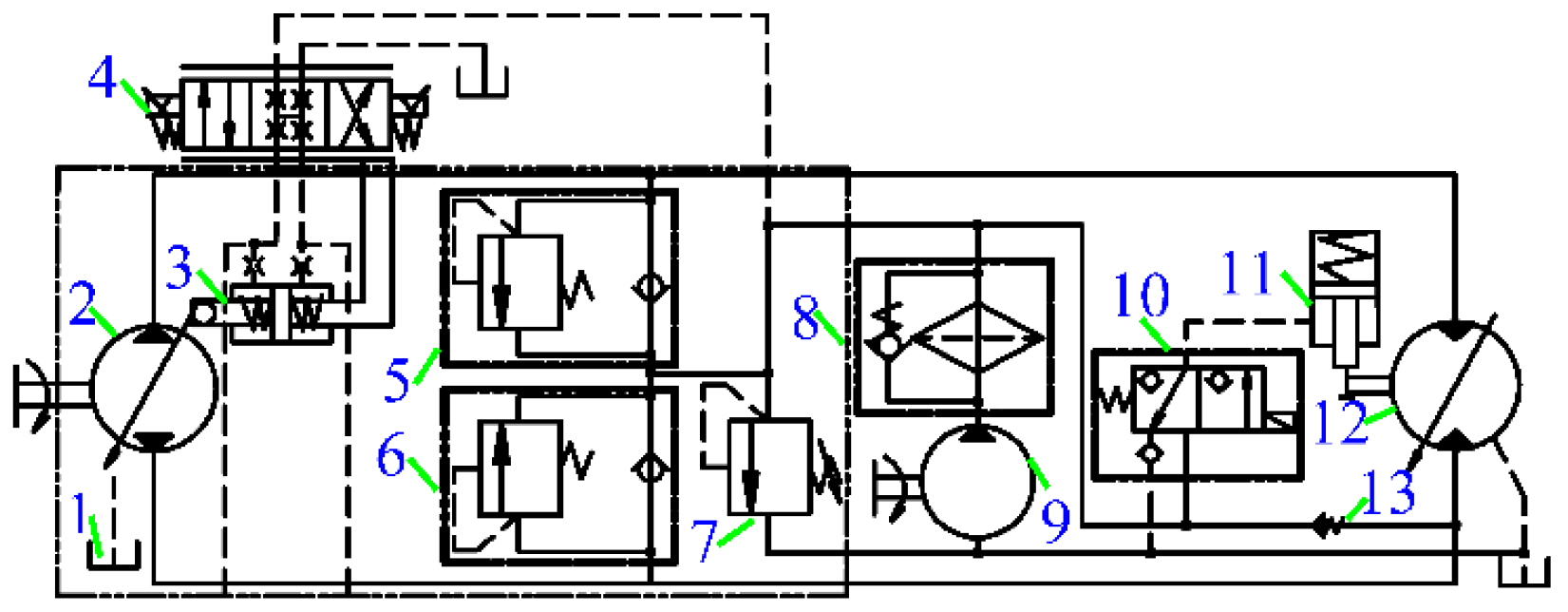
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of the slewing hydraulic system ((1) oil tank; (2) pump; (3) variable mechanism; (4,5) slewing balance valve; (6) overflow valve; (7) free sliding valve; (8,9) slewing motor; (10,11) brake; (12) pilot pump; (13) filter; (14) reversing valve; (15) slewing brake control valve; (16) accumulator).
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of the slewing hydraulic system ((1) oil tank; (2) pump; (3) variable mechanism; (4,5) slewing balance valve; (6) overflow valve; (7) free sliding valve; (8,9) slewing motor; (10,11) brake; (12) pilot pump; (13) filter; (14) reversing valve; (15) slewing brake control valve; (16) accumulator).
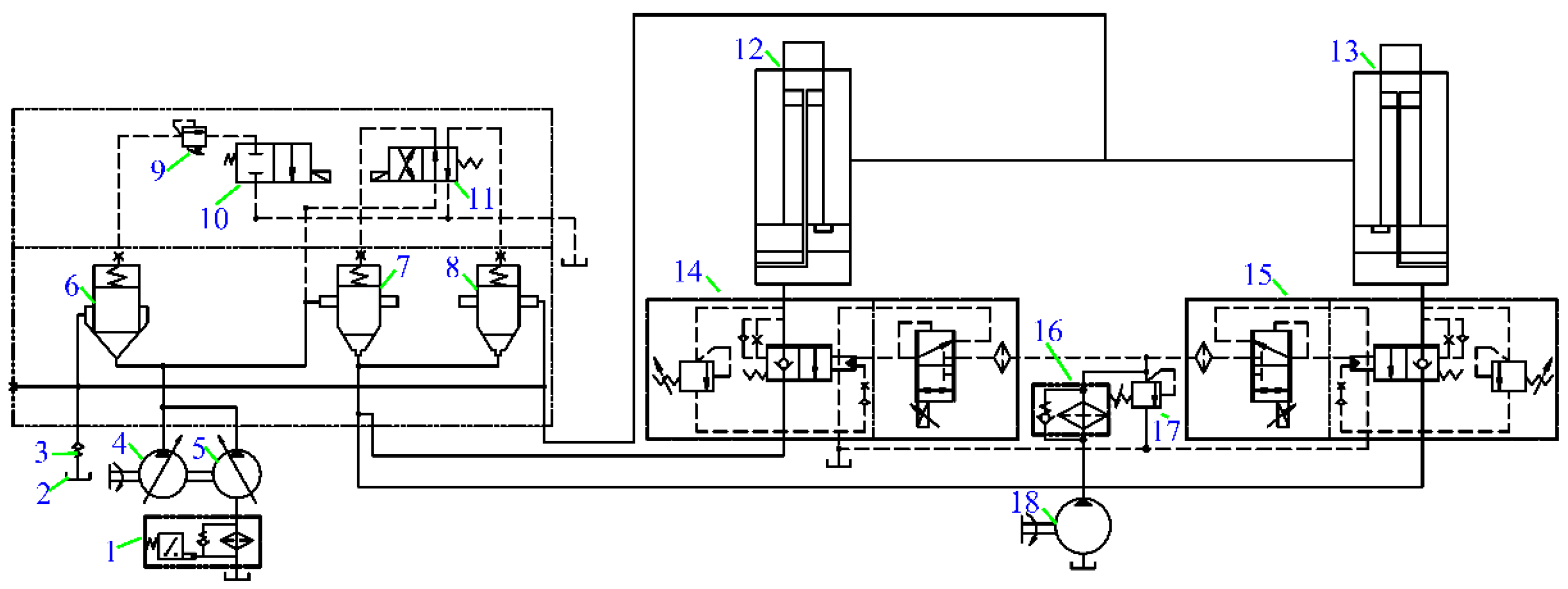
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram of the telescopic hydraulic system ((1) 21 filter; (2) oil tank; (3) check valve; (4,5) pump; (6–10) cartridge valve; (11,17,18) two-position four-way solenoid valve; (12,13,16) overflow valve; (14,15) two-position two-way solenoid valve; (19) cylinder arm pin control valve; (20) accumulator; (22) pilot pump; (23,28) arm pin; (24,26) right cylinder pin; (25,27) left cylinder pin; (29) cylinder arm pin solenoid valve; (30) balance valve).
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram of the telescopic hydraulic system ((1) 21 filter; (2) oil tank; (3) check valve; (4,5) pump; (6–10) cartridge valve; (11,17,18) two-position four-way solenoid valve; (12,13,16) overflow valve; (14,15) two-position two-way solenoid valve; (19) cylinder arm pin control valve; (20) accumulator; (22) pilot pump; (23,28) arm pin; (24,26) right cylinder pin; (25,27) left cylinder pin; (29) cylinder arm pin solenoid valve; (30) balance valve).
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of the winch hydraulic system ((1) oil tank; (2) pump; (3) variable mechanism; (4) reversing valve; (5,6) winch balance valve; (7) overflow valve; (8) filter; (9) pilot pump; (10) brake control valve; (11) brake; (12) lifting motor; (13) check valve).
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of the winch hydraulic system ((1) oil tank; (2) pump; (3) variable mechanism; (4) reversing valve; (5,6) winch balance valve; (7) overflow valve; (8) filter; (9) pilot pump; (10) brake control valve; (11) brake; (12) lifting motor; (13) check valve).
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram of the luffing hydraulic system ((1) 16 filter; (2) oil tank; (3) check valve; (4,5) pump; (6–8) cartridge valve; (9,17) overflow valve; (10) two-position two-way solenoid valve, (11) two-position four-way solenoid valve; (12,13) luffing oil cylinder; (14,15) luffing balance valve; (18) pilot pump).
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram of the luffing hydraulic system ((1) 16 filter; (2) oil tank; (3) check valve; (4,5) pump; (6–8) cartridge valve; (9,17) overflow valve; (10) two-position two-way solenoid valve, (11) two-position four-way solenoid valve; (12,13) luffing oil cylinder; (14,15) luffing balance valve; (18) pilot pump).
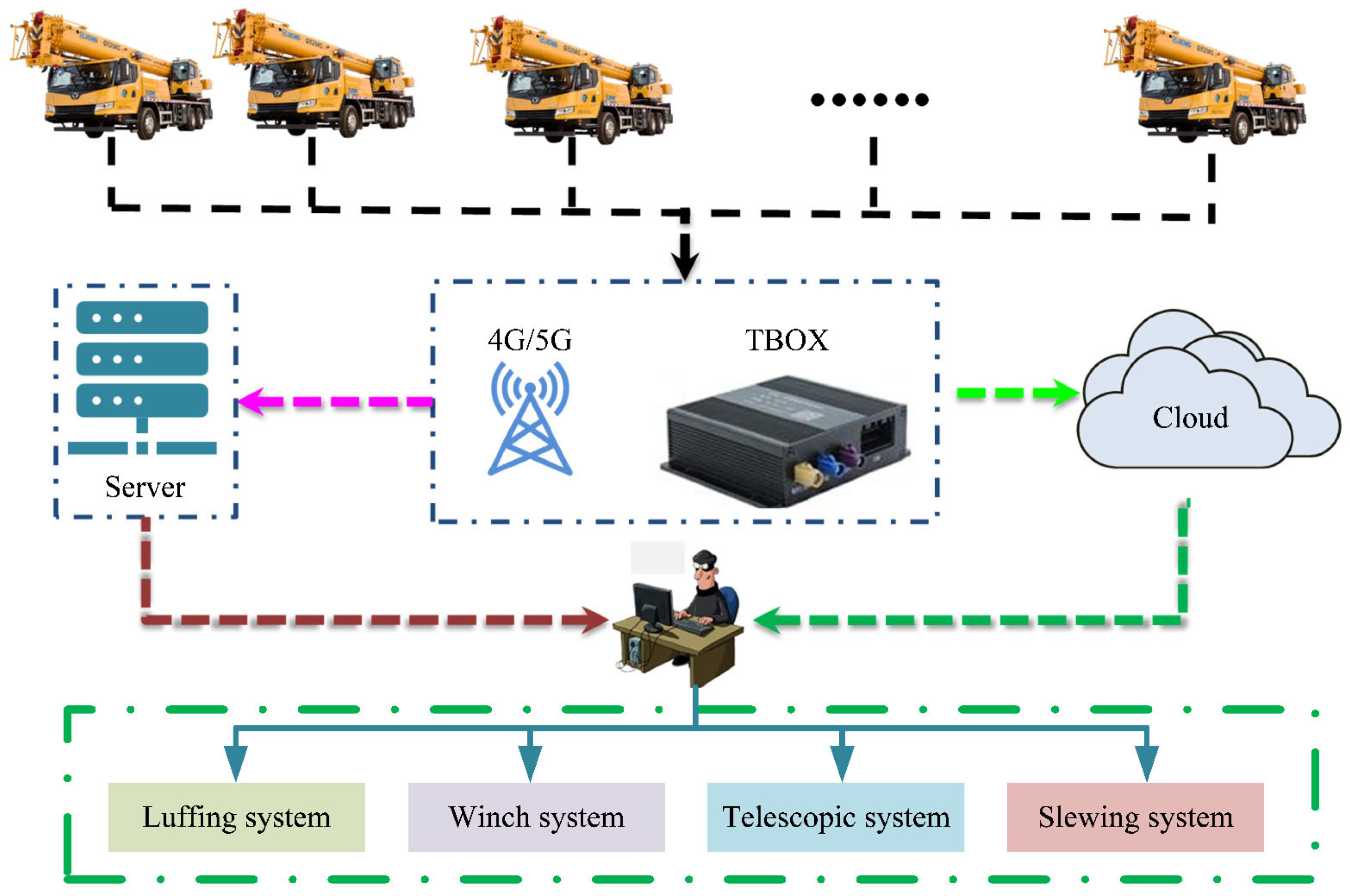
Figure 9.
Schematic diagram of data acquisition.
Figure 9.
Schematic diagram of data acquisition.
