Abstract
Human driving behavior significantly affects vehicle fuel economy and emissions on hilly roads. This paper presents an ecological (eco) driving scheme (EDS) on hilly roads using nonlinear model predictive control (NMPC) in a mixed traffic environment. A nonlinear optimization problem with a relevant prediction horizon and a cost function is formulated using variables impacting the fuel economy of vehicles. The EDS minimizes vehicle fuel usage and emissions by generating the optimum velocity trajectory considering the longitudinal motion dynamics, the preceding vehicle’s state, and slope information from the digital road map. Furthermore, the immediate vehicle velocity and angle of the road slope are used to tune the cost function’s weight utilizing fuzzy inference methods for smooth maneuvering on slopes. Microscopic traffic simulations are used to show the effectiveness of the proposed EDS for different penetration rates on a real hilly road in Fukuoka City, Japan, in a mixed traffic environment with the conventional (human-based) driving scheme (CDS). The results show that the fuel consumption and emissions of vehicles are significantly reduced by the proposed NMPC-based EDS compared to the CDS for varying penetration rates. Additionally, the proposed EDS significantly increases the average speed of vehicles on the hilly road. The proposed scheme can be deployed as an advanced driver assistance system (ADAS).
1. Introduction
In recent years, the growing number of automobiles on the road networks has resulted in enormous fuel consumption and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. With a total energy consumption of around 28% and a contribution to GHG emissions of about 28.5% in the United States in 2021, the transportation industry is the second-largest emitter in the country [1]. Particularly, emissions from gasoline-fueled vehicles, respectively, cause 28%, 36%, and 55% of hydrocarbon (HC), nitrogen oxide (NOx), and carbon monoxide (CO) emissions [2]. In Europe, transportation accounts for 33% of total energy use and 23% of total GHG emissions [3]. Therefore, researchers and policymakers are concerned about increasing energy efficiency and lowering GHG emissions.
The various physical factors that affect fuel economy and emissions in automobiles include the design of the vehicle, the engine, and the power train system [4]. Moreover, road-geometry characteristics, e.g., road grades, have considerable effects on the fuel economy and GHG emissions of both light-duty and heavy-duty vehicles [5]. Specifically, due to the need for a high power to overcome gravity, vehicles use between 5% and 20% more fuel on uphill stretches of hilly roads than on flat roads [6], while the gravitational force works in favor of a vehicle while moving downhill, lowering fuel consumption and emissions [7]. On the other hand, recent research has demonstrated that driving behavior substantially affects fuel usage and GHG emissions, with braking and acceleration being two well-known ways to conserve or waste energy [8]. To resolve this issue, eco-driving is a promising approach that encourages fuel-efficient driving by avoiding unnecessary braking and acceleration and by optimizing the vehicle velocity profile while forecasting surrounding road-traffic situations [9,10]. Studies have shown that an eco-driving system can lower fuel consumption by about 4–25% [11,12].
In the literature, several eco-driving systems have been reported for sloping roads. Early studies primarily suggested that driving at a steady speed on constant road grades reduces fuel usage. Particularly, the first effort aimed at optimizing the velocity trajectory using a feedback control algorithm that allows the driver to adjust the speed for an optimum fuel economy on different road grades [13]. A nonlinear vehicle model and Pontryagin’s maximum principle (PMP) were used to determine the optimal velocity, and it was found that a constant velocity was most suitable for some constant slopes. A related study found that keeping a constant speed within the predetermined limits of a constant road slope produced the best result [14]. In another investigation, a point-mass eco-driving control system was developed employing PMP for a constant road gradient [15]. These approaches were proposed under the assumption that road slopes would remain constant; hence, they are not suitable for situations where there are hilly roads with variable up and down slopes.
In [16], a dynamic programming (DP)-based on-board look-ahead controller was developed for a diesel truck using information on the upcoming terrain of the route, which reduced fuel consumption by 3.5%. A similar study developed an optimal control problem using DP to minimize the fuel consumption of a light-duty vehicle and achieved fuel savings of about 5.5% [17]. In [18], an optimal energy management system for fuel cell hybrid electric vehicles (FCHEVs) was developed using DP considering upcoming road grade data. Although the solvers based on DP produced a global minimum, they are not appropriate for actual deployment since they require information on the complete driving cycle in advance.
Some other works developed model predictive control (MPC) frameworks for energy-efficient driving on sloping roads. In [19], an eco-driving method was proposed utilizing MPC, considering vehicle dynamics, road grade data, and the fuel consumption characteristics of the engine. Another work proposed MPC for eco-driving of hybrid vehicles using traffic signals and road grade information [20]. In our previous work [21], an MPC-based eco-driving method was proposed using fuzzy-based rules and tested with a single vehicle on a typical road stretch with simple up-slopes and down-slopes only, whereas in [22], fuzzy-based MPC was developed for dynamic eco-driving of a host vehicle on hilly roads in both free-flow and dense traffic environments. The findings demonstrated that a single host vehicle based on MPC could improve the overall traffic performance by reducing energy waste (caused by acceleration and braking) compared to traditional MPC-based approaches.
In this paper, we present an NMPC-based EDS with fuzzy-tuned weights to reduce the fuel consumption and emissions of vehicles, and we assess its efficacy on a real, hilly route (with differing up and down slopes) in Fukuoka City, Japan, under a mixed traffic environment. We design a nonlinear optimization problem that dynamically computes the optimum velocity trajectory of vehicles considering their longitudinal motion dynamics, the preceding vehicle states, and information on road grades derived from a digital map of the route while ensuring driving safety. To better utilize the kinetic energy of a vehicle and consequently further reduce fuel consumption and emissions, the fuzzy inference method (considering the instantaneous vehicle speed and road slope angle) is used to tune the weight of the objective function associated with the velocity term. The fuzzy inference technique with NMPC is crucial because it allows the velocity increase gained by gravity to be mostly permitted while running down a slope, preventing frequent braking and capturing the gravitational potential energy. The findings demonstrate that the proposed scheme significantly minimizes vehicle fuel usage and emissions compared to the CDS for different penetration rates while increasing the average speed on the road. As a result, this study advances the development of eco-driving techniques, which may enhance overall driving strategies on hilly roads with varying up–down slopes.
The paper is structured as follows. In Section 2, the comprehensive idea behind our proposed EDS is first explained. Next, we describe the vehicle longitudinal dynamics model. Then, we explain the proposed NMPC system and the fuzzy inference technique. In Section 3, we present numerical simulation results on an actual hilly road, and finally, Section 4 provides the conclusions and future research directions.
2. Eco-Driving on Hilly Roads
We recall that driving behavior and road slopes have a significant impact on a vehicle’s fuel economy and emissions. For instance, excessive acceleration, braking, and speeding consume/waste significant energy and cause emissions. To drive ecologically on a hilly road, it is crucial to forecast driving states, traffic conditions, and road grades; however, such predictions are challenging for a human driver. Hence, an eco-driving scheme is a potential approach to assist a driver on hilly roads to reduce emissions and fuel usage.
