A Novel Approach for Train Tracking in Virtual Coupling Based on Soft Actor-Critic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
3.1. Soft Actor-Critic
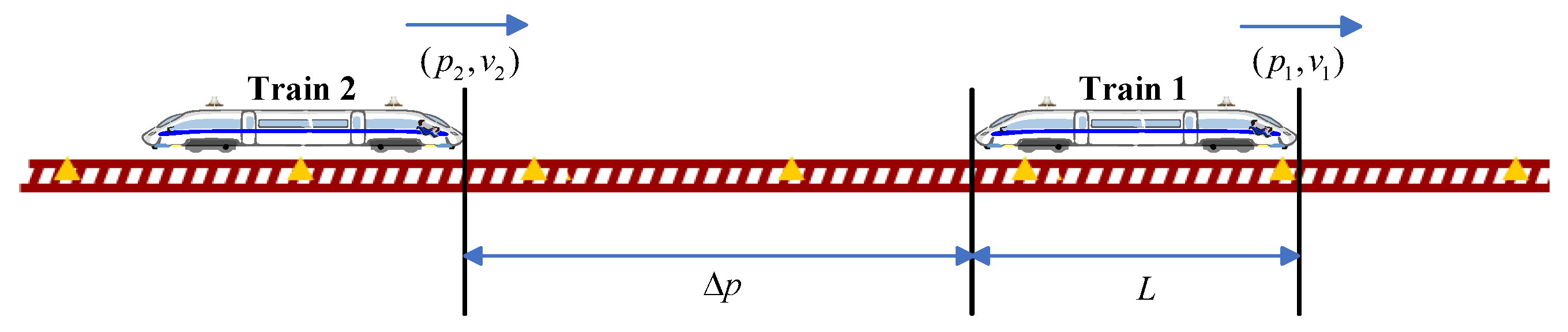
3.2. Train Tracking Model Based on Reinforcement Learning
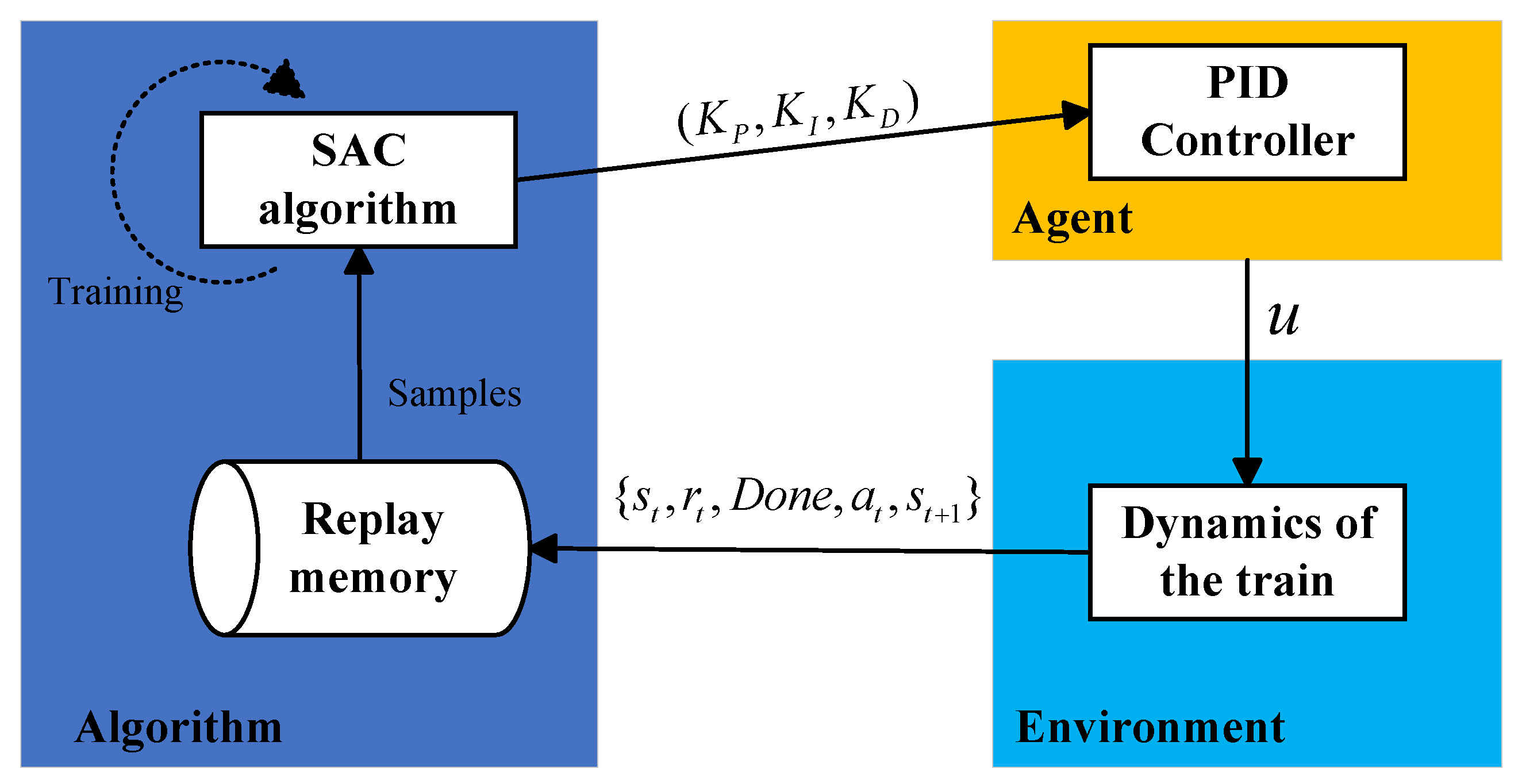
3.3. The Train Tracking Control Method Based on SAC
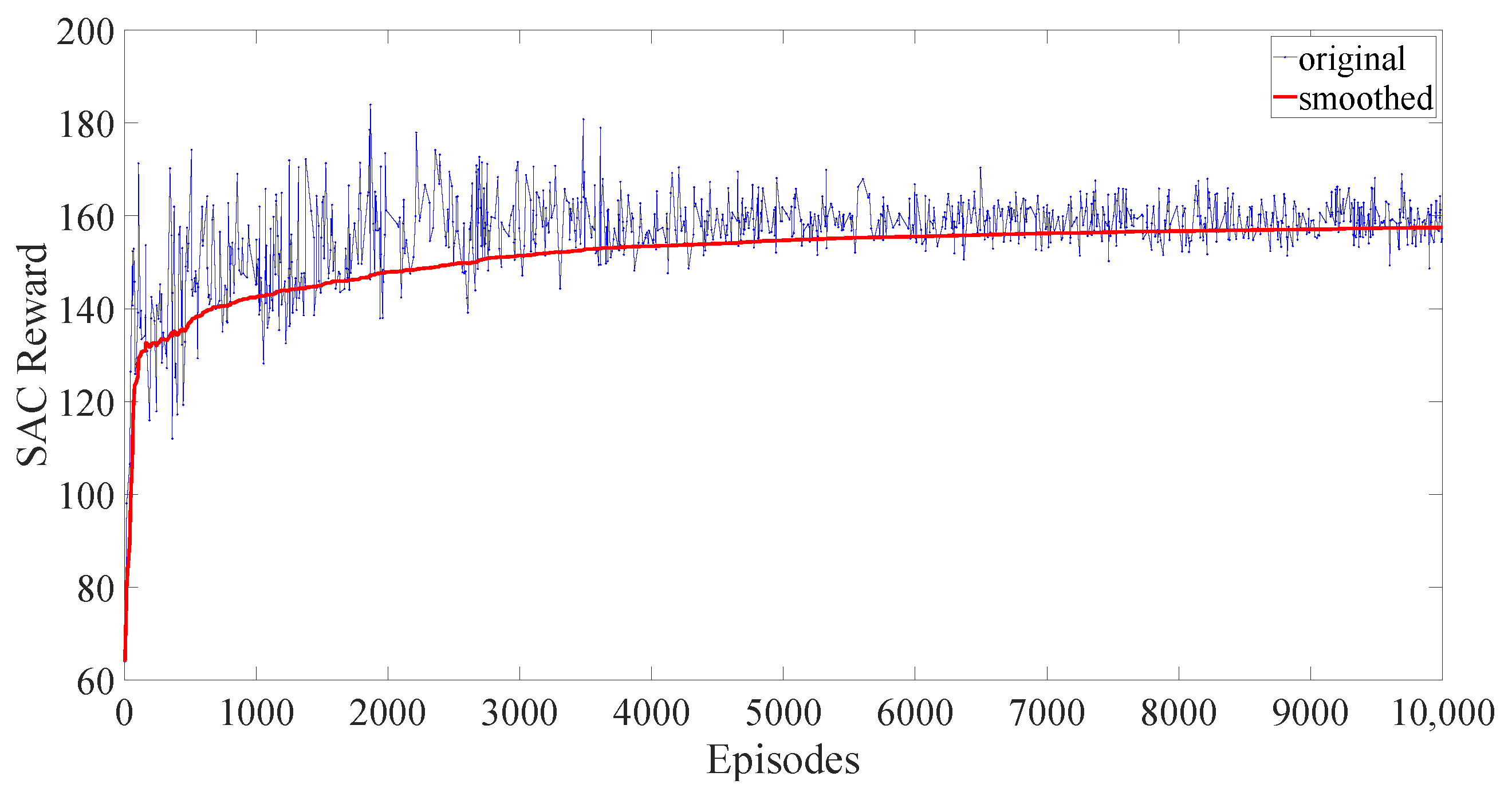
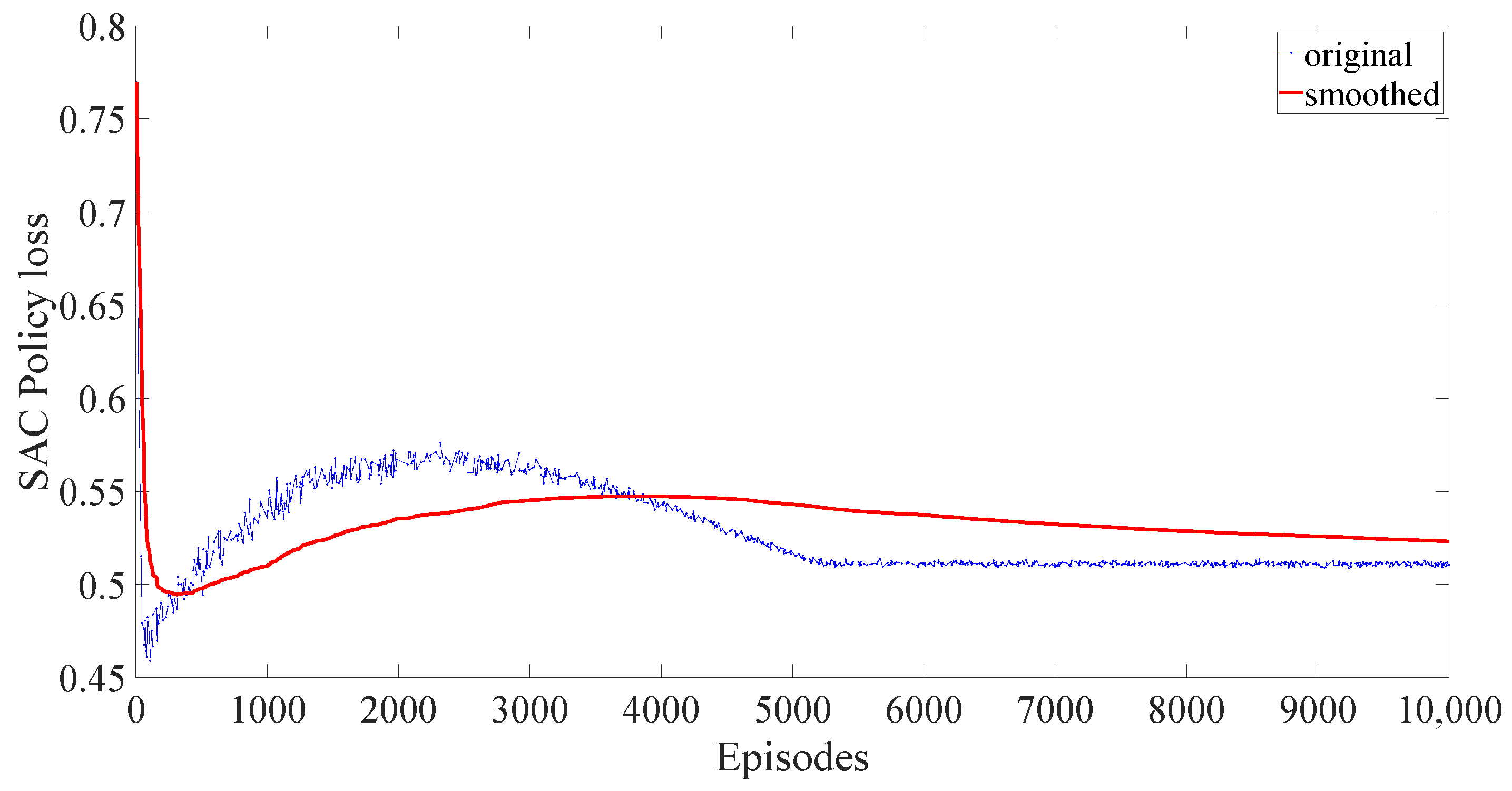
4. Case Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PID | Proportional Integral Derivative |
| MPC | Model Predictive Control |
| SAC | Soft Actor-Critic |
| RL | Reinforcement Learning |
| ATC | Automatic Train Control |
| DDPG | Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient |
Appendix A
| Algorithm A1: SAC algorithm |
 |
References
- Bock, U.; Varchmin, J.-U. Improvement of line capacity by using “virtually coupled train formations”. VDI Berichte 1999, 1488, 315–324. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, U.; Bikker, G. Design and development of a future freight train concept—“Virtually coupled train formations”. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2000, 33, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, S.; Bikker, G. Developing and Implementing a Framework for CASE Tool Coupling-Object Orientation upon Tool Level. In Proceedings of the European Concurrent Engineering Conference, Leicester, UK, 17–19 April 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, U.; Varchmin, J.U. Virtually coupled train formations: Wireless communication between train units. In Proceedings of the General Traffic Forum, Braunschweig, Germany, 6–7 April 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bikker, G.; Bock, U. Einsatz eines Prozeßmodells zur Analyse und Spezifikation von Bussystemen. EKA 1999, 99, 509–526. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Wen, J.; Ma, L. Tracking and collision avoidance of virtual coupling train control system. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 120, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ma, L.; Wen, J. Research on Virtual Coupled Train Control Method Based on GPC & VAPF. Chin. J. Electron. 2022, 31, 897–905. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, Z. Distributed velocity and input constrained tracking control of high-speed train systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2020, 51, 7882–7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Su, S.; Xun, J.; Tang, T. An analytical optimal control approach for virtually coupled high-speed trains with local and string stability. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2021, 125, 102886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Tang, T.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, K. An Adaptive Model Predictive Control System for Virtual Coupling in Metros. Actuators 2021, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chai, M.; Liu, H.; Tang, T. Optimized Control of Virtual Coupling at Junctions: A Cooperative Game-Based Approach. Actuators 2021, 10, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, D.; Li, Y.; Feng, X. A novel iterative learning approach for tracking control of high-speed trains subject to unknown time-varying delay. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2020, 19, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felez, J.; Vaquero-Serrano, M.A.; de Dios Sanz, J. A Robust Model Predictive Control for Virtual Coupling in Train Sets. Actuators 2022, 11, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; She, J.; Li, K.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y. A nonlinear safety equilibrium spacing-based model predictive control for virtually coupled train set over gradient terrains. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 8, 2810–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chengwei, W.; Weiran, Y.; Wensheng, L.; Wei, P.; Guanghui, S.; Xie, H.; Wu, L. A Secure Robot Learning Framework for Cyber Attack Scheduling and Countermeasure. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2023, 39, 3722–3738. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Pan, W.; Staa, R.; Liu, J.; Sun, G.; Wu, L. Deep reinforcement learning control approach to mitigating actuator attacks. Automatica 2023, 152, 110999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lv, J.; Liu, H.; Tang, T. Toward the Trajectory Predictor for Automatic Train Operation System Using CNN–LSTM Network. Actuators 2022, 11, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lv, J.; Tang, T. Communication-Based Train Control with Dynamic Headway Based on Trajectory Prediction. Actuators 2022, 11, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, P.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.; Peng, J. Cooperative tracking control of the multiple-high-speed trains system using a tunable artificial potential function. J. Adv. Transp. 2022, 2022, 3639586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yin, C.; Ji, H.; Hou, Z. Constrained spatial adaptive iterative learning control for trajectory tracking of high speed train. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 11720–11728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H. Research on Tracking Control of Urban Rail Trains Based on Improved Disturbance Observer. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, S.; Cao, Y.; Xin, T.; Yang, L. Dynamic speed trajectory generation and tracking control for autonomous driving of intelligent high-speed trains combining with deep learning and backstepping control methods. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 115, 105230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarnoja, T.; Zhou, A.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S. Soft Actor-Critic: Off-Policy Maximum Entropy Deep Reinforcement Learning with a Stochastic Actor. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Gao, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Optimal Control Algorithm for Subway Train Operation by Proximal Policy Optimization. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ang, K.H.; Chong, G.C. PID control system analysis and design. IEEE Control. Syst. Mag. 2006, 26, 32–41. [Google Scholar]