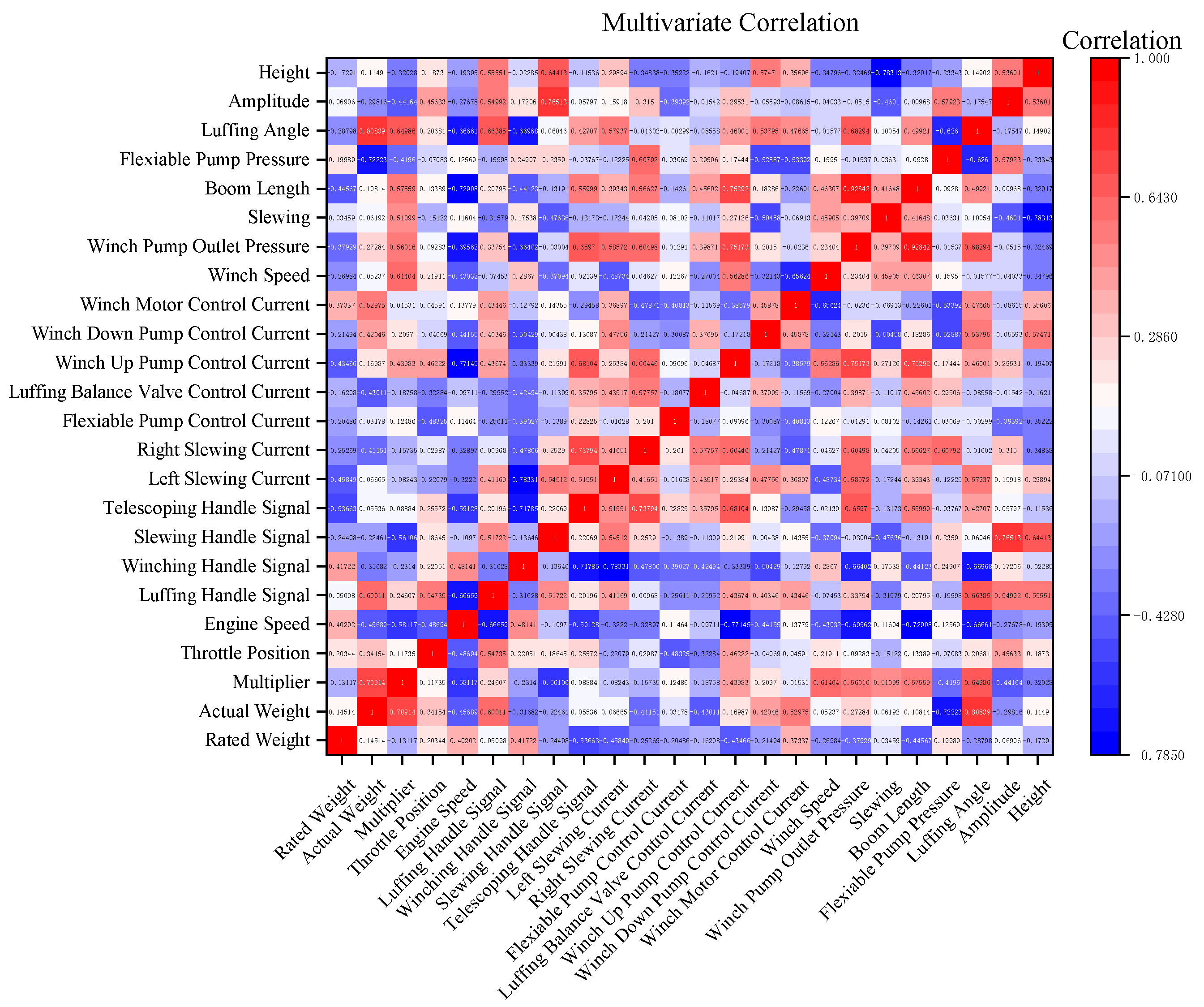
Figure 10.
The correlation between target variables and input variables based on GCN.
Figure 10.
The correlation between target variables and input variables based on GCN.
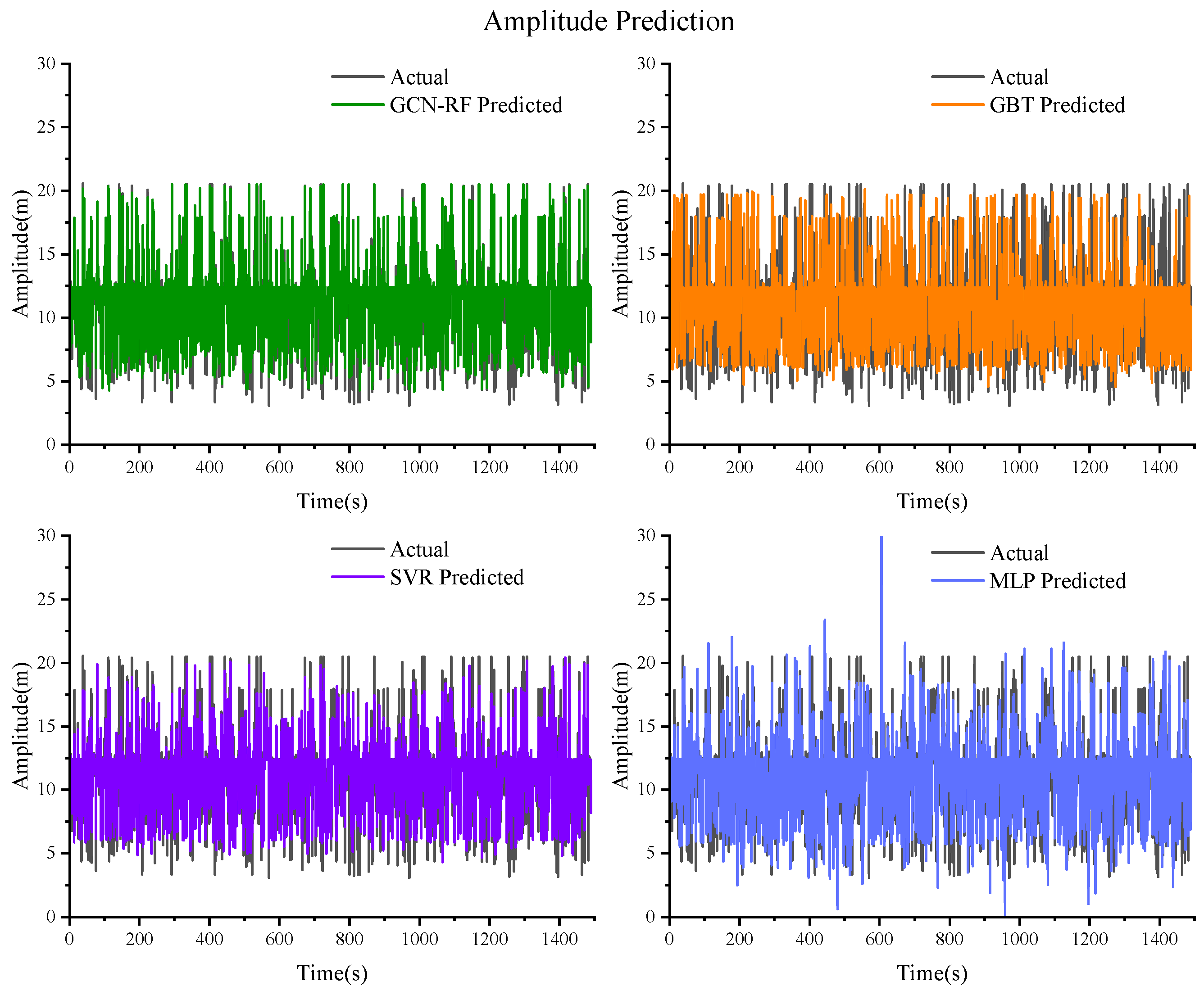
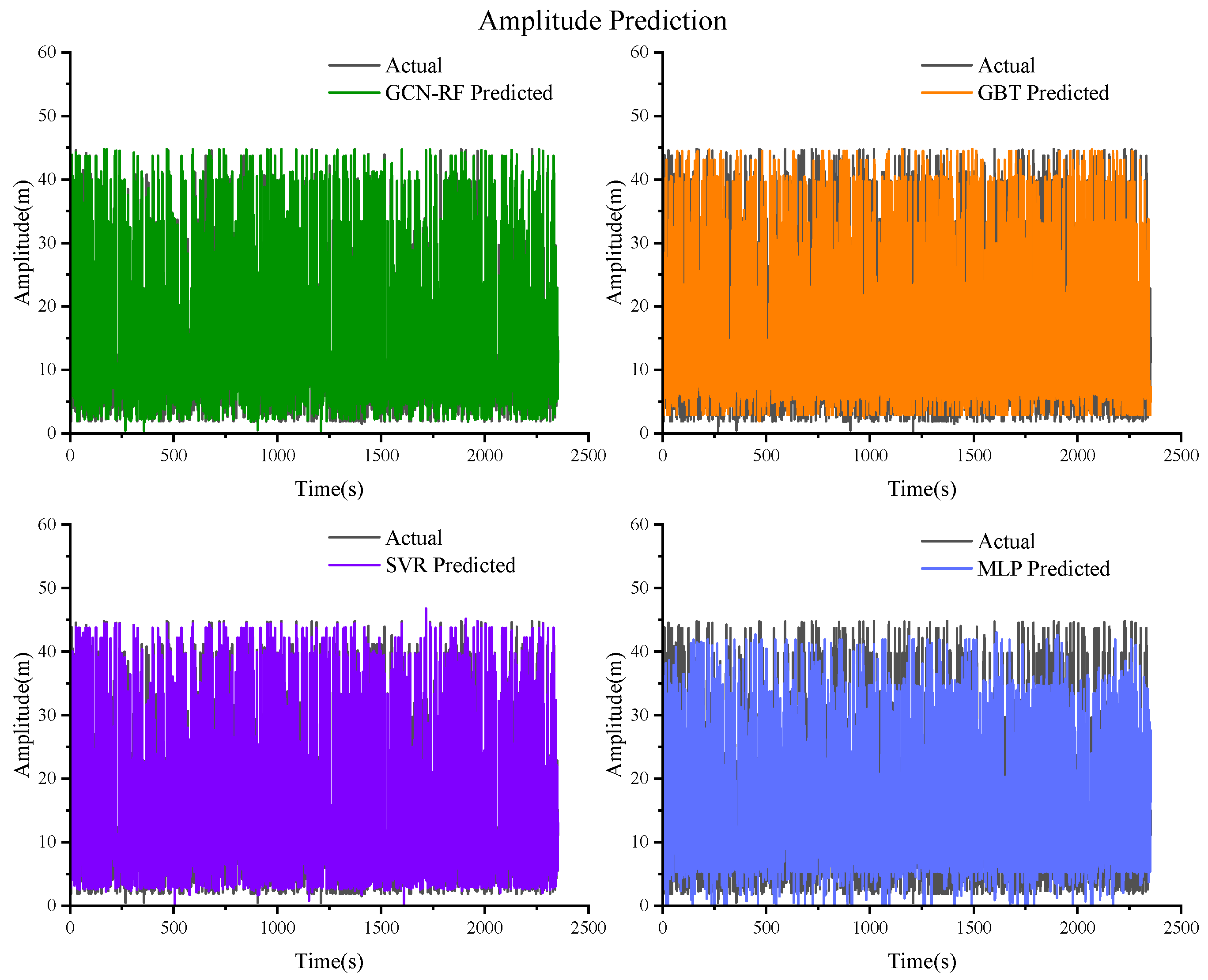
Figure 11.
Prediction results of the amplitude based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 11.