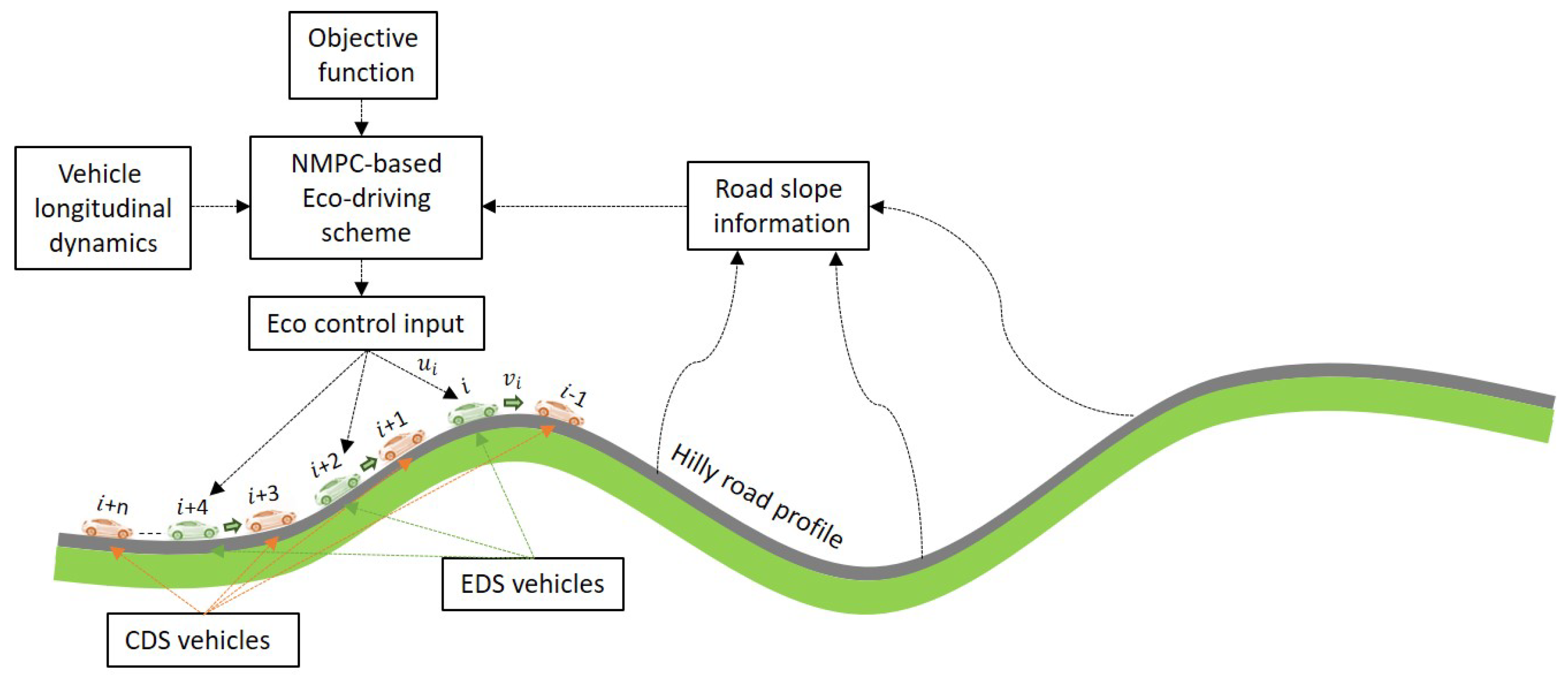
The comprehensive idea of our proposed NMPC-based EDS on a hilly route is depicted in Figure 1. The EDS incorporates information on road grades up ahead and the longitudinal motion dynamics of vehicle i in the presence of its preceding vehicle to determine the eco-control input that generates the optimum velocity during the trip interval. The traffic environment is considered to be mixed with conventional human-driven vehicles and is referred to as the conventional driving scheme (CDS) hereafter. The dynamic behavior of CDS vehicles is modeled using the intelligent driver model (IDM), a microscopic car-following model that imitates human driving behavior [23]. For each vehicle, the acceleration function defines the IDM regarding the position and velocity dynamics. The IDM computes the effect of road grades on vehicle acceleration and produces the control input necessary for maintaining a constant speed on hills. The instant acceleration of CDS vehicle (as shown in Figure 1) in response to its preceding vehicle i is given by the function as
where is the position, is the velocity, is the acceleration, is the desired velocity, is the driver assertiveness, is the minimum gap, T is the minimum time headway, a is the maximum acceleration, and b is the comfortable deceleration. and , respectively, denote the space gap and velocity difference between vehicles.
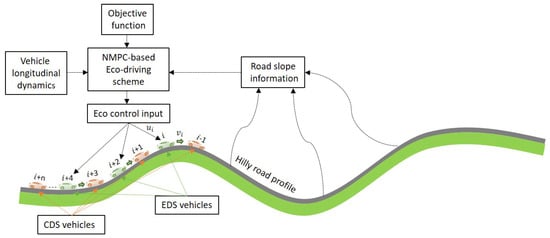
Figure 1.
Fundamental idea of the proposed EDS using NMPC. The vehicles are traveling on a hilly road with up–down slopes. The traffic environment includes the EDS (green) and CDS (orange) vehicles. The system is constantly updated with information on the road grade and neighboring traffic conditions.
We presume the traffic environment is dense and mixed, and vehicles are running in synchronous flow. The location of vehicles is determined by the global positioning system (GPS), and the EDS has access to the information on the road slope of the entire route from three-dimensional (3D) digital road maps. We develop a suitable performance metric and adjust one of its weights via fuzzy inference methods to assess the effectiveness of the proposed EDS, which generates the optimal speed trajectories using NMPC.
2.1. Vehicle Dynamics Model
In this study, the optimization solely employs the vehicles’ longitudinal motion dynamics; the driver is responsible for controlling the lateral dynamics. The state transition function of vehicle i at time t is given by
where denotes the state vector, with and as the position and speed of the following vehicle i and and as the position and speed of the preceding vehicle ; is the eco-control input (or acceleration/braking); and is an external parameter denoting the acceleration of the preceding vehicle , which is obtained from the measured speed.
