Sliding-Mode Control for PMLSM Position Control—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
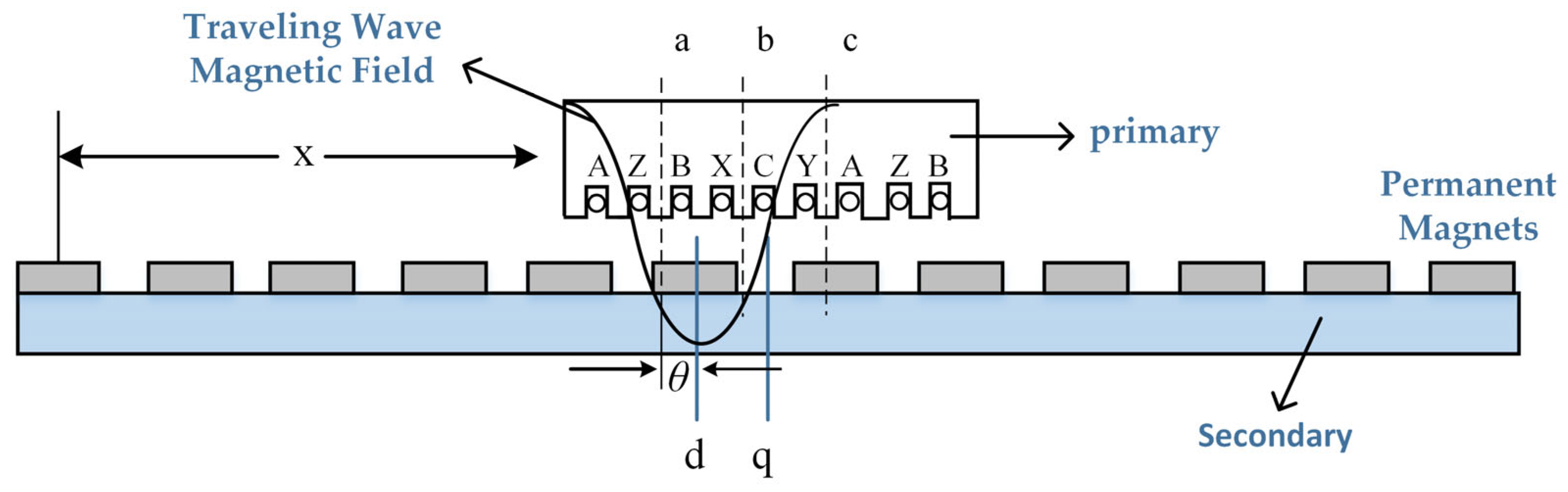
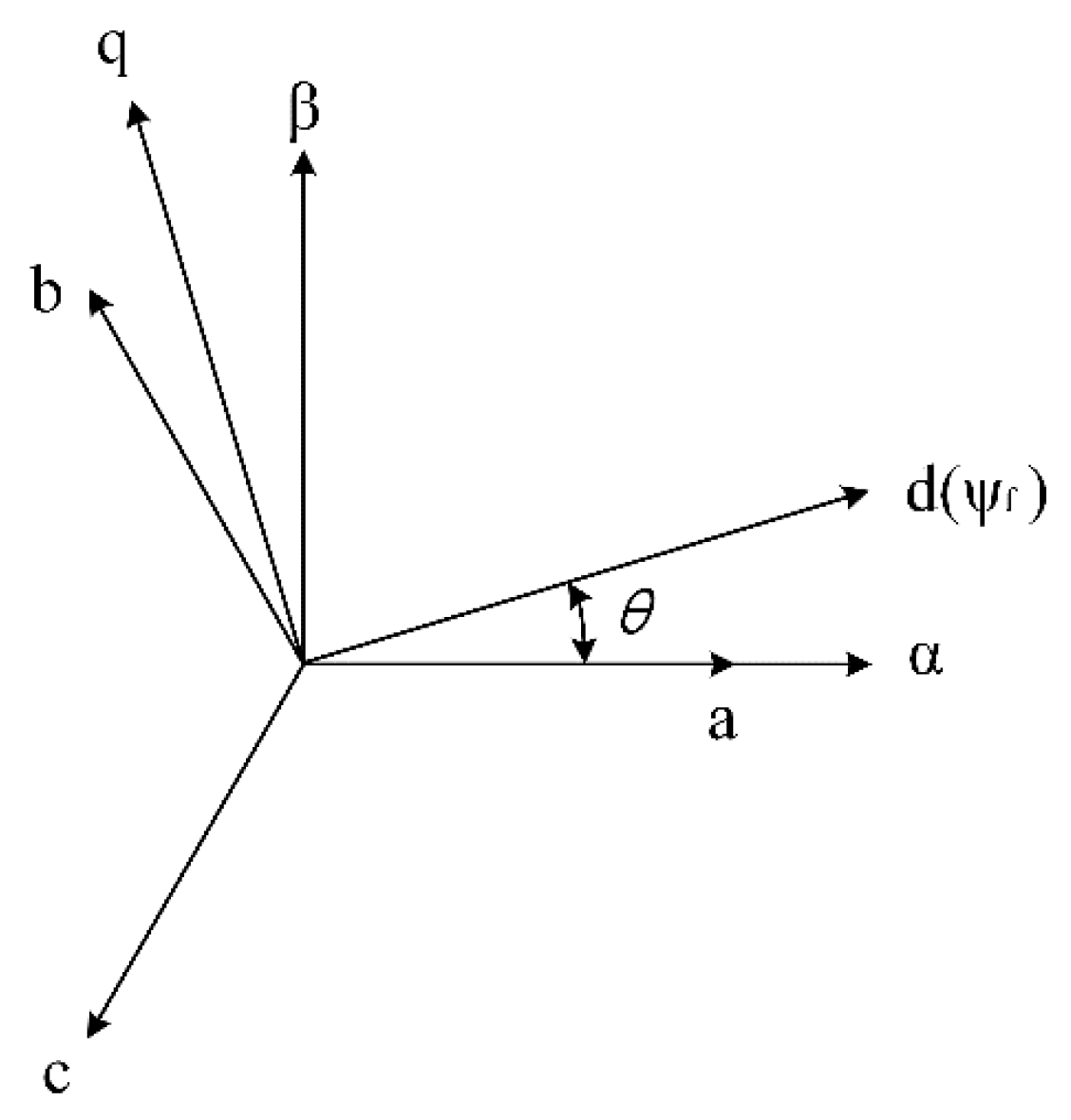
2. Dynamic Model of PMLSM
3. SMC Theory
3.1. Fundamental Theroy of SMC
3.2. SMC Design
- (1)
- Constant rate reaching law:
- (2)
- Constant plus proportional rate reaching law:
- (3)
- Power rate reaching law:
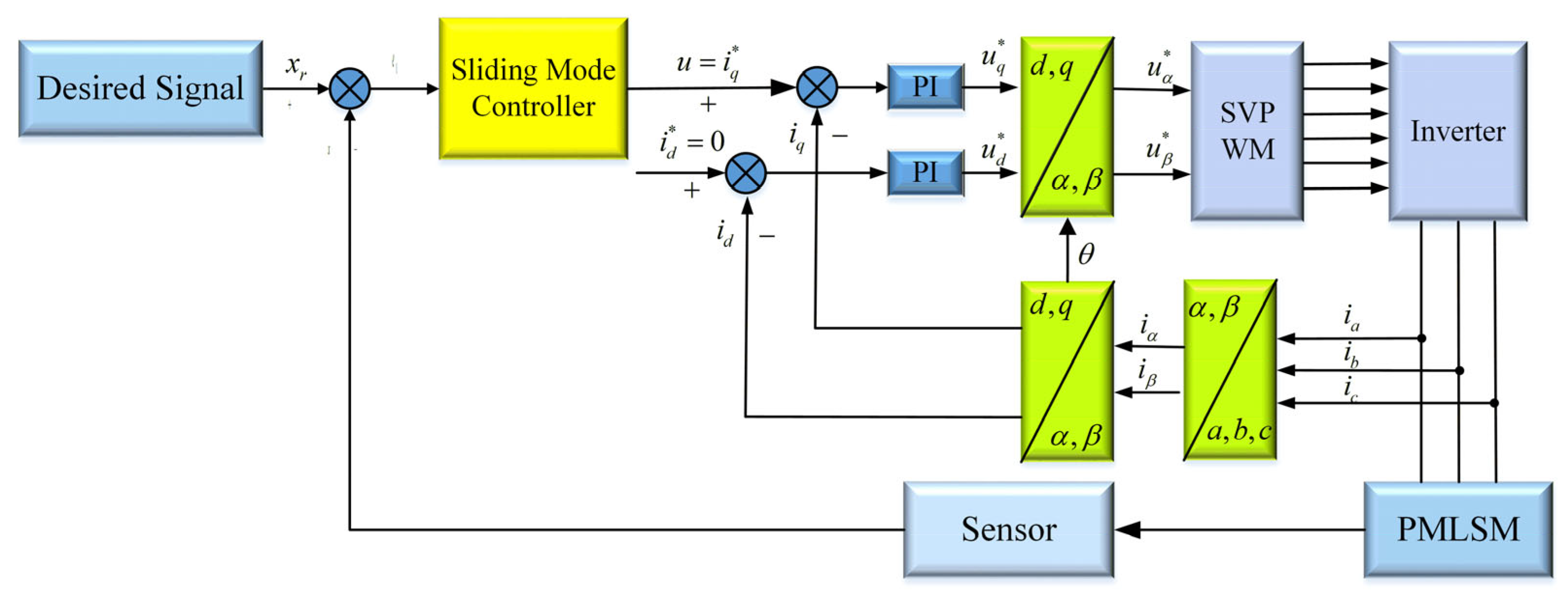
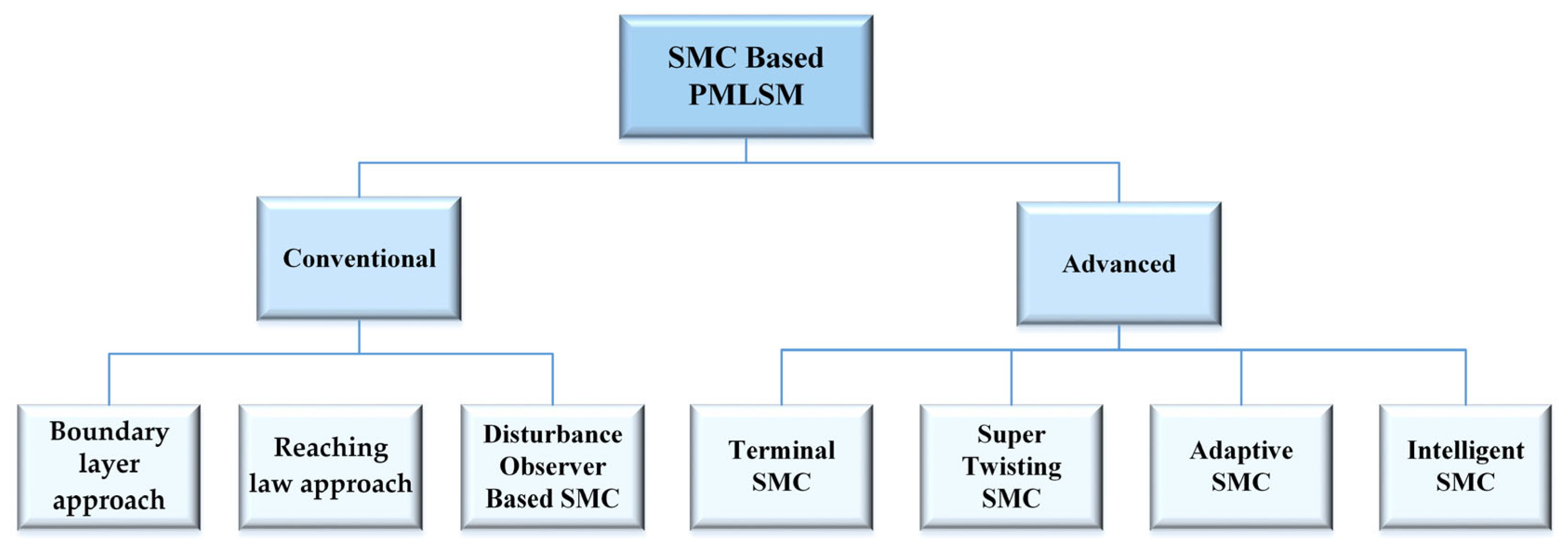
4. SMC for Position Control of PMLSM
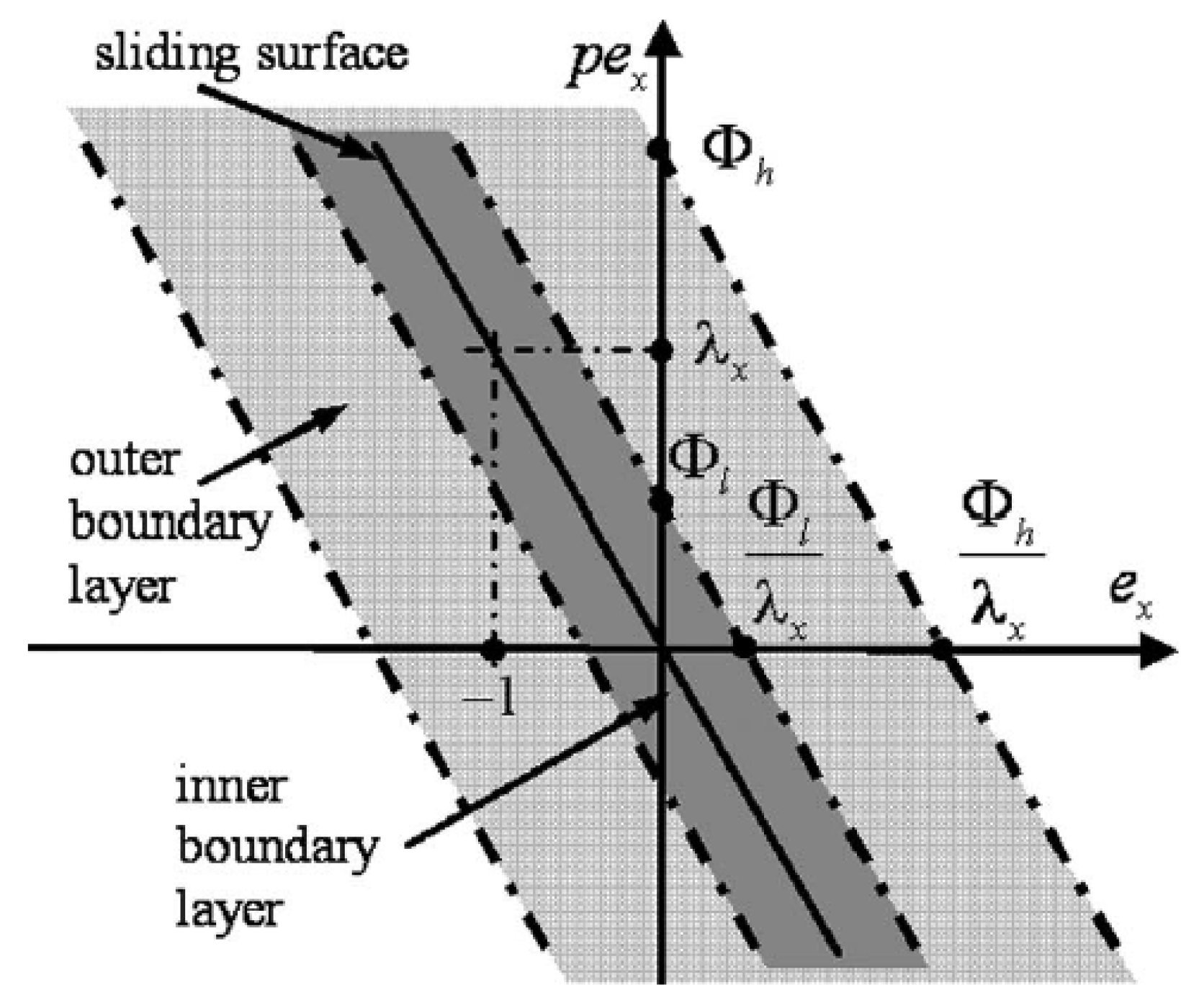
4.1. Boundary Layer Approach
4.2. Reaching Law Approach
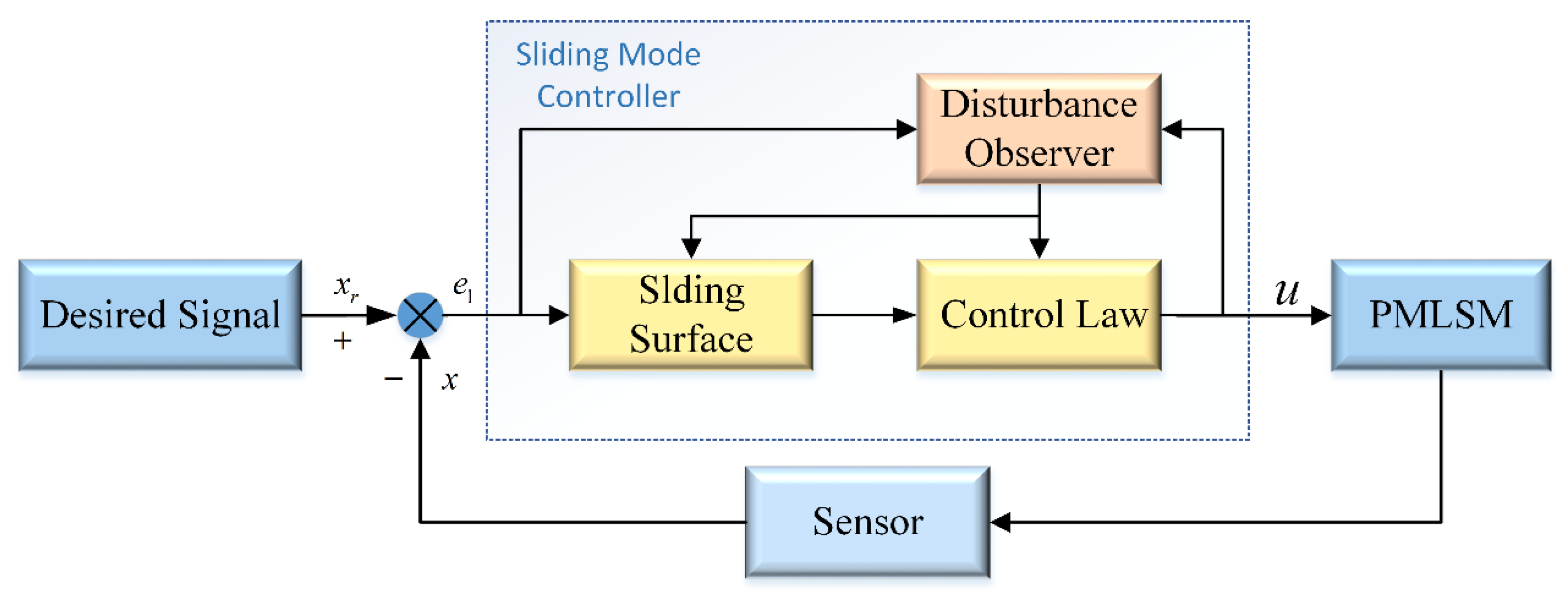
4.3. Disturbance Observer-Based SMC
4.4. Terminal SMC
4.5. Super-Twisting SMC
4.6. Adaptive SMC
4.7. Intelligent SMC
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, K.K.; Huang, S.N.; Lee, T.H. Robust adaptive numerical compensation for friction and force ripple in permanent-magnet linear motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2002, 38, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, M.A.M.; Fletcher, J.E.; Farshadnia, M.; Xiao, D.; Rahman, M.F. Combined Speed and Direct Thrust Force Control of Linear Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors with Sensorless Speed Estimation Using a Sliding Mode Control with Integral Action. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 3489–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, M.A.; Manzie, C.; Good, M.C. Model Predictive Control for Reference Tracking on an Industrial Machine Tool Servo Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2013, 9, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sousy, F.F.M.; Abuhasel, K.A. Nonlinear Robust Optimal Control via Adaptive Dynamic Programming of Permanent-Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Drive for Uncertain Two-Axis Motion Control System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 1940–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieras, J.F.; Piech, Z.; Tomczuk, B.Z. Linear Synchronous Motors: Transportation and Automation Systems, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.K.; Lee, T.H.; Dou, H.F.; Chin, S.J.; Zhao, S. Precision motion control with disturbance observer for pulsewidth-modulated driven permanent-magnet linear motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2003, 39, 1813–1818. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, D. Application of fuzzy PID control in PMLSM servo drive system. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics & Automation, Beijing, China, 5 August 2015; pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.B.; Chen, X.P.; Wen, G.H.; Yu, X.H.; Lu, J.H. Discrete-Time Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control for Permanent Magnet Linear Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 9916–9927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, C.S.; Chang, Y.N.; Shi, B.W.; Lieu, J.F. Adaptive backstepping control for permanent magnet linear synchronous motor serv-o drive. IET Electr. Power. Appl. 2015, 9, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Liu, T.S. Intelligent tracking control of a PMLSM using self-evolving probabilistic fuzzy neural network. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2017, 11, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.W.; Wang, L.J.; Li, M.; Hu, Y.P. Combined Vector Resonant and Active Disturbance Rejection Control for PMSLM Current Harmonic Suppression. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2020, 16, 5691–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, V.I. Survey Paper: Variable Structure Systems with Sliding Modes. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control 1977, 22, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.D.; Utkin, V.I.; Ozguner, U. A control engineer’s guide to sliding mode control. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 1999, 7, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.B.; Hung, J.C. Variable Structure Control of Nonlinear Systems: A New Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1993, 40, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Belai, I.; Huba, M.; Vranic, D. Comparing traditional and constrained disturbance-observer based positional control. Meas. Control. 2021, 54, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabanovic, A. Variable Structure Systems With Sliding Modes in Motion Control—A Survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2011, 7, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhier, Y.; Shaw, R.N.; Bures, M.; Islam, M.R.; Bajaj, M.; Albalawi, F.; Alqurashi, A.; Ghoneim, S.S.M. Robust interconnection and damping assignment energy-based control for a permanent magnet synchronous motor using high order sliding mode approach and nonlinear observer. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhier, Y.; Achour, A.; Shaw, R.N.; Ullah, N.; Chowdhury, M.S.; Techato, K. Fuzzy supervisory passivity-based high order-sliding mode control approach for tidal turbine-based permanent magnet synchronous generator conversion system. Actuators 2021, 10, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhier, Y.; Achour, A.; Ullah, N.; Shaw, R.N.; Farooq, Z.; Ullah, A.; Alzaed, A.N. Intelligent energy-based modified super twisting algorithm and factional order PID control for performance improvement of PMSG dedicated to tidal power system. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 57414–57425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.X.; Zhao, X.M.; Zhu, J.G. A Novel Robust Super-Twisting Nonsingular Terminal Sliding Mode Controller for Permanent. Magnet Linear Synchronous Motors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 37, 2936–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decarlo, R.A.; Zal, S.H.; Matthews, G.P. Variable Structure Control of Nonlinear Multivariable Systems: A Tutorial. Proc. IEEE 1988, 76, 212–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotine, J.J.E. Sliding controller design for non-linear systems. Int. J. Control 1984, 40, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C.; Spurgeon, S. Sliding Mode Control: Theory and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Polyakov, A.; Fridman, L. Stability notions and Lyapunov functions for sliding mode control systems. J. Frankl. Inst. 2014, 351, 1831–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotine, J.J.; Sastry, S.S. Tracking control of nonlinear systems using sliding surface with application to robot manipulator. Int. J. Control 1983, 38, 465–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.S.; Sung, C.C. Implementation of sliding mode controller for linear synchronous motors based on direct thrust control theory. IET Control Theory Appl. 2010, 4, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupertino, F.; Naso, D.; Mininno, E.; Turchiano, B. Sliding-Mode Control with Double Boundary Layer for Robust Compensati-on of Payload Mass and Friction in Linear Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2009, 45, 1688–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.Y.; Zhao, X.M. Approach Angle-Based Saturation Function of Modified Complementary Sliding Mode Control for PMLSM. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 126014–126024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.C.; Jiang, M.; Chen, Q.Q.; Wei, L.S.; Gao, W.G. Sliding Mode Control of PMLSM for High Speeding Gringding Machine. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Material Science and Engineering Technology, Zhengzhou, China, 13 November 2011; pp. 701–706. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.F.; Wu, G.Q.; Wu, A.H.; Zhang, X.D. Nonlinear Decoupling Sliding Mode Control of Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Based on α-th Order Inverse System Method. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Advanced in Control Engineering and Information Science, CEIS, Dali, China, 18 August 2011; pp. 561–567. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.Y.; Yang, R.; Zhang, C.M.; Cao, J.W.; Li, L.Y. Inner Loop Design for PMLSM Drives with Thrust Ripple Compensation and High-Performance Current Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 9905–9915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.L.; Lan, Y.P.; Sun, Y.P.; Lei, C. A new reaching law for sliding mode observer of controllable excitation linear synchronous motor. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control. 2021, 44, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Zhao, J.W.; Zheng, Z.L. Robust Speed Tracking Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Linear Motor Based on a Discrete-Time Sliding Mode Load Thrust Observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 4758–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschemann, H.; Haus, B.; Mercorelli, P. Sliding Mode Control and Observer-Based Disturbance Compensation for a Permane-nt Magnet Linear Motor. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Milwaukee, WI, USA, 27–29 June 2018; pp. 4141–4146. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Chen, X.P.; Du, H.B.; Bai, S. Position tracking control for permanent magnet linear motor via fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode control. J. Control Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 3813624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.Y.; Zhao, X.M.; Wang, T.H. Modified complementary sliding mode control with disturbance compensation for permanent magnet linear synchronous motor servo system. IET Electr. Power. Appl. 2020, 14, 2128–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.J.; Liu, L.; Cai, M.J.; Shao, N. Backstepping Sliding Mode Control for the Displacement Tracking of Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Based on Nonlinear Disturbance Observer. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Modelling, Identification and Control, Tianjin, China, 13–15 July 2019; pp. 373–382. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, K.; Zheng, J.C.; Wang, H.; Xu, F.; Wang, X.Q.; Liang, B. Recursive sliding mode control with adaptive disturbance observer for a linear motor positioner. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 146, 107014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, L.M.; Fang, X. High-Order Fast Nonsingular Terminal Sliding Mode Control of Permanent Magnet Linear Motor Based on Double Disturbance Observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 3696–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.H.; Yu, X.H.; Shirizadeh, B.; Man, Z.H. Continuous finite-time control for robotic manipulators with terminal sliding mode. Automatica 2005, 41, 1957–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.H.; Man, Z.H. Fast terminal sliding-mode control design for nonlinear dynamical systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 2002, 49, 261–264. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Yu, X.H.; Man, Z.H. Non-singular terminal sliding mode control of rigid manipulators. Automatica 2002, 38, 2159–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, J.Y. Terminal sliding-mode control for nonlinear dynamical systems. Int. J. Robust. Nonlin. 2011, 21, 1865–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.H.; Lan, Q.X. Finite-Time Integral Sliding Mode Control for Motion Control of Permanent-Magnet Linear Motors. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 567610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.C.; Wang, H.; Man, Z.H.; Jin, J.; Fu, M.Y. Robust Motion Control of a Linear Motor Positioner Using Fast Nonsingular Terminal Sliding Mode. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, Y.J. Nonsingular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control of Permanent Magnet Linear Motors. In Proceedings of the 28th Chinese Control and Decision Conference, Yinchuan, China, 28–30 May 2016; pp. 649–653. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.H.; Ma, Z.Q.; Yu, J.Y. Discrete-Time Fractional Order Terminal Sliding Mode Tracking Control for Linear Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 3386–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.H.; Wu, L.G.; Kuang, Z.; Ma, Z.Q.; Liu, J.X. Practical tracking control of linear motor via fractional-order sliding mode. Automatica 2018, 94, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.H.; Wang, H. Discrete time fast sliding-mode control for permanent magnet linear motor with nonlinear extended state observer. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Power and Energy Systems, Perth, Australia, 10–12 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Cao, Z.W.; Zheng, J.C.; Yu, M.; Yazdani, A.; Shahnia, F. Fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode control for permanent-magnet linear motor via ELM. Neural Comput Appl. 2020, 32, 14447–14457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.X.; Zhao, X.M.; Yuan, H. Nonsingular Terminal Sliding Mode Control Based on Adaptive Time Delay Estimation for Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor. Int. J. Control Autom. 2022, 20, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettayeb, M.; Djennoune, S. Design of sliding mode controllers for nonlinear fractional-order systems via diffusive representation. Nonlinear Dynam. 2016, 84, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalaga, A.; Kamal, S.; Fridman, L.M.; Bandyopadhyay, B.; Moreno, J.A. Implementation of Super-Twisting Control: Super-Twisting and Higher Order Sliding-Mode Observer-Based Approaches. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3677–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtessel, Y.; Taleb, M.; Plestan, F. A novel adaptive-gain super twisting sliding mode controller: Methodology and application. Automatica 2012, 48, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.W.; Gao, J.; Luo, Y.H.; Zhang, L.Y. Super-twisting sliding mode control with defined boundary layer for chattering reduction of permanent magnet linear synchronous motor. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 35, 1829–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.Z.; Ding, B.; Jiang, B.; Yang, W.L.; Shi, P. Nonsingular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control for Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor via High-Order Super-Twisting Observer. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2022, 27, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, S.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, L.Y. Sensorless Vector Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Linear Motor Based on Self-Adaptive Super-Twisting Sliding Mode Controller. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 44998–45011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Niu, Y.J.; Yang, R.; Tan, Q.; Jiang, J.L.; Li, L.Y. A Robust Double Closed-Loop Control Scheme for PMLSM Drives. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 62645–62654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.; Jin, M.; Han, S. A New Adaptive Sliding-Mode Control Scheme for Application to Robot Manipulators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3628–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.H.; Xu, H.G.; Niu, X.J. Adaptive sliding mode disturbance rejection control with prescribed performance for robotic manipulators. ISA Trans. 2019, 91, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Y.; Lu, J.S. High-Precision Motion Control for a Linear Permanent Magnet Iron Core Synchronous Motor Drive in Position Platform. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2014, 10, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.H.; Ma, Z.Q. Practical Tracking Control of Linear Motor With Adaptive Fractional Order Terminal Sliding Mode Control. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 22, 2643–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, K. Finite-Time Control of a Linear Motor Positioner Using Adaptive Recursive Terminal Sliding Mode. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 6659–6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, K.; Zheng, J.C.