Prediction results of the amplitude based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
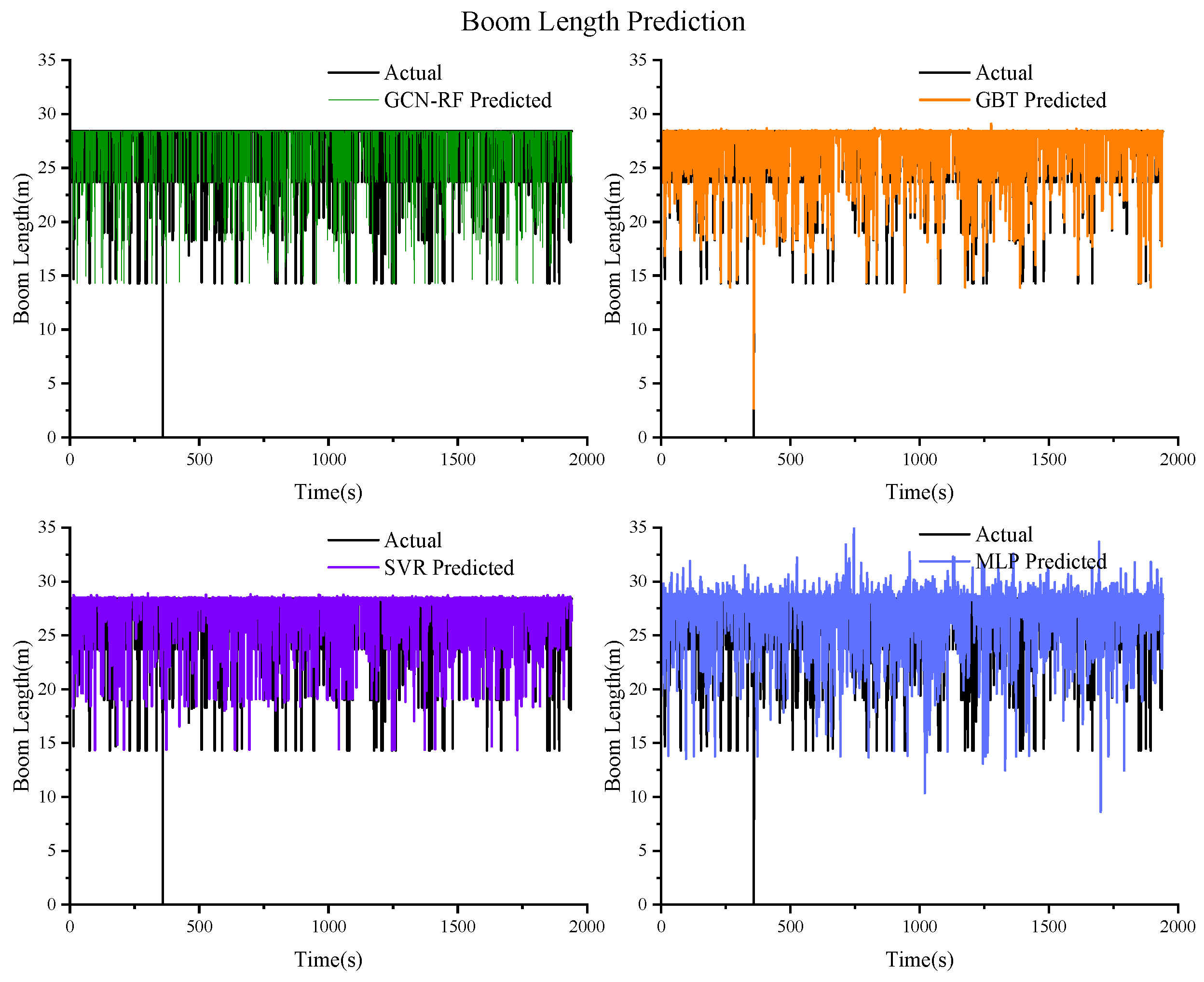
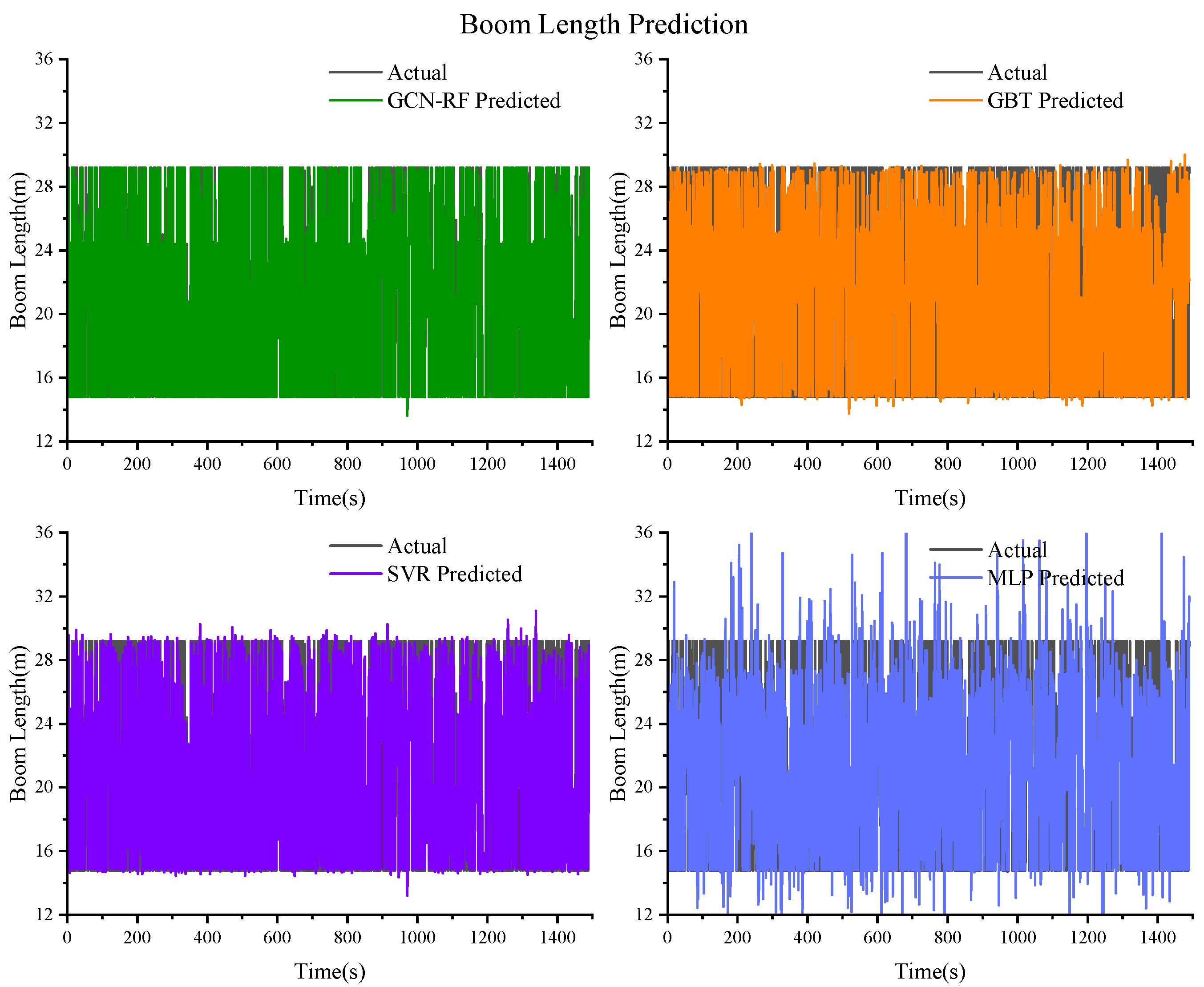
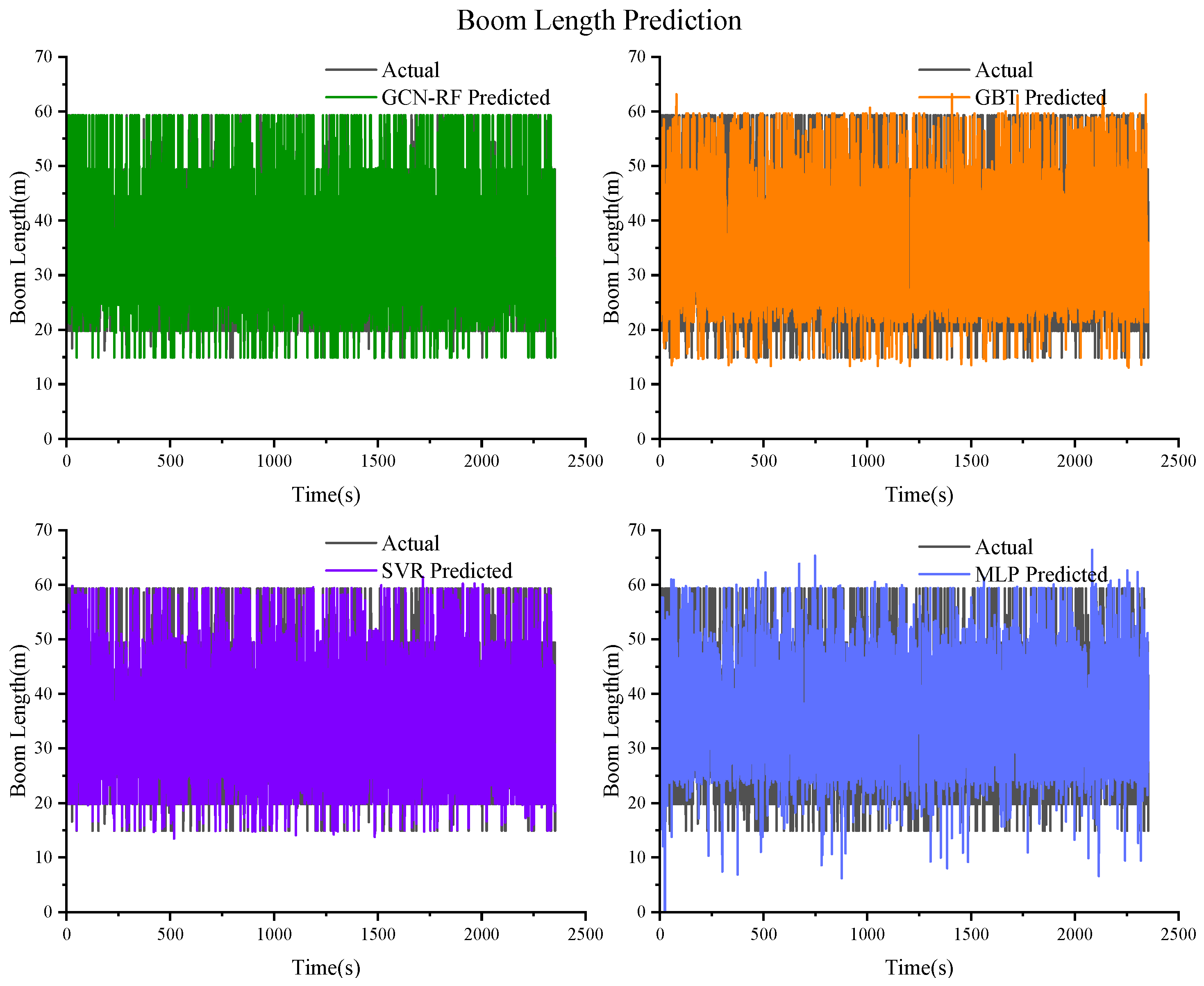
Figure 12.
Prediction results of the boom length based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 12.
Prediction results of the boom length based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
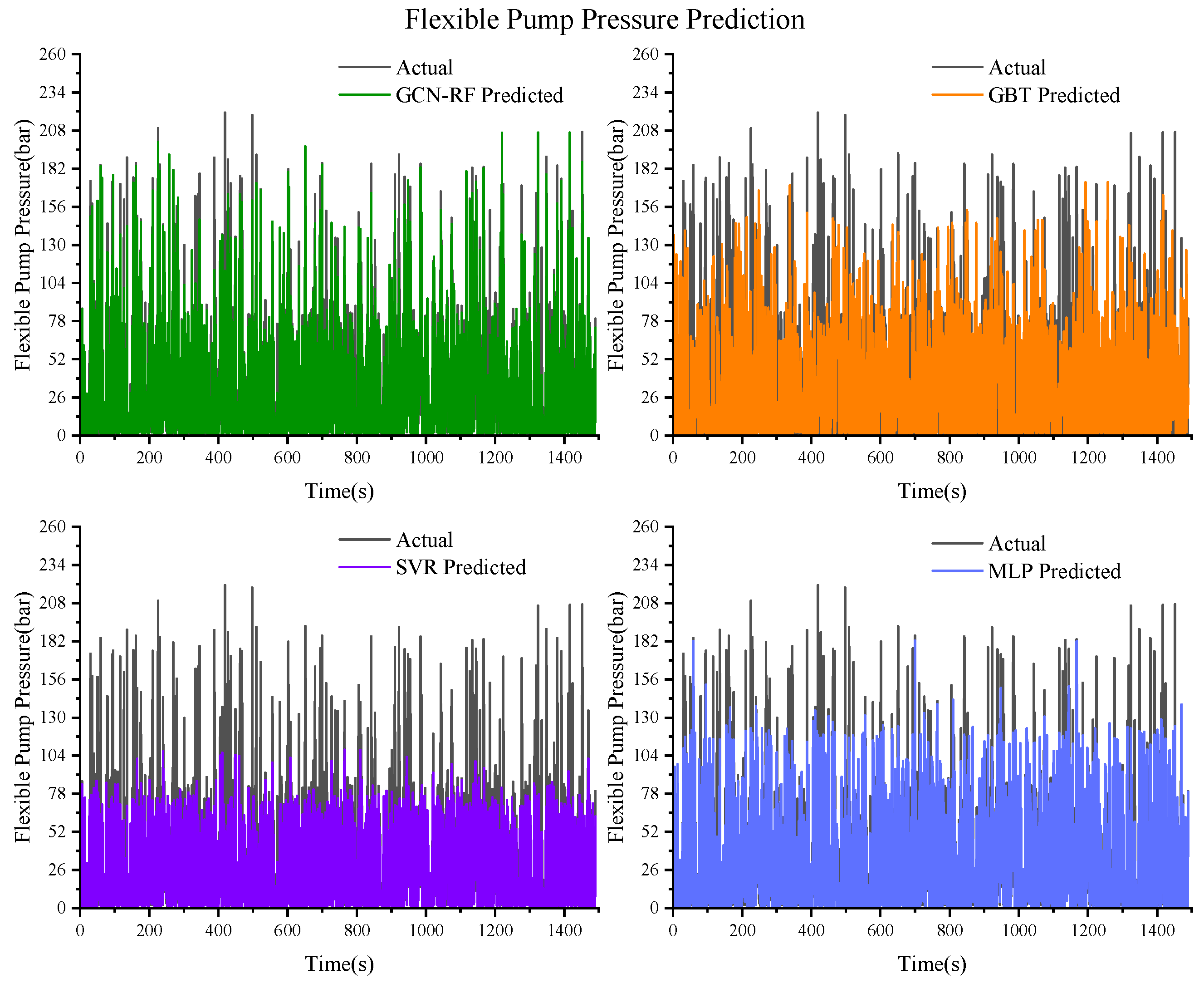
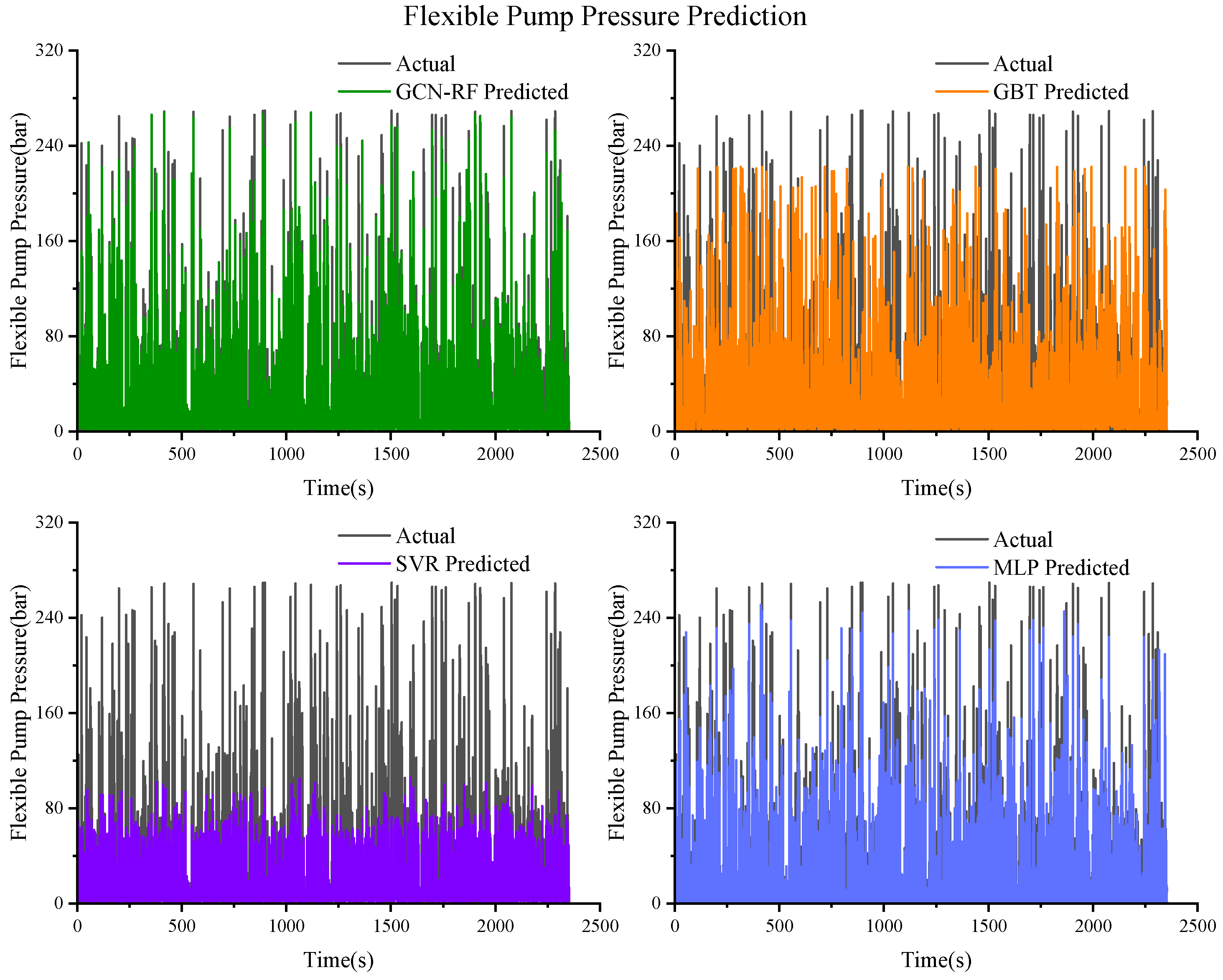
Figure 13.