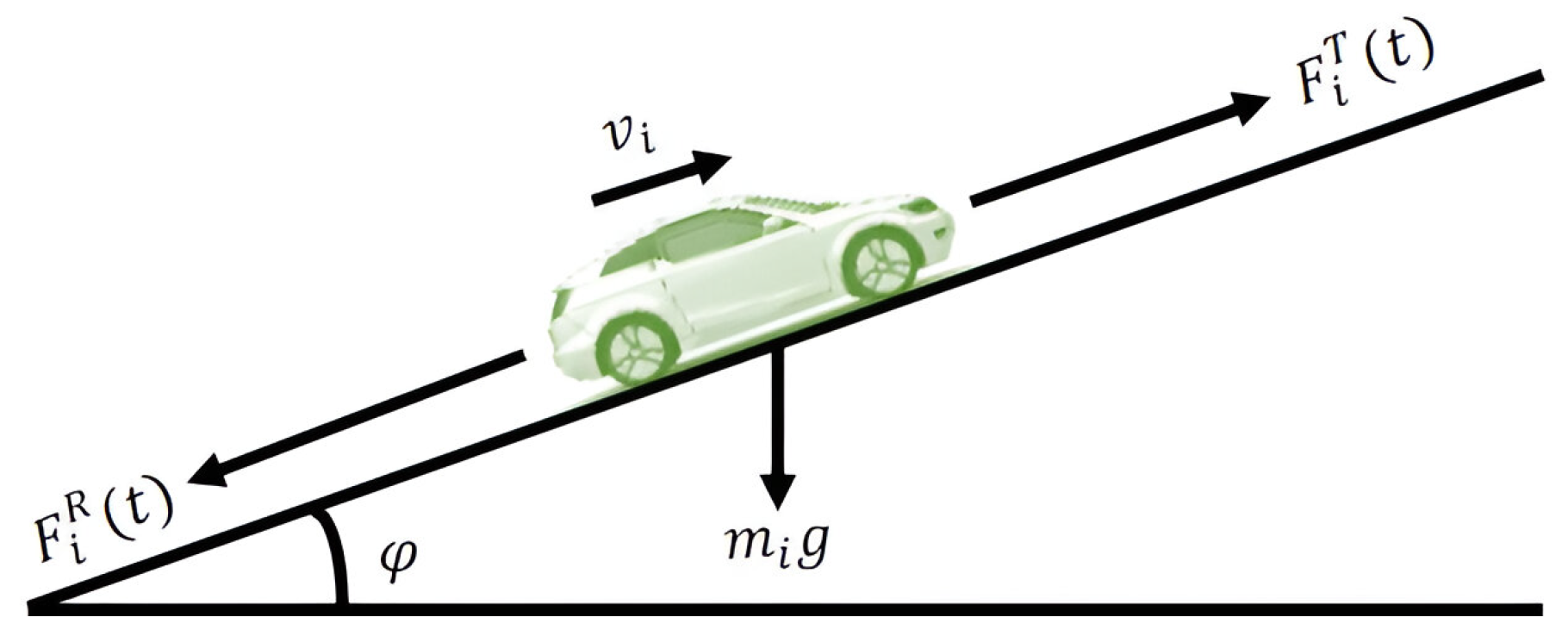
The motion of vehicle i on the slope is susceptible to the total forces working on it, as illustrated in Figure 2, and is expressed as
where is the equivalent mass, is the traction force, and is the motion resistance forces including rolling resistance, gravitational force, and aerodynamic drag, which is given as
where , g, , , , and , respectively, are the friction coefficient, gravitational acceleration, grade angle, drag coefficient, air density, and frontal area of vehicle i. The traction force is given by . Thus, the state Equation (2) is expressed as
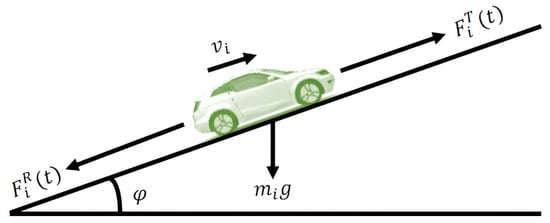
Figure 2.
Longitudinal motion dynamics of a vehicle while running on hills.
The information on route elevation is provided by a digital map, which is utilized to determine as
where is the road altitude and is the horizontal distance between vehicle and i.
2.2. Nonlinear Model Predictive Control
Notably, high levels of braking and acceleration are not advantageous for fuel economy or riding comfort. We develop an NMPC-based EDS that calculates the optimum speed profile required for safe and efficient driving within the prediction horizon by measuring the vehicle state at any given time. In particular, we develop a constrained optimization approach to determine the optimum speed for the EDS. An appropriate prediction horizon (similar to a human driver) is regarded; a long horizon would not be useful because the traffic flow is subject to significant changes. The safe gap of vehicle i from its preceding vehicle is given by
where is the minimum desired net distance and is the safe time gap to the preceding vehicle.
For vehicle i with state dynamics (2) and (5), we implement NMPC by solving an optimal control problem with a cost function, which is minimized at each time t as
subject to
where T is the prediction horizon for which the optimum profiles from present time t are calculated, is the reference speed, is a positive constant, denotes the immediate time gap with a positive threshold to avoid singularity, and , , and , respectively, are the weights associated with speed, acceleration, and safe headway terms. The cost for the present speed variation from is shown in the first part of the objective function. The second part represents the cost associated with the vehicle’s acceleration force and the third part represents the cost of deviating from the reference distance. The weight is tuned based on fuzzy inference techniques, while weights and are assigned high values.
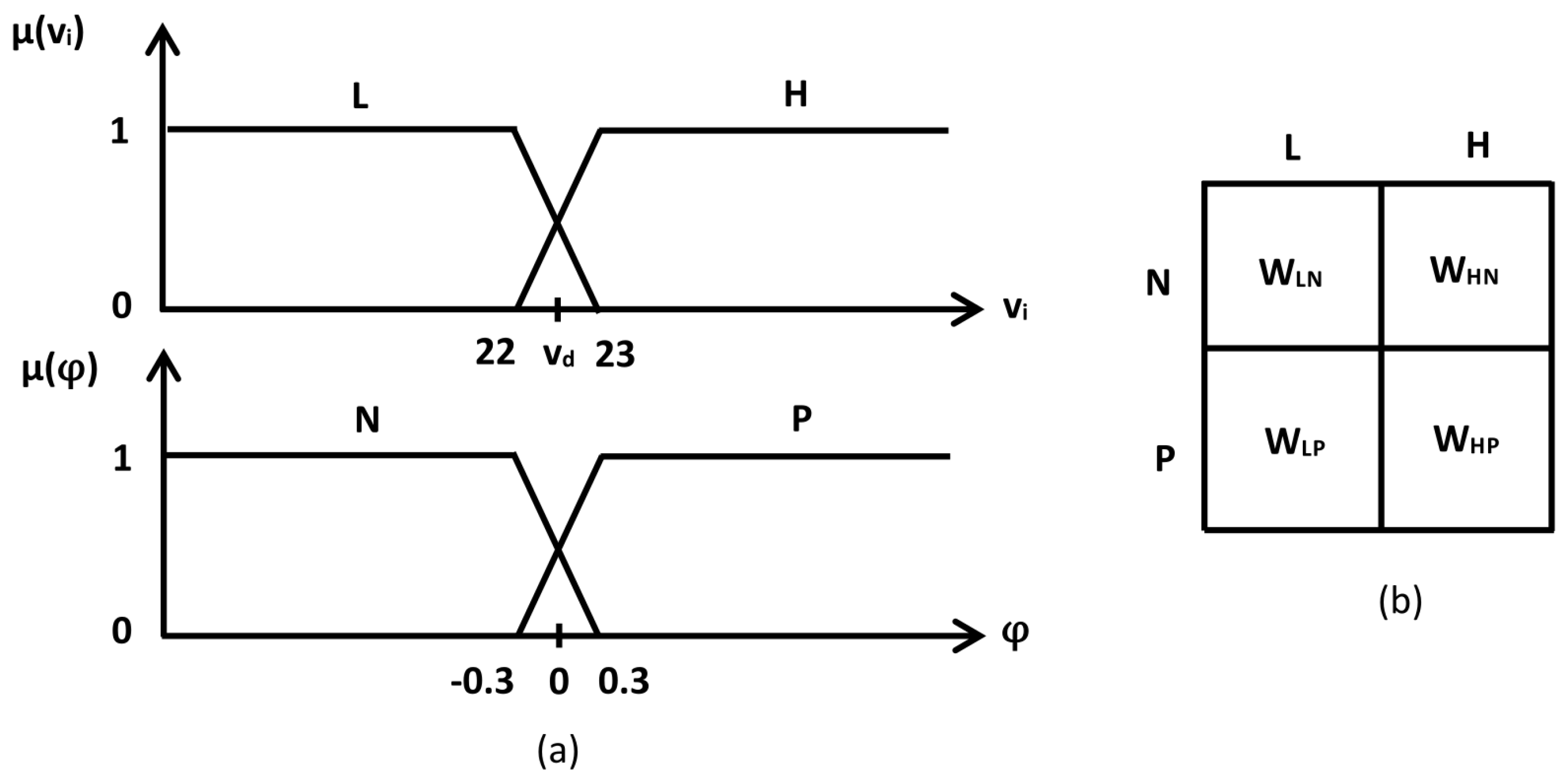
In this paper, we employ the Mamdani fuzzy inference technique, which is one of the most popular fuzzy inference techniques, and works with crisp data as inputs [24]. To implement the fuzzy logic, we apply three consecutive steps: fuzzification, fuzzy inference, and defuzzification. In the fuzzification step, we take account of the immediate speed and grade angle as inputs to tune . We define trapezoidal-shaped membership functions with ‘Low’ (L) and ‘High’ (H) for and ‘Negative’ (N) and ‘Positive’ (P) for , as illustrated in Figure 3a. Then, the corresponding membership values are computed for speed and grade . Next, the fuzzy control rules are defined as illustrated in Figure 3b, and expert knowledge is considered to develop the rules [22].