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.Q.; Lu, R.O.; Man, Z.H. Tracking Control of a Linear Motor Positioner Based on Barrier Function Adaptive Sliding Mode. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2021, 17, 7479–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Q.X.; Zhang, H.G.; Yu, R.; Liu, Y. Neural network-based H-infinity sliding mode control for nonlinear systems with actuator faults and unmatched disturbances. Neurocomputing 2018, 275, 2009–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Chen, Y.; Xue, A.K.; Zong, G.D.; Zhao, X.D. Event-trigger-based adaptive fuzzy hierarchical sliding mode control of uncertain under-actuated switched nonlinear systems. ISA Trans. 2022, 124, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.J.; Hwang, J.C.; Chou, P.H.; Hung, Y.C. FPGA-Based Intelligent-Complementary Sliding-Mode Control for PMLSM Servo-Drive System. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 2573–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Chiang, H.H.; Liu, T.S.; Chang, C.H. Precision Motion Control of Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motors Using Adaptive Fuzzy Fractional-Order Sliding-Mode Control. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.M.; Fu, D.X. Adaptive Neural Network Nonsingular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control for Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor. IEEE Access 2020, 7, 180361–180372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.M.; Wang, T.H.; Jin, H.Y. Intelligent second-order sliding mode control for permanent magnet linear synchronous motor servo systems with robust compensator. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2020, 14, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.X.; Zhao, X.M.; Yuan, H. High-precision motion control method for permanent magnet linear synchronous motor. IEICE Electron. Express 2021, 18, 20210097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xu, Y.L.; Ding, R.Z.; Liu, W.K.; Shu, S.; Yang, X.F. Multi-Kernel Neural Network Sliding Mode Control for Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motors. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 57385–57392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Number | Abbreviations | Full Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ADO | Adaptive Disturbance Observer |
| 2. | ARTSM | Adaptive Recursive Terminal Sliding Mode |
| 3. | AFOTSM | Adaptive Fractional Order Terminal Sliding-Mode Control |
| 4. | ASMC | Adaptive Sliding-Mode Control |
| 5. | BFASM | Barrier Function Adaptive Sliding Mode |
| 6. | CSMC | Complementary Sliding-Mode Control |
| 7. | DFOB-MI | Disturbance Force Observer with Mass Identification |
