Wireless Hybrid-Actuated Soft Miniature Robot for Biomedical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of the Soft Miniature Robot
2.3. Characterization of the Soft Miniature Robot
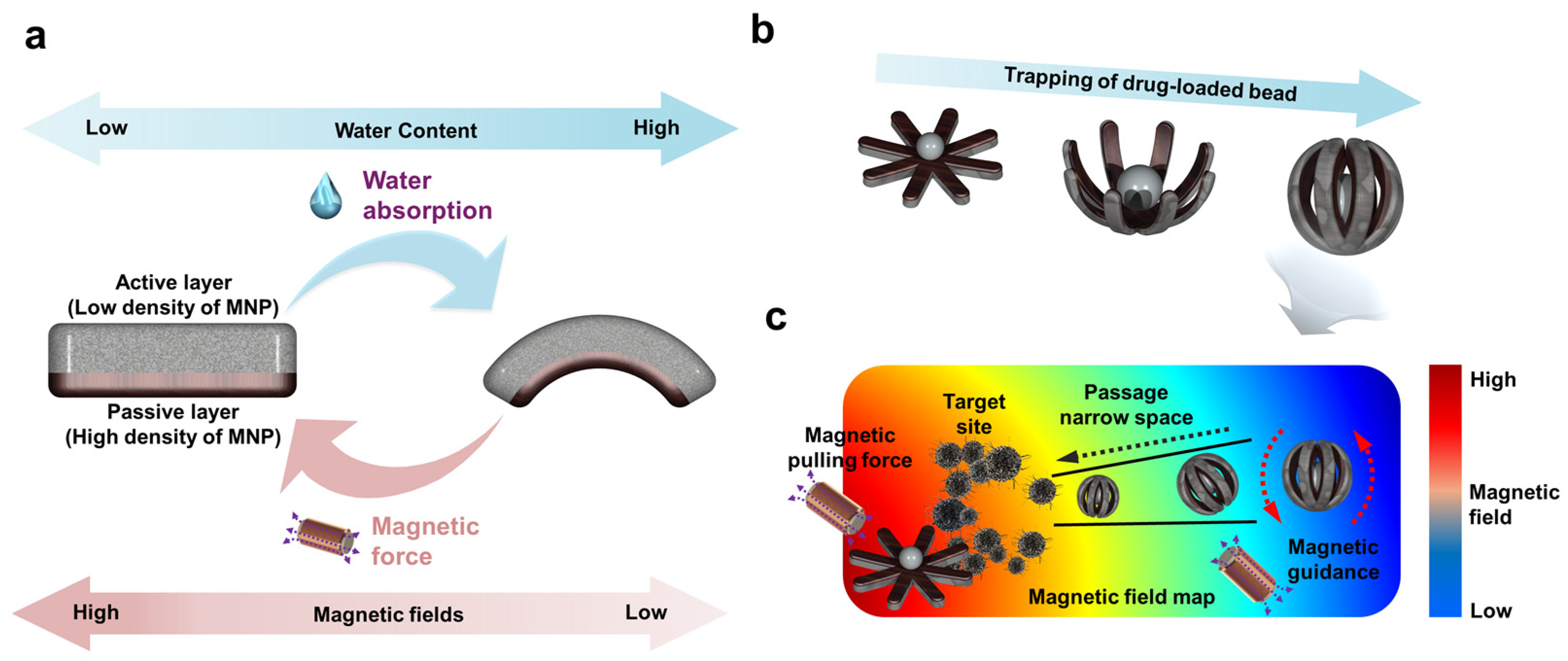
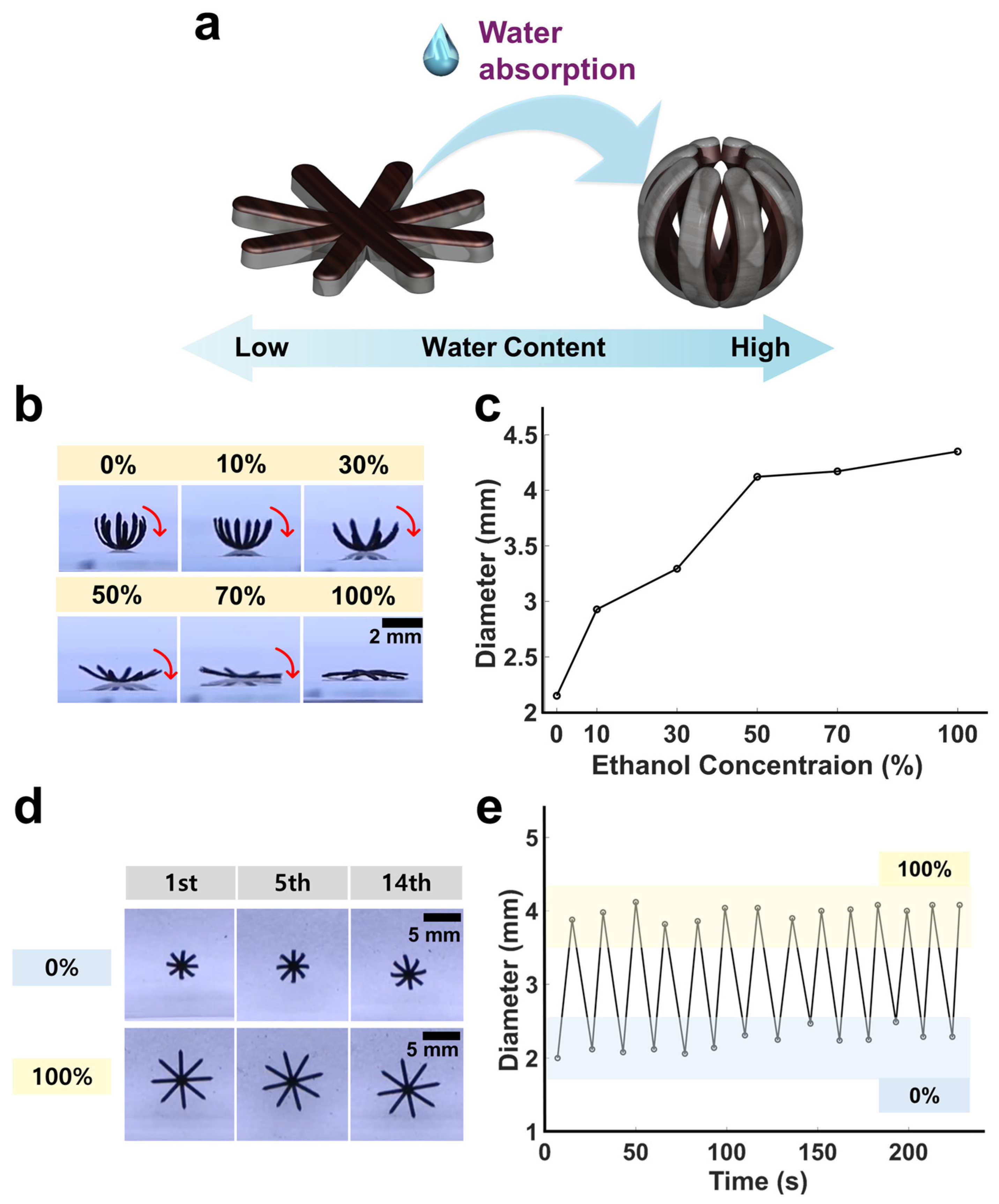
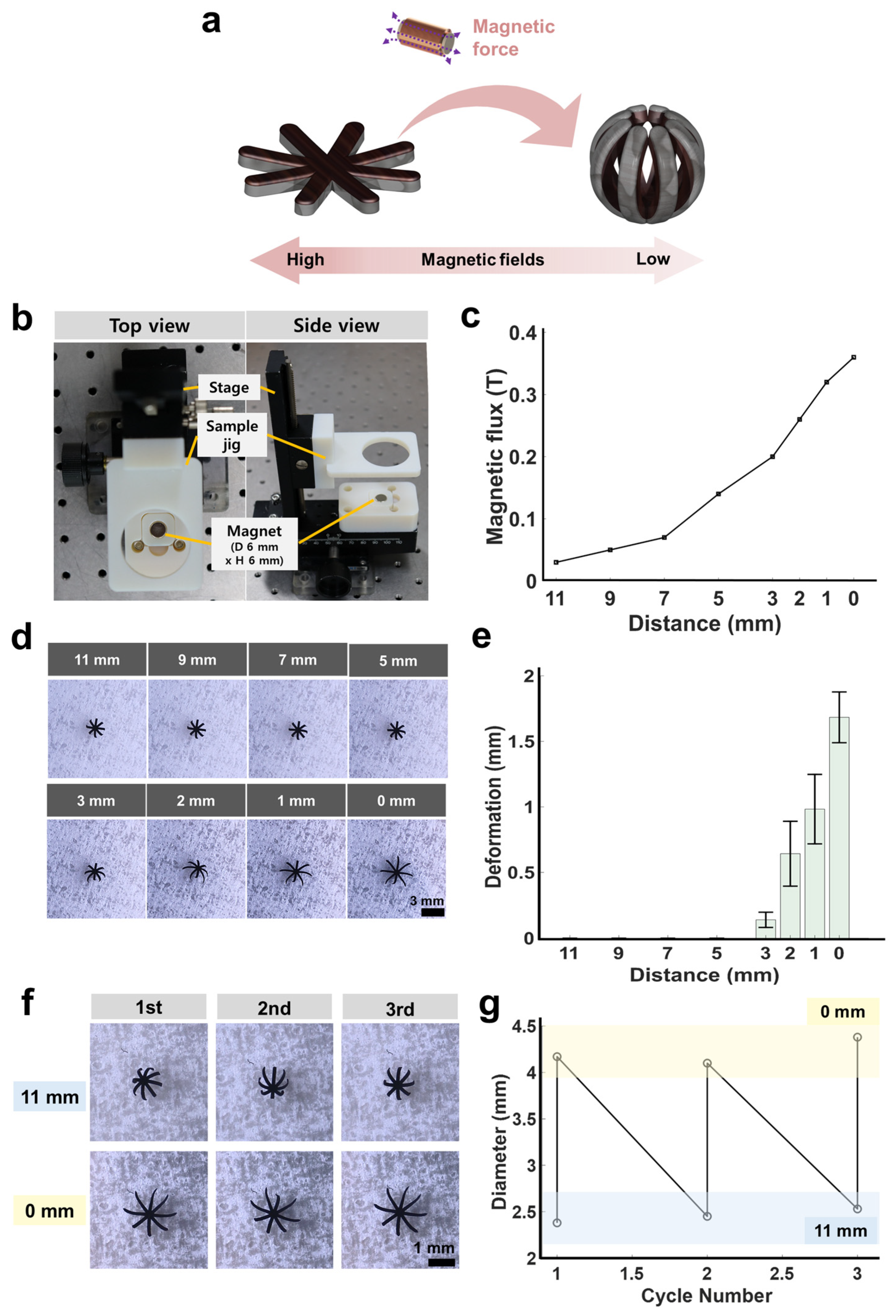
2.4. Hydrogel-Swelling- and Magnetic-Fields-Based Shape-Morphing Test of the Soft Miniature Robot
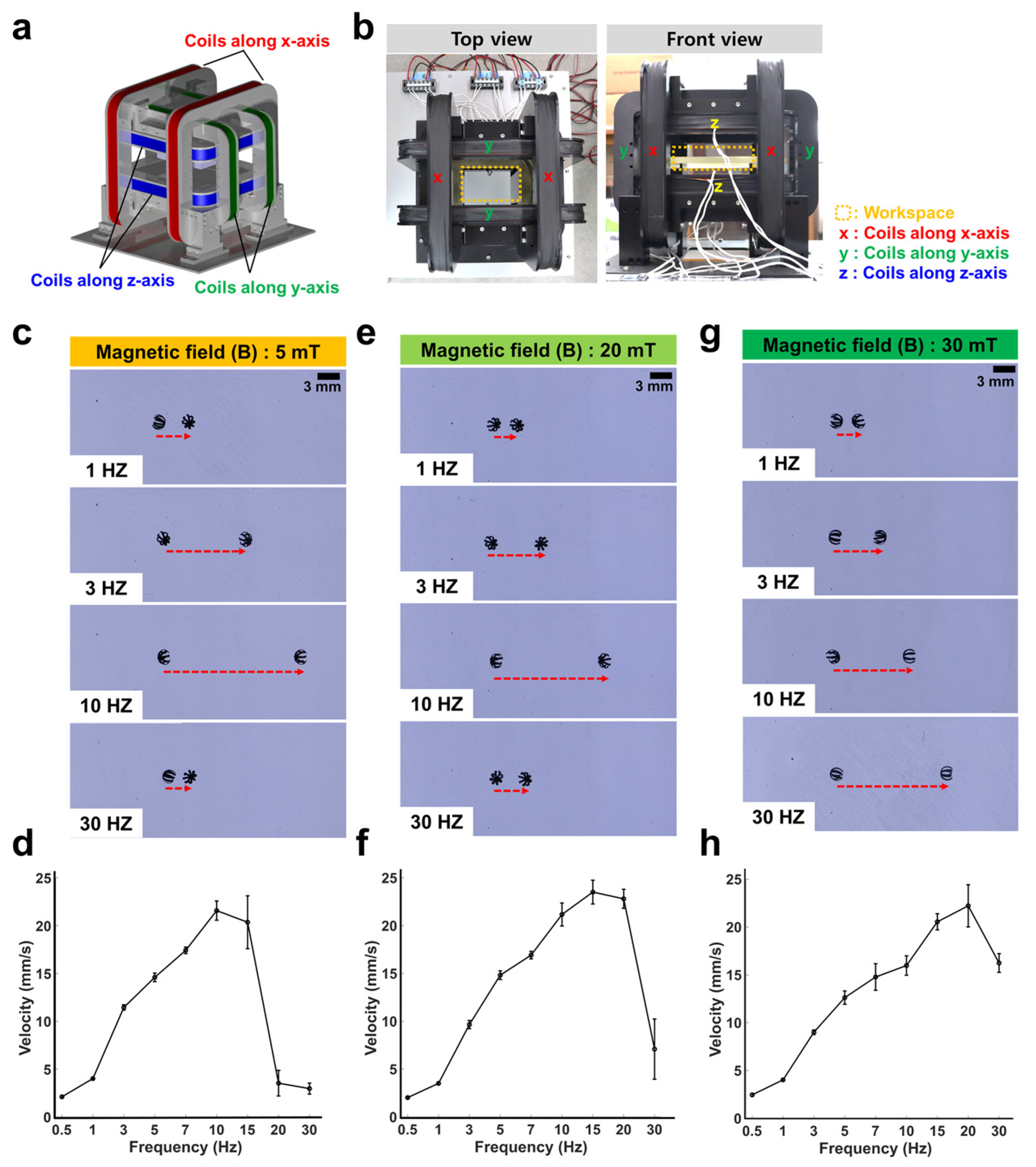
2.5. Magnetic-Field-Driven Mobility of the Soft Miniature Robot
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Magnetically Actuated Soft Miniature Robot
3.2. Hydrogel-Swelling-Actuated Bending of Soft Miniature Robot
3.3. Magnetic-Field-Actuated Shape-Morphing Test of Soft Miniature Robot
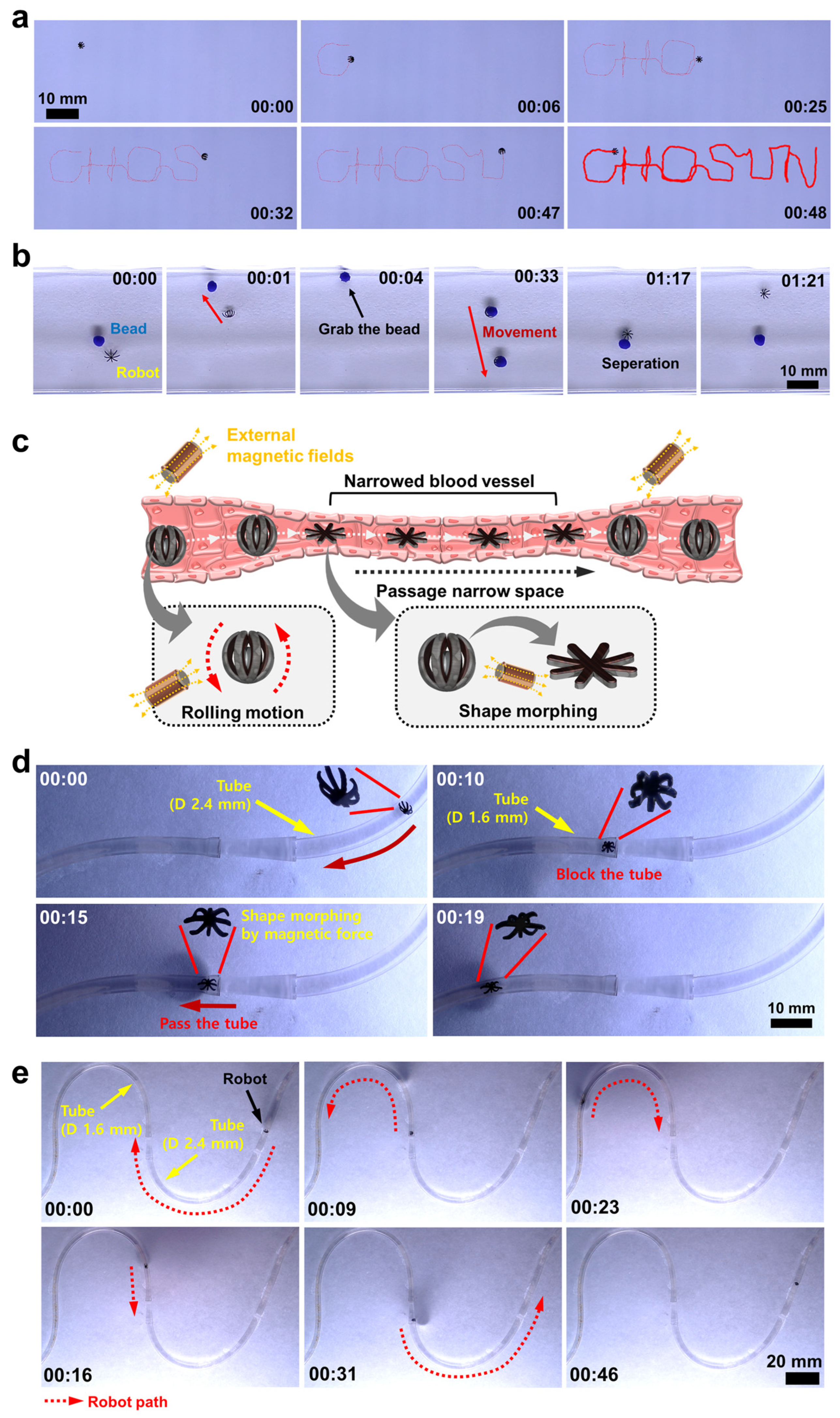
3.4. Magnetic-Field-Driven Mobility Test of Soft Miniature Robot
3.5. Bead Gripping and Targeted Delivery Test of Soft Miniature Robot
3.6. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rich, S.I.; Wood, R.J.; Majidi, C. Untethered soft robotics. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rus, D.; Tolley, M.T. Design, fabrication and control of soft robots. Nature 2015, 521, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laschi, C.; Mazzolai, B.; Cianchetti, M. Soft robotics: Technologies and systems pushing the boundaries of robot abilities. Sci. Robot. 