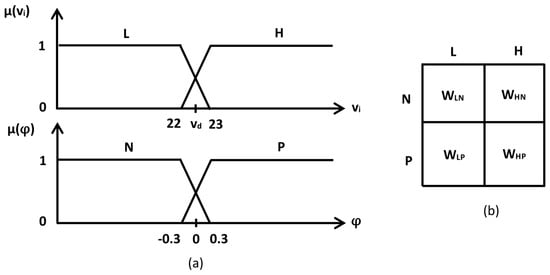
Figure 3.
Fuzzy inference (a) membership functions of velocity and grade angle , and (b) control rules.
In such a scenario, the fuzzy rules exhibit two predecessors, and thus, using the fuzzy AND operator, one value is obtained that represents the outcome of the predecessor evaluation. The conjunction of the rule predecessors is given as
Then, we determine the control output by associating membership functions with fuzzy rules as
where , denotes constant fuzzy weights. Note that is time-varying since and vary with time.
Finally, using the defuzzification () technique known as center of gravity (COG), the fuzzy output is converted into a crisp output as
The NMPC scheme avoids excessive acceleration/braking of vehicles, while tuning the objective function with fuzzy inference techniques causes smooth variations in speeds on road grades.
3. Simulation Results and Discussion
3.1. Simulation Settings
To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed NMPC-based EDS, we developed a simulation framework using MATLAB. Next, we solved the nonlinearly constrained optimization problem (8) in discrete time employing the MATLAB optimization toolbox. The vehicle parameters are set as kg, , m/s2, , kg/m3, and m2. The safe time gap and minimum desired net distance are, respectively, set as 1.7 s and 4 m. The MPC reference speed is set as 22.23 m/s or 80 km/h, and the constraints for speed and acceleration are, respectively, chosen as m/s and m/s2. The weights , , and in the cost function (8) are, respectively, chosen as 0.15, 9, and 30. Note that the weight values and are chosen to uphold the priority of acceleration and velocity on a comparable scale since the terms are squared, while the weight is selected to only dominate other terms in safety-critical circumstances (to guarantee safety). Subsequently, the weight values and are adjusted further following the fuel economy improvements. Then, the road slope angle and vehicle current speed are used to infer the fuzzy weights at any location along the slope. By tuning, the optimum fuzzy weights , , , and are determined as 0.06, 0.12, 0.17, and 0.10, respectively. Using a prediction horizon of s with 24 steps, the simulation step is set at dt = 0.5 s. The vehicles initially move at a speed of 22.23 m/s. The IDM parameters are chosen as m/s, m, s, m/s2, and m/s2.
Two types of driving schemes are assessed for comparison using microscopic traffic simulations on a real road in Fukuoka City, Japan, i.e., the conventional driving scheme, which is regarded as a fixed-speed drive (FSD), and the proposed NMPC-based EDS. The FSD precisely generates a suitable control action on road grades to maneuver vehicles at a steady speed. To calculate the fuel consumption and emission rates of vehicles, the VT-Micro model [25,26] is employed. Note that a vehicle’s fuel consumption (or engine efficiency) depends on the engine’s characteristics and working behavior (engine speed and torque). The VT-Micro model intrinsically considers the engine behavior of vehicles with an automated transmission (AT) system. In a vehicle with an AT system, by relating the instantaneous speed and acceleration to the required driving power, the appropriate gear position is automatically adjusted to track the best operating point concerning the torque–speed–efficiency characteristics of the vehicle. The VT-Micro model was developed from experiments with regular-emitting light-duty vehicles, and the polynomial fuel consumption model was developed by fitting the speed and acceleration characteristics with observed fuel consumption data. The VT-Micro model is widely used in transportation studies for computing the fuel consumption and emissions of vehicles, and is given by
where (measure of effectiveness) denotes the emission and fuel consumption rates of vehicle i, is the regression coefficient, and p and q, respectively, denote the power of velocity and acceleration. The regression coefficients of the model are calibrated using the experimental data [26] and are given in [27]. The speed and acceleration data at each simulation time step can be fed into (10) to compute the fuel consumption and CO2, HC, CO, and NOx emissions of the vehicles.
Note that traffic patterns in real-world situations are dynamic; we ran numerical simulations several times with varied speeds via random number generation of the simulator and averaged the outcomes to prevent randomness biasing the simulation results. Specifically, we simulated a similar set of tests (for varying penetration rates in the EDS) ten times using different random speeds.