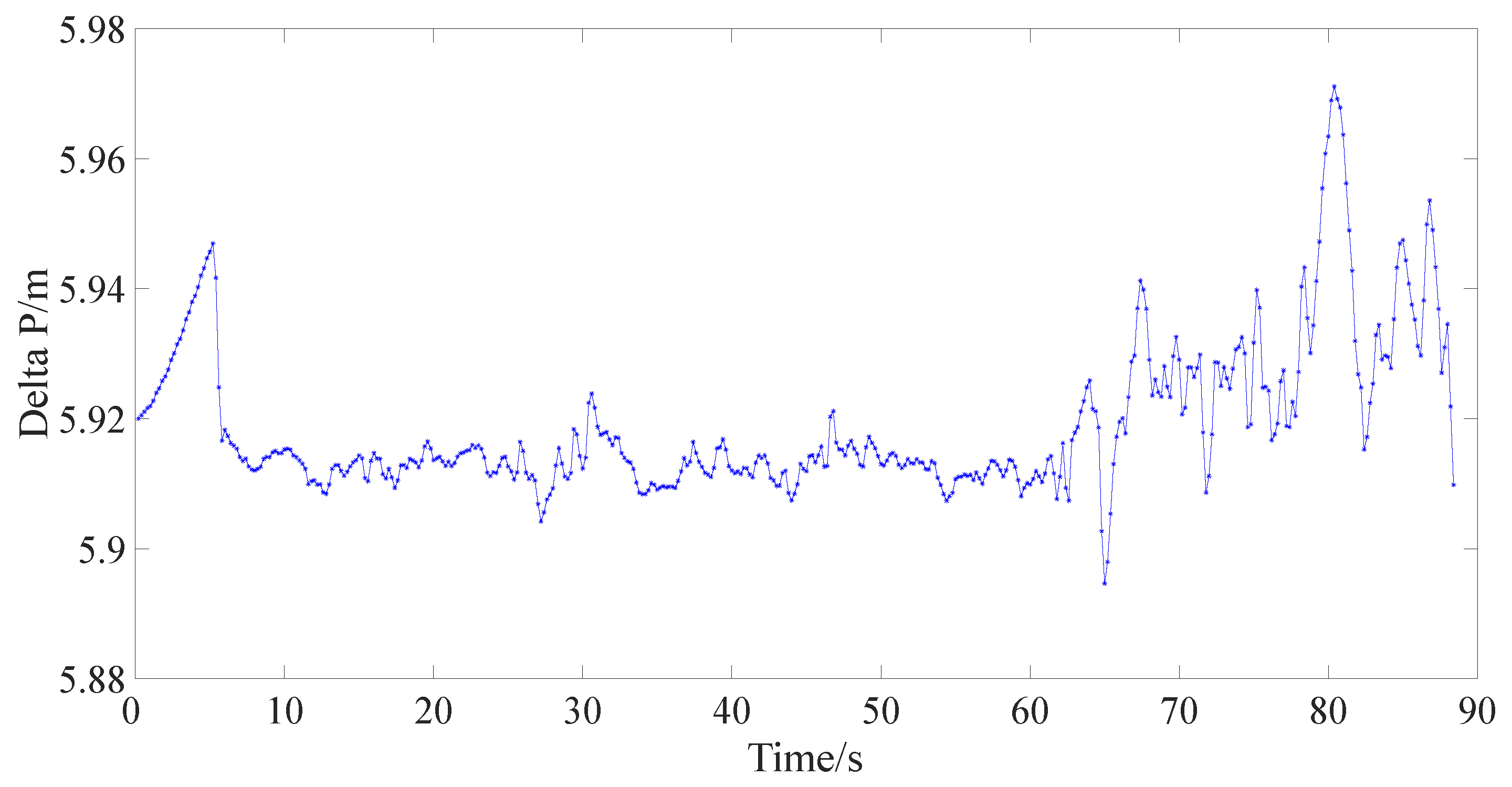
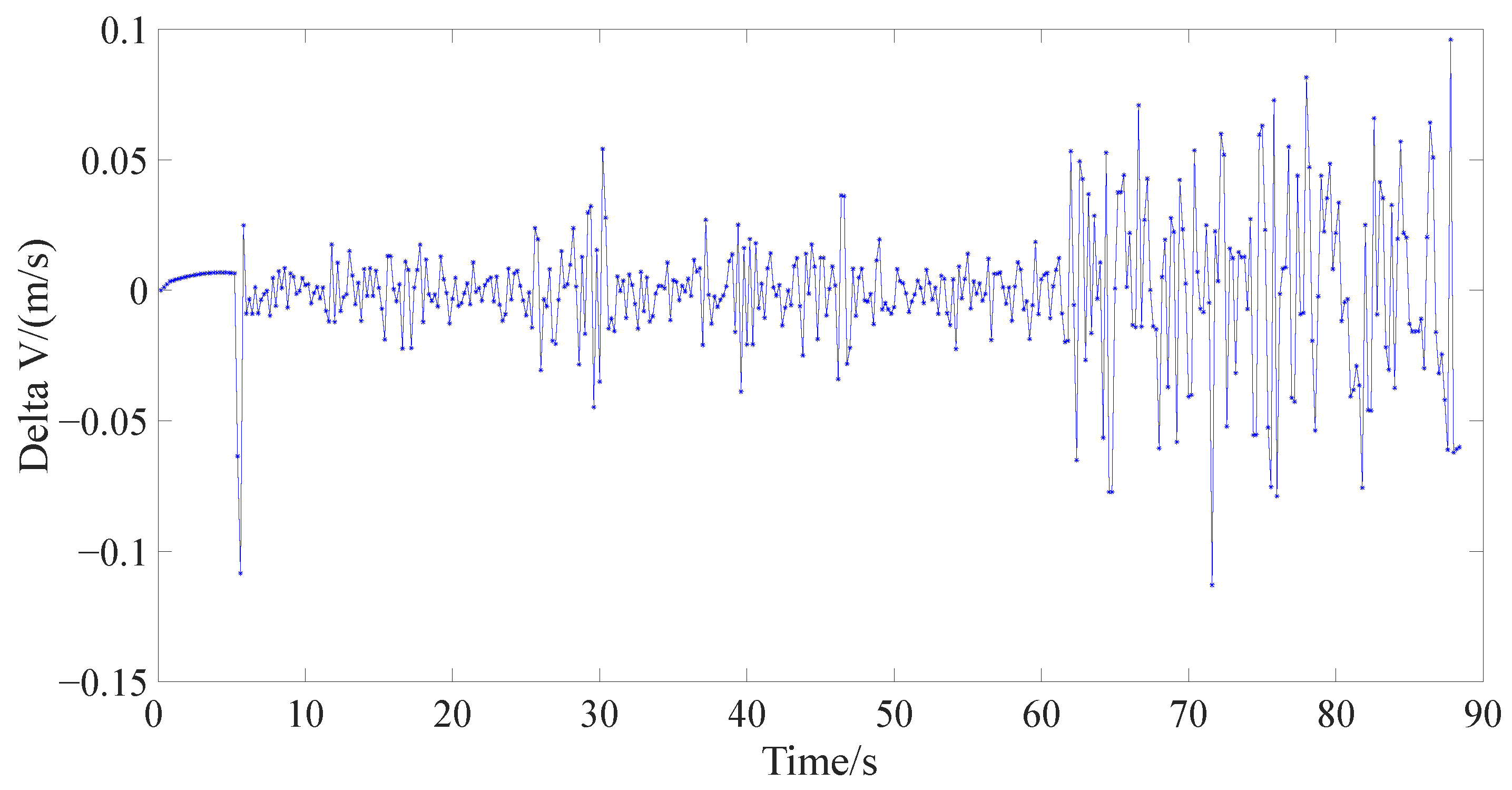
| Parameter Names | Parameters |
|---|---|
| L /m | 92 |
| /m | 5.92 |
| 1000 | |
| 1000 | |
| C | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, B.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. A Novel Approach for Train Tracking in Virtual Coupling Based on Soft Actor-Critic. Actuators 2023, 12, 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12120447
Chen B, Zhang L, Cheng G, Liu Y, Chen J. A Novel Approach for Train Tracking in Virtual Coupling Based on Soft Actor-Critic. Actuators. 2023; 12(12):447. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12120447
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Bin, Lei Zhang, Gaoyun Cheng, Yiqing Liu, and Junjie Chen. 2023. "A Novel Approach for Train Tracking in Virtual Coupling Based on Soft Actor-Critic" Actuators 12, no. 12: 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12120447
APA StyleChen, B., Zhang, L., Cheng, G., Liu, Y., & Chen, J. (2023). A Novel Approach for Train Tracking in Virtual Coupling Based on Soft Actor-Critic. Actuators, 12(12), 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12120447