Prediction results of the flexible pump pressure based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 13.
Prediction results of the flexible pump pressure based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
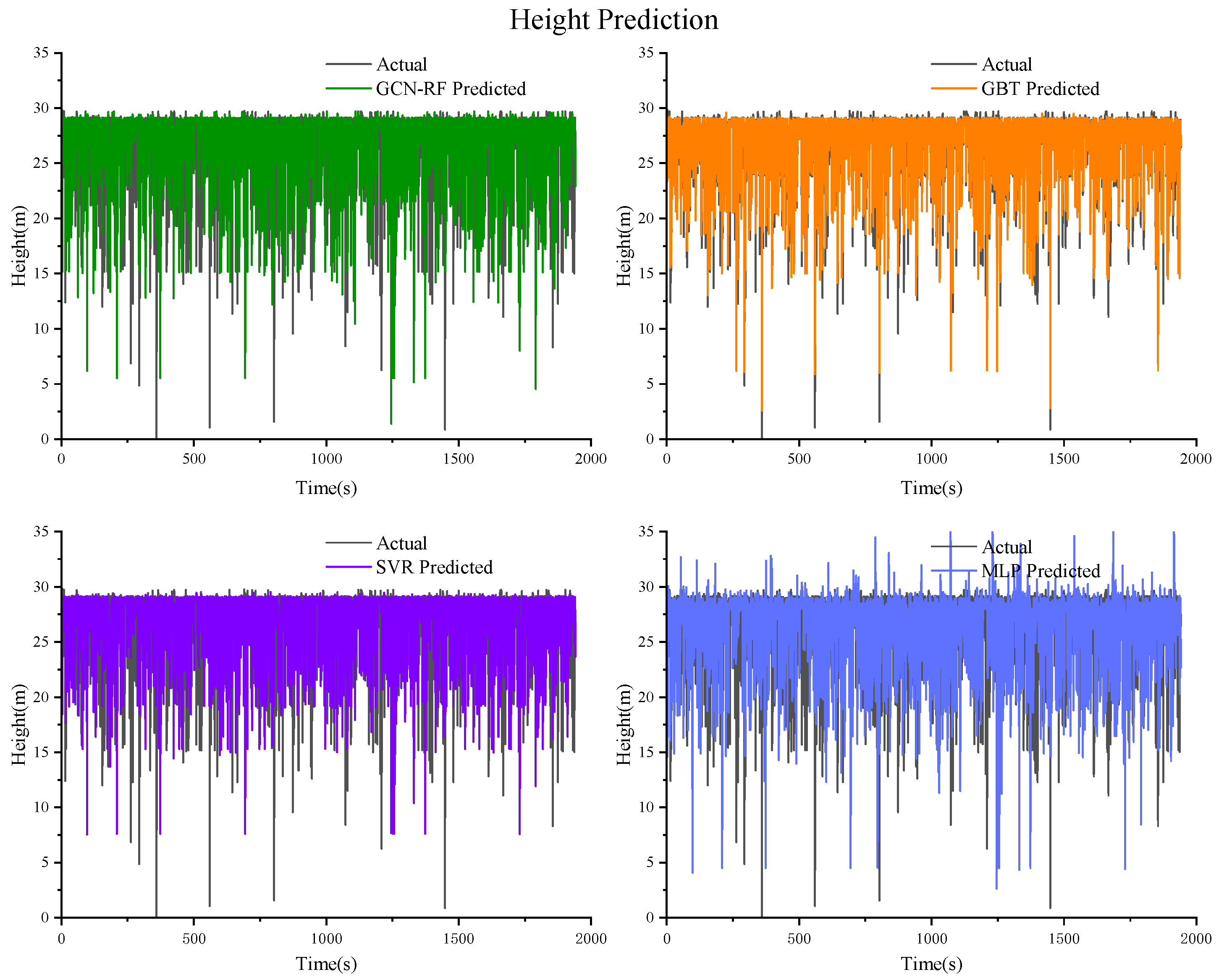
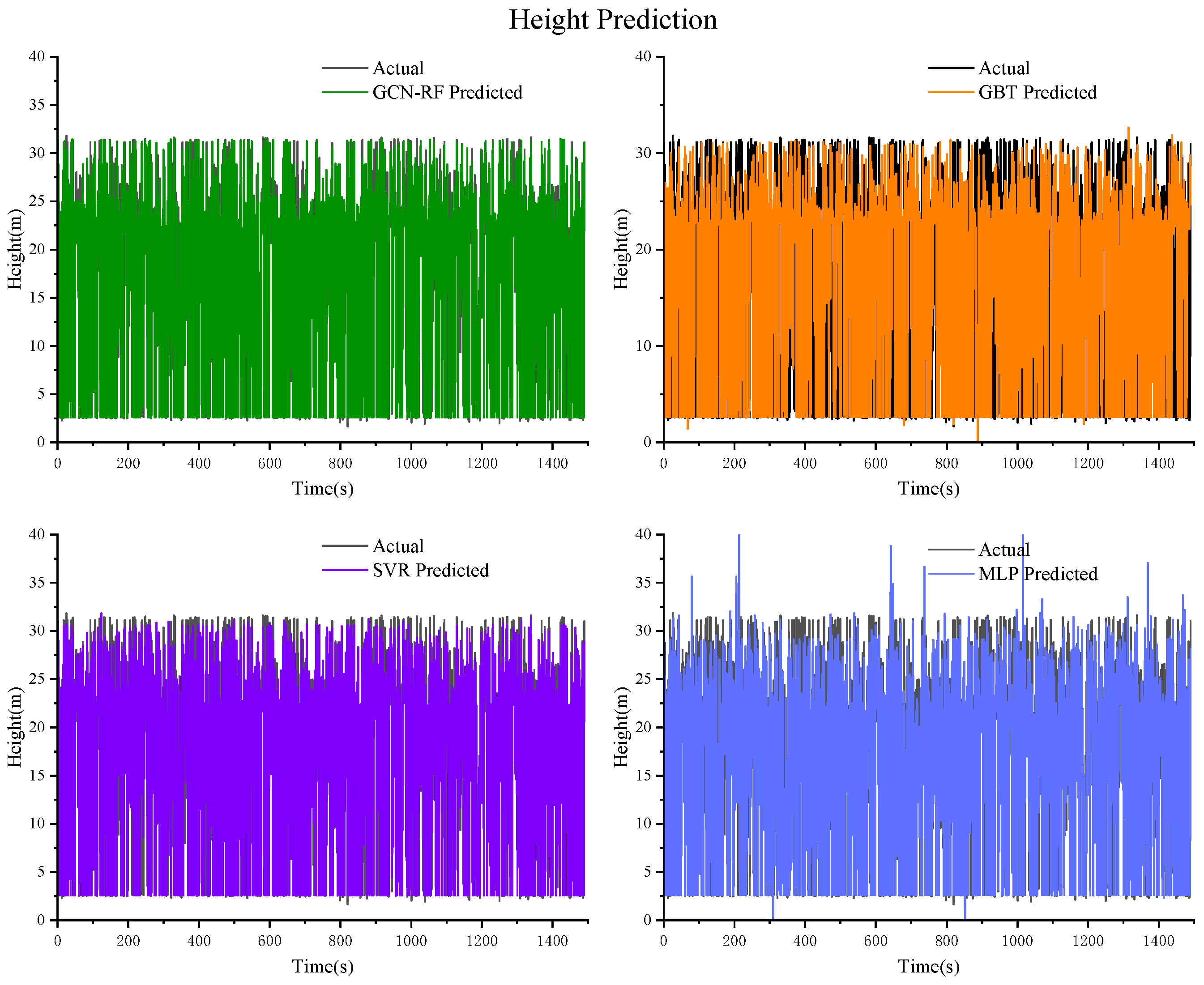
Figure 14.
Prediction results of the height based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 14.