3.2. Validation and Impact Assessment
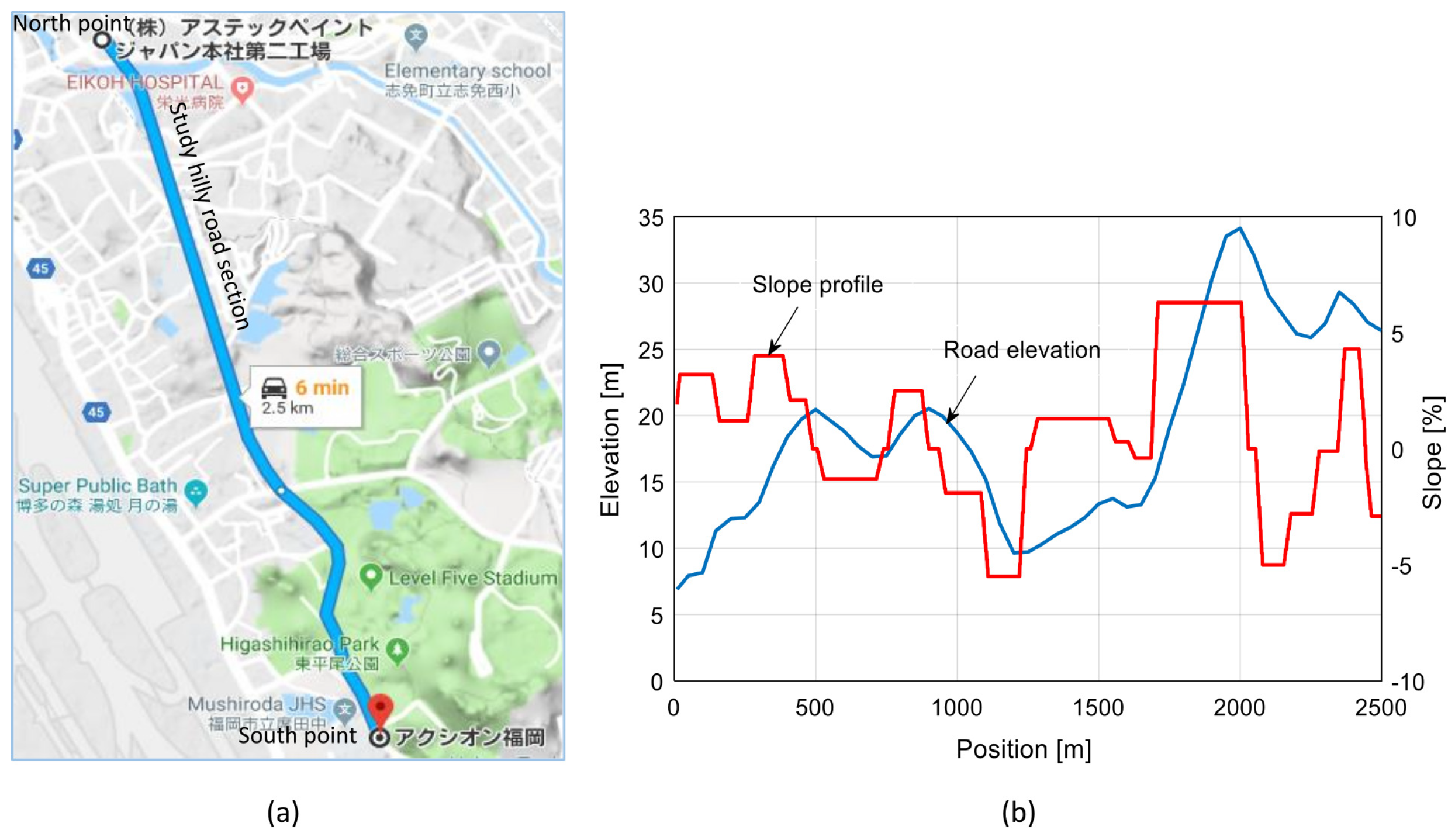
The impact of the proposed NMPC-based EDS is demonstrated and validated for different penetration rates using data of a real road section named Yuniba Dori and its extension, situated in Fukuoka City, Japan, as illustrated in Figure 4a. The road section is approximately 2.5 km long. The information on the road altitude is retrieved every five meters from Fukuoka City’s digital road–land elevation map and the grade angle is computed using (6). The elevation of the road is 26 m at the south point and 6 m at the north point and features intricate uphill and downhill grades of varying degrees, as shown in Figure 4b.
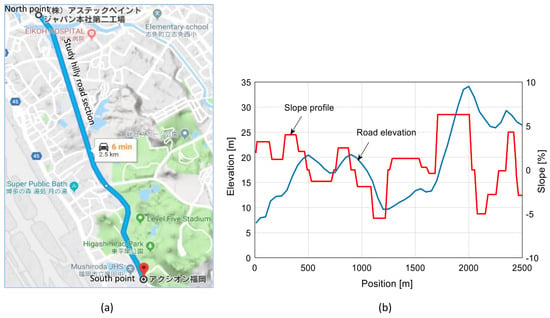
Figure 4.
(a) The studied hilly road section in Fukuoka City, Japan, captured from Google Maps, and (b) the altitude of the road and slope profile. The distance of the road section is 2.5 km.
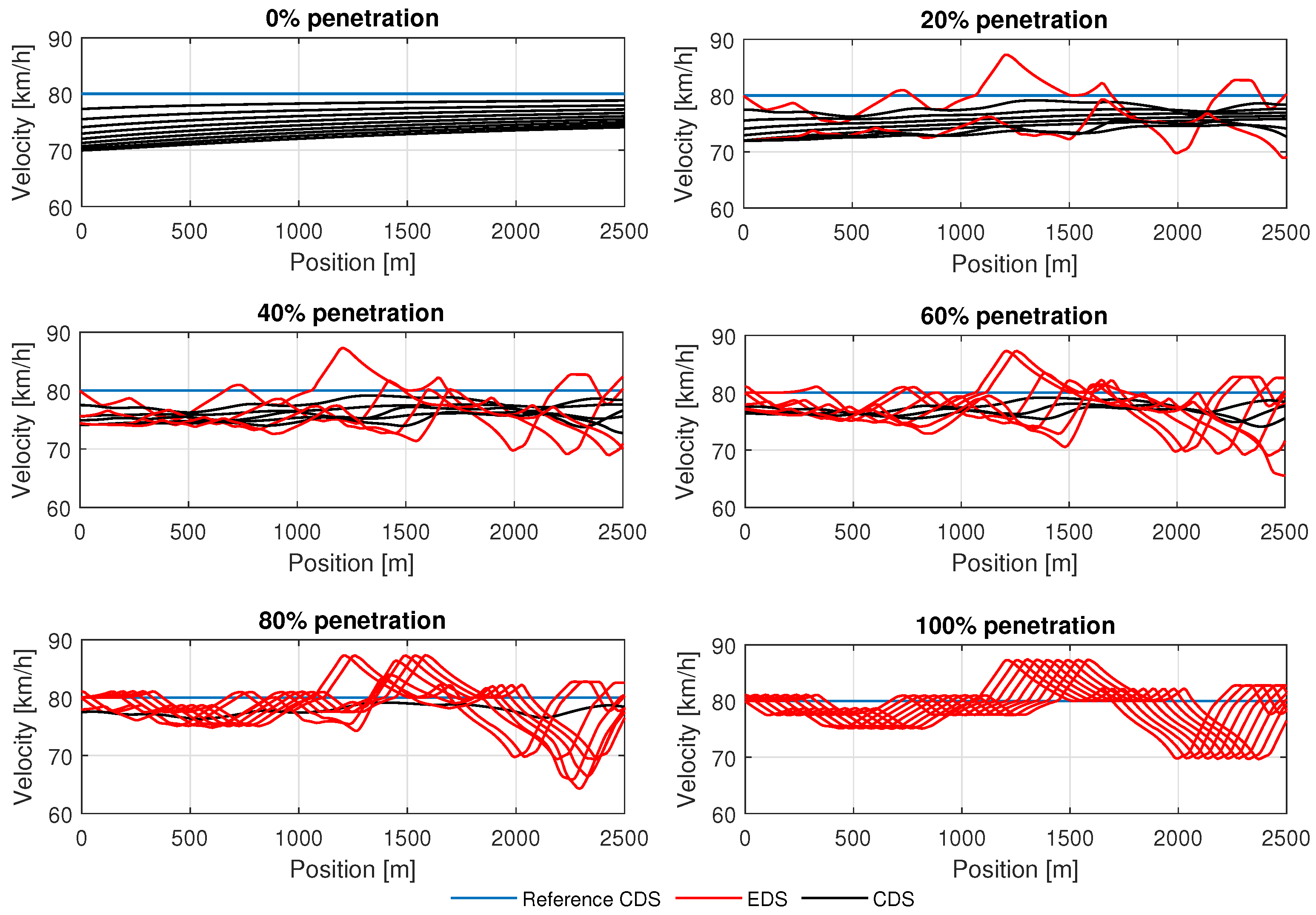
For a demonstration, we examined a ten-vehicle cluster in a synchronous and mixed traffic environment, including CDS vehicles. The first vehicle is the conventional vehicle, which is set as a reference. The objective is to determine (i) how energy-efficiently the EDS vehicles drive regarding complex up–down slopes while following the conventional vehicle (preceding the CDS) and (ii) the impact of EDS vehicles on the overall traffic flow at varying penetration rates. Therefore, the EDS vehicle penetration rates range from 0% to 100%, with a 20% increment. Next, trajectory data are generated via numerical simulations from the studied hilly road section from the north point to the south point. Figure 5 illustrates the simulation results of the velocity trajectories of vehicles for varying EDS penetration rates. It is found that when the penetration is 0%, i.e., all vehicles are conventional, the speed of the following CDS vehicles consecutively drops from the desired speed initially due to close gaps under dense traffic flow. As the penetration rates of the EDS vehicles increase from 20% to 100%, the speed of all vehicles starts to increase to about the desired speed , increasing the overall traffic average speed. This is because the EDS vehicles also improve the driving behavior by following the CDS (for 20–80% penetration rates) by minimizing their braking actions. Moreover, the higher penetration rate of the EDS (80–100%) smooths the speed trajectories of vehicles on varying up–down slopes. Such smooth trajectories are due to the anticipatory behavior of EDS vehicles.