2016, 1, eaah3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzolai, B.; Mondini, A.; Del Dottore, E.; Margheri, L.; Carpi, F.; Suzumori, K.; Cianchetti, M.; Speck, T.; Smoukov, S.K.; Burgert, I.; et al. Roadmap on soft robotics: Multifunctionality, adaptability and growth without borders. Multifunct. Mater. 2022, 5, 032001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.; Choi, S.H.; Pyun, K.R.; Jung, Y.; Hong, S.; Kim, D.; Lee, Y.; Won, D.; Jeong, S.; Shin, W.; et al. Bioinspired electronics for intelligent soft robots. Nat. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianchetti, M.; Laschi, C.; Menciassi, A.; Dario, P. Biomedical applications of soft robotics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wu, Y.; Yildiz, E.; Kanyas, S.; Sitti, M. Clinical translation of wireless soft robotic medical devices. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2024, 2, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, L.; Petersen, K.; Lum, G.Z.; Sitti, M. Soft Actuators for Small-Scale Robotics. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manduca, G.; Santaera, G.; Miraglia, M.; Jansen Van Vuuren, G.; Dario, P.; Stefanini, C.; Romano, D. A Bioinspired Control Strategy Ensures Maneuverability and Adaptability for Dynamic Environments in an Underactuated Robotic Fish. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2024, 110, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalegani Dezaki, M.; Bodaghi, M. A Review of Recent Manufacturing Technologies for Sustainable Soft Actuators. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2023, 10, 1661–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xue, P.; Tang, Y.; Bi, R.; Xu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, Q. Responsive soft actuators with MXene nanomaterials. Responsive Mater. 2024, 2, e20230026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, S.; Huang, H.-W.; Peyer, K.E.; Peters, C.; Häberli, M.; Ulbers, A.; Spyrogianni, A.; Pellicer, E.; Sort, J.; Pratsinis, S.E.; et al. Shape-Switching Microrobots for Medical Applications: The Influence of Shape in Drug Delivery and Locomotion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 6803–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, S.; Cecchini, L.; Mondini, A.; Del Dottore, E.; Ronzan, M.; Filippeschi, C.; Pugno, N.M.; Sinibaldi, E.; Mazzolai, B. A Bioinspired Plasmonic Nanocomposite Actuator Sunlight-Driven by a Photothermal-Hygroscopic Effect for Sustainable Soft Robotics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2202166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Sun, S.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Gong, X. Multi-Stimuli Responsive Soft Actuator with Locally Controllable and Programmable Complex Shape Deformations. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 6199–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Lum, G.Z.; Mastrangeli, M.; Sitti, M. Small-scale soft-bodied robot with multimodal locomotion. Nature 2018, 554, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Yang, S.; Ozen, M.O.; Chen, P.; Liu, X.; Du, W.; Xiao, F.; Demirci, U.; et al. Multi-stimuli-responsive programmable biomimetic actuator. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Han, J.; Demir, S.O.; Wang, H.; Jiang, W.; Liu, H.; Sitti, M. Electrodeposited Superhydrophilic-Superhydrophobic Composites for Untethered Multi-Stimuli-Responsive Soft Millirobots. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2302409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malachowski, K.; Jamal, M.; Jin, Q.; Polat, B.; Morris, C.J.; Gracias, D.H. Self-Folding Single Cell Grippers. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 4164–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Yoon, C.; Oh, S.H.; Pagaduan, J.V.; Gracias, D.H. Biodegradable Thermomagnetically Responsive Soft Untethered Grippers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudu, S.R.; Yasa, I.C.; Hu, X.; Ceylan, H.; Hu, W.; Sitti, M. Biodegradable Untethered Magnetic Hydrogel Milli-Grippers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, M.; Go, G.; Song, H.-W.; Darmawan, B.A.; Zheng, S.; Kim, S.; Nguyen, K.T.; Lee, K.; Kim, H.; Park, J.