Prediction results of the height based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
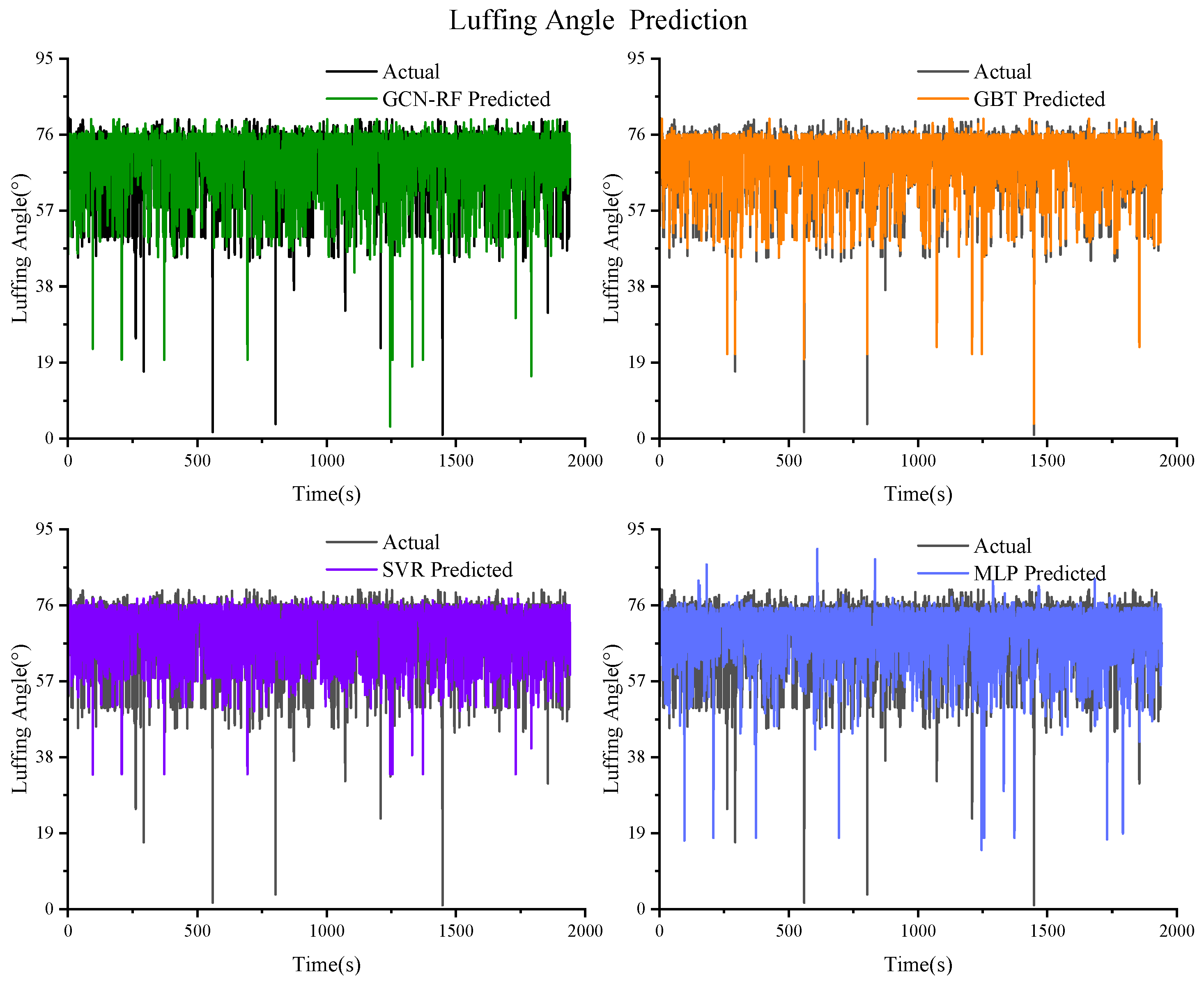
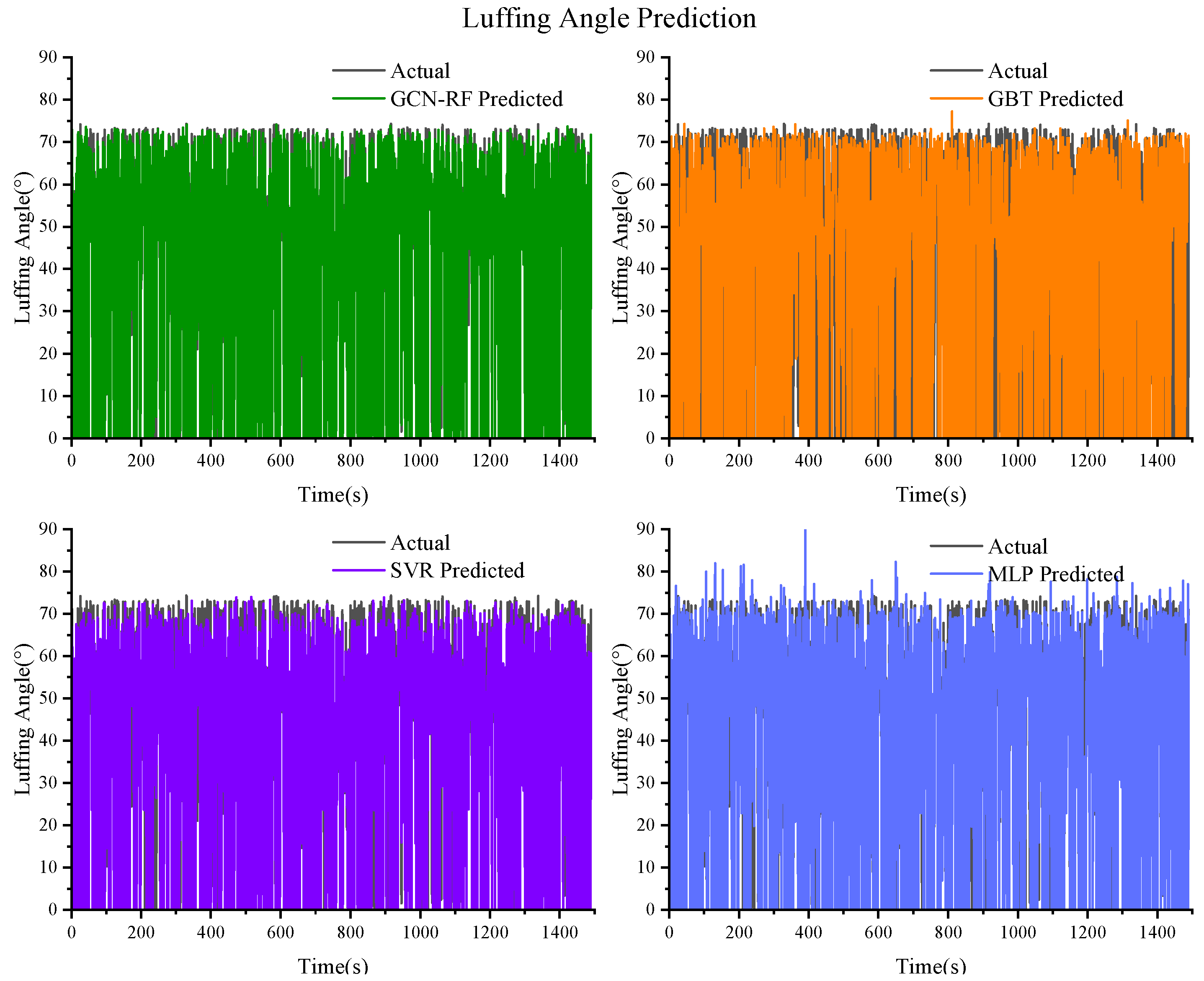
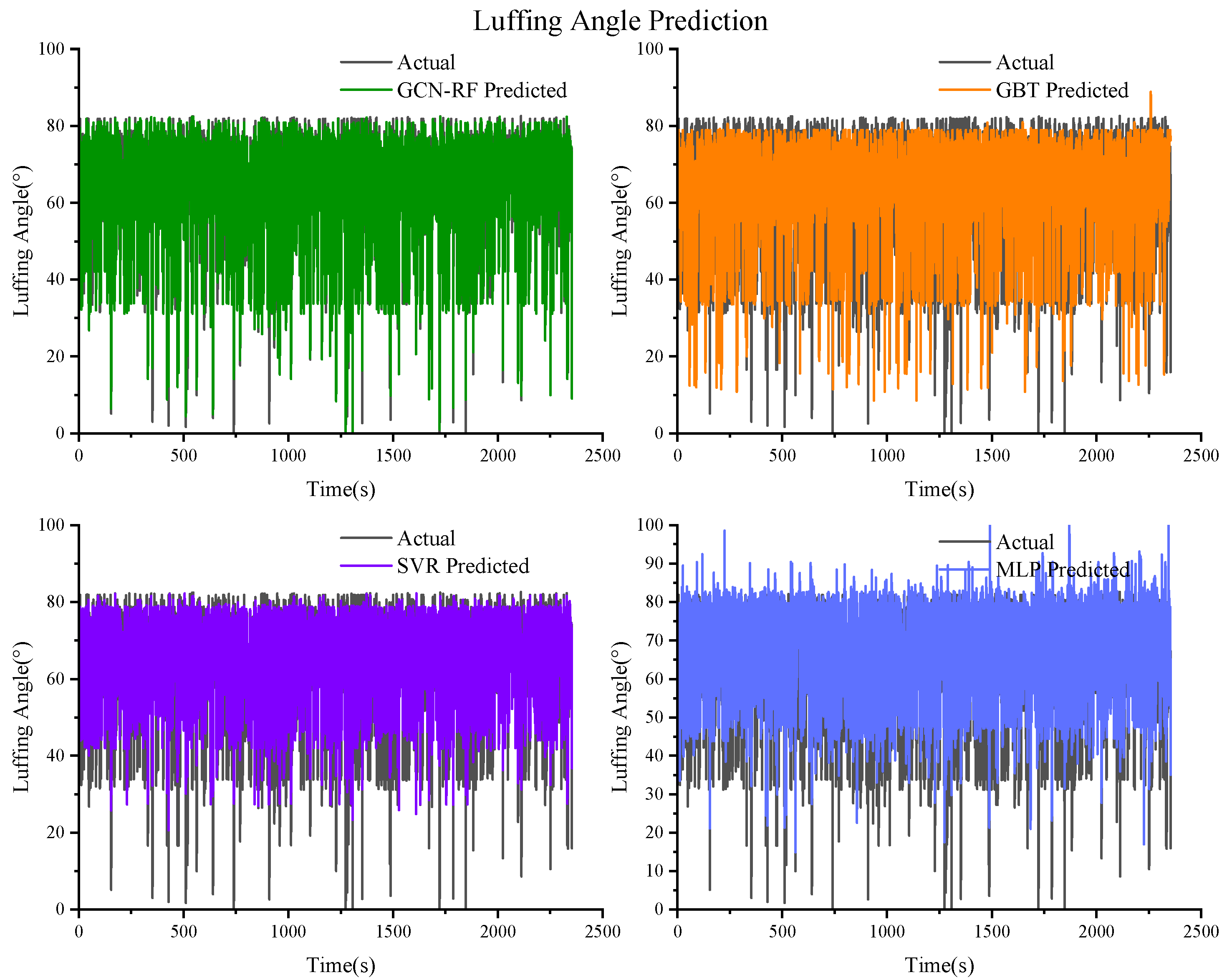
Figure 15.
Prediction results of the luffing angle based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 15.
Prediction results of the luffing angle based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