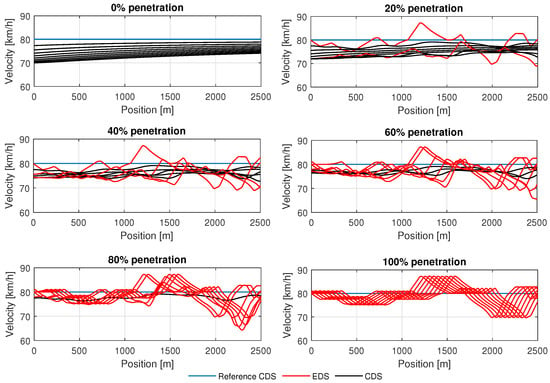
Figure 5.
Velocity trajectories of vehicles on the experimental hilly road section for various penetration rates of the EDS, while commuting a distance of 2.5 km from the north point to the south point.
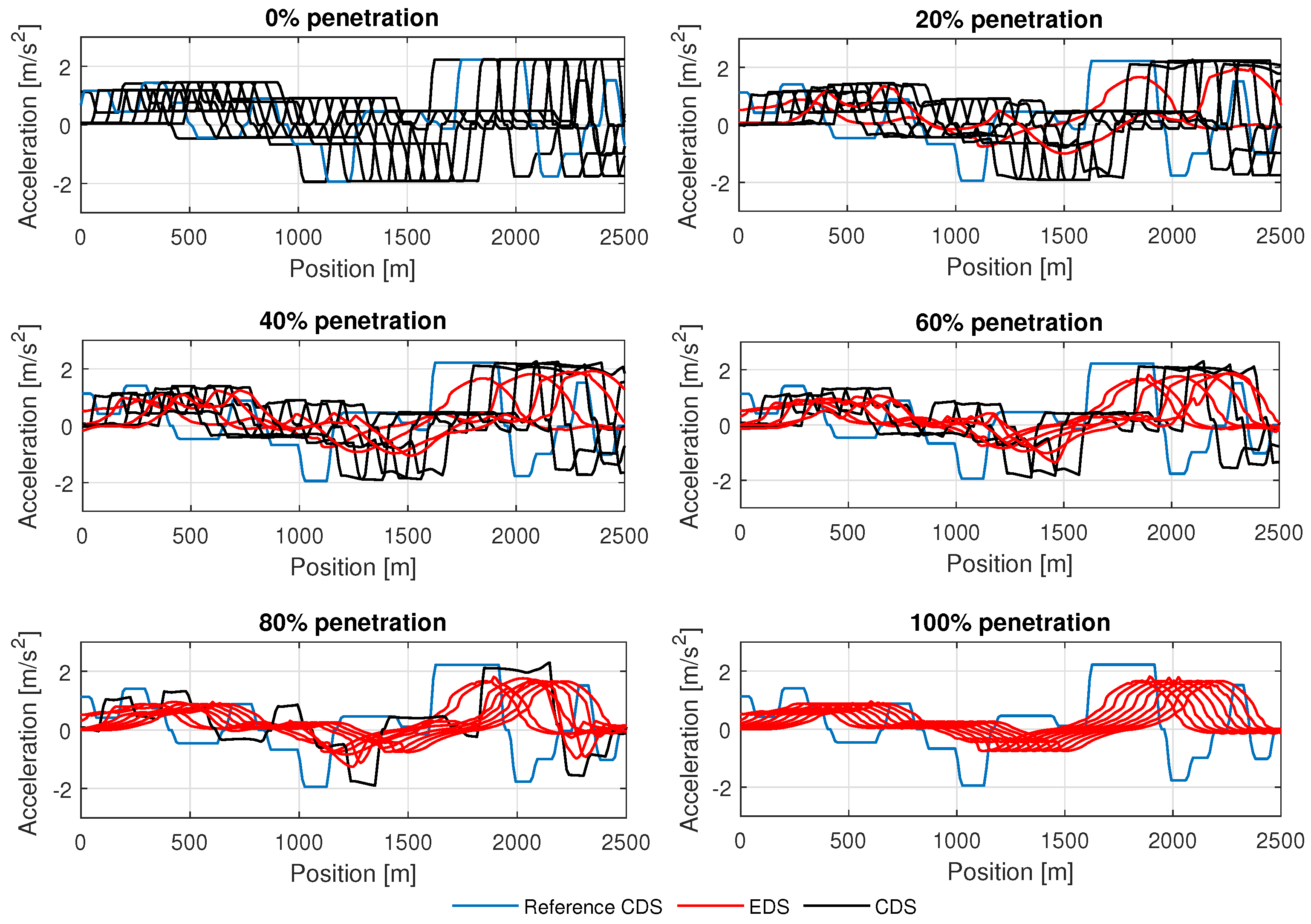
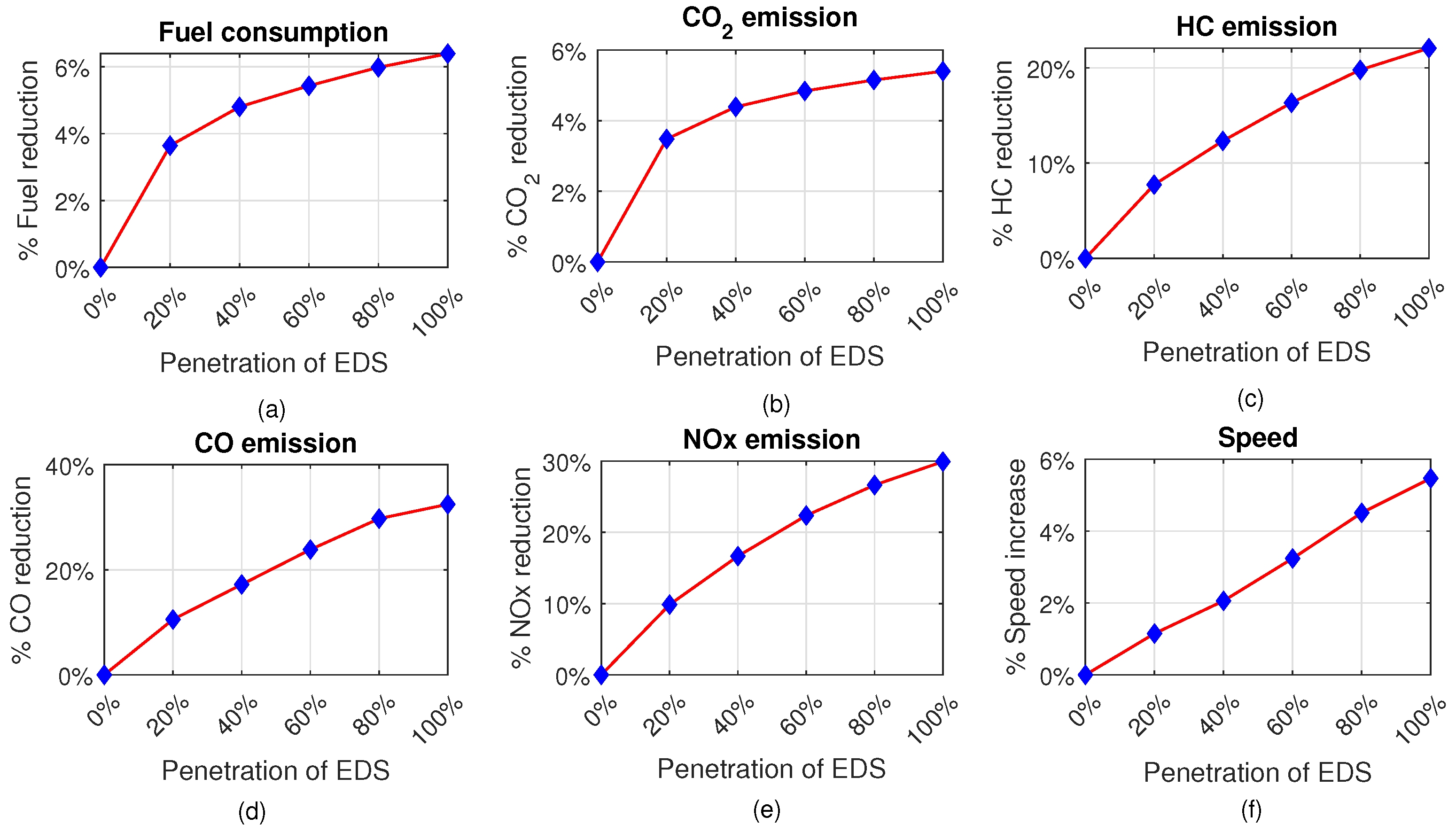
The acceleration profiles of vehicles at different penetration rates of the EDS are shown in Figure 6. It is found that the EDS vehicle can maintain acceleration and deceleration/braking (control input ) at the optimum level at different penetration rates while precisely anticipating the movement of the preceding CDS and varying up–down slopes. Such smooth variations in speed, acceleration, and deceleration can substantially reduce the GHG emissions and fuel consumption of vehicles. Table 1 gives the average total fuel consumption; CO2, HC, CO, and NOx emissions; and average speed for varying penetration rates of EDS vehicles on the studied hilly road section. The average total fuel consumption and CO2, HC, CO, and NOx emissions are calculated by summing the instantaneous fuel consumption and CO2, HC, CO, and NOx emissions (obtained from the VT-Micro model) of vehicles and averaging them over the number of simulation experiments. Then, we calculated the percentage reductions in fuel consumption, CO2, HC, CO, and NOx emissions, and average speed for different penetration rates of EDS vehicles, as illustrated in Figure 7.
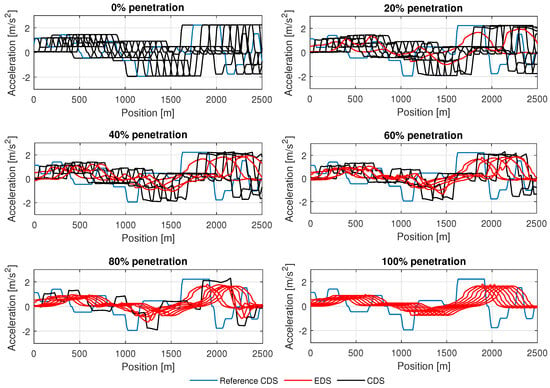
Figure 6.
Acceleration profiles of vehicles on the experimental hilly road section for various penetration rates of the EDS while commuting a distance of 2.5 km from the north point to the south point.

Table 1.
Effects of different EDS penetration rates on average total fuel consumption; CO2, HC, CO, and NOx emissions; and average speed of vehicles.