-O.; et al. Multistimulus-Responsive Miniature Soft Actuator with Programmable Shape-Morphing Design for Biomimetic and Biomedical Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2401776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaveni, B.; Ragunathan, R. Extraction and characterization of Chitin and Chitosan from Aspergillus terreus sps, synthesis of their bionanocomposites and study of their productive applications. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 115–132. [Google Scholar]
- Go, G.; Yoo, A.; Song, H.-W.; Min, H.-K.; Zheng, S.; Nguyen, K.T.; Kim, S.; Kang, B.; Hong, A.; Kim, C.-S.; et al. Multifunctional Biodegradable Microrobot with Programmable Morphology for Biomedical Applications. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 1059–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes Queiroz, M.; Melo, K.R.; Sabry, D.A.; Sassaki, G.L.; Rocha, H.A. Does the Use of Chitosan Contribute to Oxalate Kidney Stone Formation? Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, G.; Yoo, A.; Nguyen, K.T.; Nan, M.; Darmawan, B.A.; Zheng, S.; Kang, B.; Kim, C.-S.; Bang, D.; Lee, S.; et al. Multifunctional microrobot with real-time visualization and magnetic resonance imaging for chemoembolization therapy of liver cancer. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabq8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diller, E.; Giltinan, J.; Sitti, M. Independent control of multiple magnetic microrobots in three dimensions. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2013, 32, 614–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, A.W.; Nelson, N.D.; Peyer, K.E.; Nelson, B.J.; Abbott, J.J. Behavior of rotating magnetic microrobots above the step-out frequency with application to control of multi-microrobot systems. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 144101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbaut, C.; Segers, P.; Cornillie, P.; Casteleyn, C.; Dierick, M.; Laleman, W.; Monbaliu, D. Analyzing the human liver vascular architecture by combining vascular corrosion casting and micro-CT scanning: A feasibility study. J. Anat. 2014, 224, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.; Lee, K.; Go, G. Wireless Hybrid-Actuated Soft Miniature Robot for Biomedical Applications. Actuators 2024, 13, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13090341
Kim H, Lee K, Go G. Wireless Hybrid-Actuated Soft Miniature Robot for Biomedical Applications. Actuators. 2024; 13(9):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13090341
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Heera, Kyongsu Lee, and Gwangjun Go. 2024. "Wireless Hybrid-Actuated Soft Miniature Robot for Biomedical Applications" Actuators 13, no. 9: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13090341
APA StyleKim, H., Lee, K., & Go, G. (2024). Wireless Hybrid-Actuated Soft Miniature Robot for Biomedical Applications. Actuators, 13(9), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13090341