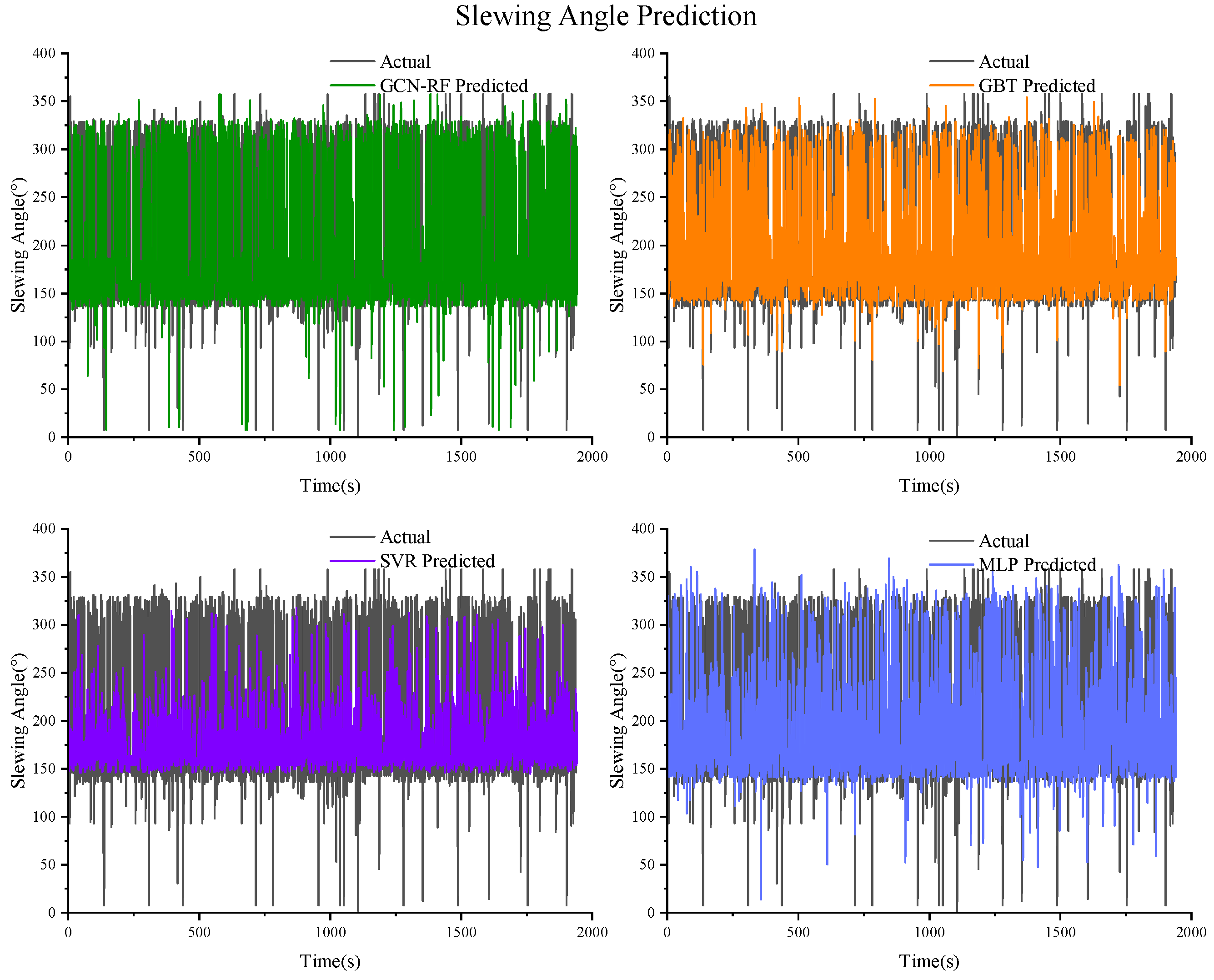
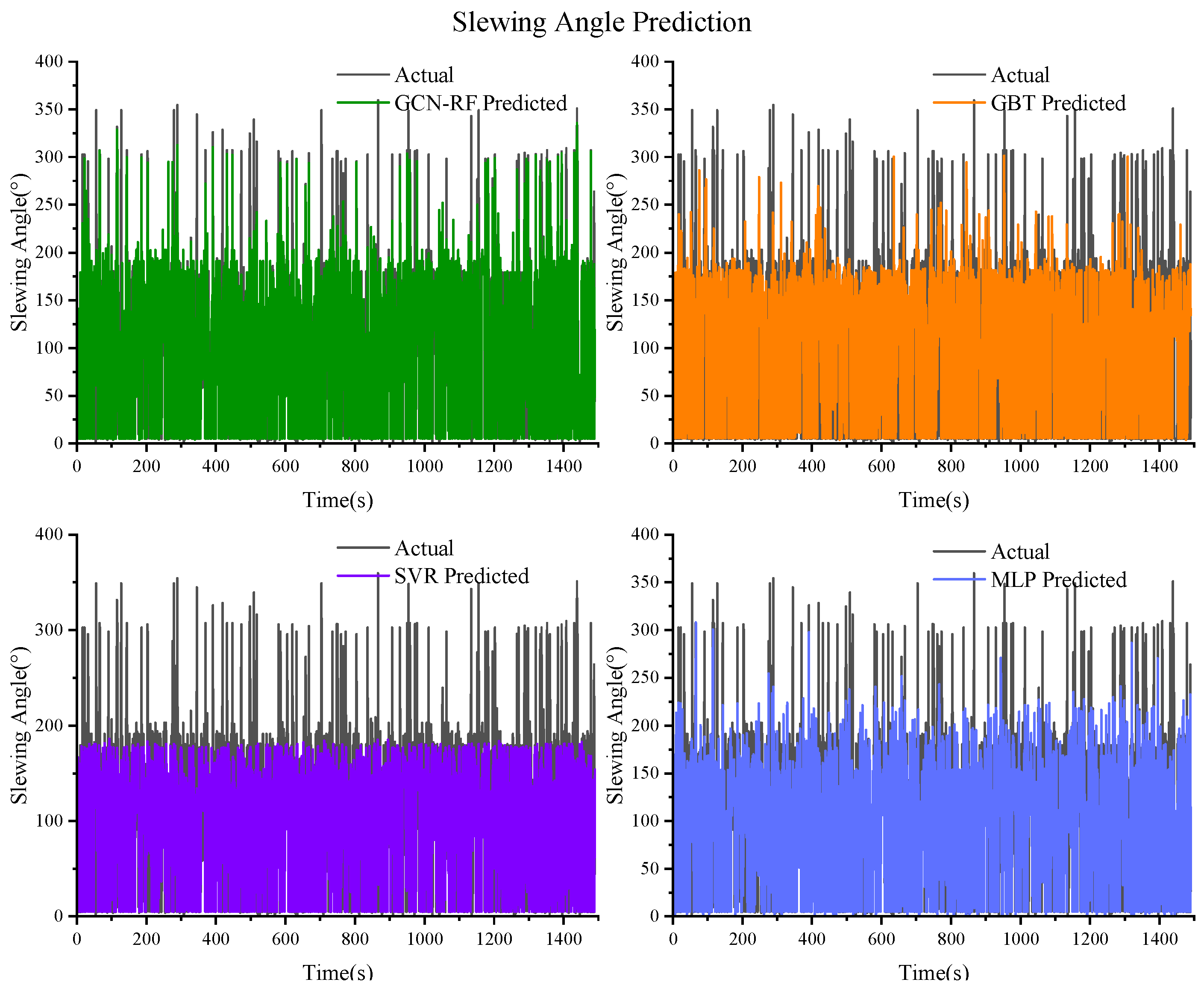
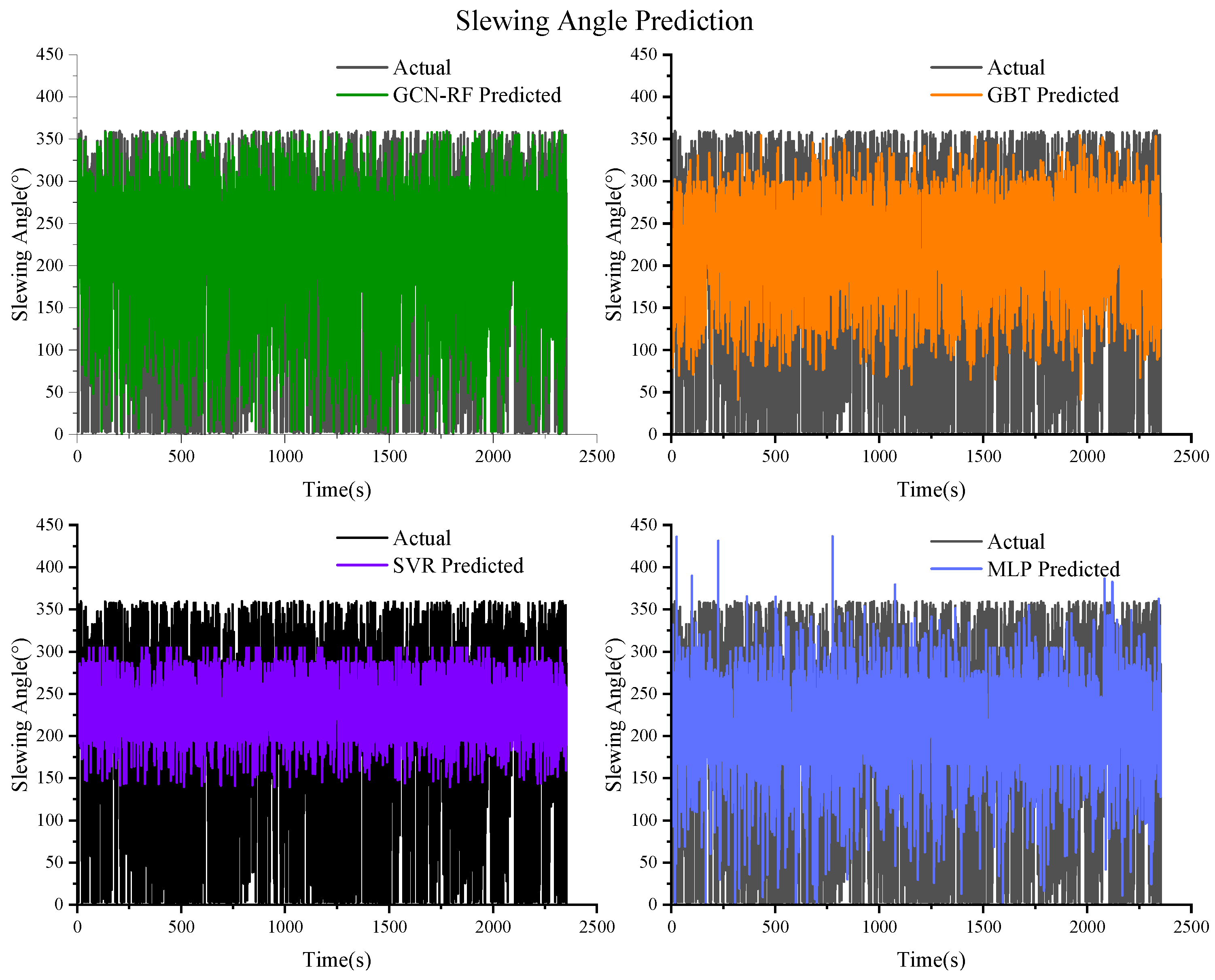
Figure 16.
Prediction results of the slewing angle based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 16.
Prediction results of the slewing angle based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
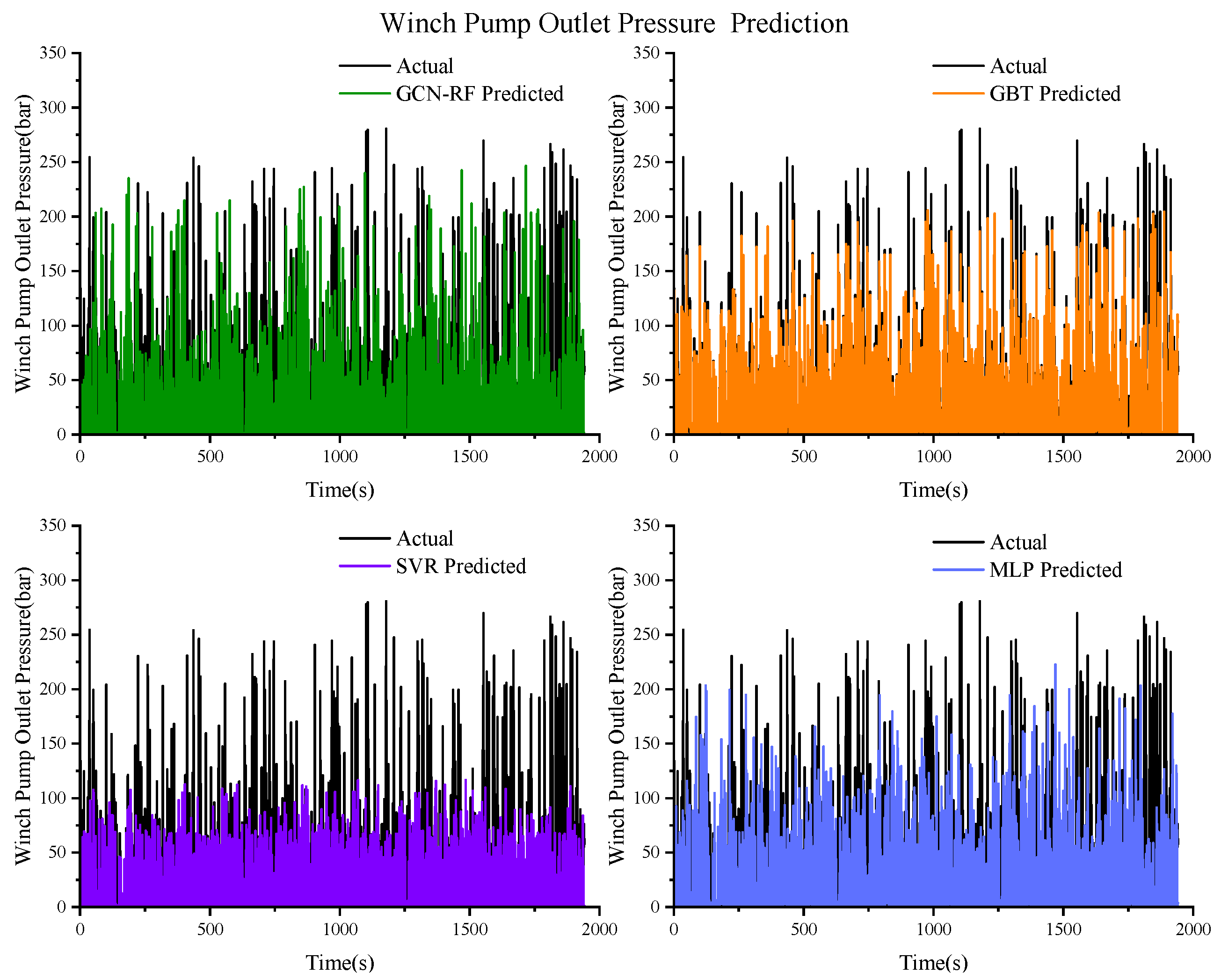
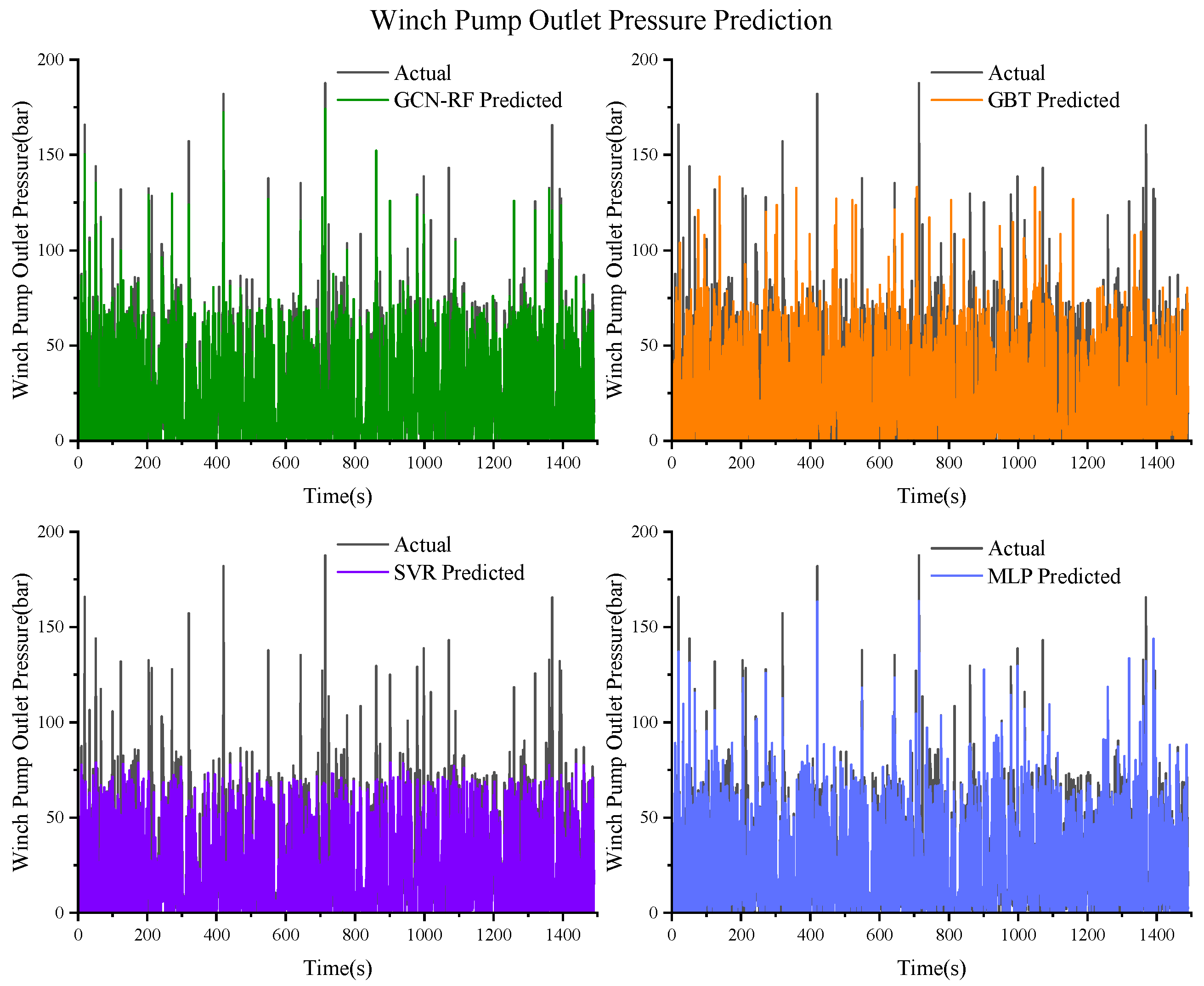