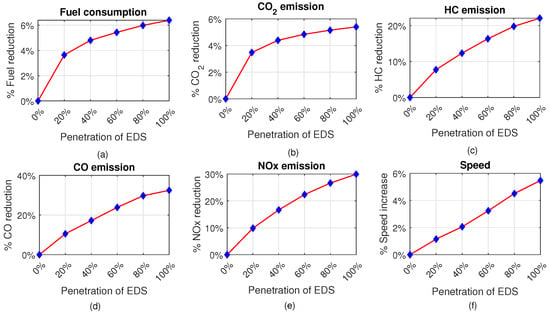
Figure 7.
The percentage improvements in (a) fuel consumption, (b) CO2 emissions, (c) HC emissions, (d) CO emissions, (e) NOx emissions, and (f) speed for different penetration rates of EDS vehicles.
Note that when a vehicle’s acceleration (including up slope factors) is high at some higher speeds, the engine often requires a large driving power at an operating point where the engine efficiency is low. Fuel is not entirely burnt in such conditions, producing more CO, HC, and NOx emissions. However, the amount of CO, HC, and NOx emissions is much lower than that of CO2 (as shown in Table 1), and a small change in driving behavior (smooth or aggressive driving) causes significant variations in their amounts. Since eco-driving avoids aggressive driving, it can remarkably reduce such emissions. Therefore, controlling the input acceleration by eco-driving significantly affects the production of CO, HC, and NOx, compared to that of CO2. Moreover, these values were calculated using the VT-Micro model that calculates fuel consumption and CO2, HC, CO, and NOx emissions by relating vehicle acceleration to the engine operating characteristics.
The findings indicate that the vehicle’s fuel consumption and CO2, HC, CO, and NOx emissions gradually reduce as the rate of EDS penetration increases. Specifically, only 20% of EDS vehicles considerably reduced the fuel usage and emissions of the overall traffic, because they also constrain the following CDS vehicles to drive ecologically. On the other hand, the average speed of vehicles significantly increases with the increased penetration rates of the EDS. Hence, managing mixed traffic on hilly roads using the EDS can remarkably improve the fuel efficiency, environmental sustainability, and overall traffic flow performance.