| 8. | DTSMC | Discrete Time Sliding-Mode Control |
| 9. | ELM | Extreme Learning Machine |
| 10. | FTDO | Finite-Time Disturbance Observer |
| 11. | FNTSMC | Fast Nonsingular-Terminal Sliding-Mode Control |
| 12. | FO | Fractional Order |
| 13. | HOSTO | High-Order Super-Twisting Sling Mode Observer |
| 14. | IBTSMC | Intelligent Backstepping Terminal Sliding-Mode Control |
| 15. | MNN | Multi-kernel Neural Network |
| 16. | MCSMC | Modified Complementary Sliding-Mode Control |
| 17. | MRAI | Minimum Route Advertisement Interval |
| 18. | NDOB | Nonlinear Disturbance Observer |
| 19. | NTSMC | Nonsingular Terminal Sliding Mode Control |
| 20. | NLESO | Nonlinear Extended State Observer |
| 21. | OSTNTSMC | Super-twisting Nonsingular-terminal Sliding-Mode Control with High-Order Sliding-Mode Observer |
| 22. | OSMC | Observer-based Sliding-Mode Control |
| 23. | PID | Proportional Integral Derivative |
| 24. | PFNN | Probabilistic Fuzzy Neural Networks |
| 25. | RWENN | Recurrent Wavelet-based Elman Neural Network |
| 26. | RSM-ADO | Sliding-Mode Controller combined with an Adaptive Disturbance Observer |
| 27. | RBFN | Radial- Basis Function-Network |
| 28. | RBF | Radial Basis Function |
| 29. | RRBFNN | Recurrent Radial Basis Function Neural Network |
| 30. | SMC | Sliding-Mode Control |
| 31. | SMO | Sliding-Mode Observer |
| 32. | STNTSMC | Super-Twisting Nonsingular-Terminal Sliding-Mode Control |
| 33. | SOSMC | Second-Order Sliding-Mode Control |
| 34. | TSMC | Terminal Sliding-Mode Control |
| 35. | TDE | Time Delay Estimation |
| Approaches | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Boundary layer approach |
|
|
| Reaching law approach |
|
|
| Disturbance observer-based SMC |
|
|
| Terminal SMC |
|
|
| Super-twisting SMC |
|
|
| Adaptive SMC |
|
|
| Intelligent SMC |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, L.; Huang, J.; Luo, W.; Chang, S.; Sun, H.; Tian, H. Sliding-Mode Control for PMLSM Position Control—A Review. Actuators 2023, 12, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12010031
Yu L, Huang J, Luo W, Chang S, Sun H, Tian H. Sliding-Mode Control for PMLSM Position Control—A Review. Actuators. 2023; 12(1):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12010031
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Lijuan, Jie Huang, Wei Luo, Shuyuan Chang, Huilu Sun, and Hailong Tian. 2023. "Sliding-Mode Control for PMLSM Position Control—A Review" Actuators 12, no. 1: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12010031
APA StyleYu, L., Huang, J., Luo, W., Chang, S., Sun, H., & Tian, H. (2023). Sliding-Mode Control for PMLSM Position Control—A Review. Actuators, 12(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12010031