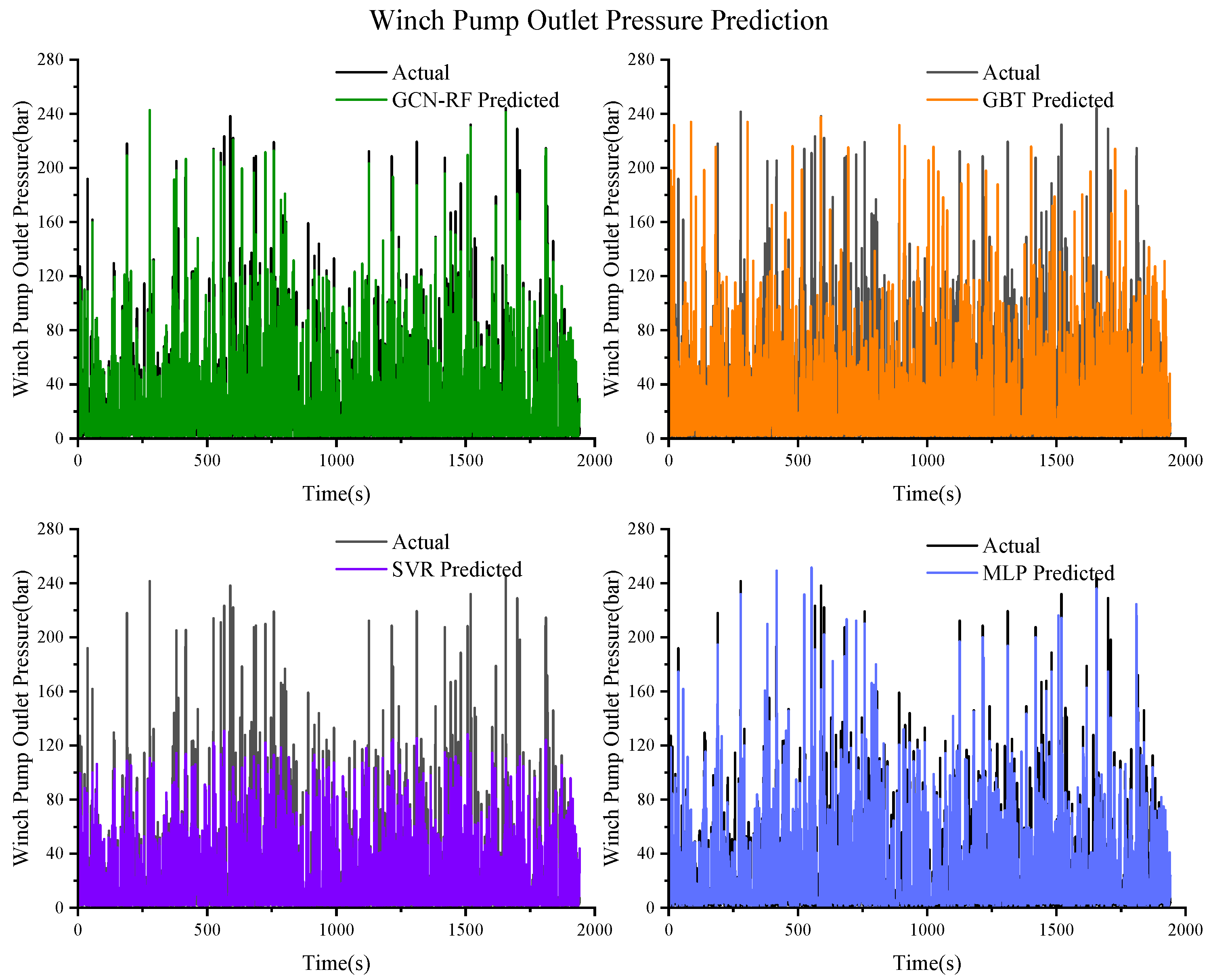
Figure 17.
Prediction results of the winch pump outlet pressure based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 17.
Prediction results of the winch pump outlet pressure based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
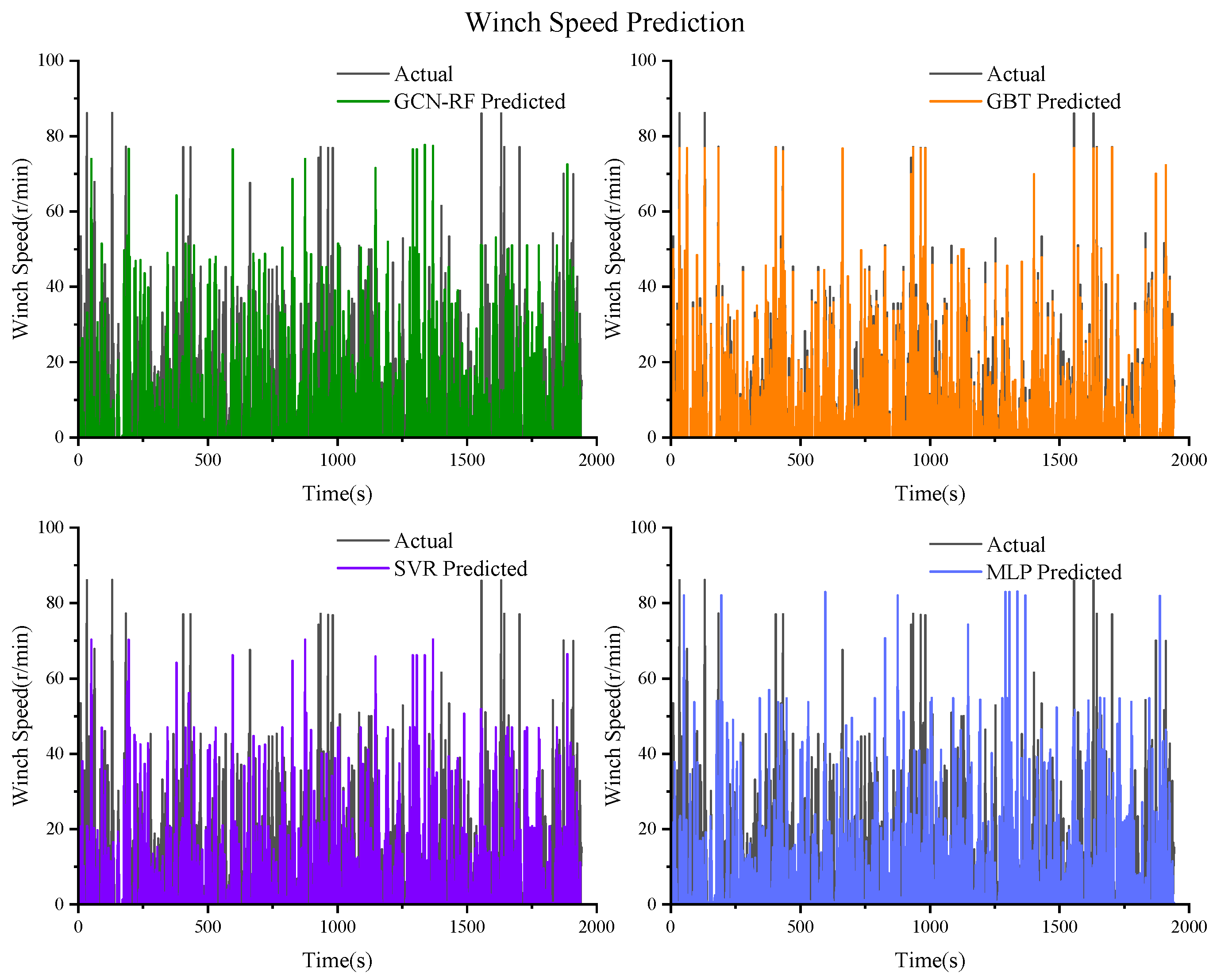
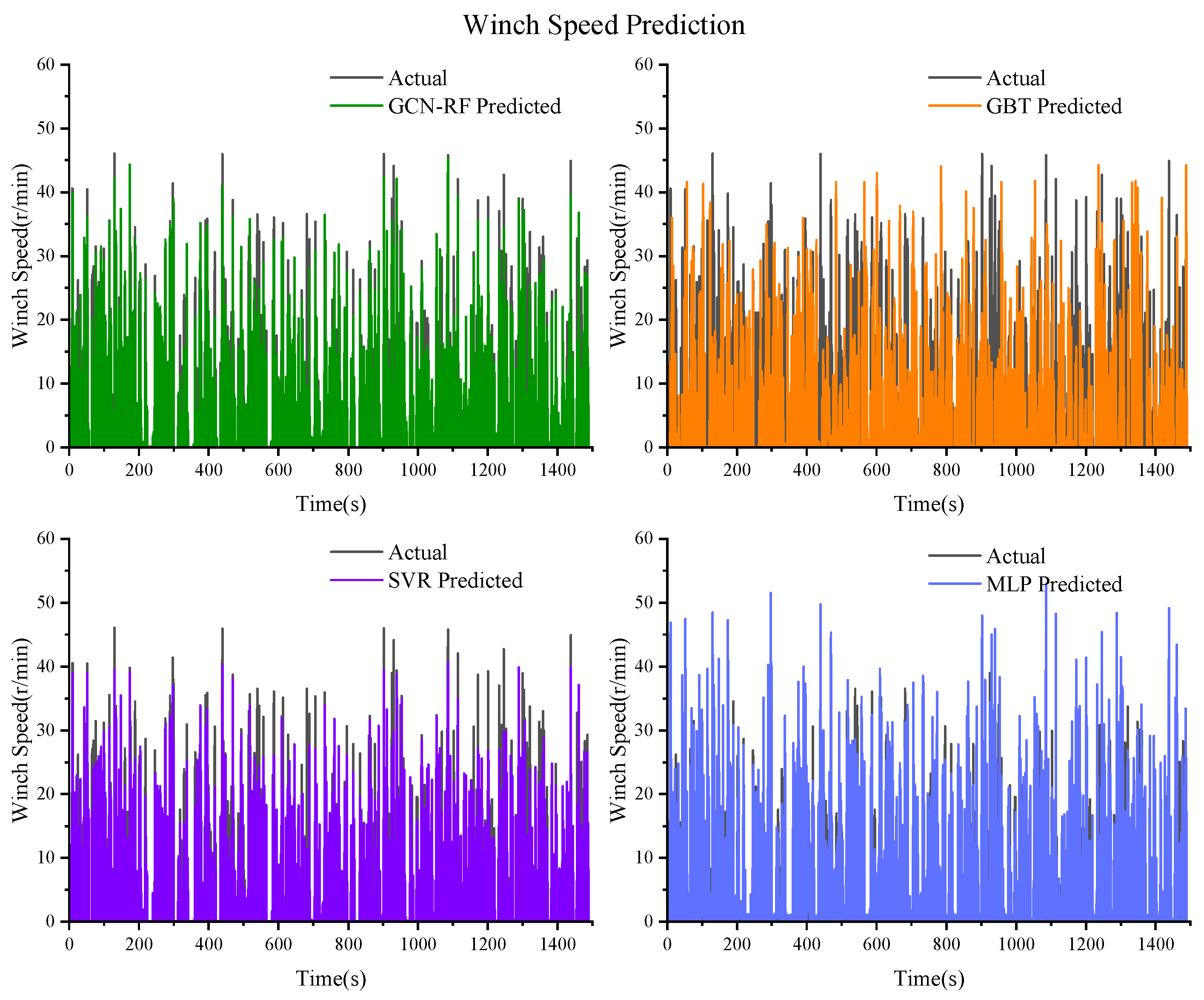
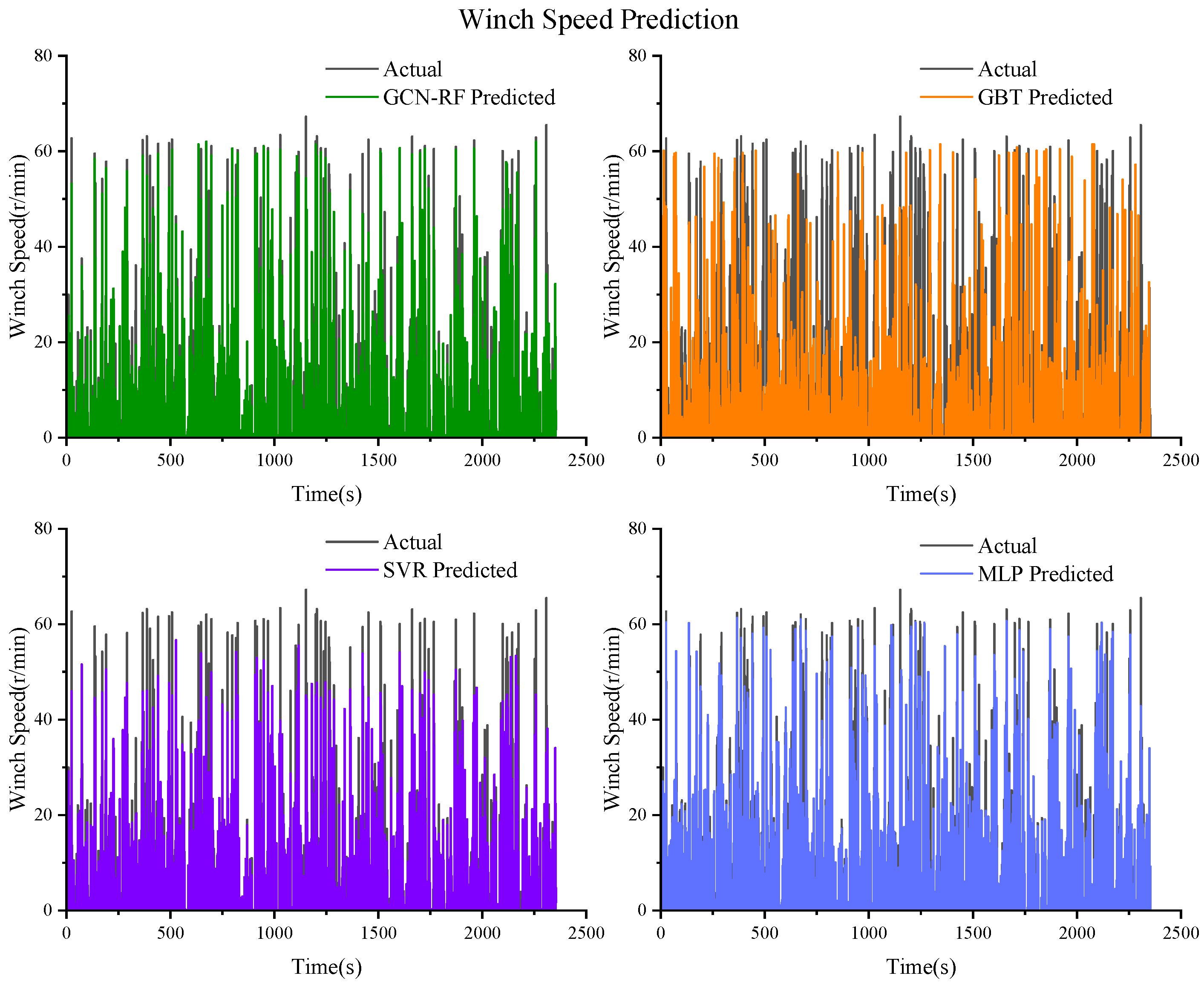
Figure 18.