In the proposed study, an eco-driving system is developed considering the driving behavior of internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. Recently, electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) have become attractive options for vehicle users due to the rising cost of gasoline, and they are prevalent in many countries worldwide. Our proposed method can be utilized to improve the driving behavior of EVs and HEVs. In some studies, the consumption of auxiliaries of electric vehicles has been optimized concerning mission profiles [28], and such an approach can be adapted to our work as possible future development.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, we have developed an NMPC-based EDS to reduce the GHG emissions and fuel consumption of vehicles on hilly roads in a mixed-traffic environment. A nonlinearly constrained optimization problem is designed that considers the host vehicle’s longitudinal motion dynamics, the preceding vehicle’s state, and the slope of the route ahead to generate the optimum speed trajectory. Moreover, using fuzzy inference techniques, the weight parameter (associated with velocity deviation) of the objective function is tuned to prevent abrupt variations in velocity, considering the vehicle’s current speed and the angle of the road slope. The effectiveness of the proposed EDS is evaluated on a real hilly road stretch. The results demonstrate that the proposed EDS significantly reduces the fuel consumption and emissions of vehicles compared to the CDS for different penetration rates. In addition, the average speed of vehicles increases by almost 5.5%.
In this work, the eco-driving actions of vehicles are independently governed by NMPC without considering vehicle–vehicle communication. However, such communications or information sharing can further benefit our proposed system. In future work, we will consider such communications between vehicles. In addition, applying the proposed method to hybrid and electric actuation considering the current development of traction systems would be an interesting future study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S.M.B. and M.A.S.K.; methodology, A.S.M.B., M.A.S.K. and J.-i.I.; software, A.S.M.B.; validation, M.A.S.K., J.-i.I. and M.M.; formal analysis, A.S.M.B.; investigation, M.A.S.K., J.-i.I., M.M. and K.Y.; resources, A.S.M.B. and M.A.S.K.; data curation, A.S.M.B. and M.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.M.B.; writing—review and editing, M.A.S.K., J.-i.I., M.M. and K.Y.; visualization, A.S.M.B.; project administration, M.A.S.K. and J.-i.I.; funding acquisition, M.A.S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge financial support from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) 23K03898.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- EPA. Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks: 1990–2021. 430-R-23-002 Report. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 2023. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/inventory-us-greenhouse-gas-emissions-and-sinks-1990-2021 (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Zhang, K.; Frey, H.C. Road grade estimation for on-road vehicle emissions modeling using light detection and ranging data. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU Commission. A European Strategy for Low-Emission Mobility. SWD 244 Report. 2016. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/es/MEMO_16_2497 (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Mendez, S.; Thirouard, B. Using multiple injection strategies in diesel combustion: Potential to improve emissions, noise and fuel economy trade-off in low CR engines. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2009, 1, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, J.; Xu, P.; Zhang, Y. Moving towards sustainability: Road grades and on-road emissions of heavy-duty vehicles—A case study. Sustainability 2015, 7, 12644–12671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrese, S.; Gemma, A.; La Spada, S. Impacts of driving behaviors, slope and vehicle load factor on bus fuel consumption and emissions: A real case study in the city of Rome. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 87, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, H.C.; Zhang, K.; Rouphail, N.M. Fuel use and emissions comparisons for alternative routes, time of day, road grade, and vehicles based on in-use measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2483–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meseguer, J.E.; Calafate, C.T.; Cano, J.C.; Manzoni, P. Assessing the impact of driving behavior on instantaneous fuel consumption. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 9–12 January 2015; pp. 443–448. [Google Scholar]
- Bakibillah, A.S.M.; Kamal, M.A.S.; Tan, C.P.; Hayakawa, T.; Imura, J. Event-driven stochastic eco-driving strategy at signalized intersections from self-driving data. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 8557–8569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Guanetti, J.; Borrelli, F.; Moura, S.J. Optimal eco-driving control of connected and autonomous vehicles through signalized intersections. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 3759–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dave, K.; Huang, Y. Fuel consumption and exhaust emissions of diesel vehicles in worldwide harmonized light vehicles test cycles and their sensitivities to eco-driving factors. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 196, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakibillah, A.S.M.; Kamal, M.A.S.; Tan, C.P.; Hayakawa, T.; Imura, J. Optimal eco-driving scheme for reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions on curved roads. Heliyon 2014, 10, e23586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzkopf, A.; Leipnik, R. Control of highway vehicles for minimum fuel consumption over varying terrain. Transp. Res. 1977, 11, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.J.; Morlok, E.K. Vehicle speed profiles to minimize work and fuel consumption. J. Transp. Eng. 2005, 131, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saerens, B.; Van den Bulck, E. Calculation of the minimum-fuel driving control based on Pontryagin’s maximum principle. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2013, 24, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, E.; Ivarsson, M.; Åslund, J.; Nielsen, L. Look-ahead control for heavy trucks to minimize trip time and fuel consumption. Control. Eng. Pract. 2009, 17, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, H.T.; Nouvelière, L.; Mammar, S. Dynamic programming for fuel consumption optimization on light vehicle. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2010, 43, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Kum, D.; Park, Y. Impact of hilly road information on fuel economy of FCHEV based on parameterization of hilly roads. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2014, 15, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.A.S.; Mukai, M.; Murata, J.; Kawabe, T. Ecological vehicle control on roads with up-down slopes. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2011, 12, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Yang, J.; Yamaguchi, D. Model predictive control for hybrid vehicle ecological driving using traffic signal and road slope information. Control. Theory Technol. 2015, 13, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakibillah, A.S.M.; Kamal, M.A.S.; Tan, C.P.; Hayakawa, T.; Imura, J. Eco-driving on hilly roads using model predictive control. In Proceedings of the Joint 7th IEEE International Conference on Informatics, Electronics & Vision (ICIEV) and 2nd IEEE International Conference on Imaging, Vision & Pattern Recognition (icIVPR) 2018, Kitakyushu, Japan, 25–29 June 2018; pp. 476–480. [Google Scholar]
- Bakibillah, A.S.M.; Kamal, M.A.S.; Tan, C.P.; Hayakawa, T.; Imura, J. Fuzzy-tuned model predictive control for dynamic eco-driving on hilly roads. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 99, 106875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesting, A.; Treiber, M.; Helbing, D. Enhanced intelligent driver model to access the impact of driving strategies on traffic capacity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. 2010, 368, 4585–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iancu, I. A Mamdani type fuzzy logic controller. Fuzzy Log. Control. Concepts Theor. Appl. 2012, 15, 325–350. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, K.; Rakha, H.; Trani, A.; Van Aerde, M. Estimating vehicle fuel consumption and emissions based on instantaneous speed and acceleration levels. J. Transp. Eng. 2002, 128, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakha, H.; Ahn, K.; Trani, A. Development of VT-Micro model for estimating hot stabilized light duty vehicle and truck emissions. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2004, 9, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhao, B.; Jiang, Y. Fuel consumption and transportation emissions evaluation of mixed traffic flow with connected automated vehicles and human-driven vehicles on expressway. Energy 2021, 230, 120766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzi, L.; Delichristov, D.; Favilli, T.; Pierini, M.; Ponchant, M.; Qehajaj, A.; Pugi, L. Smart energy management of auxiliary load for electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe (EEEIC/I&CPS Europe), Madrid, Spain, 9–12 June 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).