Prediction results of the winch speed based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 18.
Prediction results of the winch speed based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 19.
Prediction results of the amplitude based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 19.
Prediction results of the amplitude based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 20.
Prediction results of the boom length based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 20.
Prediction results of the boom length based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 21.
Prediction results of the flexible pump pressure based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 21.
Prediction results of the flexible pump pressure based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 22.
Prediction results of the height based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 22.
Prediction results of the height based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 23.
Prediction results of the luffing angle based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 23.
Prediction results of the luffing angle based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 24.
Prediction results of the slewing angle based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 24.
Prediction results of the slewing angle based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 25.
Prediction results of the winch pump outlet pressure based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 25.
Prediction results of the winch pump outlet pressure based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 26.
Prediction results of the winch speed based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 26.
Prediction results of the winch speed based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 27.
Prediction results of the amplitude based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 27.
Prediction results of the amplitude based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 28.
Prediction results of the boom length based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 28.
Prediction results of the boom length based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 29.
Prediction results of the flexible pump pressure based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 29.
Prediction results of the flexible pump pressure based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 30.
Prediction results of the height based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 30.
Prediction results of the height based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 31.
Prediction results of the luffing angle based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 31.
Prediction results of the luffing angle based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 32.
Prediction results of the slewing angle based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 32.
Prediction results of the slewing angle based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 33.
Prediction results of the winch pump outlet pressure based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 33.
Prediction results of the winch pump outlet pressure based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 34.
Prediction results of the winch speed based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Figure 34.
Prediction results of the winch speed based on GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 1.
Variables collected by crane operation system.
Table 1.
Variables collected by crane operation system.
Input
Variables | Description | Output
Variables | Description |
|---|
| x1 | Rated weight | y1 | Amplitude |
| x2 | Actual weight | y2 | Boom length |
| x3 | Multiplier | y3 | Flexible pump pressure |
| x4 | Throttle position | y4 | Height |
| x5 | Engine speed | y5 | Luffing angle |
| x6 | Luffing handle signal | y6 | Slewing angle |
| x7 | Winching handle signal | y7 | Winch pump outlet pressure |
| x8 | Slewing handle signal | y8 | Winch speed |
| x9 | Telescoping handle signal | / | / |
| x10 | Left slewing current | / | / |
| x11 | Right slewing current | / | / |
| x12 | Flexible pump control current | / | / |
| x13 | Luffing balance valve control current | / | / |
| x14 | Winch up pump control current | / | / |
| x15 | Winch down pump control current | / | / |
| x16 | Winch motor control current | / | / |
Table 2.
GCN–RF model parameter settings.
Table 2.
GCN–RF model parameter settings.
| Models | Name | Main Parameters |
|---|
| GCN | Number of graph convolution layers | 3 |
| Number of nodes per layer | 64,128,256 |
| Learning rate | 0.001 |
| Batch size | 32 |
| Epoch | 100 |
| RF | Number of decision trees | 200 |
| Maximum tree depth | 30 |
| Minimum number of sample splits | 2 |
| Minimum number of leaf nodes | 1 |
| Sample sampling strategy | Bootstrap |
Table 3.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 3.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Amplitude | R2 | 0.8875 | 0.8680 | 0.6116 | 0.6329 |
| MSE | 0.0031 | 0.0036 | 0.0108 | 0.0101 |
| RMSE | 0.0556 | 0.0603 | 0.1039 | 0.1007 |
Table 4.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 4.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Boom length | R2 | 0.8946 | 0.8904 | 0.6372 | 0.5700 |
| MSE | 0.0014 | 0.0014 | 0.0082 | 0.0059 |
| RMSE | 0.0380 | 0.0379 | 0.0906 | 0.0768 |
Table 5.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 5.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Flexible pump pressure | R2 | 0.8689 | 0.8124 | 0.6767 | 0.7200 |
| MSE | 0.0048 | 0.0080 | 0.0137 | 0.0102 |
| RMSE | 0.0691 | 0.0897 | 0.1172 | 0.1010 |
Table 6.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 6.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Height | R2 | 0.9248 | 0.9260 | 0.8078 | 0.8312 |
| MSE | 0.0015 | 0.0014 | 0.0047 | 0.0034 |
| RMSE | 0.0388 | 0.0374 | 0.0689 | 0.0583 |
Table 7.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 7.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Luffing angle | R2 | 0.8952 | 0.8917 | 0.6577 | 0.6718 |
| MSE | 0.0015 | 0.0015 | 0.0059 | 0.0046 |
| RMSE | 0.0381 | 0.0381 | 0.0768 | 0.0677 |
Table 8.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 8.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Slewing angle | R2 | 0.8752 | 0.7975 | 0.5463 | 0.5220 |
| MSE | 0.0053 | 0.0089 | 0.0193 | 0.0203 |
| RMSE | 0.0728 | 0.0944 | 0.1390 | 0.1423 |
Table 9.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 9.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Winch pump outlet pressure | R2 | 0.8948 | 0.8089 | 0.6917 | 0.7216 |
| MSE | 0.0031 | 0.0068 | 0.0114 | 0.0081 |
| RMSE | 0.0555 | 0.0826 | 0.1070 | 0.0900 |
Table 10.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 10.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Winch speed | R2 | 0.9462 | 0.9423 | 0.8740 | 0.9177 |
| MSE | 0.0010 | 0.0012 | 0.0031 | 0.0016 |
| RMSE | 0.0323 | 0.0351 | 0.0553 | 0.0400 |
Table 11.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 11.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Amplitude | R2 | 0.9258 | 0.9110 | 0.7787 | 0.8415 |
| MSE | 0.0023 | 0.0029 | 0.0078 | 0.0050 |
| RMSE | 0.0483 | 0.0542 | 0.0884 | 0.0706 |
Table 12.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 12.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Boom length | R2 | 0.9263 | 0.9051 | 0.8190 | 0.8307 |
| MSE | 0.0032 | 0.0042 | 0.0102 | 0.0074 |
| RMSE | 0.0565 | 0.0646 | 0.1010 | 0.0860 |
Table 13.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 13.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Flexible pump pressure | R2 | 0.8769 | 0.7910 | 0.7218 | 0.7440 |
| MSE | 0.0054 | 0.0087 | 0.0129 | 0.0112 |
| RMSE | 0.0733 | 0.0931 | 0.1135 | 0.1056 |
Table 14.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 14.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Height | R2 | 0.9716 | 0.9611 | 0.9234 | 0.9177 |
| MSE | 0.0032 | 0.0044 | 0.0090 | 0.0092 |
| RMSE | 0.0564 | 0.0667 | 0.0949 | 0.0957 |
Table 15.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 15.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Luffing angle | R2 | 0.9793 | 0.9660 | 0.9283 | 0.9150 |
| MSE | 0.0027 | 0.0046 | 0.0095 | 0.0109 |
| RMSE | 0.0517 | 0.0678 | 0.0974 | 0.1046 |
Table 16.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 16.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Slewing angle | R2 | 0.8220 | 0.7835 | 0.6738 | 0.6702 |
| MSE | 0.0118 | 0.0144 | 0.0225 | 0.0217 |
| RMSE | 0.1084 | 0.1201 | 0.1501 | 0.1473 |
Table 17.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 17.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Winch pump outlet pressure | R2 | 0.8932 | 0.8999 | 0.8119 | 0.8392 |
| MSE | 0.0022 | 0.0021 | 0.0047 | 0.0034 |
| RMSE | 0.0474 | 0.0459 | 0.0687 | 0.0580 |
Table 18.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 18.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Winch speed | R2 | 0.8866 | 0.9088 | 0.8174 | 0.8592 |
| MSE | 0.0049 | 0.0040 | 0.0088 | 0.0061 |
| RMSE | 0.0699 | 0.0630 | 0.0939 | 0.0779 |
Table 19.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 19.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Amplitude | R2 | 0.9872 | 0.9770 | 0.8261 | 0.9546 |
| MSE | 0.0011 | 0.0020 | 0.0152 | 0.0039 |
| RMSE | 0.0330 | 0.0448 | 0.1231 | 0.0623 |
Table 20.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 20.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Boom length | R2 | 0.9223 | 0.8945 | 0.8095 | 0.8573 |
| MSE | 0.0080 | 0.0108 | 0.0197 | 0.0147 |
| RMSE | 0.0893 | 0.1040 | 0.1404 | 0.1211 |
Table 21.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 21.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Flexible pump pressure | R2 | 0.8504 | 0.8349 | 0.7716 | 0.7983 |
| MSE | 0.0054 | 0.0065 | 0.0102 | 0.0076 |
| RMSE | 0.0736 | 0.0806 | 0.1009 | 0.0872 |
Table 22.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 22.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Height | R2 | 0.8804 | 0.8228 | 0.7097 | 0.6844 |
| MSE | 0.0047 | 0.0067 | 0.0117 | 0.0124 |
| RMSE | 0.0685 | 0.0821 | 0.1080 | 0.1112 |
Table 23.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 23.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Luffing angle | R2 | 0.9678 | 0.9261 | 0.7484 | 0.7335 |
| MSE | 0.0011 | 0.0026 | 0.0092 | 0.0094 |
| RMSE | 0.0338 | 0.0511 | 0.0962 | 0.0972 |
Table 24.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 24.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Slewing angle | R2 | 0.5705 | 0.4239 | 0.3255 | 0.3512 |
| MSE | 0.0480 | 0.0642 | 0.0757 | 0.0725 |
| RMSE | 0.2190 | 0.2534 | 0.2752 | 0.2692 |
Table 25.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 25.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Winch pump outlet pressure | R2 | 0.9167 | 0.9195 | 0.8736 | 0.8889 |
| MSE | 0.0020 | 0.0018 | 0.0065 | 0.0028 |
| RMSE | 0.0452 | 0.0430 | 0.0804 | 0.0525 |
Table 26.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
Table 26.
R2, MSE, and RMSE values of GCN–RF, GBT, SVR, and MLP.
| Target Variables | Indicators | GCN–RF | GBT | SVR | MLP |
|---|
| Winch speed | R2 | 0.8690 | 0.8908 | 0.8466 | 0.8701 |
| MSE | 0.0040 | 0.0030 | 0.0050 | 0.0043 |
| RMSE | 0.0631 | 0.0552 | 0.0707 | 0.0657 |